Topic 6: Ecosystems & Landscapes
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Trophic Pyramid
A chart composed of stacked rectangles representing the amount of energy or biomass in each trophic group
Pyramid of Energy
A trophic pyramid that displays the total energy existing at each trophic level
Pyramid of Biomass
A trophic pyramid that represents the standing crop of organisms present in different trophic groups
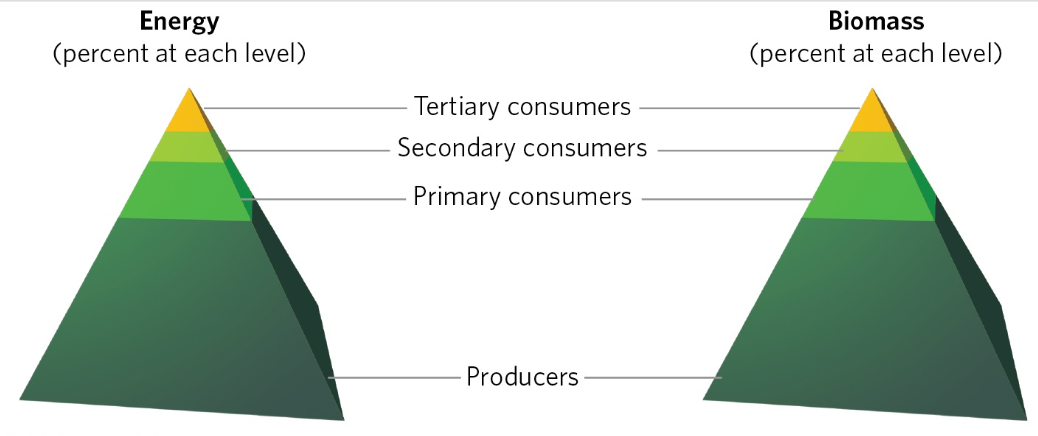
terrestrial pyramids of energy & biomass
pyramids of energy and biomass have similar shapes because most of the energy and most of the standing biomass are found in the producers
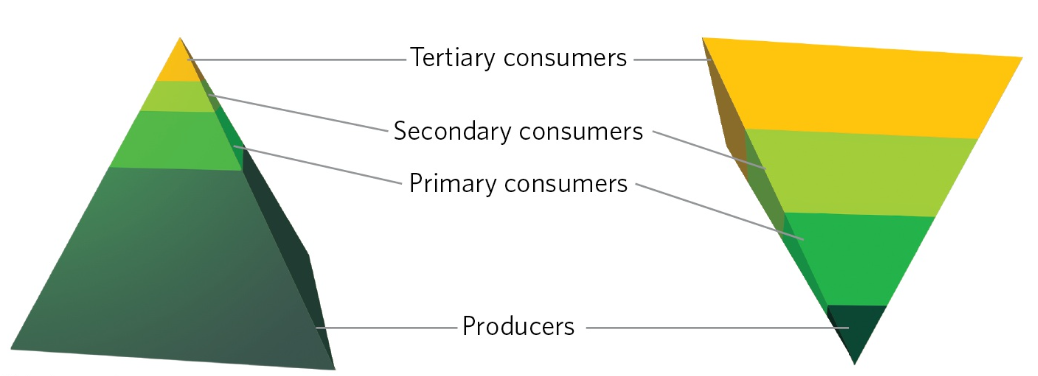
aquatic pyramids of energy & biomass
most of the energy is still found in the producers, but these producers are primarily tiny algae that do not live very long because they are rapidly consumed by herbivores
this continual rapid consumption results in a large biomass of consumers in these systems
Primary Production
The rate at which solar or chemical energy is captured and converted into chemical bonds by photosynthesis or chemosynthesis
tells us how much energy is available in an ecosystem
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
The rate at which energy is captured and assimilated by producers in a given area
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
The rate at which energy is assimilated by producers and converted into producer biomass in a given area
Remote Sensing
A technique that measures conditions on Earth from a distant location, typically using satellites or airplanes that take photographs of large areas of the globe
3 ways to measure primary producitivity
the change in the biomass of producers over time
the movement of carbon dioxide over time
the movement of oxygen over time
Secondary Production
the generation of new biomass by heterotrophic organisms (consumers) in an ecosystem
Egested Energy
The portion of consumed energy that is excreted or regurgitated
Assimilated Energy
The portion of energy that a consumer digests and absorbs
Respired Energy
The portion of assimilated energy a consumer uses for respiration
Net Secondary Production
The rate of consumer biomass accumulation in a given area
Consumption Efficiency
The percentage of energy or biomass in a trophic level that is consumed by the next higher trophic level
Assimilation Efficiency
The percentage of consumed energy that is assimilated
Net Production Efficiency
The percentage of assimilated energy that is used for growth and reproduction
Ecological Efficiency (food chain efficency)
The percentage of net production from one trophic level compared to the next lower trophic level
Describe/list what happens to the energy incorporated into in a trophic level that is not used for production at the next trophic level
used for the organism's metabolism, lost as heat, or remains in undigested food
when energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next in a food chain, only about 10% of the energy is passed on
Describe the relationship between ecological efficiency and the number of trophic levels in aquatic vs terrestrial ecosystems
aquatic ecosystems typically have more trophic levels than terrestrial
ecosystems
terrestrial producers have more defenses
there is low consumption efficiency in terrestrial ecosystems, so a large fraction of the producer biomass ultimately becomes detritus
aquatic ecosystems are composed primarily of unicellular algae that contain fewer defenses and are relatively easy for herbivores to digest
Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest
researchers removed all the trees from an entire watershed and sprayed it with herbicides for several years to suppress plant growth
as a control, adjacent watersheds were not logged
without plants to take up water and nutrients, the movement of elements in the ecosystem changed dramatically
Landscape Ecology
The field of study that is focused on the spatial arrangement of habitats at different scales and how this influences individuals, populations, communities, and ecosystems
Habitat Fragmentation
the process of breaking up large, continuous habitats into smaller, isolated patches
Edge Effect
changes in the physical and biological environment at the boundary of a habitat fragment
Edge Specialist
species that thrive in areas where two different habitat types meet
Habitat Corridor
A strip of favorable habitat located between two large patches of habitat that facilitates dispersal
Stepping Stones
Small intervening habitat patches that dispersing organisms can use to move between large favorable habitats
the relationship between landscape ecology and habitat fragments
landscape ecology providing the framework for understanding how spatial patterns, including habitat fragments, affect ecological processes