Health and Illness IV: Lifespan - Exam 1 Review: Care of the Healthy Newborn
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
how does fetal oxygenation occur
transplacental gas exchange- at birth must establish lung function
what causes spontaneous initiation of breathing at birth
-chemical
-mechanical
-thermal
-sensory
chemical factors of spontaneous initiation of breathing at birth
clamping of cord decreases prostaglandins to increase respirations; surfactant released as lungs expand
mechanical factors of spontaneous initiation of breathing at birth
compression of chest wall during birth
thermal factors of spontaneous initiation of breathing at birth
lower temp stimulates respiration
sensory factors of spontaneous initiation of breathing at birth
touch of MD/CNM/mother; bulb syringe, drying, lights
breathing in newborn
mostly abdominal- chest and abdomen rise and move with respiration
-lung sounds are loud and lclear
respiratory rate in newborn
30-60 per min
what can breathing be after birth
shallow and irregular with periodic pauses/apnea
when do CV changes occur after birth
with first breath
-lungs inflate and decrease pulmonary resistance
-causes functional closure of foramen ovale (permanent closure in 1st few months)
-ductus arteriosus closes at birth (permanently in 3-4 weeks)
HR for newborn
120-160; can be irregular for 1st few hours
-listen for full minute
HR for sleeping newborn
100
HR for crying newborn
180
heart sounds in newborn
higher pitch, shorter duration, S1>S2
murmurs in newborns
-transient murmurs common in 1st few hours (usually form PDA)
-check for other signs of CV dysfunction
