Parenterals - Basics of Sterile Compounding
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
parenteral administration bypasses the
GIT
by passing the GIT, parenterally administrated drugs are not subjected to...
pharmacodynamic properties (skips FPE)
what are the three types of routes of administration
topical
enteral
parenteral
Intravenous (IV) injection
into the veins
intramuscular (IM) injection
into the muscle
subcutaneous (SQ or SubQ) injection
into the subcutaneous tissue of the skin
intradermal (ID) injection
into the dermis of the skin
Intrathecal injection
into the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord
epidural injection
into the epidural space of the spinal cord
intra-arterial injection
into the arteries
intra-cardiac injection
into the heart
intra-articular injection
into the joint space
intra-ocular injection
into the eyes
intraperitoneal injection
into the peritoneal cavity
what angle should an IM injection be administered?
90 degrees
what angle should an IV injection be administered?
35-45 degrees
what angle should a SQ injection be administered?
45 degrees
what angle should an ID injection be administered?
10-15 degrees
what is the volume range for an ID injection
0.02-0.5 mL
what is the volume range for IV injections
unlimited
what is the max volume for IM injections
5 mL
what is the volume range for SQ injections
small volumes
what is typically administered via intra-articular injection
steroids
what diseases are usually treated with Intra-ocular injections
retinopathy
glaucoma
macular edema
what meds are usually delivered via intra-ocular injection
avastin and steroids
peritoneum
membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and hold the organs in place
what meds are usually administered via intra-ocular injection
avastin and steroids
what type of injection is the most common
IV
IV administration has ___% bioavailability
100
what are the disadvantages of IV admin
need to have access
difficult or impossible to remove or reverse drug
risk of infection, emboli, infusion related rxns
expensive
what are the advantages of IV admin
good for ppl who cant do PO
bypasses GIT
no FPE
100% bioavail
quick onset of action
localized delivery
extended duration of effects
what are the three kinds of IV injections
continuous infusion
intermittent infusion
IV push or bolus
continuous IV infusion
an IV solution infused at a continuous prescribed rate
intermittent IV infusion
A solution of a small to moderate volume infused intravenously over a short period of time at specific time intervals
IV push or bolus
A small volume of solution injected directly into the vein and infused over a short period of time (can happen in rapid succession if needed but not repeated later at set times)
needles are made of which two metals
aluminum
stainless steel
needles are packaged individually in order to
guarantee sterility
what are the parts of a needle
hub, shaft, bevel, lumen, and cap
needle length is measured from ____ to _______
hub to tip
needle gauge
diameter of the needles opening (lumen)
as gauge increases the diameter of the lumen _______
decreases
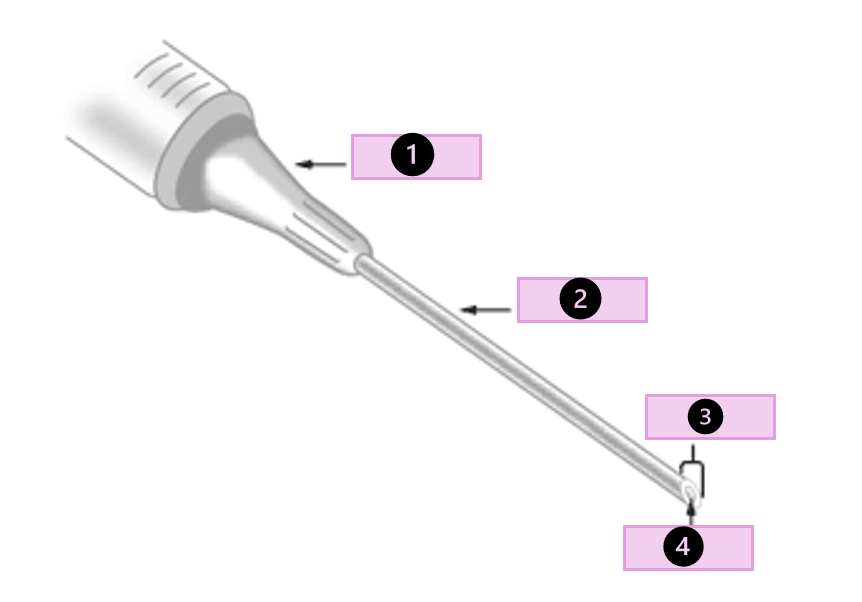
what part of the needle is 1?
