L22 Why Sequence the Human Genome?
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about sequencing the human genome.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Human Genome Project Aims
Identify all human genes and their roles, analyse genetic variation among humans, sequence the genomes of several model organisms.
Genome
Complete set of DNA of an organism, including all its genes
Nuclear DNA
22 Autosomes, X and Y; Half from each parent; <20,000 genes
Mitochondrial DNA
Many copies of a single, circular molecule; All from mother; 37 genes
Key Findings of the Human Genome
Fewer genes than expected (20,000), Less than 2% of our genome codes for proteins, The genome is dynamic, humans are 99.9% similar at sequence level. Most human genes relate to those of animals.
Human protein coding genes and roles
We still don’t know what many (20%) of these proteins code for. 20% introns, 2% exons
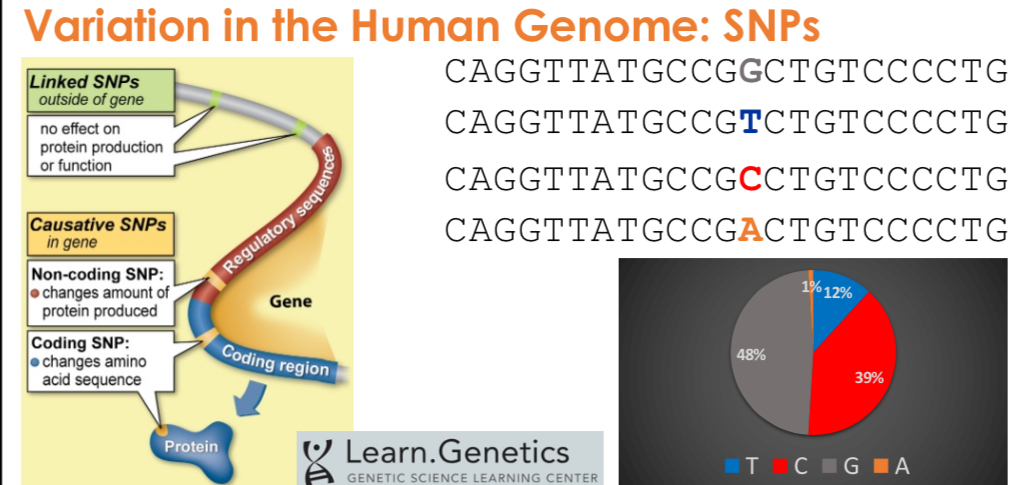
SNPs (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms)
Sites in the DNA that commonly vary within populations. Common around 1 every 300 nucleotides, mostly inherited from parents,
Why variation is important (genotyping)
Can be used to diagnose genetic disease, to determine which drugs will work best in a patient, to determine our close relatives, or our species’ origins.
Variation and SNP’s
SNP’s cause variation in human genome, and different variants may be differently abundant. Eg A is rare and G is common.
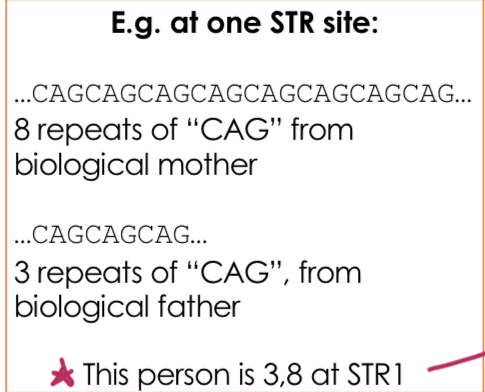
STRs (Short Tandem Repeats)
Repeats of 2-5 nucleotides, found in specific regions of the genome and used to create genetic profiles. We inherit 2 alleles (one from each parent) which can be different lengths.
InDels (Small insertions or deletions)
Second most common variant type in the human genome. Common genetic disease cystic fibrosis is caused by a 3 nucleotide deletion. Can cause frame shift, change in way DNA is read if in protein-coding regions.

CNVs (Copy Number Variations)
Chunks of DNA > 500bp that are present at different amounts relative to a reference genome. Can be deleted or duplicated and span multiple genes.
Human CNV’s
Have 10,000, found within and between genes. Many genes found in CVN are associated with sensory perception and immunity.