s/s of CV dysfunction in newborn
-tachycardia
-bradycardia
-pallor
-cyanosis
-pulse ox reading
normal color of newborn
acrocyanosis is normal in 1st 24 hours
abnormal color of newborns
central cyanosis (lips and mucous membranes)
BP for newborns
-routine BP not recommended
-if done, do a 2-4 extremity with doppler to note variation
-normal is based on fetal weight and age
normal BP in 7-8 oz term newborn
60-80/40-50
what is thermoregulation
maintenance of balance between heat loss and heat production
thermoregulation for neonates
-have to adapt to lower external temp compared to in utero
-less adipose and SQ fat; blood vessels much close to skin surface (difficult adjusting to temp)
neonatal response to cold
-increased muscle activity
-cannot generate heat by shivering
(thus use unique process of "brown fat" metabolism
increased muscle activity in response to cold
crying, acrocyanosis, increased activity
what is brown fat
unique adipose tissue found in neonates
-located in axilla, kidneys, and thoracic column
-lesser amounts in preterm
what does brown fat do
-heat produced by metabolism of brown fat can increase heat production by 100%
why do neonates need to use brown fat for thermoregulation
because they cannot generate heat by shivering
what is brown fat (and thermoregulation) rapidly depleted by
cold stress
cold stress in neonate
-Increased respiratory rate and oxygen consumption
-Oxygen consumption diverted from brain & cardiac fx
-Result if no intervention is metabolic acidosis & hypoglycemia
when does the first void occur after birth
24 hours- expect one void on first day
when does voiding increase
with increased intake
