Bonding
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
How are ions formed?
By gaining or losing an election
What is the formula for group 1 metals?
+
What is the formula for group 2 metals?
2+
What is the formula for group 3 metals?
3+
What is the formula for silver ?
Ag+
What is the formula for copper?
Cu2+
What is the formula for iron (ll) ?
Fe2+
What is the formula for iron (III) ?
Fe3+
What is the formula for lead?
Pb2+
What is the formula for zinc?
Zn2+
What is the formula for hydrogen?
H+
What is the formula for ammonium?
NH4+
What is the formula for group 5 non-metals?
3-
What is the formula for group 6 non-metals?
2-
What is the formula for group 7 non -metals?
-
What is the formula for hydroxide?
OH-
What is the formula for carbonate?
Co3 2-
What is the formula for nitrate?
NO3-
What is the formula for sulfate?
SO4 2-
What do ionic compounds consist of ?
A regular arrangement of alternating positive and negative ions in which the ions are rightly packed together
What holds the ionic compound together?
The strong electrostatic force of attraction between positive and negative ions
What do thousands of positive and negative ions in an ionic compound form?
A giant lattice structure
What do compounds with giant ionic lattice have?
High melting and boiling points
Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points?
They have a giant lattice structure with strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions in all directions which needs lots of thermal emery to overcome them
