Mieosis and Mitosis Review
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Nucleus
Both plant and animals
special operation center that controls most of cell’s activities
stores DNA
Vacuole
both plants and animals
special storage chamber in the cell
Stores food, water, and wastes are stored
Plant cells one large
Animal cells, multiple little
Mitochondria
Both plant and animals
Referred to as “powerhouse” of cell
Takes food particles and convert the food energy to ATP
Chloroplast
only in plant cell
Makes plants green
Allows cell to make food
Takes sun energy and can convert it into a usable form of food (glucose)
Lysosome
both plants and animals
Digestion of materials in the cell
Destroys invaders of the cell by digesting them away
Destroy and dispose of used organelles that do not work anymore
Cytoskeleton
Strands of protein that help the cell maintain its shape and size
Help keep the cell firm and full otherwise the cell might collapse
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
long system of tubes and sacs
“Highway” for the cell
Materials made or processed in one part of the cell are transported to new parts of the cell on the …
Rough … = has ribosomes attached
Smooth… = does not have anything attached
Cell Membrane
selectively allows certain molecules in and out of the cell
Acts as a barrier for some items
Pushes other items into the cell
Cell Wall
ONLY IN PLANT CELLS
gives plant cell such a ridged and definite shape
Protects cell from outside influences
Allows certain items in and out of cell
Ribosome
allows proteins to be assembled
Acts like a small workbench for the cell to make proteins on
Golgi Body
packaging and distribution center for the cell (like the post office of a cell)
If items need to be shipped out to other portions of the cell, the Golgi deals with it
Organelles not in animal cells
Cell wall and chloroplast
Prokaryotic Cells
Lack nucleus and other organelles
Bacteria
Eukaryotic Cells
Have nucleus
Animals
Chromatin
Spaghetti like structure in nucleus
Chromatid
Part of a sister chromatids
Sister chromatids
Two identical chromatids joined at centromere
Sister chromatids

Chromosomes
Structure in nucleus that contains DNA which hold genes
