IGCSE MARINE SCIENCE
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UNIT 1 : EARTH AND ITS OCEANS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
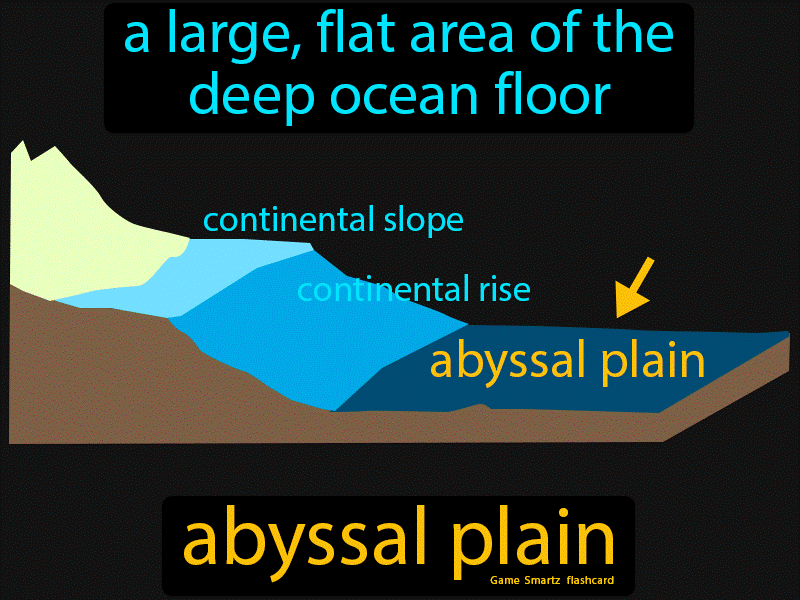
Abyssal Plain
The generally flat region of the ocean floor at a depth of 3000-6000m, usually at the base of a continental rise.
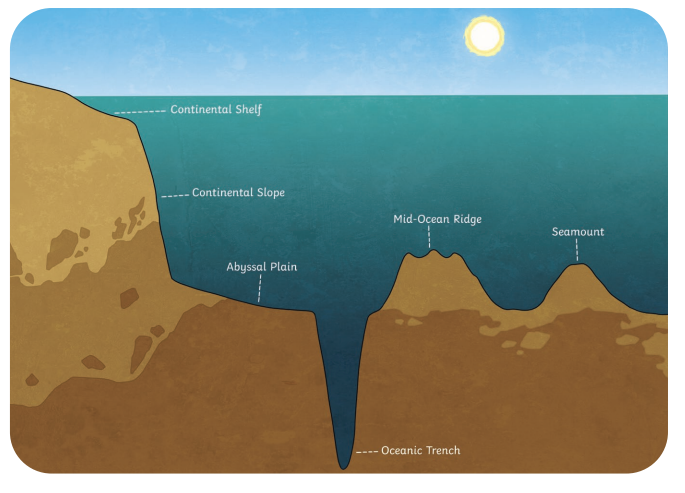
Continental Shelf
Part of a continental plate extending from the shore to the seabed, producing shallow waters with a sudden drop.
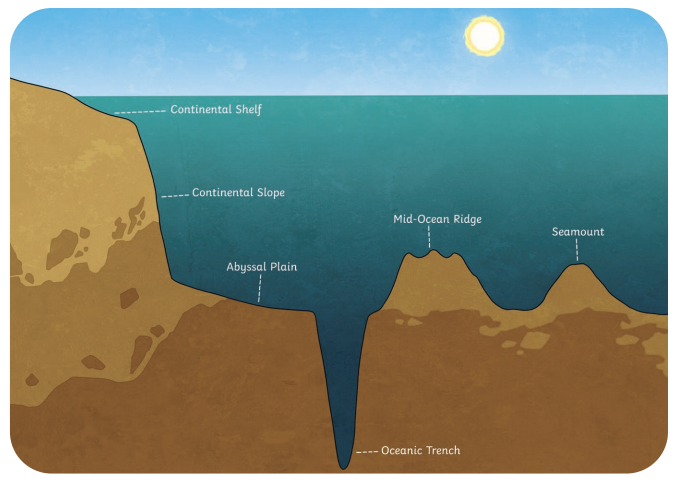
Continental Slope
The steep slope from the continental shelf to the abyssal plain.
