EASA PPL Air Law
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
Air Traffic
All aircraft in flight or operating on the manoeuvring area of an aerodrome.
What is the minimum equipment needed for VFR flight?
Compass, Timepiece, Altimeter, Airspeed Indicator
Which direction should you alter course if you are going to collide?
Right
What is the overtaking situation definition?
When the overtaking aircraft is within an angle of less than 70° from the extended centreline of the aircraft being overtaken
Which direction do you overtaking on taxiways?
Left
UK night definition
30 mins after sunset, 30 mins before sunrise
ICAO night definition
The hours between the end of civil twilight and the beginning of morning civil twilight.
What side is the red light at?
Left
What side is the green light at?
Right
What side is the white light at?
Back
What angle can the red and green lights be seen from?
110°
What angle can the white light be seen from?
140°
What does QFE setting mean?
The altimeter displays the height above a fixed aerodrome elevation (highest point on landing area)
What does QNH setting mean?
The altimeter displays the altitude above mean sea level (AMSL)
What does Standard Setting mean?
(1013 mb/hPa) The altimeter displays Flight Level (FL)
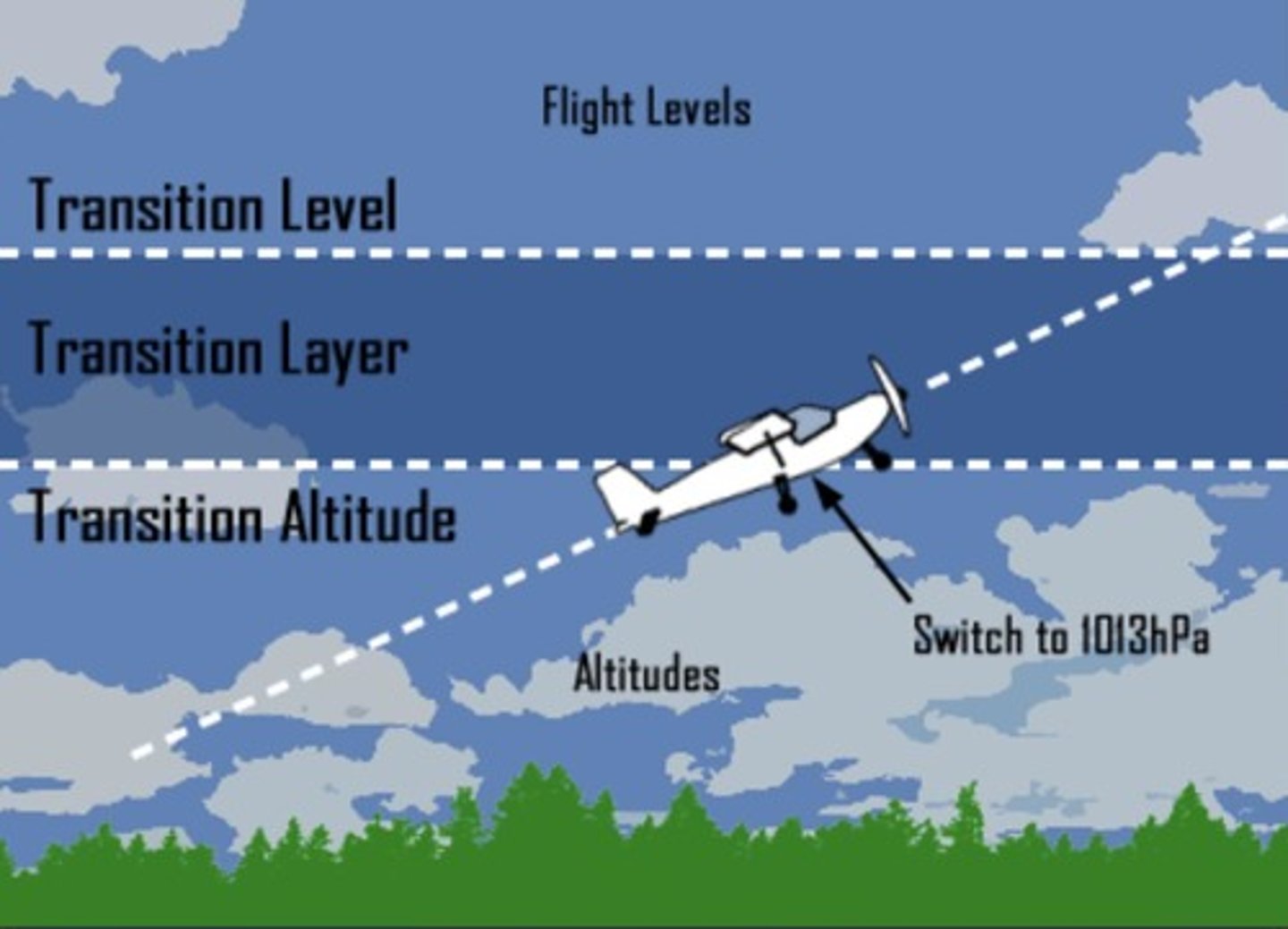
What is the transition level?