voiding amount on 5th day after birth
6-8 wet diapers/day
normal urine color for newborn
pale yellow/straw colored
-odorless
pseudomenstruation
may cause red/pink stained diaper
-vaginal bleeding in newborn girls from removal of placental hormones
uric acid crystals in newborn
may see pink urine in diaper
-dehydration
mouth in newborn
normally pink and moist if well-hydrated
what is sublingual frenulum
tongue-tied
sucking as a newborn
mature at 34+ weeks
-assess
what does coordination of suck-swallow-breath improve with
time/practice
is emesis common in newborn
yes initiatelly
-don't overfeed!
stomach size of newoborn
small (7-15 ml/day), increases with age
-more relaxed cardiac and pyloric sphincters
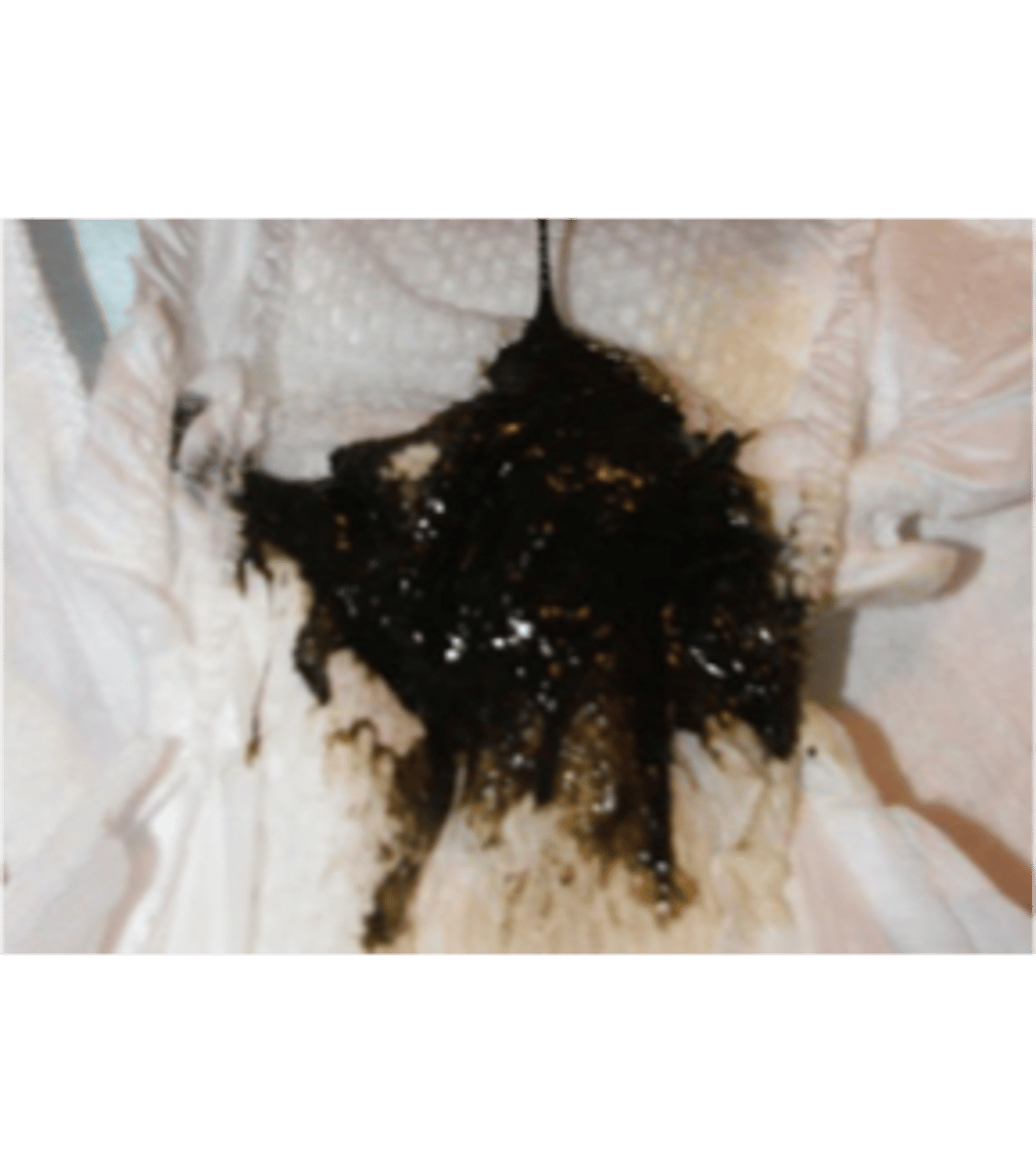
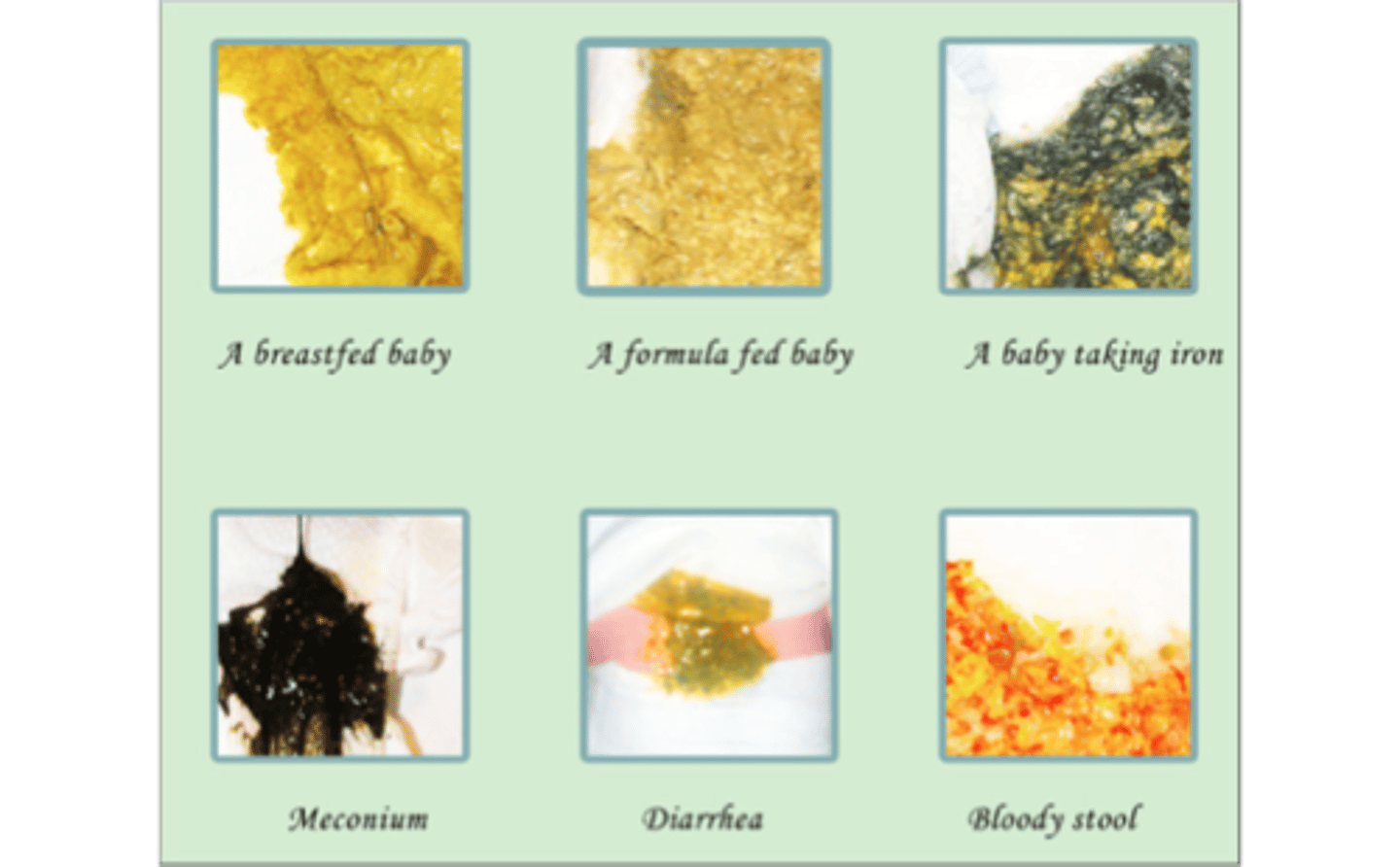
meconium
first stool
-thick, tarry green/black
-by 24 hours of life
what is transitional stool
2-3 day
green/brown
-less sticky
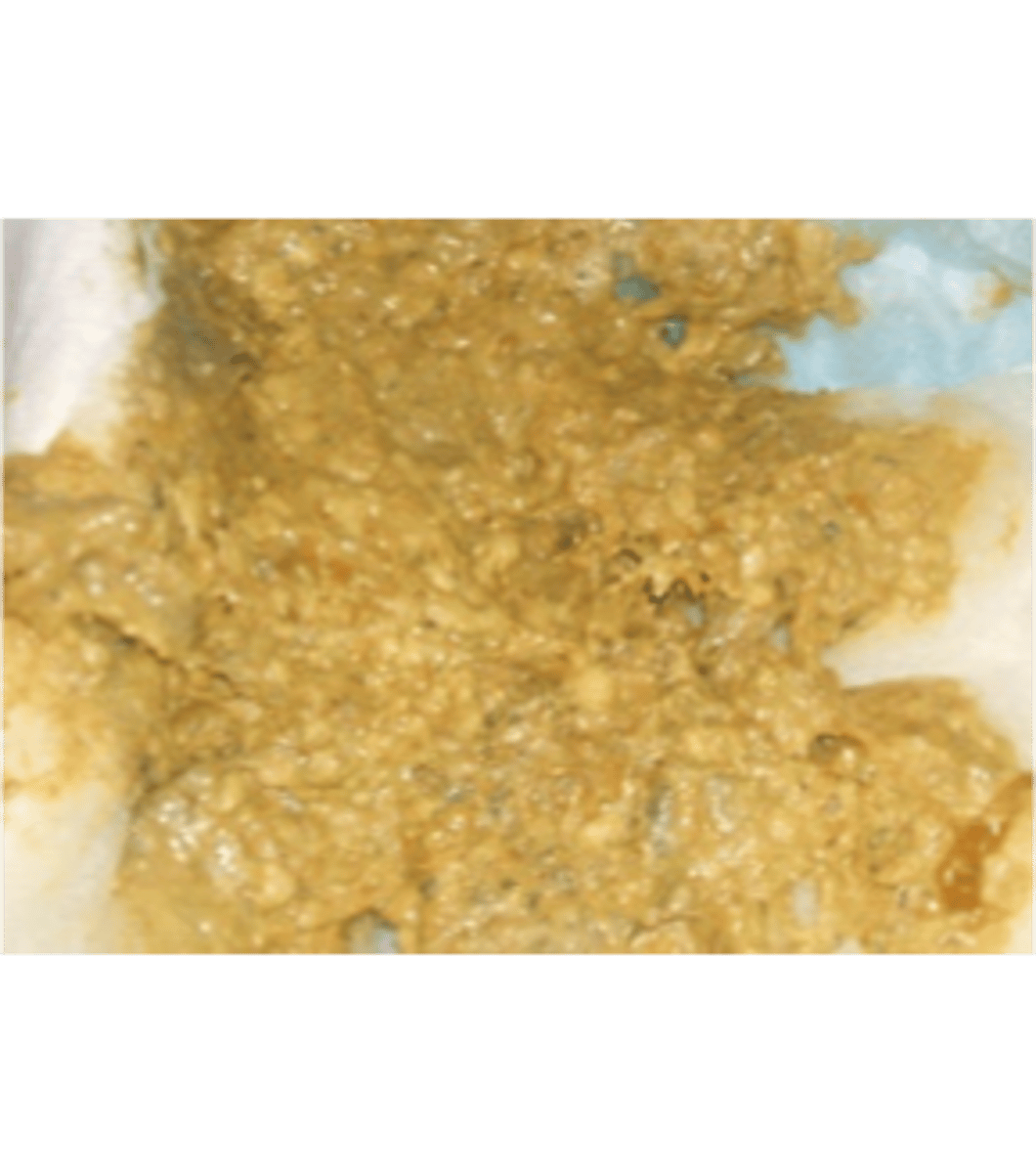
what is milk stool
3-4th day
-yellow/gold and soft in breastfed infant
-pale yellow/light brown and odorous in formula fed infant
meconium photo

milk stool photo

stool types

maternal factors that affect newborn behavior
-labor/birth
-pain meds
-pathology
-bonding
newborn factors that affect newborn behavior
-pain
-physiologic factors
-meds
-bonding
-individual personality
-sleep-wake cycles
-sense
nursing interventions for neonatal behavior
-teach parents to respond to their infants
-teach sleep-wake cycles, waking, calming, and personality and uniqueness of individual infant
physical assessment of newborn
-Maintain temperature
-Undress only as needed - work quickly!
