RCP111 Test 1 (CH 4,12,24) Full
1/212
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
213 Terms
What are Point-Of-Care-Arterial Systems (POCT)?
Portable analyzers for bedside testing that require minimal blood volume.
What happens to the oxygen dissociation curve with increased pH?
It shifts to the left, promoting increased oxygen loading.
What is high ph w/ low CO2?
hypocapnia (hyperpnea)
What is low pH w/ high CO2?
hypercapnia (hypopnea)
What factors can affect the accuracy of a pH electrode measurement?
temperature, ion concentration, and the presence of interfering substances.
Why is Central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2) measured?
For conditions like sepsis or following major surgery.
Preferred site for arterial sampling.
Radial artery
Secondarily considered for arterial sampling.
Brachial artery
When is Femoral artery used for ABG?
Last resort for arterial sampling due to depth and risk factors.
Possible medical issues with ABG blood collection?
Hematoma, Arteriospasm, Thrombosis (clot)
What is anion gap caused by?
negatively charged plasma proteins, sulfate, phospate
What kind of unmeasured anions may be represented by an anion gap?
endo-lactate/keytones
exo-salicylate (salt of salicylic acid)
Why is anion gap measurement useful?
signals presence of metabolic acidosis, helps differentiate causes, assess severity of acidosis and guide treatment (like for DKA)
What is a lactate level of 5-10mmol/L associated with?
sepsis even if AG is in reference range (up to 50% of cases)
What can decrease anion gap?
large amounts of IV saline (increases Cl- levels)
albumin
In septic shock patients, a low level of __________ can contribute to a decreased anion gap.
The mechanism for forming clots to prevent bleeding, activated by damage to internal vascular walls.
Coagulation
What are Thrombocytopenia / Thrombasthenia?
Low platelets / abnormal platelets leading to excessive bleeding.
Define Prothrombin time (PT) and normal range.
Time required by plasma to form fibrin clot; normal range is 10-14 seconds; critical level >30 seconds.
Define Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) and normal range.
Evaluates abnormalities in clotting; normal range is 32-45 seconds; critical level >50 seconds.
What is the International normalized ratio (INR)?
Expresses PT relative to established value; normal range 0.8-1.2; critical level >5.
Causes of increased PT and PTT?
Vitamin K deficiencies, anticoagulant therapies (heparin/warfarin), disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), end-stage liver disease.
What does an Allen Test do?
checks ulnar artery perfusion, confirming collateral circulation before arterial sample or cannulation.
Where is Brachial Artery found?
Upper limb, medial side of biceps tendon, distal 1-2cm to antecubital fossa.
Femoral Artery Puncture procedure
Use a perpendicular technique with the patient supine. Locate the artery just below the inguinal crease.
Why use Radial Artery Cannulation?
Continuous monitoring of arterial blood pressure and frequent ABGs.
Types of Arterial Lines (systems)
OR standard, Safe Set, Vamp System
Venous Blood Gases are used for what?
Reflect conditions of tissues from which blood originates (sepsis patients).
Why assess Central & Mixed Venous PO2 ?
Reflect tissue PO2; low/mixed venous PO2 indicates tissue hypoxia.
When are Capillary Blood Gases used?
employed in infants or adults with difficult access points.
Common Arterial Blood Gas Preanalytic Errors
room air contamination
heparin dilution
blood clots
hyperventilation during sample collection
lengthy delays before analysis
excessive sample metabolism
inadequate wait time between changes in inspired O2 or ventilation
How does Room Air Contamination impact ABG values?
bubbles can artificially elevate PO2 and lower PCO2 values.
What is affected by long Delay in Collection to Analysis?
Diffusion rates by temperature and syringe material; glass syringes preferred for delays.
What is the O2 Diffusion Rate in blood sample?
0.1 mL of O2 from 100 mL blood in 10 minutes at body temperature.
Why are Plastic Syringes only good for quick analysis times?
delays may lead to gas diffusion altering results; solubility of O2 and CO2 increases when syringe is cooled.
Describe Quality control/Proficiency Testing of ABG machines.
Calibration of analyzers is mandatory; modern devices perform automatic calibrations every 3 minutes.
Which agency provides the necessary reference materials and guidelines to ensure accuracy in measurements for ABG Analyzers.
NIST
What does CLIA do?
Regulates quality; programs must meet at least two levels of control for pH, PCO2, and PO2.
Analyzer Reporting uses what temperature?
Results are reported at normal body temperature (37°C)
What is normal Physiology of Acid-Base Balance?
regulation of hydrogen ion concentration in the body, maintaining a pH range of 7.35 to 7.45 through mechanisms including respiration and renal function.
How does bicarbonate (HCO3-) help to ventilate CO2?
Acts as buffer in the blood, facilitating the transport of carbon dioxide (CO2) from tissues to the lungs, where it can be exhaled.
How are volatile acids eliminated?
As CO2 by the lungs.
Daily CO2 Elimination
~13,000 to 20,000 mmol/day
What is vital for excreting non-volatile acids?
Kidneys (reabsorb bicarbonate) at 70-100mmol/day.
