Topic 3.3 and 5.5 Finance, sources of finance, types of costs, break even
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
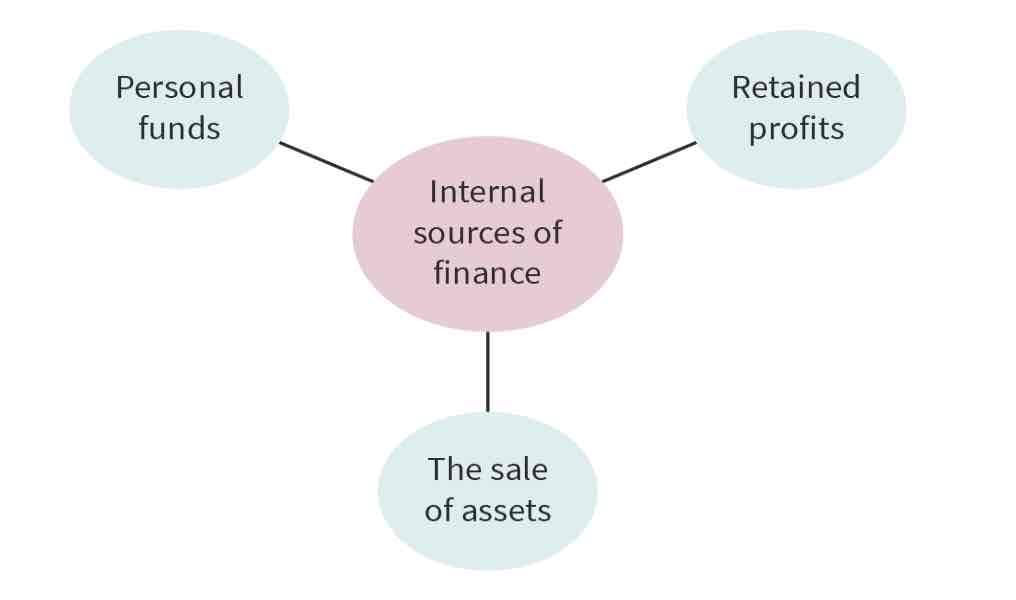
What are internal sources of finance?
Are funds generated within the organization, such as retained profit, personal funds and sale of assets.
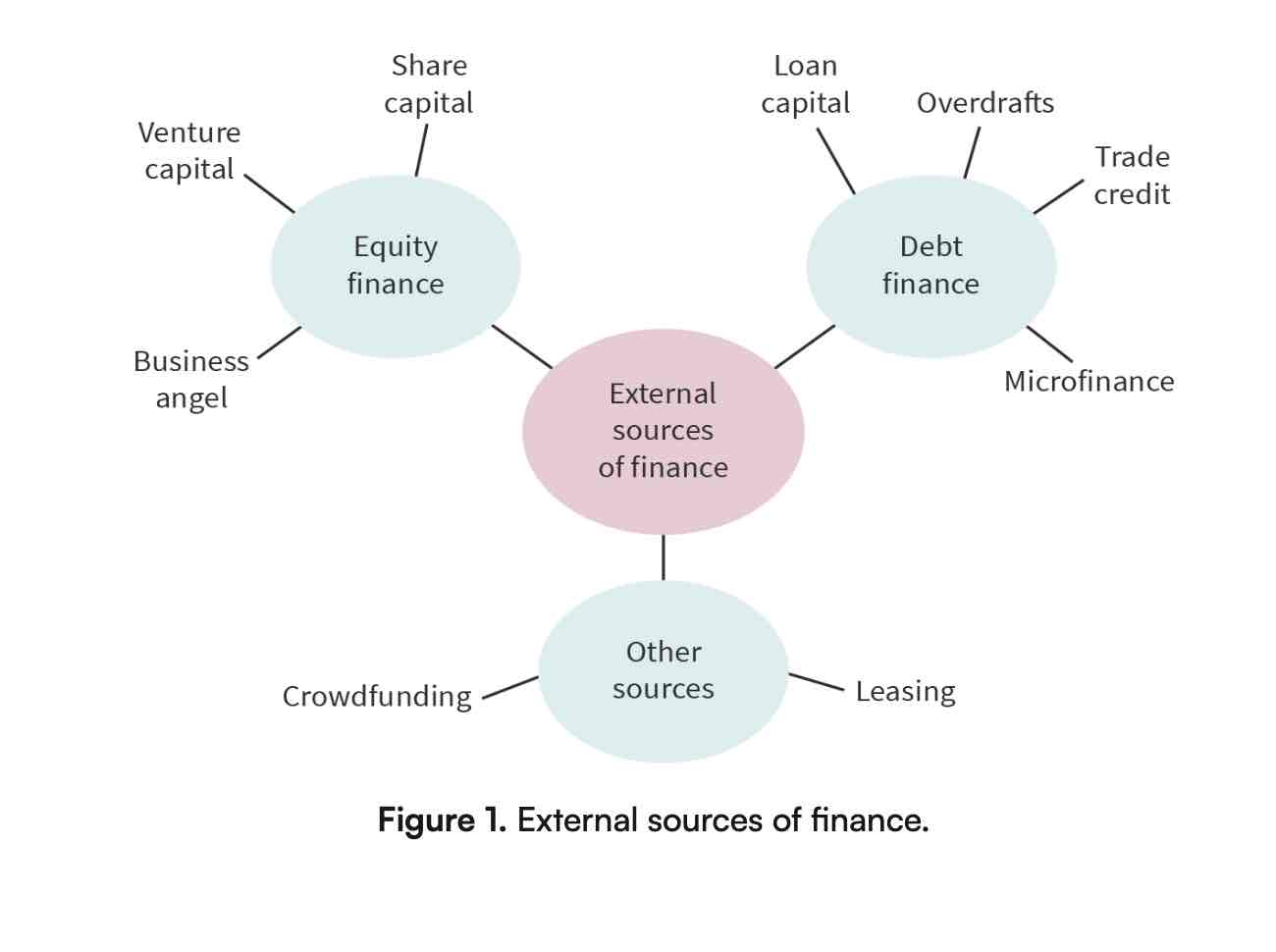
What are external sources of finance?
Are funds raised from outside the organization like loans, equity, leasing, crowdfunding and grants
What is equity financing?
Is the method of raising capital through the sale of shares in the company. Method include: share capital, venture capital, business angel
What is debt financing?
Is a type of external source of finance when a business borrows money that must be repaid over time, usually with interest. Method include: trade credit, overdrafts, loan capital, microfinance
What are retained earnings?
Is an internal source of finance in which the profits of a company is reinvested in the business after paying its dividends
What is crowdfunding?
Is an external source of finance, raising capital through the collective efforts of a large number of individuals, typically via online websites like Kickstarter.
What is venture capital?
Is financing provided to startups and small businesses with perceived long-term growth potential by investment companies. They are different compared to business angels because it is a company and a group of people instead
What is leasing?
External source of finance and a way to obtain financing by renting an asset instead of purchasing it outright, is usually lower price, and does not need to worry about meeting repairing the equipment
What is capital expenditure?
It is the funds used by a company to acquire or upgrade fixed assets such as property, buildings, copyright or equipment. And are considered long term investments