It has a very deep drop to the ocean floor and a super steep slope.
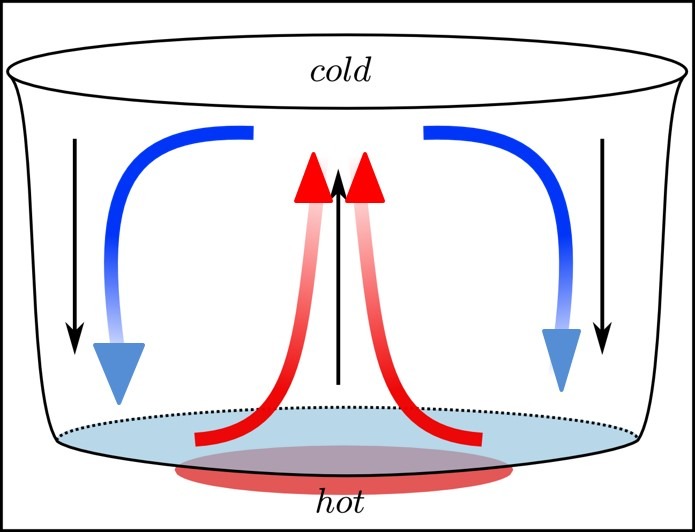
Convection Currents
Convection currents are circulatory movements in fluids (liquids and gases) caused by temperature differences, where warmer, less dense fluid rises and cooler, denser fluid sinks. These currents play a vital role in oceanic and atmospheric circulation, influencing climate patterns.
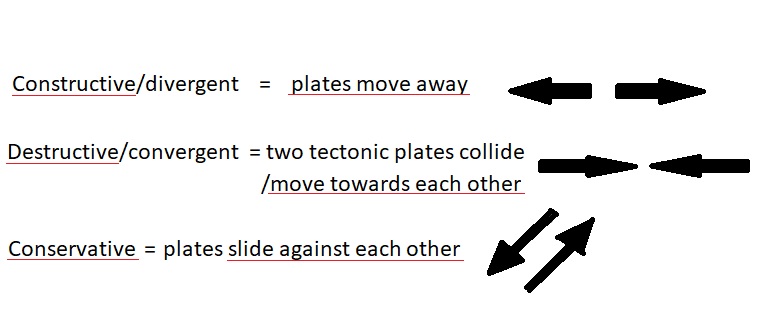
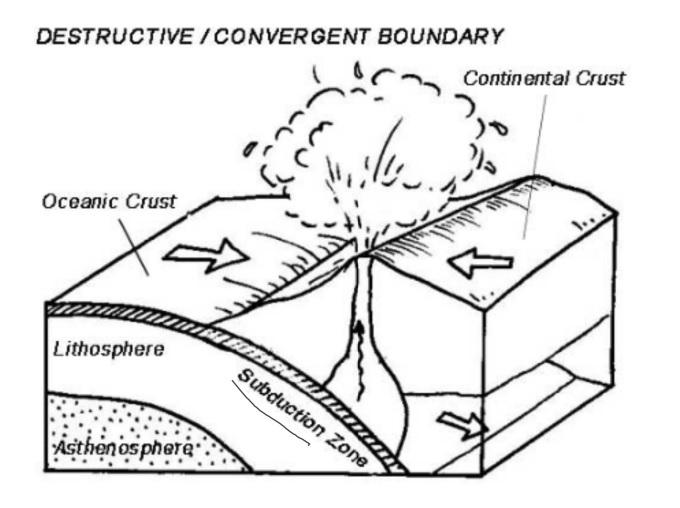
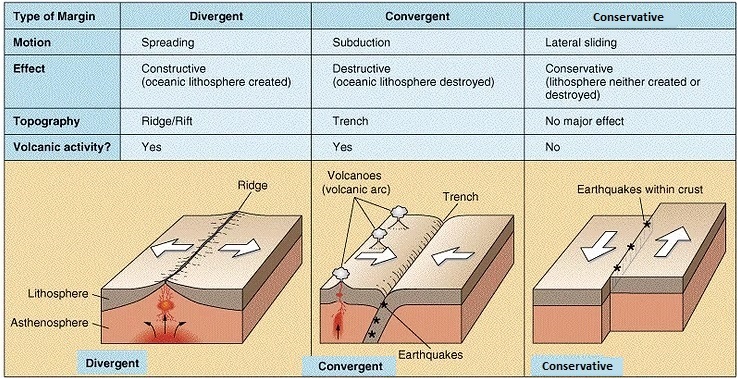
Destructive/Convergent Plate Boundary
When two tectonic plates move towards each other.
