Procedures of Alimentary Canal: Large Intestine
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Examination Protocol
• Introduce patient to radiologist
• On request, release clip to allow barium to flow
• Single-Contrast (barium only): flow of barium is suspended periodically to reduce cramping and defecation impulse
• Double-Contrast (barium and air): examinations flow of barium first, then air or other gas after barium is evacuated
• Filling is viewed on fluoroscope
• Radiologist instructs patient to rotate to visualize all portions of bowel
Routine double-contrast procedures
• AP/PA
• LPO/RPO
• PA/AP Axial
• RAO/LPO Axial
• Lateral Rectum
• Rt./Lt. Lateral Decubitus
• Lateral Rectum (ventral decubitus)
• Post -evacuation
Routine single-contrast procedures
• AP/PA
• LPO/RPO
• PA/AP Axial
• RAO/LPO Axial
• Lateral Rectum
• Post-evacuation
AP/PA Large Intestine
• Collimation: 14 x 17"
• SID: 40"
• Prone or supine
• Respiration: suspended
• CR level of iliac crest and MSP
• Most commonly is AP
AP vs PA
SLIDE 5
- See polyps (inpouchings) and diverticulum (outpouchings)
- Barium in term-5transverse colon (PA)/barium in ascending and descending colon (AP)
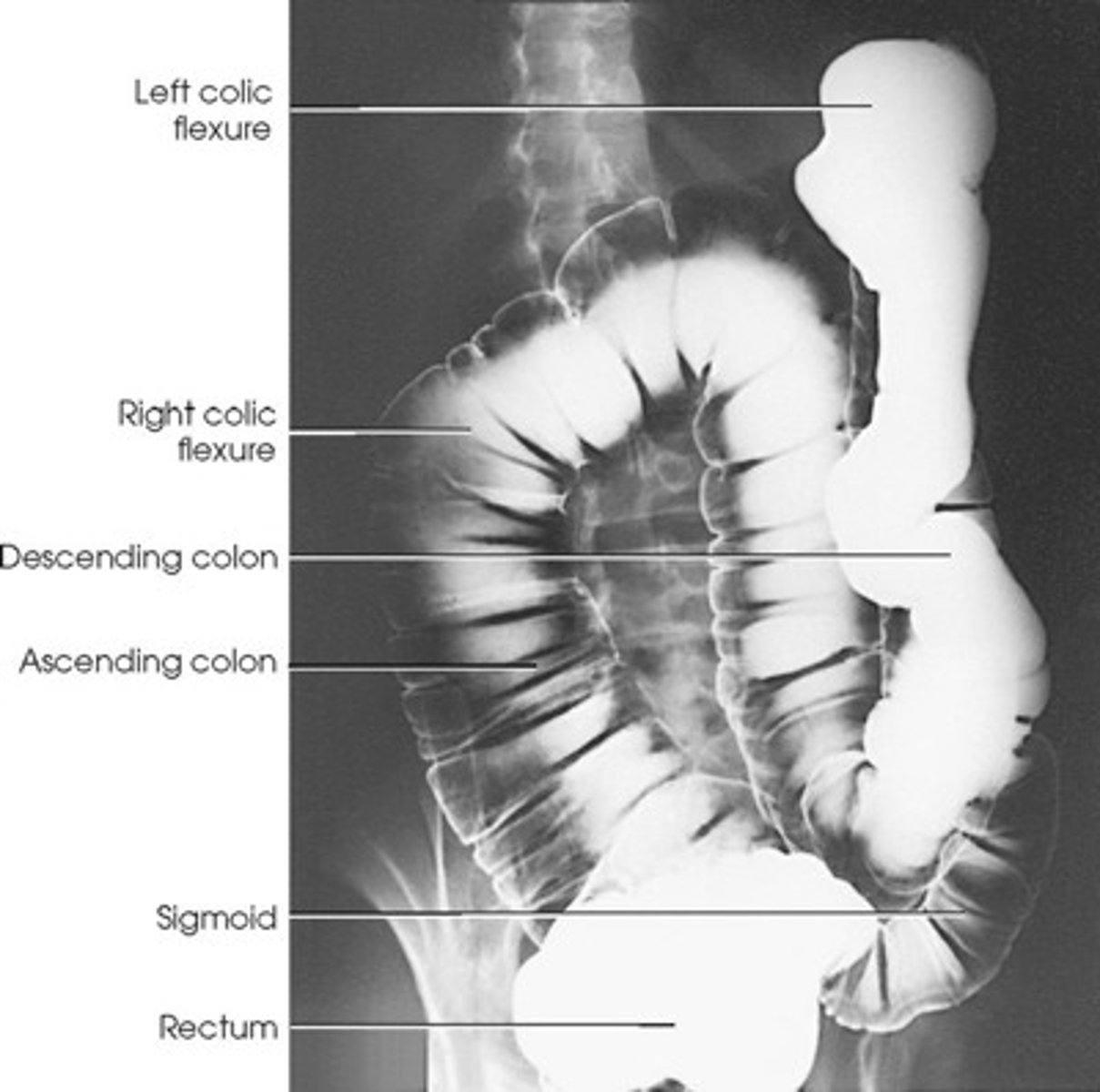
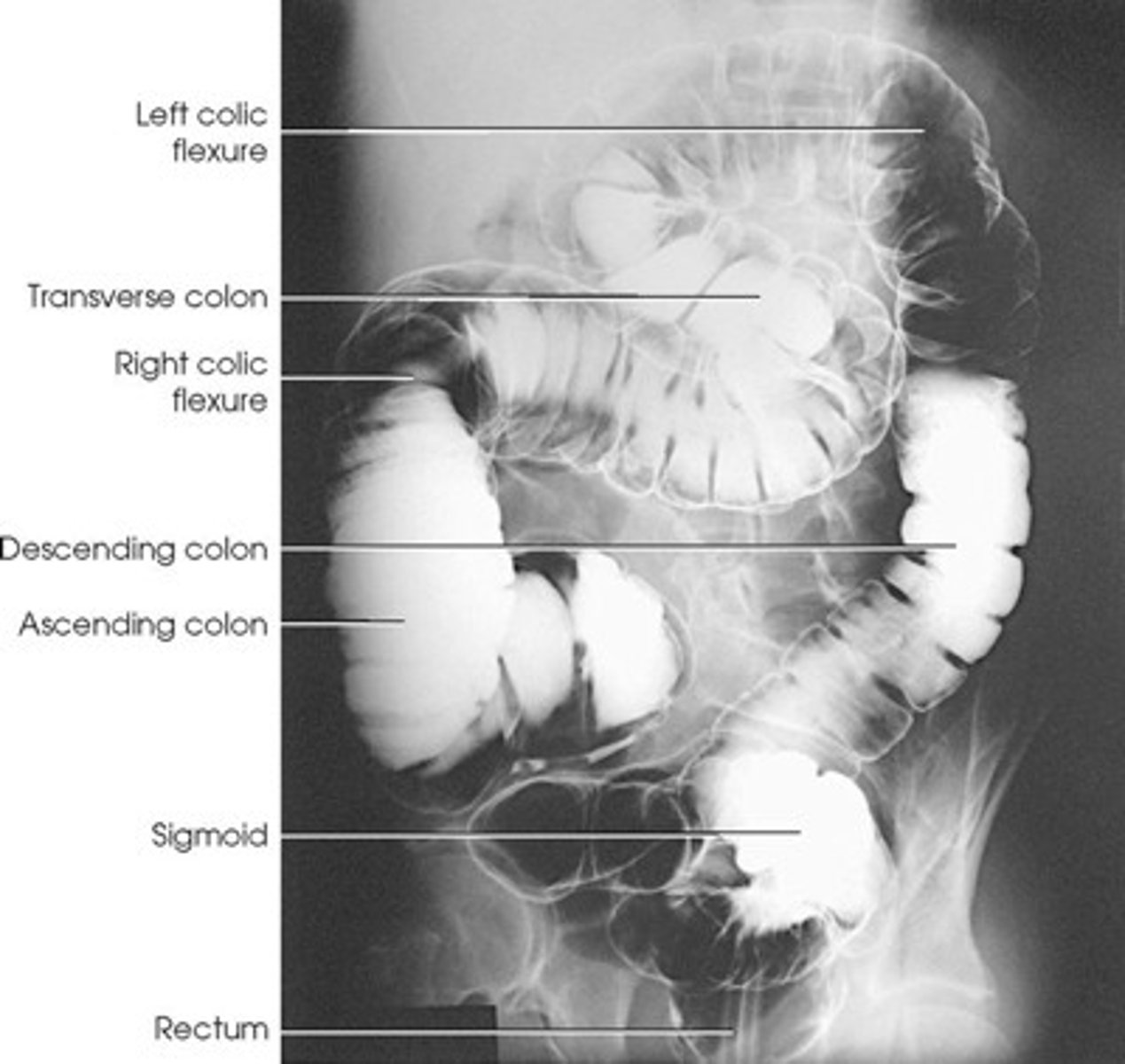
Structure shown: AP
• The entire contrast-filled large intestine.(the exception to this is the lt. Colic flexure)
• The barium will go to the most posterior parts (air in transverse colon).
• Ascending colon, Descending colon, and Rectum
SLIDE 6
structures shown: PA
• The entire contrast-filled large intestine.
• The barium will go to the most anterior parts. (air in ascending and descending)
• Transverse colon, and Sigmoid colon
SLIDE 7
how much barium is in barium enema bag?
1,500 cc
How long is the alimentary canal?
