ID 2242 (Townsend): Exam 3 Study Guide
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
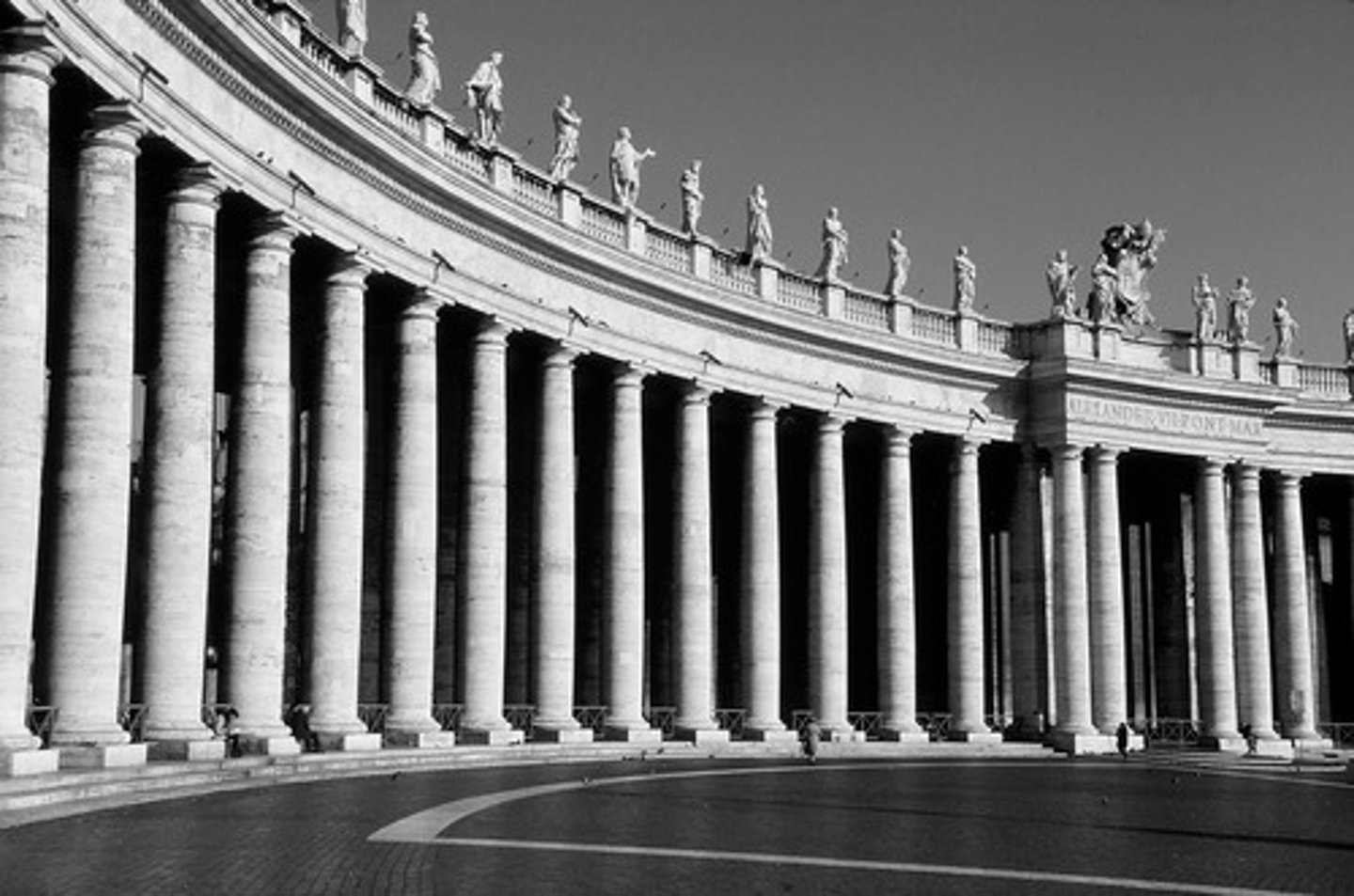
Doric column
Simple columns with no decoration on the capital, often chunky/heavy/weight-bearing.
