3 Vertebrate Embryology
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:13 AM on 6/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
1
New cards
Vertebrate Embryology
1. **Fertilization**
* Embryology, Embryological Development
* Gametes
* Fertilization
* Journey of an Egg Cell
* Sperm-Egg Association (Acrosomal Process)
2. **Types of Egg Cells**
3. **Blastulation**
* Blastula vs Blastocyst
* Types of Cleavage
* Blastulation in Chordates
4. **Gastrulation**
* Types of Morphogenetic/Gastrulation Movements
* Gastrulation in Chordates
* Human Blastocyst at Implantation
5. **Neurulation**
* Neurulation vs Neural Induction
* Neurulation in Chordates
6. **Germ Layer Origin**
* Ectoderm
* Mesoderm
* Endoderm
2
New cards
Embryology
* often studied prior to morphology
* study of the early developmental stages of sexually reproducing organisms
* study of the early developmental stages of sexually reproducing organisms
3
New cards
Embryonic Development
Fertilization → Zygote → Cleavage → Morula → Blastula → Gastrula
4
New cards
Gametes
* mature sex cells, including male sperm and female ovum or egg
* each carries a haploid (n) number of chromosomes
* each carries a haploid (n) number of chromosomes
5
New cards
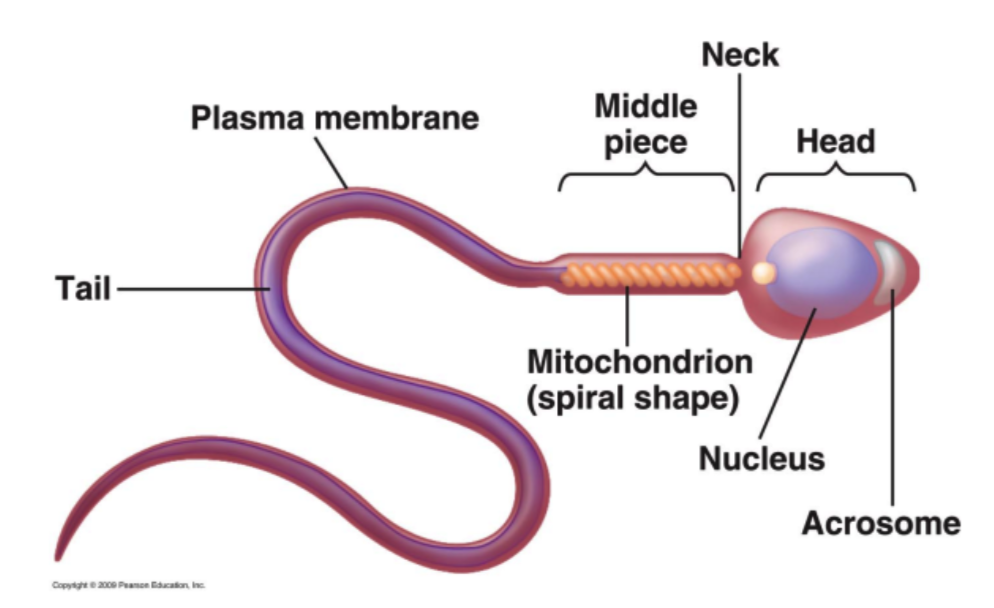
olfactory, nucleus, mitochondria
**Sperm cell**
* highly varied in appearance
* have ______ receptors; receive signals from egg
1. **Head**
* contains the ______
* may be:
* spherical
* spatulate
* hooked
* lance-shaped
* spiraled
* capped by acrosome
2. **Middle Piece or Neck**
* Contains ______ needed to provide energy
3. **Flagellum**
* propels the cell
* highly varied in appearance
* have ______ receptors; receive signals from egg
1. **Head**
* contains the ______
* may be:
* spherical
* spatulate
* hooked
* lance-shaped
* spiraled
* capped by acrosome
2. **Middle Piece or Neck**
* Contains ______ needed to provide energy
3. **Flagellum**
* propels the cell
6
New cards
Miroslav Holub
Between the 5th and 10th days the lump of stem cells differentiates into the overall building plan of the \[mouse\] embryo and its organs. It is a bit like a lump of iron turning into the space shuttle. In fact, it is the profoundest wonder we can still imagine and accept, and at the same time so usual that we have to force ourselves to wonder about the wondrousness of this wonder.
7
New cards
haploid, spermatozoa, oocyte, zygote, **genome**
**Fertilization**
* is the initiating step in development
* can be defined as the union of two ____ gametes, the _____ and the _____, hereto referred to as egg, to restore the diploid state, form a _____ through the process of egg activation, and commence a series of mitotic divisions that results in cell differentiation and embryo development.
* the process whereby **two cells fuse together** to create a **new individual** with **a _____ derived from both parents.**
* is the initiating step in development
* can be defined as the union of two ____ gametes, the _____ and the _____, hereto referred to as egg, to restore the diploid state, form a _____ through the process of egg activation, and commence a series of mitotic divisions that results in cell differentiation and embryo development.
* the process whereby **two cells fuse together** to create a **new individual** with **a _____ derived from both parents.**
8
New cards
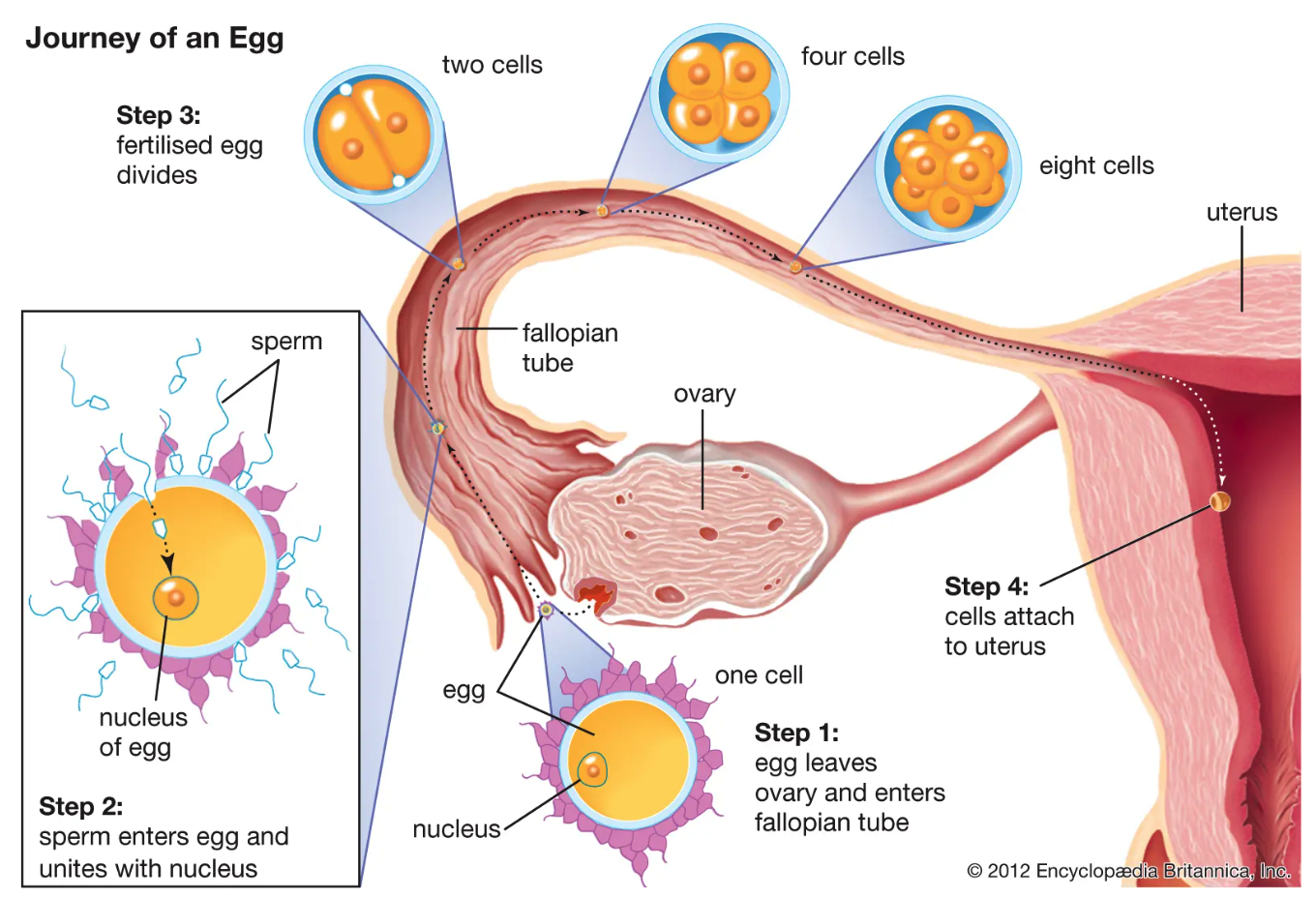
**Journey of an Egg Cell**
1. Egg leaves ovary and enters fallopian tube
2. Sperm enters egg and unites with nucleus
3. Fertilized egg divides (2→ 4→ 8 cells)
4. Cells attach at uterus
9
New cards
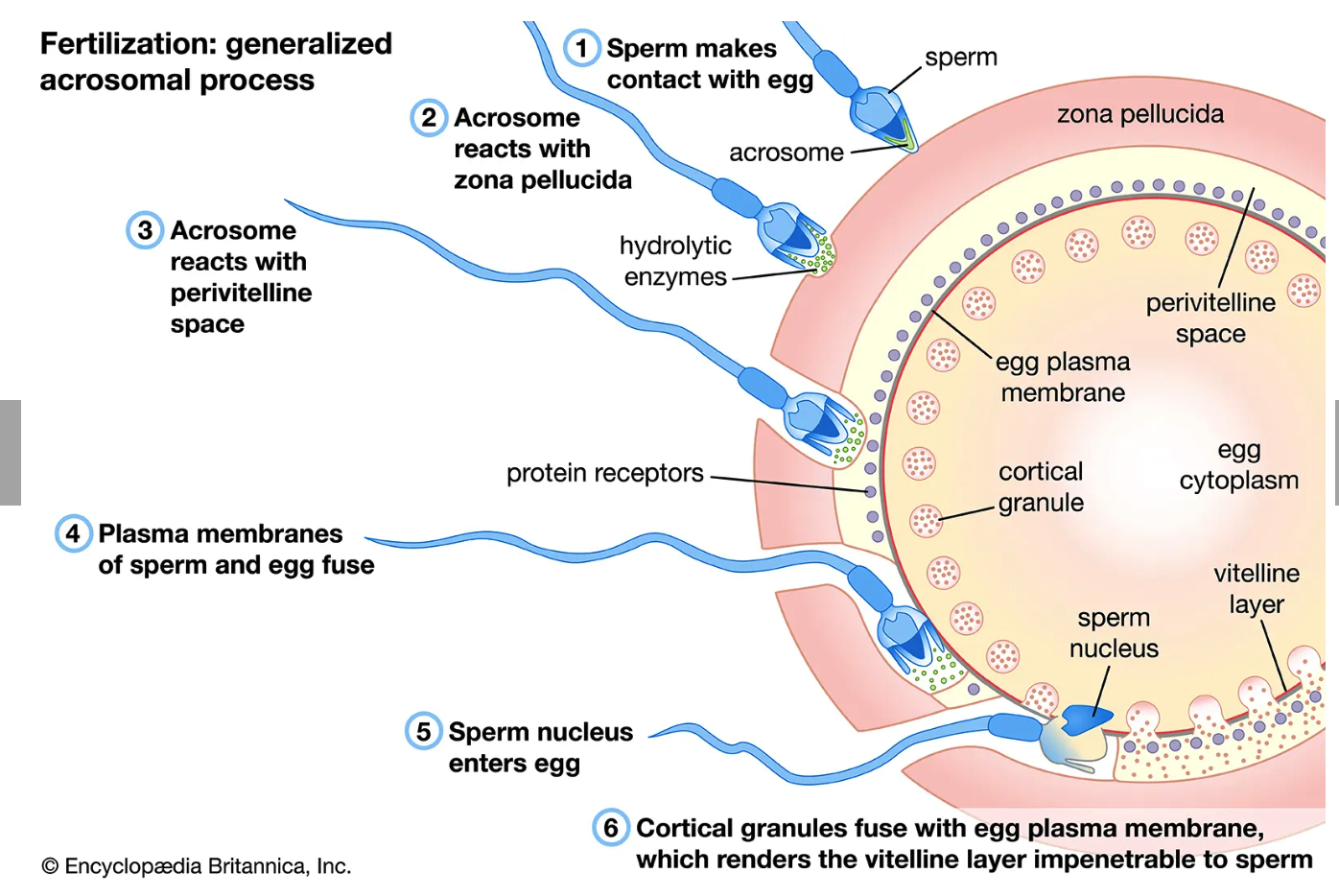
pellucida, hydrolytic, perivitelline, protein, membranes, nucleus, Cortical, polyspermy
**Sperm-Egg Association (Acrosomal Process)**
1. Sperm makes contact with egg
2. Acrosome reacts with zona ______
* Releases _____ enzymes
3. Acrosome reacts with ______ space
* _____ receptors
4. Plasma _______ of sperm and egg fuse
5. Sperm _____ enters egg
6. _____ granules fuse with egg plasma membrane (exocytosis) which renders vitelline layer impenetrable to sperm
1. This creates a hardened vitelline layer and prevents ______, or fertilization by multiple sperm cells
1. Sperm makes contact with egg
2. Acrosome reacts with zona ______
* Releases _____ enzymes
3. Acrosome reacts with ______ space
* _____ receptors
4. Plasma _______ of sperm and egg fuse
5. Sperm _____ enters egg
6. _____ granules fuse with egg plasma membrane (exocytosis) which renders vitelline layer impenetrable to sperm
1. This creates a hardened vitelline layer and prevents ______, or fertilization by multiple sperm cells
10
New cards
Cell-cell recognition
* Proteoglycans and glycoproteins within egg and sperm recognize each other and communicate
11
New cards
Acrosome
* This acidic vacuole contains a number of hydrolytic enzymes that, when secreted, help the sperm penetrate the egg's coats
12
New cards
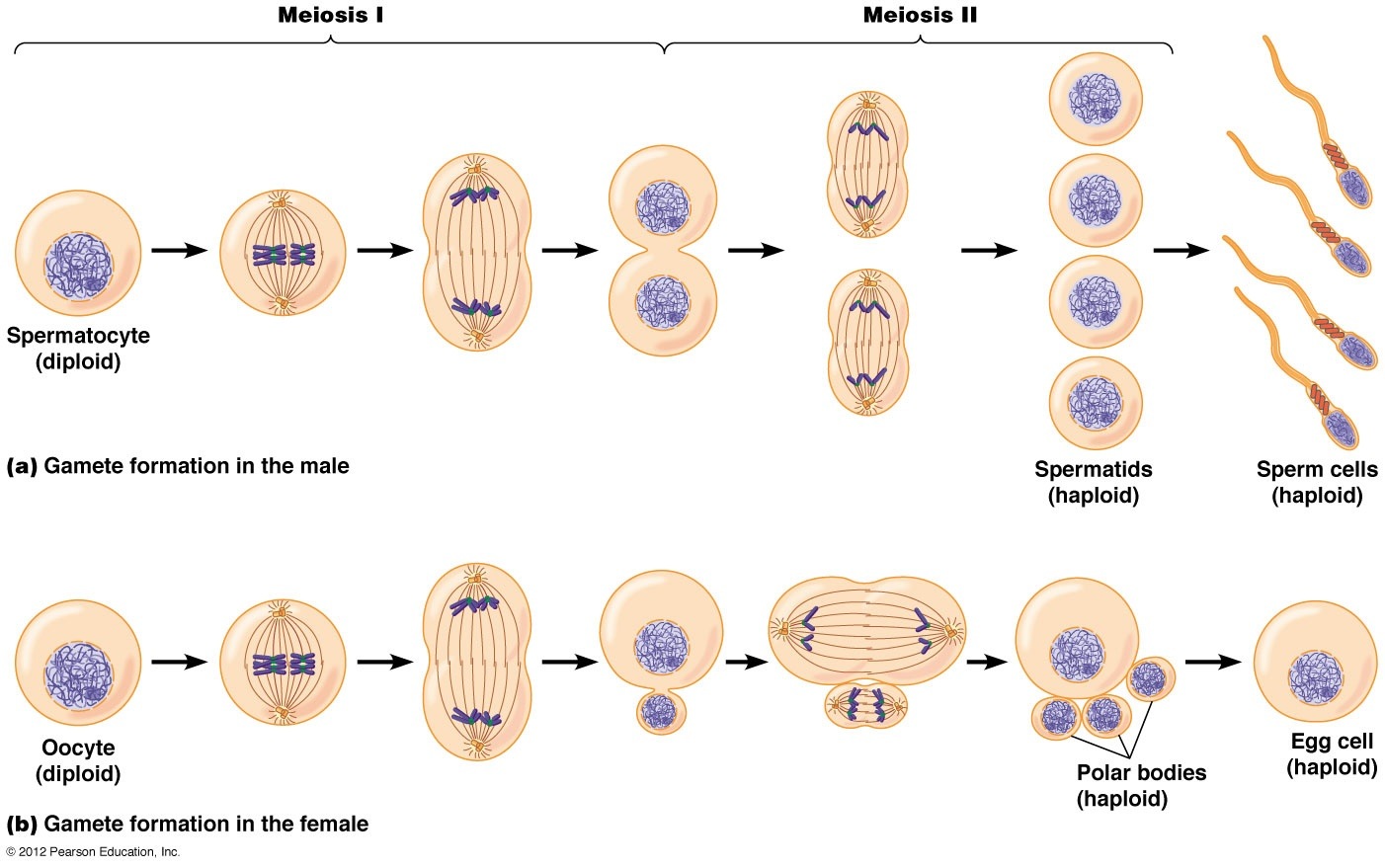
homologous, polar, animal, haploid
**Egg cell division**
* Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cells.
