Infection and response
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
what is a communicable disease?
diseases caused by microorganisms (pathogens) they can be transmitted from person to person
cell structures for bacteria?
loop of DNA
plasmids (resistance)
antigen
flagella
what is a virus not?
LIVING OR A CELL
structure of virus?
protein coat
genetic material
what is an antigen
foreign molecule, usually protein, recognised by WBC
how do bacteria reproduce?
bacteria enter body
feed on nutrients
divide by binary fission - large numbers
how do viruses reproduce?
enter the body and invade body cells
cause host cells to make more virus
how do bacteria cause symptoms?
produce waste products which are poisonous
toxins which damage/destroy body cells
who do viruses cause symptoms?
take over cells, therefore cells get DAMAGED
4 methods of pathogen transmission
direct contact
STD
re-using dirty needles
through a cut
Water/food
humans - contamination (salmonella/cholera)
plants - fungal spores via water
air (droplet infection)
coughing/sneezing when ill in humans - breathed in
plants - fungal spores by wind
Animals spread pathogens as vector - rabid dog/mosquito
4 primary and non specific defence systems
skin - covers the body acting as a barrier
nose - hair and mucus trap pathogens
trachea/bronchi also produce mucus. moved by cilia to throat (mexican wave) swalled to stomach
stomach - produces HCl to destroy pathogens
Measles
type of pathogen
symptoms
method of transmission
treatment/prevention
virus
red skin rash, fever
droplets from infected person’s cough/sneeze
vaccination, no treatment
HIV
type of pathogen
symptoms
method of transmission
treatment/prevention
virus
flu like symptoms for a few weeks
sexual contact, exchanging bodily fluids (sharing needles)
Antiretroviral prevents development of AIDS. no cure/vaccine. use of condoms/not sharing needles
TMV
type of pathogen
symptoms
method of transmission
treatment/prevention
virus
mosaic pattern on leaves of plants - discoloured
contact disease/healthy plant - insect vectors
no treatment, good field hygiene + pest control to prevent
salmonella
type of pathogen
symptoms
method of transmission
treatment/prevention
bacteria
fever, abdominal cramps, vomiting, diarrhoea
eating undercooked poultry/eggs, eating food prepared in unhygienic places
vaccinate poultry, cook poultry thoroughly
gonorrhoea
type of pathogen
symptoms
method of transmission
treatment/prevention
bacteria
green/yellow discharge from penis/vagina, pain when urinating
sexual contact
treated with antibiotics, use condoms
rose black spot
type of pathogen
symptoms
method of transmission
treatment/prevention
fungus
purple/black spots on rose leaves
spores of fungus carried by wind
cut off leaves - burn, fungicides
malaria
type of pathogen
symptoms
method of transmission
treatment/prevention
protist
episodes of fever/shaking
mosquito - vector
treated using combination of drugs, prevent with antimalarial drugs, insecticides, preventing breeding
4 methods to prevent spread of disease
isolate infected individuals
hygiene
vaccination
destroying vectors
how does isolating individuals work/prevent spread of disease?
stay at home until no longer infectious
remove infected plants + burn them to prevent spread
how does destroying vectors work/prevent spread of disease?
use insecticides to destroy insects that may transmit disease
avoid/kill animals that have rabies
kill mosquitos - repellent spray, sleep in insect net
how does hygiene work/prevent spread of disease?
washing hands/sanitise
face masks
clean surfaces
cook food thoroughly
how does vaccination work/prevent spread of disease?
makes people immune to that disease so they can’t pass it on
herd immunity
poultry vaccinated against salmonella
immune response on first infection?
slow response, time for the pathogens to increase and cause symptoms, get ill
3 things WBC do
Phagocytosis
antibody production
antitoxin production
how does phagocytosis work?