What is revenue expenditure?
It refers to spending on the day-to-day operational costs of running a business, such as rent, utilities, and salaries. And is considered short-term
What is insolvency?
When a business is unable to pay it’s debts
What is a business angel?
An individual who provides financial investment to startups in exchange for ownership equity or convertible debt. It is different to venture capital because they are individuals and use personal money
What is share capital?
The funds generated by a company through the issuance of shares to new investors on the stock market.
What is loan capital?
Refers to the funds that a business borrows from external sources, such as banks or a mortgage, typically in the form of loans that must be repaid over time. Businesses can also provide an asset as collateral in the event that the business does not pay their loan
What are overdrafts?
Are a form of credit that allows a business to withdraw more money from its account than is available, up to a certain limit and must be paid back before spending anymore
What is microfinance?
Is a financial service that provides small loans and financial support to individuals and small businesses lacking access to traditional banking and can include transaction, saving accounts and insurance products. Typically have high interest rates
What is trade credit?
Is a form of short-term financing where a business receives goods or services and agrees to pay for them later. Typically has no interest
Personal Funds/savings
Is an internal source of income that comes directly from the stakeholder’s own money. It will affect their personal finance
Sales of assets
An external source of finance where a business sells their assets(machinery, land, patents, brandnames) to buyers.