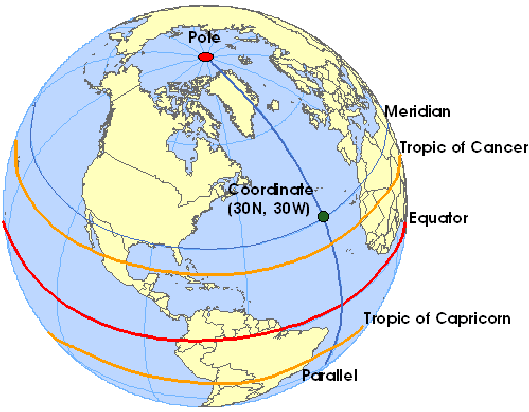
Coordinates
A pair of numbers used to identify a point.
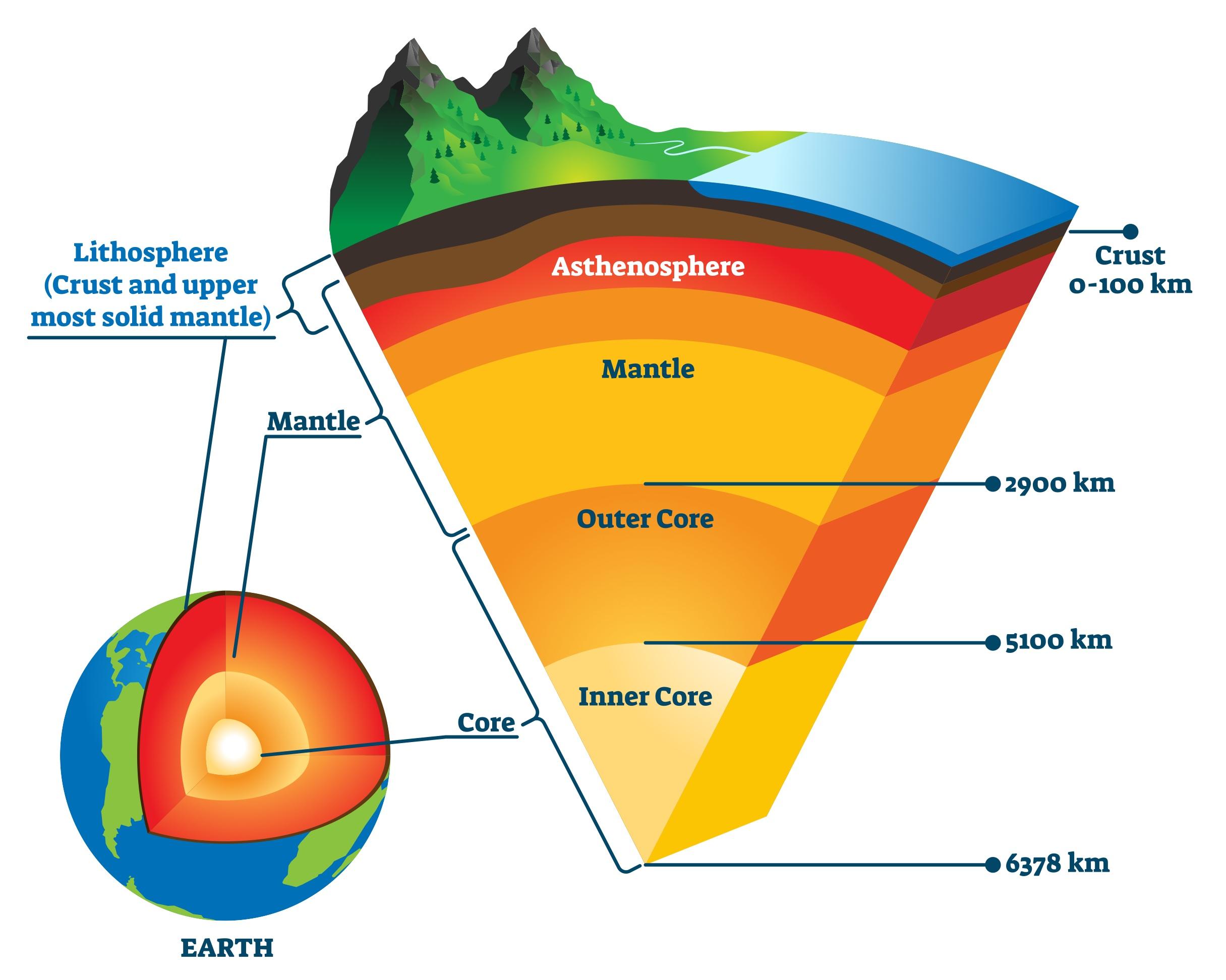
Core
The hot, dense center of the Earth, divided into inner (solid, mainly metal, radioactive) and outer (molten metal, creates magnetic field) cores.
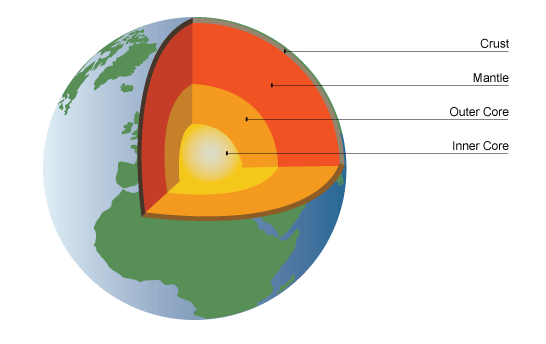
Crust
The outermost layer of the Earth, made of solid rock.
Currents (Sea or Ocean)
The continuous flow of water in a particular direction.
Divergent Plate Boundary
When two tectonic plates move apart from each other.
What is an Ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms interacting with non-living elements like air, water, and soil.
Equator
A line drawn around the Earth, separating the northern and southern hemispheres; the central line of latitude.
Erosion
The wearing away of rock along a coastline.
Freshwater
Water with a very low concentration of salts, suitable for drinking.
Geomorphology
The study of rocks and the structures and processes of the crust.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A network of artificial satellites that form a navigational system.
Gravity/Gravitational Pull
The force that exists between two objects with mass.
Gyre
A large system of circular currents in the ocean.
Iron
A metallic, magnetic element.
Latitude
The distance from the equator to the Poles (0 degrees at the equator, 90 degrees at the Poles).

Longitude
The distance east or west from the Prime Meridian (0 degrees at Greenwich, London, 180 degrees on the opposite side of the Earth).

Magma
Molten rock that is semi-liquid, found in the mantle; becomes lava when it appears on land.
Mantle
The region of the Earth between the crust and core, predominantly made up of magma that moves via convection currents.
Melt
The change of a solid to a liquid as heat is taken in from the environment.
Migration
Movement of organisms from one place to another, seasonally or over years, vertically or horizontally in the oceans.
Minerals
Nutrients needed for the survival of living organisms, e.g., calcium and iron.
Navigate
Plotting a course from one place to another.
