a&p lab organs, systems, and organization of the body
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exercise 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
11 organ systems:
reproductive
urinary
nervous
muscular
respiratory
skeletal
lymphatic
integumentary
digestive
endocrine
circulatory
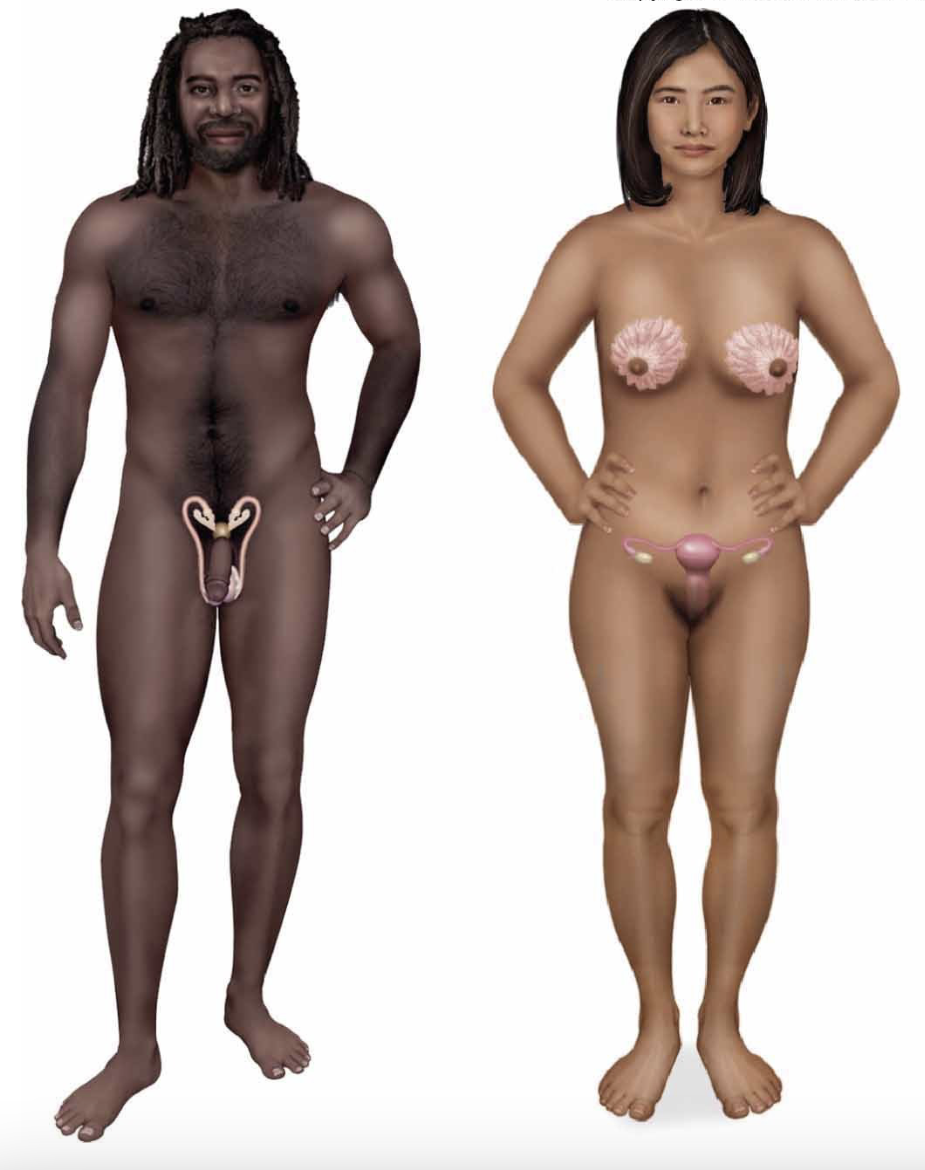

reproductive system
the gonads (testes and ovaries) contain sex producing cells
the accessory organs (uterus, vagina, penis, etc) play a part in the transport of sex cells and fetus development
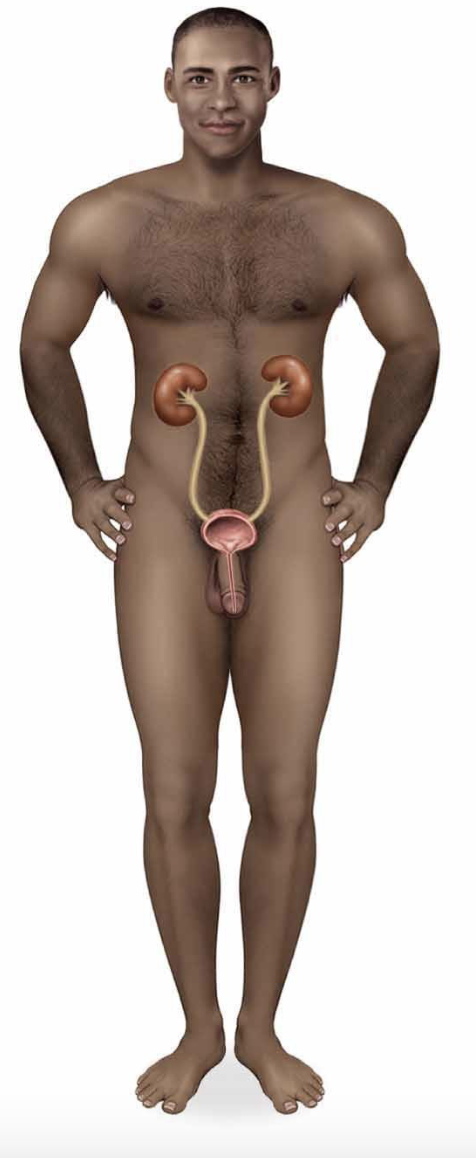
urinary system
kidneys are the filters of the body