* Meiosis I
* involves pairing of ______ chromosomes, exchange of genetic material, and separation into two daughter cells, one of which is the sterile ___ body located near the ______ pole of the egg.
* Meiosis II
* involves separation of sister chromatids, resulting in four _____ daughter cells, each of which becomes a sperm cell in males.
* Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cells.
* Meiosis I
* involves pairing of ______ chromosomes, exchange of genetic material, and separation into two daughter cells, one of which is the sterile ___ body located near the ______ pole of the egg.
* Meiosis II
* involves separation of sister chromatids, resulting in four _____ daughter cells, each of which becomes a sperm cell in males.
13
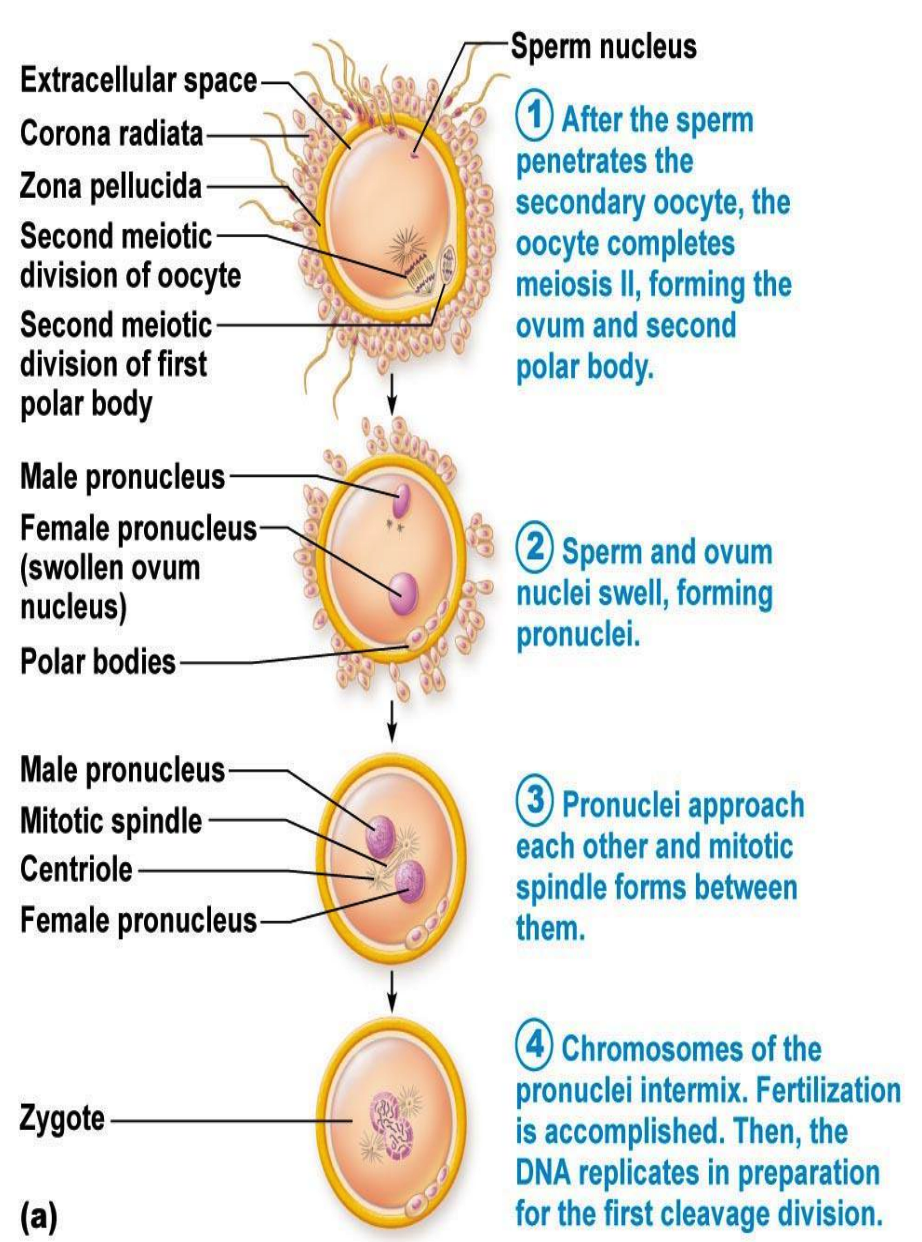
New cards
pronucleus, pronucleus, mitosis
**Fertilization**
* After fertilization
* egg undergoes cell divisions (G1, S, and G2 phases) to form the female _____
* while the sperm undergoes interphase to form the male _____
* Which merge and divide through _____ and cytokinesis to form a two-cell embryo.
* After fertilization
* egg undergoes cell divisions (G1, S, and G2 phases) to form the female _____
* while the sperm undergoes interphase to form the male _____
* Which merge and divide through _____ and cytokinesis to form a two-cell embryo.
14
New cards
Gastru
* Two critical stages between the events of fertilization & organ formation
1. Cleavage
2. ____lation
1. Cleavage
2. ____lation
15
New cards
Rapid, cytoplasm, pattern, amount, distribution, where, size, **inhibits,** angle, timing
**Cleavage**
* ___ cell divisions which divide the _____ of the fertilized egg into numerous cells, called blastomeres
* The _____ of cleavage is determined by two major parameters
1. The ____ and _____ of yolk protein within the cytoplasm
* Determines ____ cleavage can occur and the relative ___ of the blastomeres.
* In general, yolk ____ cleavage
2. Factors in the egg cytoplasm that influence the ____ of the mitotic spindle and the ____ of its formation
* ___ cell divisions which divide the _____ of the fertilized egg into numerous cells, called blastomeres
* The _____ of cleavage is determined by two major parameters
1. The ____ and _____ of yolk protein within the cytoplasm
* Determines ____ cleavage can occur and the relative ___ of the blastomeres.
* In general, yolk ____ cleavage
2. Factors in the egg cytoplasm that influence the ____ of the mitotic spindle and the ____ of its formation
16
New cards
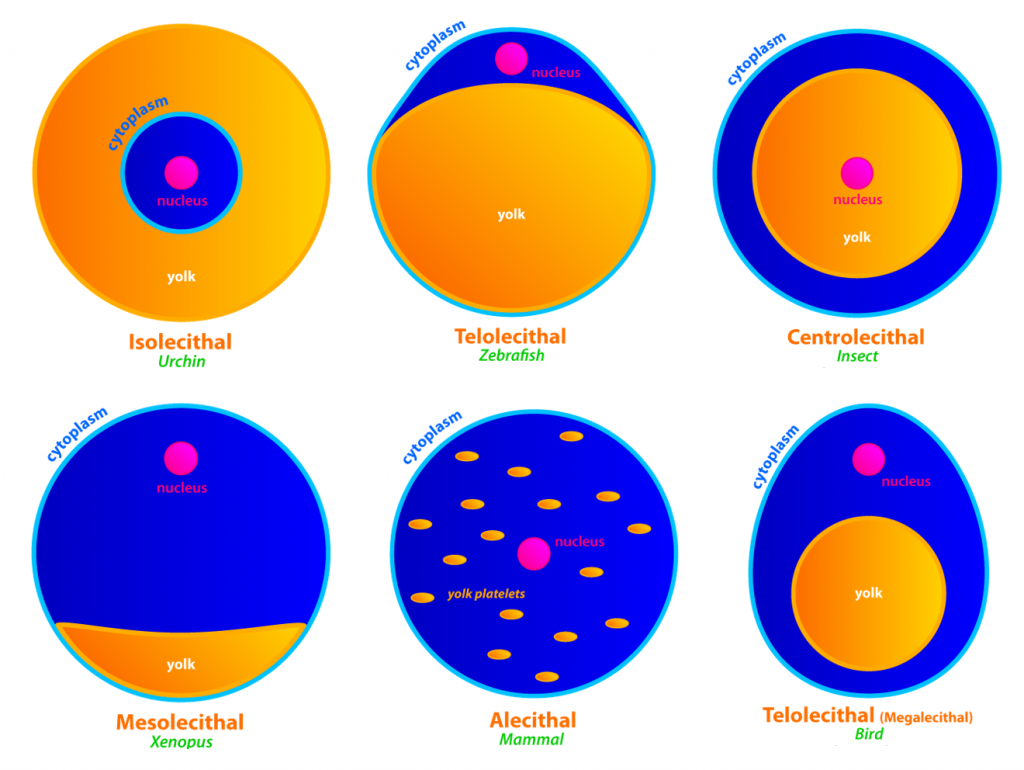
Egg cell
* Classified by:
1. **Based on Amount of Yolk**
* Microlecithal
* Mesolecithal
* Megalecithal
2. **Based on Yolk Distribution**
* Isolecithal
* Telolecithal
* Centrolecithal
1. **Based on Amount of Yolk**
* Microlecithal
* Mesolecithal
* Megalecithal
2. **Based on Yolk Distribution**
* Isolecithal
* Telolecithal
* Centrolecithal
17
New cards
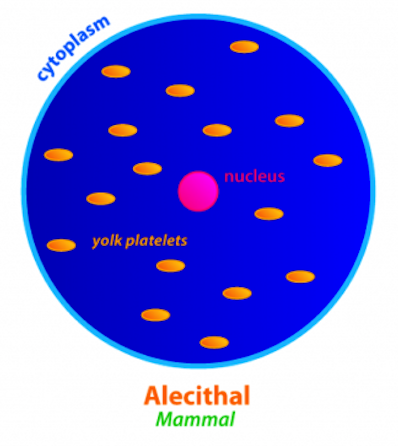
Microlecithal
* small eggs containing yolk (yolk platelets)
* may be an ancestral chordate condition
* e.g. Amphioxus and Eutherian mammals (with placenta to nourish their embryo)
* humans are alecithal
* may be an ancestral chordate condition
* e.g. Amphioxus and Eutherian mammals (with placenta to nourish their embryo)
* humans are alecithal
18
New cards
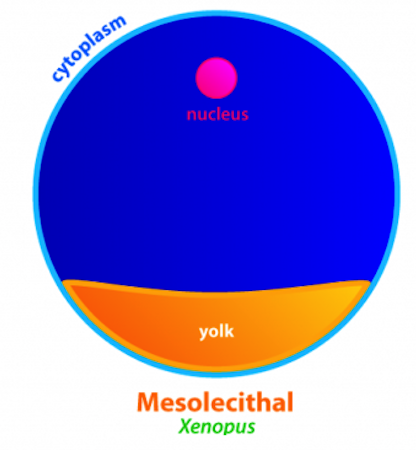
Mesolecithal
* Eggs containing moderate amount of yolk
* e.g. freshwater lampreys, some fishes and amphibians, basal bony fish, dipnoids
* e.g. freshwater lampreys, some fishes and amphibians, basal bony fish, dipnoids
19
New cards
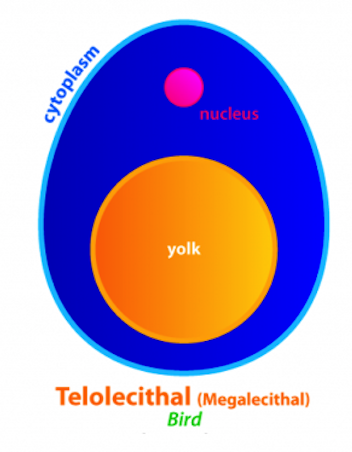
Megalecithal
* eggs laden with large amounts of yolk
* e.g. most fishes, elasmobranchs, teleosts, marine lampreys, reptiles, birds, and monotremes
* e.g. most fishes, elasmobranchs, teleosts, marine lampreys, reptiles, birds, and monotremes
20
New cards
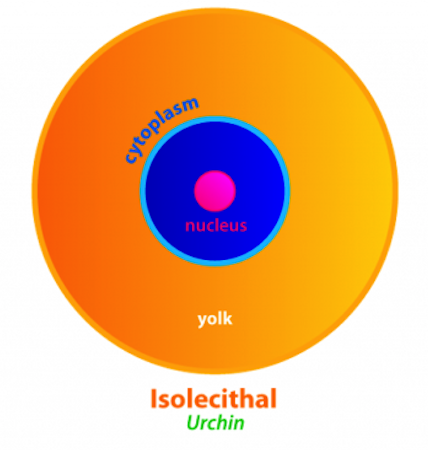
Isolecithal
* have sparse, equally spaced yolk
* common among microlecithal eggs
* Sea urchins, mammals, and snails
* common among microlecithal eggs
* Sea urchins, mammals, and snails
21
New cards
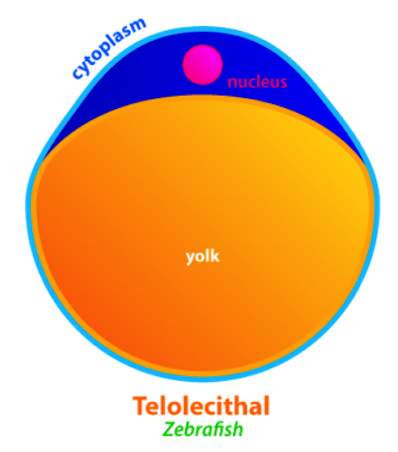
Telolecithal
* have dense yolk concentrated at one end
* Birds, reptiles
* Birds, reptiles
22
New cards
Centrolecithal
* yolk proteins are concentrated at the center
* insects
* insects
23
New cards
Animal pole
* yolk-free cytoplasmic material
24
New cards
Vegetal pole
* where yolk is concentrated
25
New cards
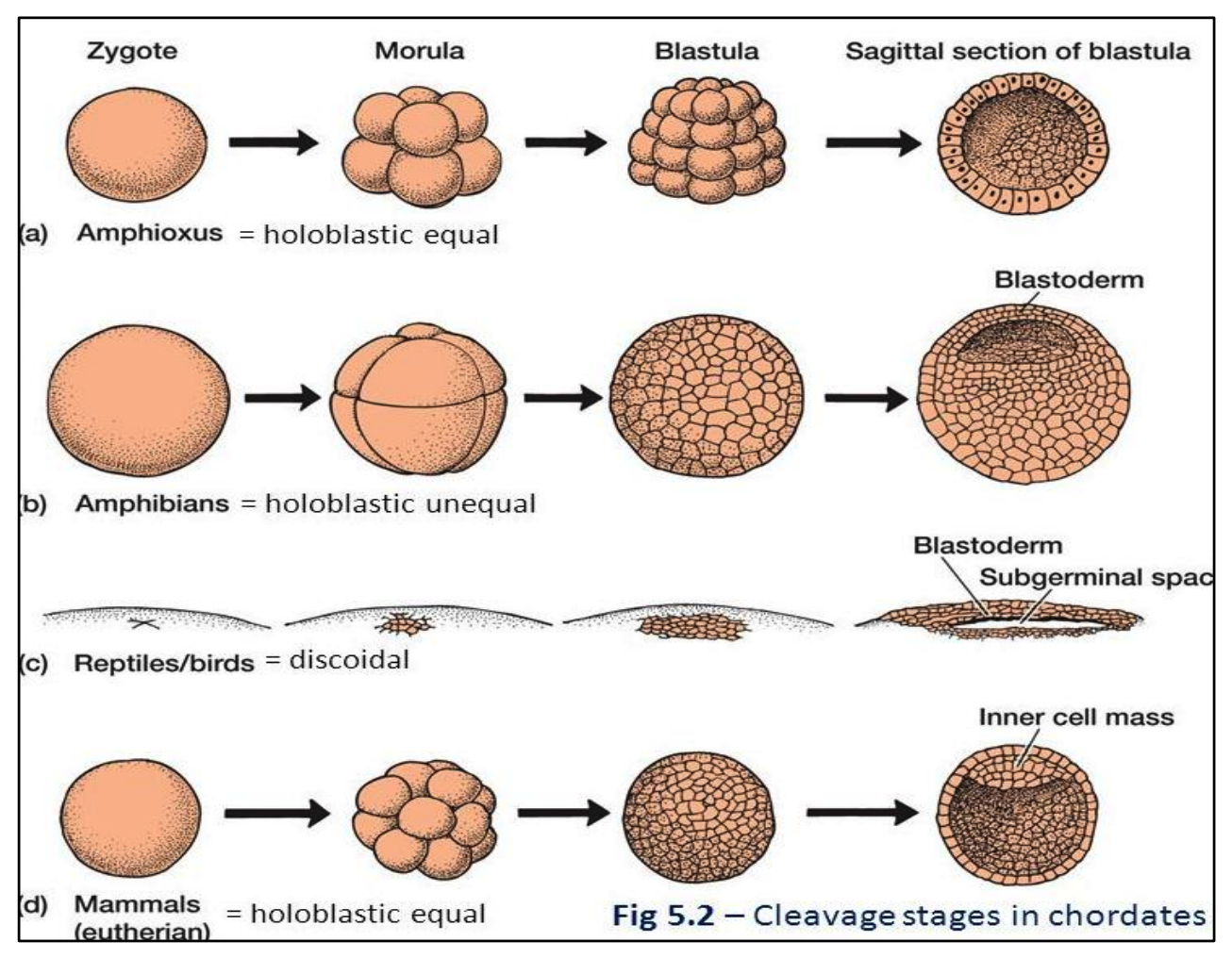
Chordates
1. Amphioxus / Lancelet
2. Amphibians
3. Reptiles & Birds
4. Mammals
26
New cards
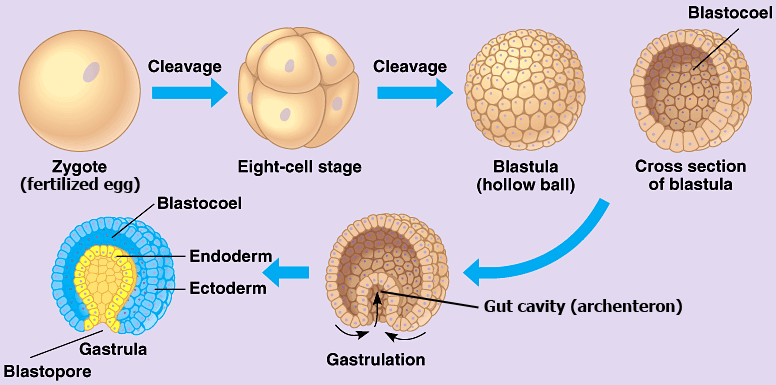
multi, hollow, blastocoel
**Blastula**
* A ____cellular embryo formed by the cell division (cleavage) of the fertilized egg (zygote)
* A ____ ball of cells with a cavity called the _____
* A ____cellular embryo formed by the cell division (cleavage) of the fertilized egg (zygote)
* A ____ ball of cells with a cavity called the _____
27
New cards
Blastulation
* is the process of **forming a blastula**, which is an early stage in embryonic development of animals.