30 feet
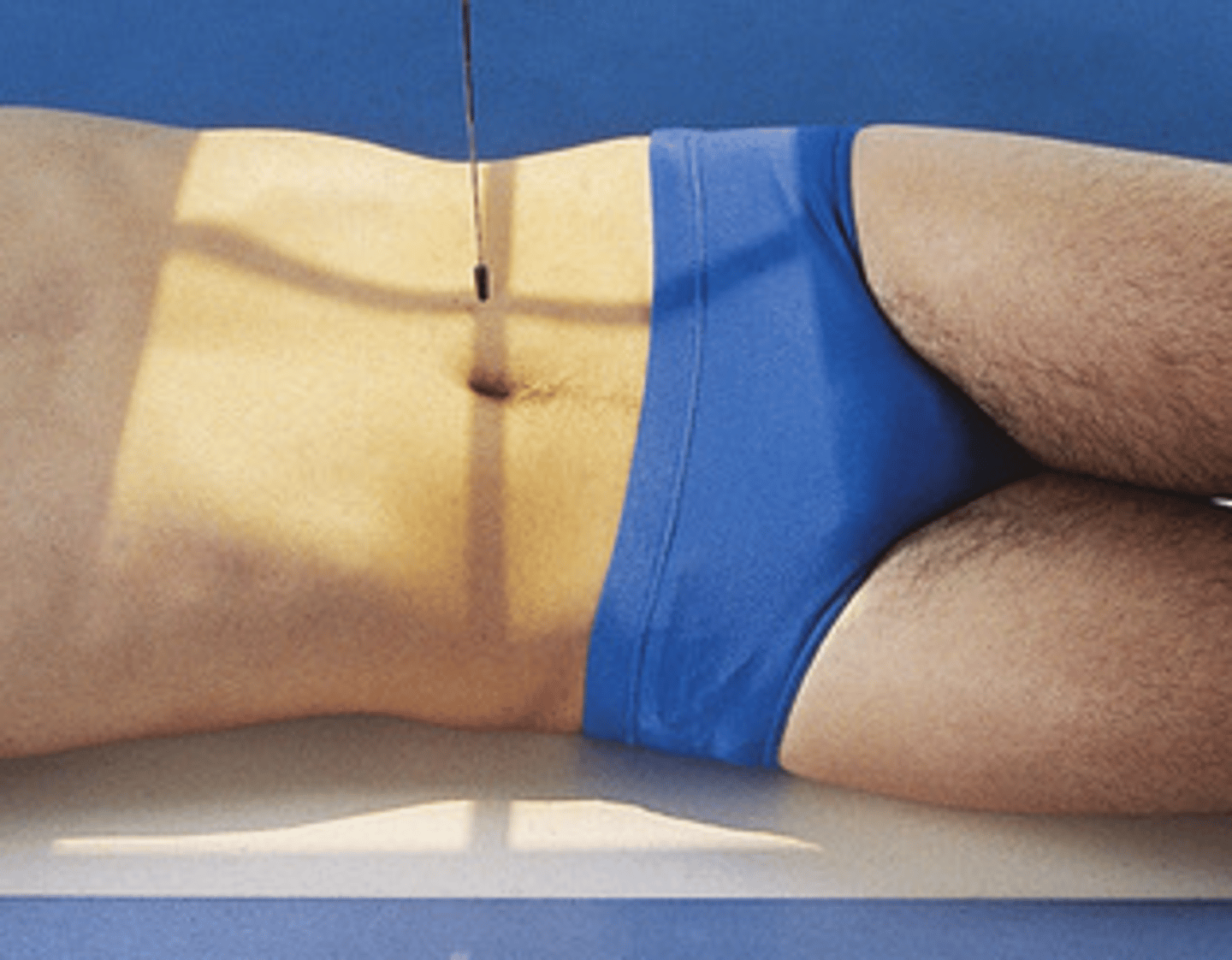
AP or PA axial large intestine
• Collimation: 10 x 12"
• Supine or prone
• Respiration: suspended
• CR• AP: angled 30-40º(ave 35º) cephalic
