Year 12 Gene Expression - mutations to phenotype and environment
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Mutation
change in the base sequence of DNA to make new alleles.
Spontaneous mutation
Mutation caused by mistake happening in DNA REPLICATION.
Sometimes can be reversed (enzymes).
Generally get more as get older
Induced mutation
Mutation caused by MUTAGENS (virus, radiation, chemicals).
Can change genotype and then phenotype of living thing.
Insertion mutation
Insert bases(s) in DNA

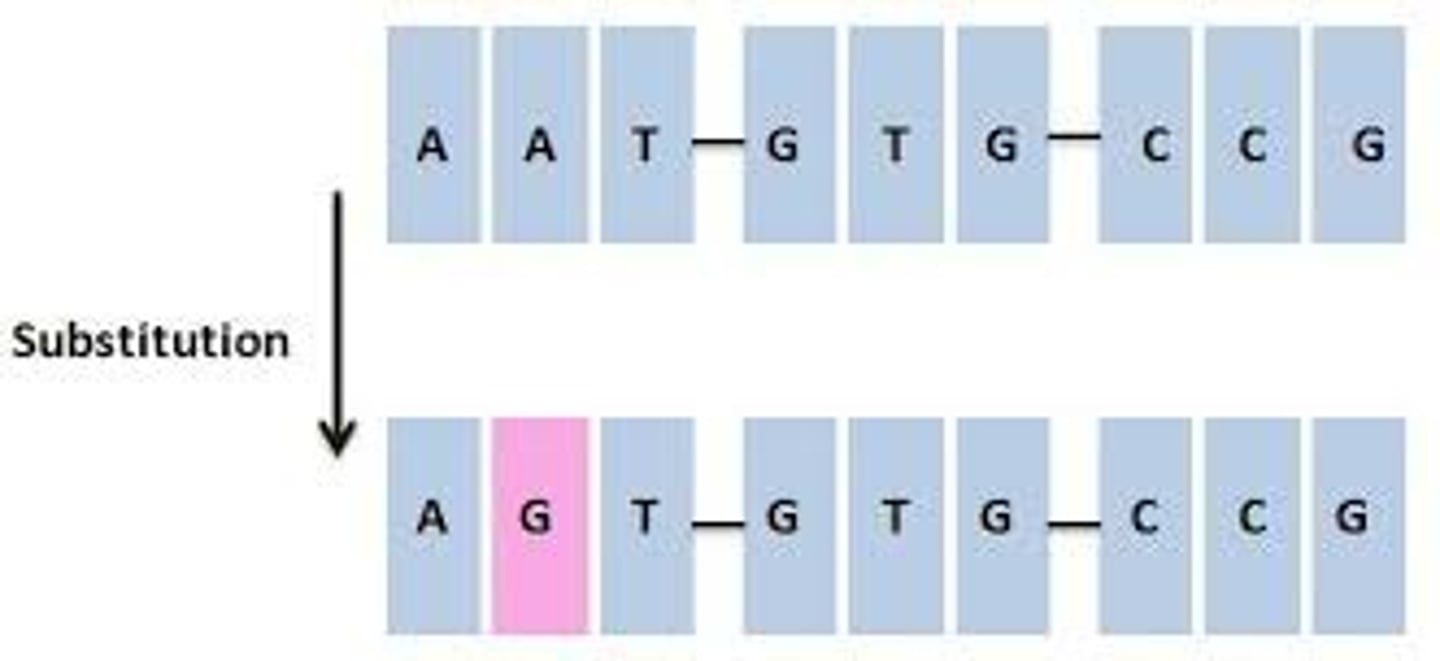
Substitution mutation
Different base in DNA than original base
Deletion mutation
Remove base(s) from DNA

Same-sense mutation
Change of base doesn't change amino acid being coded for
