Meteorology Final Exam
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
yes girl you got this
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
nowcasting forecasting
present - 6 hours from now
short-range forecasting
1 - 3 days
long-range forecasting
5 - 10 days
extended range forecasting
up to 90 days
folklore forecasting
sayings to predict weather, some are accurate while others are not
persistence forecasting
what happened yesterday will likely happen today, works best in North Pole and in tropics
climatology forecasting
long-term average of weather conditions used to predict weather for the day, fairly accurate
trend forecasting
uses short-term trend of temp/precip based on observations of nearby locations, assumes speed and direction of weather systems will not change, accuracy of method drops dramatically with time
analogue forecasting
find a date in the past where weather looks the same as it does today, relies heavily on forecaster experience, works best with severe and winter weather events
numerical weather prediction forecasting (NWP)
forecasts pressure, temp, wind, humidity, clouds, and precip using equations consisting of pressure variations, gravity, friction, how heat and moisture are transferred, and how water vapor changes state, accuracy drops dramatically after day 4
the forecasting process
observations (what’s happening to the W and NW?), analysis (storm systems, temp, pressure, dew point), prediction (look at models, ask what would make this event not happen?), post-processing (evaluate your accuracy)
station model plots
temp (upper left #), dew point (lower left #), sky cover (fill of circle), pressure (upper right #), wind speed and direction (half stick equals 5 knots, stick equals 10 knots, triangle equals 50 knots)
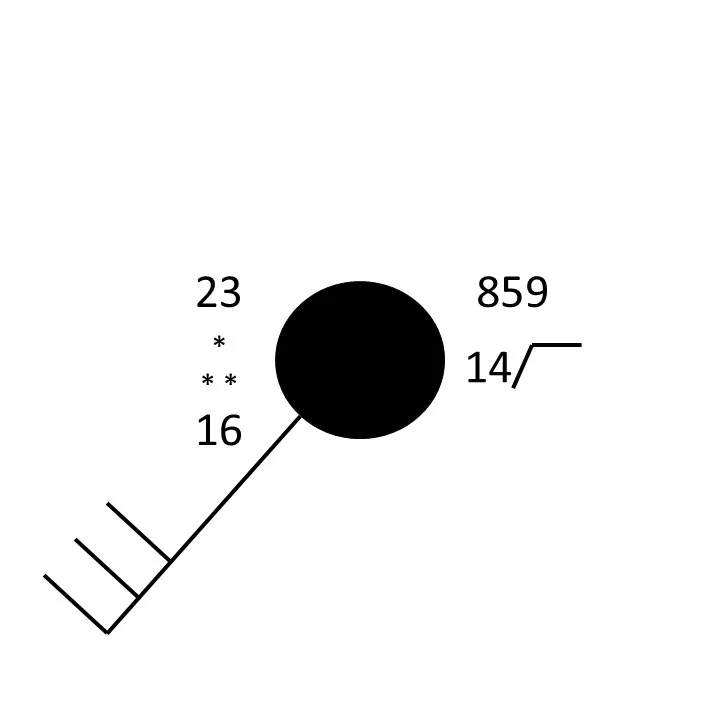
comma weather symbol
drizzlet
three commas weather symbol
moderate drizzle
arrow up and zig zag down weather symbol
thunderstorm
period weather symbol
rain
three periods weather symbol
moderate rain
)( weather symbol
funnel cloud
asterisk weather symbol
snow
three asterisks weather symbol
moderate snow
ordinary (air mass) thunderstorms
most common, form in areas with weak wind shear, self-extinguishing (fall apart with colder, downdraft air), short lifetimes (almost always one hour or less)
growth stage of thunderstorms
first stage
rising air parcels cool and condense, forming a cumulus cloud
rising air continues to cool and condense, making cloud taller
latent heat release changing from vapor to liquid
keeps rising air warmer than surrounding air
cloud continues to grow as long as updrafts continue
mature stage of a thunderstorm