What does it mean when the greater the charge on the ions?
The greater the charge on the ions, the stronger the electrostatic forces and the higher the melting and boiling point will be
When do ionic compounds conduct electricity?
Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity when solid but do conduct electricity when molten and in aqueous solution
How is a covalent bond formed?
When atoms share pairs of elections, a covalent bond is formed
What are covalent bonds between atoms like?
Covalent bonds between atoms are very strong
What are elections on the outer shell which are not involved in the covalent bond(s) called?
Non-bonding electrons
Understand covalent bonds in terms of electrostatic attractions
A covalent bond is an electrostatic attraction between the positive nuclei of two atoms and the negative electrons they share between them
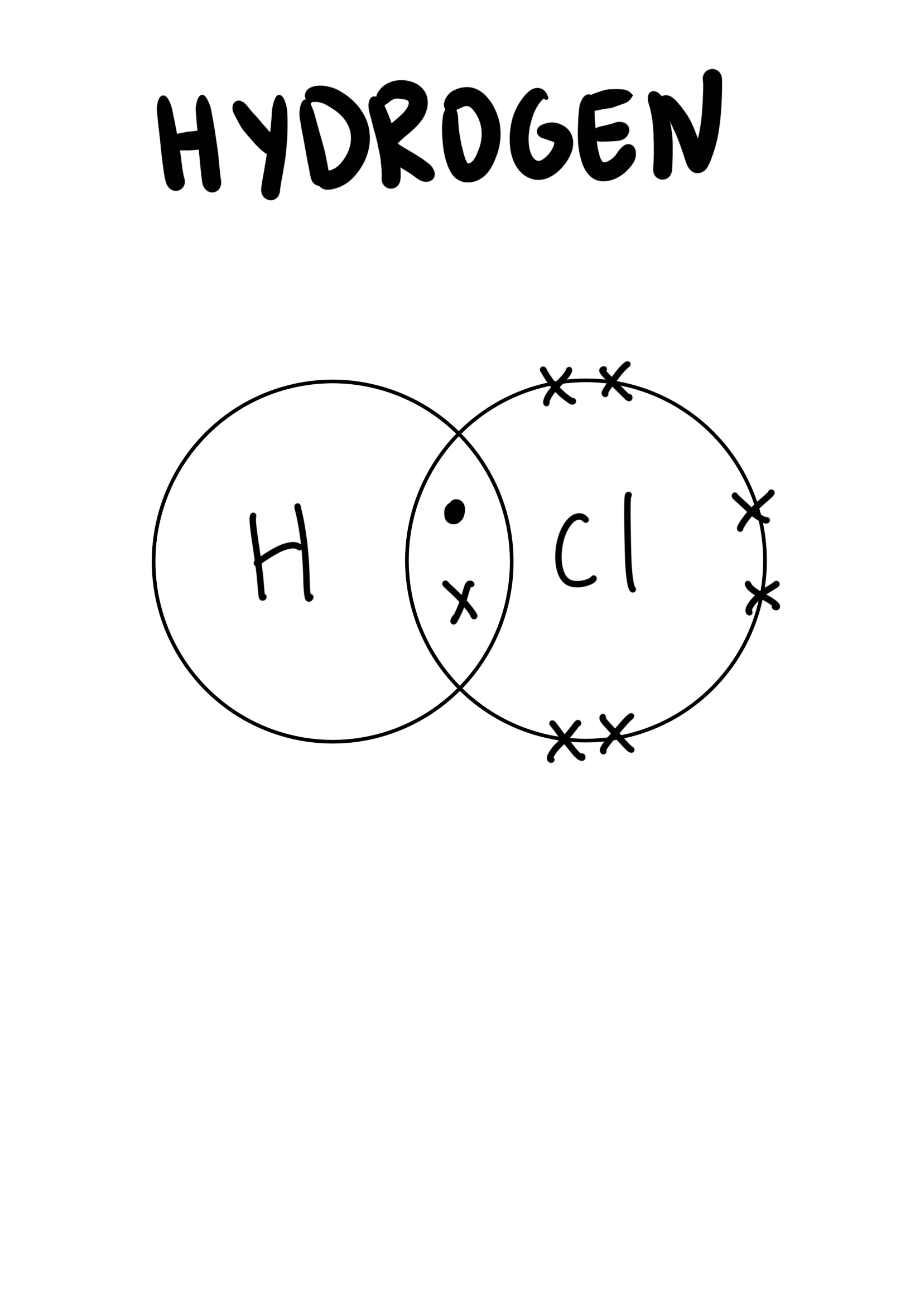
The dot-and-cross diagram to represent covalent bonds in hydrogen
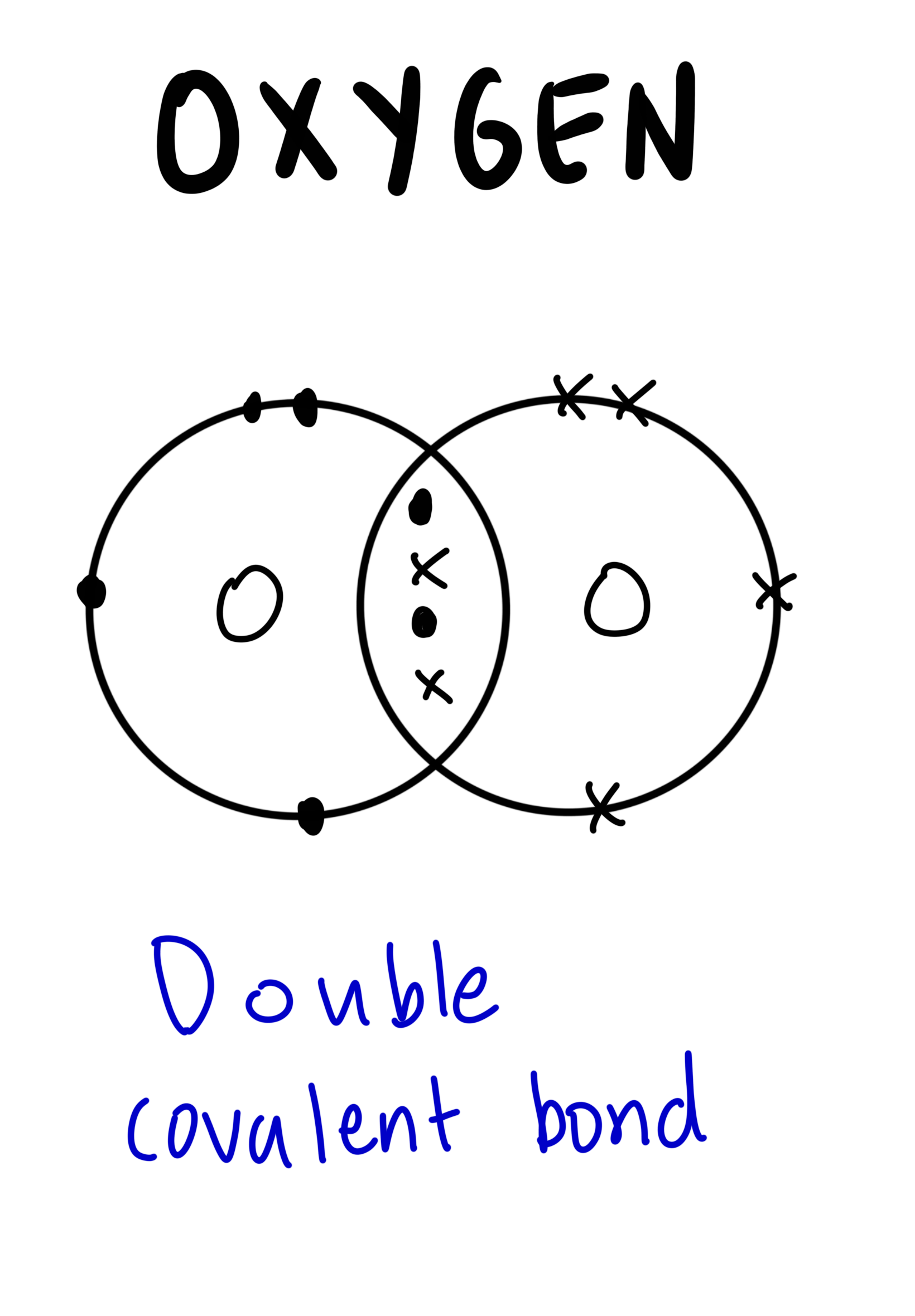
The dot-and-cross diagram to represent covalent bonds in oxygen
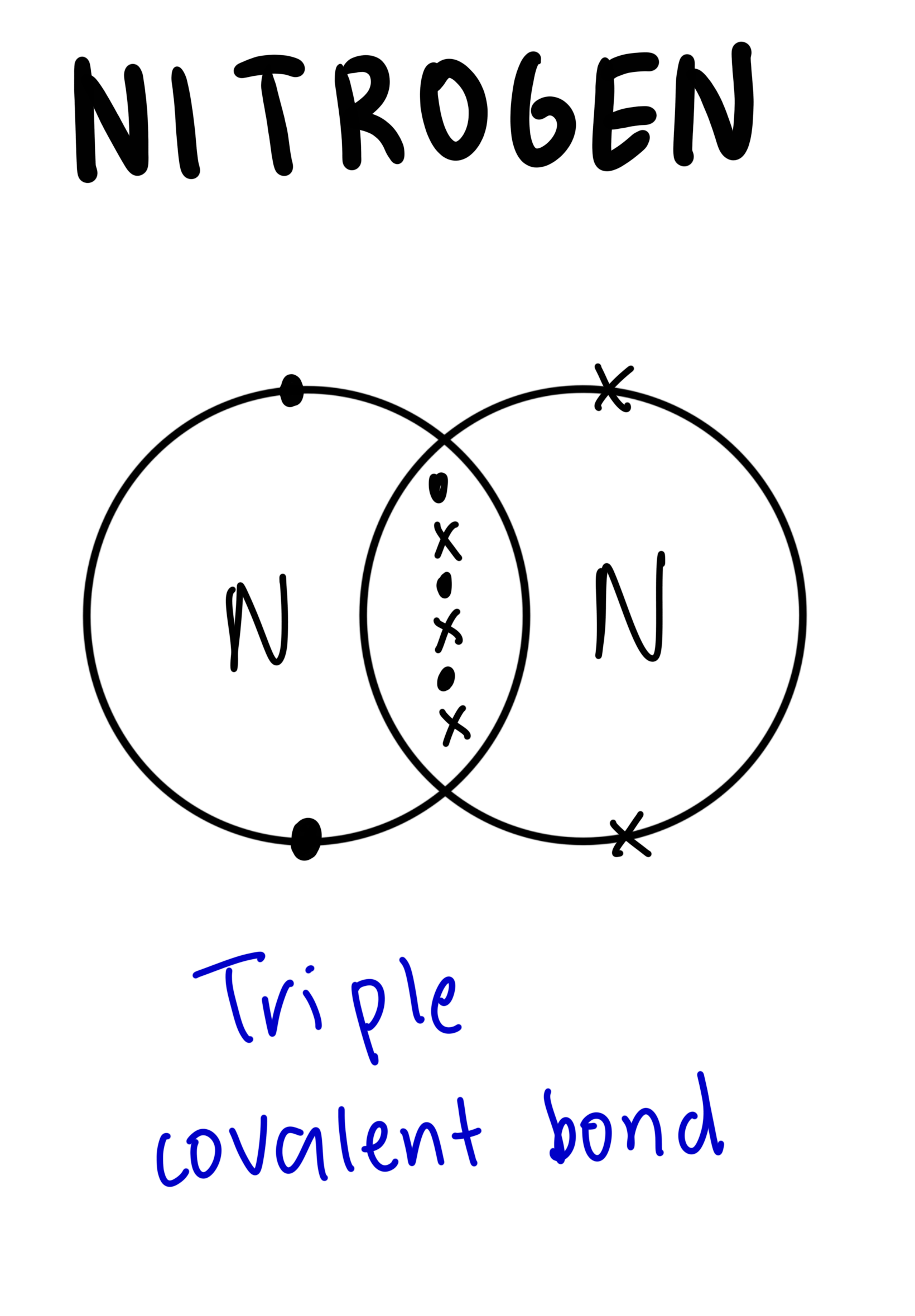
The dot-and-cross diagram to represent covalent bonds in nitrogen
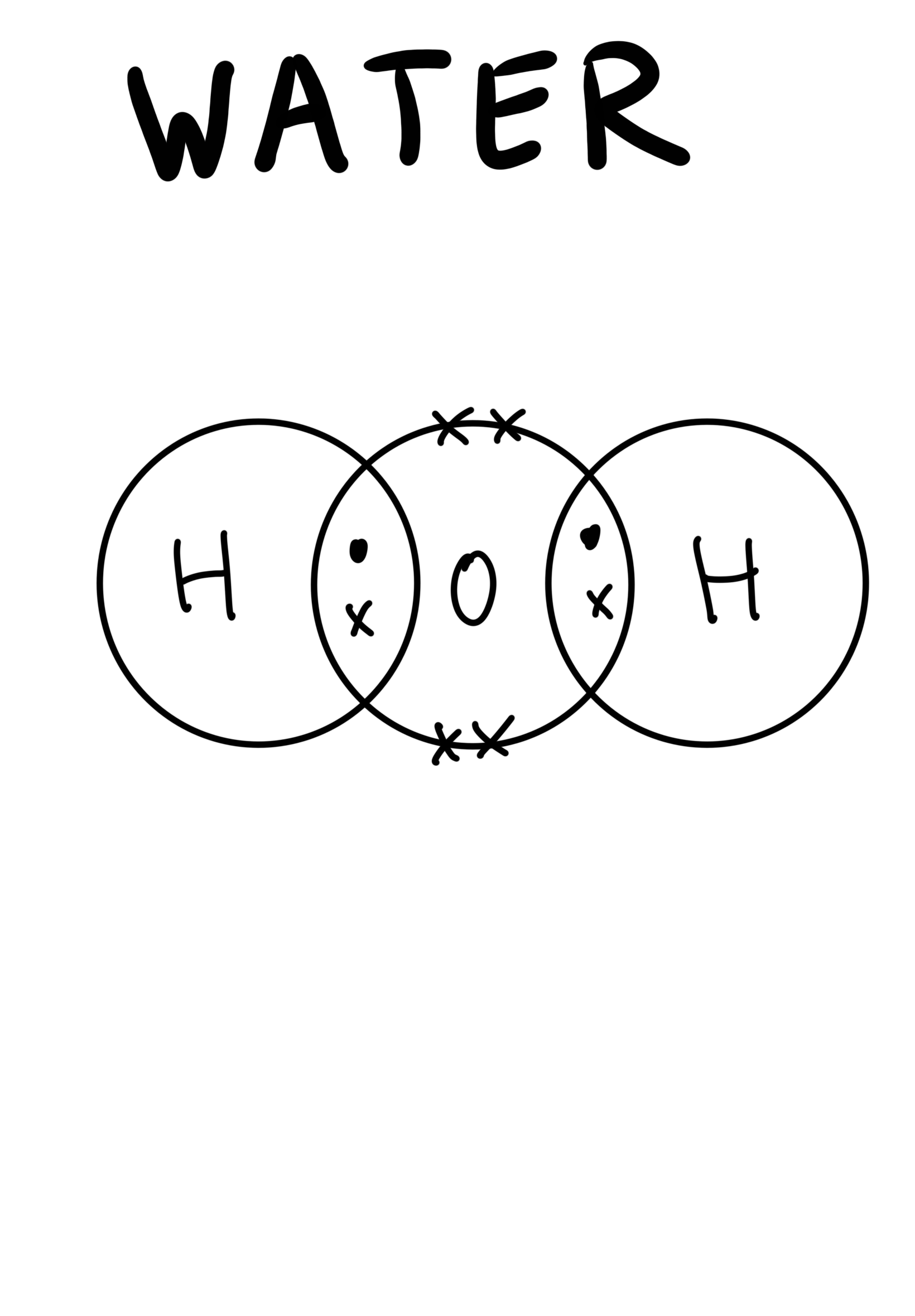
The dot-and-cross diagram to represent covalent bonds in water
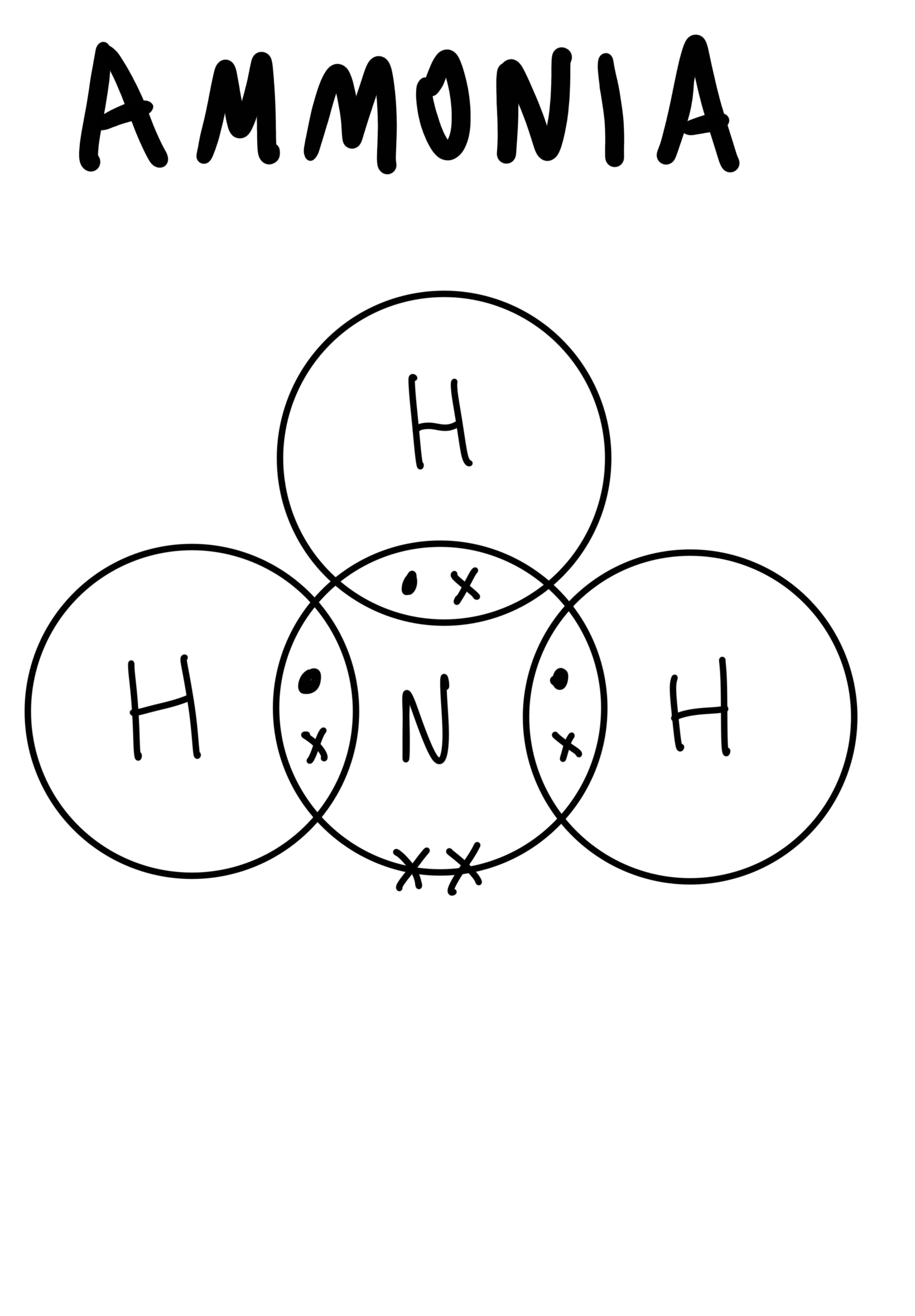
The dot-and-cross diagram to represent covalent bonds in ammonia