urinary bladder is storage organ
urethra connects the 2
urethra is exit tube from the body
plays an important role in:
ridding the body of nitrogenous wastes
adjusting the chemical balance of body fluids
maintaining blood volume
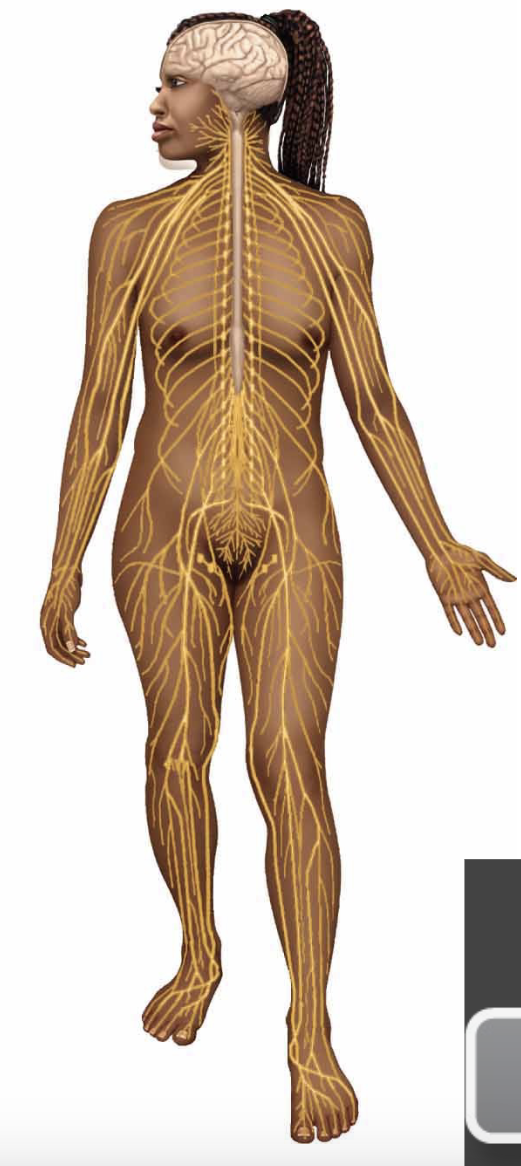
nervous system
consists of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
coordinates body regions, interprets environmental cues, and integrates info
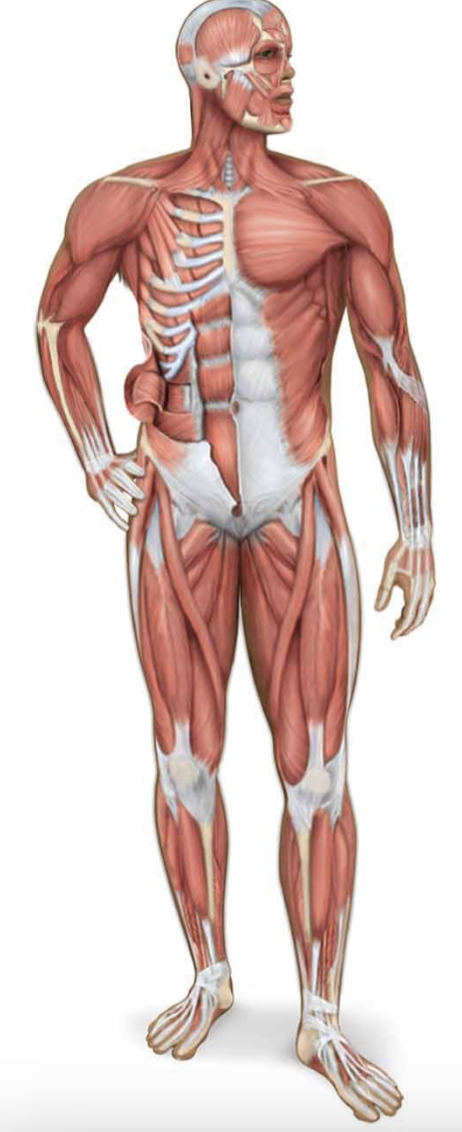
muscular system
individual muscles make up the organs in this system
move and strengthen joints + generate heat
along with other functions like abdominal compression