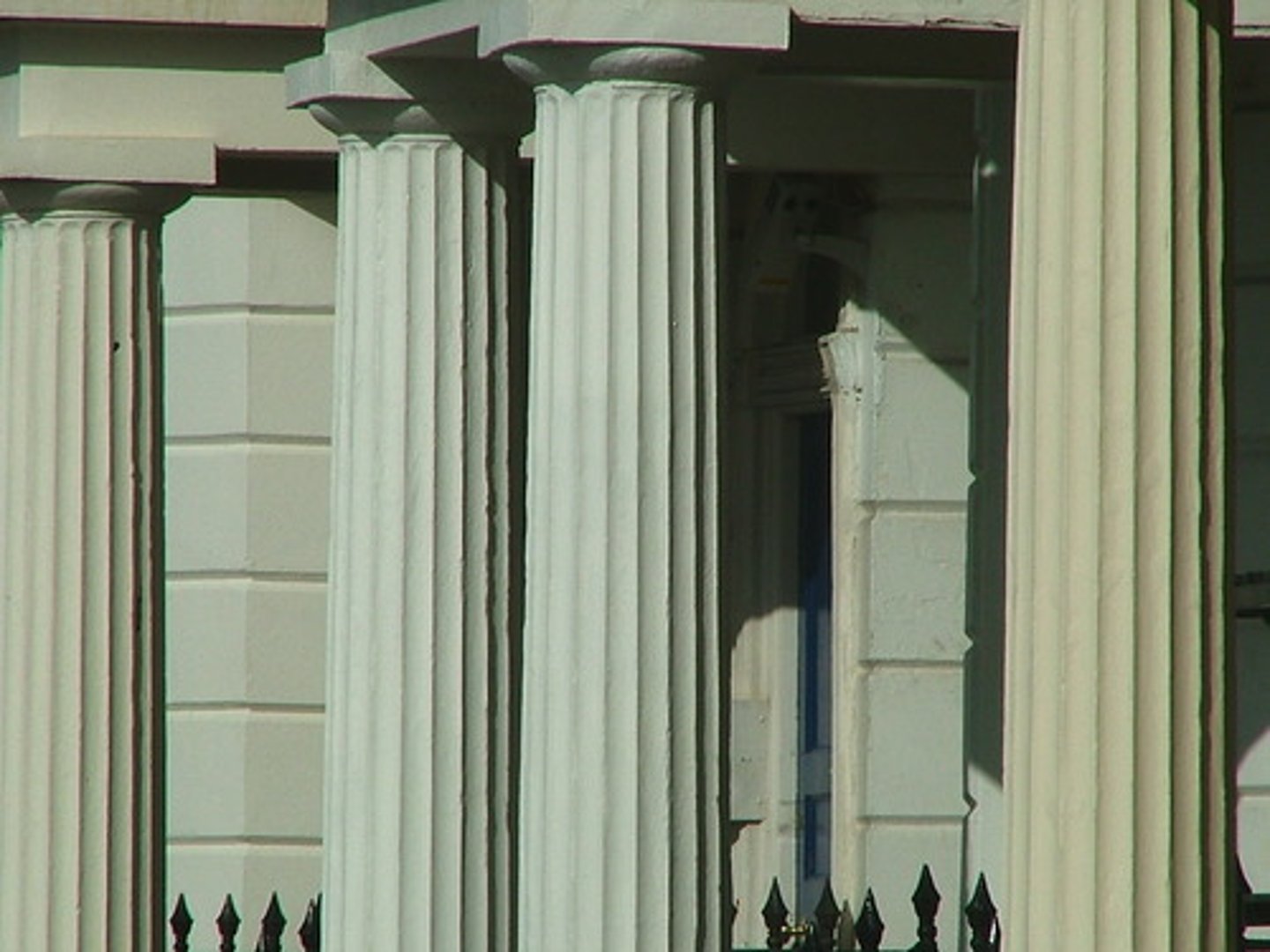

Ionic column
Columns with scrolls (volutes) on the capital. They are also slimmer.
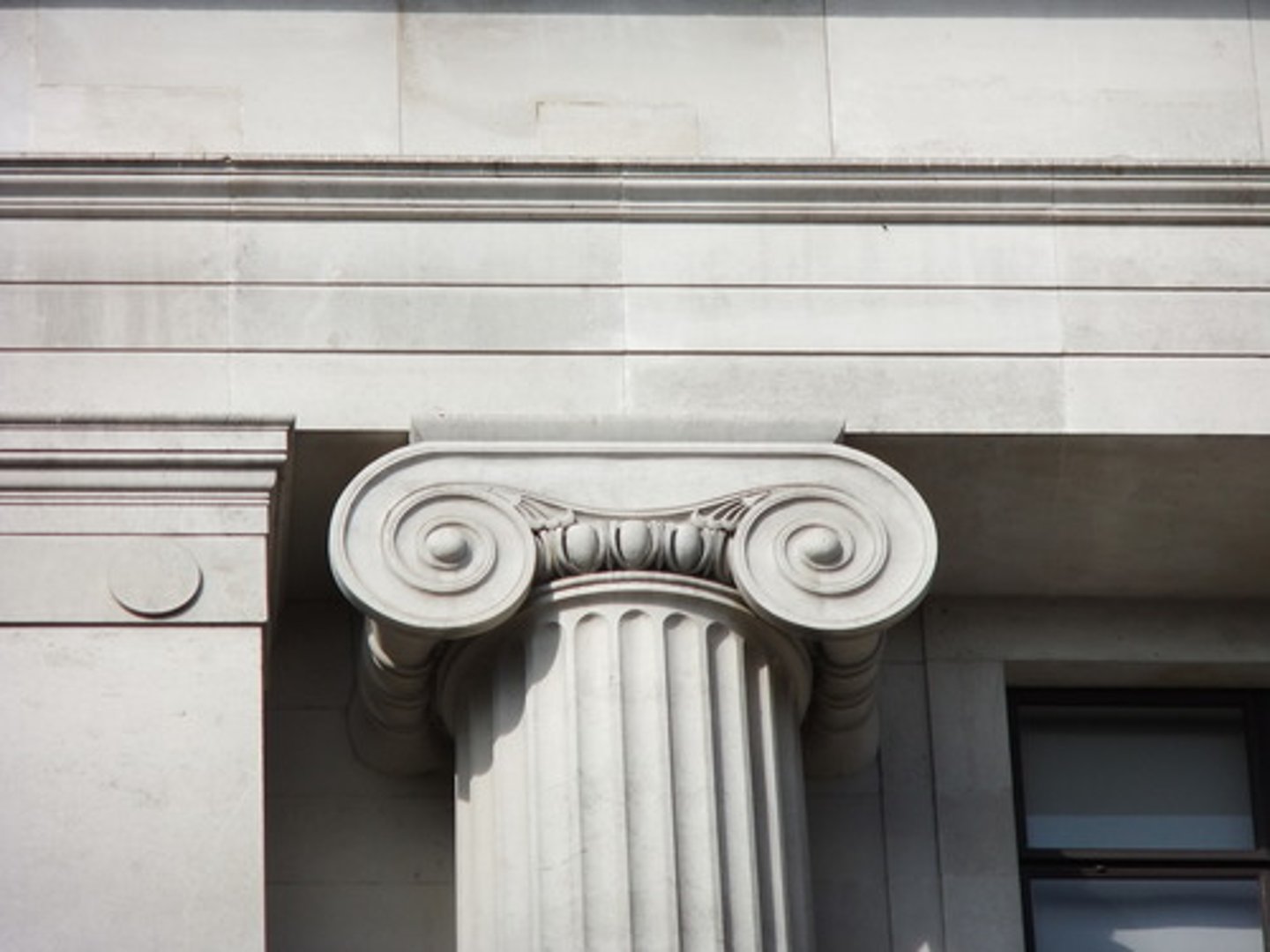

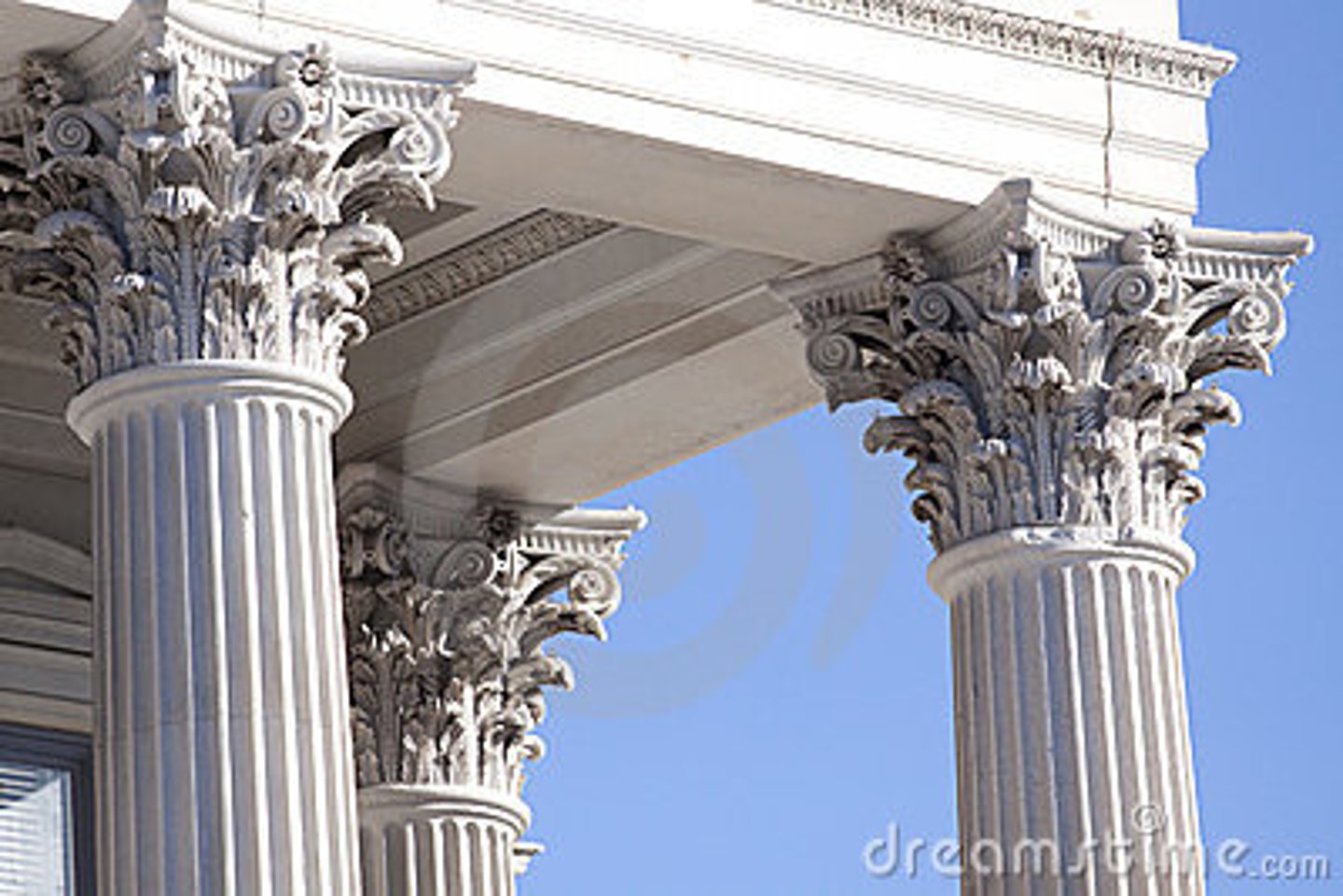
