QA QC ADDITIONAL TERMS
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Grab sample
A single sample of water collected at a particular time and place that represents the composition of the water only at that time and place.
Random sampling
A sample resulting from a sampling plan that can be expected to adequately reflect
the properties of interest of the parent populatio
Selective sample
A sample that is deliberately chosen by using a sampling plan that screens out
materials with certain characteristics and/or selects only material with other relevant
characteristics
Stratified sample
A sample consisting of portions obtained from identified subparts (strata) of the
parent population. Within each stratum, the samples are taken randomly
Convenience sample
A sample chosen on the basis of accessibility, expediency, cost, efficiency, or other
reason not directly concerned with sampling parameters
Umpire or referee or reserve sample
A sample taken, prepared, and stored in an agreed upon manner for the purpose of
settling dispute
Replicate (duplicate) sample
Multiple (or two) samples taken under comparable conditions. This selection may be
accomplished by taking units adjacent in time or space.
Sequential sample
Units, increments, or samples taken one at a time or in successive predetermined groups, until the cumulative result of their measurements assessed against predetermined limits, permits a decision to accept or reject the population or to
continue sampling
Multistage sample
Sample taken in a series of steps with the sampling portions being selected from the
larger or greater number of portions of the previous step
Combined sample
A sample obtained by removing specific fractions by separation or selection techniques (heavy liquid, magnetic, sieving, etc.), analyzing the fractions separately, and combining the results mathematically.
Modified sample
A sample or a known fraction of the parent population in which the analyte has been
isolated or (usually) concentrated before being submitted to the laboratory
Increment
An individual portion of material collected by a single operation of a sampling device.
Usually taken from parts of a lot separated in time or space
Primary sample
The collection of one or more increments or units initially taken from a population
- The portions may be either combined (composited or bulked sample) or kept separate
(gross sample).
Reduced sample
- A representative part of the primary (composite or gross) sample obtained by a
division and reduction process
Subsample
- Portion of the sample obtained by selection or division
- Individual unit of the lot taken as part of the sample
- The final unit of multistage sampling
Laboratory sample
The sample or subsample sent to or received by the laboratory
Test sample/analytical sample
- The sample, prepared from the laboratory sample, from which test portions are
removed for testing or for analysis
Test portion/analytical portions
- The quantity of material, of proper size for measurement of the concentration or
other property of interest, removed from the test sample.
Test solution/analytical solution
- Solution prepared by dissolving, with or without reaction, the test portion in a liquid
Treated solution
The test solution that has been subjected to reaction or separation procedures prior to measurement of some property.
Aliquot
A known amount of a homogeneous material, assumed to be taken with negligible
sampling error.
Sodium chloride, NaCl
What is the primary standard for Titration of silver nitrate?
Sodium carbonate, Na2CO3
What is the primary standard for titration of acids?
Potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP), KHC8H4O2
What is the primary standard for Titration of bases, perchloric acid and aqueous base in an acetic solution
Potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7
What is the primary standard for redox reaction?
Zinc powder (in HCl or H2SO4)
What is the primary standard for Standardization of EDTA solution?
Globally Harmonized System (GHS)
Presents the guidelines proper labelling, storage and manegement of chemical waste; pursuant to the Republic Act No. 6969, DAO 2015-09
Safety Data Sheet
technical documents that contain all the information related to the health effects upon exposure, hazard and storage handling, precautionary measures and emergency procedures
True
An SDS can be an MSDS but an MSDS is not an SDS
pH<= 2
What should be the pH of a waste for it to be considered as an acidic waste
ph=> 12.5
What should be the pH of a waste for it to be considered as an alkali waste?
waste generator
Refers to a person who produces hazardous wastes, through any institutional, commercial, industrial or trade activities
wastes with inorganic materials
Wastes containing mercury and arsenic should be classified as _____
Rubber gloves
In handling acid wastes, what type of protective gloves should be used?
Polyethylene Drums
What type of container must be used for acid or alkali wastes
sodium bicarbonate
In case of acid spils, what can be applied to the spill before treatinf it with adsorbent material
Ignitability
Hazardous waste characteristic which applies to waste liquids with a flash point less than 140 F
Corrosivity
Hazardous waste characteristic which applies to aqueous solution with a pH less than or equal to 2 or greater than or equal to 12.5
Reactivity
Hazardous waste characteristic which applies to materials that are normally unstable or explosive
Toxicity
Hazardous waste characteristic which applies to wastes that have the potential to contaminate groundwater if improperly disposed
Composting
Solid waste management practice which refers to the controlled decomposition of organic matter by microorganisms, mainly bacteria and fungi, into a humus-like product
Compostable wastes
Biodegradable wastes such as food waste, garden waste, animal waste and human waste that undergo biological degredation under controlled conditions
Persistent Organic Chemicals (POPs)
These are organic chemicals that are resistant to environmental degradation through chemical, biological, and photolytic processes
Leachate
This refers to any liquid that passes through a landfill and has extracted dissolved and suspended matter from it.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Store concentrated acids and bases separately in enclosures made of corrosion-resistant materials.
False
TRUE OR FALSE. Keep fire extinguishers away from locations where chemicals are stored or used
Safety Data Sheet
It is a document that provides useful information on the chemical hazards, advice on safe handling, use and storage, and the emergency measures to be followed in case of an accident. It usually contains 16 headings.