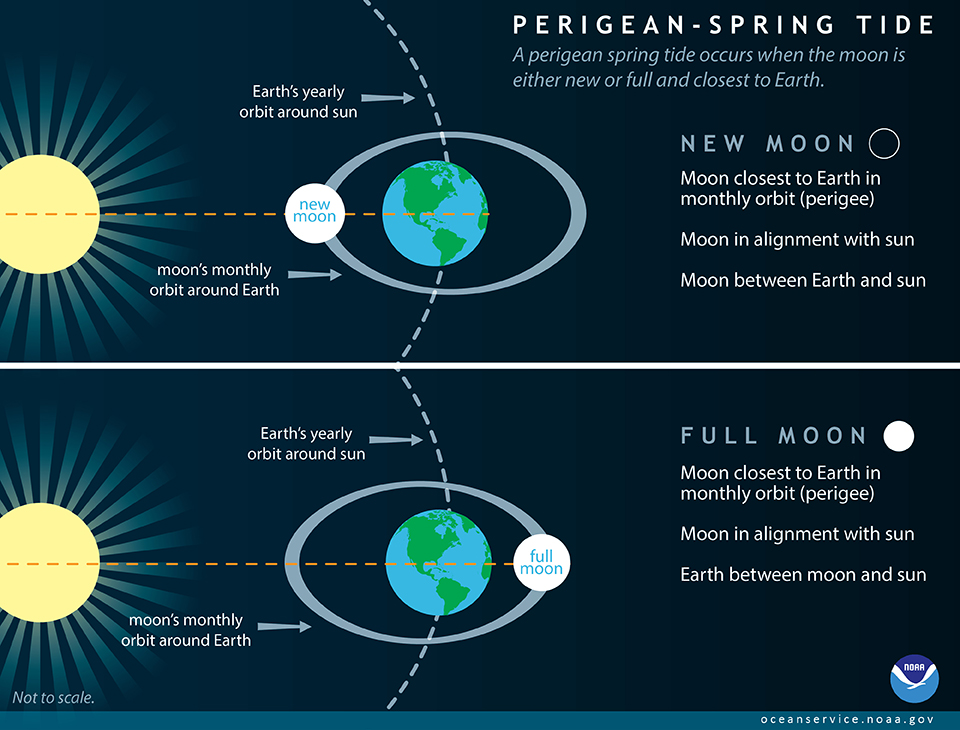
Neap Tides
Tides at the quarter Moons, with lower high tides and higher low tides (less tidal range than Spring Tides).
Ocean Trench
A deep underwater valley formed by subduction.
Orbit
The path that an object takes as it moves around a larger object.
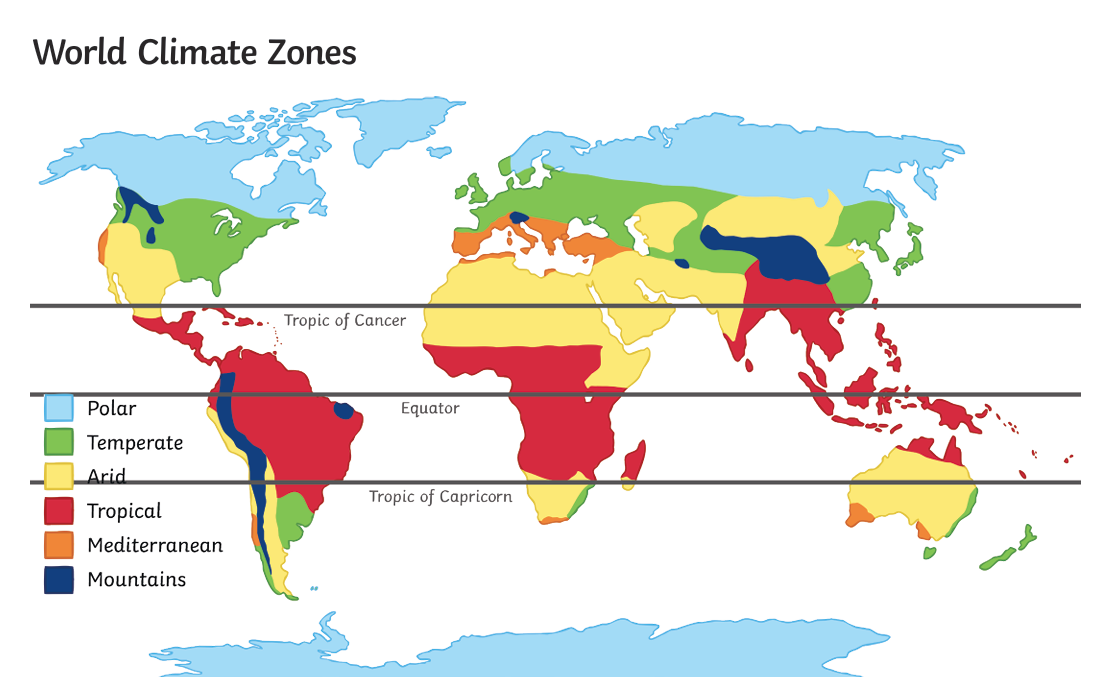
Polar Zones
The areas north of the Arctic Circle and south of the Antarctic Circle.