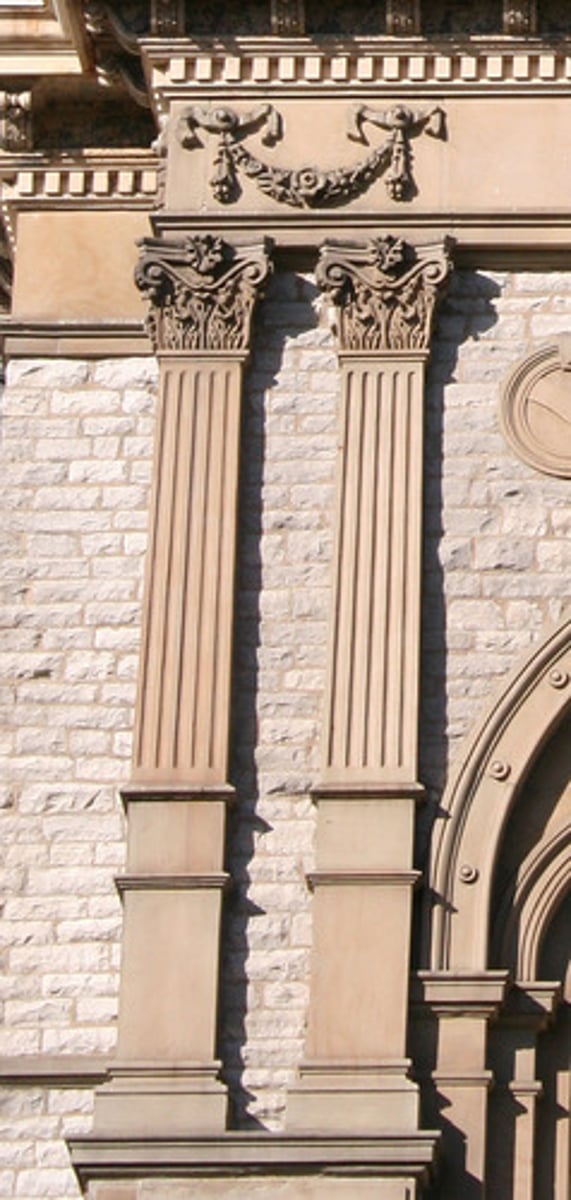
Corinthian column
Columns with decorative and foliate capitals.

Tuscan column
Columns that have a completely smooth length and simple capitals.

Colonnade
A row of columns.