Centromere
Region of a chromosome that holds the two sister chromatids together during mitosis and meiosis
Cell cycle
Made up of interphase and cell division/PMAT
Produces 2 daughter cells
Asexual Reproduction
Offspring arise from a single organism and inherit genes of that parent only
Sexual Reproduction
Two parent cells create one unique offspring
Mitosis
Cell division that results in 2 daughter cells each having same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical ordinary tissue growth
Meiosis
Results in 4 daughter cells each with ½ number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes and plant spores
Why cells divide and not just keep growing
Information overload (DNA can’t process all the information)
Can’t efficiently move nutrients and waste across cell membrane
Cell Theory
all living organisms are contained if one or more cells
Cell is basic unit of structure and organization in organisms
Cells arise from pre existing cells
Cells that go through Mitosis
Somatic (body cells)
G1
Cell growth happens here
S
Synthesis happens here and the DNA replicates
G2
Preparation for mitosis
M phase
Cell division occurs
Cell cycle

Phase of cell cycle that DNA replication occurs in
S phase
Apoptosis
Death of a cell
Reasons apoptosis occurs
infection
DNA damage
Nutrient deficiency
Daughter cells and mitosis
If if parent cells create has 8 then daughter cells will have 8
Prophase
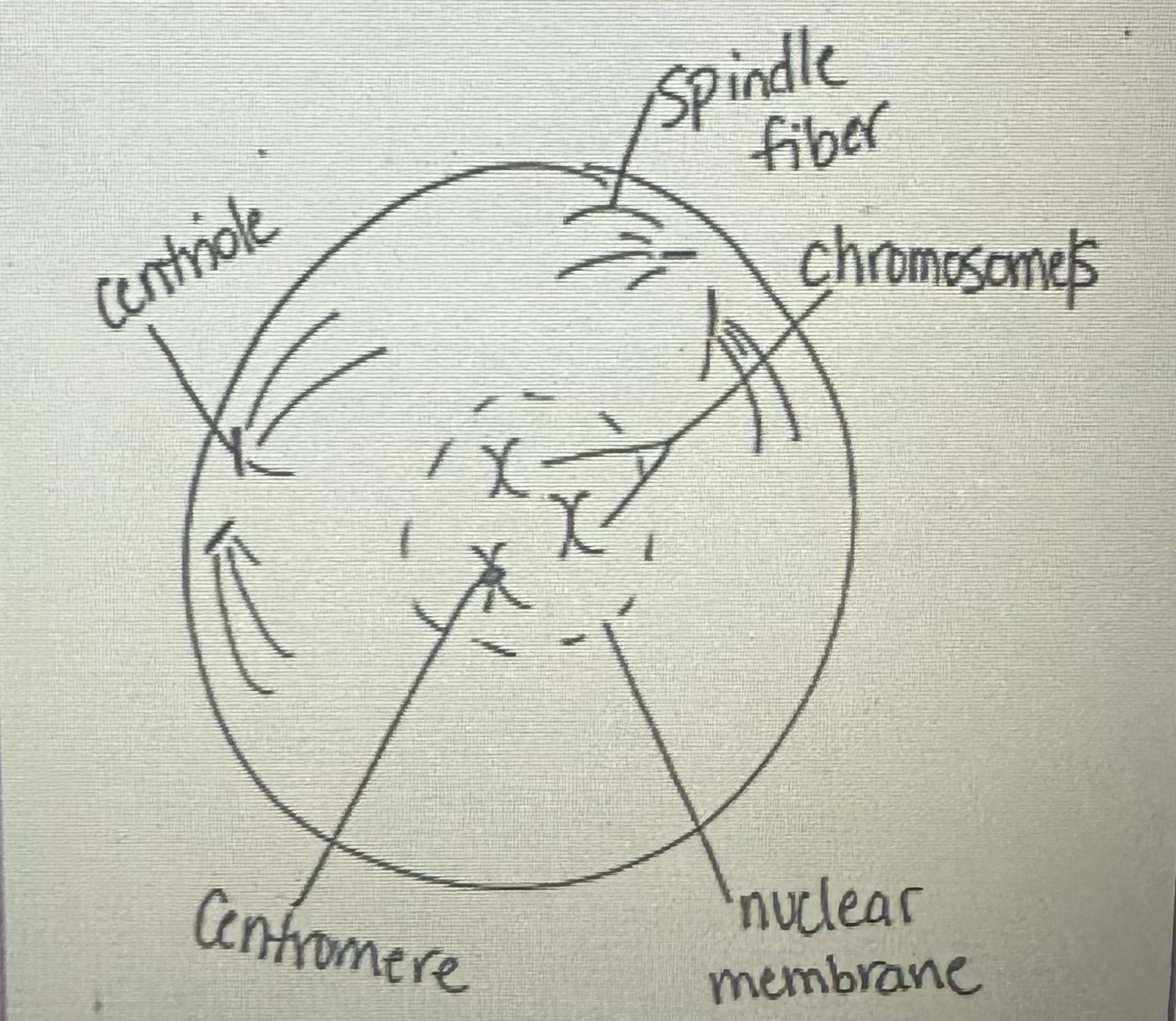
Prophase