Respiratory Sensitizer
Type of chemical that can cause an allergic reaction in the airways following inhalation of the chemical
a. acetic acid solution
Ammonia solution can be stored with the following chemicals except for:
a. acetic acid solution b. sodium hydroxide solution
c. 2-propanol solution d. cyclohexane solution
compatibility with other chemicals
First consideration for chemical storage shall be based on its:
potassium dichromate
Which of the following is an oxidizing chemical?
a. potassium dichromate
b. sodium hydride
c. magnesium
d. sodium
Desiccator
Sealable enclosures containing desiccants used to protect chemicals which are hygroscopic or which react with water from humidity.
b. pycnometer
To determine the specific gravity of a liquid, which of the following glass wares should be used?
a. volumetric flask
b. pycnometer
c. pipette
d. graduated cylinder
fume hood
Preparation of highly toxic and volatile compounds should be carried out in an efficient _____________.
False
TRUE OR FALSE. The conductivity value of a liquid solution increases as the temperature decreases as a result of higher ion mobility.
False
TRUE OR FALSE. The conductivity value of a liquid solution increases as the temperature decreases as a result of higher ion mobility.
True
True or false.The alkaline effect is the phenomenon where H+ ions in the gel layer of the pH-sensitive membrane are partly or completely replaced by alkali ions.
False
TRUE OR FALSE. In pH measurements, if the solution is acidic, the H+ ions diffuse out of the layer and a negative charge is established on the outer side of the membrane.
False
TRUE OR FALSE. Karl Fischer titrator is used to determine viscosity of liquids
True
TRUE OR FALSE. For pipettes marked with To Deliver (TD), a small amount of liquid remaining on the tip should not be blown out.
False
TRUE OR FALSE. Cuvettes must be cleaned in an ultrasonic cleaning bath
True
TRUE OR FALSE. In operating the centrifuge, opposing tubes must be of equal weight
False