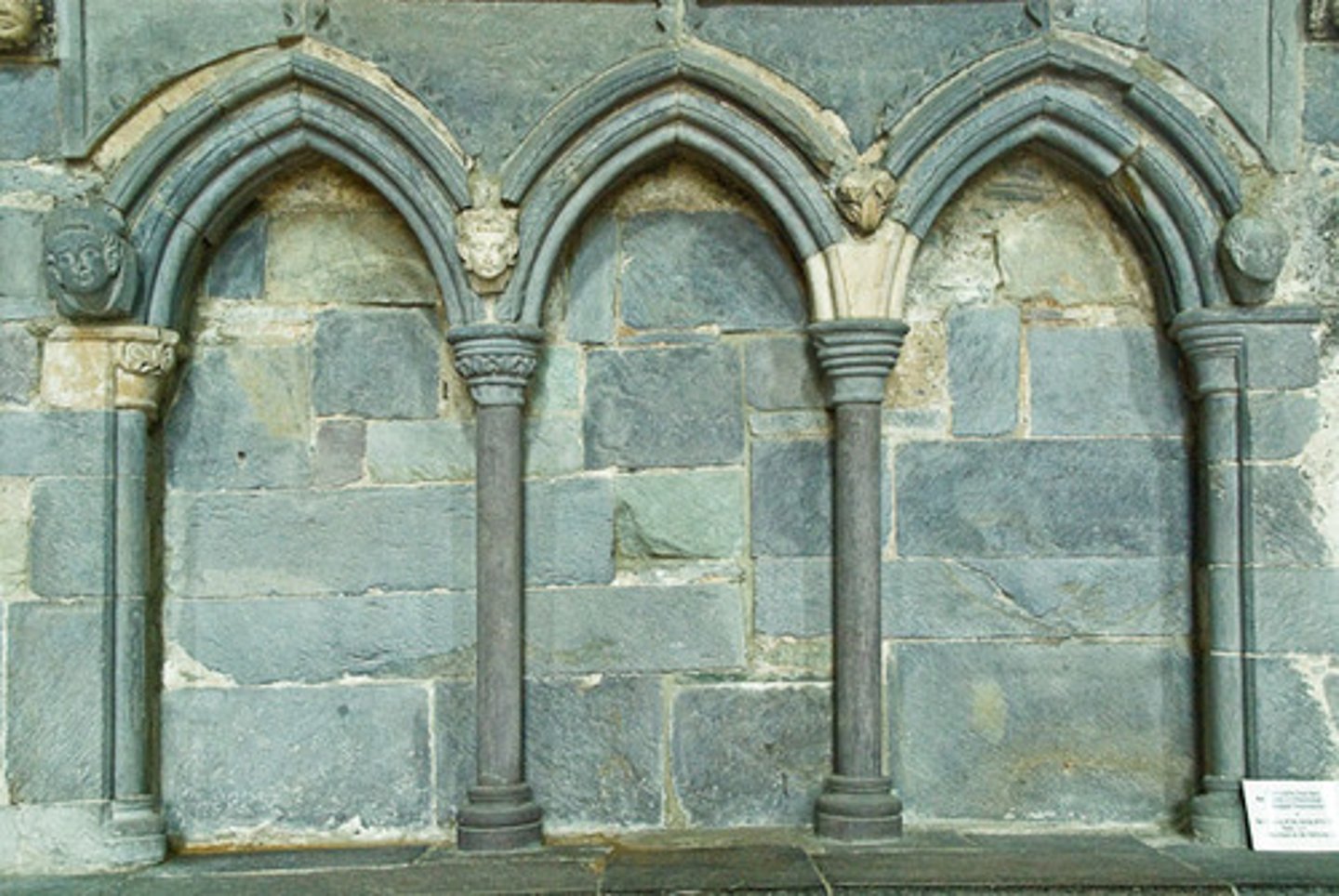
Arcade
A row of arches.

Capital
The top part of a column.
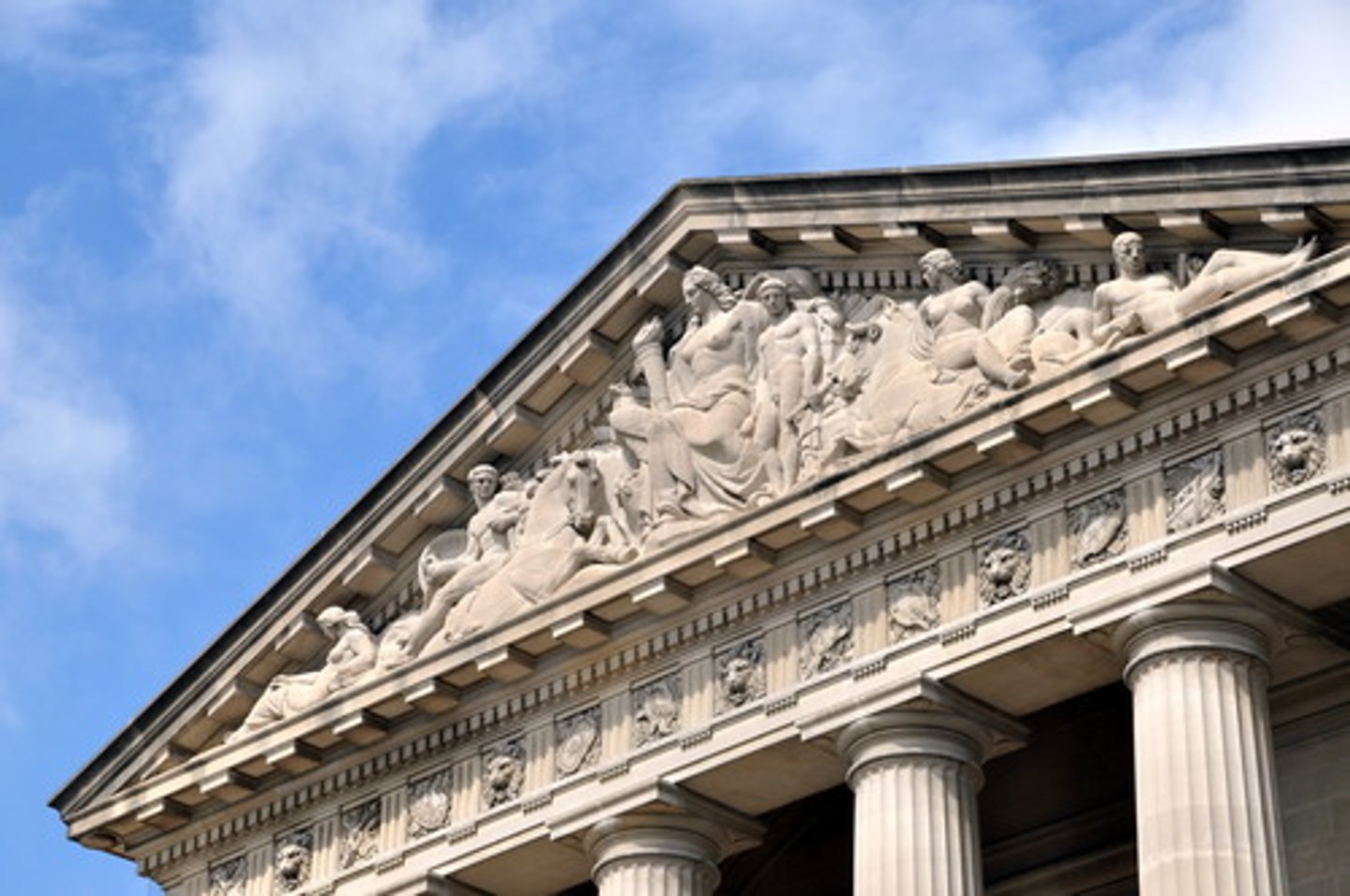
Pediment
The gabled portion of a Greek temple.