Spindle fibers form and nuclear membrane breaks down
Metaphase
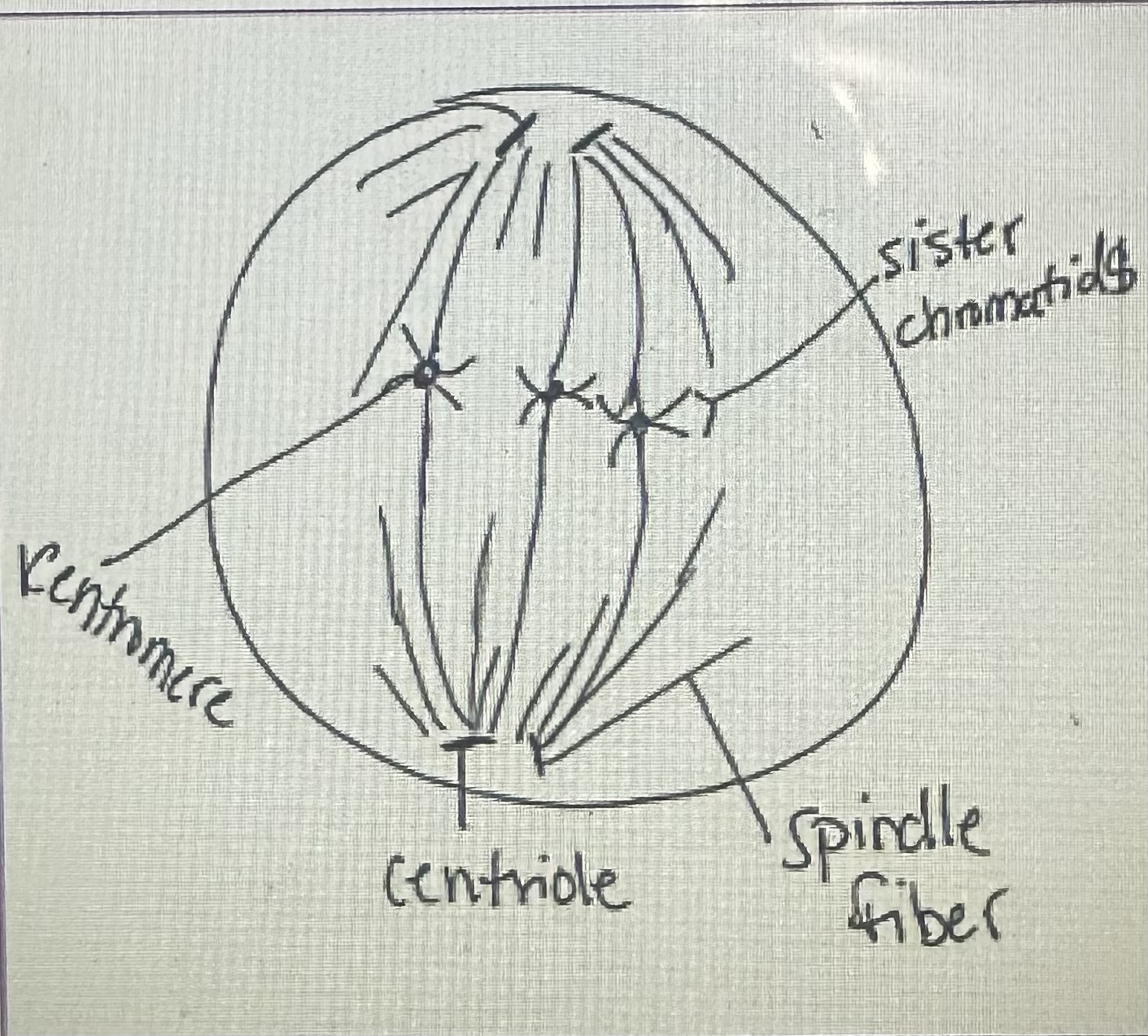
Metaphase
Centromeres of chromosomes are lined up at middle of cell
Anaphase
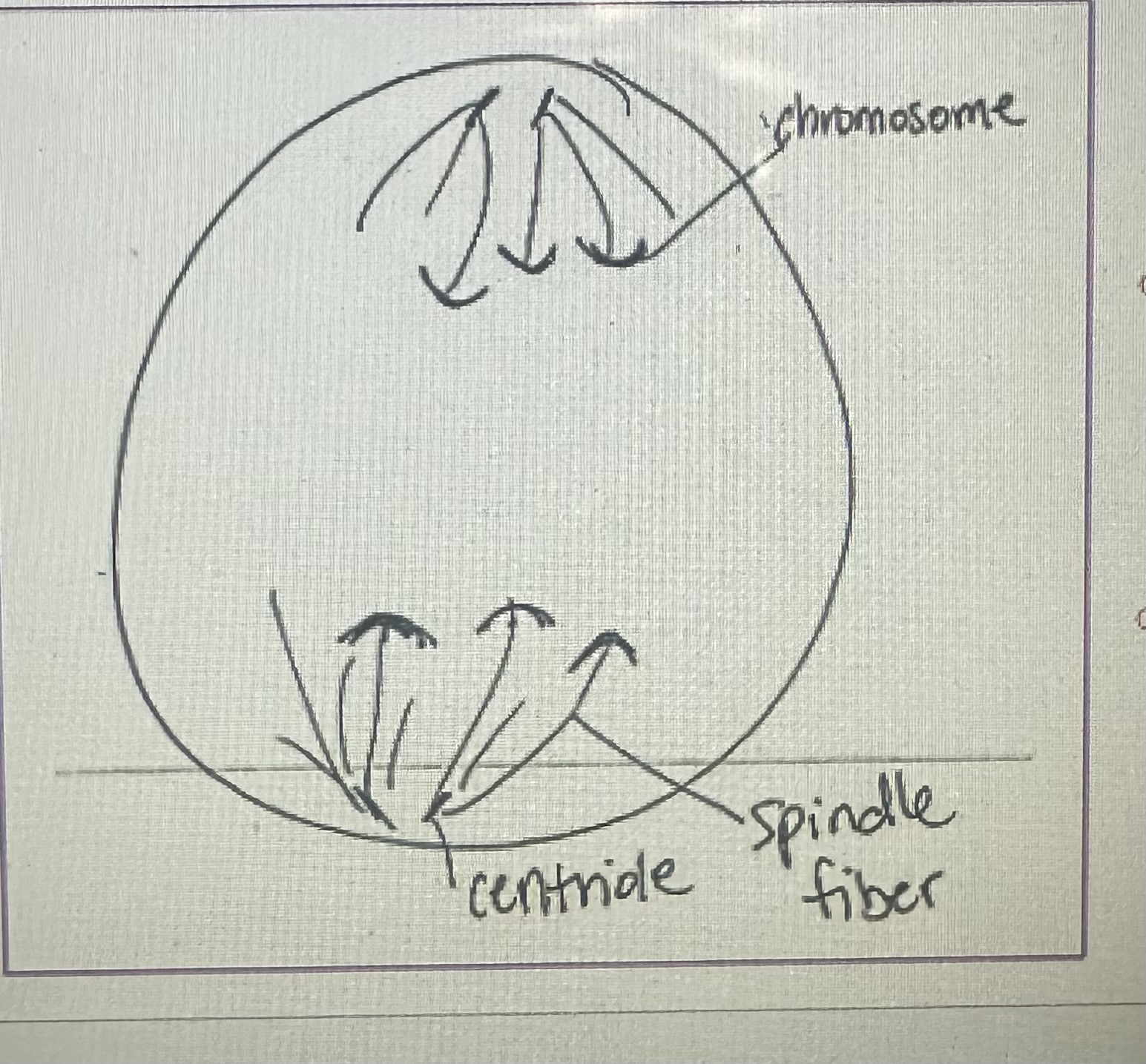
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate
Telophase

Telophase
Chromosomes uncoil
Are cells in meiosis diploid or haploid
Meiosis 1 diploid
Meiosis 2 haploid
Prophase 1

Prophase 1
Nuclear membrane breaks down around 1 nucleus
CROSSING OVER OCCURS HERE
Metaphase 1
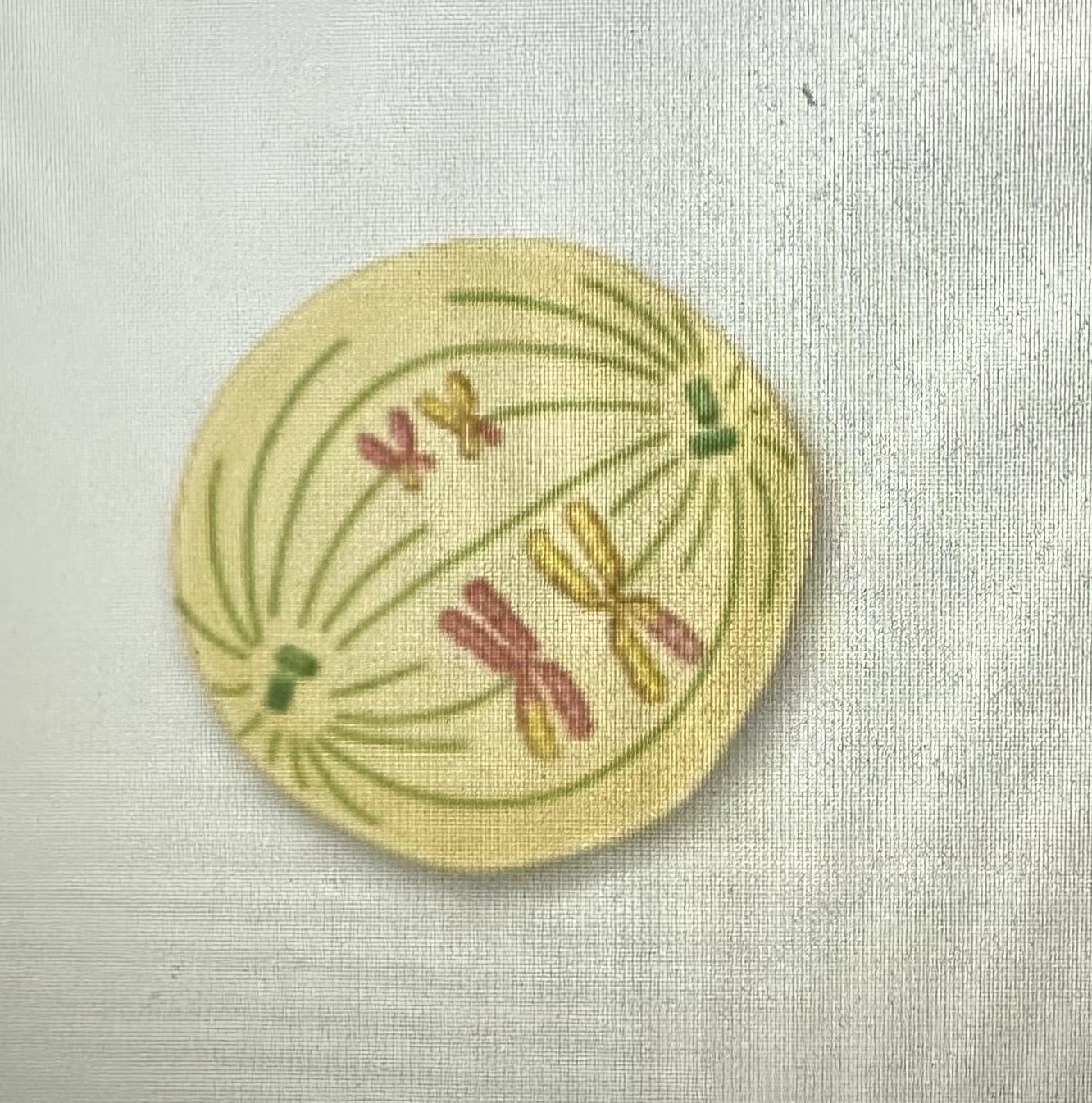

Metaphase 1
Homologous chromosomes (tetrads) line up in middle of cell
Anaphase 1
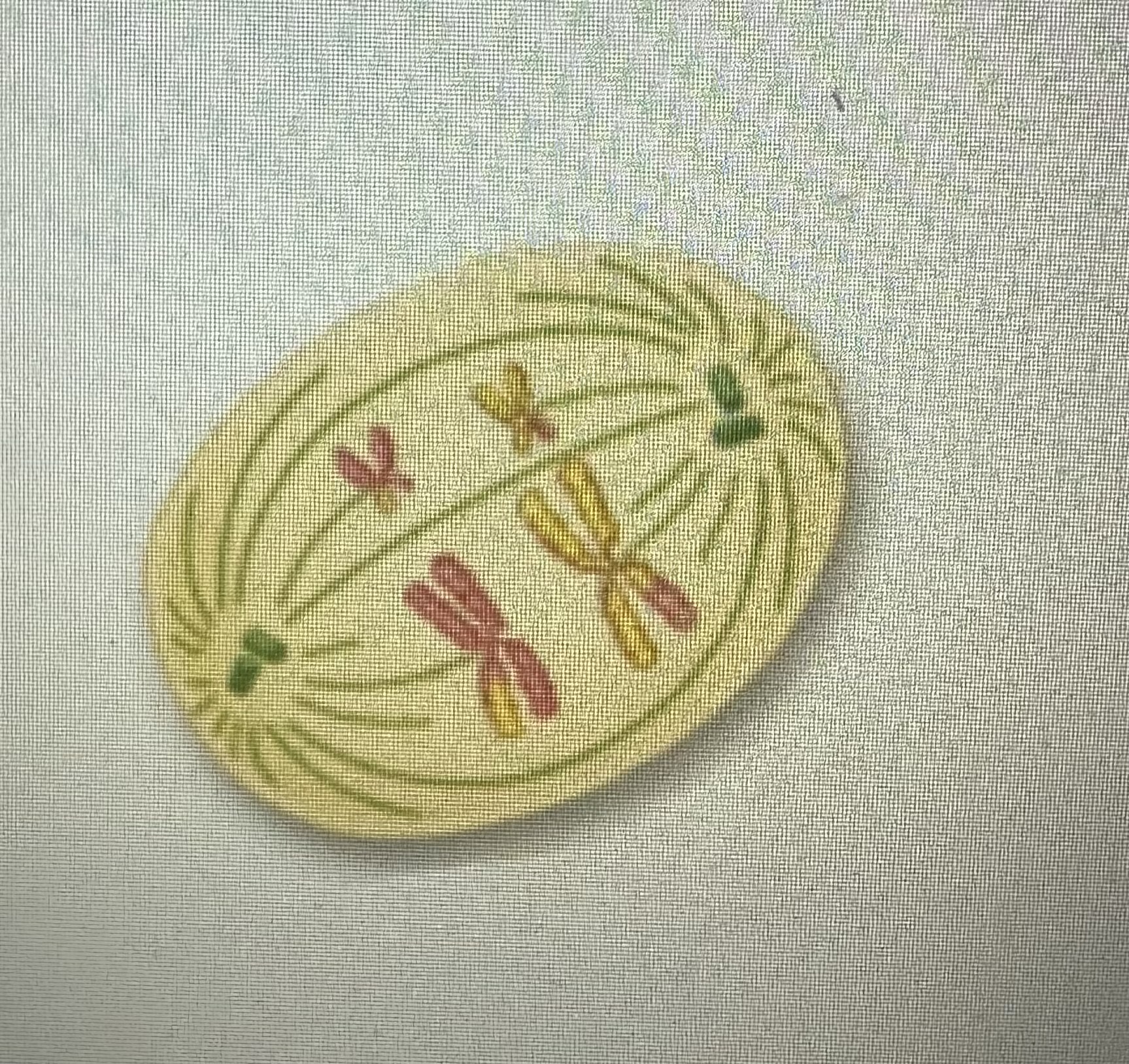

Anaphase 1
Homologous chromosomes separate
Ana away separate
Telophase 1