Missense mutation
Change in base changes amino acid, but not over protein
nonsense mutation
Change in base completely changes DNA (stop codon) and protein
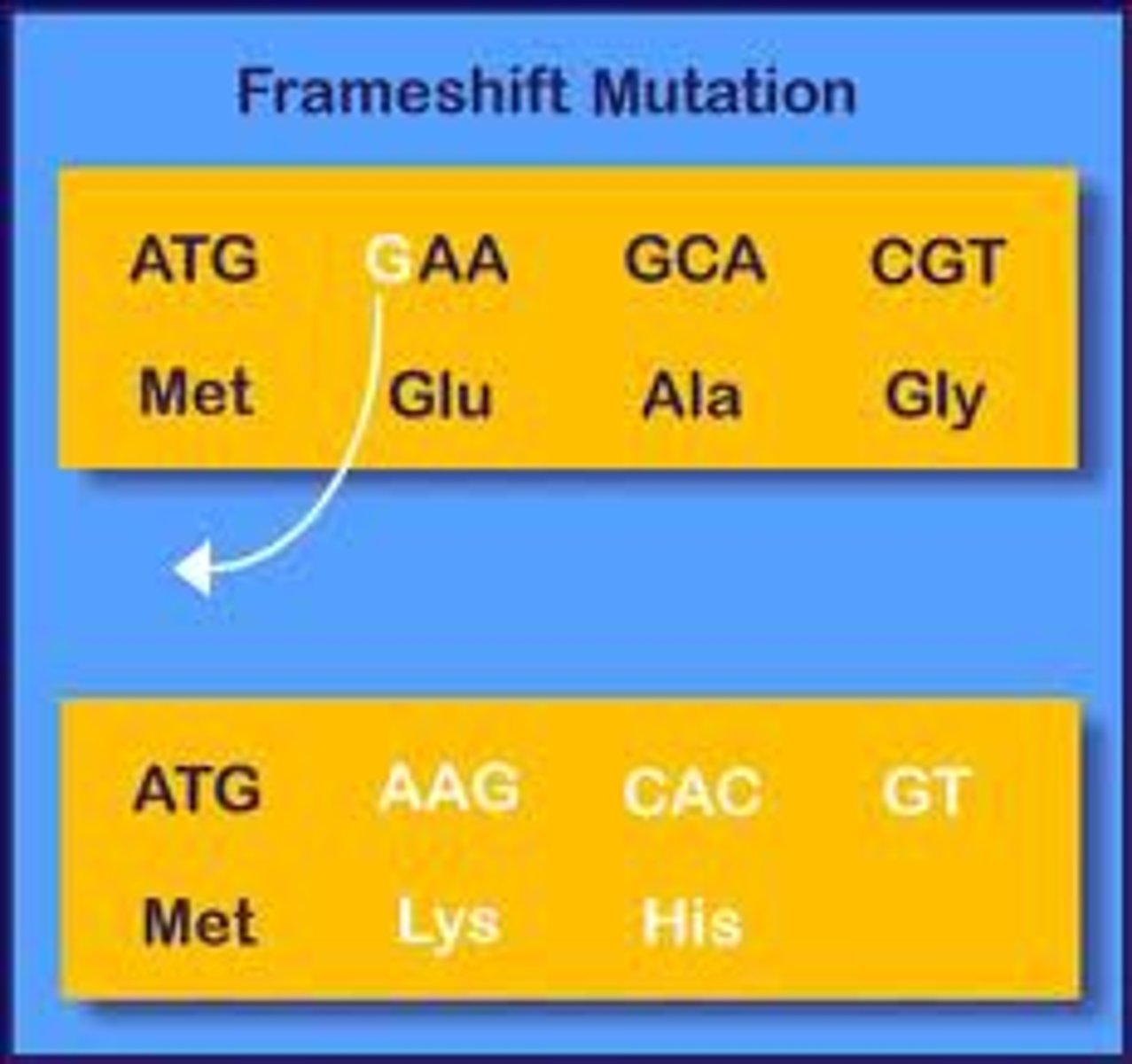
Frame-shift