* It occurs **after fertilization**, when the zygote undergoes a series of cell divisions called cleavage.
* During blastulation, these cells divide and rearrange to form a hollow ball of cells called a blastula.
* It occurs **after fertilization**, when the zygote undergoes a series of cell divisions called cleavage.
* During blastulation, these cells divide and rearrange to form a hollow ball of cells called a blastula.
28
New cards
Blastomeres
* The individual daughter cells during cleavage
29
New cards
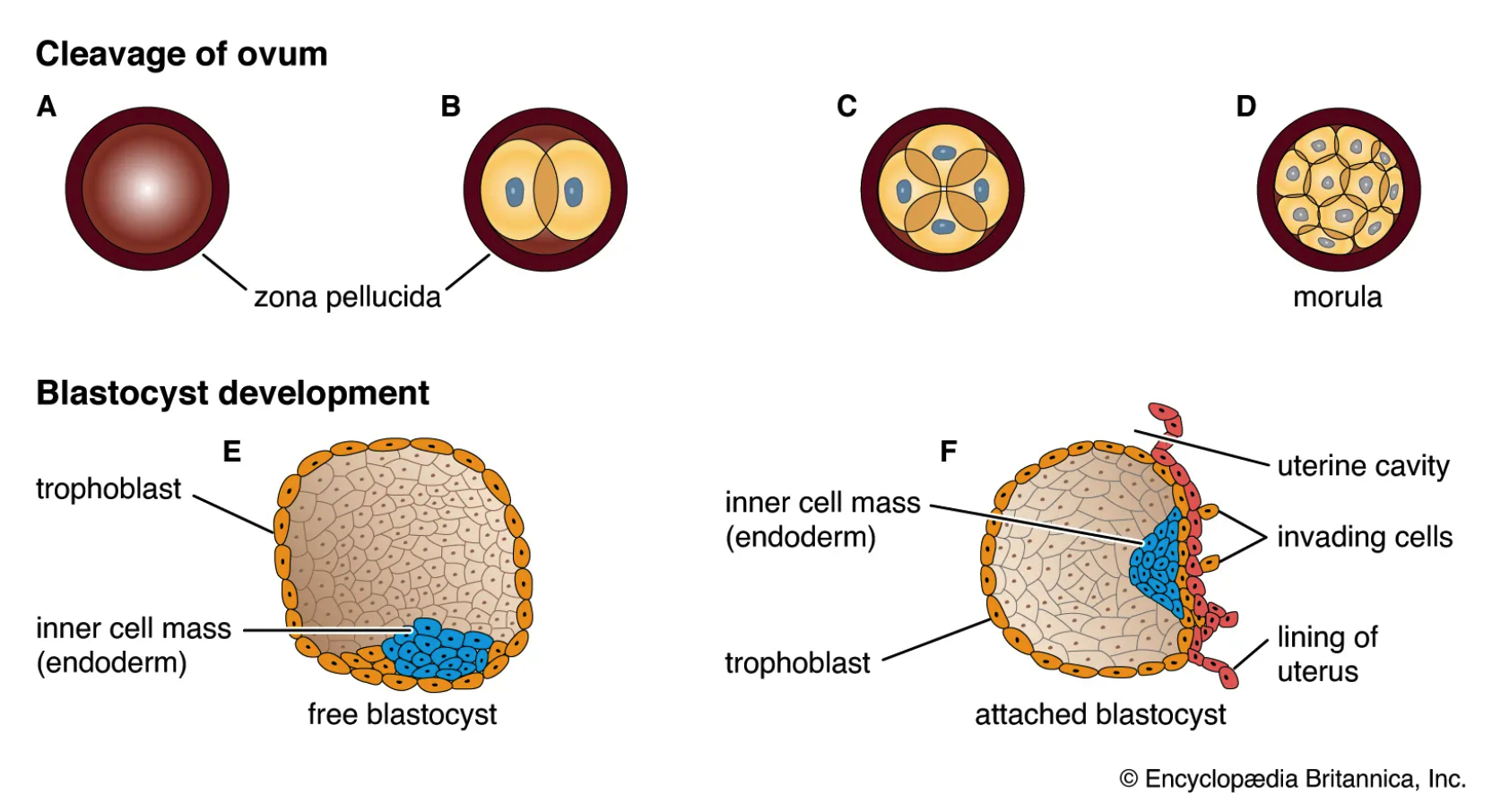
during, blastoderm, gastrula, mammals, after, trophoblast, placenta
**Blastula vs Blastocyst**
* Both blastula and blastocyst are early embryonic stages in the development of many animals, including humans
1. **Blastula**
* amphibians, fish, and birds
* is formed _____ the blastulation stage, which is a series of cell divisions that occur after fertilization
* is a hollow ball of cells with a fluid-filled cavity called the blastocoel
* inner cell mass (ICM)
* outer ______ layer
* earliest embryonic stage and undergoes further development to form a ______, which eventually forms different tissues and organs of the developing organism
\
2. **Blastocyst**
* only in ______
* is formed during the embryonic development _____ the blastulation stage
* has a fluid-filled cavity, but it is more complex than the blastula, with two distinct cell types:
* inner cell mass (ICM)
* outer ______ layer
* is a later stage and undergoes implantation into the uterine wall and the development of the _____
* Both blastula and blastocyst are early embryonic stages in the development of many animals, including humans
1. **Blastula**
* amphibians, fish, and birds
* is formed _____ the blastulation stage, which is a series of cell divisions that occur after fertilization
* is a hollow ball of cells with a fluid-filled cavity called the blastocoel
* inner cell mass (ICM)
* outer ______ layer
* earliest embryonic stage and undergoes further development to form a ______, which eventually forms different tissues and organs of the developing organism
\
2. **Blastocyst**
* only in ______
* is formed during the embryonic development _____ the blastulation stage
* has a fluid-filled cavity, but it is more complex than the blastula, with two distinct cell types:
* inner cell mass (ICM)
* outer ______ layer
* is a later stage and undergoes implantation into the uterine wall and the development of the _____
30
New cards
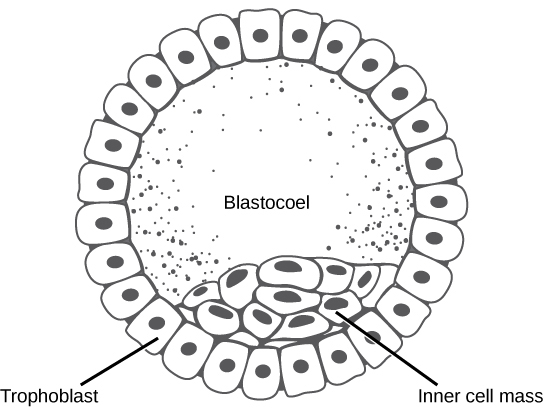
placenta, extraembryonic, embryo
**Parts of a Blastocyst**
* **Trophoblast**
* an outer layer of cells called the trophoblast, which will eventually form the ___ and other ______ tissues,
* **Inner cell mass**
* will develop into the ____ proper.
* **Trophoblast**
* an outer layer of cells called the trophoblast, which will eventually form the ___ and other ______ tissues,
* **Inner cell mass**
* will develop into the ____ proper.
31
New cards
size, yolk
**Cleavage**
* Active mitotic division with **no increase in the ___ of the cell**
* The process of cleavage and the structure of the blastula are related to the amount of ___ present.
* Active mitotic division with **no increase in the ___ of the cell**
* The process of cleavage and the structure of the blastula are related to the amount of ___ present.
32
New cards
Types of Cleavage
1. **Holoblastic cleavage**
* Isolecithal
* Radial: Echinoderms, amphioxus
* Spiral: Annelids, molluscs, flatworms
* Bilateral: Tunicates
* Rotational: Mammals, nematodes
* Mesolecithal
* Radial: Amphibians
2. **Meroblastic Cleavage**
* Telolecithal
* Bilateral: Cephalopod molluscs
* Discoidal: Fish, reptiles, birds
* Centrolecithal
* Superficial: Most insects
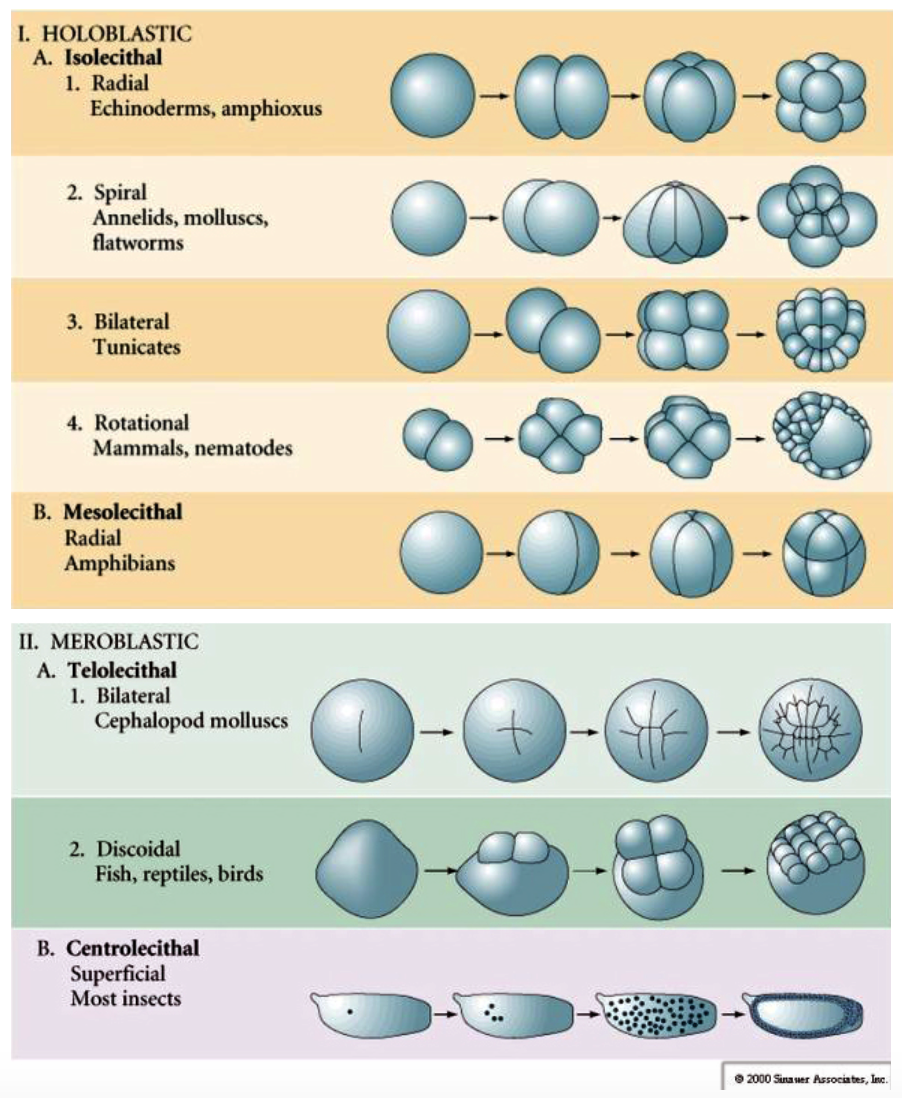
33
New cards
Holoblastic
* (Greek *holos,* “complete”)
* cleavage furrow extends through the entire egg
* Equal holoblastic
* Unequal holoblastic
* cleavage furrow extends through the entire egg
* Equal holoblastic
* Unequal holoblastic
34
New cards
Equal holoblastic
* When the cleavage furrow cuts the egg into two equal cells.
* It may be radially symmetrical, bilaterally, symmetrical, spirally symmetrical or irregular.
* Occurs on isolecithal eggs
* It may be radially symmetrical, bilaterally, symmetrical, spirally symmetrical or irregular.
* Occurs on isolecithal eggs
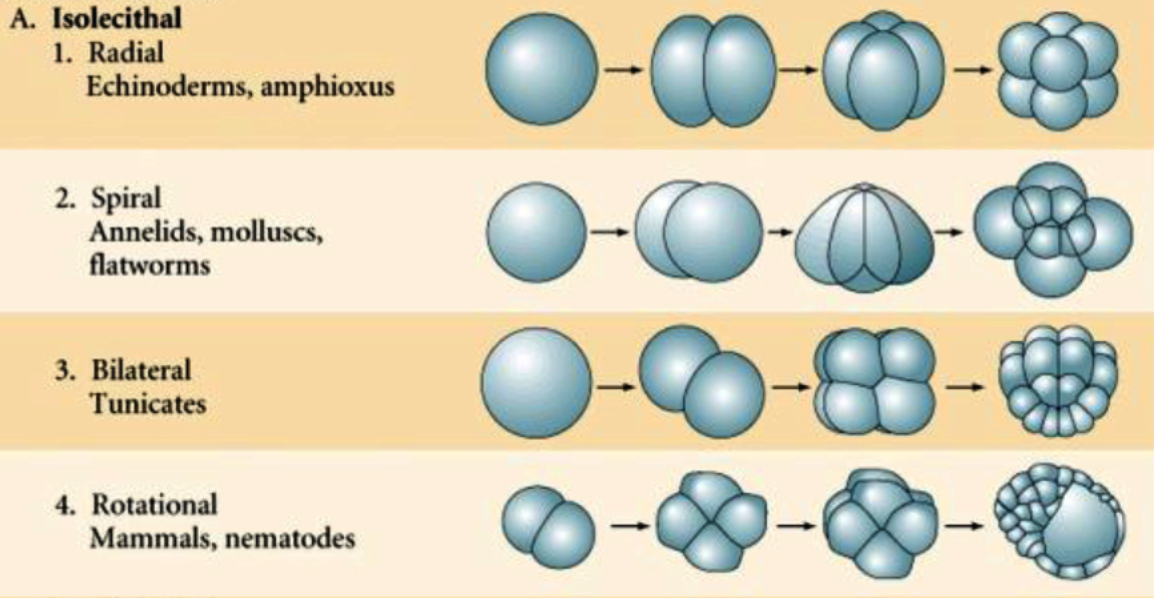
35
New cards
Radial holoblastic cleavage
* Micromeres, mesomeres, macromeres
* The cells in the top half divide equally, but those in the bottom half divide unequally
* The cells in the top half divide equally, but those in the bottom half divide unequally
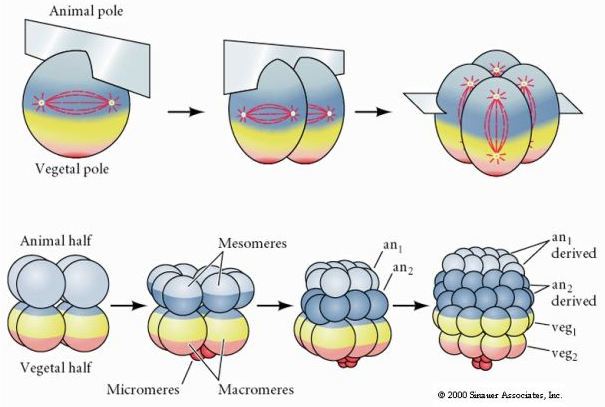
36
New cards
Rotational holoblastic cleavage
\
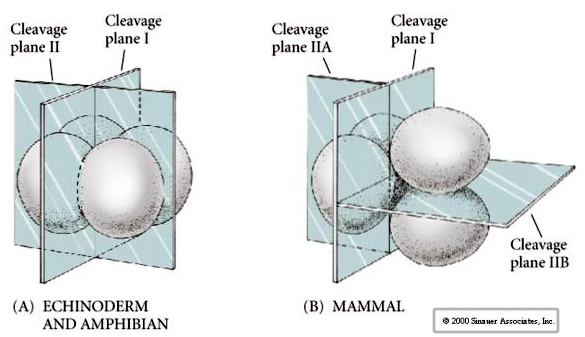
37
New cards
Unequal holoblastic
* When the resultant blastomeres become unequal in size
* Occurs on mesolecithal eggs
* Occurs on mesolecithal eggs
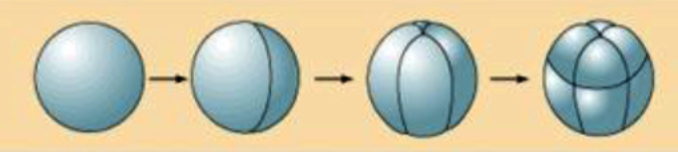
38
New cards
Meroblastic
* (Greek *meros* “part”)
* only a portion of cytoplasm is cleaved.