WBC engulf and digest pathogens
how does antibody production work(+immunity)?
produced by lymphocytes ( WBC)
able to bind to pathogens as complimentary shape to antigen
each wbc can make one antibody
if invaded by pathogen, correct wbc is selected and divides by mitosis
release millions into blood
antibodies attach to pathogens and destroy them
large number of specific wbc stay in blood as memory cells
if same pathogen invades again, memory cell found quickly and produce many antibodies before symptoms (immune to this pathogen)
how does producing antitoxins work?
antibodies called antitoxins bind to toxins (released by bacteria) to make them harmless
how do vaccines work?
vaccine contains antigens of either dead or weakened pathogens
stimulates same specific lymphocytes, which stay in blood as memory cells
what is herd immunity?
approx 90% of pop vaccinated - so few vulnerable people that spread of disease is reduced
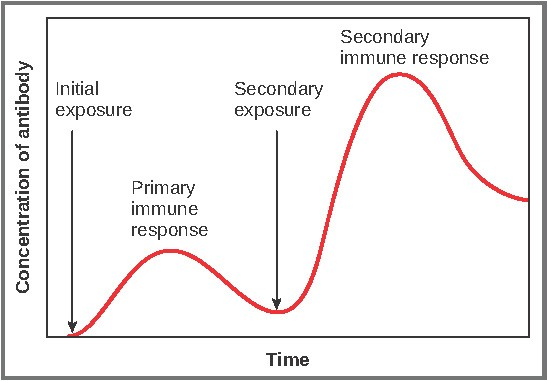
what happens at each stage?
INITIAL - primary response is slow, takes time to select specific and divide by mitosis
person develops symptoms
PRIMARY RESPONSE - pathogen destroyed
SECONDARY EXPOSURE(same pathogen) - most antibodies broke down, memory cells remain
much quickER response, produces MORE antibodies to destroy pathogen quickly due to memory cells = no symptoms = immune
SECONDARY RESPONSE - pathogen destroyed
2 main treatment methods
relieve symptoms - doesn’t destroy pathogens - paracetamol, ibuprofen
destroy pathogens- anti- viral drugs, antibiotics
what are anti-viral drugs?
few exist, difficult to develop drugs that destroy viruses without damaging body’s tissues
what are antibiotics?
used to kill bacteria in body → NOT VIRUSES
decreased deaths from bacterial infections greatly
some antibiotics treat some bacteria, others needed to be treated with different ones
must be used carefully to prevent resistance(mutation
how do bacteria become resistant, what is an example?
MRSA
bacteria divide by binary fission, one undergoes a mutation of DNA
bacteria not resistant killed by antibiotics
bacteria with resistant allele divides many times by binary fission - survives and reproduce
3 ways to reduce development of antibiotic resistant strains?
doctors should not prescribe antibiotics inappropriately
for viral infections
non serious infections
patients must complete full course of antibiotics so ALL bacterial pathogens are killed
limit use of antibiotics in agriculture
is it possible to keep up with emergence of new resistant strains?
no, development of new antibiotics is costly and slow
what drug is extracted from willow, what does it do?
Aspirin - painkiller, treats fevers
what drug is extracted from foxgloves, what does it do?
Digitalis - treats heart conditions
what drug is extracted from mould, what does it do?
Penicillin - kill bacteria, treat infections
conditions needed for bacteria to reproduce?
oxygen
warmth
nutrients
4 parts of aseptic technique
petri dishes and culture must be sterilised before use - kills unwanted microorganisms
inoculating loop/glass spreader sterilised by heating in roaring bunsen flame
lid of petri dish secured with adhesive tape to prevent microorganisms from contaminating, store upside down to stop condensation falling on agar surface
school/college - incubated max temp 25 degrees, reduces likelihood of harmful pathogens
formula for calculating number of bacteria in population
bacteria at end of growth = bacteria at beginning x 2number of divisions
7 stage of drug development
disease is targeted. chemical extracted from a plant or microorganism, or synthesis of new drugs
drugs tested in lab to see if they are toxic and if they work
Preclinical testing in lab - cells, tissues, organs
testing carried out on live animals - efficacy, dosage and side effects
Clinical trials carried out using healthy volunteers then patients. scientists start with a low dose. if drug is safe, more trials carried out to find optimum case. may be double blind with placebo
peer review to prevent false claims
results are published
What is a double blind trial?
Patients randomly allocated to drug or placebo group
Scientists and patients DO NOT know whether they are getting drug or placebo
avoids bias
what is a placebo?
a drug with no therapeutic effect (e.g. sugar pill)
act as a control so you can see how effective the new drug is