second stage
as cooler and drier air helps to evaporate water droplets, heavy air descends
downdraft happens - the exhaling process of wind/cool air from a cloud
thunderstorm is now inhaling and exhaling air, feeding itself
storm most intense during this stage
takes on an anvil shape and may grow up to 40,000 ft
overshooting top
strong updrafts push cumulonimbus clouds into the stratosphere past the tropopause, indicator of a very strong storm that may have rotation at the surface underneath the top
decaying stage of a thunderstorm
third stage
updrafts weaken and downdrafts dominate
normally occurs thirty minutes after the storm develops
multicell thunderstorms
clusters of thunderstorms that form in different growth stages in the same area, have stronger winds than ordinary thunderstorms, last longer and often more severe than ordinary thunderstorms
multicell: squall-line thunderstorms
organized line of thunderstorms with most intense rainfall at the leading edge, form along or ahead of a cold front, intense storms, most moisture comes from the south so the southernmost part of the storm is usually the strongest
bow echo
when a portion of a squall-line’s leading edge curves out ahead of the rest of the line, produces damaging winds
supercell thunderstorms
thunderstorm with a rotating updraft (mesocyclone, most organized and long-lived thunderstorm, (2+ hours and 100+ mi), come in HP and LP varieties, all are severe
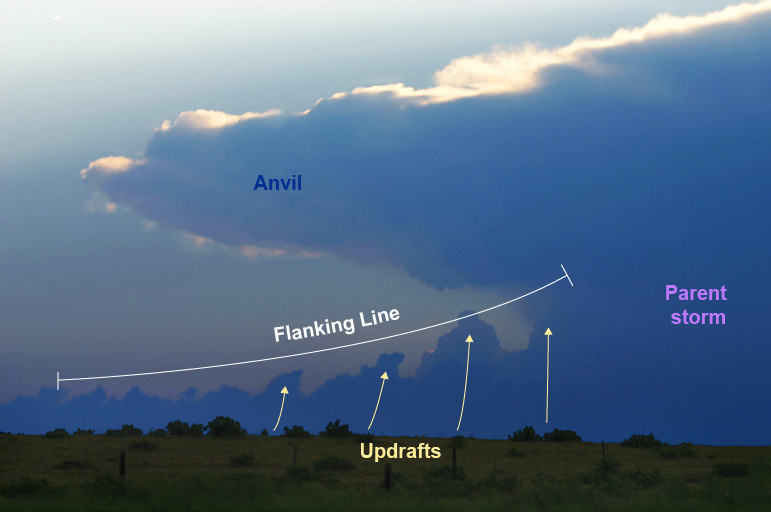
flanking line
updraft/food supply for mesocyclone
rear-flank downdraft
rear portion of the mesocyclone’s downdraft
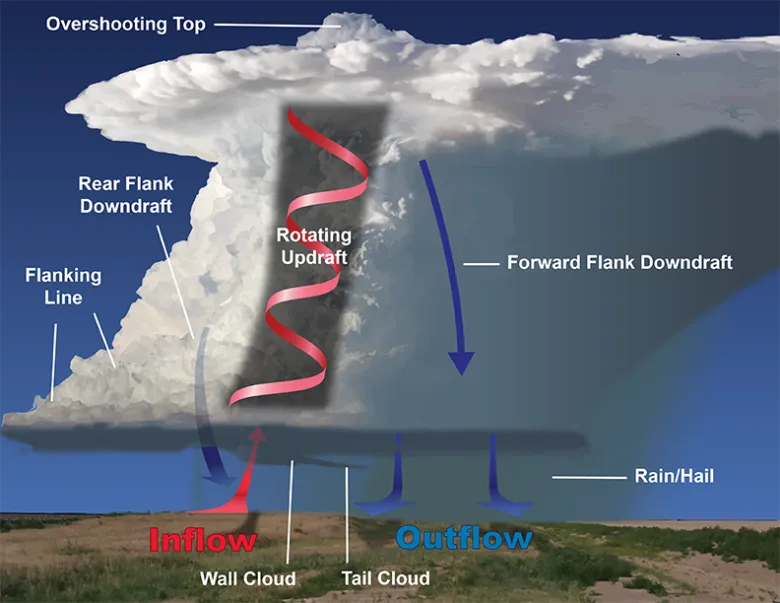
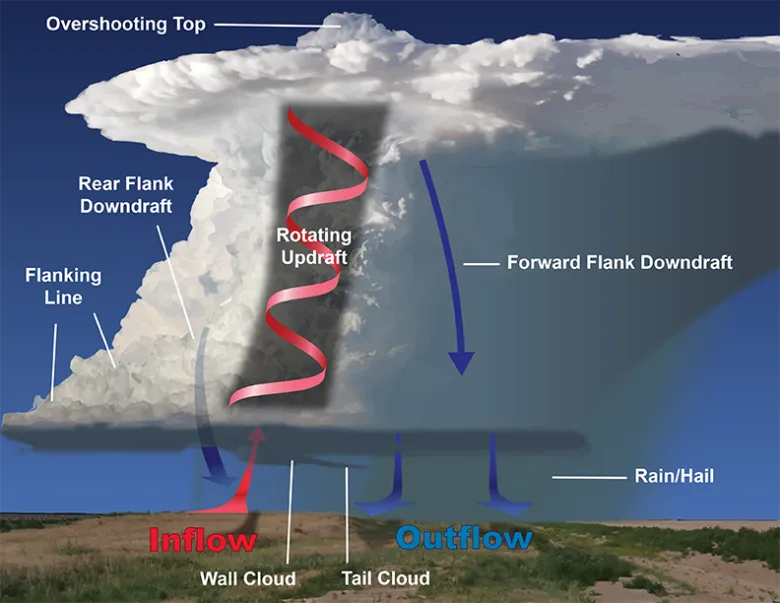
inflow
“suck-zone”, influx of moisture-rich air into a mesocyclone
mesoscale convective systems (MCS)
large grouping of multiple storms that move together and last for hours
circular MCS
covers many states, can produce severe winds and hail, heavy rain producers, low chance of tornadoes
linear MCS
very strong winds, can produce isolated and quick tornadoes
gust fronts
leading edge of cold air coming from a large, severe thunderstorm
microbursts
a localized column of sinking air that produces damaging straight-line winds at the surface, can be confused with tornadic damage
derechos
a widespread, long-lived, violent windstorm associated with a fast moving band of severe thunderstorms that usually take a bow echo form
usually associated with a warm airmass
occurs most often in July
thunder and lightning
have to exist together
thunder
the heating and expansion of the air creating a shock wave
if thunder is heard 15 seconds after lightning strike, how far away is the storm?