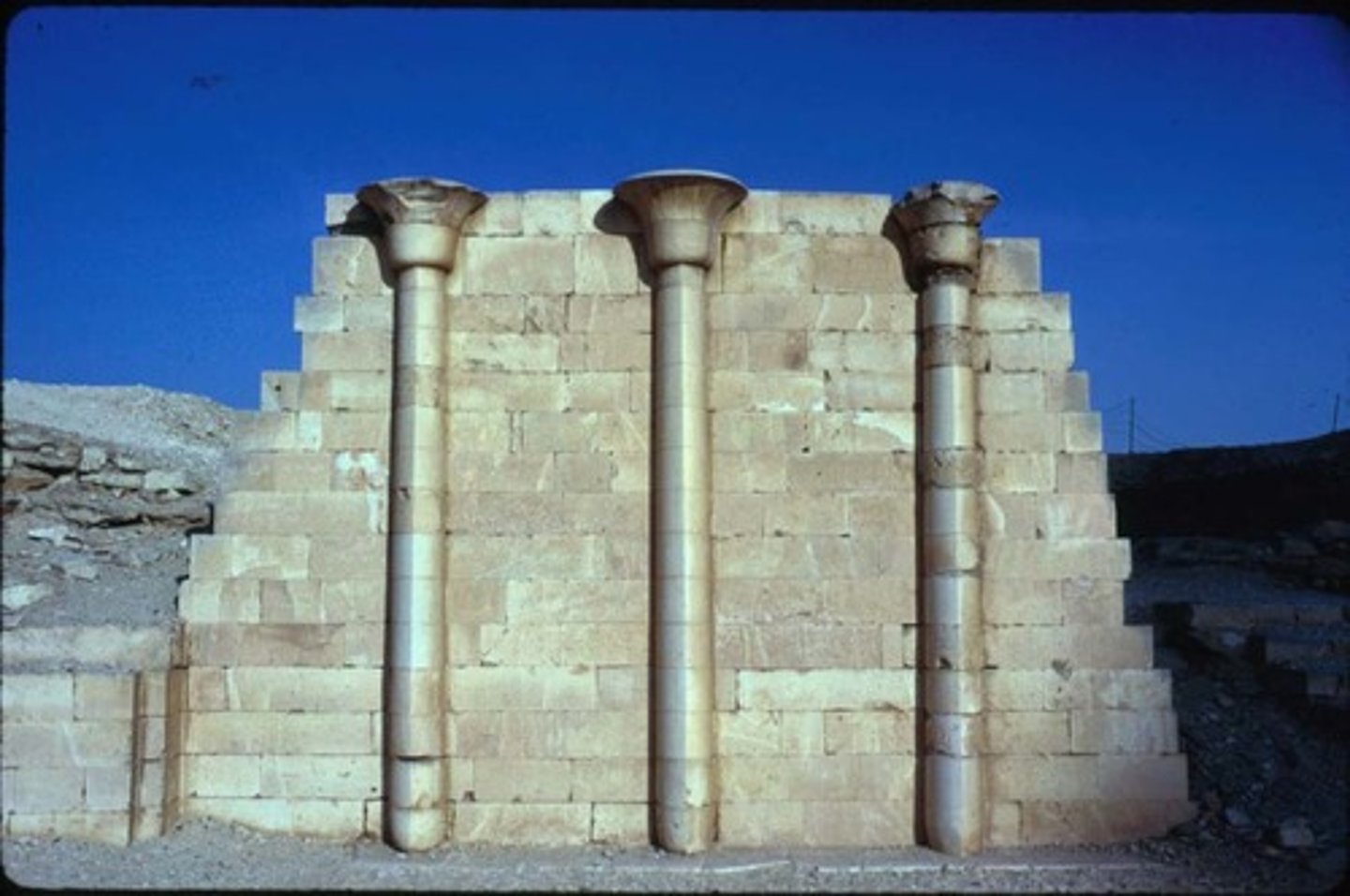
Engaged columns
Columns which jut into / connect to a wall.

Pilaster
Flat columns which are carved out of a wall.