hub
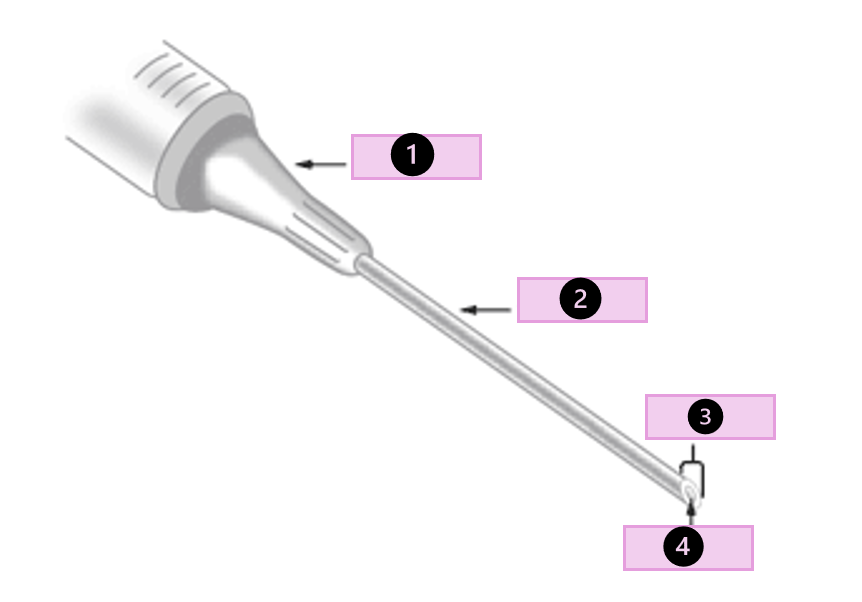
what part of the needle is 2?
shaft
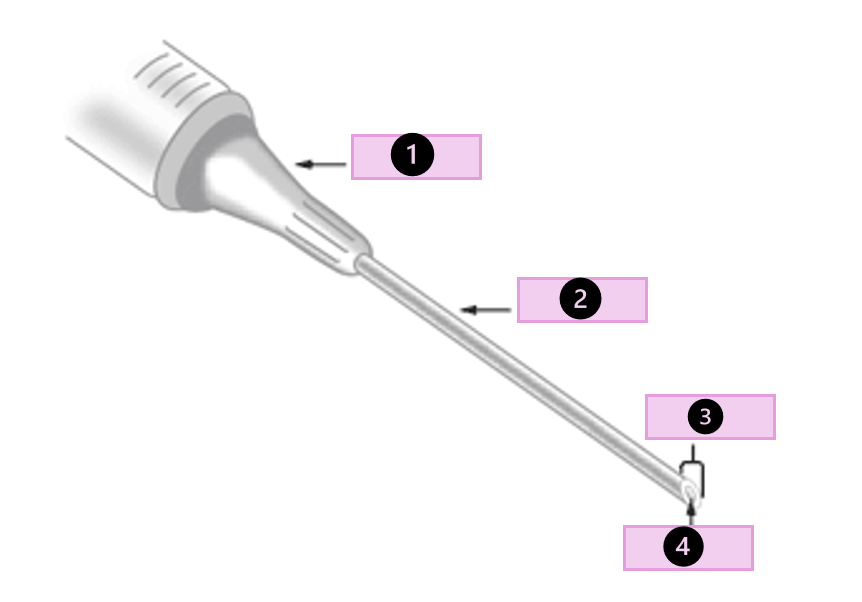
what part of the needle is 3?