Define pH
A measure of hydrogen ion concentration, representing the acidity/alkalinity of a solution.
What is pH negative logarithm?
[H+]: pH = -log [H+].
Define the pH Scale.
Ranges from 0-14; decreasing pH denotes increasing [H+], increasing pH indicates decreasing [H+].
What are the pH Ranges for Arterial Blood?
6.0-6.9: Death; 7.0-7.34: Acidosis; 7.35-7.45: Normal; 7.46-7.79: Alkalosis; 7.8-9.0: Death.
What is combinations of weak acid and conjugate bases or weak base and conjugate acid (e.g., carbonic acid and its base bicarbonate)?
Buffer Solutions
What is the function of a buffer?
Resists a big change in H+, and pH, when acid or base is added.
What shows how buffers minimize changes in pH?
Dissociation of carbonic acid
What reacts with buffers to form weaker bases and water?
Strong bases
Kinds of buffers in body?
Numerous systems including bicarbonate, hemoglobin, plasma proteins, and phosphate buffers.
What and where is the Primary buffer?
Bicarbonate in plasma, interstitial, and intracellular H2O.
What allows for conversion and elimination of CO2 through lungs?
Bicarbonate (HCO3-)
What facilitates the reaction of bicarbonate in acid-base neutrality?
Carbonic anhydrase
What does the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation describe?
The relationship among pH, PCO2, and HCO3- to assess acid-base balance.
What is Henderson-Hasselbalch formula?
[H+]=24 x PCO2/([HCO3-])
What does Base excess indicate?
amount of strong acid required to normalize pH while maintaining PCO2 at 40mmHg.
What is normal base excess value?
± 2 mmol/L; calculated during ABG analysis.
Anion gap normal range?
8 to 16 mEq.
Causes of high anion gap acidosis?
Include ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, renal failure, and toxins.
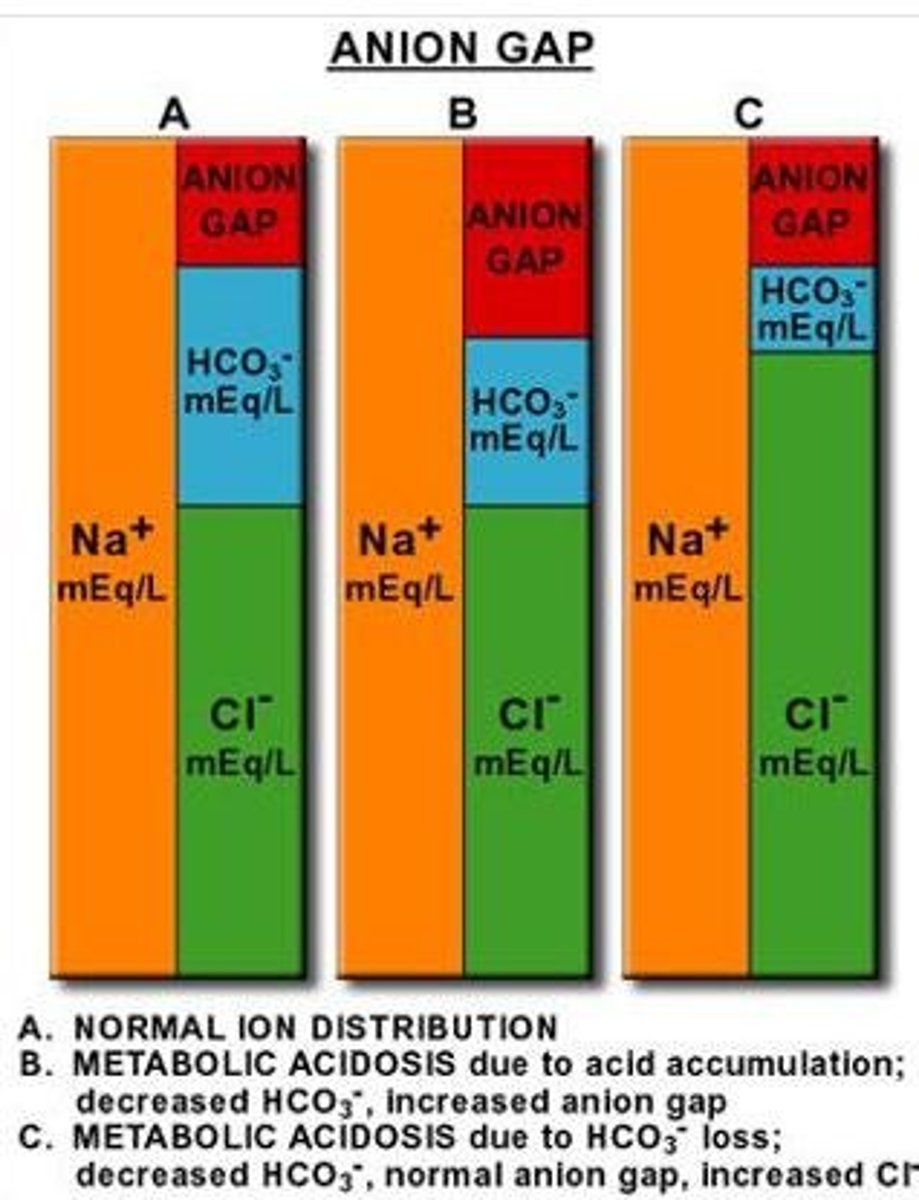
Causes of normal anion gap acidosis?
diarrhea, pancreatic or small bowel fistula, or administration of saline or HCl.