Fixed costs
Costs that stay the same at all levels of output eg:Rent, salaries, accounting fees, insurance premiums

Variable costs
Costs of production that are based on the level of usage/output eg:raw materials, utility, packaging, delivery costs

total costs
Costs consisting of both variable and fixed costs. FC+VC
Semi-variable costs
Costs that are fixed until a level of production is reached where they become variable eg: Labour cost, telephone, Internet, and maintenance
direct costs
Cause identified with a particular and specific product or process from the business eg: raw materials, direct labour, packaging
Indirect cost/overhead
Costs that come from the business as a whole and isn’t a specific product or process eg:rent, insurance, admin salaries
Revenue
Is the income that a business earns from goods and services. Formula:price*quantity of sales
Contribution
Money leftover from selling a product to pay for the variable cost needed to produce it. Formula: selling price-variable cost per unit. It isn’t profit yet
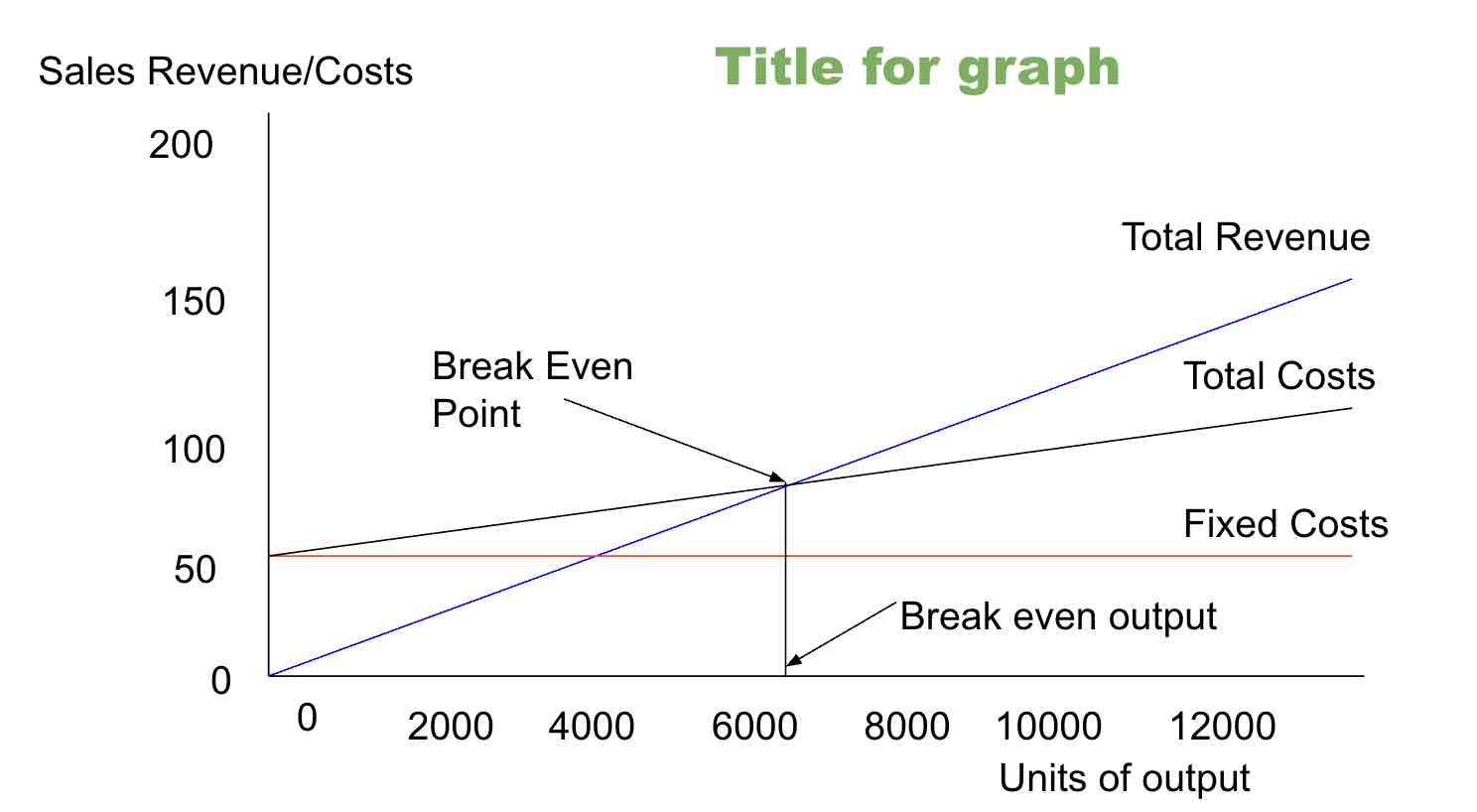
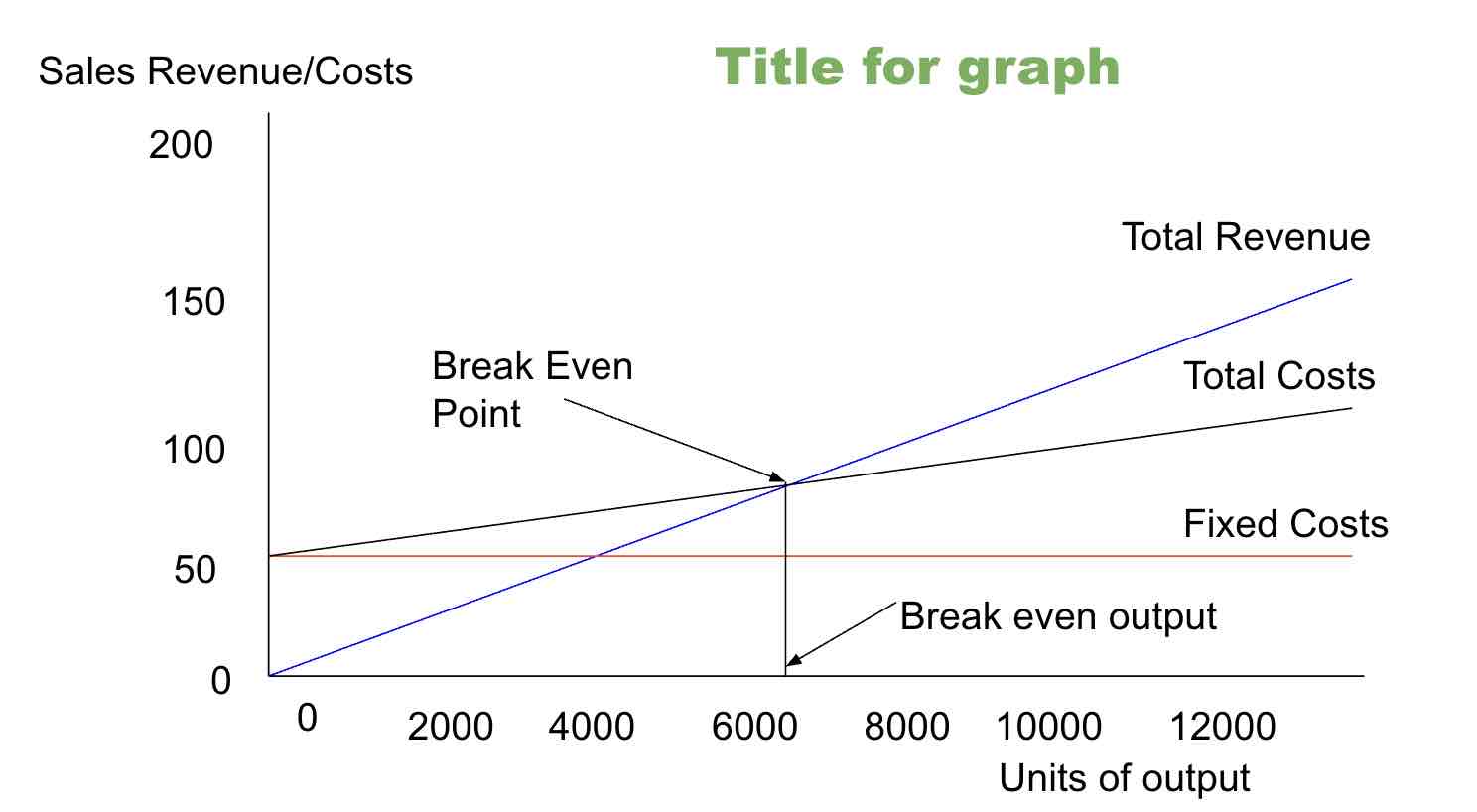
Break even(quantity)
It is the stage where a business neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss, meaning all expenses are equal to the income. Formula: fixed costs/contribution per unit
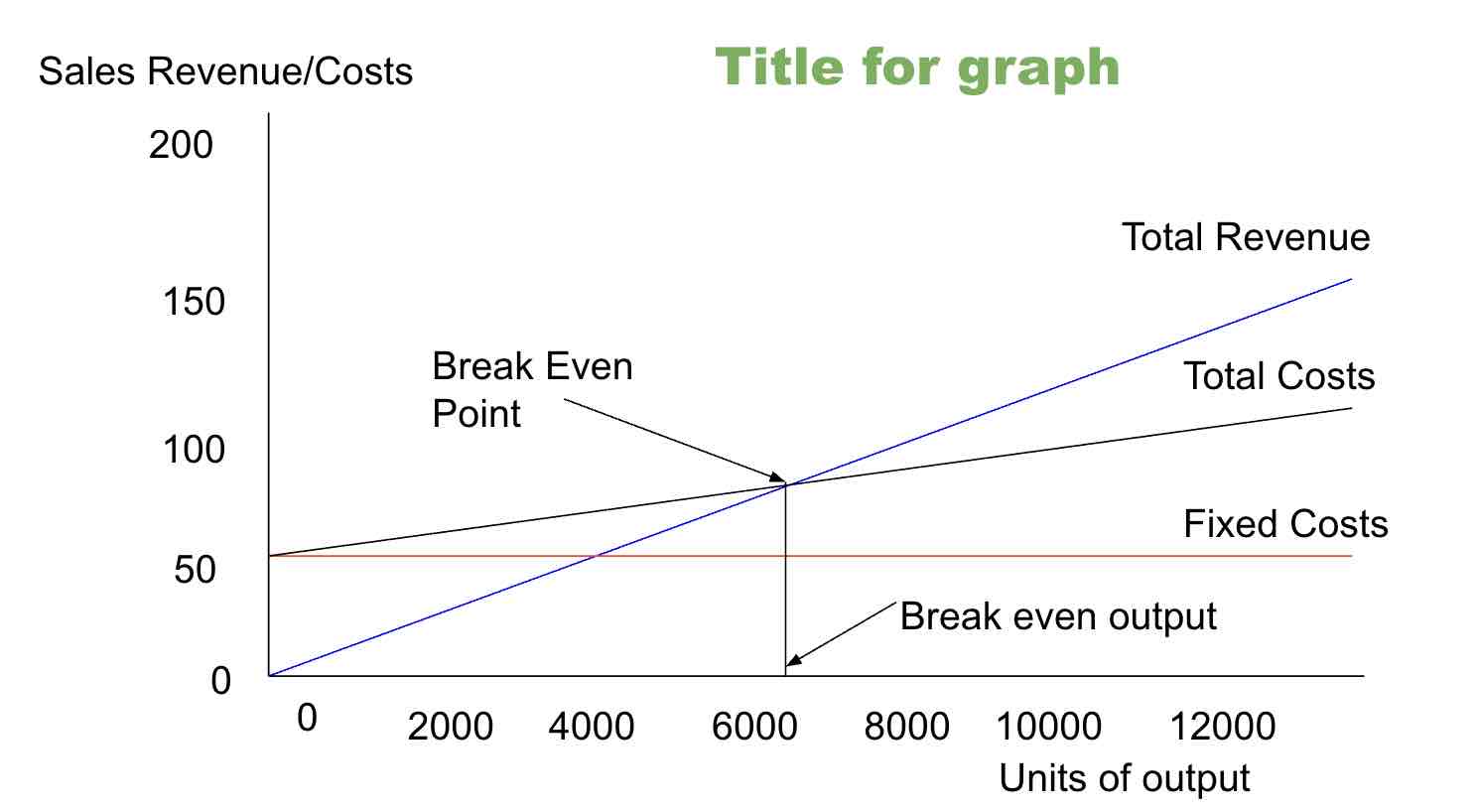
Break-even point (BEP)
The position where total cost and total revenue lines cross in a graph
Margin of safety
Is the cushion between expected performance and the worst case scenario. Formula:(Current sales-break even point)/ current sales
Pros of break even analysis
Allows a firm to see profits at different levels of production
Help businesses understanding pricing decisions, changes in its profitability resulting from the impact of changes in sales, pricing, fixed costs, and variable costs
Easy to interpret
Can be used to support of raising of finance
Limitations of a break even analysis
Reliance on assumptions, such as fixed cost and selling price remaining the same
Lack of consideration for external factors, such as market changes
Simplicity compared to real world complexities
Expects everything to go perfectly
Target profit
Profit that the business expects to get
Price x Quantity – [Fixed Costs (FC) + Average Variable Cost (AVC) x Quantity])
Absorption costing
Is a managerial accounting method for capturing all costs associated with manufacturing a particular product. Under this method, all manufacturing costs, whether variable or fixed, are allocated to the product.