bevel
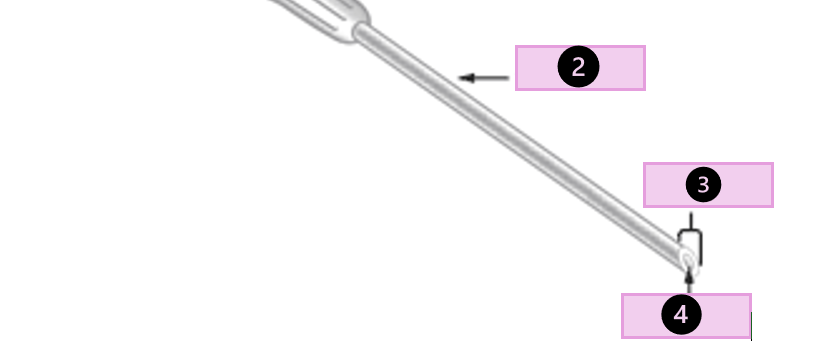
what part of the needle is 4?
lumen
if syringe size is 1, 3, or 5 mL:
needle gauge = ______
needle length = _______
20 gauge
1 inch
if syringe size is 10, 20, 30, or 60 mL:
needle gauge = ______
needle length = _______
18 gauge
1.5 inches
if syringe size is for a large volume or a viscous solution:
needle gauge = ______
needle length = _______
16 gauge
1.5 inches
what type of needle is needed for withdrawing from ampules
filter
types of needles
-Double ended needles and Transfer Sets
-Filter needle and Filter straws
-Vented Needles
opening needles:
needle must be at least ________ inches in the hood
6
opening needles:
you should tilt the needle hub to the (front or back) of the hood
back
opening needles:
you should pull the packaging from the hub towards _____
you
opening needles:
you should never touch which parts of the needle when opening
the hub or the needle itself
what are the parts of a syringes
collar, barrel, calibrations,tip, flange, ribs, and piston
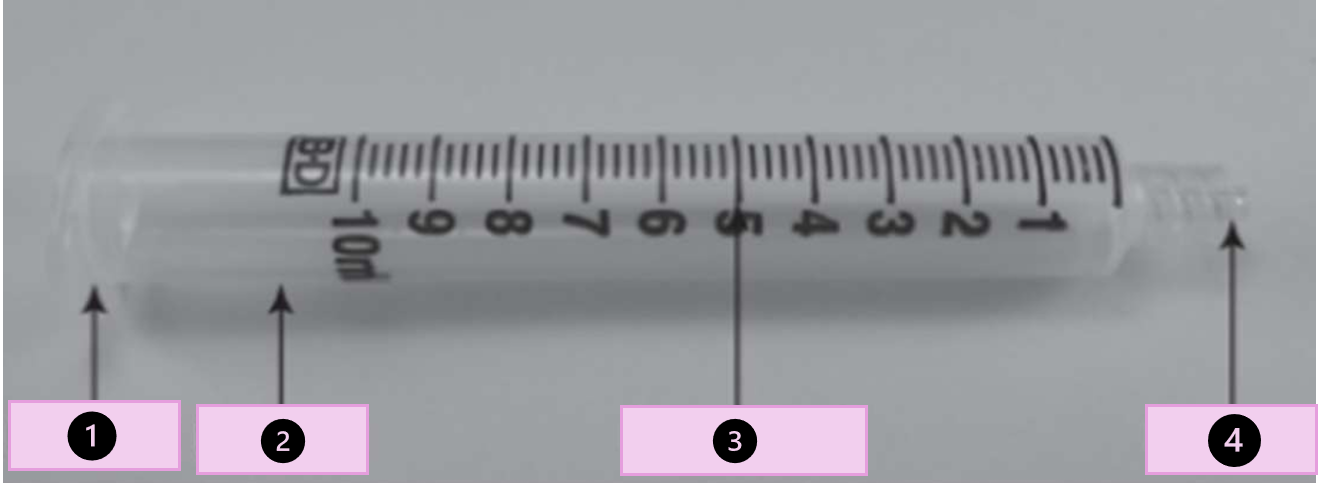
what part of the syringe is 1?