* The cleavage furrow does not penetrate into the yolky portion
* Discoidal meroblastic
* Superficial meroblastic
* only a portion of cytoplasm is cleaved.
* The cleavage furrow does not penetrate into the yolky portion
* Discoidal meroblastic
* Superficial meroblastic
39
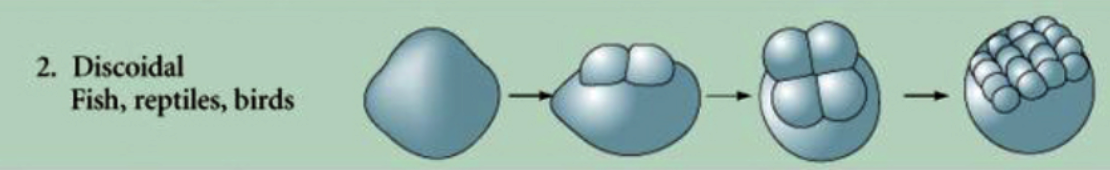
New cards
Discoidal meroblastic
* cleavage occur only in the small disk that is free of yolk.
* Ex. Fish, reptiles, birds
* Ex. Fish, reptiles, birds
40
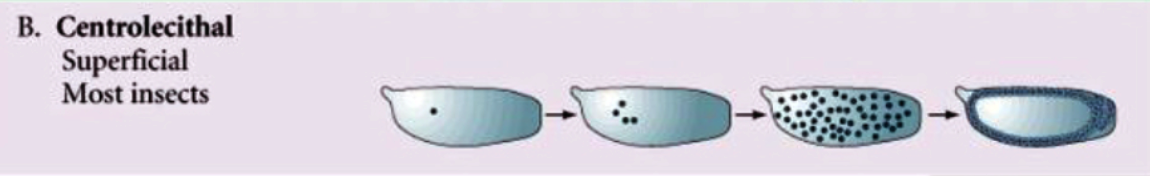
New cards
Superficial meroblastic
* cleavage occur only in the rim of the cytoplasm.
* Ex. Most insects
* Ex. Most insects
41
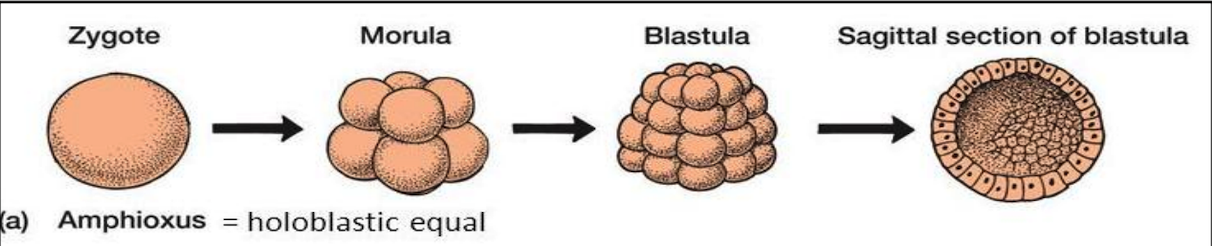
New cards
equal, radial, equal
1. **Amphioxus**
* Isolecithal egg, microlecithal egg
* Holoblastic _____ cleavage (_____)
* the cleavage furrows penetrate the entire yolk
* The cleavage is _____ and all blastomeres are almost the same size at any given time
* The resultant blastula is a hollow ball of cells with blastocoel
42
New cards
Mesolecithal, unequal, larger,
2. **Amphibians**
* _______ egg
* Holoblastic ______ cleavage (radial)
* yolk interferes with cytoplasmic division
* Blastomeres near the vegetal pole are _____ than those near the animal pole
* Development is slower in the vegetal pole
* The blastocoel is displaced into the animal hemisphere
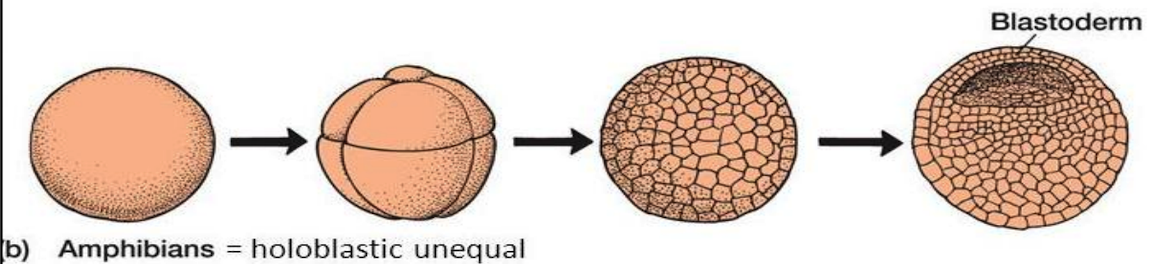
43
New cards
Telolecithal, Meroblastic, unequal, subgerminal
3. **Reptiles & Birds**
* _______, macrolecithal egg
* ______ _____cleavage (discoidal)
* The yolk mass is too great to be penetrated by the cleavage furrows
* A cellular blastoderm is separated from the uncleaved yolk by a narrow cavity (_______ space)
* Ex: sharks, teleosts, gar
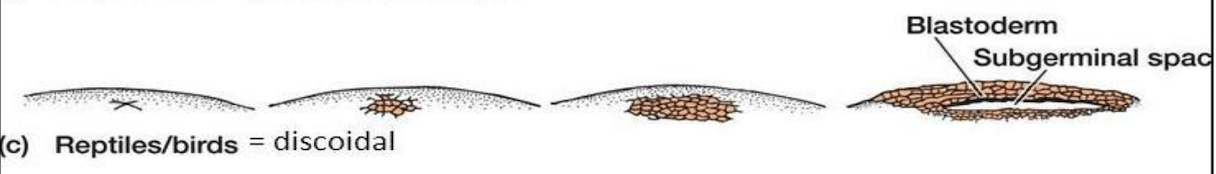
44
New cards
Alecithal, rotational, trophoblasts, vegetal
4. **Mammals**
* Microlecithal/______ egg
* Holoblastic equal cleavage (______)
* The blastula has a superficial layer of cells called _______, which surrounds an inner mass of cells
* The blastocoel is displaced toward the _____ pole
* The vertebrate blastula is composed of single tissue layer made up of several hundred cells with polarity that relates to the axes of the adult body
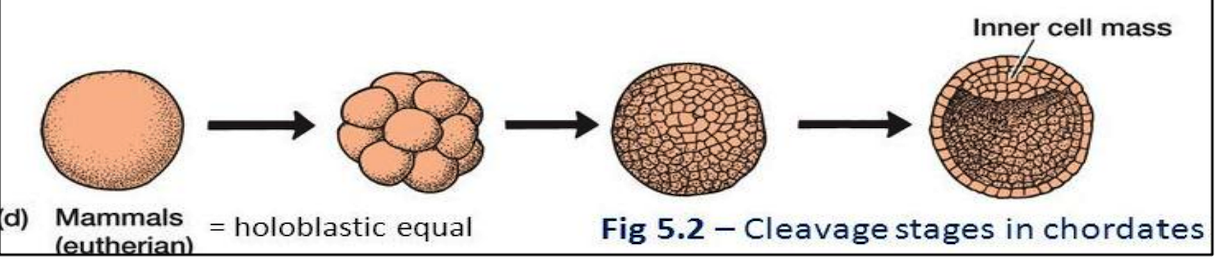
45
New cards
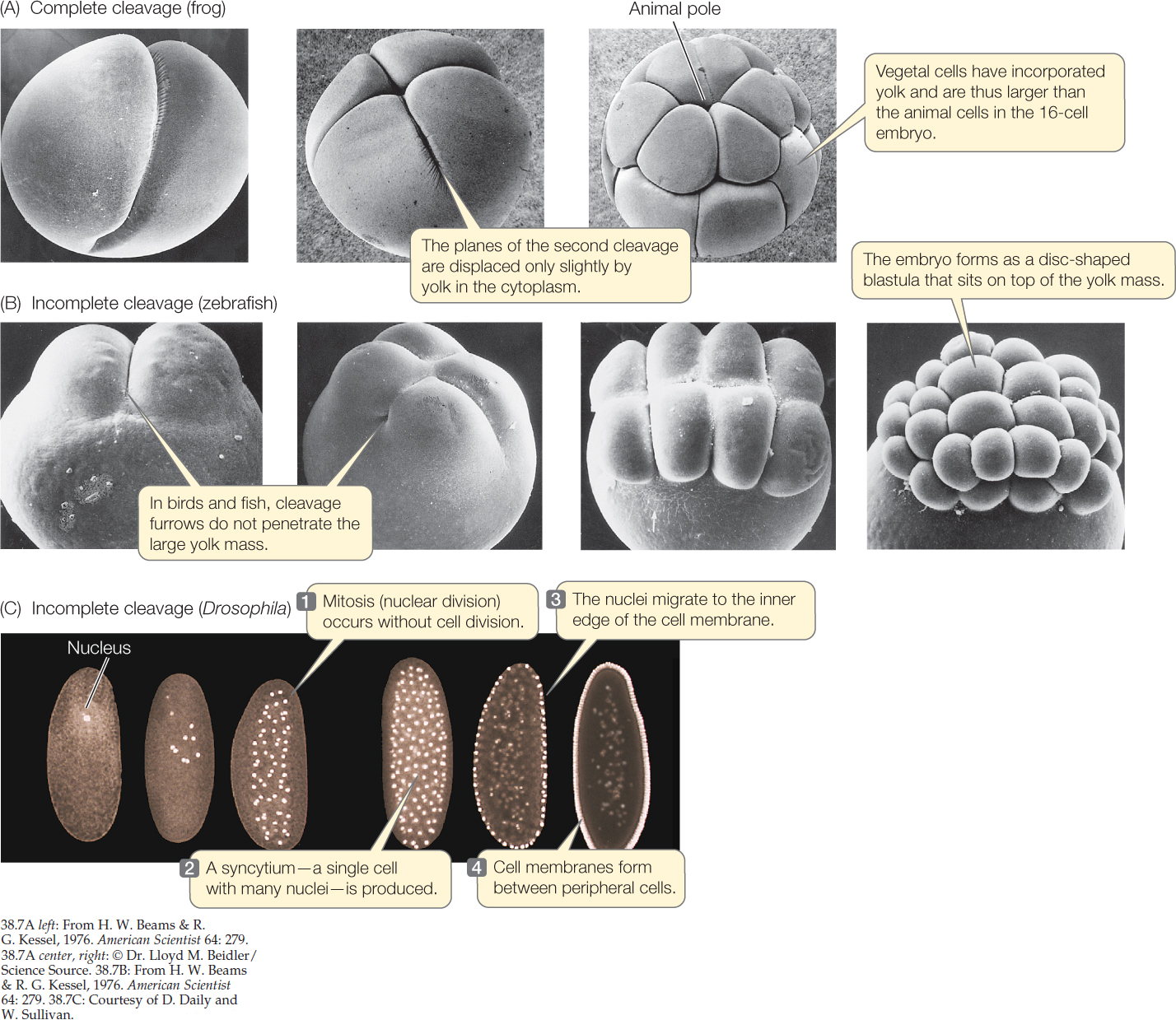
frog, yolk, furrows
**Patterns of Cleavage**
* Differences in patterns of early embryonic development reflect differences in egg cytoplasm.
* (A) The ___ is a model organism representing complete cleavage.
* (B) Zebrafish embryos illustrate incomplete cleavage, in which the large ___ mass limits the planes of cleavage.
* (C) Fruit flies have another type of incomplete cleavage. Nuclear staining reveals the syncytial nuclei characteristic of their early development.
* These nuclei migrate to the periphery of the egg.
* Cleavage _____ then move inward to separate the nuclei into individual cells.
* Differences in patterns of early embryonic development reflect differences in egg cytoplasm.
* (A) The ___ is a model organism representing complete cleavage.
* (B) Zebrafish embryos illustrate incomplete cleavage, in which the large ___ mass limits the planes of cleavage.
* (C) Fruit flies have another type of incomplete cleavage. Nuclear staining reveals the syncytial nuclei characteristic of their early development.
* These nuclei migrate to the periphery of the egg.
* Cleavage _____ then move inward to separate the nuclei into individual cells.
46
New cards
Lewis Wolpert
It is not birth, marriage, or death, but **gastrulation,** which is truly the most important time in your life.
47
New cards
**coordinated,** gastrula, **ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm**
**Gastrulation**
* the process of **highly ______ cell and tissue movements** whereby the cells of the blastula are dramatically arranged.
* a blastula undergoes a complex series of morphological changes that result in the formation of a _____, **a structure with distinct layers of cells**
* involves the formation of three germ layers - the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm - that give rise to different tissues and organs in the body
* **Embryonic ______:** epidermis, CNS, PNS, eyes and internal ears, neural crest cells, and many connective tissues of the head.
* **Embryonic ______:** source of the epithelial linings of the respiratory and alimentary (digestive) tracts, including the glands opening into the gastrointestinal tract, and glandular cells of associated organs such as the liver and pancreas
* **Embryonic ______:** all skeletal muscles, blood cells, the lining of blood vessels, all visceral smooth muscular coats, serosal linings of all body cavities, ducts and organs of the reproductive and excretory systems, and most of the cardiovascular system.
* the process of **highly ______ cell and tissue movements** whereby the cells of the blastula are dramatically arranged.
* a blastula undergoes a complex series of morphological changes that result in the formation of a _____, **a structure with distinct layers of cells**
* involves the formation of three germ layers - the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm - that give rise to different tissues and organs in the body
* **Embryonic ______:** epidermis, CNS, PNS, eyes and internal ears, neural crest cells, and many connective tissues of the head.
* **Embryonic ______:** source of the epithelial linings of the respiratory and alimentary (digestive) tracts, including the glands opening into the gastrointestinal tract, and glandular cells of associated organs such as the liver and pancreas
* **Embryonic ______:** all skeletal muscles, blood cells, the lining of blood vessels, all visceral smooth muscular coats, serosal linings of all body cavities, ducts and organs of the reproductive and excretory systems, and most of the cardiovascular system.
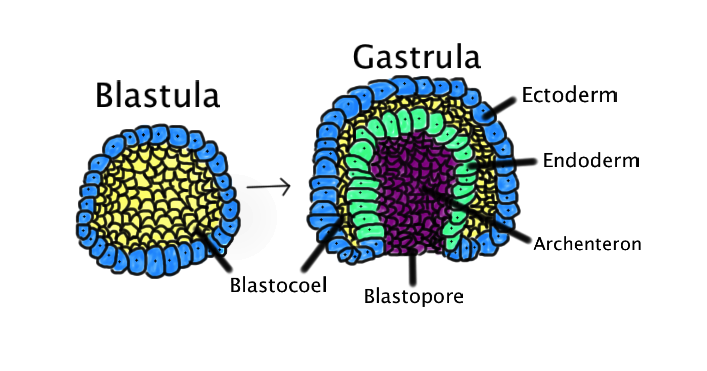
48
New cards
differentiation
**Primitive Streak**
* Gastrulation involves a series of movements and cell migrations that lead to the formation of this characteristic structure
* The cells in the blastula move towards the primitive streak and undergo changes that result in their _______ into the three germ layers.
* This process is tightly regulated by various molecular signals and genetic programs.
* Gastrulation involves a series of movements and cell migrations that lead to the formation of this characteristic structure
* The cells in the blastula move towards the primitive streak and undergo changes that result in their _______ into the three germ layers.
* This process is tightly regulated by various molecular signals and genetic programs.