-Assessment requiring quiet first (cardiac, respiratory, bowel sounds)
-Invasive tasks last (temperature, reflexes)
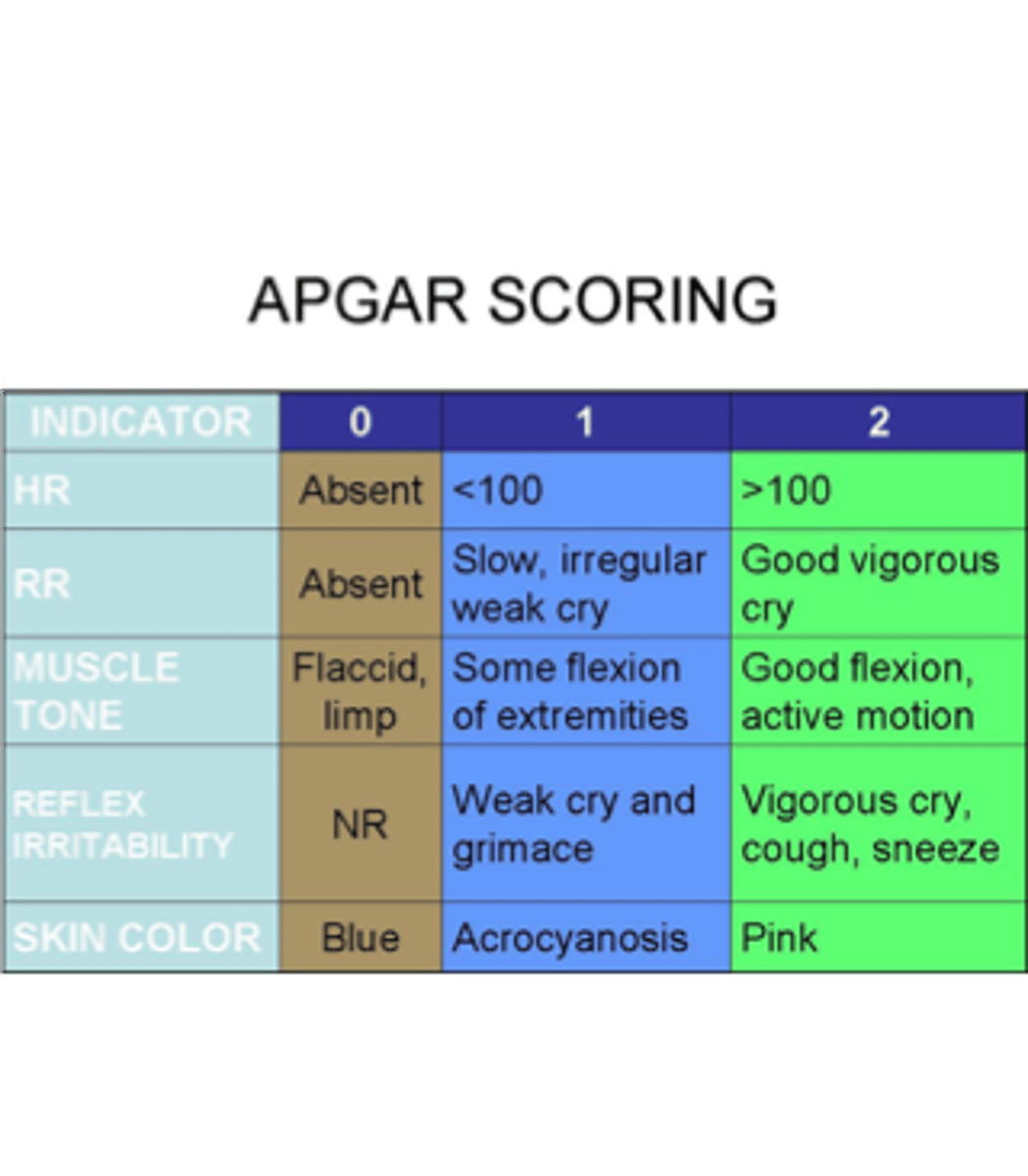
max apgar score
10
apgar score components
-color
-respirations
-reflex irritability
-HR
-muscle tone
apgar score chart
neonatal resuscitation
-initiated right after birth PRN
-nurses and RTs present at birth usually certified
normal temp of newborn
97.7-99.6
normal weight of newborn
2500 - 4000 g or 5 1/2 lb - 8 1/2 lb.