Deletion or insertion bases changes reading of triplets. (usually lethal)
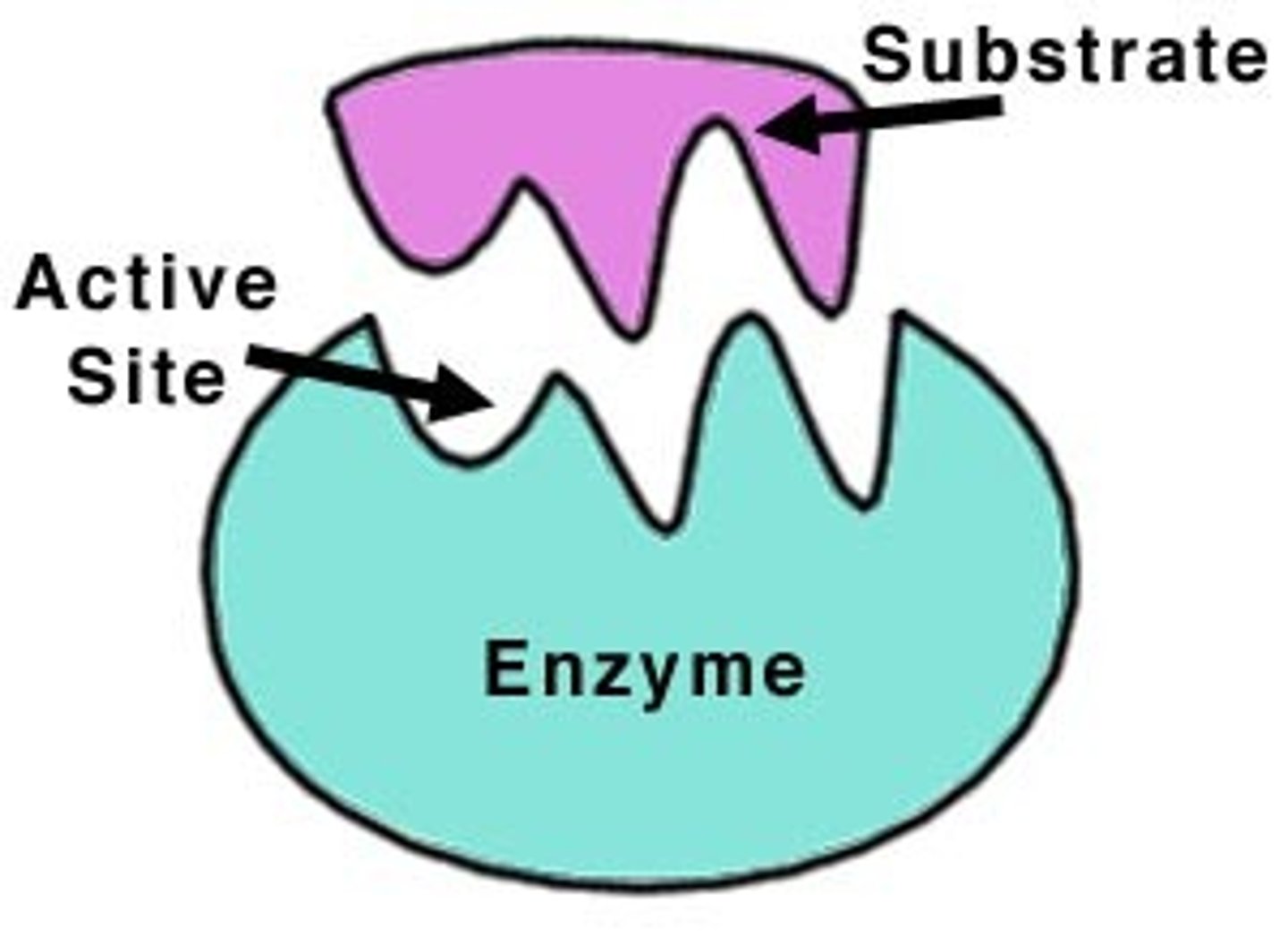
Enzyme
Biological catalysts, type of protein (speed up or slow down chemical reactions in living things)
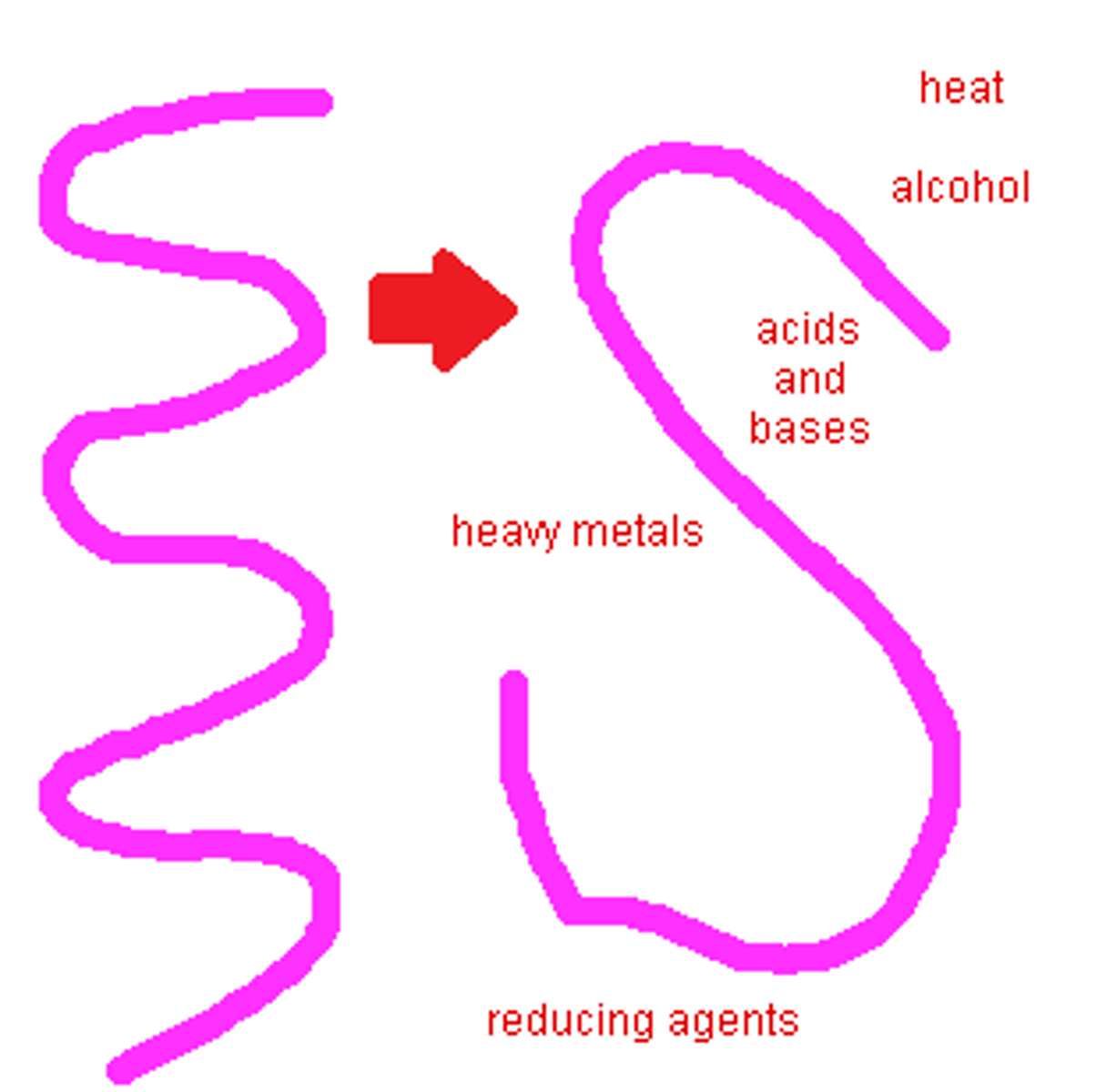