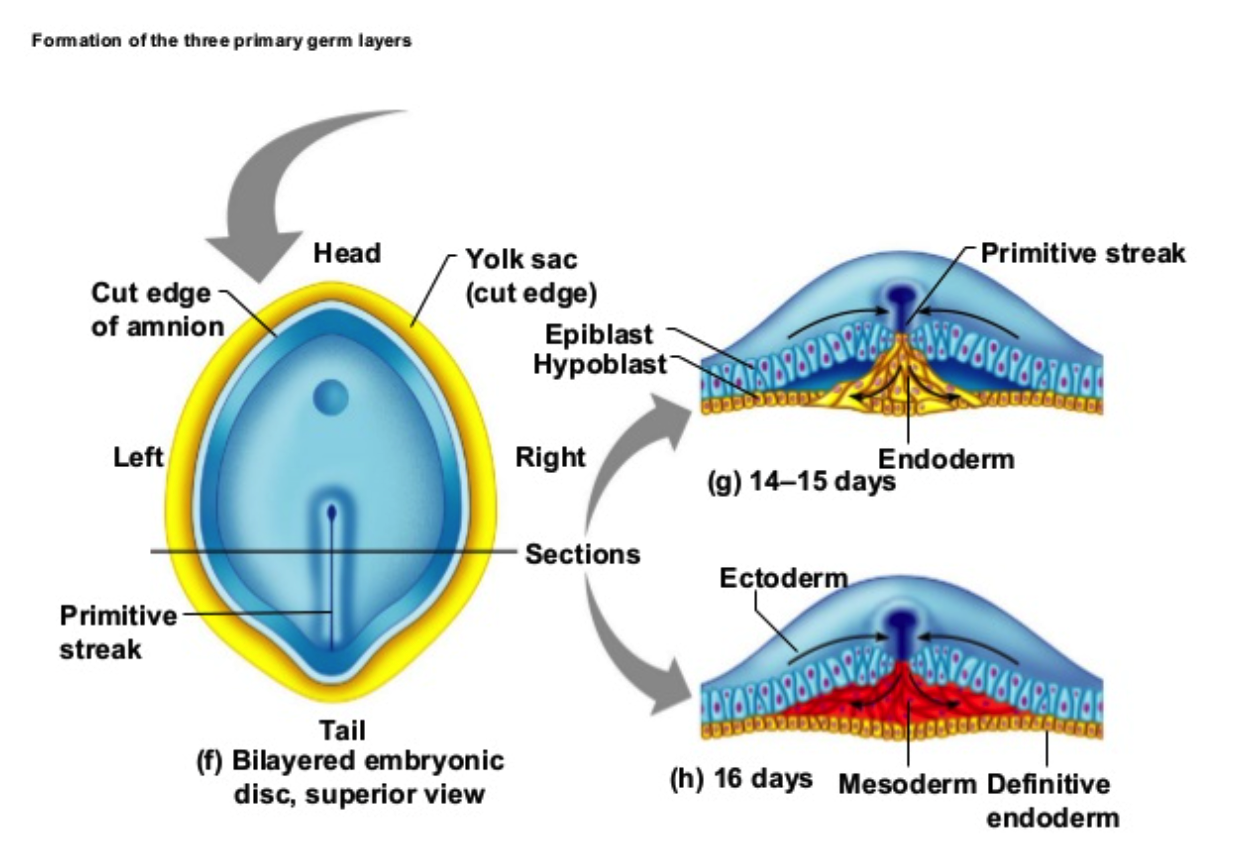
49
New cards
Infolding, inturning, Migration, Splitting, Expansion
**Types of Morphogenetic/Gastrulation Movements**
1. **Invagination**
* _____ of the cell sheet into embryo
* much like indenting of a rubber ball when it is poked.
* Sea urchin endoderm
2. **Involution**
* _______ of cell sheet over the basal surface of an outer layer
* Amphibian mesoderm
3. **Ingression**
* ______ of individual cells into the embryo
* Drosophila neuroblasts
4. **Delamination**
* _____ of one sheet into two
* Mammalian hypoblast
5. **Epiboly**
* _____ of one cell sheet over other cells
* Amphibian ectoderm
1. **Invagination**
* _____ of the cell sheet into embryo
* much like indenting of a rubber ball when it is poked.
* Sea urchin endoderm
2. **Involution**
* _______ of cell sheet over the basal surface of an outer layer
* Amphibian mesoderm
3. **Ingression**
* ______ of individual cells into the embryo
* Drosophila neuroblasts
4. **Delamination**
* _____ of one sheet into two
* Mammalian hypoblast
5. **Epiboly**
* _____ of one cell sheet over other cells
* Amphibian ectoderm
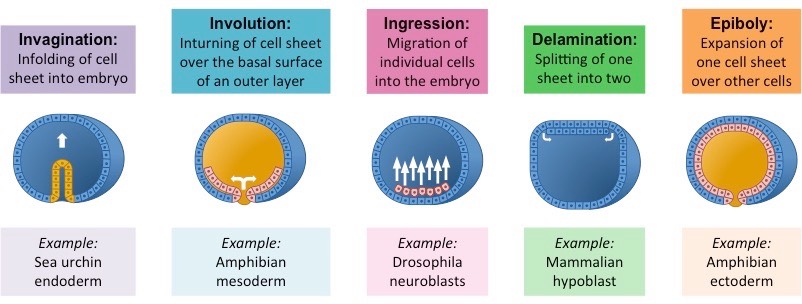
50
New cards
invagination, archenteron, gut, blastopore, anus
1. **Amphioxus**
* Gastrulation occurs through ________
* The blastula invaginates to form a tube-like structure called the gastrula.
* The invagination results in the formation of the _______, which is the primitive ___.
* The ____, which is the opening of the archenteron, later develops into the __.
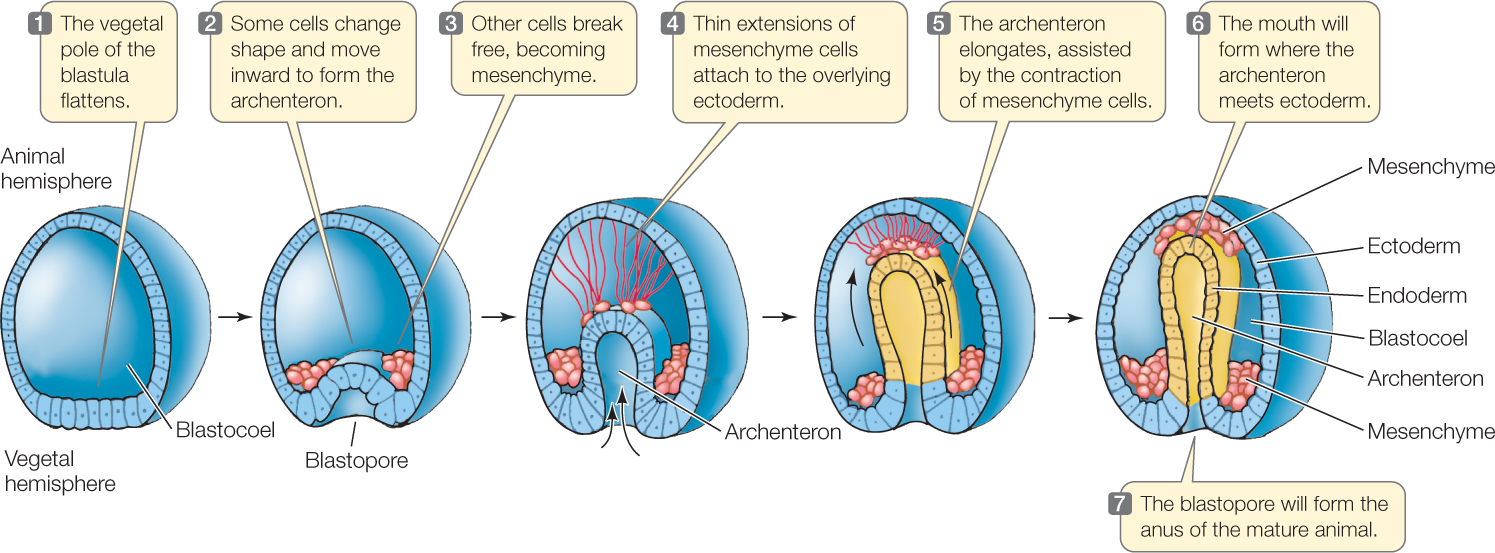
51
New cards
epiboly, enveloping, endoderm
2. **Amphibians**
* Have a process called _____
* The blastula cells divide and migrate to the surface, eventually ______ the yolk to form a multilayered blastoderm.
* The blastopore develops into the anus, and the primitive gut forms from the _____.
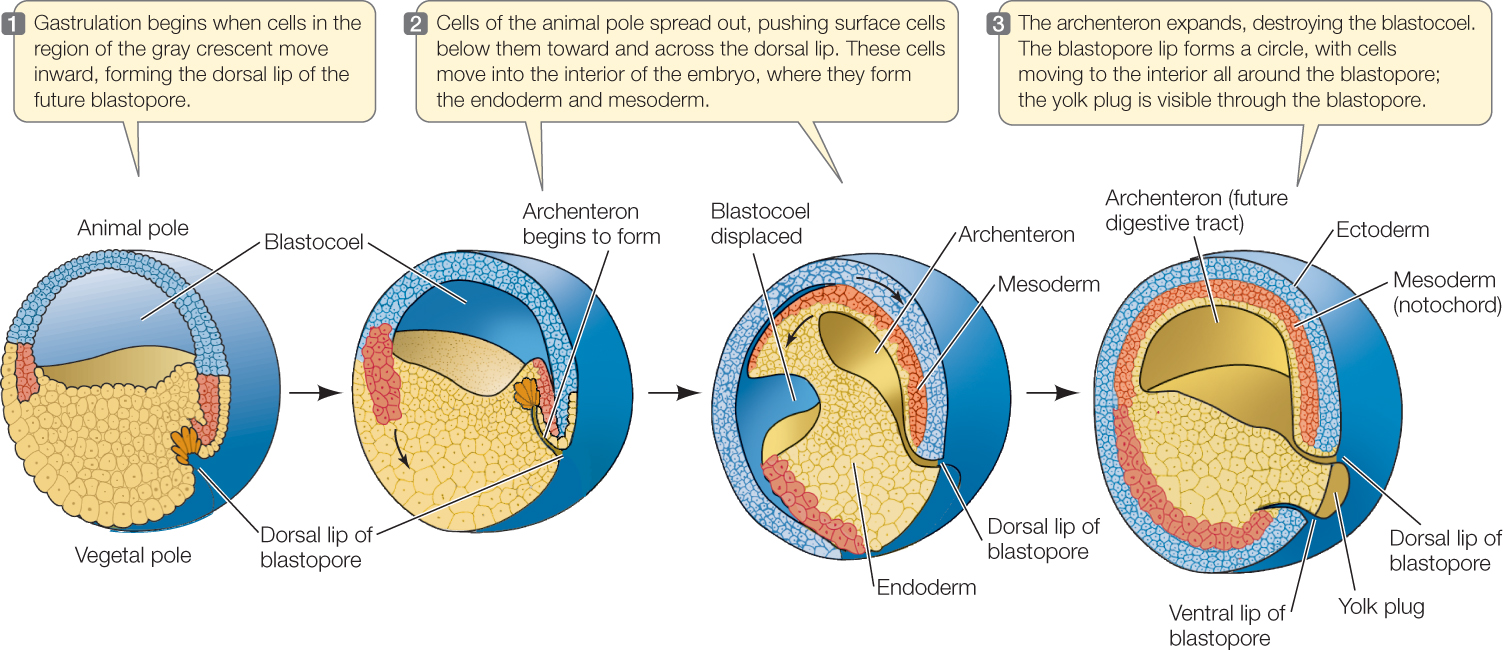
52
New cards
top, cloaca, primitive
**Reptiles & Birds**
* have a similar process to amphibians, but with some variations.
* The blastoderm forms on ___ of the yolk, which is not enveloped.
* The blastopore develops into the ____, and the primitive gut forms from the endoderm.
* However, there is a process called the _____ streak, where a thickening of cells marks the location of the future dorsal midline of the embryo.
* have a similar process to amphibians, but with some variations.
* The blastoderm forms on ___ of the yolk, which is not enveloped.
* The blastopore develops into the ____, and the primitive gut forms from the endoderm.
* However, there is a process called the _____ streak, where a thickening of cells marks the location of the future dorsal midline of the embryo.
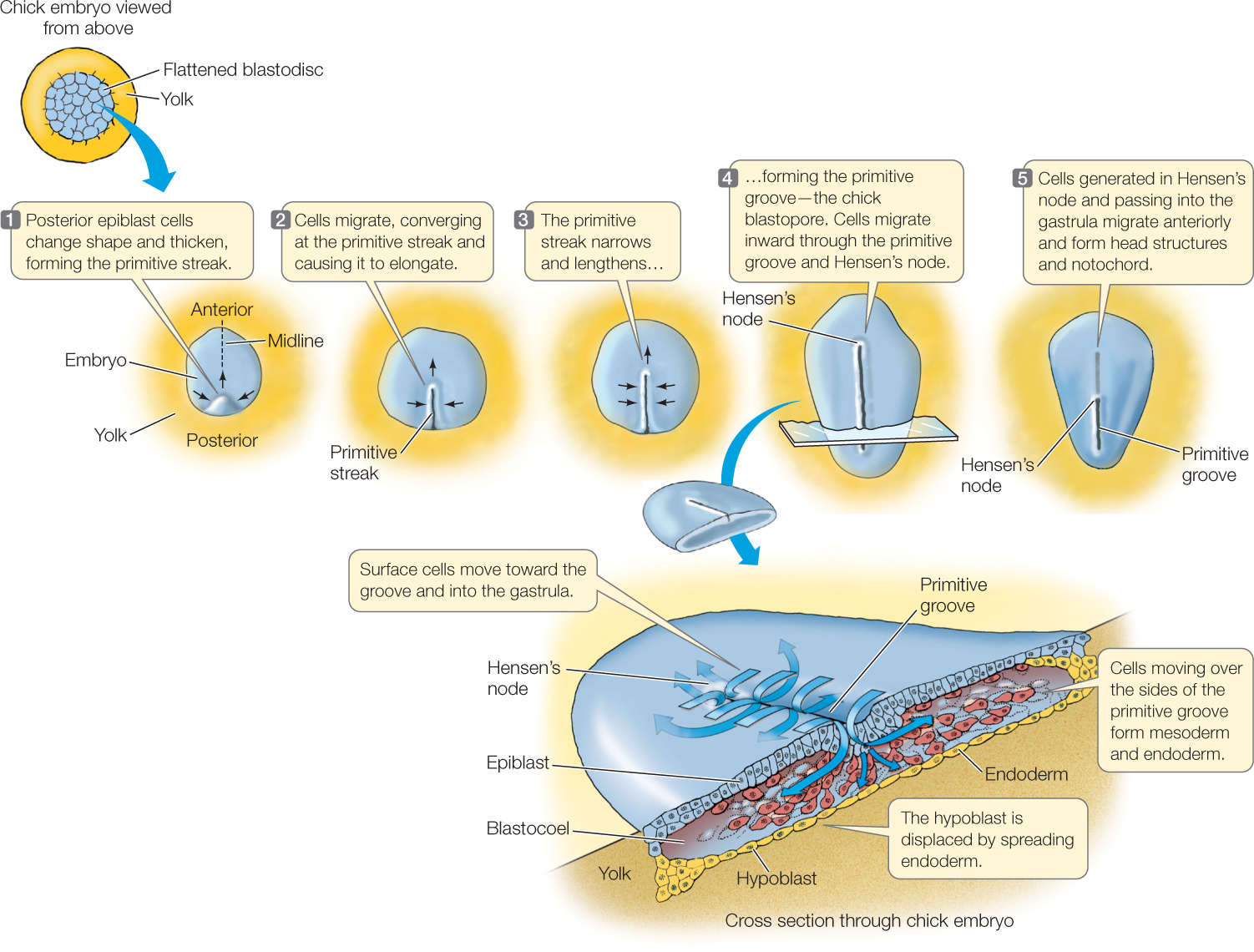
53
New cards
posterior, anterior, Hensen’s, notochord
3. **Reptiles & Birds**
* The cells are enclosed in the **primitive streak**
* Develops from **____ end towards the _____ end**
* Common feature of deuterostomes
* The primitive streak is enclosed in the area pellucida, marginal zone, and area opaca
* Area pellucida is the blastoderm
* Marginal zone is the subgerminal zone
* Area opaca is the yolk
* As the cells move from the posterior end to the anterior end, ______ node is developed.