normal length of newborn
45-55 cm (18-22 in)
normal head circumference of newborn
33-35 cm (largest point)
normal chest circumference of newborn
30-33 cm (nipple line)
colors of newborn
pink, tan, jaundiced, cyanosis, circumoral cyanosis, pallor, ruddy, acrocyanosis (normal in the first 24 hours)
acrocyanosis photo
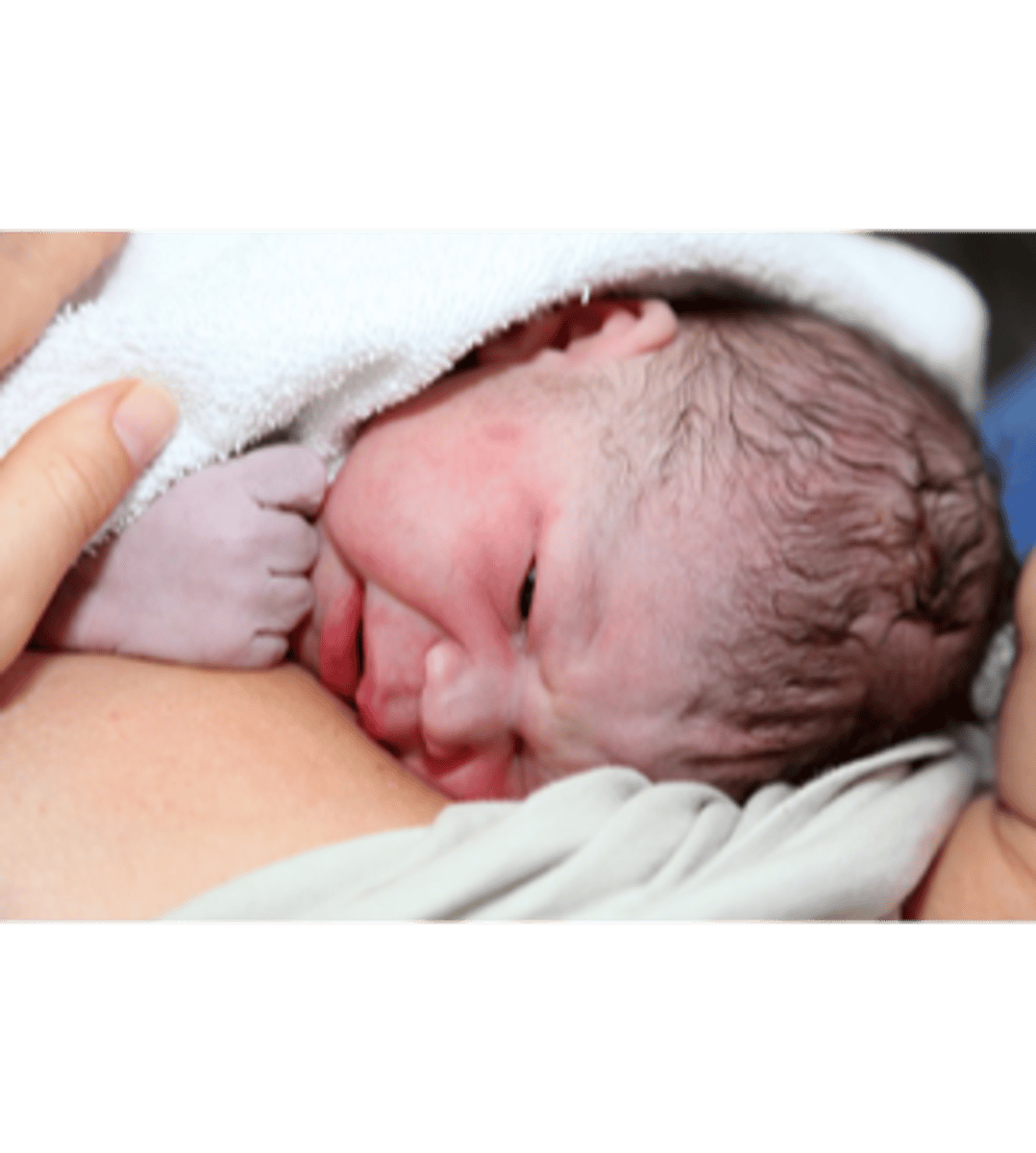

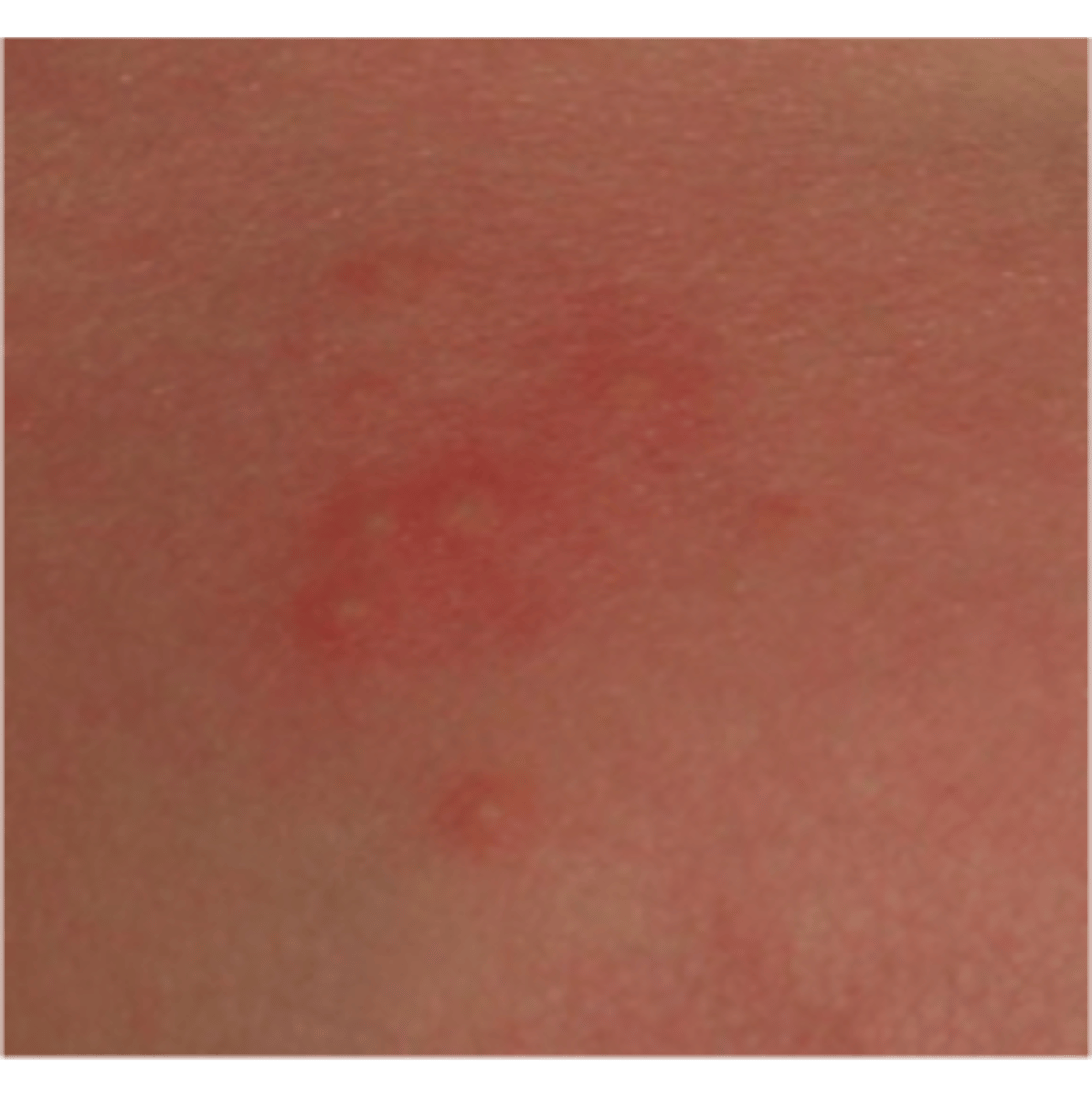
lesions or rashes of newborns
Erythema toxicum (newborn rash); bruising, milia, blisters, petechiae, melanosis
birthmarks of newborns
Mongolian spots (75-80% newborns of color), telangiectatic nevi ("stork bite marks"), hyperpigmentation, hemangiomas; skin tags
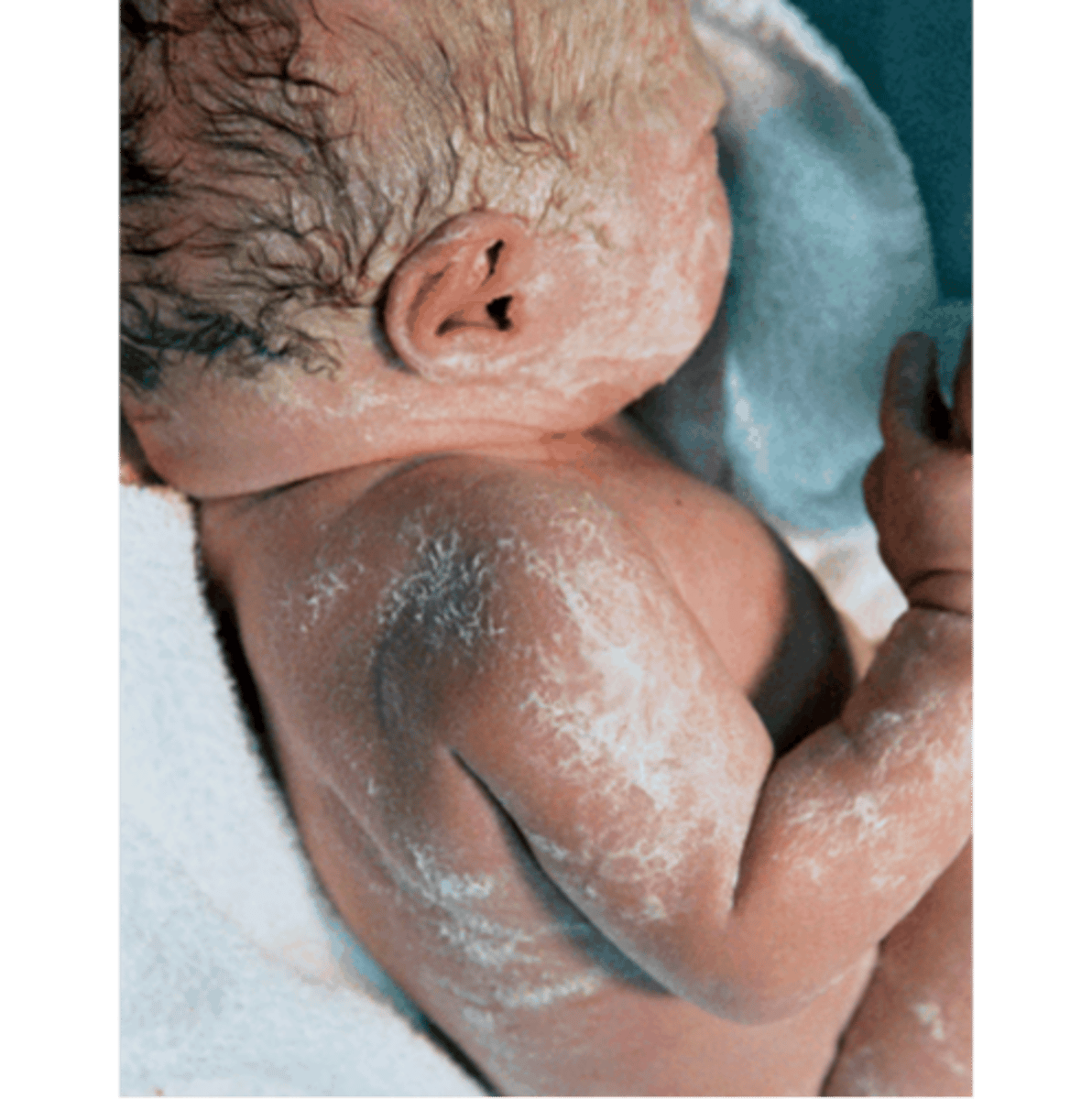
hydration of newborns
vernix (white/cheesy), lanugo (soft hair), dry skin, turgor
telangiectatic nevi (stork bite marks)
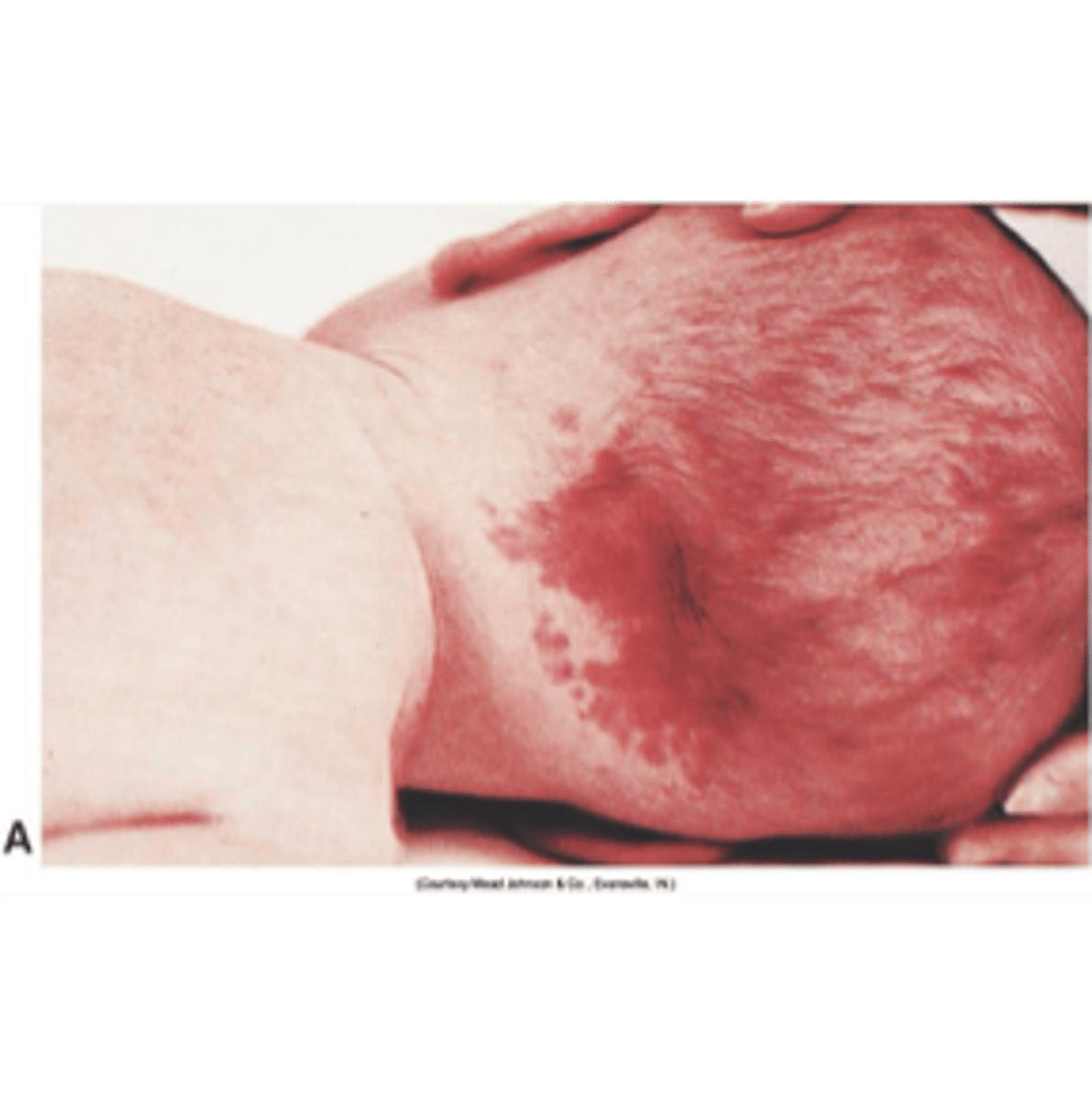