Prevailing Winds
The usual direction that the wind blows in a particular location.
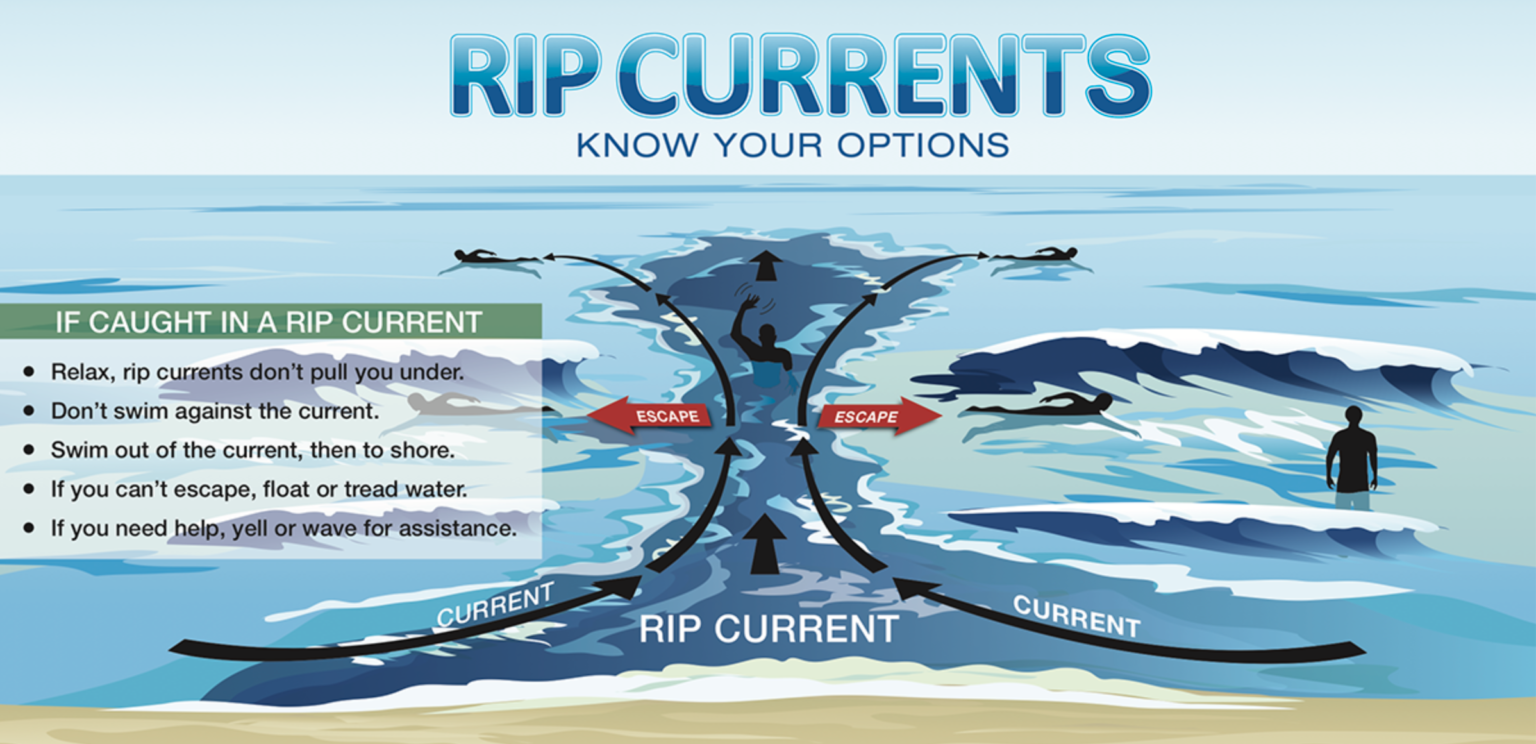
Rip Current
A narrow current moving from the beach to the ocean that can be dangerous.