* Cells will ingress forming the _______
54
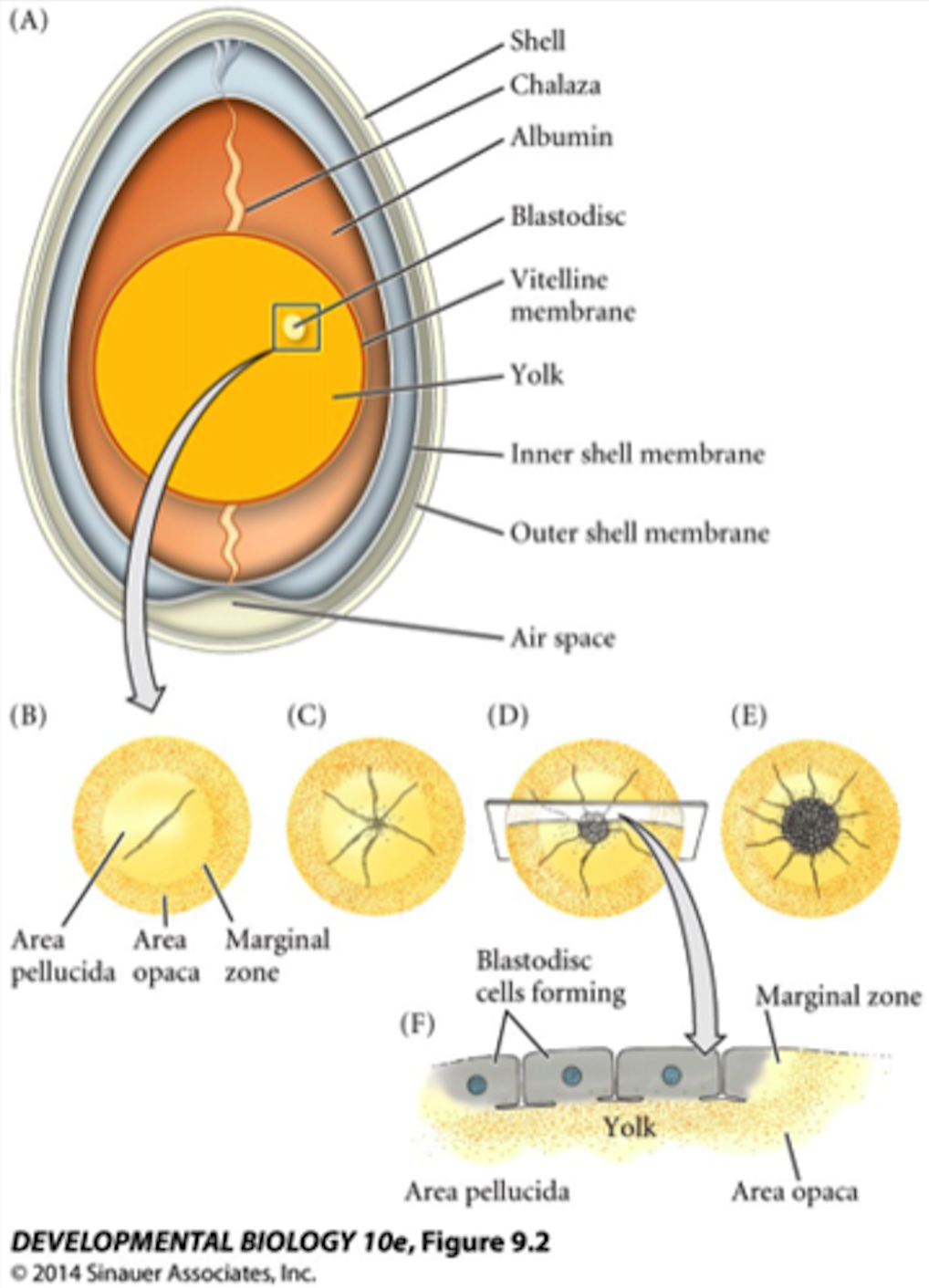
New cards
delaminate, subgerminal, Koller’s, ingresses, blastocoel
3. **Reptiles & Birds**
* Cells in area pellucida/blastoderm/primitive streak will ______ (form a new cell layer)
* The new cell layer will move toward the middle of the _______/marginal zone
* Forming two new layers:
* epiblast
* primary hypoblast
* Cells in the ____ sickle region _____ toward the primary hypoblast
* Once they mix, a secondary hypoblast is formed
* Since only two layers are formed, a ______ is formed
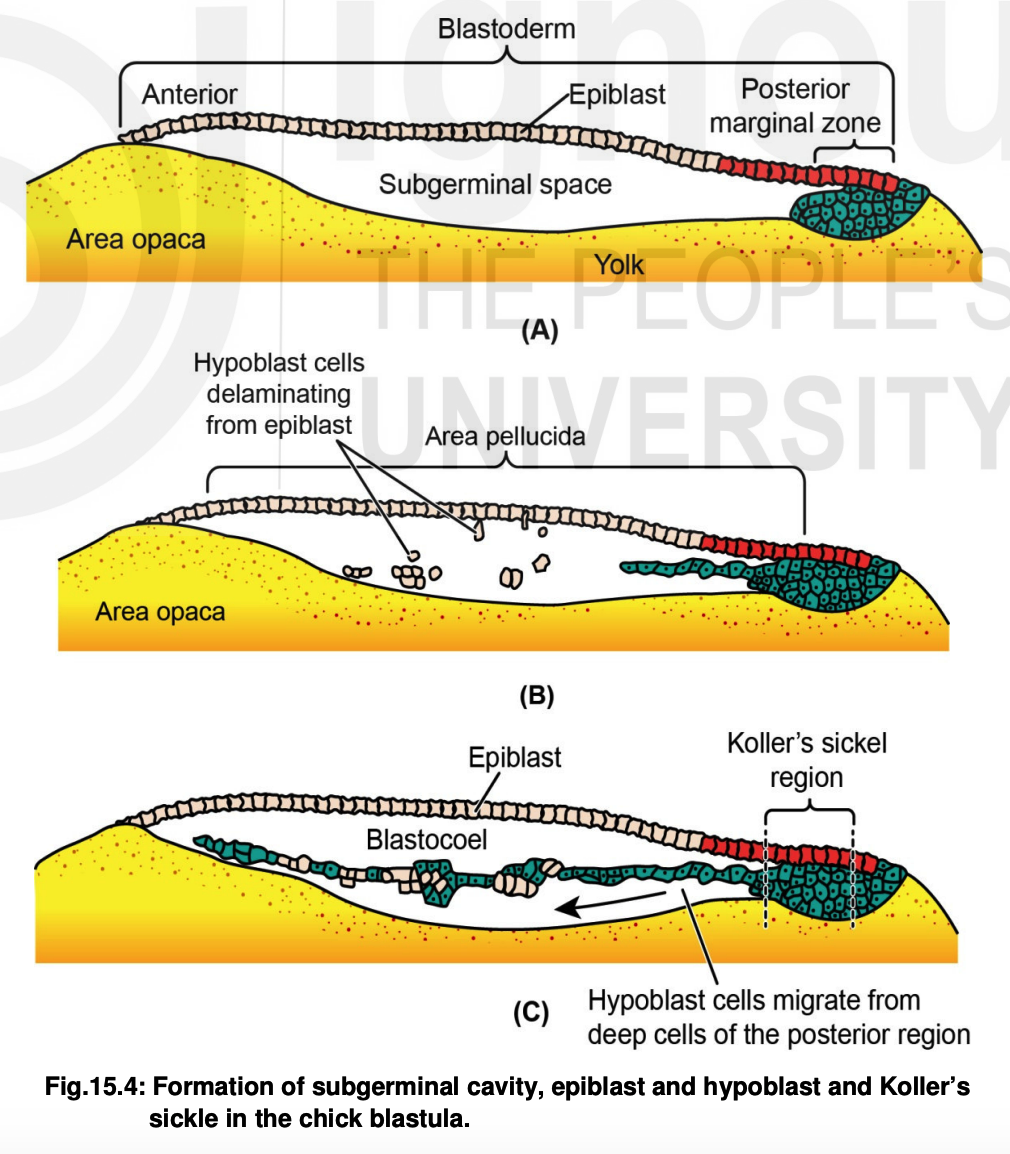
55
New cards
blastocyst, primitive, disappears
4. **Mammals**
* Blastula transforms into a structure called the ______, which has an inner cell mass and an outer layer of cells called the trophoblast.
* Gastrulation begins with the formation of the _____ streak, similar to reptiles and birds.
* The endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm layers form from cells migrating through the primitive streak.
* The blastopore ______, and the anus and mouth form later in development.
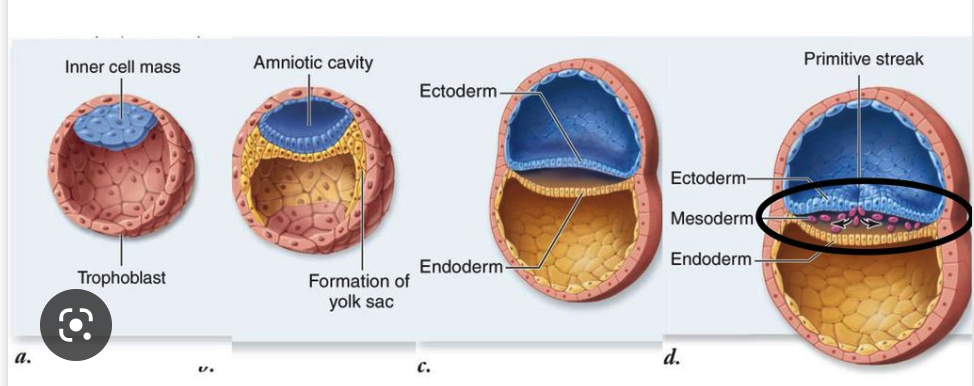
56
New cards
Amphioxus
* Gastrulation Movement: Invagination
* End Product: 3 germ layers, Gastrocoel
* End Product: 3 germ layers, Gastrocoel
57
New cards
Amphibians
* Gastrulation Movement: Involution/Epiboly
* End Product: 3 germ layers, Gastrocoel
* End Product: 3 germ layers, Gastrocoel
58
New cards
Reptiles & Birds
* Gastrulation Movement: Ingression/ Delamination
* End Product: Epiblast, Hypoblast, Blastocoel
* End Product: Epiblast, Hypoblast, Blastocoel
59
New cards
Mammals
* Gastrulation Movement: Ingression/ Delamination
* End Product: Extraembryonic membranes, Gastrocoel
* End Product: Extraembryonic membranes, Gastrocoel
60
New cards
endometrium, trophoblast, chorionic
**Human Blastocyst at Implantation**
* (A) The mammalian blastocyst consists of an inner cell mass adjacent to a fluid-filled blastocoel and surrounded by trophoblast cells.
* (B) Molecules and enzymes secreted by trophoblast cells allow the blastocyst to adhere to and burrow into the ______.
* Once the blastocyst is implanted in the uterine wall, the _____ cells send out _____ villi—projections that increase the embryo’s area of contact with the maternal bloodstream
* (A) The mammalian blastocyst consists of an inner cell mass adjacent to a fluid-filled blastocoel and surrounded by trophoblast cells.
* (B) Molecules and enzymes secreted by trophoblast cells allow the blastocyst to adhere to and burrow into the ______.
* Once the blastocyst is implanted in the uterine wall, the _____ cells send out _____ villi—projections that increase the embryo’s area of contact with the maternal bloodstream
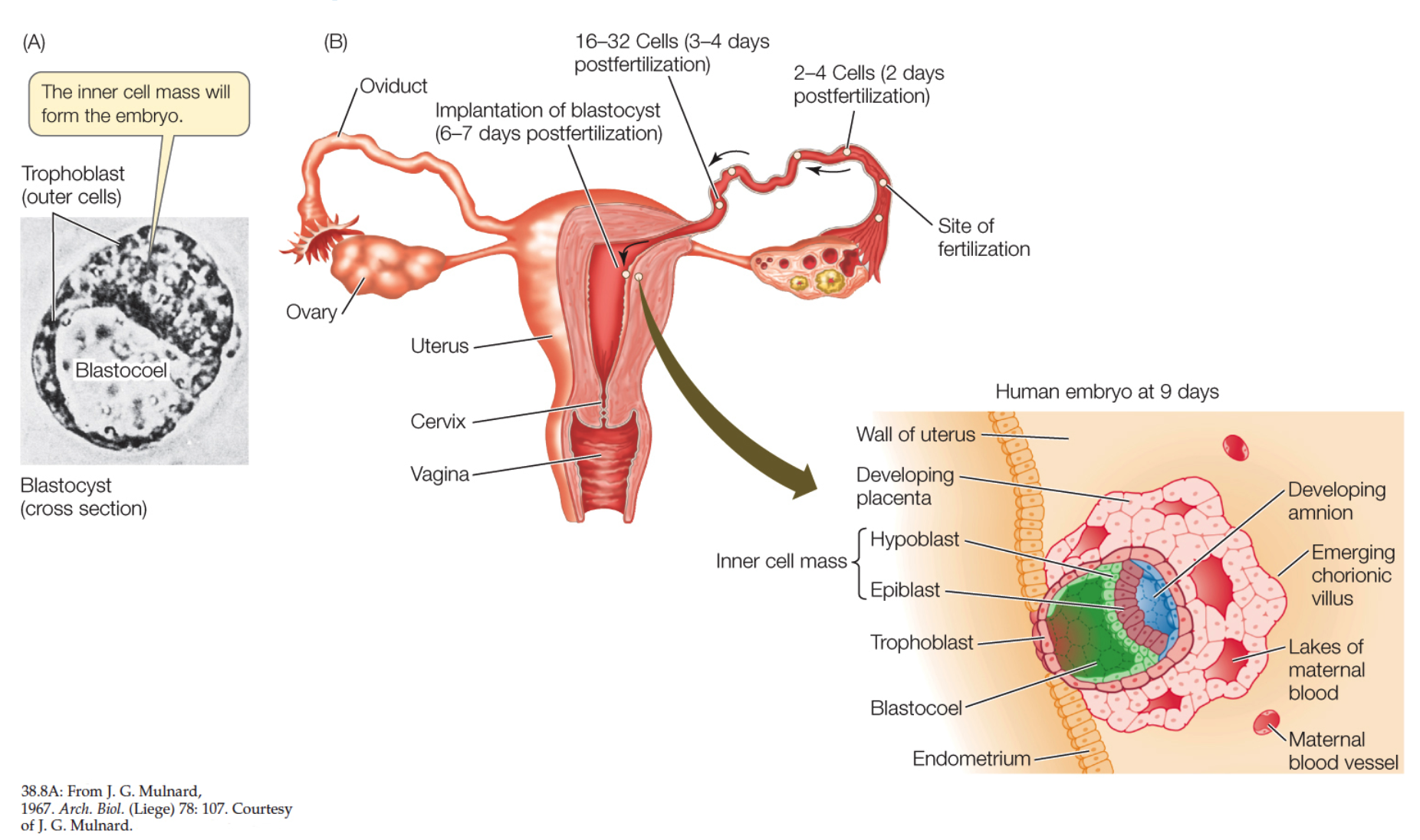
61
New cards
Neural induction
* cells of the **embryonic ectoderm** (outermost layer of cells) are directed to become neural cells, which will eventually form the nervous system.
* This process involves **signals** from the underlying mesoderm and endoderm that instruct the ectodermal cells to form the **neural plate**, a flat sheet of cells that will give rise to the neural tube.
* This process involves **signals** from the underlying mesoderm and endoderm that instruct the ectodermal cells to form the **neural plate**, a flat sheet of cells that will give rise to the neural tube.
62
New cards
Neurulation
* is the process by which the neural tube is formed during embryonic development.