Cause of decreased anion gap?
hypoalbuminemia.
What is Strong Ion Difference?
Another approach to determine unmeasured anions and is considered more refined than the anion gap.
Strong Ion Gap provides clarification for what?
various acid-base disturbances noted in critical care settings.
Why is Albumin-Corrected Anion Gap used?
Traditional anion gap measurements overlook albumin variations in critically ill patients.
What is Histidine?
An amino acid that buffers at a pH range of 6.0 - 7.4.
Elements of Respiratory Acidosis
Low pH and elevated PaCO2 (hypercapnia) associated with alveolar hypoventilation.
Elements of Respiratory Alkalosis
High pH with decreased PaCO2 from hyperventilation (hypocapnia).
El;ements of Metabolic Acidosis
pH decreased with decreased HCO3-; increase the production of nonvolatile acids or lead to excessive loss of bases.
Elements of Metabolic Alkalosis
High pH with increased HCO3-; usually occurs when loss of fixed acids or gain in blood buffer base.
Strong Ion Difference Formula
[SID] = [Na+] + [K+] - [Cl-]
Daily Bicarbonate Filtration rate?
equals the product of the glomerular filtration rate (180 L/day).
What is Importance Erythrocyte Hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is 6x important due to its 2x larger presence and 3x more histidine buffers compared to plasma proteins.
What is Anion Gap Adjustment Formula?
Anion gap + 2.5(4.2 - albumin)
Normal Arterial Blood Gas Values (list)
pH: 7.35-7.45
PaCO2: 35-45 mm Hg
PaO2: 80-100 mm Hg
HCO3-: 22-26 mEq/L
SaO2: 95%-98%
Seven Step Approach to ABG Interpretation
Step 1: Conduct a physical assessment; Step 2: Examine arterial pH; Step 3: Assess the PaCO2; Step 4: Assess the HCO3-; Step 5: Determine the acid-base disorder; Step 6: Determine if the PaCO2 and HCO3- are moving in the same or opposite direction; Step 7: Look at the PaO2 and SaO2 to determine adequacy of oxygenation.
What are the key measurements of ABG?
PO2 (Partial Pressure of Oxygen), PCO2 (Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide), acidity or alkalinity of pH
What do blood gas analyzers calculate?
Oxygen Saturation (SaO2), and HCO3- (Bicarbonate)and base excess (BE).
What amount of blood do samples require for ABG?
2.7-3.0 mL
Why do we use blood gas analyzers?
evaluate lung efficiency of o2 delivery and co2 elimination
assess cooperation b/w lungs and kidneys
help manage ventilation for patients on o2 therapy
What is the role of the Sanz pH electrode in blood gas analysis?
measures voltage differences across a glass membrane to determine pH.
What is the function of the 'Severinghaus electrode'?
It measures PCO2 by detecting changes in pH across a semipermeable membrane, measures amount of H+ generated
What principle does the 'Clark electrode' utilize to measure PO2?
Polarography, where current changes are measured between the electrodes to determine oxygen levels.
What do Oximetry and Co-Oximeters measure?
Oximetry measures oxyhemoglobin saturation, while Co-Oximeters differentiate among hemoglobin species.
What are 4 types of hemoglobin species?
oxyhemoglobin, deoxyhemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin, and methemoglobin
What is a major disadvantage of the ABG Analyzer?
It is invasive and may be inaccurate in patients with dyshemoglobinemias.
What are ideal sites for arterial blood gas sampling?
Sites that are easily accessible, have collateral blood flow, and minimal pain sensitivity like the radial artery.
What medical complication may arise from arterial puncture?
Hematoma, arteriospasm, and thrombosis.
What condition is indicated by a high anion gap acidosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, renal failure, and toxins.
What is the significance of bicarbonate (HCO3-) in acid-base balance?
It allows for the conversion and elimination of CO2 and assists in acid-base neutrality.
What are the risks associated with practicing arterial blood gas sampling?
Infection, inaccurate management based on results, and cross-contamination.
What does base excess indicate in blood gas analysis?
The amount of strong acid required to normalize pH at a constant PCO2.
What is the normal range for base excess?
± 2 mmol/L.
In which conditions is the modified Allen test performed?
To check ulnar artery perfusion before arterial cannulation.
Define Cardiopulmonary Function.
Assessment of heart and lung performance during exercise.
What is Pathophysiology Clarification?
Understanding disease mechanisms in cardiac and pulmonary conditions.
What is the body’s Normal Response to Exercise?
Increased oxygen demand and metabolic waste clearance.
What is a By-product of anaerobic metabolism during high exertion?
Lactate (lactic acid)