Denatured
Change the shape of an enzyme so that it can no longer speed up a reaction.
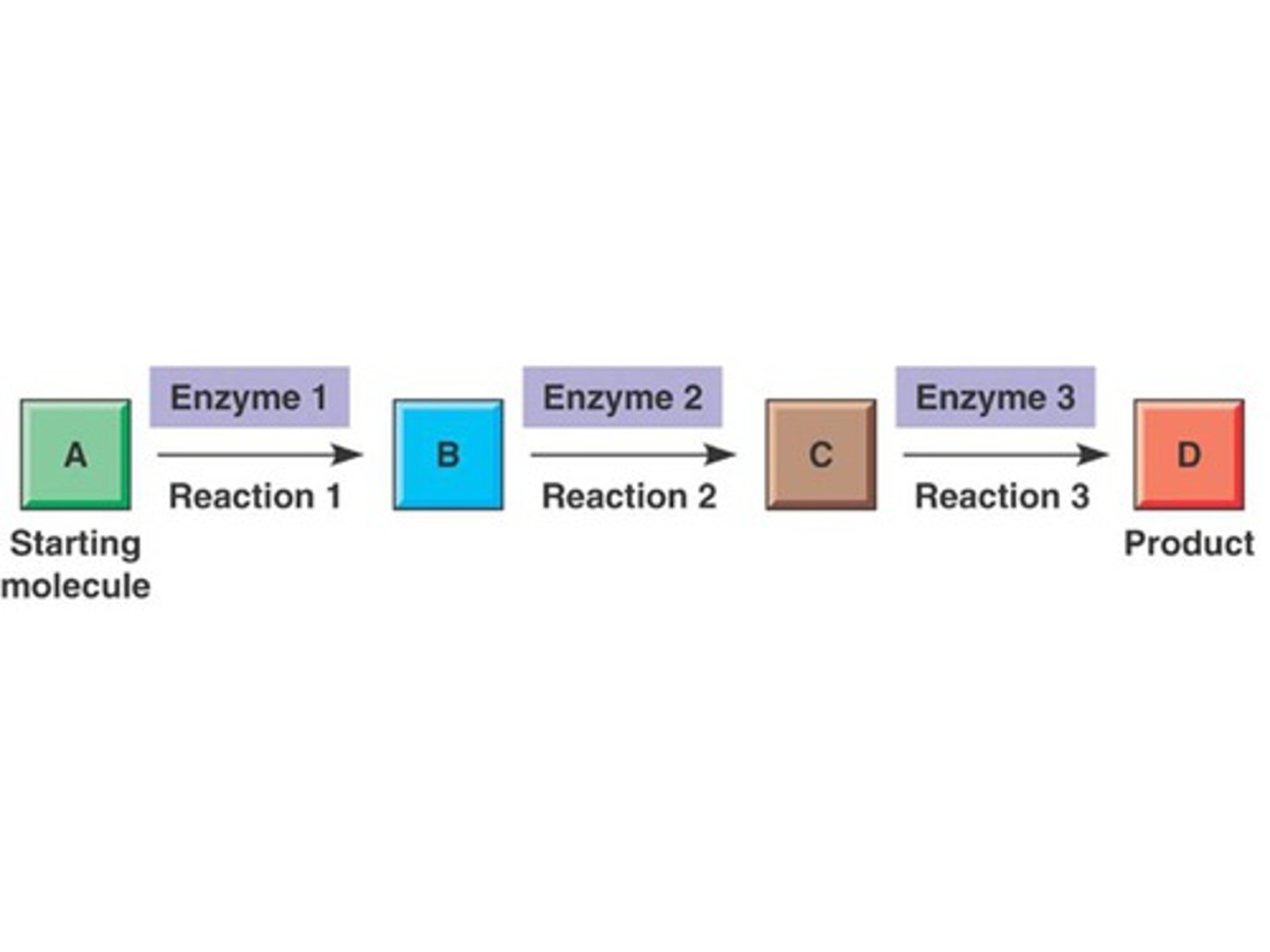
Metabolic pathway
Series of enzyme controlled reactions where the reactants (substrate) become products