PLTW PBS Principles of Biomedical Science 3.1.4-3.1.7 Quiz WCHS Mrs.McCormick
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Etiology (Ex. Flu)
The cause of a disease or a condition (Ex. Influenza Viruses)
How are bacterial species named?
By their genus and species; The first letter of the genus is always capitalized, and both names are either italicized or underlined
What do microbiologists do?
Investigate the growth, structure, development, and other characteristics of microorganisms like bacteria
What is used to culture bacteria?
A petri dish and clear plastic container
What does agar provide for bacteria?
Nutrients and water
Why isn’t a valuation of colony morphology enough to identify the agent responsible for causing a disease?
Because different types of bacteria can have extremely similar looking colonies
Aseptic Technique
The practice and/or process of preventing contamination
Bacterial Colonies
Bacteria grows in groups called colonies, on a growth media called agar
Broth
A clear, nutrient-rich liquid used to culture bacteria, usually in tubes
Morphology
The study of the internal structure of an organism
Binary Fission
A type of asexual reproduction typically observed in prokaryotes and a few single-celled eukaryotes
Gross Morphology
Collective structure of an organism as a whole as a general description of the form and structure of an organism
Margin
Describes the shape of the edge of the colony when magnified
Isolation Streak
The process by which bacteria are streaked onto a plate to form isolated colonies
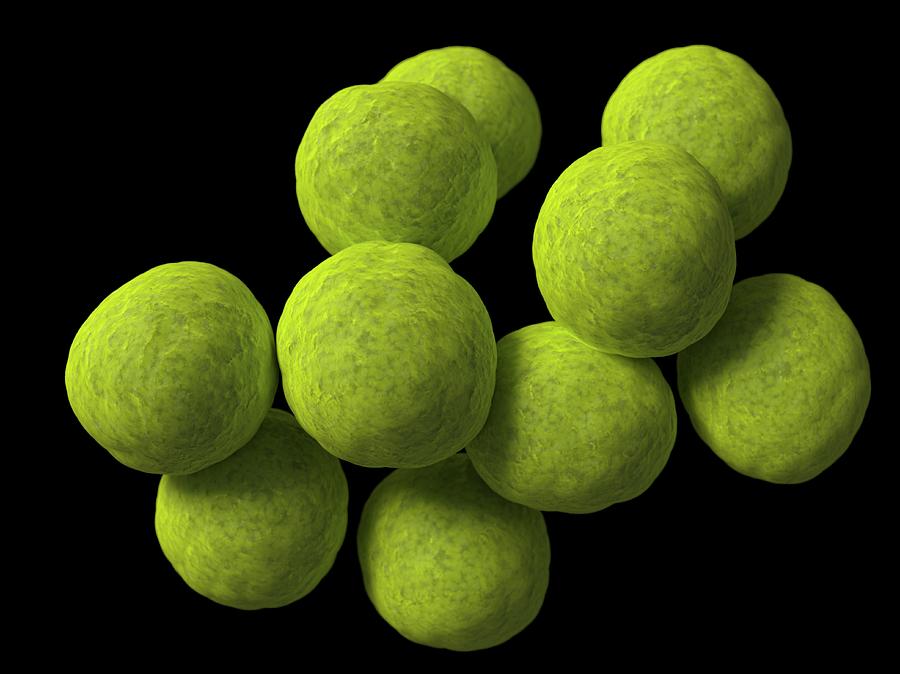
What kind of bacterial cells are these?
Coccus
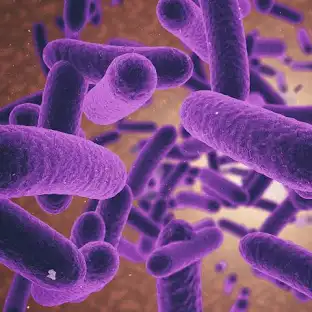
What kind of bacterial cells are these?
Bacillus
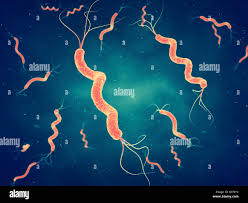
What kind of bacterial cells are these?
Spirillum

Diplococci
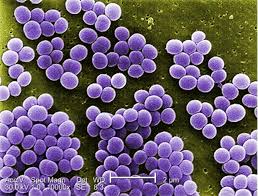
Staphylococci
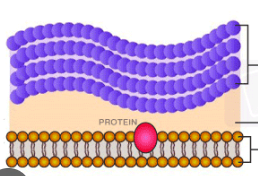
Gram positive or Gram negative?
Gram positive
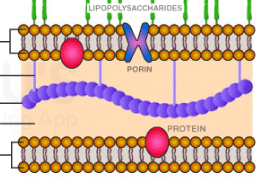
Gram positive or Gram negative?
Gram negative
What makes Gram negative more dangerous?
They have an additional layer outside of their petidoglycan layer that can have toxic effects. It can induce a serious immune response that can lead to septic shock
Coccus
Any spherically, or generally round, bacterium; plural is cocci
Bacillus
A rod shaped (cylindrical) bacterium; plural is bacilli
Spirillum
A spiral shaped bacterium
Cell Morphology
The study of the shape, structure, and appearance of cells
Peptidoglycan
A unique, mesh-like polymer composed of sugars and amino acids that forms the cell wall of most bacteria, providing structural support and protection against osmotic pressure
Gram’s Stain
A staining technique used to characterize the cellular structure of Gram positive bacteria. Gram negative bacteria have a lipopolysaccharide coating, which typically makes them more pathogenic
Hans Christian Gram
Microbiologist who discovered that certain stains were preferentially taken up and retained by bacterial cells
Septic Shock
Comes from a serious immune response. It can cause death due to a drop in blood pressure
Decolorization
Ethyl alcohol is applied to the cells. In Gram positive cells, water leaves the cell, blocking the CVI from leaving. In Gram negative cells, the outer membrane gets dissolved and the CVI can leave the cell
Counterstain
Safranin is applied to the cells. In Gram positive cells, safranin penetrates the cell, but is not seen. In Gram negative cells, safranin stains the cell a reddish-pink color
Morbidity refers to…
Having a disease or a symptom of disease, or the rate of disease within a population
Mortality refers to…
The number of deaths in a certain group of people in a certain period of time
What is the purpose of a streak plate?
To isolate single colonies
Is Staph aureus gram negative or positive?
Positive
Does bacteria require a host in order to reproduce?
No
Small circular pieces of DNA that can be exchanged between bacteria; humans don’t have them
Plasmids