Biology ✿ cells (FULL TOPIC)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
eukaryotic cells (animal and plant cell)
cells which store DNA in a nucleus
prokaryotic cells (bacteria cell)
cells which store DNA as plasmids
state 2 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
prokaryotic cells are smaller
prokaryotic cells store genetic material in a plasmid
what 2 cell structures are only found in the plant cell?
chloroplasts
permanent vacuole
state the function of a nucleus
to control the cell and store genetic material
state the function of a ribosome
to synthesis protein
state the function of cytoplasm
the site where chemical reactions take place
state the function of a cell membrane
controls what subtances enters and leaves the cell by diffusion
state the function of mitochondria
site where aerobic respiration takes place and release energy
state the function of a cell wall
strengthens and supports the cell
state the function of chloroplasts
site where photosynthesis happens
state the function of a permanent vacoule
keeps cell rigid to support the plant
what is a cell wall made up of?
cellulose
specialised cell
a cell that has specific functions and structures so it can carry out a particular job
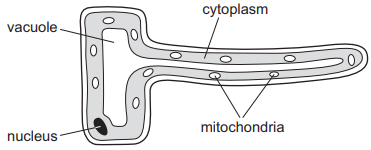
state 2 adaptations and their functions of a root hair cell
thin walls → to allow more water to be absorbed easily by osmosis
long and thin → increases surface area for more mineral uptake
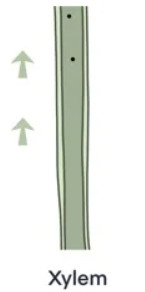
state 3 adaptations and a function of a xylem cell
transports water and minerals from roots to the plant
no end walls between cells to allow water to pass through easily
thick walls lined with lignin to support the plant
cells are dead and hollow allows water to pass through easily
transpiration
The evaporation of water from leaves
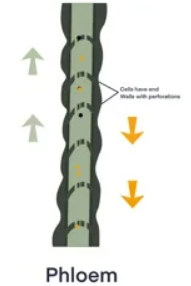
state 2 adaptations and their functions of a phloem cell
sieve tubes between cells → allow dissolved sugars to move through phloem
companion cells → provides energy for active transport of sugars out of phloem
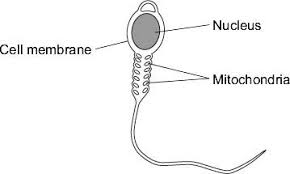
state 2 adaptations and their functions of a sperm cell
long tail → allows sperm to swim to egg
enzymes in the head → allows sperm to fertilise the egg
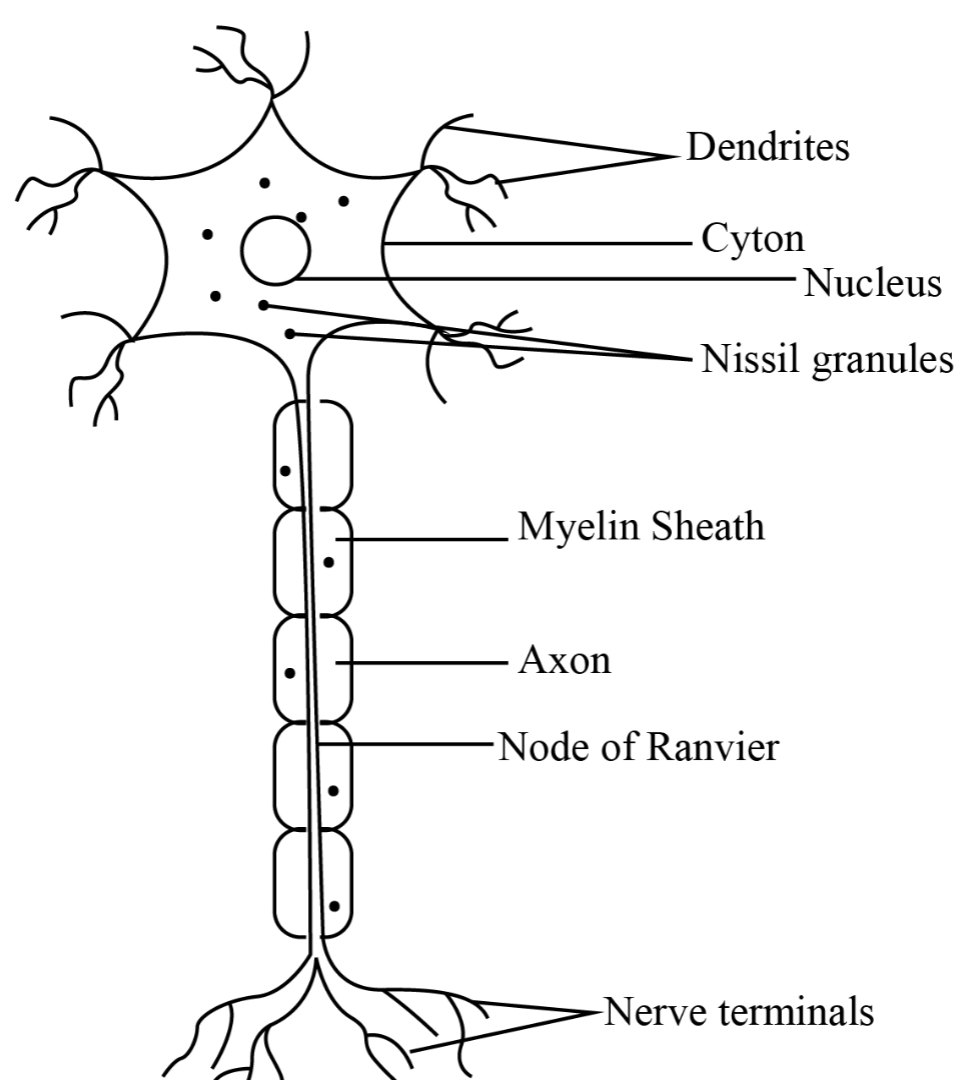
state 2 adaptations and their functions of a nerve cell
long axon → to carry electric impulses over long distances quickly
myelin sheath around axon → insulates axon to speed up transmitting of electric impulses
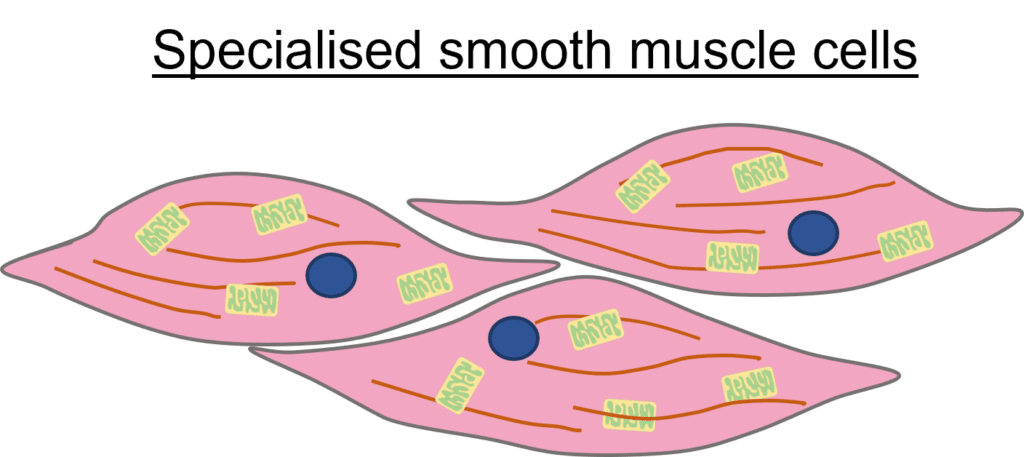
state 2 adaptations and their functions of a muscle cell
a lot of mitochondria → to provide energy for muscle movement
long and can contract → allows muscle to move
differentiation
the process of unspecialised cells forming different types of specialised cells to carry out specific jobs
when does differentiation happen in an animal?
early stage of development
when does differentiation happen in a plant?
throughout life
resolution
the ability to distinguish between 2 objects (the smallest measurment)
magnification
how much bigger the image is than the actual object
why are electron microscopes better than light microscopes?
they have a greater magnification and resolution which allow more subcellular structures to be seen
equation for magnification
size of image / size of real object
nucleus
contains chromosomes made of DNA molecules
chromosomes are found __ ____
in pairs
why is mitosis important?
helps with growth, repair and asexual reproduction