The lowest flight level available for use
What is the transition layer?
Airspace between the transition altitude and the transition level
What is the transition altitude?
The altitude at which you can switch to 1013 hPa
What would FL, Trans Level, Layer, Altitude and Altitudes look like?
Aircraft shall not be flown closer than ___ft to any person, vessel, vehicle or structure.
500ft
An aircraft should not Flt over a connected area of a city, town or settlement, below a rule height of ____ft above the highest fixed object within a radius of ___m
1000ft and 600m
An aircraft shall not fly overrun organised open-air assembly of more than 1000 persons below ____ft or be able to glide clear, whichever is higher.
1000ft
What does transponder mode A transmit?
Squawk code
What does transponder mode C transmit?
Squawk code, Pressure Altitude
What does transponder mode S transmit?
Squawk code, Pressure Altitude, Flight Identifier
What is a runway?
A defined rectangular surface on a land aerodrome prepared or suitable for the landing or take off of aircraft.
What is a taxi holding point?
The point at which the aircraft must stop unless further permission is given to proceed
How are parallel runways named?
L, R, C
What are the requirements for Simulated Instrument Conditions?
Dual controls, An additional pilot, Another pilot if needed due to FOV issues
What does the AIP contain?
General (GEN), En-route (ENR) and Aerodrome (AD) information
When does an AIP expire?
28 days
What do NOTAMs contain?
the condition/change, to any facility, service or procedure notified within the AIP.
Where can you get NOTAMs?
Pre-Flight Information Bulletin (PIB) using a live database
What colour is an information sign?
Yellow or black background with black or yellow inscription
What colour is a mandatory instruction sign?
Red background with white inscription
What colour are runway markings?
White
What colour are taxiway markings?
Yellow
What colour are runway end lights?
Red
What colour are runway threshold lights?
Green
At what height should an obstruction be lit?
150m (AGL above ground level)
What colour are high intensity obstacle lights?
Flashing white
What colour are low intensity obstacle lights?
Flashing yellow
What colour is a civil aerodrome ID beacon?
Green
What colour is a military aerodrome ID beacon?
Red
What does a solid red light mean to aircraft in flight?
Give way to other aircraft and continue circling
What does a solid red light mean to aircraft on the ground?
Stop
What does a flashing red light mean to aircraft in flight?
Do not land, airport unsafe
What does a flashing red light mean to aircraft on the ground?
Move clear of landing area
What does a solid green light mean to aircraft in flight?
You may land
What does a solid green light mean to aircraft on the ground?
You may take off
What does a flashing green light mean to aircraft in flight?
Return to aerodrome wait for permission to land
What does a flashing green light mean to aircraft on the ground?
You may move on the manoeuvring area and apron
What does a flashing white light mean to aircraft in flight?
Land after receiving continuous green light then after wait for further instructions
What does a flashing white light mean to aircraft on the ground?
Return to starting point on the aerodrome
If in an emergency, what should you immediately squawk?
7700
What is the emergency frequency?
121.500 MHz
What does rocking wings and a slow level turn to the left mean?
Follow me
What airspace is controlled?
A,B,C,D,E
What airspace is uncontrolled?
F,G
What is controlled airspace?