and can then become reactants for the next reaction step.
Substrate
The reactant on which an enzyme works.
Phenotype
Characteristic (or feature) expressed
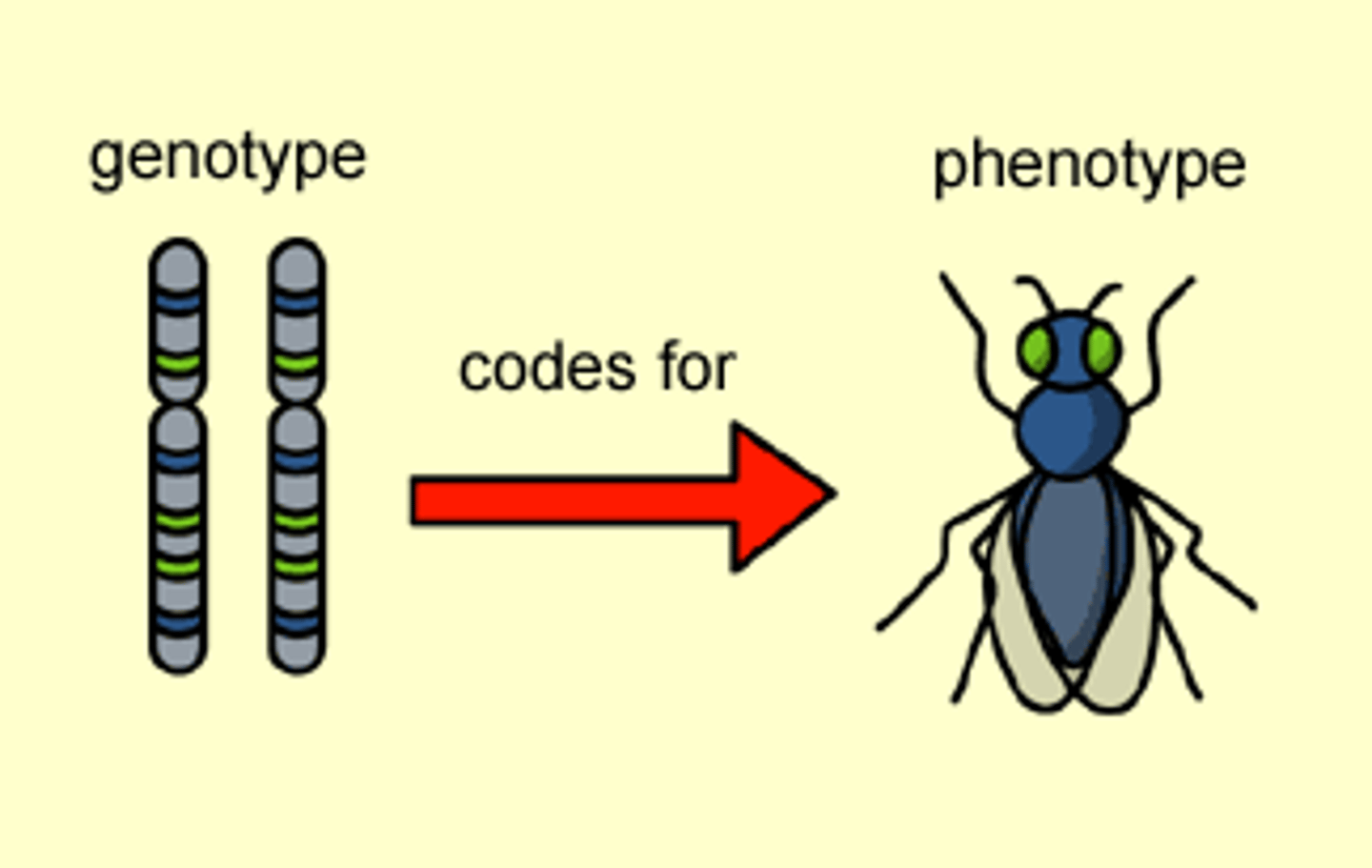
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.