TRUE OR FALSE. To ensure that glass wares is properly cleaned, the film of water which adheres to the inner glass wall of the glass ware as it is emptied must not be uniform
False
TRUE OR FALSE. . Class B volumetric glass ware provides the highest accuracy and passes the ASTM standard specification for laboratory volumetric glass ware.
False
TRUE OR FALSE. In calibration of burettes, volume reading shall be taken with the eye higher than the liquid level to avoid parallax error
Hydrochloric Acid
Which of the following chemicals may be used to neutralize waste containing caustic soda?
a. Potassium Hydroxide b. Ammonia
c. Hydrochloric Acid
d. Buffer 10 Solution
chlorine
This chemical is usually used to disinfect waste containing microbial organisms.
Pictogram
Symbols indicated in waste labels that instantly identify the kind of hazard the chemical possesses
Waste containing dichloromethane
Which of the following waste is classified as halogenated waste?
A. Waste containing toluene
B. Waste containing dichloromethane
C. Waste containing acetone
D. Waste containing ammonia
Waste containing acetonitrile
Which of the following waste is classified as non-halogenated waste?
A. Waste containing acetonitrile
B. Waste containing chloroform
C. Waste containing polychlorinated hydrocarbons
D. Waste containing bromine
200 ppm
What is the minimum concentration of cyanide contained in a waste to be classified it under A101( wastes containing cyanide )?
All of the above
According to Revised DAO 04-36, the appropriate waste labels shall include:
A. Volume of Waste
B. Generator ID Number
C. Container Material D. All of the above
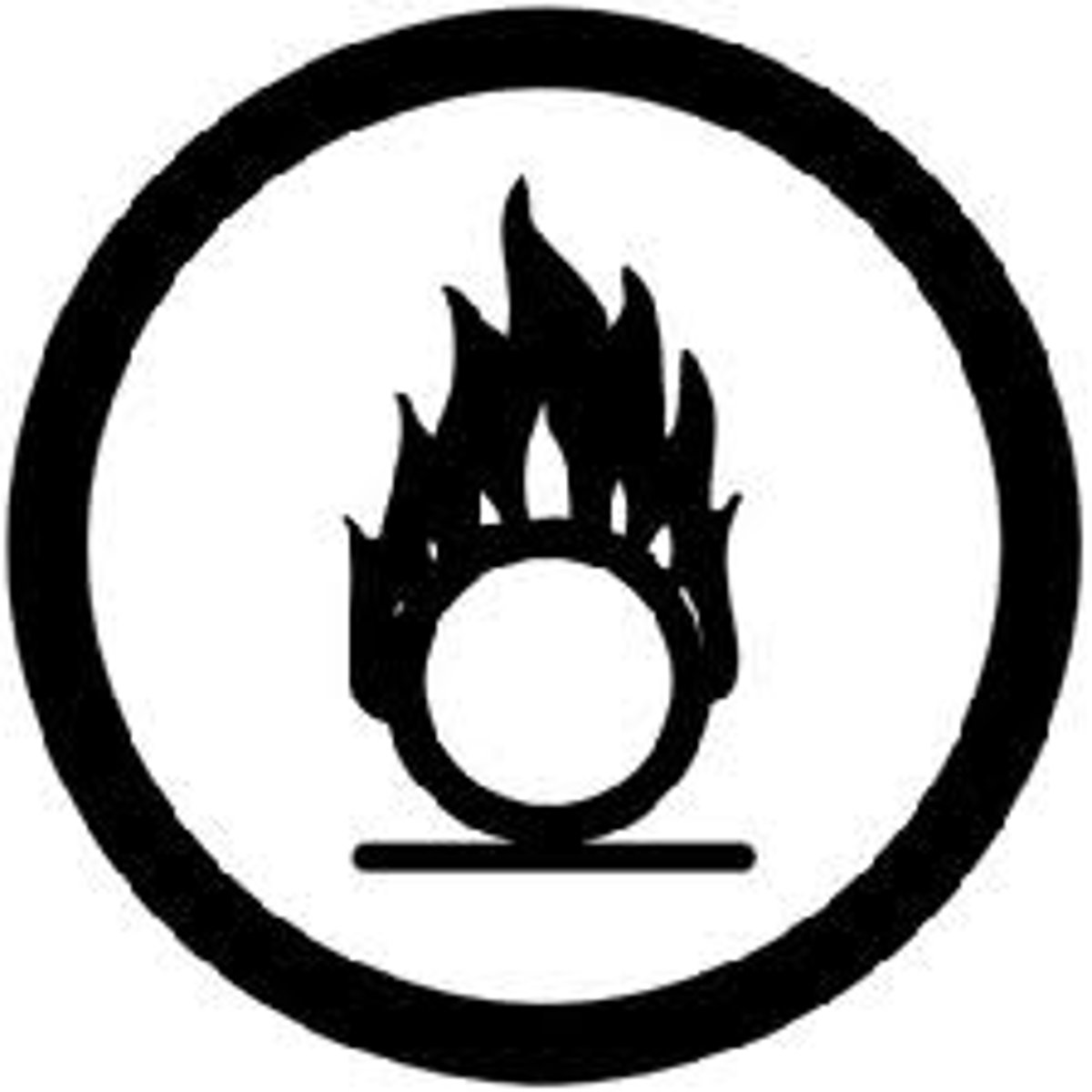
Oxidizer
GHS HAZARD SYMBOL: O na may apoy

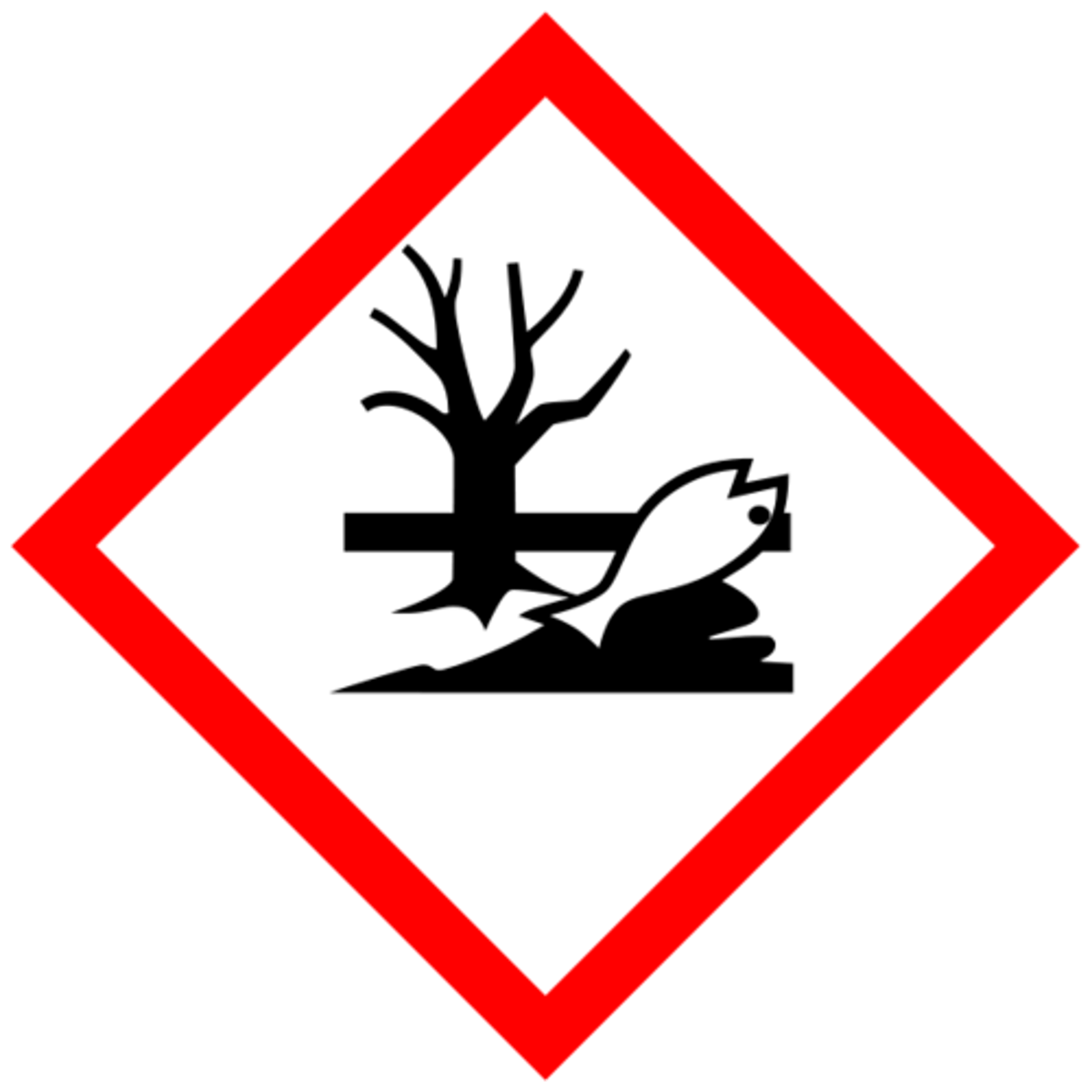
Environmental Hazard
GHS HAZARD SYMBOL: May puno yung picture and fish

Corrosive
GHS HAZARD SYMBOL: Dalawang test tube na tinapon yung laman in opposite directions
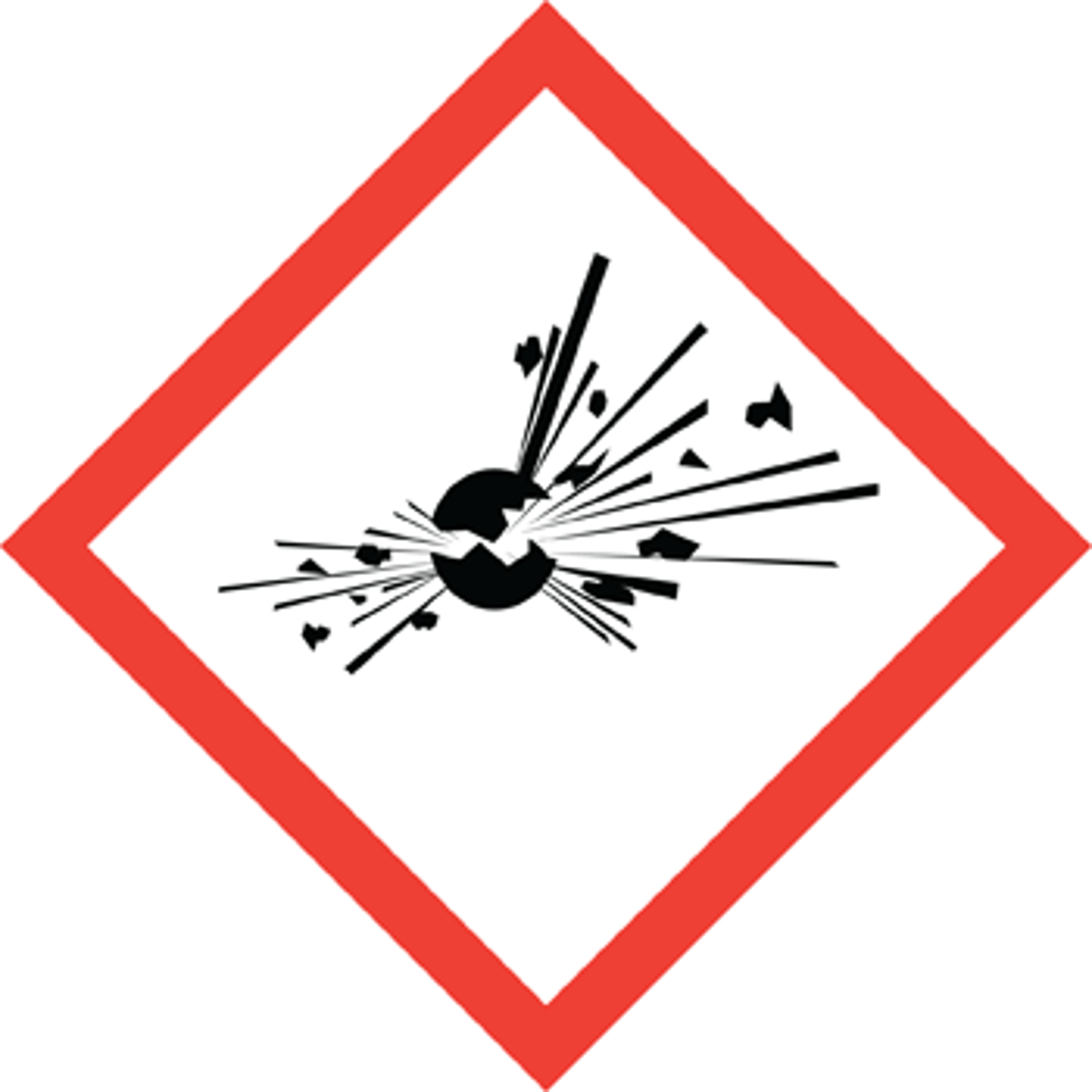
explosive
GHS HAZARD SYMBOL: parang firework

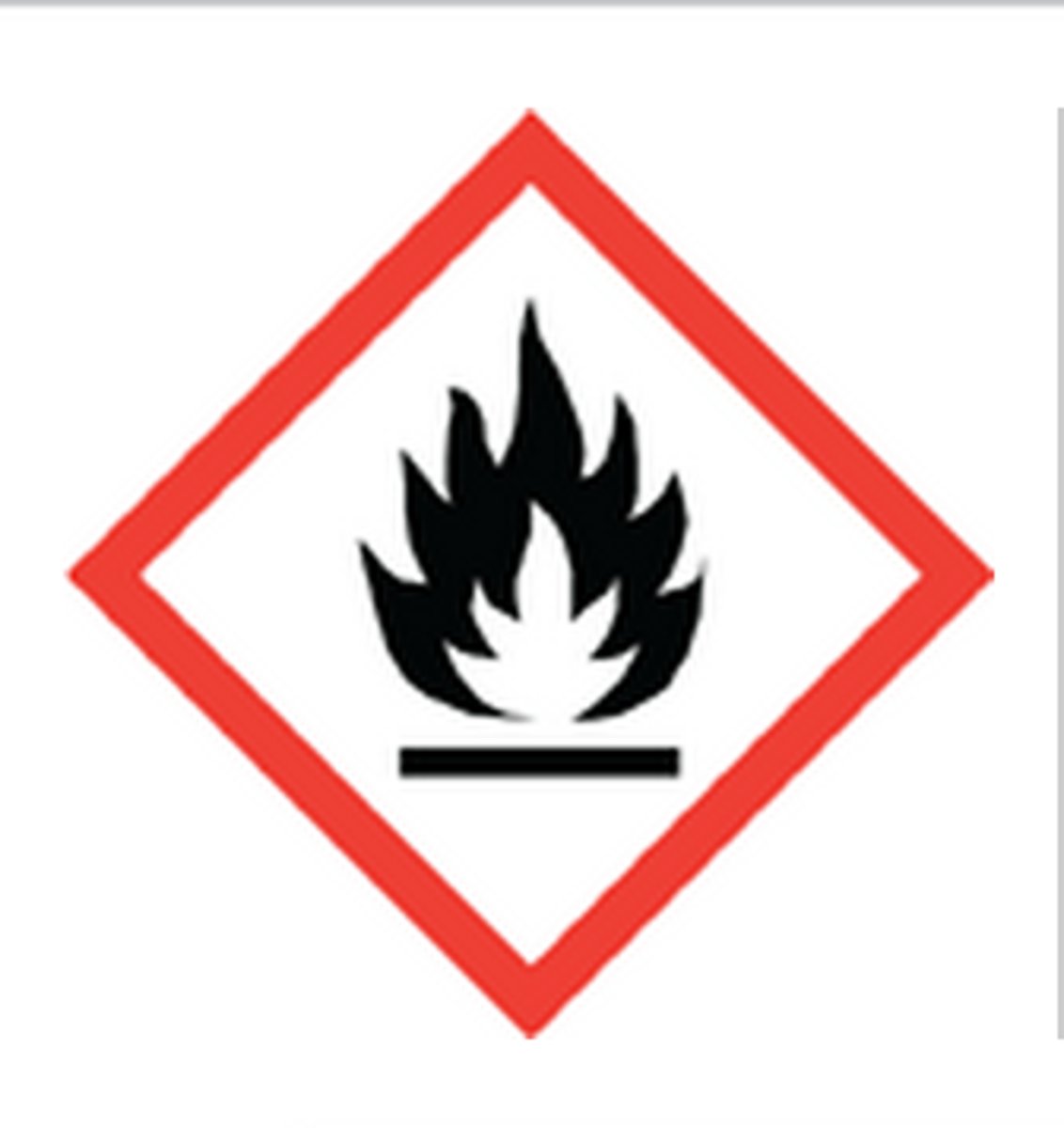