* The **neural tube** is a structure that eventually develops into the **brain and spinal cord.**
* Neural plate stage
* Neural groove stage
* Neural tube stage
* The **neural tube** is a structure that eventually develops into the **brain and spinal cord.**
* Neural plate stage
* Neural groove stage
* Neural tube stage
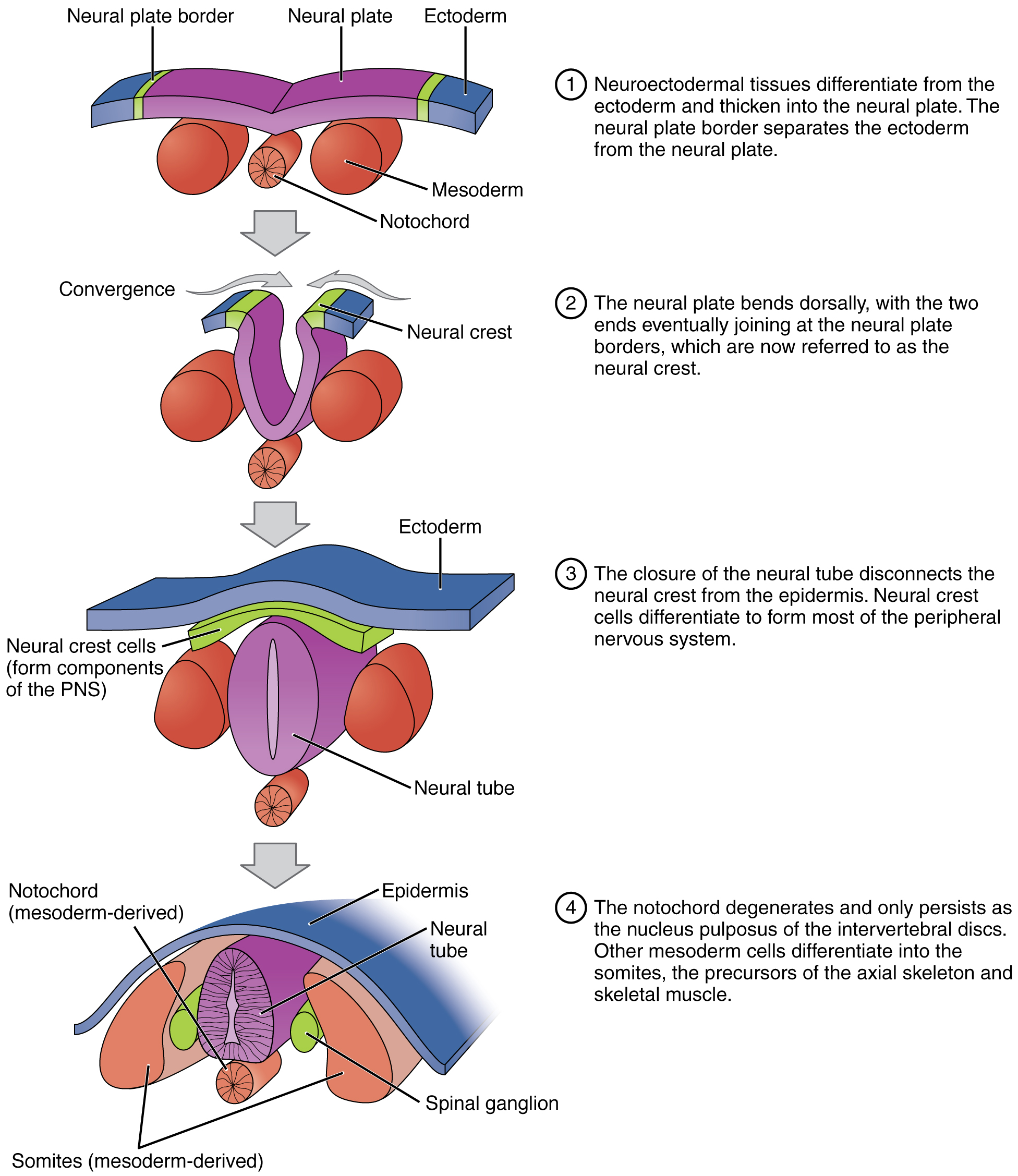
63
New cards
**3 Subphases of Neurulation**
1. Neural plate stage
2. Neural groove stage
3. Neural tube stage
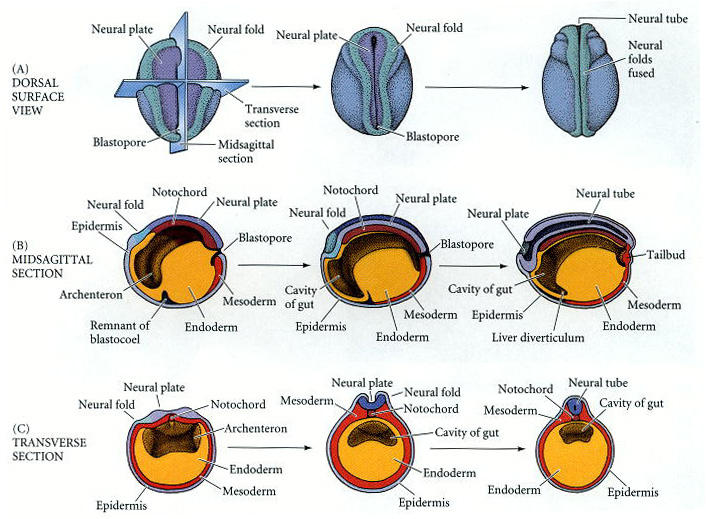
64
New cards
Neural plate stage
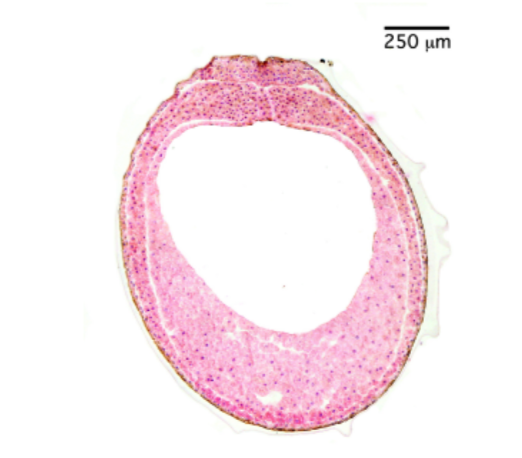
65
New cards
Neural groove stage
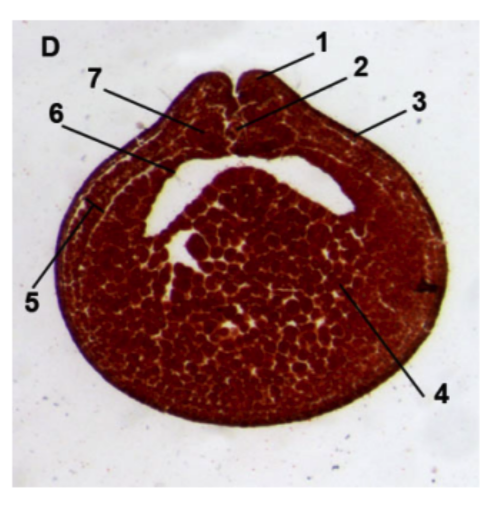
66
New cards
Neural tube stage
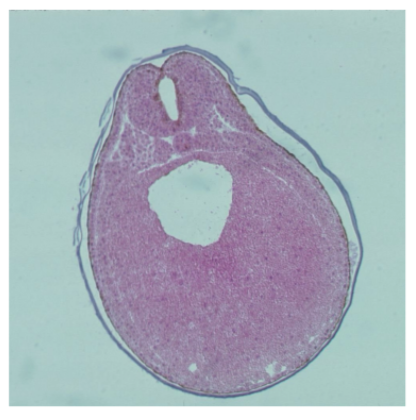
67
New cards
Notochord
* mesoderm in origin
* becomes intervertebral disc
* becomes intervertebral disc
68
New cards
plate, ectodermal, tube, crest, sensory
1. **Amphioxus**
* Process of neurulation begins with the formation of the neural ____, which is a thickened region of ______ cells.
* The neural plate folds in on itself to form the neural ___, which is then separated from the surface ectoderm.
* The neural ____ cells, which give rise to a variety of cell types, including ____ neurons, are formed from the ectodermal cells adjacent to the neural tube.
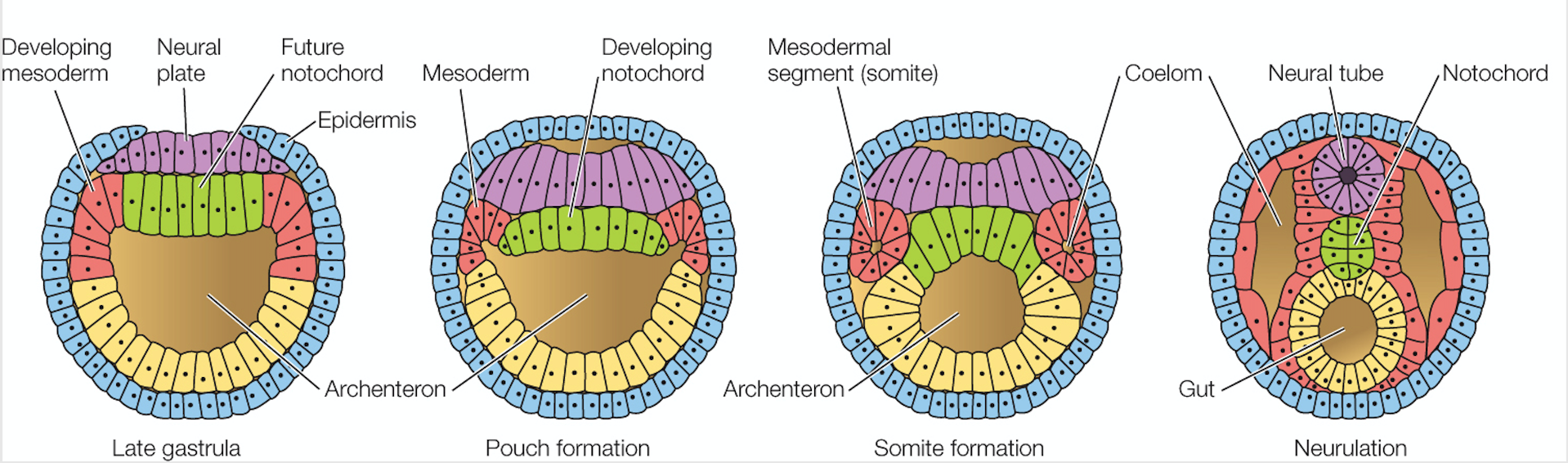
69
New cards
primary, invaginates
2. **Amphibians**
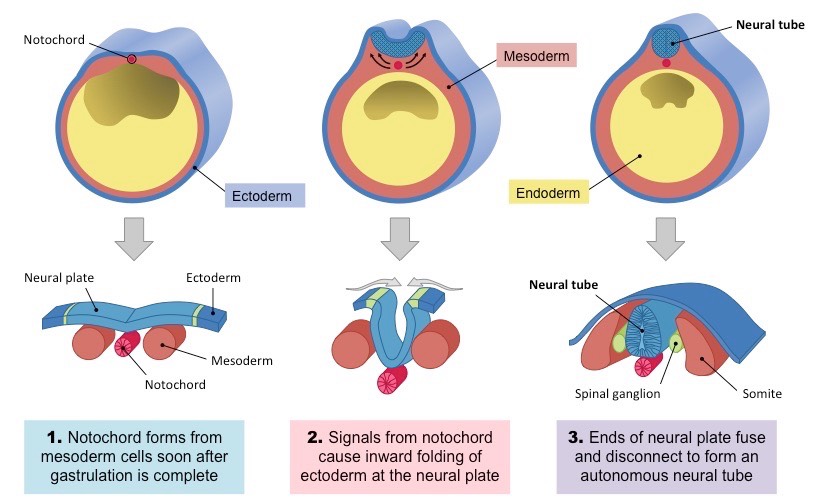
* process of neurulation begins with the formation of the neural plate, similar to amphioxus.
* The neural plate then folds in on itself to form the neural tube, which is separated from the surface ectoderm.
* However, there is a variation in the process called ____ neurulation, where the neural plate _____ to form the neural tube.
* Secondary neurulation, a different process, is also observed in some amphibians.
70
New cards
groove, fuses
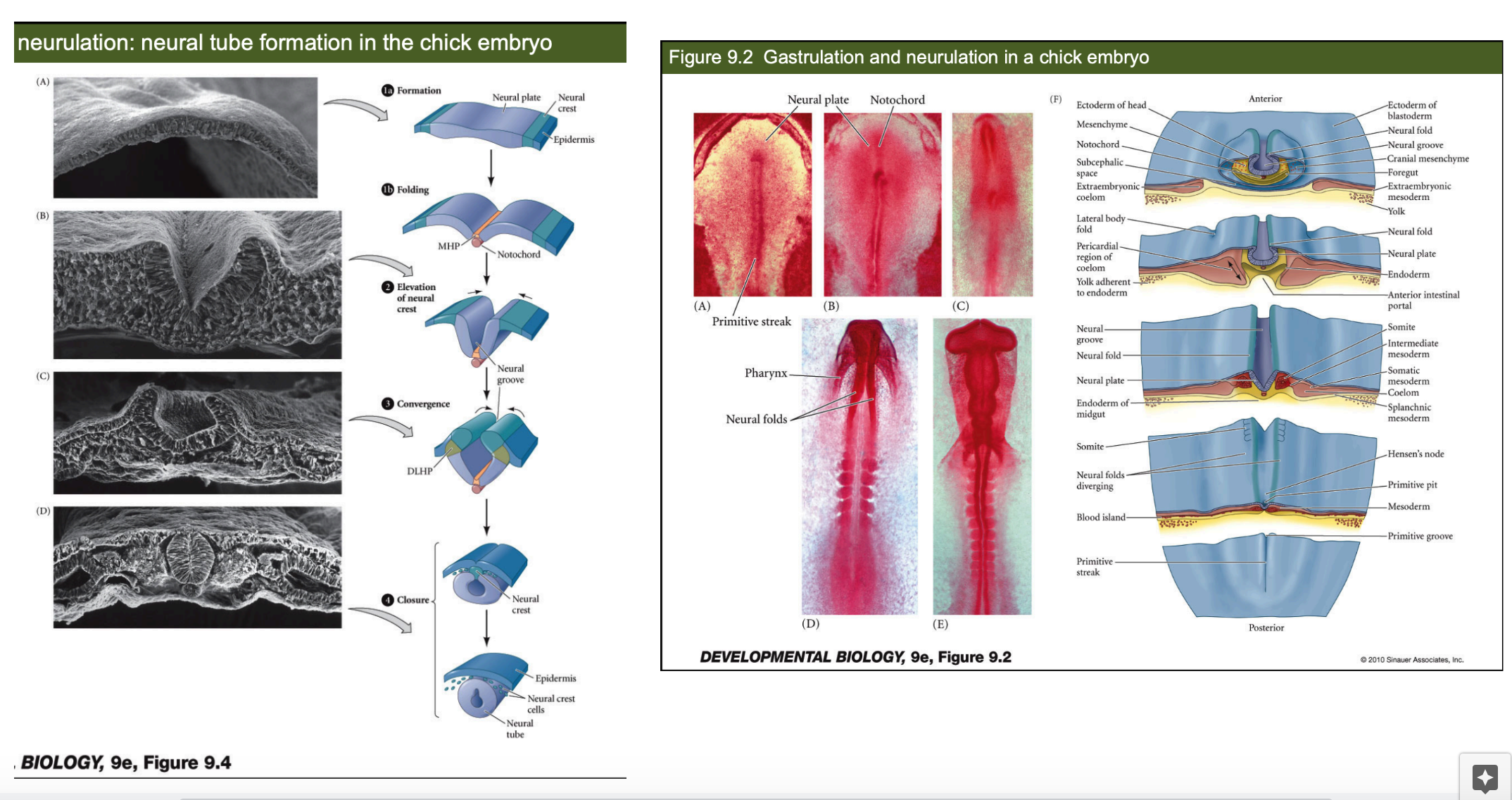
3. **Reptiles & Birds**
* have a similar process to amphibians, but with some variations.
* The neural tube is formed through primary neurulation, where the neural plate invaginates to form the neural ___, which then ___ to form the neural tube.
* The neural crest cells are formed from the ectodermal cells adjacent to the neural tube.
71
New cards
primary
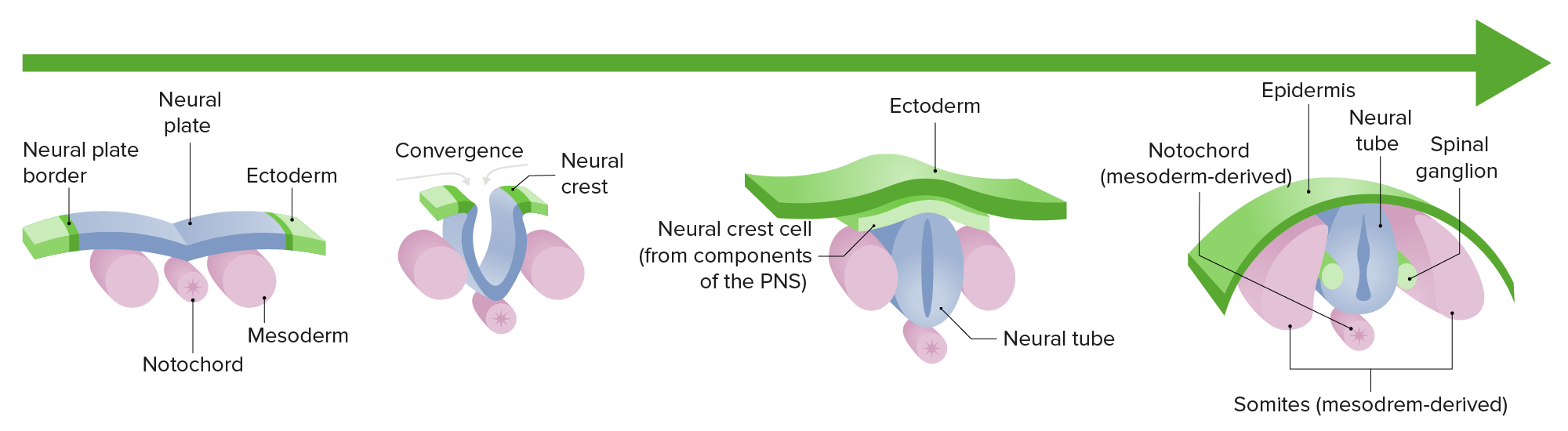
4. **Mammals**
* process of neurulation is also through _____ neurulation.
* The neural plate folds in on itself to form the neural groove, which then fuses to form the neural tube.