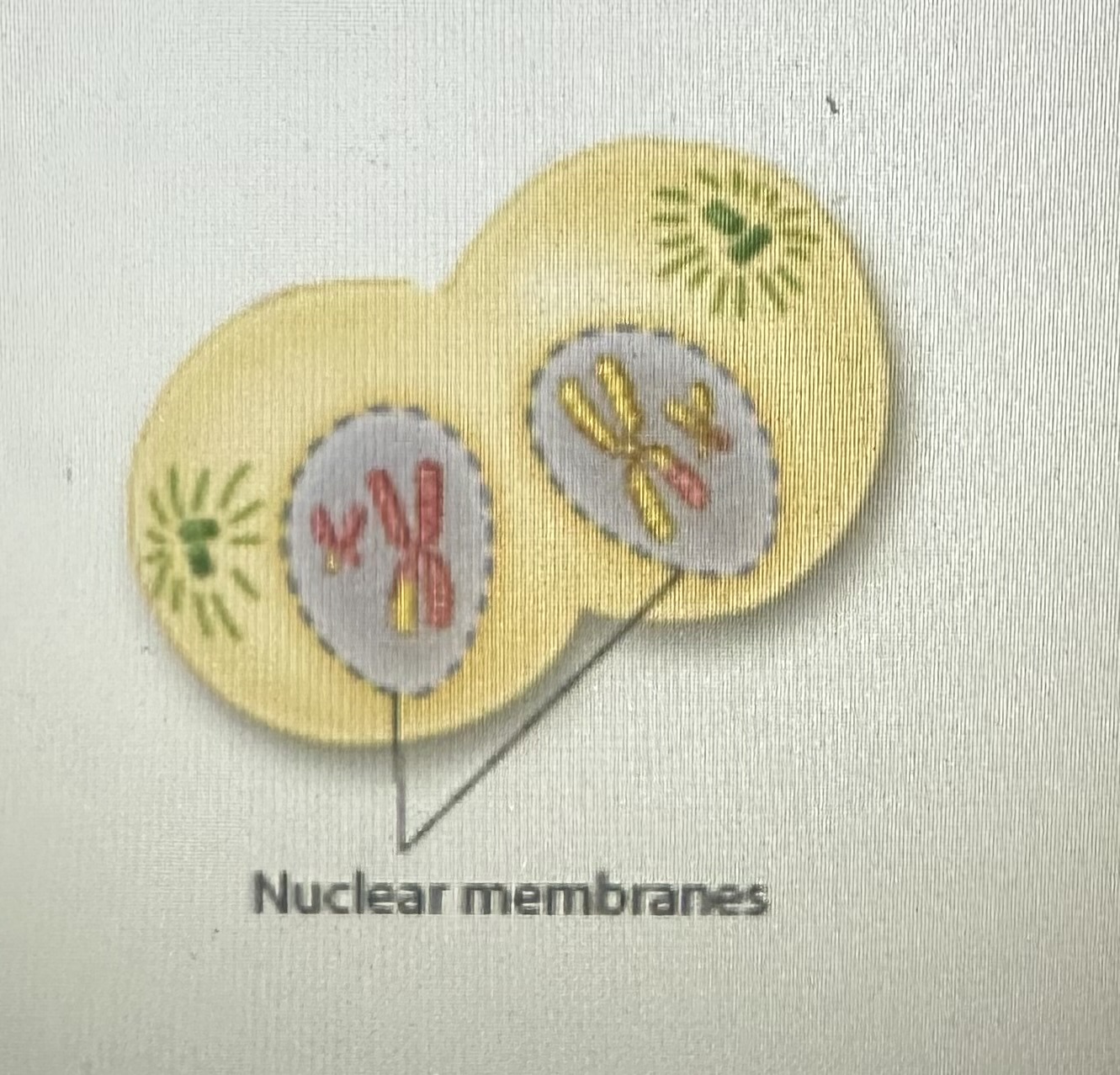
Telophase 1
Results in 2 haploid cells
Cytokines
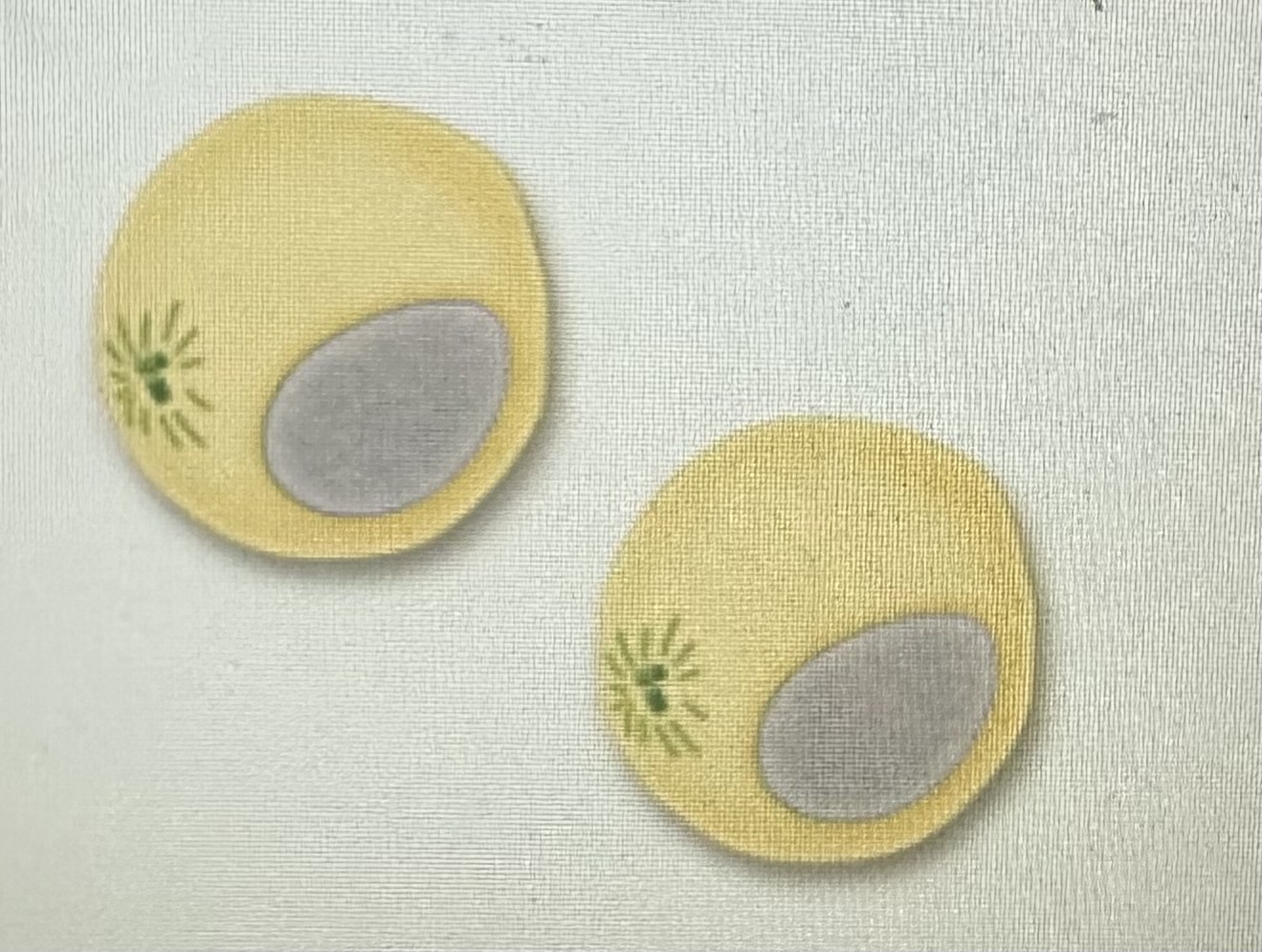

Prophase 2

Prophase 2
Nuclear membrane breaks down around 2 nuclei
Metaphase 2
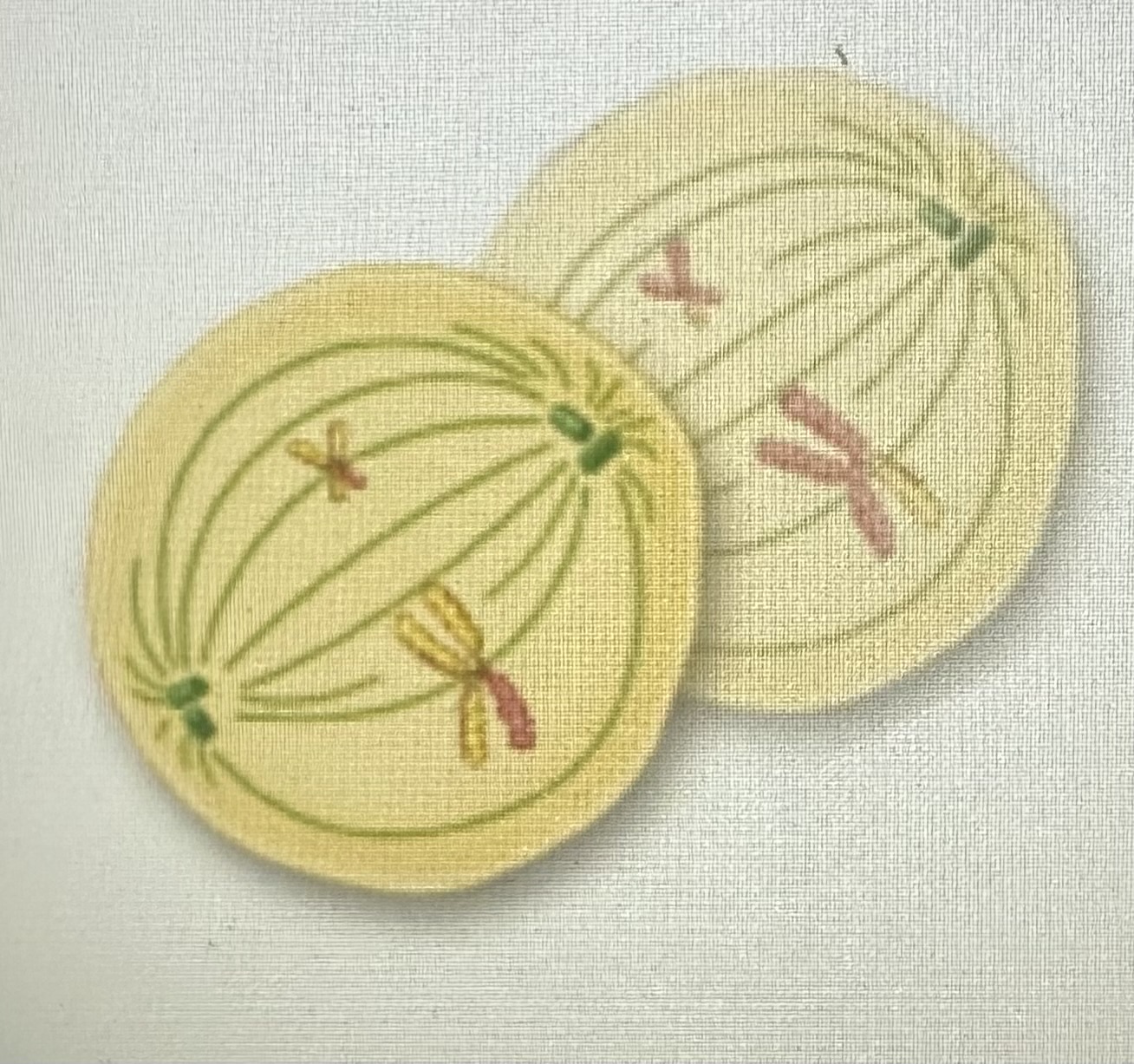

Metaphase 2
Sister chromatids line up in middle of cell
Anaphase 2
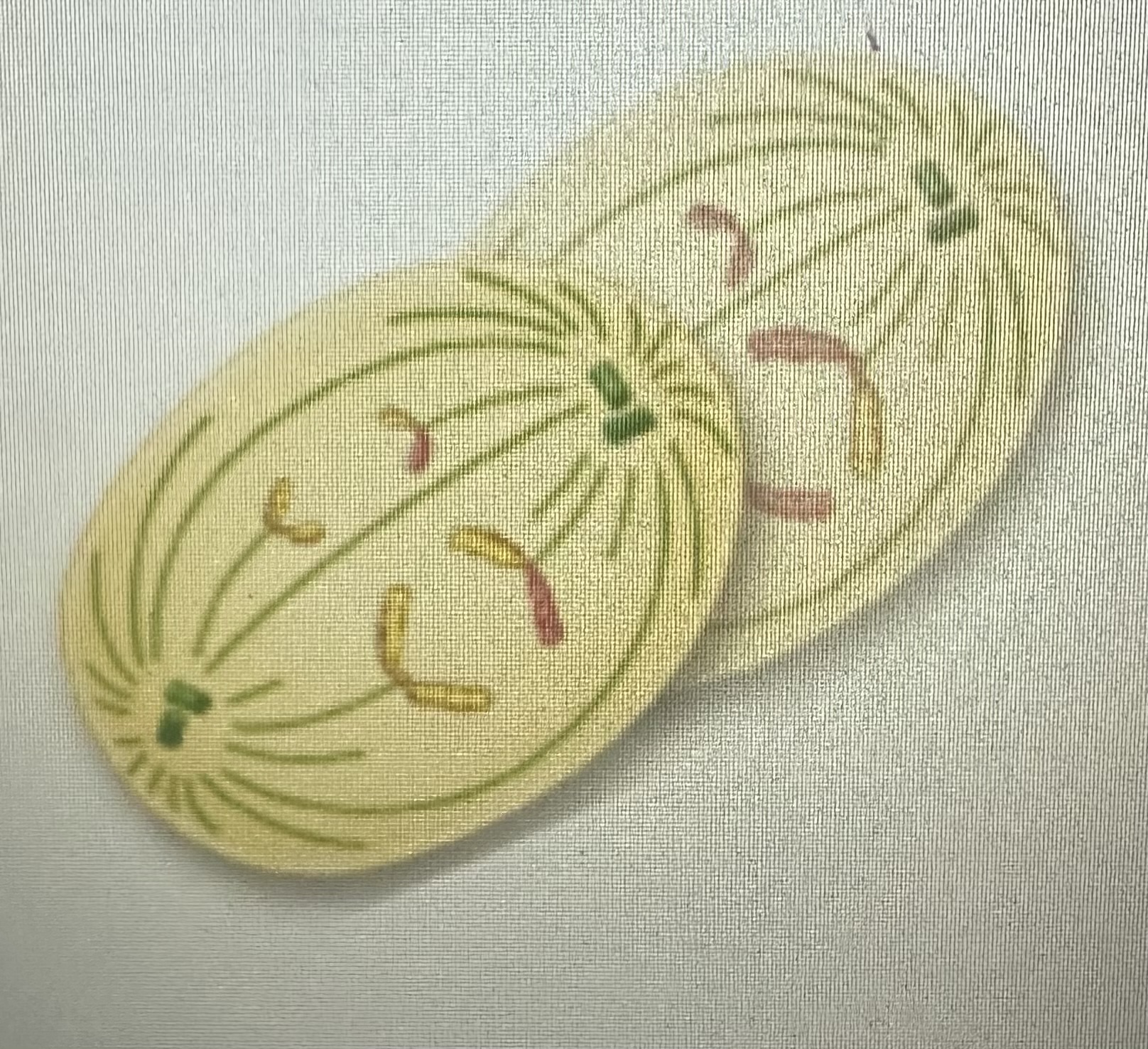

Anaphase 2
Sister chromatids separate
Telophase 2
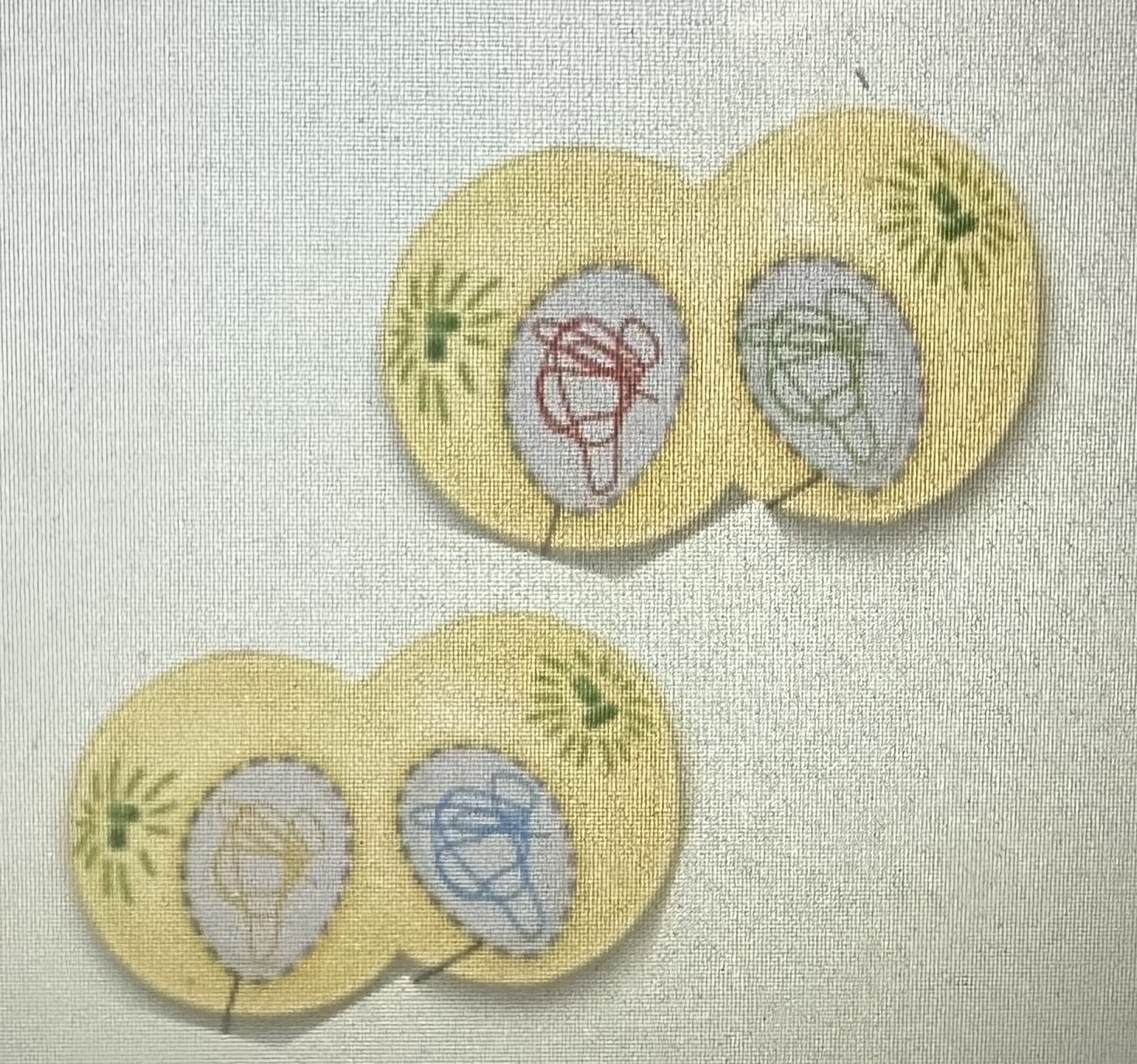

Telophase 2
Results in 4 haploid cells
Cytokinesis
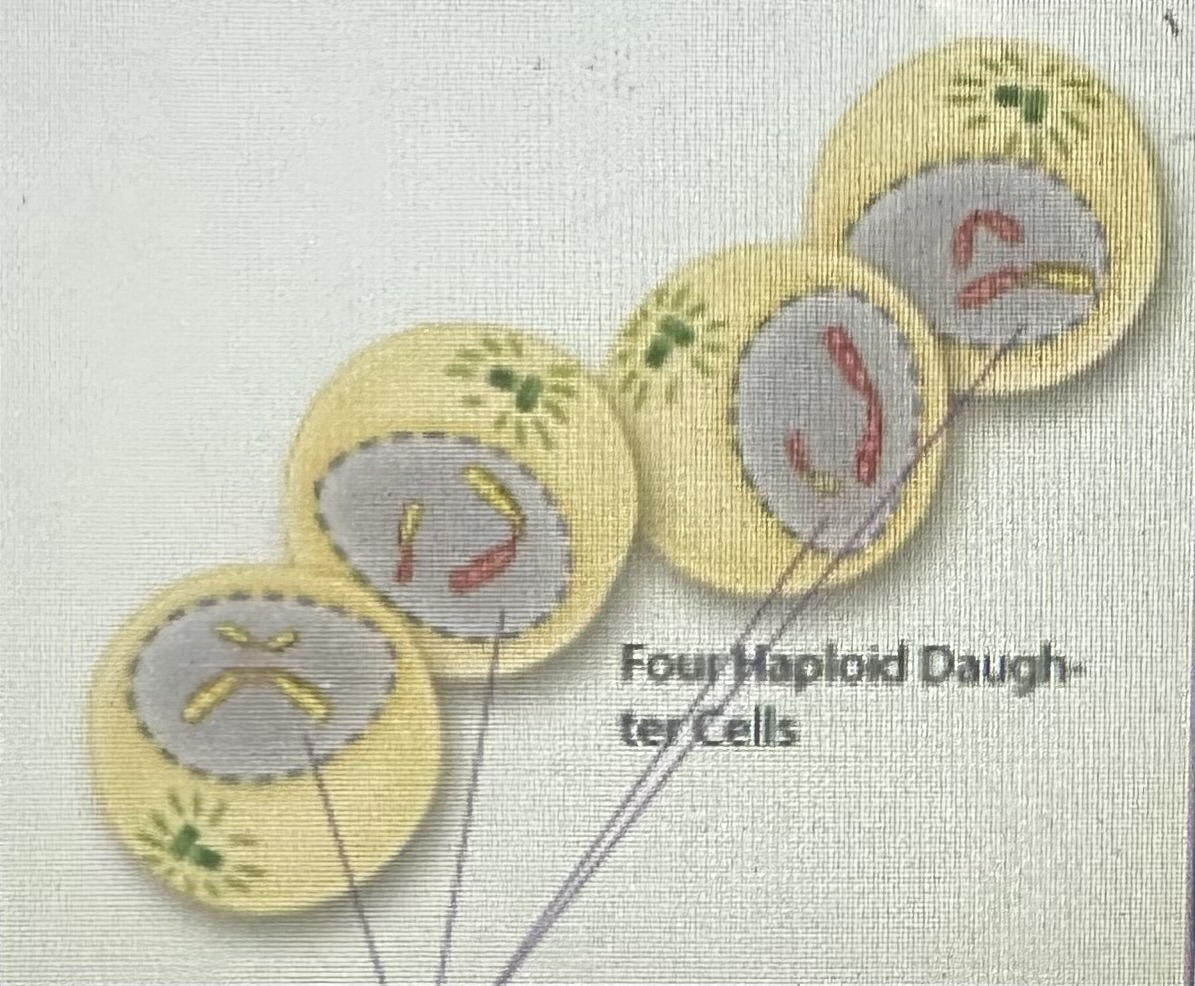
Why meiosis provides more Genetic diversity than Mitosis
Crossing over happens in meiosis
Homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange segments of a material
Homologous chromosomes
Both chromosomes are from different parent
Sister chromatids
Interkinesis
2 cells formed in Meiosis 1 appear to be in a resting state for a short period of time
No replication of the chromosomes for any cells between Meiosis 1 and Meisosis 2
Does DNA replication happen during interkinesis
When crossing over occurs
Metastasis
Spread of cancer
Stage 1 cancer
Cancer in a small area with no spread
Stage 2 cancer
Cancer has grown but not spread to lymph nodes or other tissue
Stage 3 cancer
Cancer growth larger and potentially spread to lymph nodes or other tissue
Stage 4 cancer
Cancer spread to other organs or areas of the body
Benign
Does not invade surrounding tissue
Malignant
Invade surrounding tissue and can spread to other parts of the body