flammable
GHS HAZARD SYMBOL: apoy

harmful
GHS HAZARD SYMBOL: exclamation point
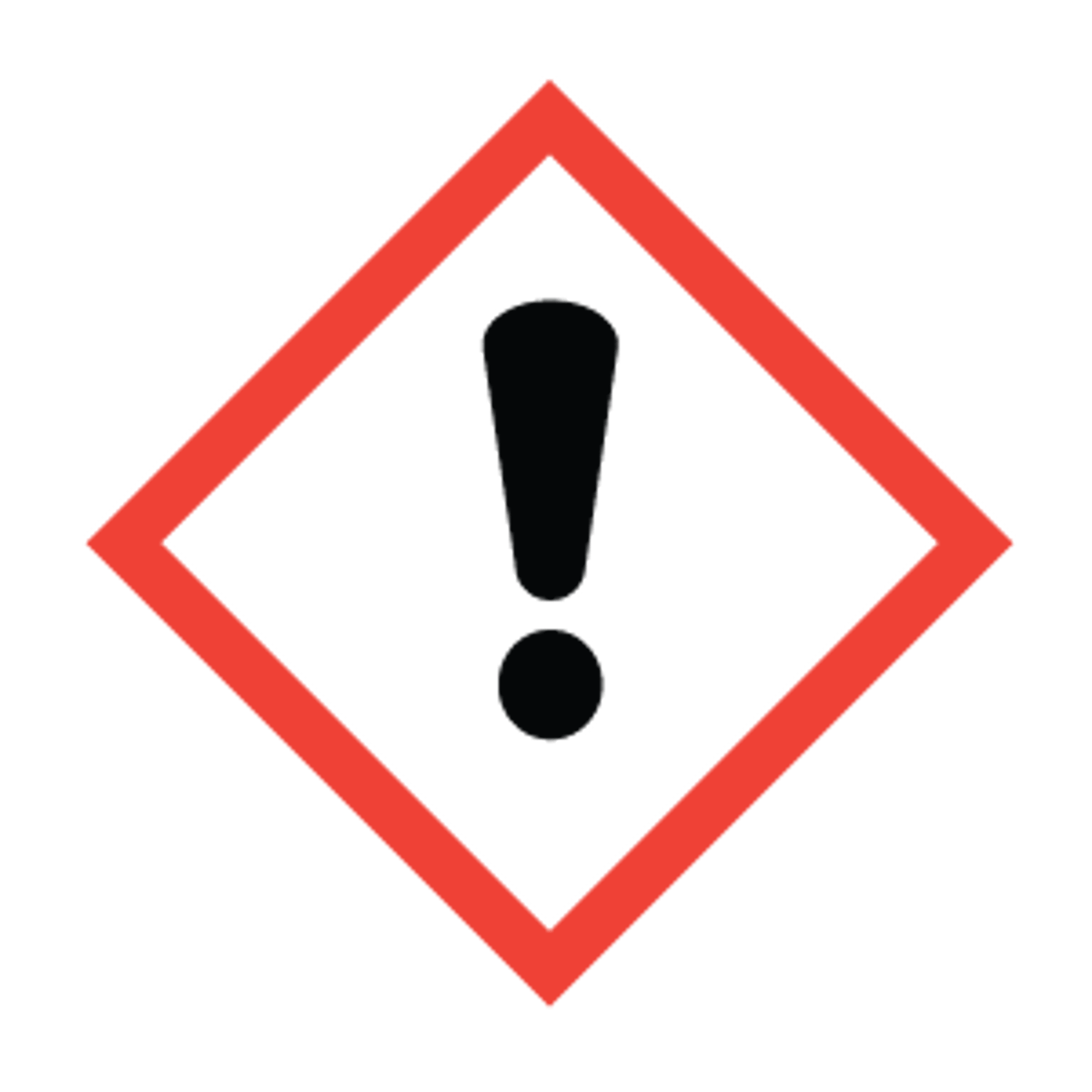

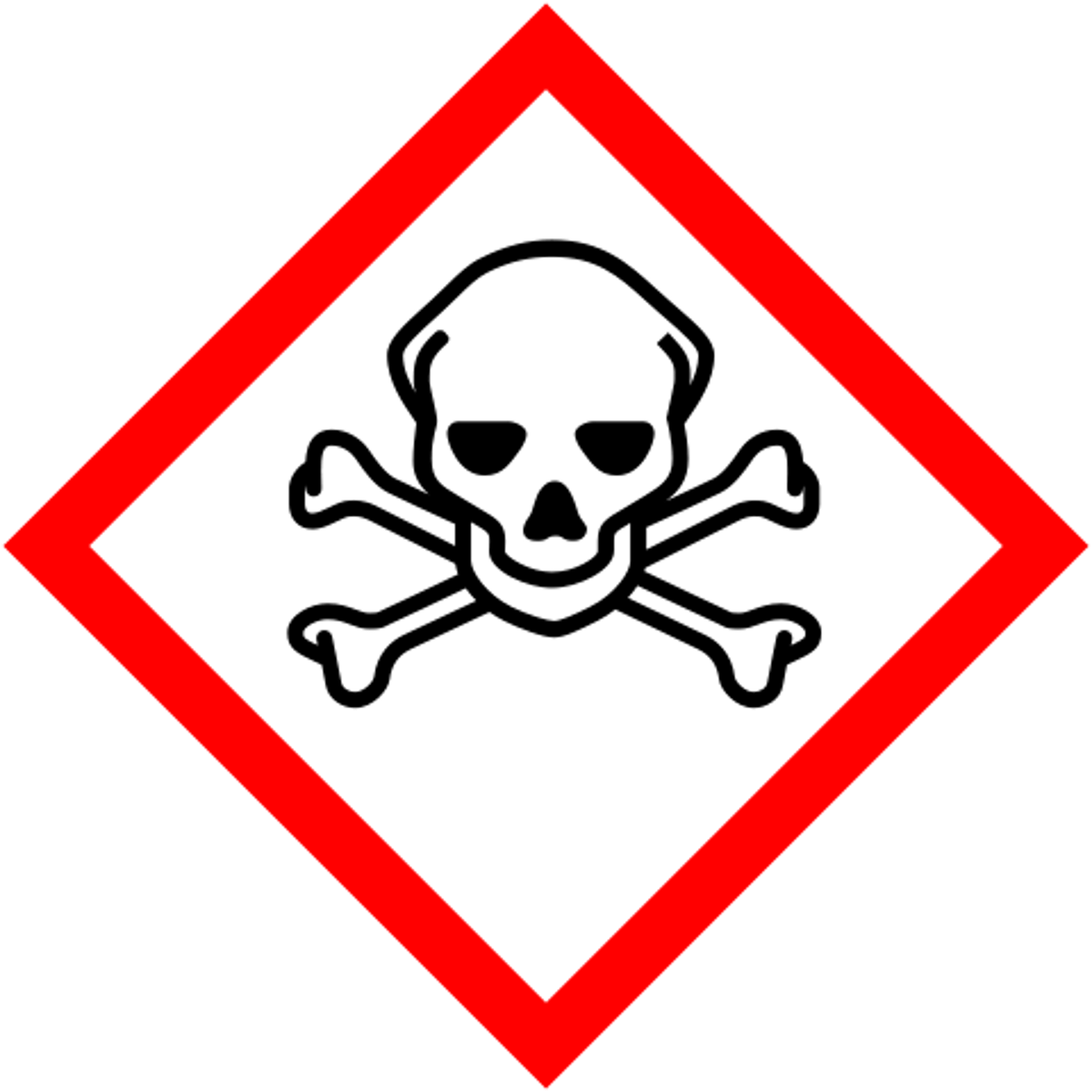
toxic
GHS HAZARD SYMBOL: skull

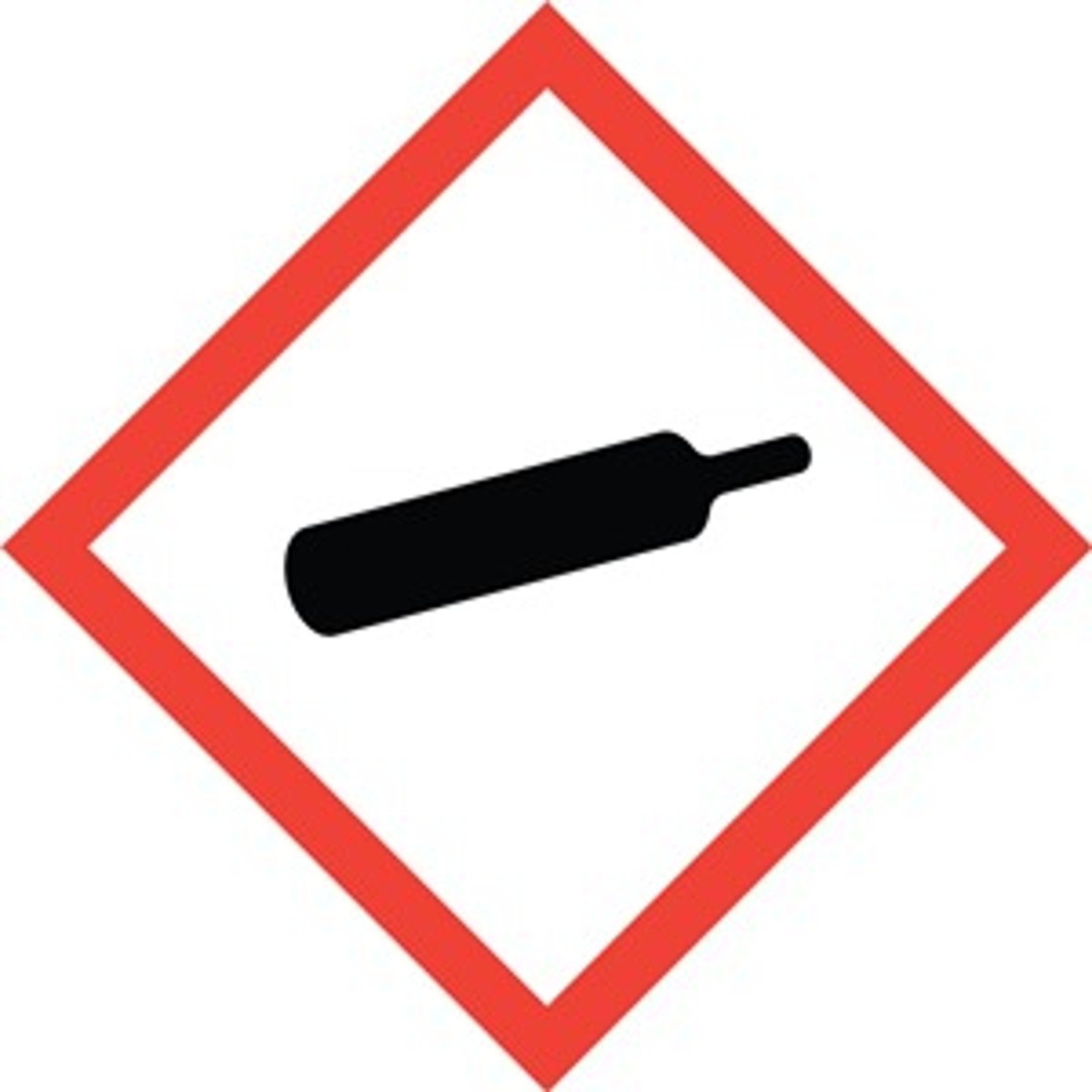
compressed gas
GHS HAZARD SYMBOL: Cylinder tank pero mukang dinamita

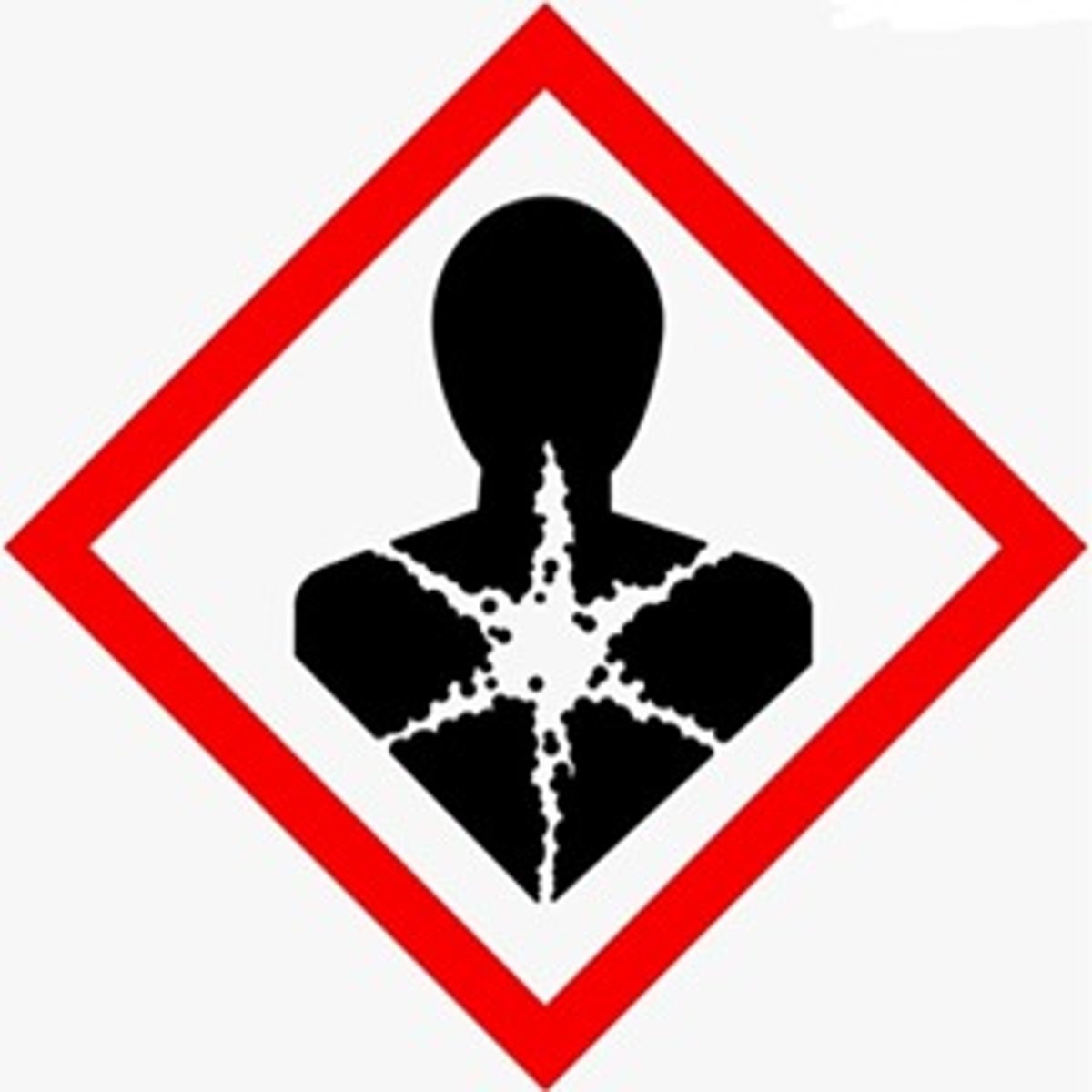
health hazard
GHS HAZARD SYMBOL: tao na may star sa dibdib

Calibration curve
It is a general method for determining the concentration of a substance in an unknown sample by comparing the unknown to a set of standard samples of known concentration.
UV-Vis Spectrophotometer
Which of the following instruments uses a cuvette? Flame- AAS b. UV-Vis Spectrophotometer c. Gas Chromotograph d. pH Mete
. Buffer Solutions
A series of reference standards solutions that have known and accurate pH values at different temperatures used for pH meter calibration.
wavelength
A property of a wave which is described as the distance between a point on one wave and the same point on the next wave.