collar
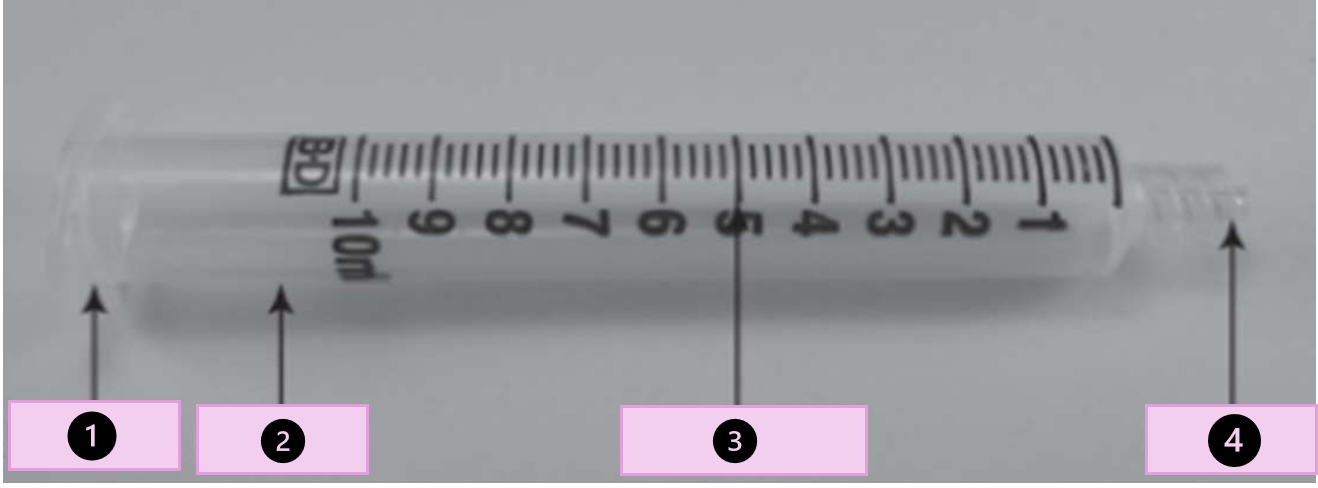
what part of the syringe is 2?
barrel
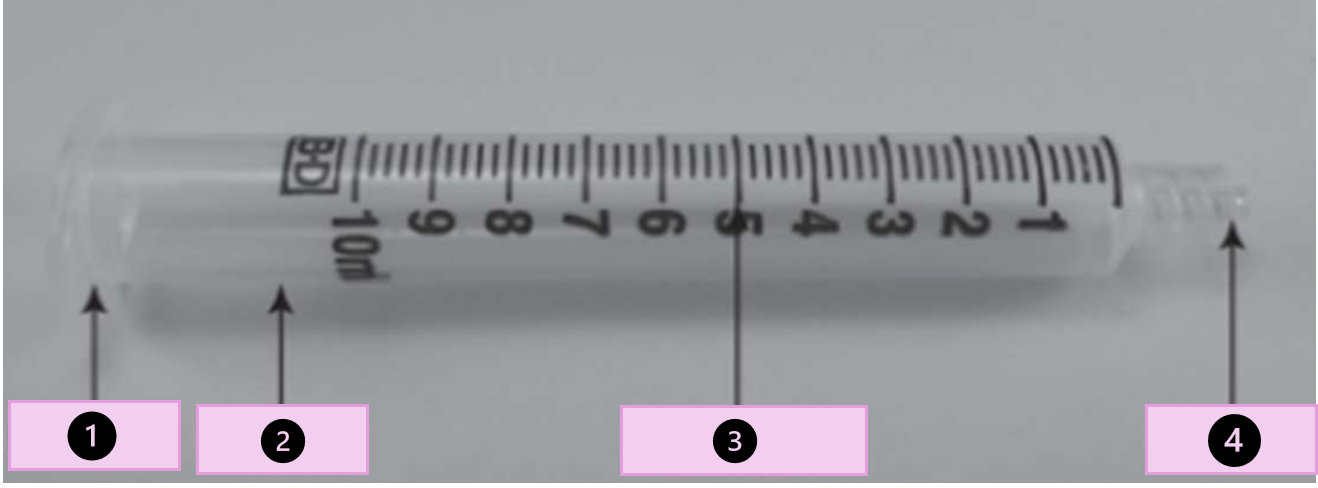
what part of the syringe is 3?