• PA: angled 30-40º(ave 35º) caudal
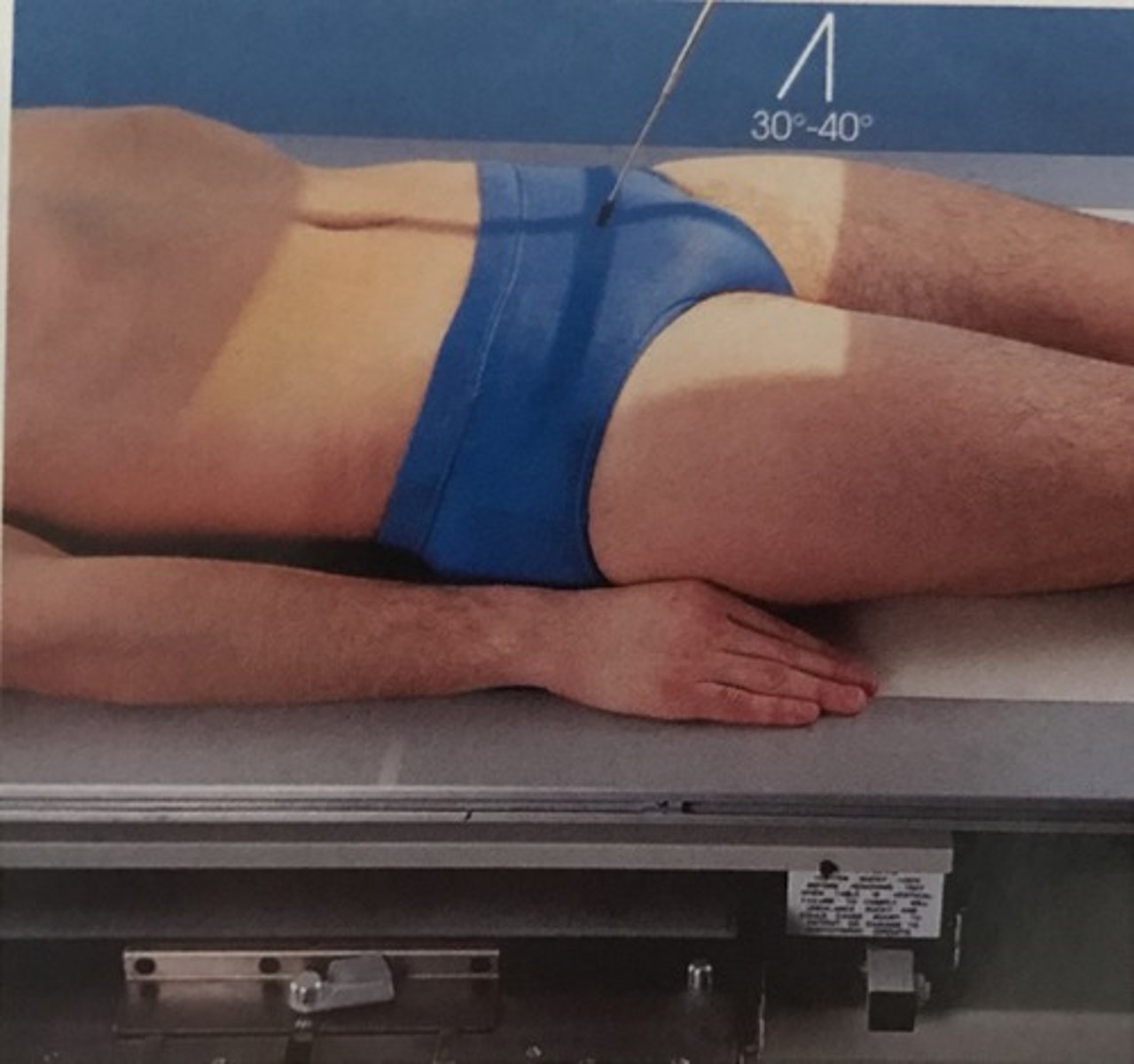
Structures shown: AP or PA axial
• An elongated projection of the rectosigmoid region of the large intestine.