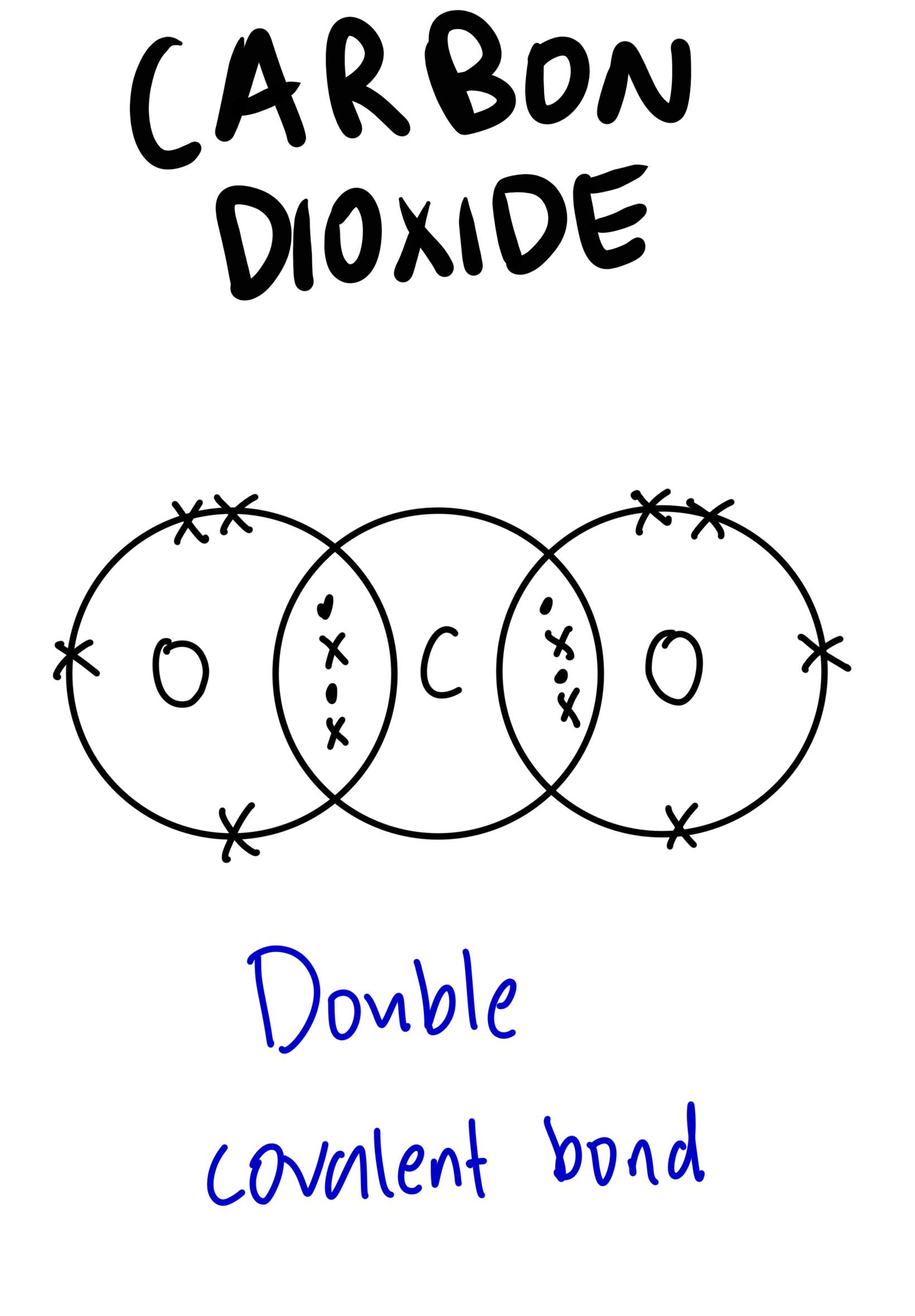
The dot-and-cross diagram to represent covalent bonds in carbon dioxide
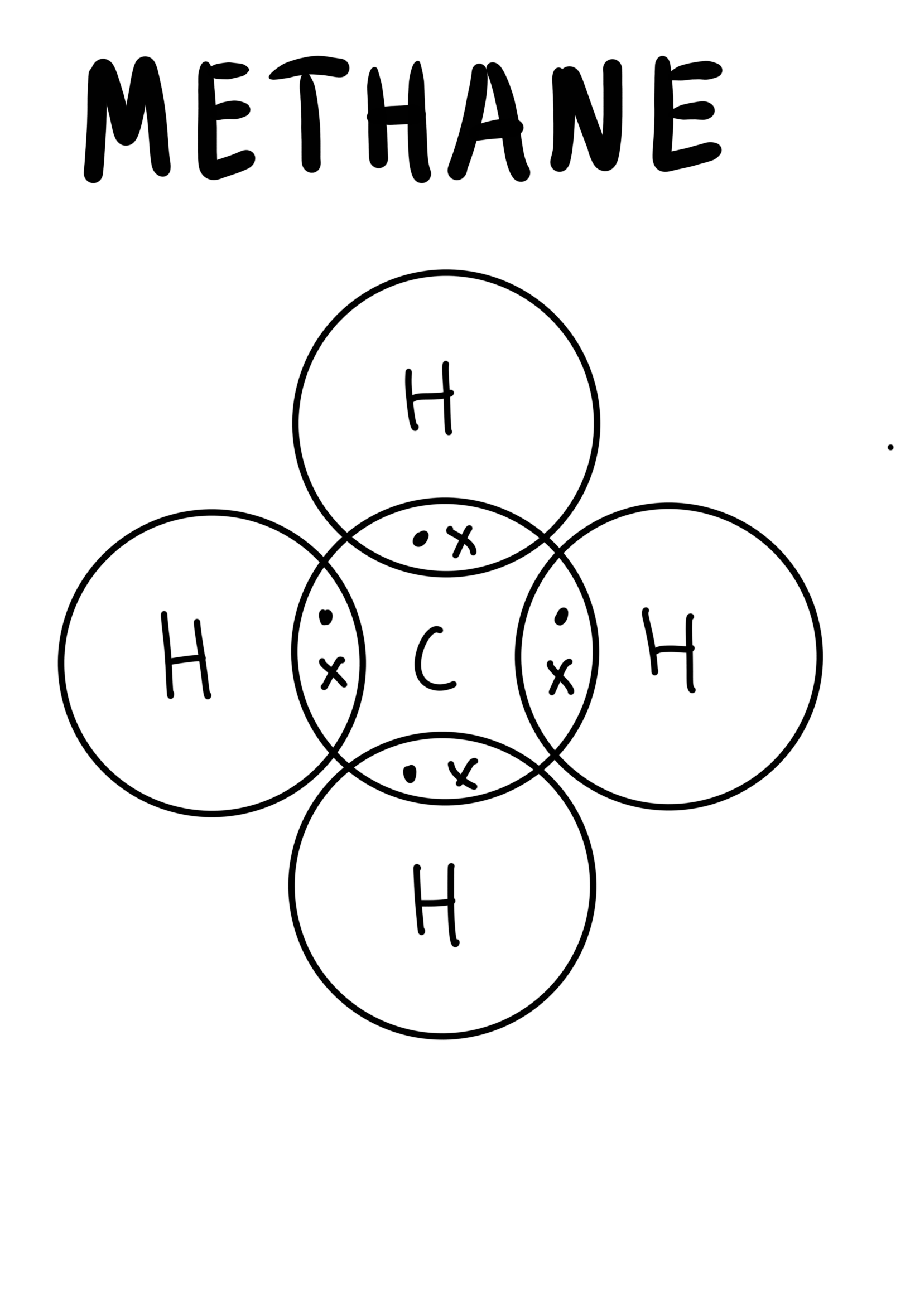
The dot-and-cross diagram to represent covalent bonds in methane
Why do simple molecular structures have a low melting and boiling points?
There are weak intermolecular forces between the molecules and these forces require little energy to overcome
What are most simple molecular structures?
Gases or liquids at room temperature or solids with low melting and boiling point but it is less common
What happens when molecules increase in size?
As the molecule increase in size, the melting and boiling point generally increase because the strength of these intermolecular forces increases and so more energy is needed to break them