Satellite
An object that orbits a planet.
Sediment
Small fragments of rock, e.g., sand, silt, gravel.
Species
Organisms that can breed and create viable offspring.
Spring Tides
Tides at new and full Moon, with higher high tides and lower low tides.
Supercontinent
A large landmass that once existed before being broken up by tectonic movement (Pangea).
Tectonic Plates
Large sections of the crust.
Temperate Zones
The areas outside of the tropics or the polar zones.
Theory of Plate Tectonics
Developed in the 1960s, states that the crust is made up of slow-moving plates and explains the movement of the continents.
Tidal Amplitude
Half the distance in height between high and low tides in a particular area.
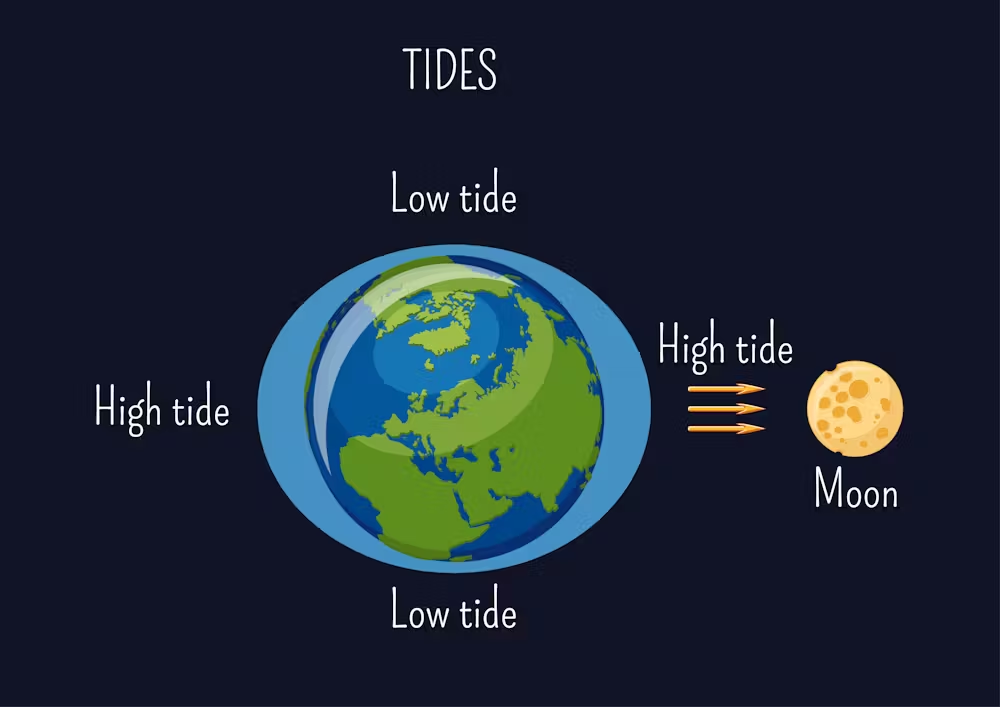
Tides
The regular, cyclical rising and falling of the sea, caused by the gravitational pulls between Earth, Moon, and Sun.
Tourism
Visitors to an area that bring in money.