• The barium will be located in the rectum (supine) or sigmoid (prone)
• Sigmoid colon superior to rectum
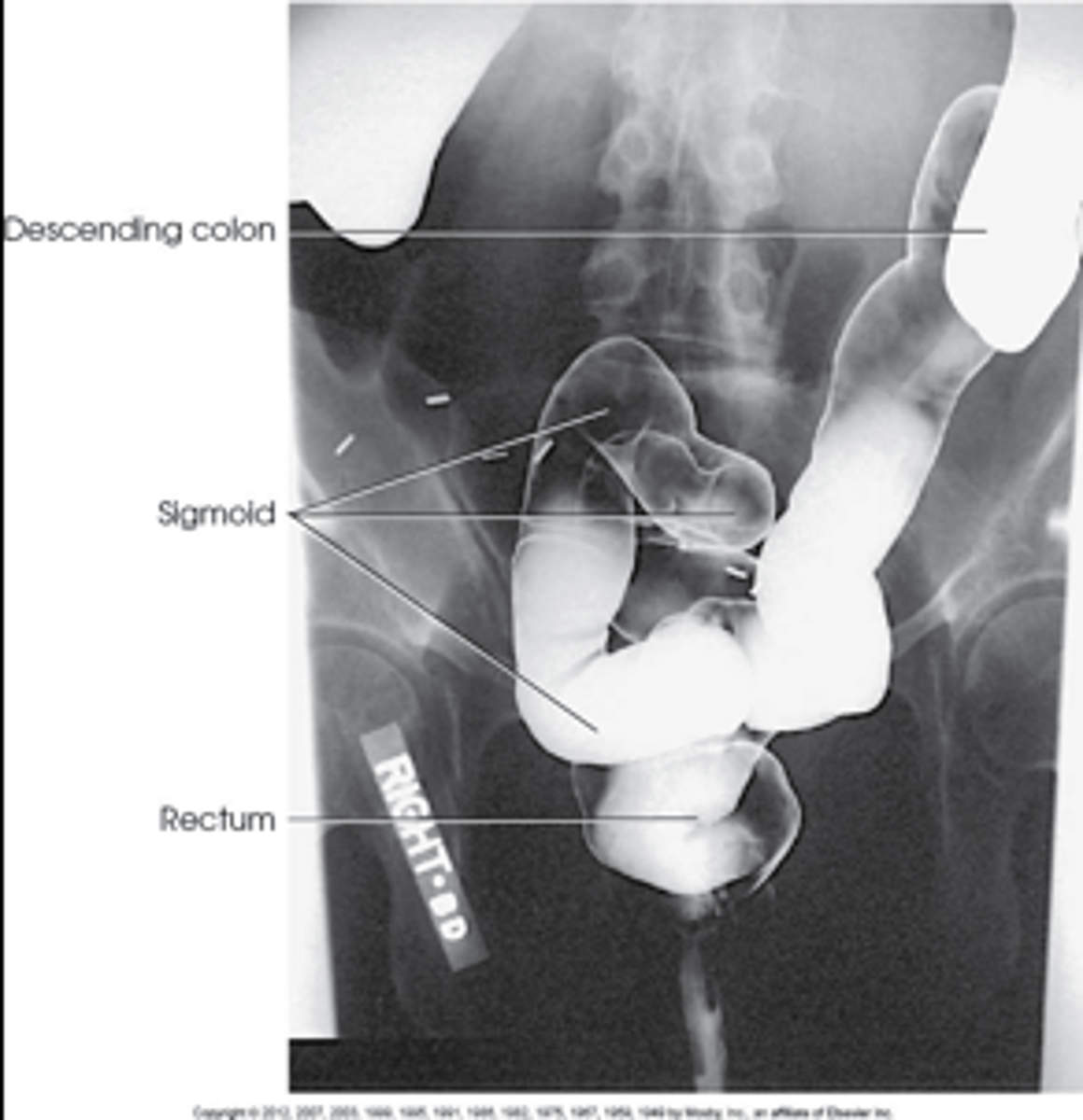
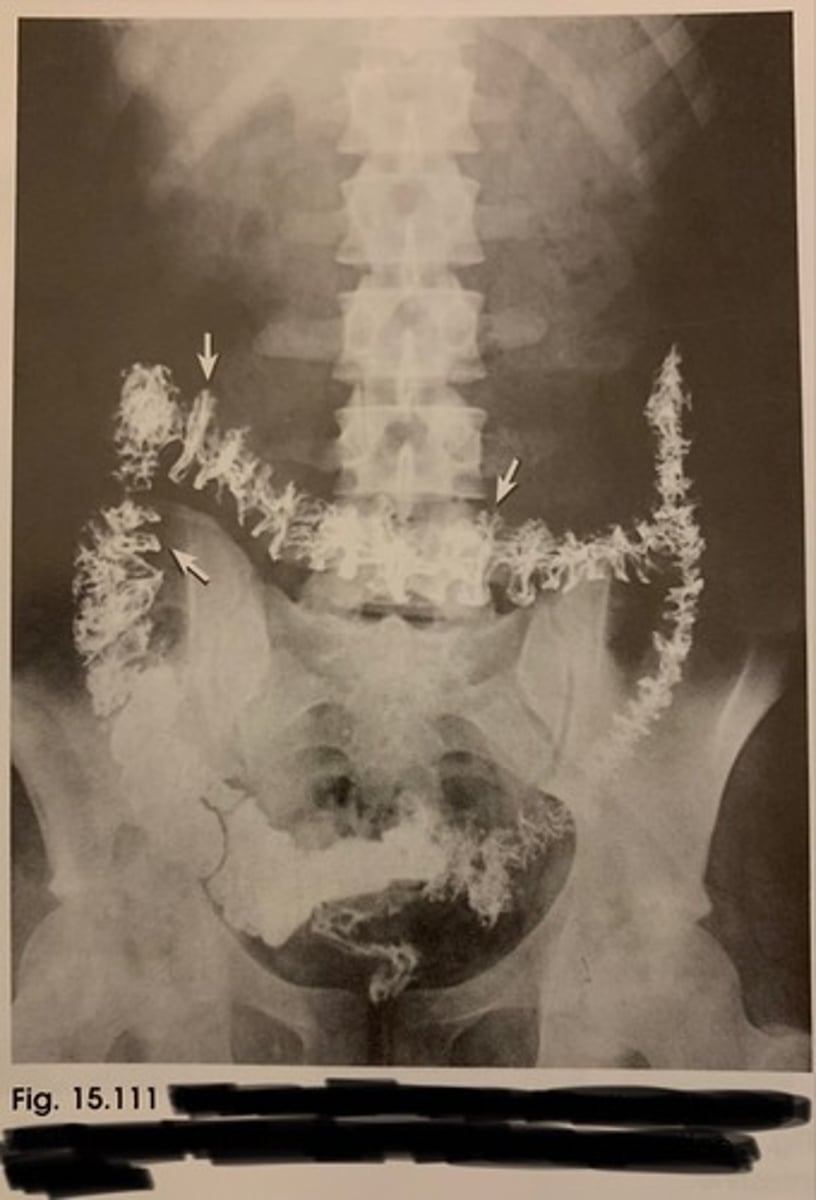
LAO/RAO or LPO/RPO large intestine
• Collimation: 14 x 17"
• SID: 40"
• Semi-prone or semi-supine
• Oblique 35-45º (45 for asthenic and 35 for hypersthenic)
• Respiration: suspended
• CR perpendicular at the level of iliac crest and 1" lateral to the MSP toward the elevated side (LPO/RPO)
• CR perpendicular at the level of iliac crest and 1" lateral to the MSP toward the unelevated side (LAO/RAO)

Structures shown: LPO/RAO
• The Rt. Colic flexure is demonstrated.