3 miles, storms move at 5 seconds per mile
thunder sounds like
a crack followed by a bang when you are close to a storm, a rumble when you are far away
lightning
happens because negative charges are found near the base of a cloud, positive charges higher up in the cloud and at the ground, the buildup of negative charges at the base eventually overcomes the insulation of the air and electricity is created
stepped leader
initial spark of lightning that leaves the cloud base, as it approaches the ground, a positive charge starts upward and meets the negative charges
return stroke
the upward flow of current that we see as lightning
heat lightning
distant lightning that illuminates the sky but is too far away for thunder to be heard
tornado
a rapidly rotating column of air that reaches the ground
has a diameter of 50-100 yds
path length: 2-4 mi
lifespan: 5-10 min
wind speed: 80-300 mph
waterspouts
similar to tornadoes but over water and with much slower wind speeds (30-40 mph)
landspouts
similar to tornadoes but from from the ground up because of low-level circulation
funnel cloud
a cloud of condensed water droplets associated with a rotating column of air, extends from the base of a cloud (usually cumulonimbus), but don’t reach the ground
dust-whirl stage of a tornado
first stage
dust swirls upwards from the ground and grows toward the funnel cloud
damage usually minimal in this stage
organizing stage of a tornado
downward extension of funnel cloud and connection with dust whirl on ground
damage light in this stage
mature stage of a tornado
tornado is on the ground
strong winds and a howling noise
damage most severe during this stage
decaying stage
rotation slows and stops
tornado is stretched into a thin funnel-shaped rope as storm moves away
what time do tornadoes occur most often?
in the late afternoon due to daytime heating and the atmosphere being more unstable
suction vortices
mini-tornadoes within the tornado that have stronger winds and produce significant damage
doppler radars detect
wind (velocity) and precipitation (reflectivity)
red on a doppler radar indicates that wind
is blowing away from the radar
green on a doppler radar indicates that wind
is blowing towards the radar
enhanced Fujita scale
measures tornado damage on a scale from EF-0 to EF-5
warning signs for tornadoes
strong, persistent rotation, circling dust and debris, hail preceding rapid quiet, a loud roar with heavy rain
Doppler radar is helpful for measuring precipitation, but not wind
false
A forecast of an extended period of dry weather would be made for a region beneath
an upper-level ridge
Suppose that where you live, the middle of January is typically several degrees warmer than the rest of the month. If you forecast this "January thaw" for the middle of next January, you would have made a
climatological forecast
A weather forecast that predicts that the future weather will be the same as the present weather is called
persistence forecast
The ASOS system is designed to provide nearly continuous information about wind, temperature, pressure, cloud-base height, and runway visibility at various airports.
true
Sinking air warms, yet the downdrafts in a thunderstorm are usually cold.
true
Supercell thunderstorms are different from ordinary thunderstorms in that supercell thunderstorms
have a tilted, rotating updraft
squall lines generally do not form
behind a cold front
Each year, U.S. fire departments respond to more than ____ fires started by lightning in the United States.
20,000
To be rated a severe thunderstorm by the National Weather Service, the storm has to have at least one of the following: large hail with a diameter of at least an inch, surface wind gusts of 40 knots or greater, or produces a tornado
false - wind speeds must be 50 knots or greater
The greatest frequency of hailstorms in the United States is
over the great plains
Is this statement true or false: "Lightning never strikes twice in the same place"?
false
Tornadoes that form ahead of an advancing cold front tend to move from the ____.
southwest toward the northeast
The tornado alley of the United States ____.
stretches from central Texas to Nebraska
With the Doppler radar, a radar transmitter sends out ____, and when they strike an object, some are reflected and scattered back to the antenna.
microwave pulses
The Central Plains region is susceptible to tornadoes because ____.
warm, humid surface air is overlain by cooler, drier air aloft