History of the Periodic Table
4.0(1)
4.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
1
New cards
Arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic weight and similar chemical properties.
Mendeleev

2
New cards
The reason that there were gaps in Mendeleev's table.
Undiscovered elements
3
New cards
When the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain sets of properties recur periodically
Mendeleev's Periodic Law

4
New cards
What was missing from Mendeleev's table
Noble gases
Transition elements not in a separate block
Transition elements not in a separate block
5
New cards
Discovered atomic number.
Arranged elements in order of increasing atomic number and similar chemical properties.
Arranged elements in order of increasing atomic number and similar chemical properties.
Mosely

6
New cards
When the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, certain sets of properties recur periodically
Modern Periodic Law
7
New cards
Arranged elements in triads.
Dobereiner

8
New cards
Group of elements with similar chemical properties in which the middle element has an atomic weight equal to the average of the other two.
Triad

9
New cards
Arranged elements in order of increasing atomic weight where the 1st and 8th have similar chemical properties.
Newlands

10
New cards
The problem with Newlands' octaves
Nobel gases not included. No gaps.
11
New cards
Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
Atomic number
12
New cards
Number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
Mass number
13
New cards
The number of electrons in a nucleus.
Atomic number
14
New cards
The reason Triads did not work as a theory.
They did not follow a Mathematical Law.
15
New cards
Ancient Greeks
• 4 elements: earth, air, fire, water
16
New cards
Robert Boyle
•From waterford
•Discovered elements cant be broken down
•Discovered compounds are a combination of elements which can be broken down
•Discovered elements cant be broken down
•Discovered compounds are a combination of elements which can be broken down
17
New cards
Humphrey Davy
•Devolped techniques for breaking compounds into mixtures
•Electrolyzed a sample of potassium hydroxide and isolated potassium which burst into lilac flames
•Isolated more elements
•Electrolyzed a sample of potassium hydroxide and isolated potassium which burst into lilac flames
•Isolated more elements
18
New cards
Moseley
• 1913 used xrays to discover a positive charge in the atomic nucleus of each element
• He called this charge the atomic number
• Defined an element as a substance whose atoms all have the same atomic number
• He called this charge the atomic number
• Defined an element as a substance whose atoms all have the same atomic number
19
New cards
What is the periodic table?
• It is a list of all known chemical elements arranged by increasing atomic number and groups of elements according to recurring properties.
20
New cards
Dobereiner’s Triads
• groups of three elements
• similar chemical properties
• atomic weight of the second is midway between that of the first and the third
• example: Li, Na, K
• restricted to a small number of elements
• similar chemical properties
• atomic weight of the second is midway between that of the first and the third
• example: Li, Na, K
• restricted to a small number of elements
21
New cards
Newlands’ Octaves
• when in order of atomic weight, properties repeat every eight elements
• worked for first 17 elements
• forced all known elements - Cu & Ag with Li, Na, K
• principle: periodic reoccurrence of properties when elements are arranged in order of
increasing atomic weight.
• worked for first 17 elements
• forced all known elements - Cu & Ag with Li, Na, K
• principle: periodic reoccurrence of properties when elements are arranged in order of
increasing atomic weight.
22
New cards
Newlands’ Octaves
• when in order of atomic weight, properties repeat every eight elements
• worked for first 17 elements
• forced all known elements - Cu & Ag with Li, Na, K
• principle: periodic reoccurrence of properties when elements are arranged in order of
increasing atomic weight.
• worked for first 17 elements
• forced all known elements - Cu & Ag with Li, Na, K
• principle: periodic reoccurrence of properties when elements are arranged in order of
increasing atomic weight.
23
New cards
Moseley 2
• discovery of characteristic positive charge / atomic number
• table in order of increasing atomic number
• table in order of increasing atomic number
24
New cards
Compare Mendeleev’s and the modern periodic table
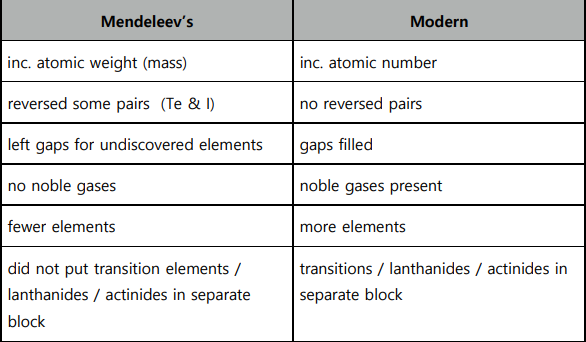
25
New cards
The Alkali Metals
• increasing reactivity going down the group
• soft metals - can be cut with a knife
• low densities
• shiny but tarnish quickly
• soft metals - can be cut with a knife
• low densities
• shiny but tarnish quickly
26
New cards
The Alkaline Earth Metals
• increasing reactivity going down the group
• harder than the alkali metals
• less reactive than their corresponding alkali metals
• react with water but less vigorously than their corresponding alkali metals
• calcium + water ⟶ calcium hydroxide + hydrogen
• harder than the alkali metals
• less reactive than their corresponding alkali metals
• react with water but less vigorously than their corresponding alkali metals
• calcium + water ⟶ calcium hydroxide + hydrogen
27
New cards
The Halogens
nonmetals
• decreasing reactivity going down the group
• low melting/boiling points
• react with hydrogen to form acidic soln.s
• hydrogen + chlorine
• react vigorously with alkali metals forming white salts
• sodium + chlorine ⟶ sodium chloride
• decreasing reactivity going down the group
• low melting/boiling points
• react with hydrogen to form acidic soln.s
• hydrogen + chlorine
• react vigorously with alkali metals forming white salts
• sodium + chlorine ⟶ sodium chloride
28
New cards
The Noble Gases
• all gases at room temp.
• boiling point and density increase going down the group
• least reactive
• boiling point and density increase going down the group
• least reactive
29
New cards
Mass number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
30
New cards
Atomic number
The number of protons
31
New cards
isotope
Atoms with the same number of protons but with different numbers of neutrons
32
New cards
Relative atomic mass
The RAM of an element is the average mass of an atom of the element compared to one twelfth the mass of an atom of the carbon-12 isotope
33
New cards
Aufbau principle
When building up the electron configuration of an atom in its ground state, the electrons occupy the lowest avaliable energy levels.