calibration
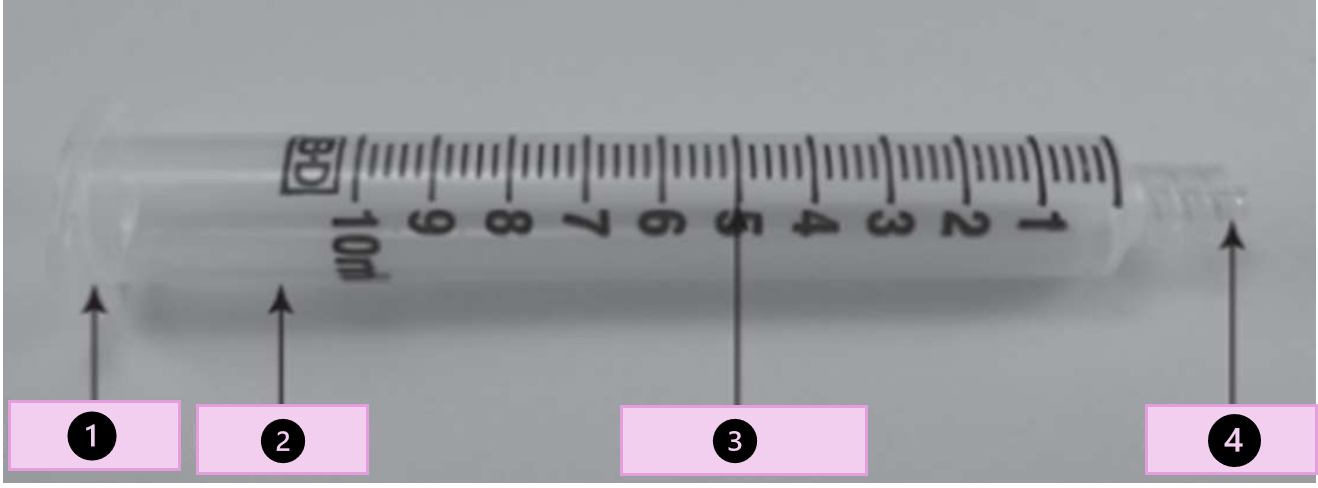
what part of the syringe is 4?
tip
what part of the syringe is 1?
plunger
what part of the syringe is 2?
flange
what part of the syringe is 3?
ribs
what part of the syringe is 4?
piston
what are the types of syringes
luer lock/slip tip
oral
prefilled
glass/plastic
how should you measure when filling a syringe?
the final edge of the plunger piston should be aligned with the calibration marks on the syringe
syringe size = 1 mL
calibration = _____
0.01 mL
syringe size = 3 mL
calibration = _____
0.1 mL
syringe size = 5 mL or 10 mL
calibration = _____
0.2 mL
syringe size = 20 mL or 30 mL
calibration = _____
1 mL
syringe size = 60 mL
calibration = _____
