CHEM 1C Midterm 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
Does tetrahedral have geometric isomers?
No! Regardless of how you organize, the bond angles do not change
2
New cards
Can tetrahedral be optically active?
Yes! If the central atom is bonded to 4 different things, then it is chiral
3
New cards
Geometric isomers
different in positions (cis/trans) (subset of stereoisomers) \n - cis = ligands are side-by-side or at 90° angle \n - trans = ligands are across from each other at 180° angle
4
New cards
Linkage isomers
different binding sites (subset of structural isomers)
5
New cards
Coordination isomers
different atoms inside the complex ion
6
New cards
Optical isomers
nonsuperimposable mirror images
for unidentate ligands: if pair of the same thing \[(aa)\] or a repeating pair \[(ab)(ab)\], then it does not have optical isomers. If each pair is unique, then it has optical isomers
for bidentate ligands: Look at the axis of symmetry (which does not spilt the bidentate ligands). If symmetrical, it does not have optical isomers. If it is not symmetrical, it has optical isomers
the cis or trans version can exhibit different optical isomerism, as in one could be optically active which one is not, vive-versa, neither, or both
for unidentate ligands: if pair of the same thing \[(aa)\] or a repeating pair \[(ab)(ab)\], then it does not have optical isomers. If each pair is unique, then it has optical isomers
for bidentate ligands: Look at the axis of symmetry (which does not spilt the bidentate ligands). If symmetrical, it does not have optical isomers. If it is not symmetrical, it has optical isomers
the cis or trans version can exhibit different optical isomerism, as in one could be optically active which one is not, vive-versa, neither, or both
7
New cards
Chiral
molecule with nonsuperimposable mirror image
optical isomerism
optical isomerism
8
New cards
achiral
superimposable mirror images
does not exhibit optical isomerism
does not exhibit optical isomerism
9
New cards
Alkane reactions
**combustion reactions:** CₙH₂ₙ₊₂ + (3n + 1)/2 O₂ + n CO₂ + (n+1) H₂O
**halogenation reactions:** CH₄ + Cl₂ → CH₃Cl + HCl
**dehydrogenation reactions:** saturated hydrocarbon (CnH2n+2) → unsaturated hydrocarbon w/ double bond (CnH2n) + H2
**halogenation reactions:** CH₄ + Cl₂ → CH₃Cl + HCl
**dehydrogenation reactions:** saturated hydrocarbon (CnH2n+2) → unsaturated hydrocarbon w/ double bond (CnH2n) + H2
10
New cards
Ketoses
carbohydrate with ketone group, usually C2
11
New cards
What is boiling point elevation caused by?
The nonvolatile solute decreases the vapor pressure, effectively increasing the boiling point
12
New cards
What is a monosaccharide?\`
a simple sugar with multiple OH groups
disaccharides are two of these and polysaccharides are a polymerized chain of these (which lowers the osmotic effects (M decrease)
disaccharides are two of these and polysaccharides are a polymerized chain of these (which lowers the osmotic effects (M decrease)
13
New cards
Protein structures
Primary: amino acids linked by amide (peptide) bonds (H-N-C=O)
Secondary: Short term structure. Alpha helix and Beta (Pleated) sheet
Tertiary: Long term structure, 3D. Dictated by intermolecular forces and R groups finding those similar to them.
Secondary: Short term structure. Alpha helix and Beta (Pleated) sheet
Tertiary: Long term structure, 3D. Dictated by intermolecular forces and R groups finding those similar to them.
14
New cards
How do you identify condensation polymerization?
Check for amide bond (H-N-C=O) created by a carboxylic acid and amine or an ester link (R1-(O=C)-O-R2) created by a carboxylic acid and an alcohol
15
New cards
How do proteins form?
A condensation reaction between amino acids, where the amino group of one bonds with the carboxyl group of another to form an amide (peptide) bond
H-N-C=O
H-N-C=O
16
New cards
Amino Acid structure?
C bonded to an H, an amino group, an R group, and a carboxyl group
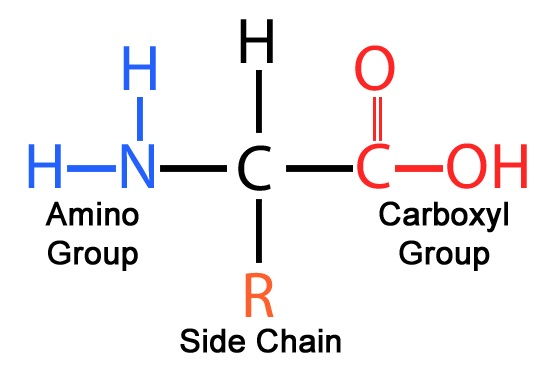
17
New cards
How do esters form?
A condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to form an ester link
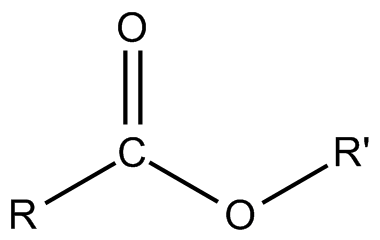
18
New cards
What is an ether?
R1-O-R2
19
New cards
Tonicity
hypertonic - one solution has a higher concentration of solute than another (water in cells, causing to swell and burst) (BAD!)
isotonic - both solutions have the same concentrations of solute (saline bags)
hypotonic - one solution has a lower concentration of solute than another (BAD!)
isotonic - both solutions have the same concentrations of solute (saline bags)
hypotonic - one solution has a lower concentration of solute than another (BAD!)
20
New cards
carboxylic acid
R-(C=O)-OH
Can H-bond with itself and water
Most soluble in water
Higher BP than alcohol
Can H-bond with itself and water
Most soluble in water
Higher BP than alcohol
21
New cards
Synthesis of a carboxylic acid
Oxidizing a primary acid
OR oxidizing an aldehyde
OR oxidizing an aldehyde
22
New cards
Aldoses
Sugar with an aldehyde group at the end
23
New cards
freezing point depression
the solvent is diluted by the addition of a solute, so that fewer molecules are available to freeze, causing the freezing point to decrease
24
New cards
Paramagnetic vs Diamagetic
Paramagnetic: unpaired electrons
Diamagnetic: all paired up
Diamagnetic: all paired up
25
New cards
Nucleotides
5 Carbon sugar
Nucleobase (base with N)
Phosphate group
Link by ester bonding (sugar base of one and phosphate group of another)
Nucleobase (base with N)
Phosphate group
Link by ester bonding (sugar base of one and phosphate group of another)
26
New cards
Colligative Properties
depend on how much is present, not on what is present
27
New cards
Aldehydes
H-(C=O)-R
Cannnot hydrogen bond with itself
Cannnot hydrogen bond with itself
28
New cards
Amines
C-N single bond
Primary: 1 substituent
R1-NH2
Secondary: 2 substituents
R1-NH-R2
Tertiary: 3 substitutents
3 Rs bonded to N
Primary: 1 substituent
R1-NH2
Secondary: 2 substituents
R1-NH-R2
Tertiary: 3 substitutents
3 Rs bonded to N
29
New cards
Carbohydrates
CH2O
30
New cards
Ketone
C doubled bonded to an O and 2 R groups
Synthesis: oxidize a secondary alcohol
The two R groups cannot be Hs, they must be carbon chains to be a ketone
Synthesis: oxidize a secondary alcohol
The two R groups cannot be Hs, they must be carbon chains to be a ketone
31
New cards
Can tetrahedrals be low spin?
Tetrahedral is ALWAYS high spin
32
New cards
An R group can start with…
Really, anything. It is mainly Carbons, but an R group can be just an H, or halogens.
The only exception is ketones, where the two R groups must be carbon chains and cannot be just an H (that would be an aldehyde).
The only exception is ketones, where the two R groups must be carbon chains and cannot be just an H (that would be an aldehyde).
33
New cards
Can Square Planar be chiral?
NO! ALWAYS ACHIRAL
can have geometric isomers
can have geometric isomers
34
New cards
Can Tetrahedral be chiral?
YES! IF IT HAS 4 DIFFERENT BONDS
35
New cards
Can Tetrahedral have geometric isomers?
NO! NO CHANGE IN BOND ANGLE NO MATTER WHAT YOU DO
36
New cards
Which octahedral configurations has geometric isomerism?
\[M(a)4(b)2\] (1 cis, 1 trans)
\[M(a)3(b)3\]
\[M(a)3(b)3\]
37
New cards
Which square planar configurations have geometric isomerism?
\[M(a)2(b)2\] (1 cis, 1 trans)
\[M(a)(b)(c)(d)\] (3 isomers: 2 cis, 1 trans)
\[M(a)(b)(c)(d)\] (3 isomers: 2 cis, 1 trans)
38
New cards
Which tetrahedral complexes are optically active?
\[M(a)(b)(c)(d)\]
39
New cards
What octahedral configurations have geometric isomers?
\[M(a)5(b)\] (2 isomers)
\[M(a)3(b)2(c)\] (3 isomers)
\[M(a)3(b)3\] (2 isomers)
\[M(a)3(b)(c)(d)\] (4 isomers)
\[M(a)2(b)2(c)2\] (5 isomers)
\[M(a)3(b)2(c)\] (3 isomers)
\[M(a)3(b)3\] (2 isomers)
\[M(a)3(b)(c)(d)\] (4 isomers)
\[M(a)2(b)2(c)2\] (5 isomers)
40
New cards
What octahedral configurations are optically active?
\[M(a)3(b)(c)(d)\]
\[M(a)2(b)2(c)2\]
\[M(a)2(b)2(c)2\]