INHIBITION OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis
New peptidoglycan monomers are inserted by transglycosylase (transglycosidase)
The final rigidity of the cell wall is imparted by cross-linking of the peptide chains by transpeptidase enzyme
Penicillin-Binding Proteins (PBP)
may act as transglycosylase or as transpeptidase
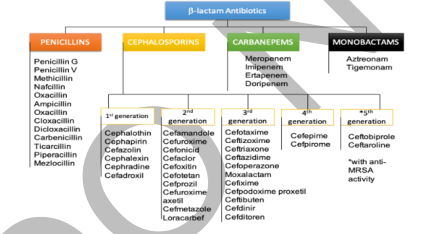
β-Lactam Drugs
• All ___ drugs are selective inhibitors of bacterial cell wall synthesis
• Destruction of bacterial autolysins (murein hydrolase)
• Core structure of penicillins (top) and cephalosporins (bottom) ___ ring in red.
memo the gen
Penicillins
The ___ are derived from molds of the genus Penicillium
Natural Penicillins
β-lactamase resistant
Aminopenicillins
Ureidopenicillins
Carboxypenicillins
5 Principal Groups of penicillin
Natural Penicillins
They have the highest activity against Gram-positive organisms, spirochetes, and susceptible to β lactamase
Penicillin V (phenoxymethylpenicillin)
Penicillin G (Benzylpenicillin)
Aqueous penicillin G (IV)
Procaine penicillin G (IM)
Benzathine penicillin G (IM)
Penicillin G (Benzylpenicillin)
β-Lactamase Resistant
• Antistaphylococcal penicillins
• Lower activity against Gram-positive organisms and inactive against Gram-negative organisms.
o Nafcillin, Methicillin, Oxacillin, Dicloxacillin
• Staphylococci resistant to oxacillin and nafcillin have the mecA gene
Aminopenicillins
• Extended-Spectrum Penicillins
• They have high activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms but are destroyed by βlactamases
• Ampicillin
• Amoxicillin
Aminopenicillins + β-Lactamase Inhibitors
• Ampicillin + Sulbactam (Sultamicillin)
• Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid (Co-Amoxiclav)
Ureidopenicillins
• Piperacillin (anti-pseudomonal)
• Mezlocillin
Carboxypenicillins – anti-pseudomonal
• Carbenicillin
• Ticarcillin
• Piperacillin + Tazobactam
• Ticarcillin + Clavulanic acid
Other preparations:
Cephalosporins
• The mechanism of action is analogous to that of penicillins
• ___ tend to be resistant to the βlactamases
• ___ have been arranged into major groups, or “generations”
1st Generation
Gram (+) cocci and PEcK (P. mirabilis, E. coli, K. pneumoniae)
2nd Generation
Gram (+) cocci and HENPEcK (H. influenzae, E. aerogenes, N. gonorrhae, P. mirabilis, E. coli, K. pneumoniae)
3rd Generation
Gram (+) cocci and HENPPEcK (H. influenzae, E. aerogenes, N. gonorrhae, P. aeruginosa, P. mirabilis, E. coli, K. pneumoniae
4th Generation
Gram (+) cocci [MRSA] and E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. mirabilis, and P. aeruginos
Carbanepams
• Imipenem + Cilastatin – has good activity against many Gram-negative rods, Gram-positive organisms, and anaerobes.
• Meropenem
• Ertapenem
Monobactams
• Aztreonam
• It has antimicrobial activity directed primarily against the Enterobacteriaceae, including P. aeruginosa.
• No activity against Gram-positive organisms and anaerobes
Other Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors
• Glycopeptide antibiotics such as vancomycin and teicoplanin
• Lipoglycopeptides such as oritavancin, telavancin, and dalbavancin.
• Fosfomycin
• Bacitracin
• Cycloserine
• Novobiocin
penicillin

cephalosporins
carbapenems

Monobactam

Vancomycin

Penicillin cephalosporins
Type of act: bactericidal

Vancomycin bacitracin
process: mucopeptide synthesis
type of act: bactericidal
cycloserine
process: synthesis of cell wall peptides
type of act: bactericidal