Chapter II: Chemistry and Biological Compounds
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Ionic Bond
Transfer of electrons between atoms.
Valence
Charge from electron gain or loss.
Ion
Atom or group with electrical charge.
Salt
Compound of positive and negative ions.
Cation
Ion with a positive charge.
Anion
Ion with a negative charge.
Aqueous Solution
Water-based solution weakening ionic bonds.
Ionization or Dissociation
Salts breaking into ions in water.
Covalent Bond
Sharing of electrons between atoms.
Disulfide Bond
Covalent bond between sulfur atoms.
Hydrogen Bond
Weak bond between hydrogen and oxygen.
Chemical Reaction
Change from forming or breaking bonds.
Synthesis Reaction
Formation of new compounds from bonds.
Decomposition Reaction
Breaking down large molecules into smaller.
Water
Makes up 60-75% of human body.
Solvent
Dissolves salts and facilitates reactions.
Buffer System
Minimizes pH changes in solutions.
Base
Decreases hydrogen ion concentration.
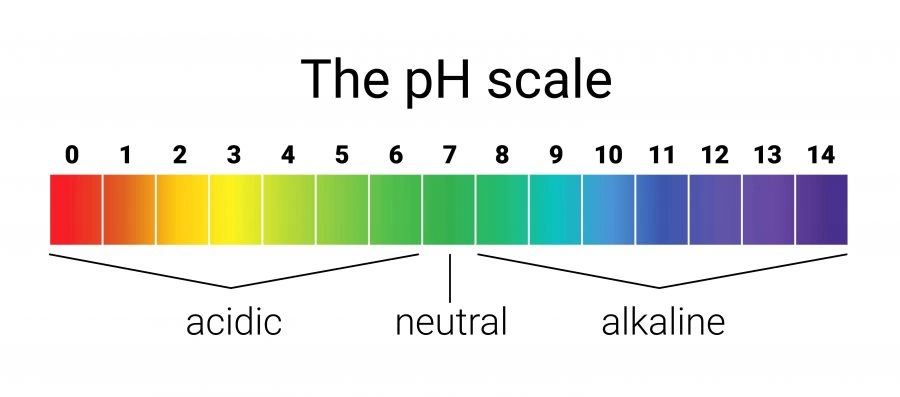
pH Scale
Measures acidity from 0 to 14.
Trace Elements
Needed in small amounts for body functions.
Carbohydrates
Primary energy source with C, H, O.
Monosaccharides
Single sugar compounds like glucose.
Disaccharides
Double sugars made from two monosaccharides.
Polysaccharides
Thousands of saccharides linked together.
Lipids
Fats containing C, H, O, and P.
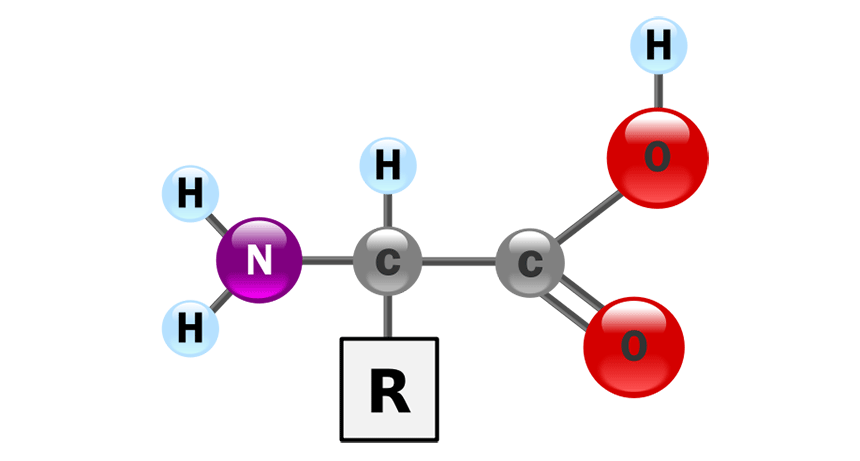
Proteins
Composed of amino acids, essential for body.
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins, about 20 types.
Enzymes
Proteins that act as catalysts in reactions.
Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA, composed of nucleotides.
ATP
Energy source produced in mitochondria.