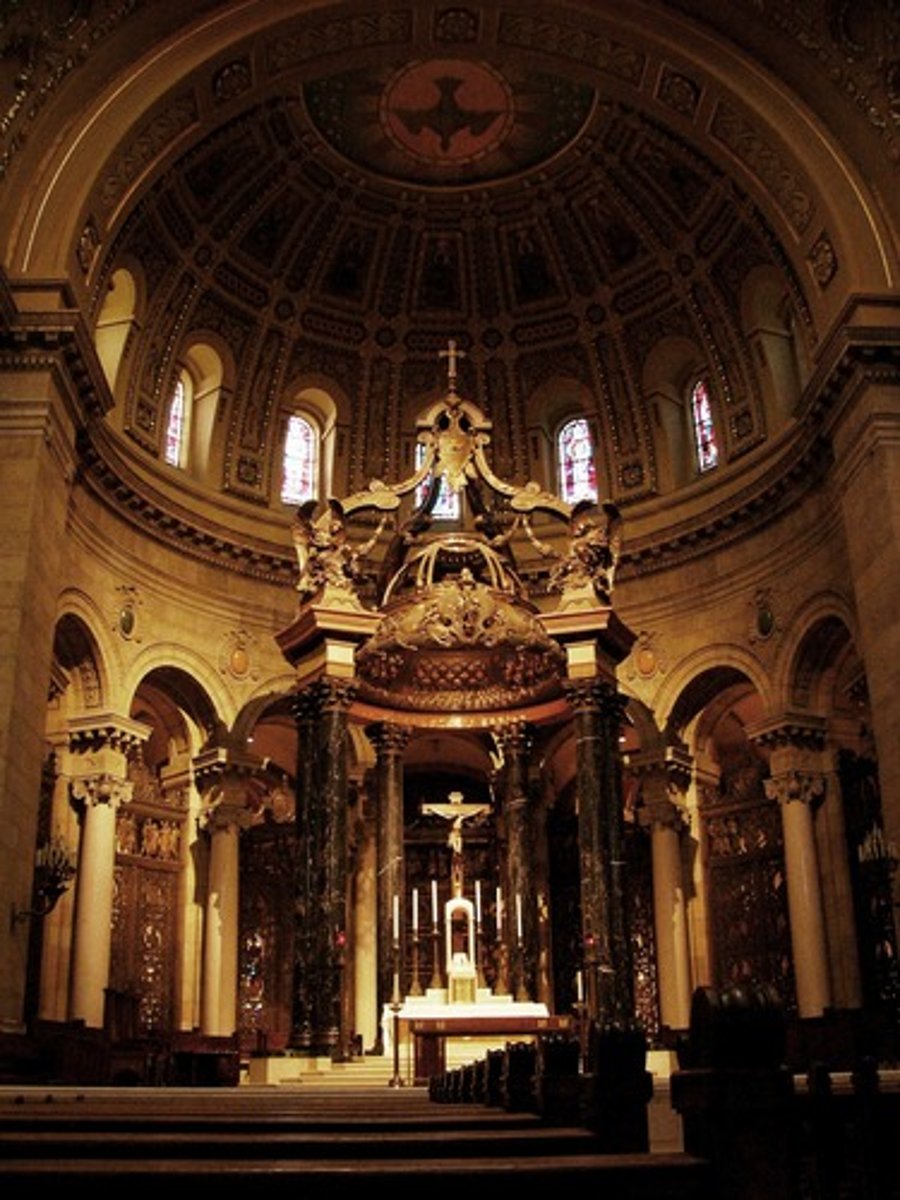
Apse
The part of a church where the main altar usually is.

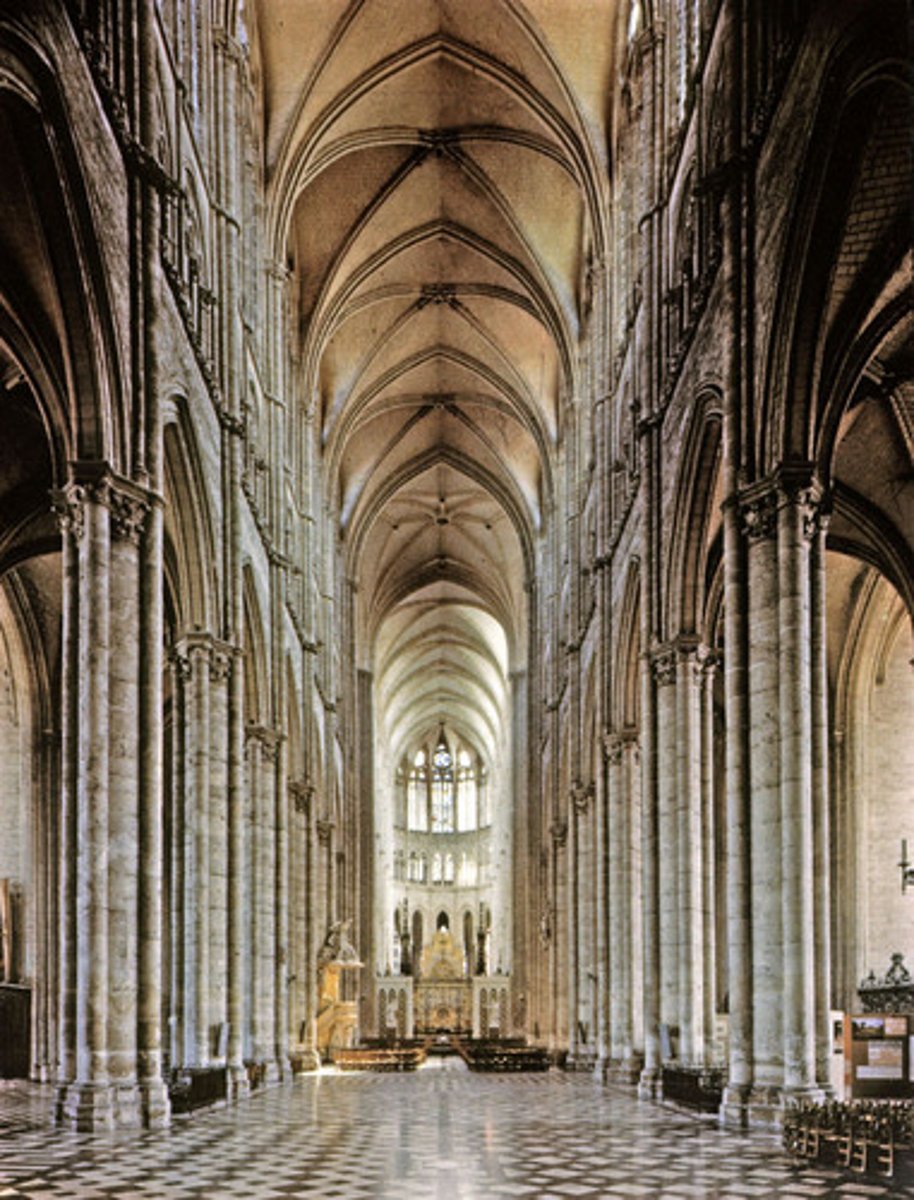
Transept
The part of a church which makes a right angle to the nave, meant to reflect a cross.