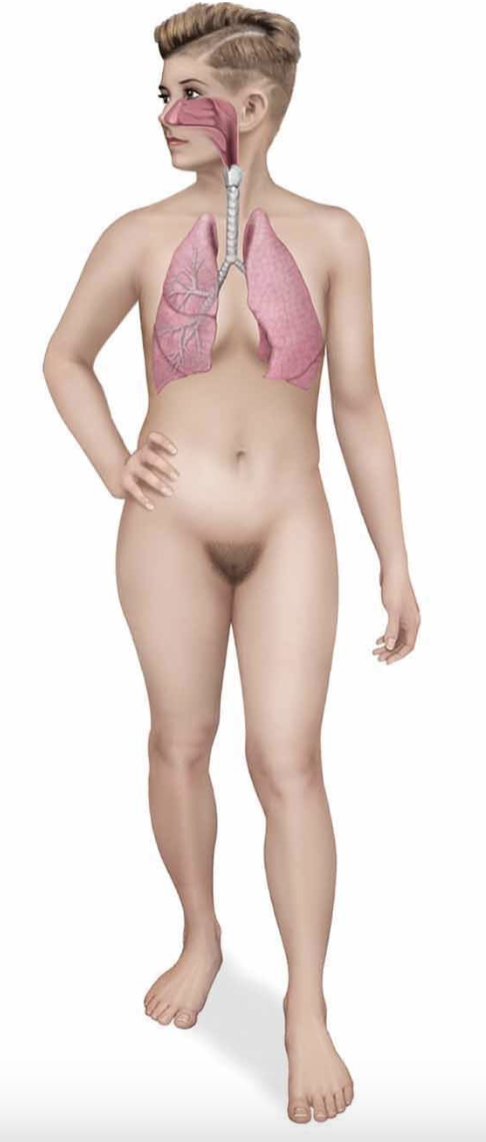

respiratory system
nose, larynx, trachea, and lungs make up this system
lungs exchange gases (O & CO2) between blood and air
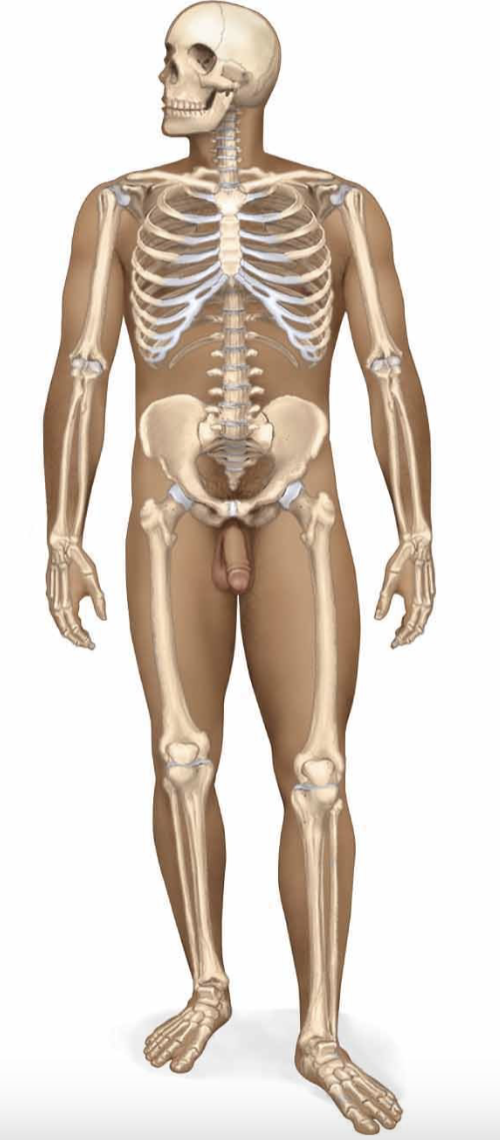
skeletal system
each bone is considered an organ (with blood vessels and nerves in each)
supports the body, protects delicate organs, and produces blood
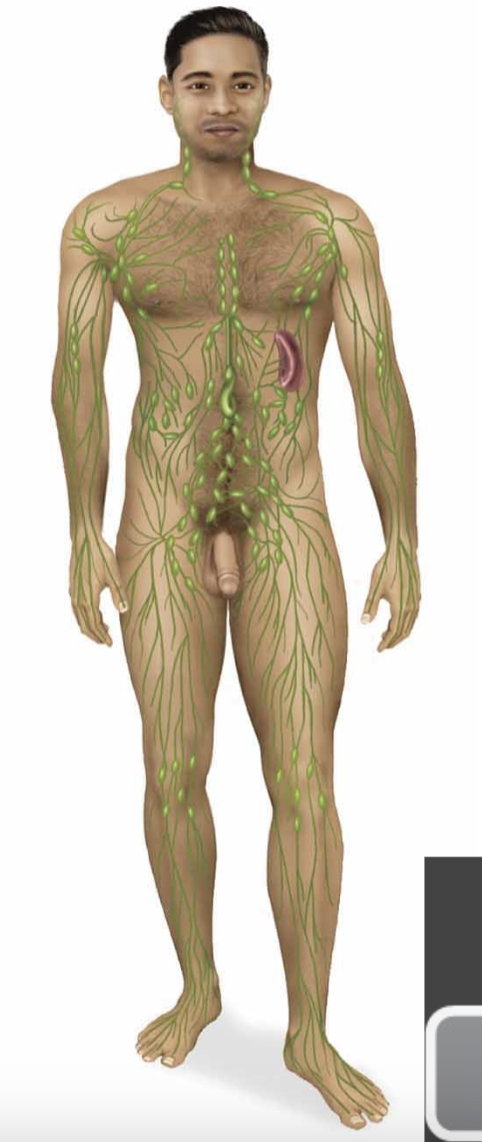
lymphatic system
lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, and tonsils are a part of this system
major system function is to protect the body from foreign particles (bacteria, viruses, and fungi)
cells from here make up the immune system