Airspace of defined dimensions within which all aircrafts are controlled
How is visibility measured?
km
How is distance from cloud vertically (ceiling) measured?
ft
How is distance from cloud horizontally measured?
m
To fly VFR you must be in?
VMC (These vary with airspace and altitude)
What VMC minima is it for class A airspace?
VFR not allowed
What VMC minima is it for class B airspace?
FL 100 - 8km visibility, clear of cloud
3000ft AMSL - 5km visibility, clear of cloud
What VMC minima is it for class C-E airspace?
FL 100 - 8km visibility, 1000ft vertically, 1500m behind
3000ft ASML - 5km visibility, 1000ft vertically, 1500m behind
What VMC minima is it for F-G airspace?
FL 100 - 8km visibility, 1000ft vertically, 1500m behind
3000ft ASML - 5km visibility, 1000ft vertically, 1500m behind
IAS < 140kts - 5km visibility, Clear of cloud or 1500m visibility and surface in sight
What is the Aerodrome Traffic Zone (ATZ) radius when the runway is < 1850m?
2 nm
What is the Aerodrome Traffic Zone (ATZ) radius when the runway is > 1850m?
2.5 nm
What is constant Aerodrome Traffic Zone (ATZ) height at any runway length?
2000 ft
What does Special VFR allow?
Non-IFR flights to be in Class A airspace or class D airspace when weather is less than VMC
What is IFR?
Rules which allow properly equipped aircraft to be flown under IMC (Instrument meteorological conditions)
What are the 4 types or Air Traffic service?
Air Traffic Control Service, Air Traffic Advisory Service, Flight Information Service, Alerting Service
Where is Air Traffic Control Service provided?
IFR in class A,B,C,D,E; VFR in B,C,D; all SVFR flights; all aerodrome traffic at controlled aerodromes
What should you do if you are given an unsuitable ATC clearance?
Request an amended clearance
What is a radio mandatory zone (RMZ)?
Airspace where Radio equipment is mandatory
What should you do when entering a RMZ?
A call containing, designation of station being called, call sign, type of aircraft, level, intentions of flight
What is a transponder mandatory zone (TMZ)?
Airspace where Transponder equipment is mandatory
What should you do when entering a TMZ?
Set your transponder mode in compliance with mode prescribed for that particular airspace
What does article 5 of the Chicago convention state?
The aircraft of states other than scheduled international air services have the right to make flights across state territories and to make stops without prior permission
What does an international private flight need to carry?
Radio Licence, Certificate of Airworthiness (Non-EASA aircraft), Flight Crew Licences, Certificate of Registration
What must aircraft ID plates be made from?
Fireproof material
What should an aircraft ID plate contain?
Registration, Model, Serial Number
What is the objective of the investigation of an aircraft accident?
Prevention of accidents and incidents. It is not the purpose to place blame or liability
What is distress?
A condition of being threatened by serious and/or imminent danger and requiring immediate assistance
What is urgency?
Condition concerning the safety of an aircraft or other vehicle, or of come person onboard or within sight, but which does not require immediate assistance.
What is the way of remembering transponder codes?
Hi Jack, I can't talk right now, I'm on fire
Transponder code 7500
Unlawful interference
Transponder code 7600
Radio Failure
Transponder code 7700
general emergency
Transponder code 7000
VFR conspicuity code
Transponder code 2000
When entering UK airspace from region where transponders are not required
What should you say as a light aircraft following an aircraft of a higher wake turbulence category?
Caution wake turbulence
How to declare a fuel low distress situation?
MAYDAY MAYDAY MAYDAY FUEL
What aircraft can a PPL holder fly?
Any types they have on their licence
When can a PPL holder receive any renumeration for services as a pilot?
Towing a glider, dropping parachutists, or has a Flight Instructors Rating
What limitations is there on flying passengers?
In the past 90 days they must have had 3 take-offs and 3 landings, in an aircraft of the same class
Minimum hours for PPL
45 hours of flight instruction in aeroplanes, 25 hours of dual flight instruction, 10 hours of supervised solo (5 hours cross country)
The minimum age for EASA PPL student to fly solo
16