2 mL
how do you select the right sized syringe:
accuracy method
divide the smallest increment of the calibration marks in 1/2
how do you select the right sized syringe:
general rule
dont use a large syringe for a small volume, use the smallest possible syringe to accommodate for the desired volume
T or F:
oral syringes cannot have needles attached to them structurally
T
T or F:
oral syringes are labeled with "for oral use only"
T
pros of prefilled syringes
improved accuracy and safety
convenient
efficient
easy to use
cons of prefilled syringes
complex
potential accidental needle sticks
malfunctions
breakage
clogging
safety syringe:
the plunger is (activated or inactivated) once the plunger is fully depressed
inactivated
safety syringe
needle is shielded either by retracting the needle into the syringe barrel when the plunger is pulled back o by deploying a protective shield over the needle
opening syringes:
you should remove from packaging at least _________ inches inside the hood
6
opening syringes:
you should hold the syringe by the __________
barrel
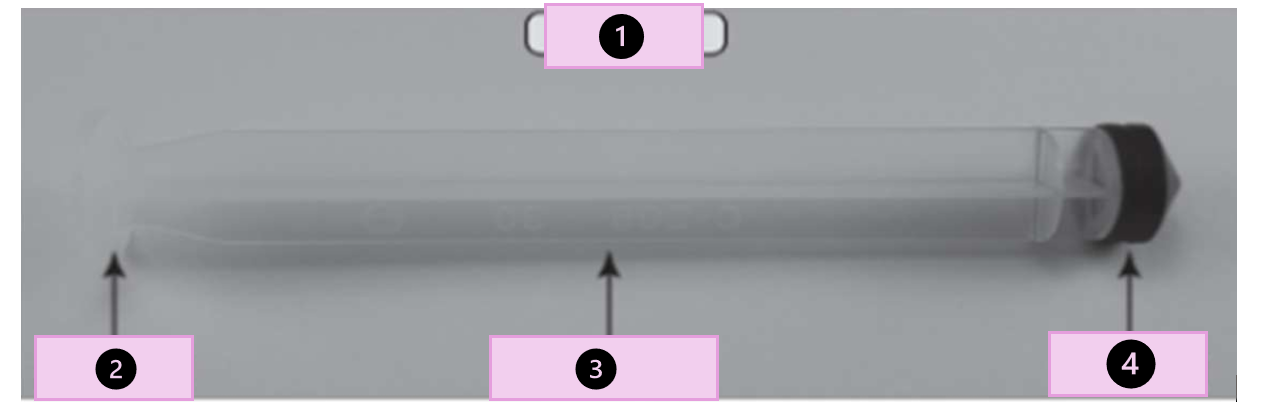
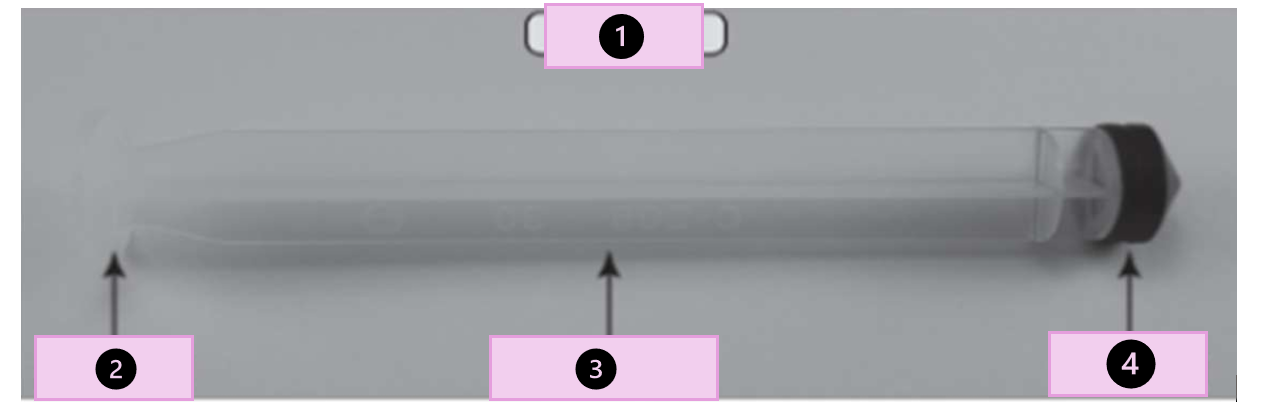
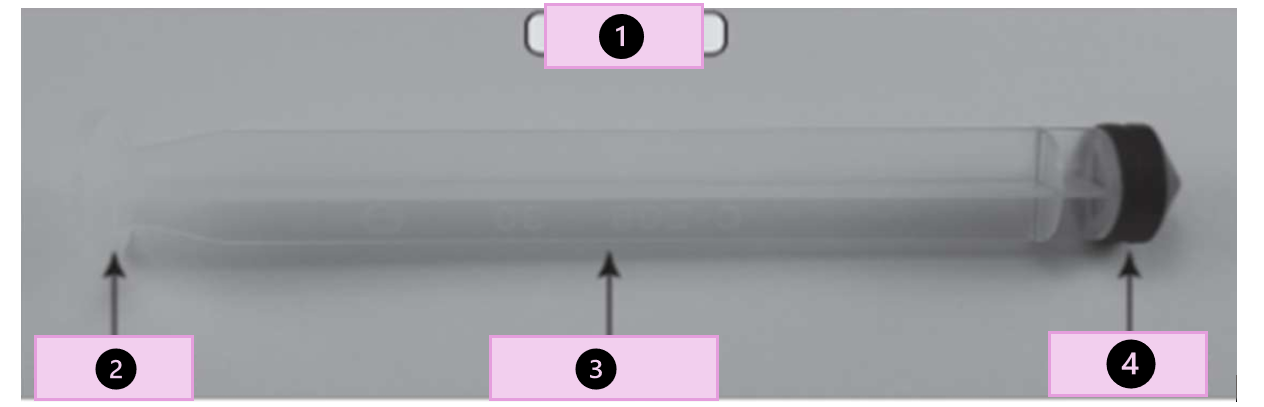
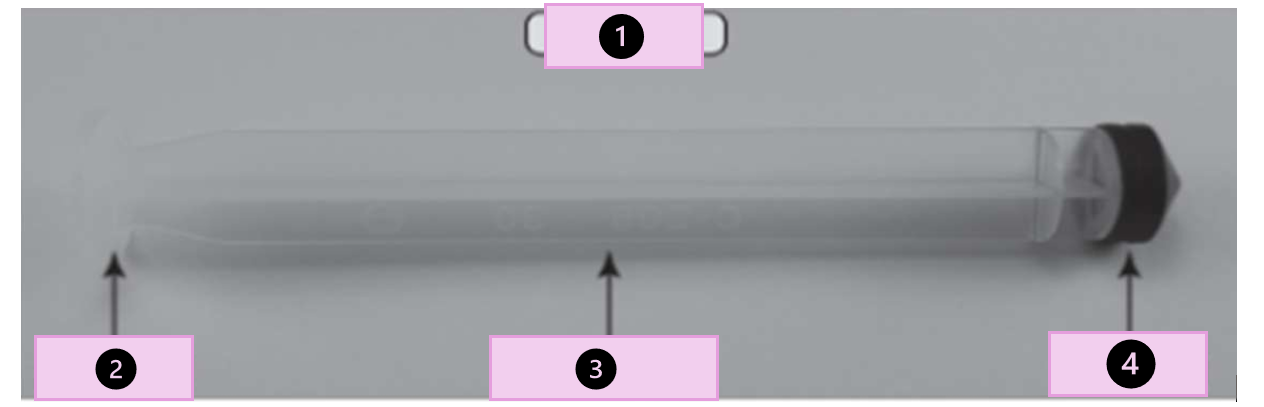
ampule
glass container that hold a single dose of medication
ampules:
what are the parts
tip, scored point, neck, body
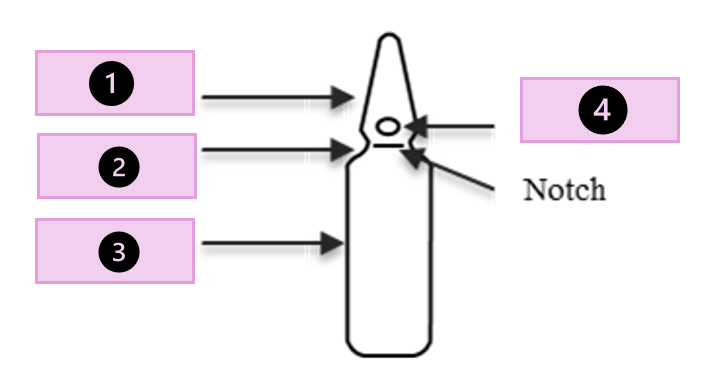
what part of the ampule is 1?