erythema toxicum (newborn rash)
vernix
mongolian spots
size and shape of head assessment
note molding, skull shape
trauma head assessment
-palpate for caput or cephalohematoma
-bruising or lacerations on face or head
suture lines assessment
palpate for overlaping
fontanels assessment
palpate anterior and posterior for bulging (increased ICP) or depression
-should be flat
mouth assessment
-rooting
-sucking
-tongue
-epstein's pearls
-teeth
-frenulum
-palpate
nose assessment
-obligate nose breathers
-sound
-mucous
-abnormal shape/placement
molding assessment
-shaping of the fetal head by overlapping of skull bones
-resolves within a few days
-creates smaller fontanels
what do fontanels allow for
molding
normal fontanels
flat
bulging fontanels
ICP
depressed fontanels
dehydration
location of fontanels
-Larger anterior (2-5cm)
-Smaller posterior (1-2cm)
how large is the newborn head
1/4 of body length
eyes assessment
-Placement, discharge, sclera color, redness
-Can focus, fix & track
-Lids may be edematous
-Lacrimal glands non-functional for 2 - 3 months
-"Pseudostraubismus"
ears assessment
-Abnormal placement, deformities, cartilage
-Newborn Hearing screen mandatory - (1 in 1000 have hearing loss)
what are retractions and nasal flaring
ABNORMAL
-first sign of respiratory distress
-retractions can be substernal or intercostal
retractions
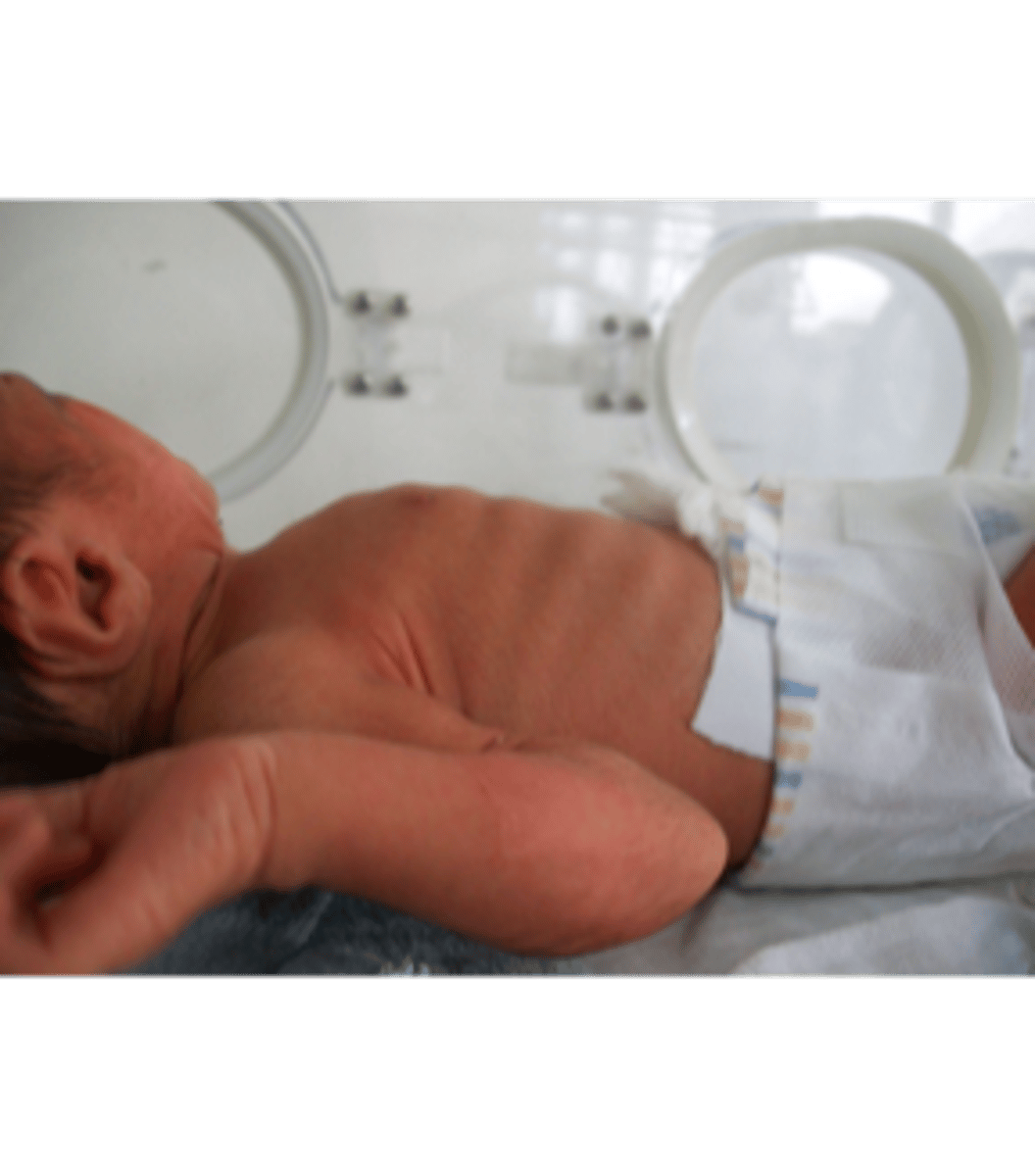

breath sounds assessment
should be clear and vesicular A/P/L bilaterally
adventitious sounds
-coarse
-rales/rhonchi
-stridor
pulses assessment
femoral and brachial pulses should be equal and strong
what are the pulse ox screen/SHINE test
screening for critical congenital cardiac disease that are mandatory in WI
abdomen assessment
-Inspect cord - 3 vessel, drying, healing, discharge, odor
-Abdominal tone - rounded and protuberant but no distention in normal neonate
-Bowel sounds - active in all 4 quadrants within 1st hour
-Stools - assess frequency, color, consistency
what are the newborn reflexes
-sucking
-rooting
-swallowing
-moro
-palmar grasp
-tonic neck (fencing)
-stepping
-babinski
what is the sucking reflex
turn to suck when mouth/lip touched
what is the rooting reflex
turn to open mouth and search for food with touch of lip/mouth/cheek
swallowing reflex
swallows food
moro reflex
startle; abduction and extension of arms, fingers fan out and form a C
palmar grasp
curls fingers around object in palm
tonic neck (fencing)
arm/leg extend on one side/flex on other
stepping reflex
simulated walking
positive babinski reflex
sole of foot stroked; toes fan out