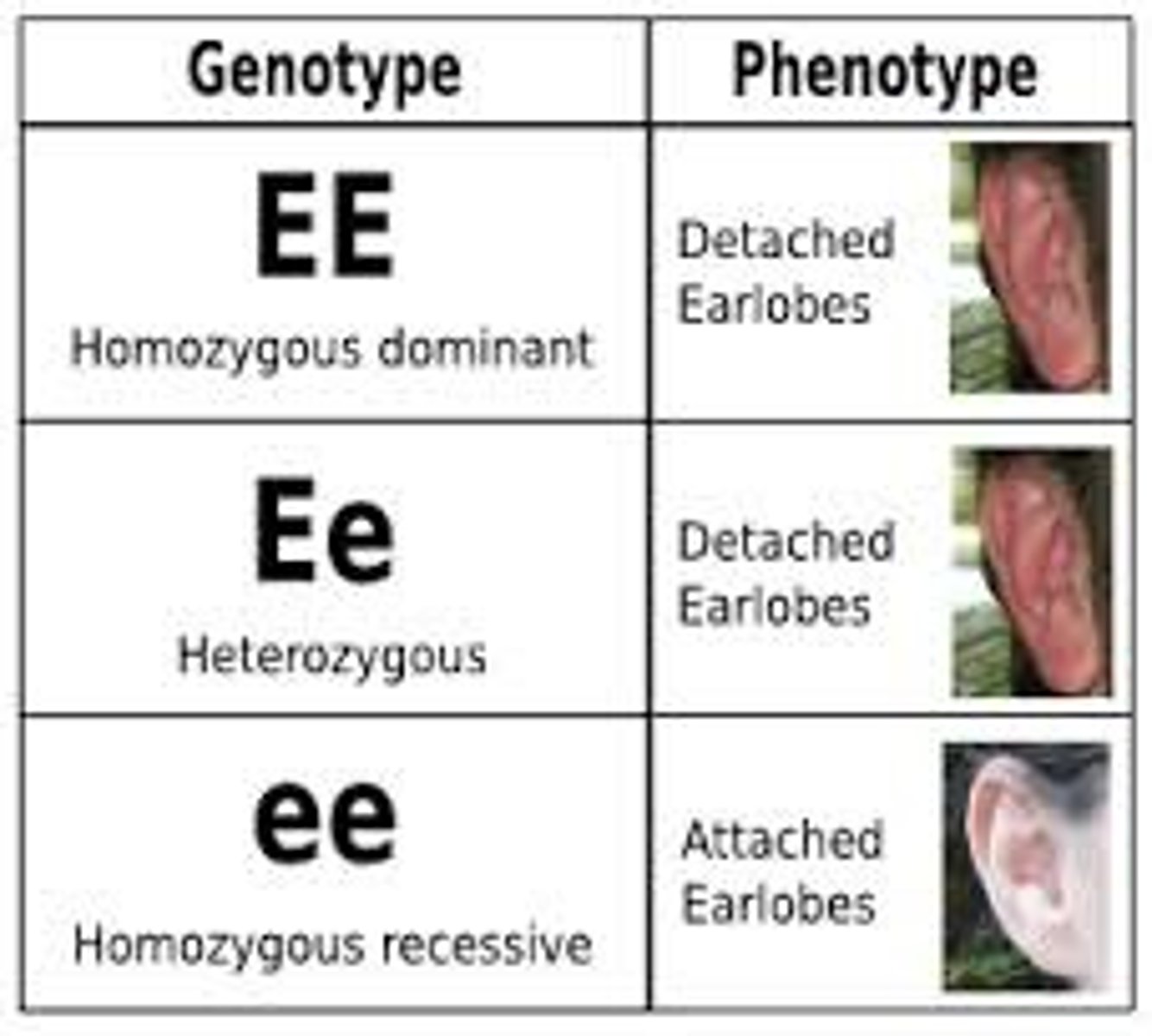
Allele
An alternative form of a gene.
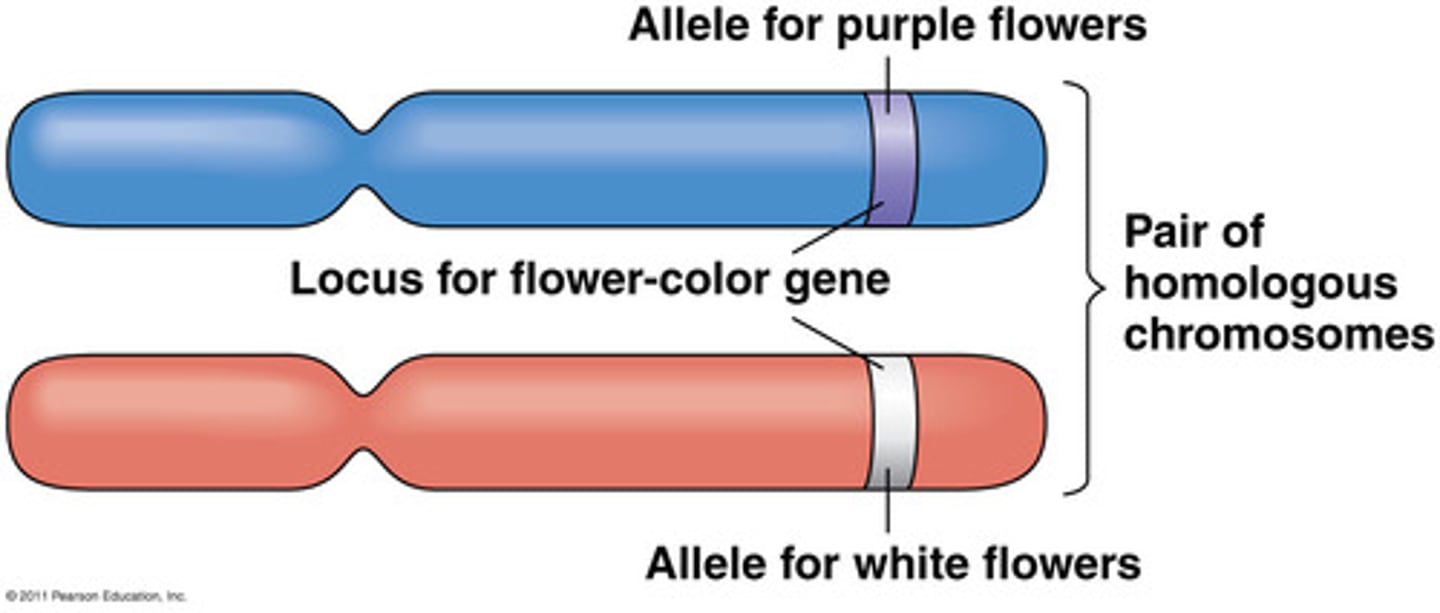
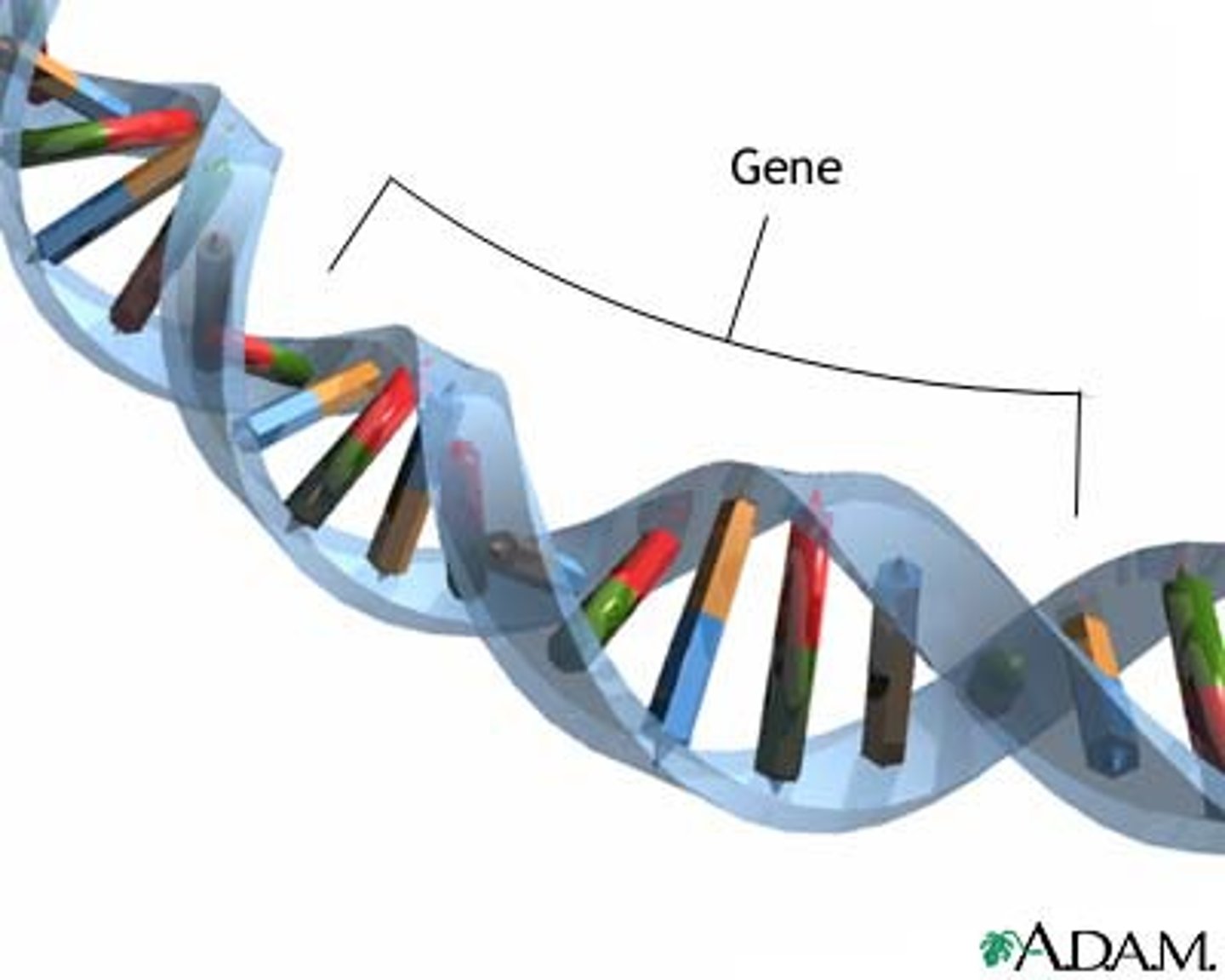
Gene
A section of DNA that codes for a particular phenotype.