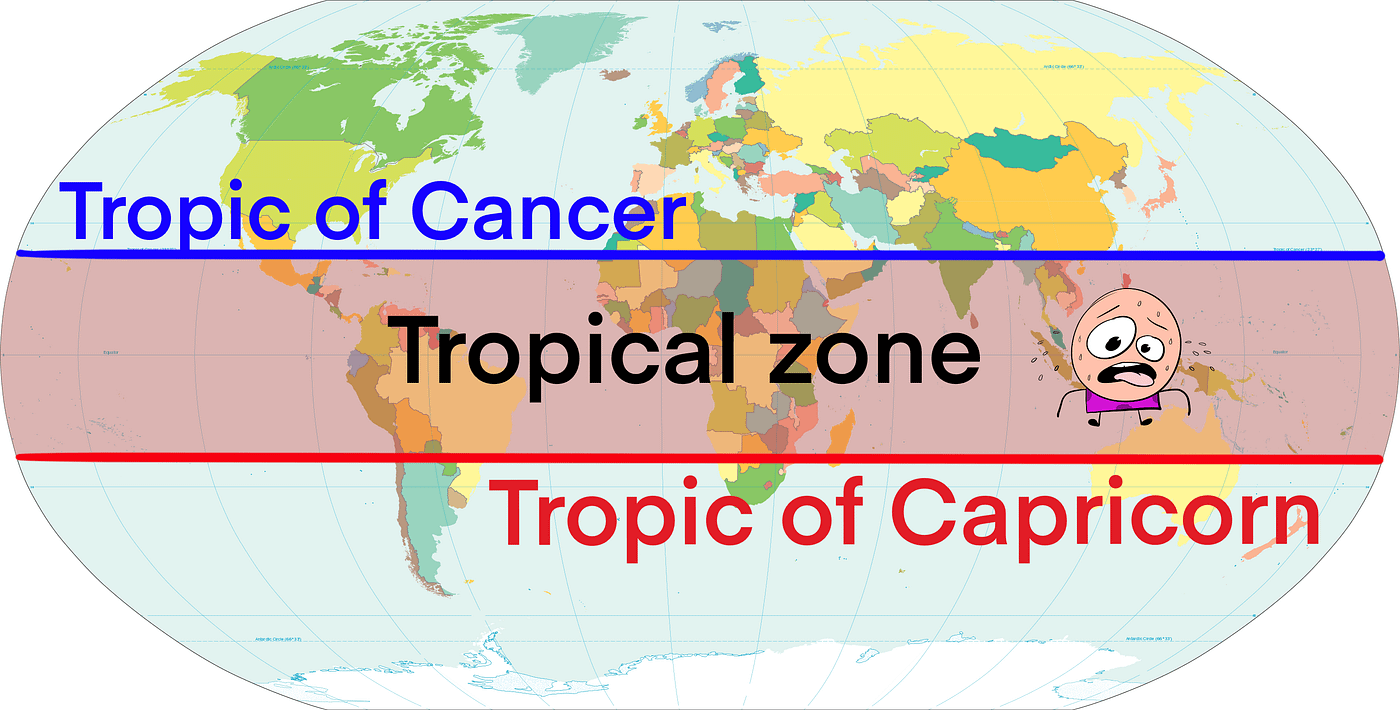
Tropics/Tropical Zones
The area between the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, characterised by hot and wet conditions.
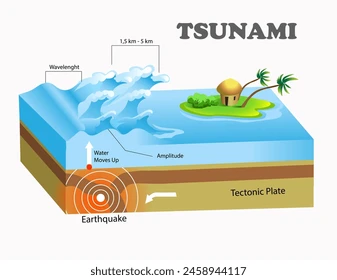
Tsunami
A large wave with long wavelength and moves quickly, caused by displacement of water, often by earthquake or landslides.
Upwelling
Cold, nutrient-rich water that rises from the deep ocean to the surface, beneficial for marine ecosystems.
Viscous
A liquid that flows slowly.
Volcanic Islands
Chains of islands formed by volcanic eruptions, e.g. Lanzarote.
Volcanoes
Parts of the Earth’s crust from which lava erupts.
World Ocean
All of the oceans seen as an interconnected body that circles the Earth.
Hints to remember tectonic plates movements
Constructive= move away from each other
Destructive = move towards each other
Conservative = plates slide against each other