• The flexure should be open & free of superimposition
Structures shown: RPO/LAO
• The Left Colic flexure is best demonstrated
• The flexure should be open and free of superimposition
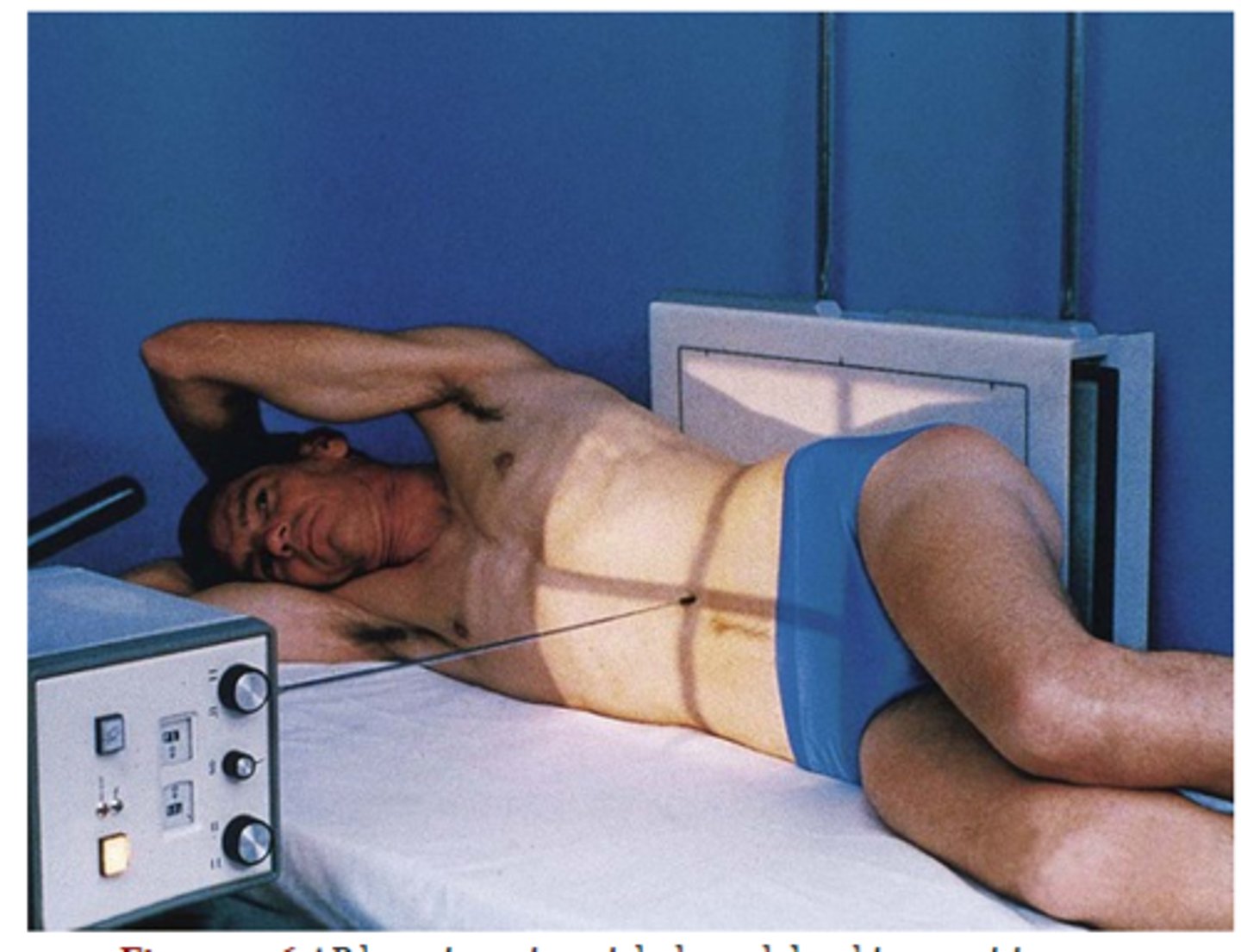
right and left lateral decubitus large intestine
• Collimation: 14 x 17"
• Place the patient in a true recumbent lateral position.
• Body elevated on radiolucent sponge
• Respiration: Suspended
• CR horizontal at the level of iliac crest and MSP
structures shown: left lateral decubitus
• An air-filled Rt. Side of the intestine.
• This projection is helpful in demonstrating polyps
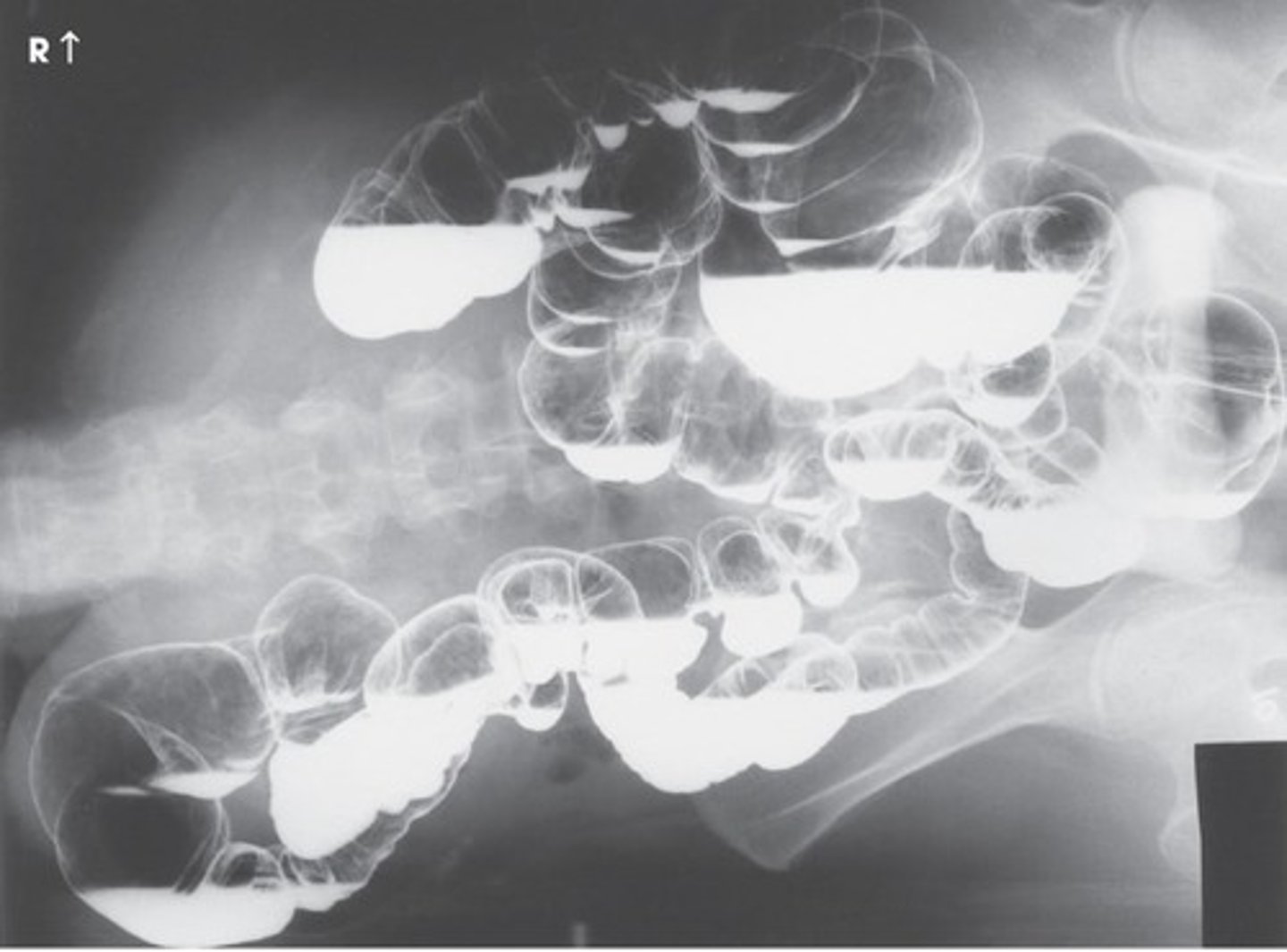
structures shown: right lateral decubitus
• An air-filled Lt. Side of the intestine.
• This projection is helpful in demonstrating polyps
• Medial side of ascending and lateral surface of descending
SLIDE 15