Crossing
The part of a church where the nave and transept intersect.
Nave
The main central length of a church, from the front portal to the apse.

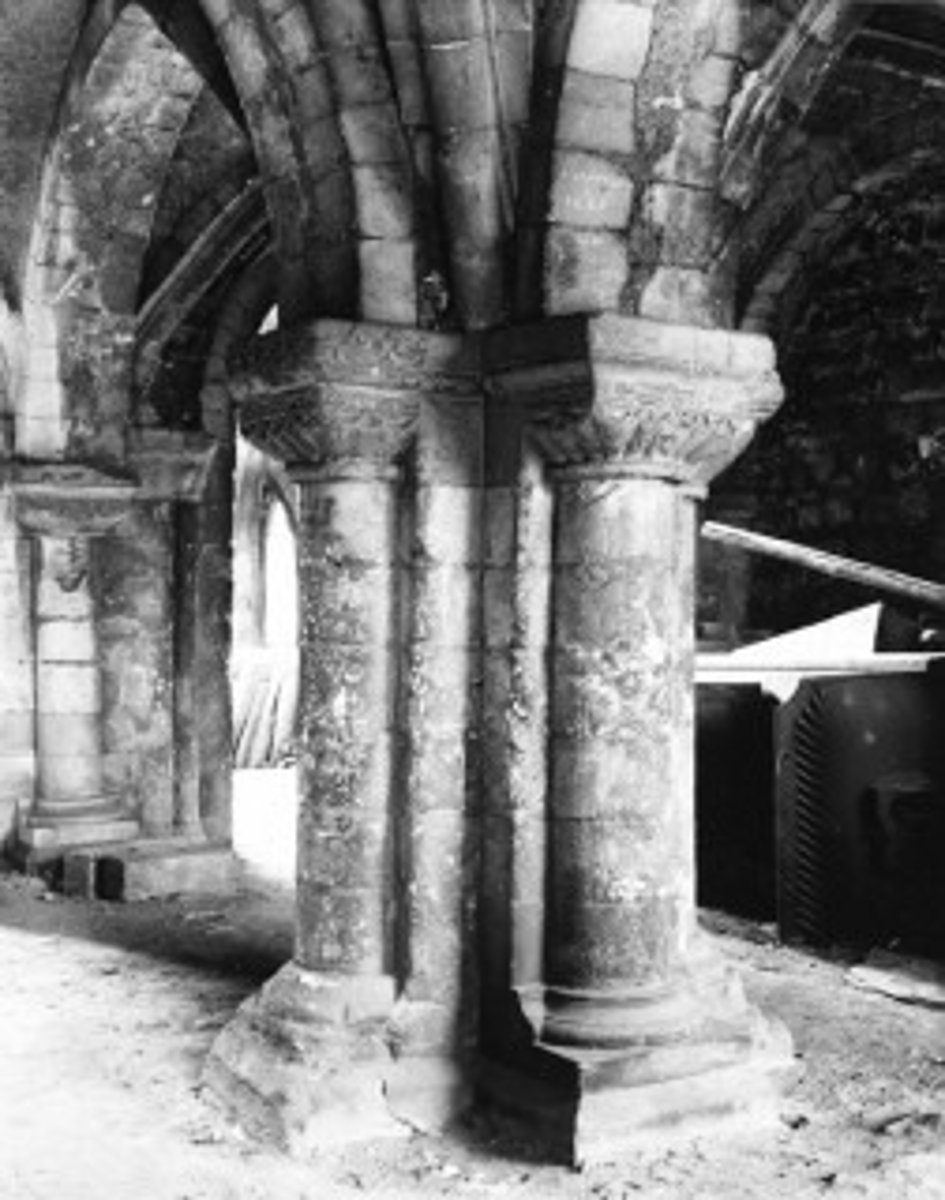
Piers
Large support columns meant to hold up a dome, usually around a square base.

Loggia
A covered exterior gallery or corridor, often on an upper level, sometimes on the ground level of a building.
Pendentive
A triangular segment of a spherical surface, filling in the upper corners of a room, in order to form, at the top, a circular support for a dome.
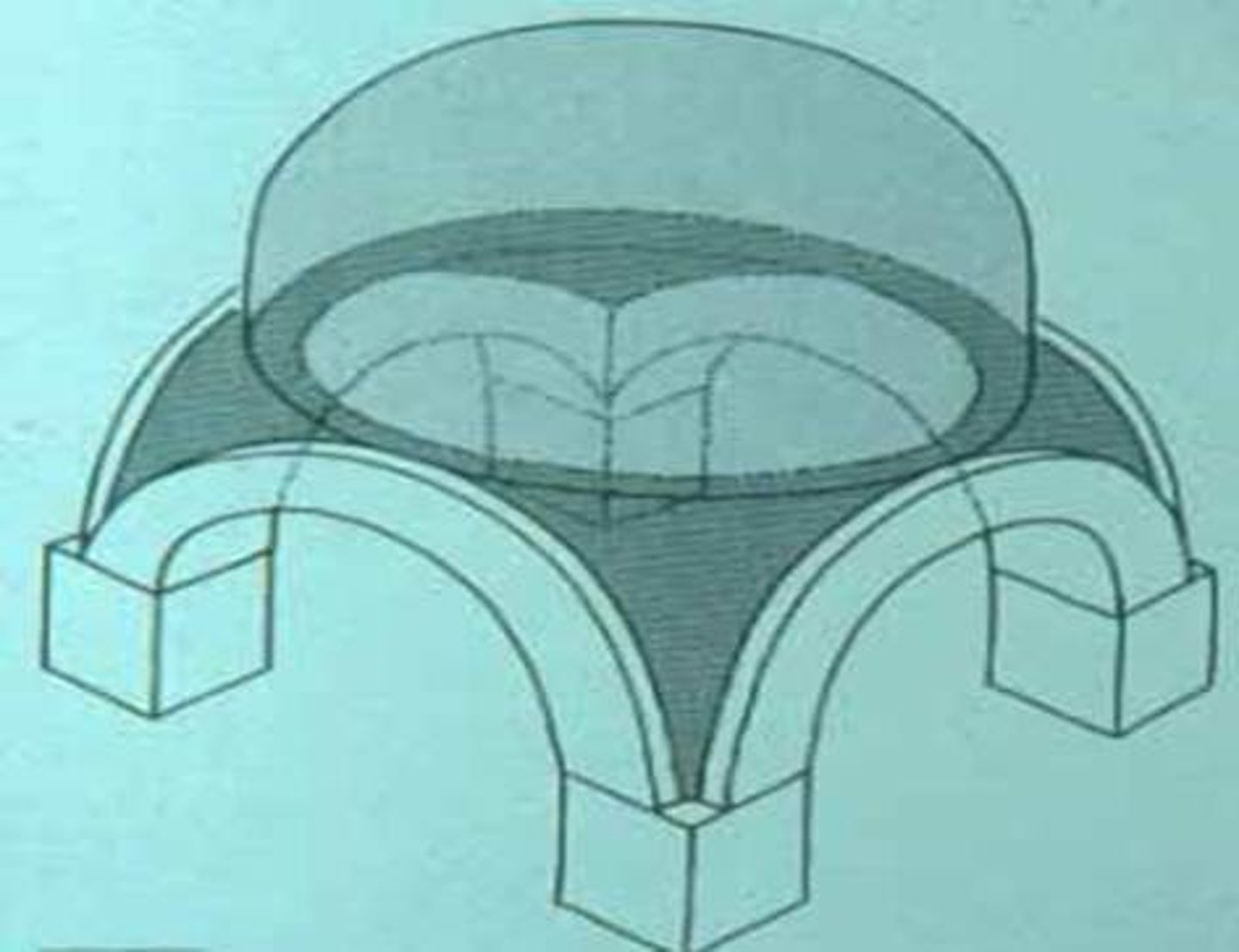