conical tip
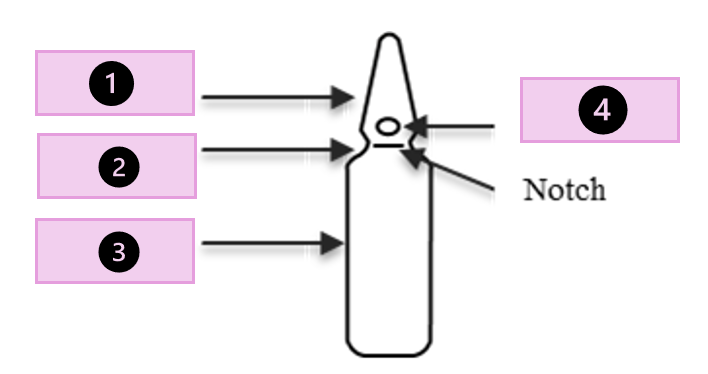
what part of the ampule is 2?
neck
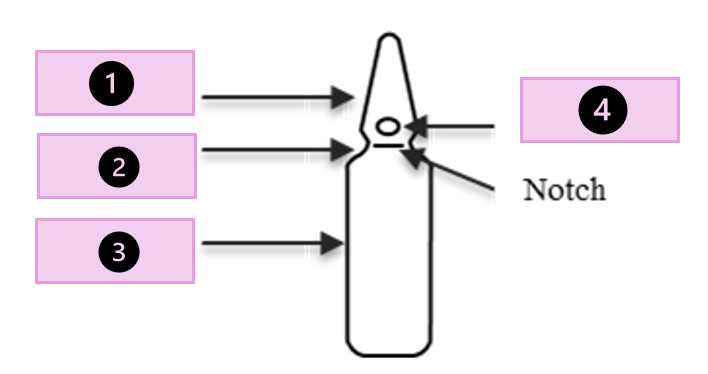
what part of the ampule is 3?
body
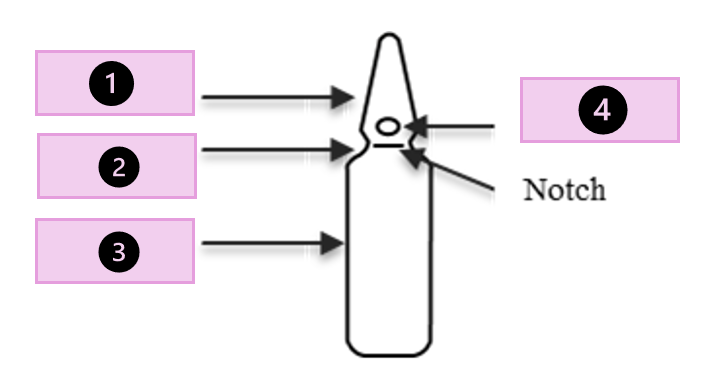
what part of the ampule is 4?
scored point
ampules:
T or F: must be broken to use
T
ampules:
T or F: have multiple doses
F
ampules must have what type of needle
filter
an ampule when opened should never have _______ injected into it
air
withdrawing from an ampule option 1:
tilt the ampule and place the ______ of the needle in the corner near the opening, then pull the syringe plunger back to w/d
bevel
withdrawing from an ampule option 2:
keep ampule in a _________ position, place needle bevel in the corner space at the bottom of the ampule, pull back on plunger to w/d
vertical
withdrawing from an ampule option 3:
turn ampule over, ending up with opening ___________, insert needle, keep bevel just open opening but surrounded by liquid contents and draw liquid out
down
Vials are made of either _____ or _________
plastic or glass
vials are (open or closed) system containers
closed
vials either have ________ or _________ for reconstitution
solution or powder
T or F:
vials are only for single use
F:
there are single and multi dose vials
T or F:
most vials contain overfill
T
medications that contain preservatives or are prepared with bacteriostatic water for injection should NEVER be used for which kinds of injections?
epidural and intrathecal
how should you pierce a vial, list the steps in order
1. remove the flip tip cap
2. swab the top w/ an alcohol swab
3. let the alcohol dry
4. insert the needle with the bevel up into the rubber closure