functional system of cells that protect the body

integumentary system
skin is the largest organ of the body (and makes up most of this system)
hair follicles, hair, nails, and skin glands are also in this system
protects the body from microorganisms, prevents drying out, and produces vitamin D
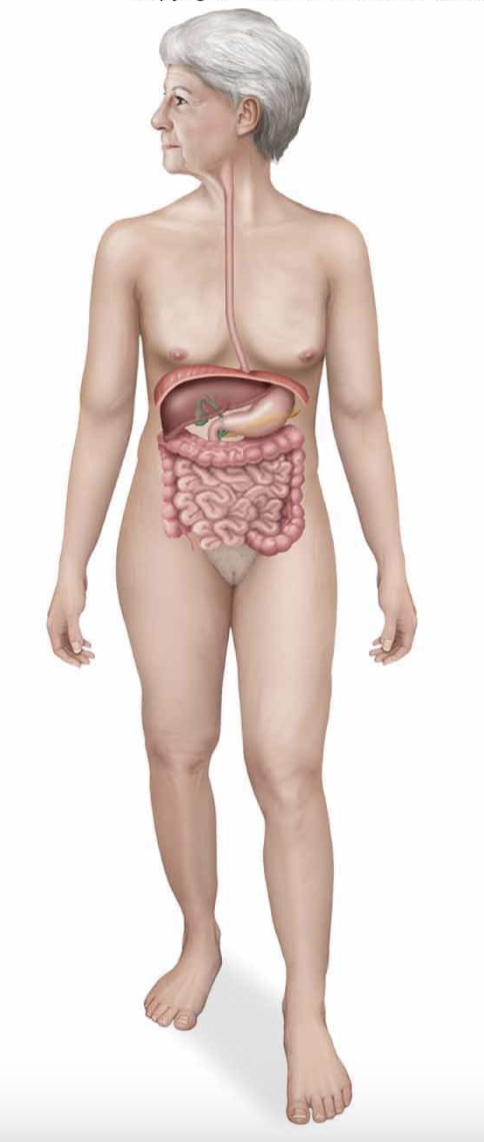
digestive system
mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, and intestines
provides nutrients and water to the body and removes waste
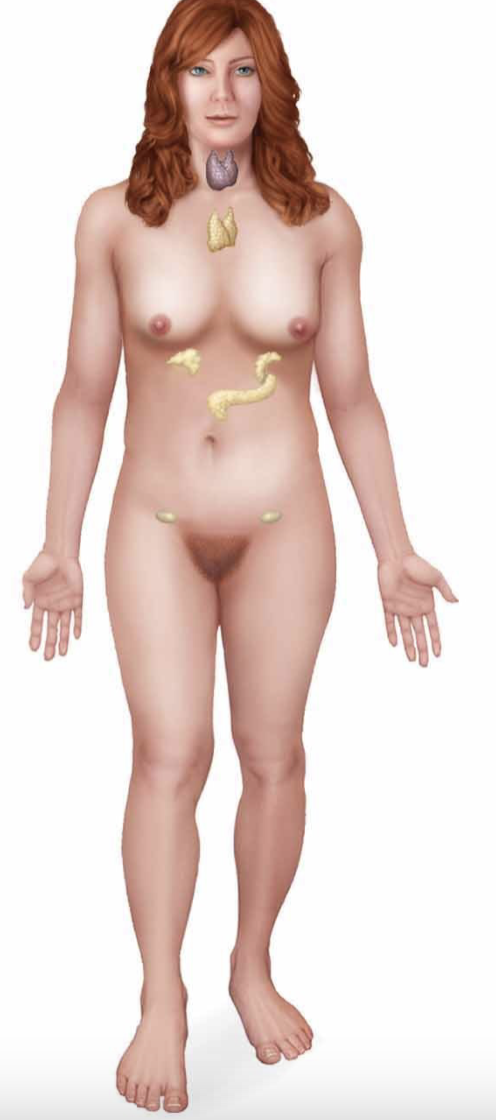
endocrine system
composed of organs that produce hormones
hormones are vital in regulating growth and development + maintaing internal body condition