which projections demonstrate air fluid levels
decubitus
lateral rectum large intestine
• Collimation: 10 x 12"
• Left or Right True Lateral (Left lateral commonly performed)
• Respiration: suspended
• CR perpendicular at the level of the ASIS and mid-axillary plane.
SLIDE 16
structures shown: lateral rectum
• Lateral projection of the rectosigmoid region.
• Either left or right laterals may be performed.
• Left is preferred due to the location of the barium
SLIDE 17
ventral decubitus lateral rectum
• Collimation: 10 x 12"
• prone, no rotation
• Respiration: suspended
• CR horizontal at level of the ASIS and mid-axillary plane
SLIDE 18
structures shown: ventral decubitus
• This is usually performed with a double contrast exam.
• This is an excellent projection to demonstrate the rectum
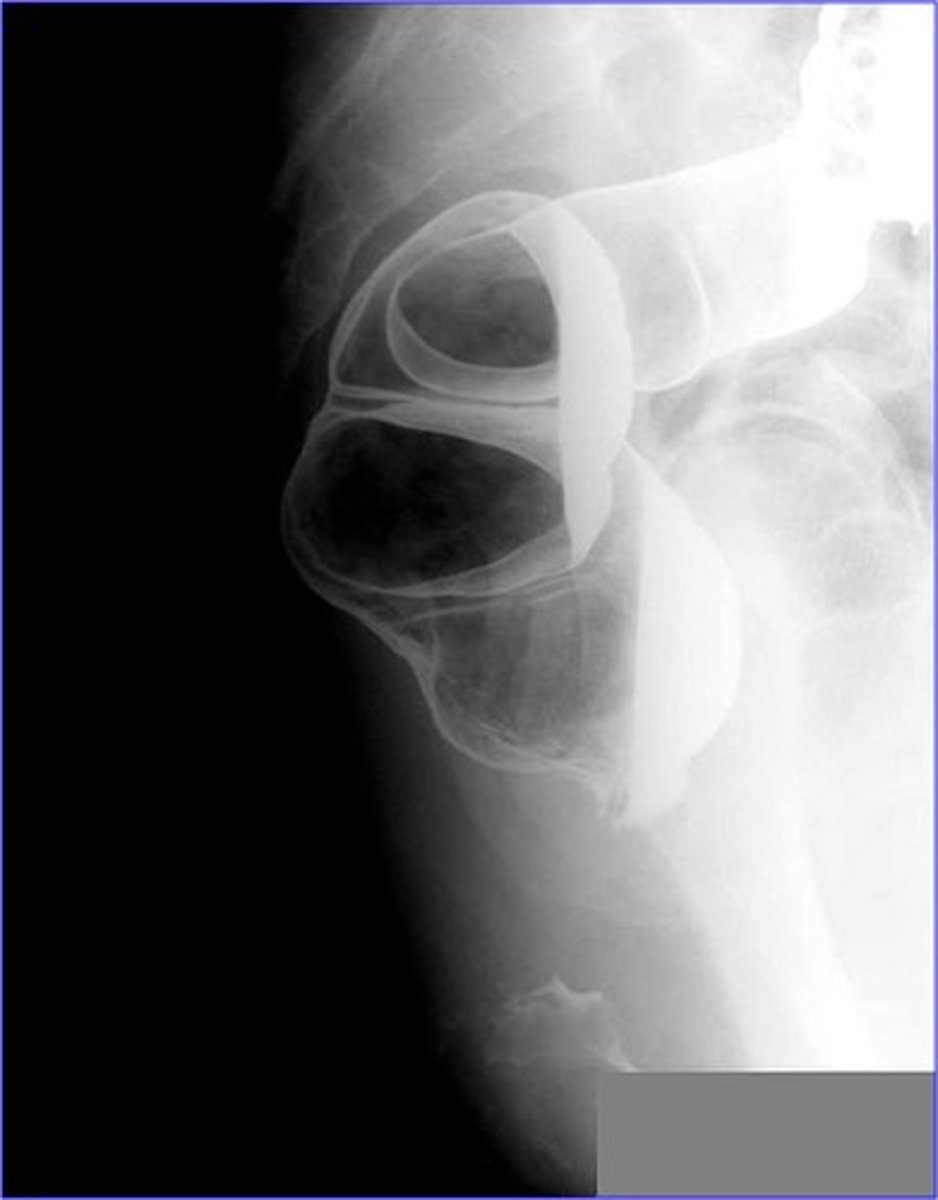
best projection of rectum?
