Topic 6: Estimating time of death I (temperature + rigor mortis)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What are the key changes to a body once it’s dead?
Decrease in body temperature
Rigor mortis
Decomposition
Why does the body temperature decrease after death?
As exothermic reactions such as respiration stop, this means the body temperature will begin to decrease.
How is core body temperature measured?
Through the rectum or through an abdominal stab with the use of a long thermometer
What is the average internal temperature of a human body?
37 Celsius
What type of curve does the cooling of the body follow?
Sigmoid curve
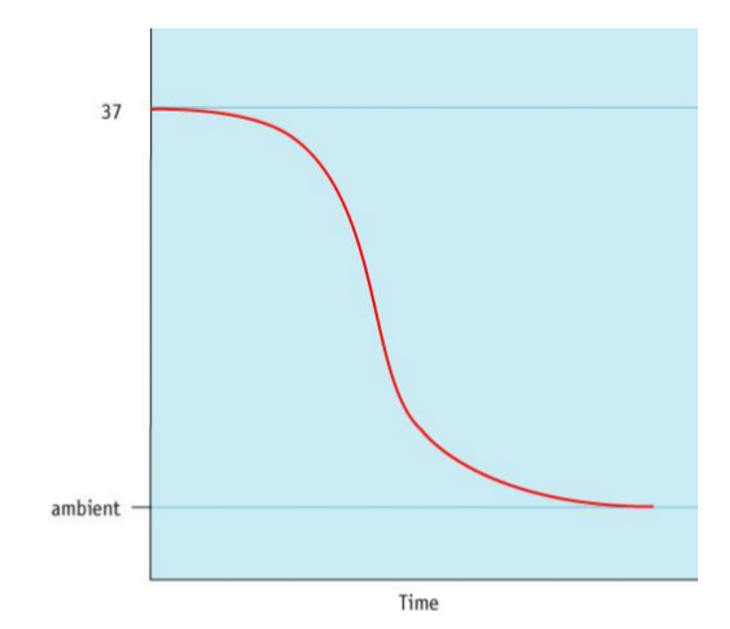
Describe the process of algor mortis?
Metabolic reactions slow down and eventually stop, causing body temperature to fall until it is equal to the ambient temperature.
Why does body temperature decrease slowly at first?
As there is still some heat being generated due to ongoing chemical reactions (specifically exothermic reactions), however, over time these reactions will no longer linger as organs will gradually cease to function
Rate of cooling = proportional to difference in temperature of surroundings and body (greater difference → increased rate of cooling)
What are factors that can affect rate of decrease in body temperature?
Body size
Posture
Clothing
Wind conditions
How does body size affect the rate of decrease in body temperature?
The bigger the body (smaller surface to volume ratio), this means they lose less heat because less surface area is exposed relative to their volume
More cells which means more metabolic reactions will be occurring as higher metabolic rate
Which as a result will decrease the rate of cooling of a dead body
How does posture affect the rate of decrease in body temperature?
Surface area exposed will vary depending on the posture of the dead body, the greater the surface area exposed the faster the rate of decrease in body temperature.
How does clothing affect the rate of decrease in body temperature?
More clothing → greater insulation → lower rate of decrease in body temperature
How do wind conditions affect the rate of decrease in body temperature?
The more intense the wind conditions, the greater the rate of decrease in body temperature as wind will blow heat away (specifically the heat produced by the body).
How does rain affect the rate of decrease in body temperature?
Evaporation of water droplets on skin → heat energy from the skin used by water droplets to evaporate as water droplets require energy to evaporate → therefore cools faster
How does immersion in water affect the rate of decrease in body temperature?
Increases the rate of decrease in body temperature → heat produced from body due to metabolic reactions is being transferred to water → water conducts the heat better than air
How does temperature of surroundings affect the rate of decrease in body temperature?
The greater difference between body temperature and surroundings, the faster the rate of cooling of the body
What is rigor mortis?
The medical term that is used to describe the stiffening of body muscles after death.
What is rigor mortis caused by?
Lack of ATP.
What happens to the pH of the cells after death?
pH falls
What happens to muscle cells after death?
Muscle cells become oxygen starved and oxygen-dependent reactions stop.
Rigor mortis also will occur
Why is there a lack of ATP after death?
No aerobic respiration (no ATP produced)
Respiration in cells become anaerobic and produces lactic acid
pH of cells fall, inhibiting enzymes, thus inhibiting anaerobic respiration (no ATP produced anymore)
Why does lack of ATP cause stiffening of muscles?
Lack of ATP will cause bonds between muscle proteins to remain fixed in place.
In which size muscles does rigor mortis occur faster in?
In smaller muscles
Why does rigor mortis occur first in smaller muscles before spreading to larger muscles of the body?
Smaller muscles -> store less ATP -> therefore run out of ATP faster
What are two situations in which rigor mortis may set in more quickly?
Starvation → lack of glucose from lack of food → lack of aerobic respiration taking place (glucose is needed) → lack of ATP due to lack of ATP produced from aerobic respiration
Exercise right before death → lack of glucose and oxygen → as muscle cells carried out aerobic respiration → aerobic respiration used to release enough energy for muscles to contract and relax → if exercise is very vigorous, anaerobic respiration takes place, which is less energy efficient → this results in lack of ATP
When does rigor mortis pass?
After about 36 hours.
Why does rigor mortis pass after about 36 hours?
As muscle tissue start to break down as protein cells begin to break down.
After no more than 3 hours what is the temperature an stiffness of the body (on average)?
Temperature: warm
Stiffness of body: not stiff
Between 3-8 hours what is the temperature an stiffness of the body (on average)?
Temperature: warm
Stiffness of body: Stiff
Between 8-36 hours what is the temperature an stiffness of the body (on average)?
Temperature: Cold
Stiffness of body: 8-36 hours