thyroid and adrenal glands are endocrine glands (secrete with no ducts)
pancreas and gonads have dual functions- endo & exocrine
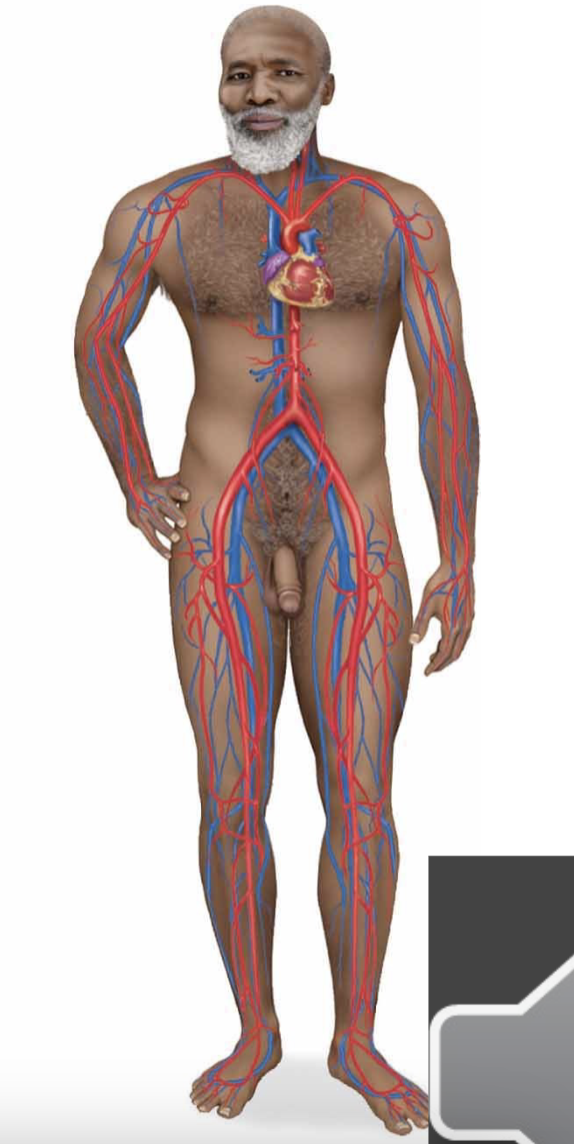
circulatory system
heart, blood, and vessels
heart is the pump of the system
blood vessels are delivery and return portion
primarily involved in transporting oxygen, CO2, and more throughout the body
anatomical position
body is upright, facing forward
arms and legs are straight
palms facing forward
feet flat on ground
eye open
superior
above
inferior
below
medial
toward the midline
lateral
toward the side
superficial
toward the surface