pH
It is the measure of hydrogen ion activity in aqueous solutions.
Beer-Lambert's Law
Law that states the linear relationship between absorbance and concentration of an absorbing species
Matrix Spike
Type of quality-control sample used to evaluate the effects of sample matrices on the performance of an analytical method
Instrument Blank
A clean sample (e.g., distilled water) processed through the instrumental steps of the measurement process to determine instrument contamination
Method Detection Limit
Minimum concentration of a substance that can be measured and reported with 99% confidence that the analyte concentration is greater than zero
Systematic Error
Component of error which, in the course of a number of analyses of the same measurand, remains constant or varies in a predictable way
Random Error
Component of error which arises from unpredictable variations of influence quantities.
Quality Control
Series of analytical measurements used to assess the quality of the analytical data
Light
Q part of the Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer that Provides the analytical light line for the element of interest
Nebulizer
Part of AAS that Creates a fine aerosol for introduction into the flame
Flame
part of AAS that Destroys any analyte ions and breakdown complexes to create atoms (the elemental form) of the element of interest.
Monochromator
part of AAS that Separates and transmits a narrow portion of the optical signal chosen from a wider range of wavelengths available at the input.
Detector
part of AAS that Determines the intensity of photons of the analytical line exiting the monochromator.
amber bottle container
Light sensitive samples should be collected in a/an __________ container.
Dichloromethane
A solution consisting of petroleum ether, nhexane and ethyl acetate is subjected to fractional distillation. What compound will be recovered first given the following boiling points? Dichloromethane = 39.6°C, n-hexane = 68°C, Xylene = 140°C.