What are giant covalent structures?
Solids with high melting and boiling points
Why do giant covalent structures have high and boiling points?
There are strong covalent bonds between atoms and these require lots of energy to overcome
What are diamond and graphite?
Allotropes of carbon
How many carbon atom does each carbon atom bond with in diamond?
In diamond, each carbon atom bonds with four other carbon atoms, forming a tetrahedron
Why is diamond very hard?
Each carbon is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms and the covalent bonds are very strong
Why does diamond have a high melting point?
It has a giant lattice structure with many strong covalent bonds between atoms which require lots of energy to break
Description of graphite's structure
Each carbon atom in graphite is bonded to three other carbon atoms forming grant lattice of hexagonal atoms with delocalised elections in between the layers
What are the properties of graphite?
Soft and slippery , can conduct electricity and heat
Why is graphite soft and slippery?
Each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atom forming layers and the layers are free to slide over each other because there are only weak forces between the layers, not covalent bonds
Why can graphite conduct electricity and heat?
Due to each carbon atom only forming three bonds, one election from each carbon atom is delocalised and the delocalised electrons are free to move. Graphite is similar to metals in that it has delocalised elections
Why does graphite have a high melting point?
It has a giant lattice structure and the strong covalent bonds between atoms which need lots of energy to break
What is fullerene's melting and boiling point like?
Not so high
Why is tullerene's melting and boiling point not so high?
Need to overcome relatively weak forces between molecules (no covalent bonds broken)
Is fullerene a conductor or insulator of electricity?
Insulator
Why can't fullerene conduct electricity?
Fullerene has delocalised electrons, however, they cannot move from one molecule to another
What is fullerene's strength like?
Soft and brittle