deep
toward the core
anterior (ventral)
to the front
posterior (dorsal)
to the back
proximal
for extremities- meaning near the trunk
distal
for extremitities- meaning away from the trunk
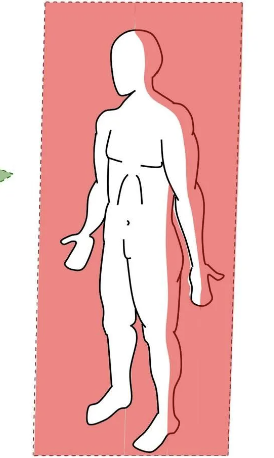
frontal plane
vertical plane that divides body in front (anterior) and back (posterior) sections
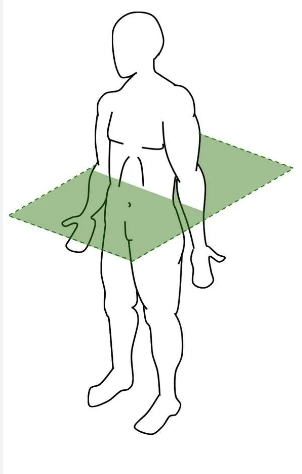
transverse plane
horizontal plane that divides body into upper (superior) and lower (inferior) sections
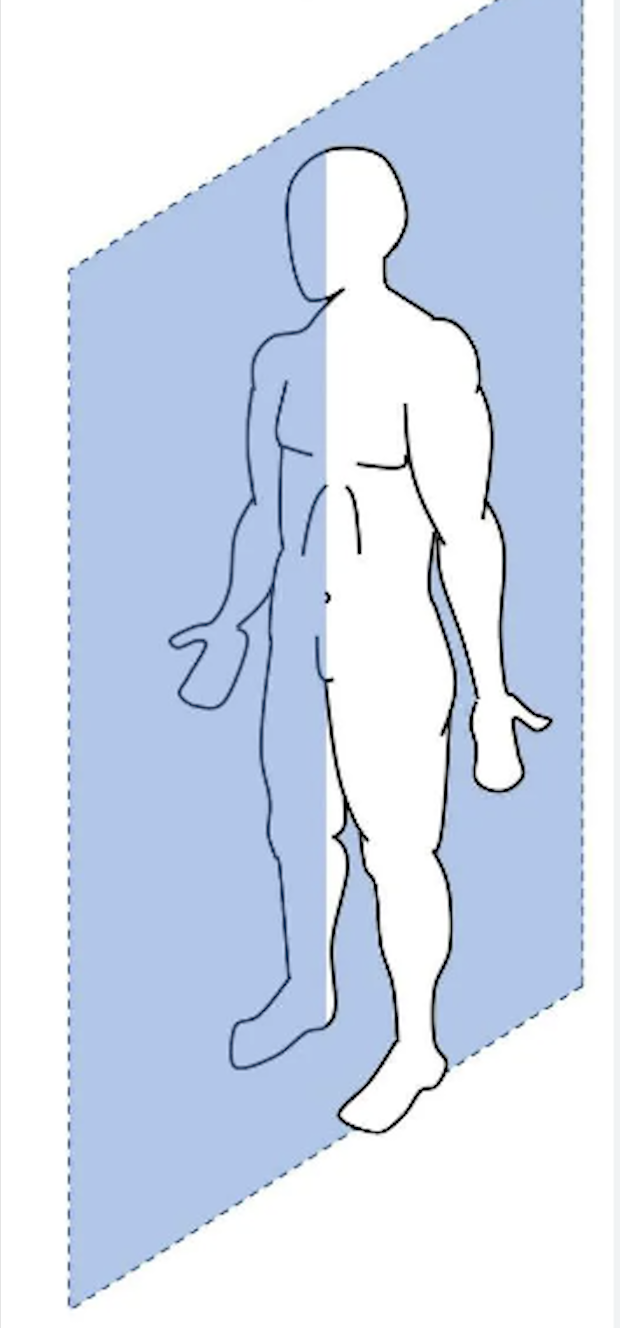
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right sections
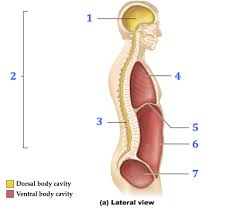
cranial
…
vertebral
thoracic
diaphragm
abdominal
pelvic
cranial cavity
houses the brain
vertebral canal
encloses the spinal cord
thoracic cavity
superior to diaphragm, housing the lungs and mediastinum
mediastinum: contains heart, pericardial membranes (large vessels that go with the heart), trachea, and esophagus
abdominopelvic cavity
inferior to diaphragm, split into 2 smaller cavities- abdominal and pelvic
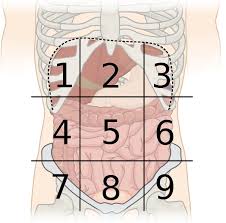
9 abdominal regions:
right hypochondriac
epigastric
left hypochondriac
right lumbar
umbilical
left lumbar
right iliac
hypogastric
left iliac
4 quadrants:
right upper
left upper
right lower
left lower