ventral decubitus
what demonstrates rectosigmoid region?
lateral, ventral decubitus, PA/AP Axial
post-evacuation large intestine
- demonstrates haustra
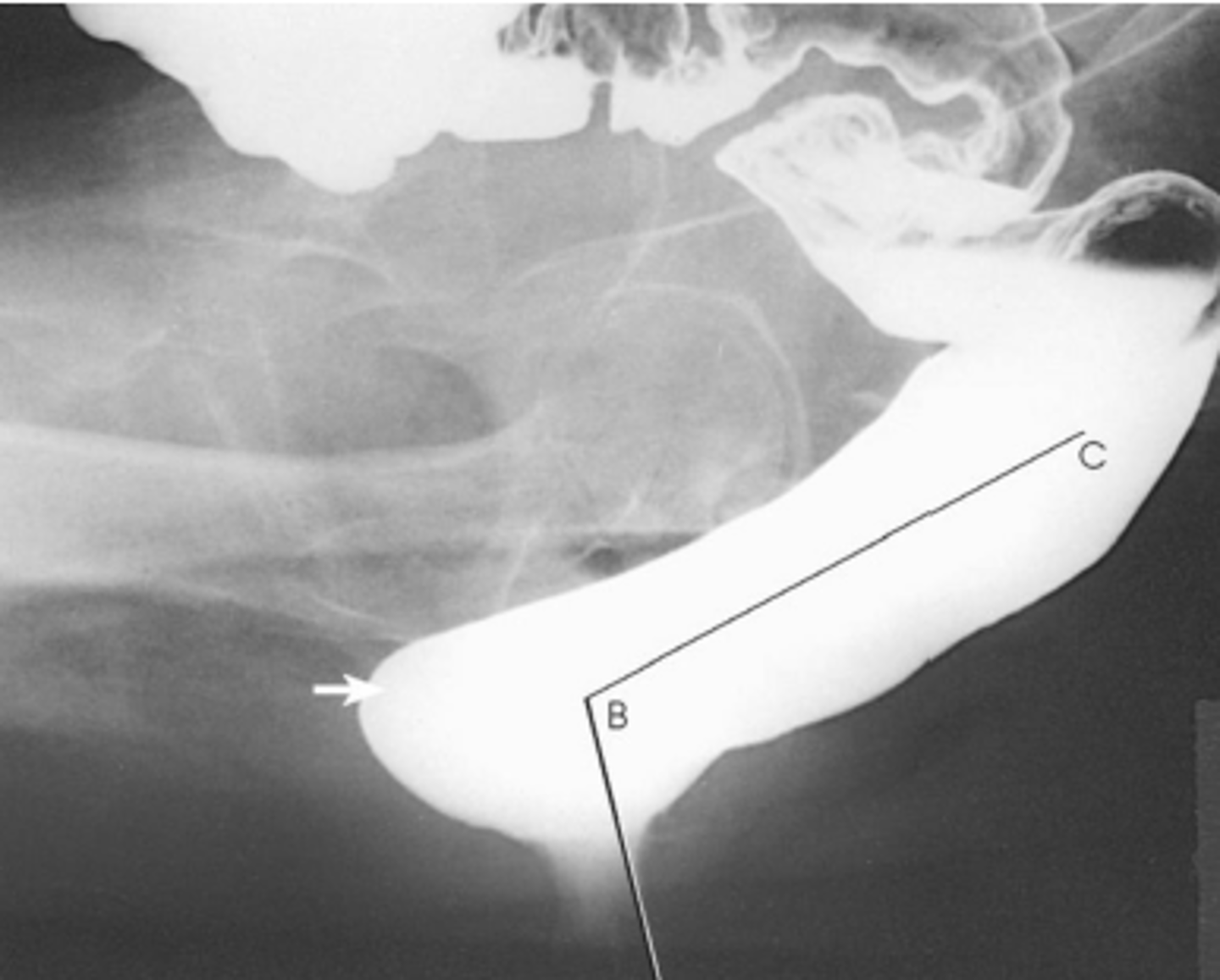
defecography
Performed on Patients with defecation dysfuntion
No patient preparation required
Barium paste inserted with a special injector into the rectum
Patient seated in lateral position on a radiolucent commode
Under fluoroscopic guidance (or videorecording), images are saved during defecation at a rate of 1-2 frames per second (fps)
Measurements are taken of:
The anorectal angle
The angle between the long axis of the anal canal
rectum
Which body positions best demonstrate left colic flexure?
RPO/LAO
which projection best demonstrates haustra?
post evacuation