what are the 3 stages of the cell cycle
DNA replicates and forms 2 copies of each chromosome and it’s subcellular structures
mitosis; each set of chromosomes are pulled to each end of cell and nucleus divides to form two new nuclei
cytoplasm and cell membrane splits, 2 genetically identical daughter cells are formed
what happens during mitosis?
chromosomes are duplicated and are pulled apart
nucleus divides and forms 2 new nuclei
forming 2 genetically identical daughter cells
where does mitosis occur?
everywhere in the body except in the gametes
stem cell
undifferentiated cells that can form specialised cells
where are stem cells found in a human and in a plant?
human
embryos
bone marrow
plants
meristem tissue
what are stem cells from adult bone marrow only used for
blood cells
what are stem cells from embryos used for?
to treat diabetes and paralysis
what are stem cells from plants/ meristems used for?
to preserve rare species and to produce more disease resistant crops
state 1 advantage and 2 disadvantages of embryonic stem cells
advantage
not rejected by body
disadvantage
risk of viral transmission
ethical/ religious objections
diffusion
the movement of gas particles down a concentration gradient
give 3 factors which affect the rate of diffusion
difference in concentrations
temperature
surface area of membrane
how can you give an object a larger surface area to volume ratio?
cut it up in smaller pieces
state 4 ways the small intestines are adapted for absorption (exchanging materials)
villi provide a larger surface area
villi are one cell thick to allow faster diffusion
good blood supply maintains concentration gradient
long for more absorption time
state 4 ways the lungs are adapted for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide with the blood
alveoli are one cell thick allow faster diffusion
alveoli provides large surface area
moist surface allows gases to diffuse
continually ventilated to bring in more oxygen and maintains concentration gradient
state 3 ways fish gills are adapted for uptake of oxygen from the water
thin layer allows faster diffusion
good blood supply maintains concentration gradient
well ventilated to bring in more oxygen and maintains concentration gradient
state 3 ways plant roots are adapted for uptake of water from the soil
root hair cells increase surface area
hairs are one cell thick for quick diffusion
a lot of mitochondria to transfer energy for active transport
state 3 ways plant leaves are adapted for gas exchange
flat and thin for quick diffusion
air spaces in spongey mesophyll allow gases to move easily
stomata allow gases in and out leaf
osmosis
the movement of water from a dilute to concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane
active transport
movement of substances across a cell membrane against the concentration gradient
why is active transport necessary in plants?
allows mineral ions to be absorbed into plant root hairs from very dilute solutions in the soil
this allows plant to grow healthy
why is active transport necessary in the gut?
allows sugar molecules to be absorbed from lower concentrations in the gut into the blood
sugar molecules are used for cell respiration
which transport process require energy?
active transport
which transport processes dont require energy?
diffusion and osmosis
Transpiration stream
The continuous flow of water from the roots to the leaves through the xylem
What process occurs in the xylem?
Translocation
What process occurs in the phloem?
Transpiration