* The neural crest cells are formed from the ectodermal cells adjacent to the neural tube
72
New cards
mesoderm, differentiation, induction
**Organogenesis**
* Once the _____ divisions are set up, ontogenetic development proceeds to embryonic ______ of the body
* Gives rise to the organ systems
* Differentiation is caused by _____
* Various regions of germ layers develop into rudimentary organs
* Once the _____ divisions are set up, ontogenetic development proceeds to embryonic ______ of the body
* Gives rise to the organ systems
* Differentiation is caused by _____
* Various regions of germ layers develop into rudimentary organs
73
New cards
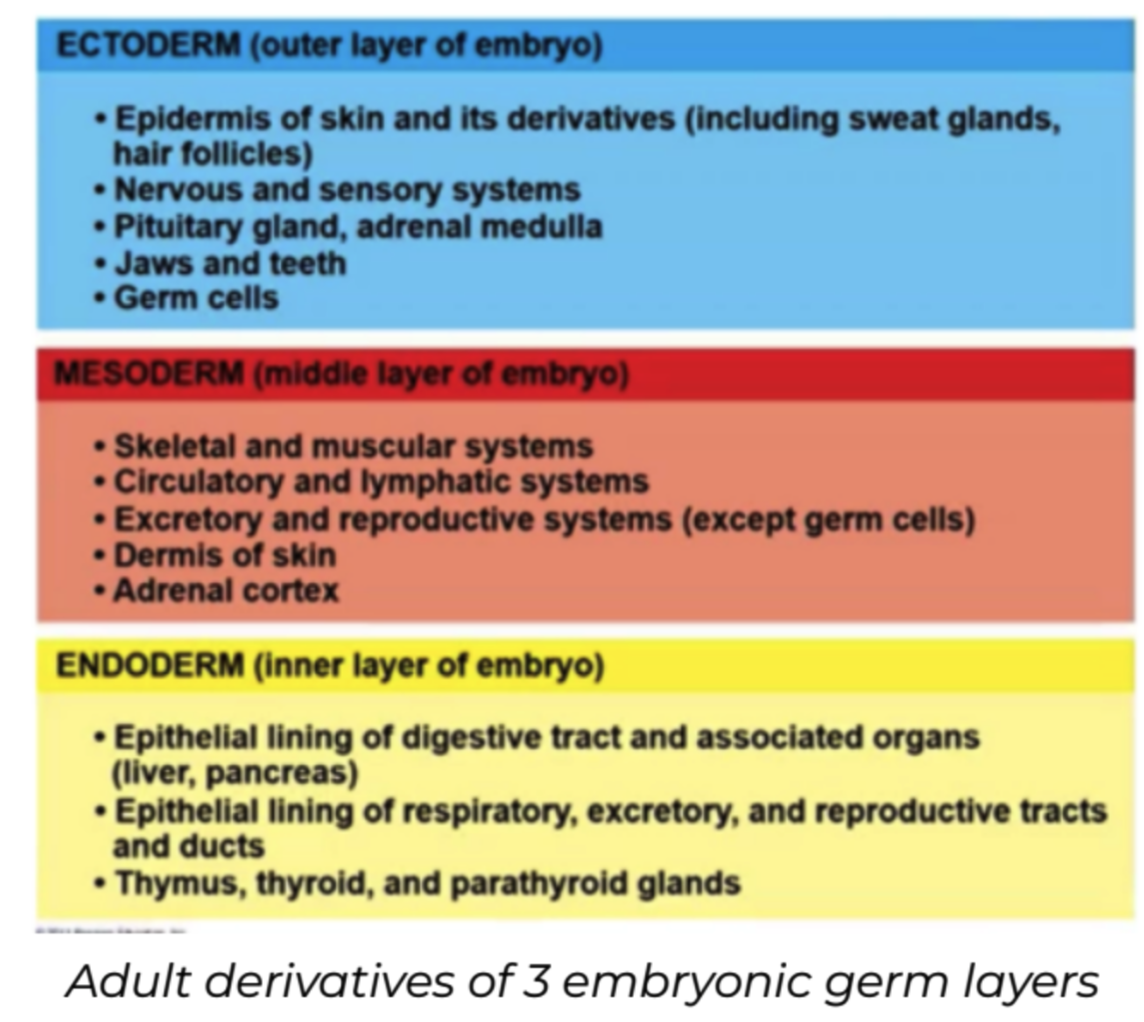
Germ Layers
1. Ectoderm
2. Mesoderm
3. Endoderm
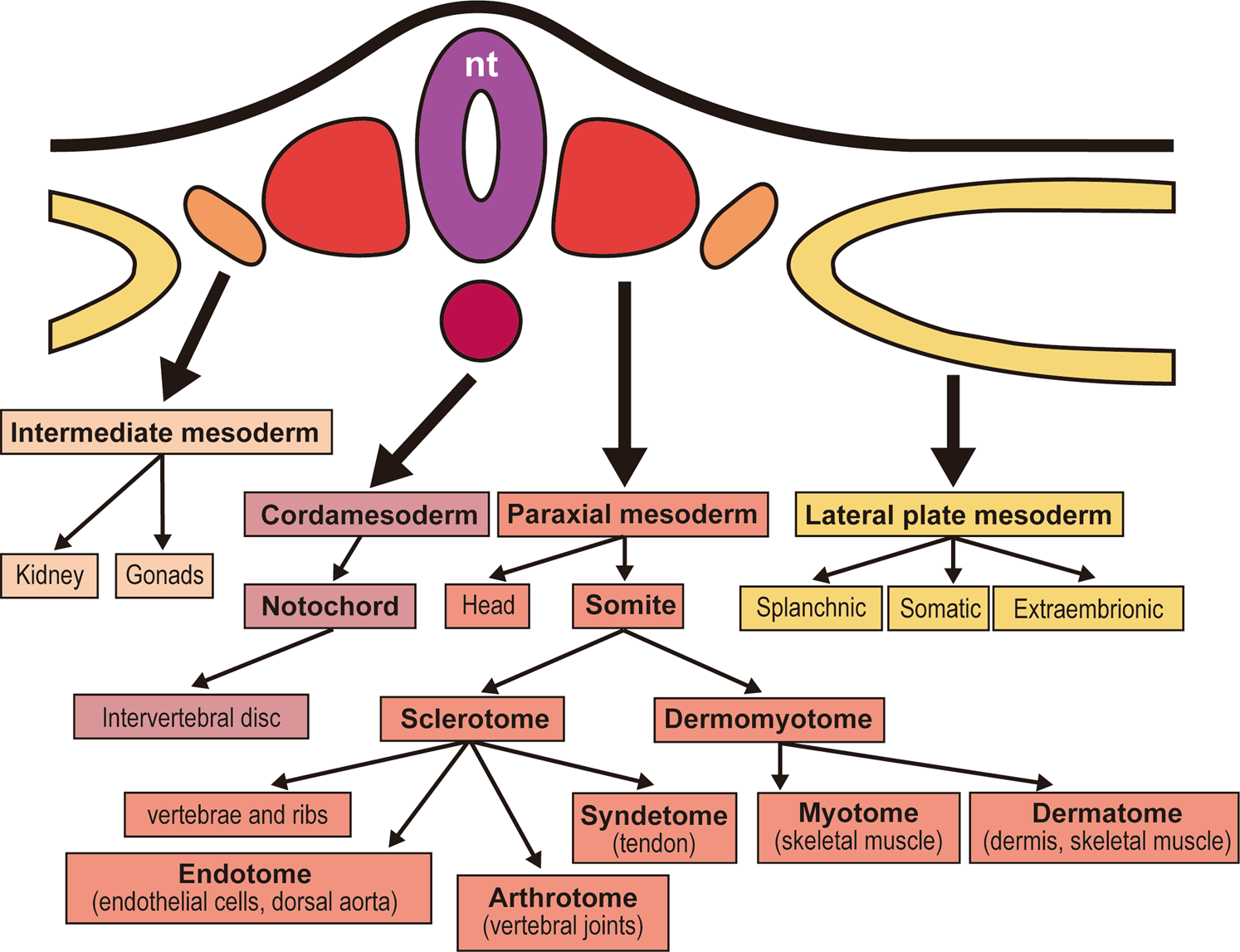
74
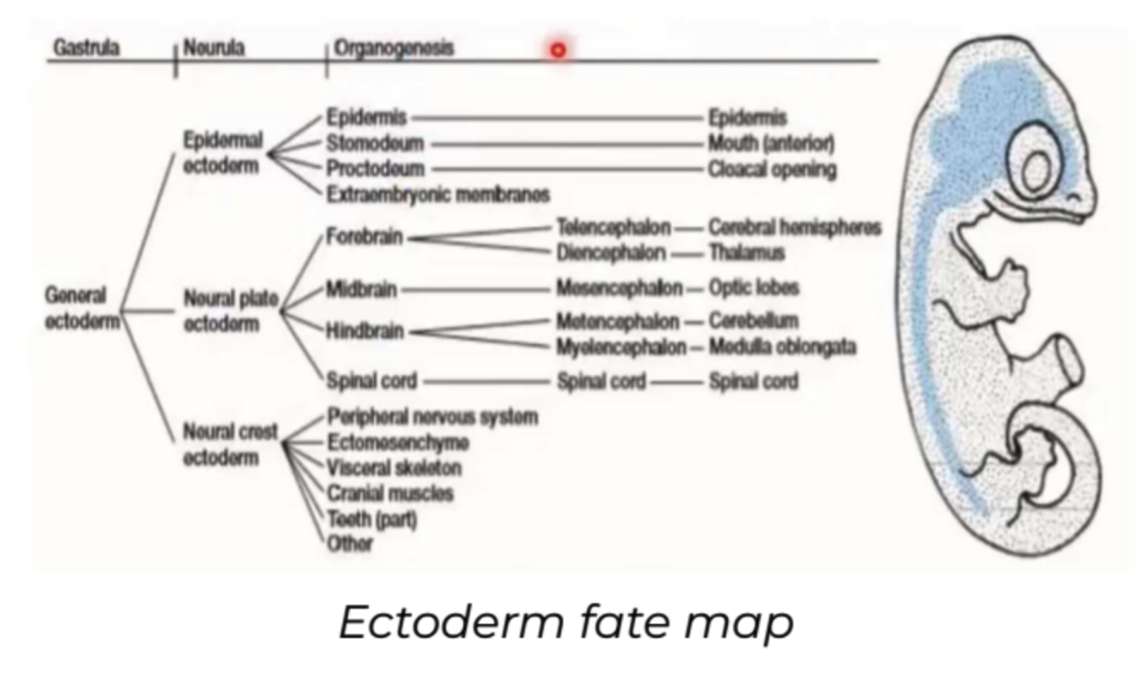
New cards
Ectoderm
* **Neural ectorderm**
* Nervous System
* **Epidermal ectoderm**
* Integumentary System
* **Extraembryonic membranes**
* Only **chorion and amnion** have contributions from the ectoderm
* Nervous System
* **Epidermal ectoderm**
* Integumentary System
* **Extraembryonic membranes**
* Only **chorion and amnion** have contributions from the ectoderm
75
New cards
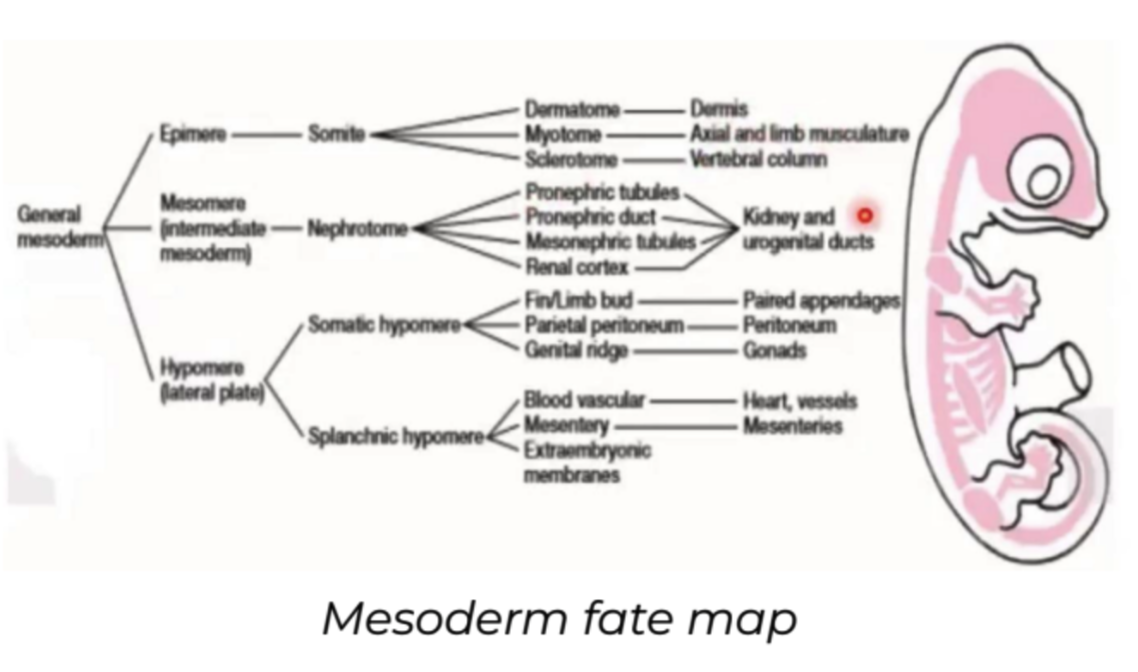
Mesoderm
* **Epimere:** dorsal part of the embryonic mesoderm
* Vertebral column
* Dermis (mid-dorsal)
* Skeletal muscles
* **Mesomere:** middle part of the embryonic mesoderm
* Kidneys
* **Hypomere:** ventral part of the embryonic mesoderm
* **Somatic:** body wall and limbs
* Organs
* Chorion and amnion
* **Splanchnic**: viscera or internal organs
* Circulatory system
* Yolk sac and allantois
* Vertebral column
* Dermis (mid-dorsal)
* Skeletal muscles
* **Mesomere:** middle part of the embryonic mesoderm
* Kidneys
* **Hypomere:** ventral part of the embryonic mesoderm
* **Somatic:** body wall and limbs
* Organs
* Chorion and amnion
* **Splanchnic**: viscera or internal organs
* Circulatory system
* Yolk sac and allantois
76
New cards
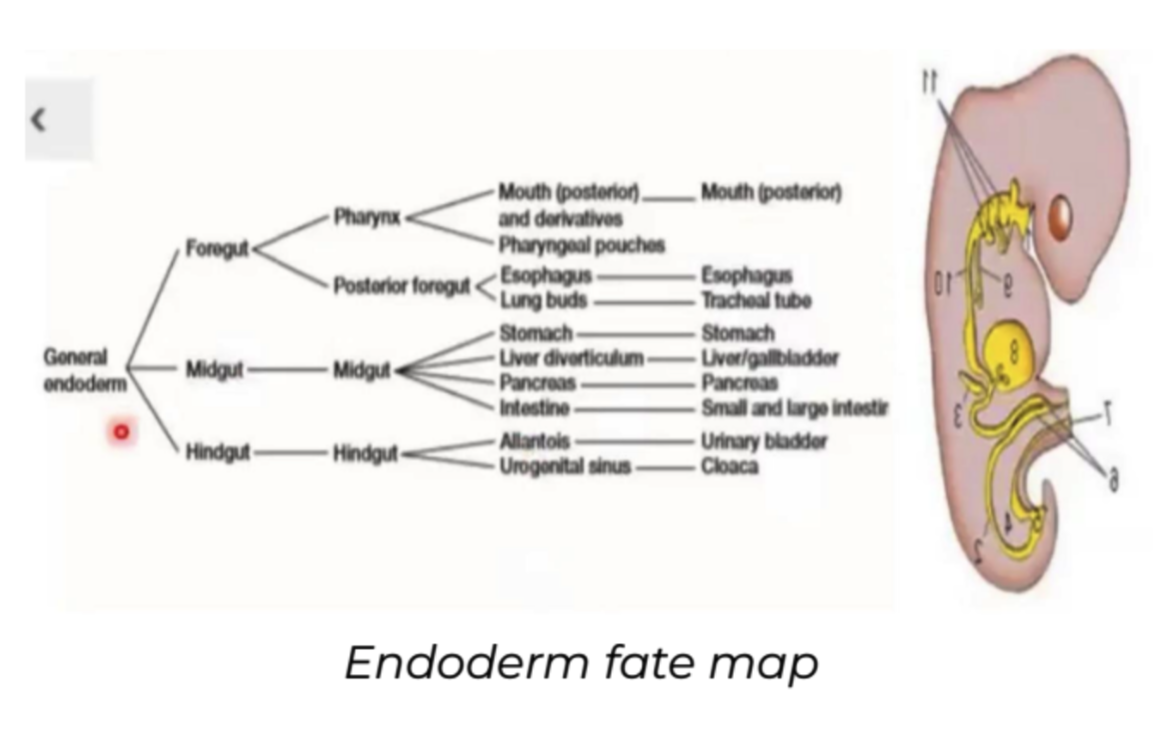
Endoderm
* GI Tract
* Stomach
* Liver
* Pancreas
* Intestines
* Lining of respiratory and digestive system
* Mouth posterior to internal anal sphincter
* Stomach
* Liver
* Pancreas
* Intestines
* Lining of respiratory and digestive system
* Mouth posterior to internal anal sphincter