Vitamins
Organic molecules needed for metabolism.
Fat Soluble Vitamins
A, D, E, K
Water Soluble Vitamins
B, C
ADP
precursor for ATP. Is formed when ATP is broken down
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid, Similar to DNA, Usually single stranded
DNA
Primary Component of chromosomes, carries our genetic information
Nucleotide
Subunit of nucleic acid, consists of sugar, nitrogen base, and phosphate group.
Denatured
enzyme looses its shape, causes change in pH and heat
Substrates
the reacting substance with and enzyme
Active site theory
lock and key
Amino Acid
peptide bond
holds the amino acid together (polypeptides)
Cholesterol
Used to make important hormones and other bodily compartments. EX: Cell membrane, bile, Vitamin D
Steroids
Cholesterol, much different structure from other lipids
True fats
Phospholipid
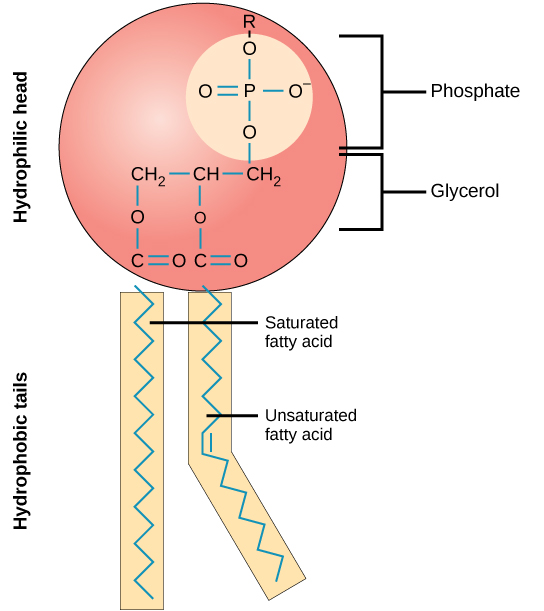
Phospholipid
diglycerides with a phosphate group found in our cell membranes
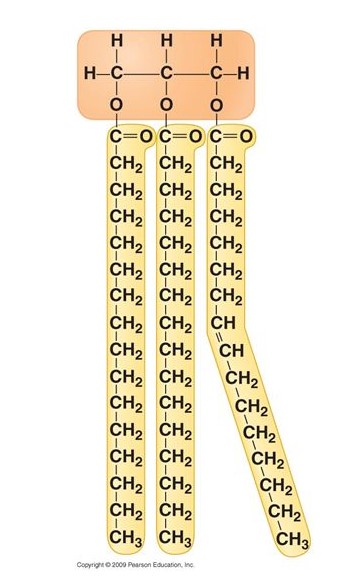
True Fats
lipid, contains one glycerol and 1 to 3 fatty acids. Ex: Triglycerides
Cellulose
long straight chunks of glucose, structural sugar. Ex: Fiber, wood, paper
Starch
long branched chains of glucose, stored carbohydrates in plants
Glycogen
Stored glucose (liver and Muscles), stored carbohydrates in animals
Oligosaccharides
consists of 3 - 20 monosaccharides
Ex: antigens (cell surface proteins), vegtables
Organic Compounds
contain covalently bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms, and possibly other atoms.
Sodium Bicarbonate
NaHCo3—>Na+ +HCo3
Carbonic Acid
H2Co3 —> H+ +HCo3
Acidosis
Occurs when carbon dioxide builds up in the blood thus decreasing the blood pH
Carbon Dioxide
byproduct of cellular respiration
is carried in the blood to the lungs for removal
Oxygen
used for cell respiration
used to break glucose down into useful energy
Aqueous Humor
water found in the eyeball
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
water found in and around the brain and spinal cord
Synovial Fluid
water found in joints
Tissue Fluid
water found in between cells
Lymph
water found in lymphatic Vessels
Plasma
water found in blood vessels
Extracellular Fluid
remainder of water in the body. Ex: Plasma, Lymph, Tissue Fluid, Synovial Fluid, Cerebrospinal Fluid, Aqueous humor
Intracellular Fluid
water within cells about 65% of our total water count
Temperature
Accepts a lot of temperature this helps maintain homeostasis
Lubricant
around bones, mucus and saliva