Ambulatory
In a church, the continuation of the aisled spaces on either side of the nave (central part of the church) around the apse.
Radiating chapel
A small, semi-circular chapel that projects out from the area behind the altar of a church.
Tympanum
The semi-circular or triangular decorative wall surface over an entrance, door, or window, which is bounded by a lintel and an arch. It often contains imagery or ornaments.
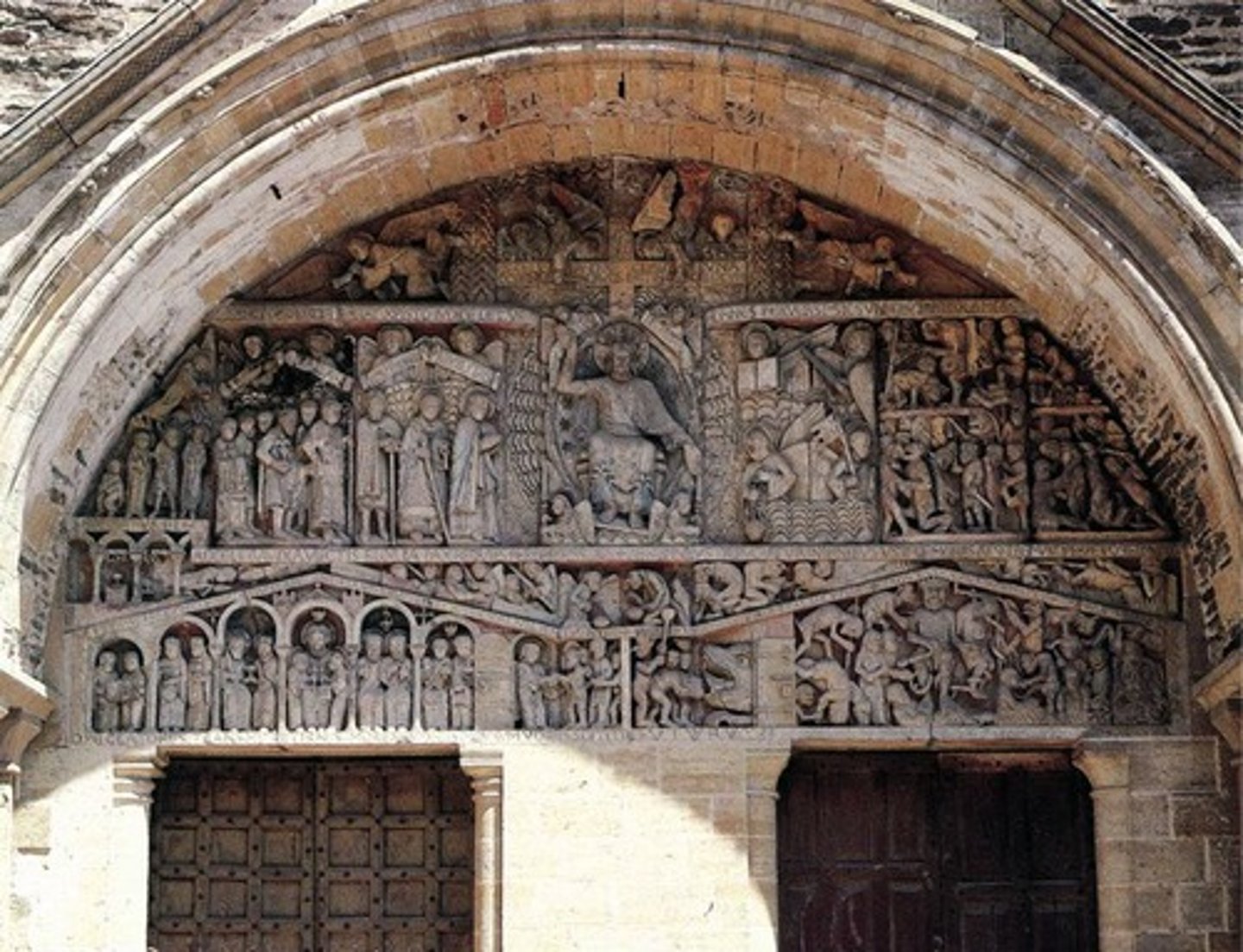

Archivolt
Elaborately carved decorative moldings that run along the curve of an archway.

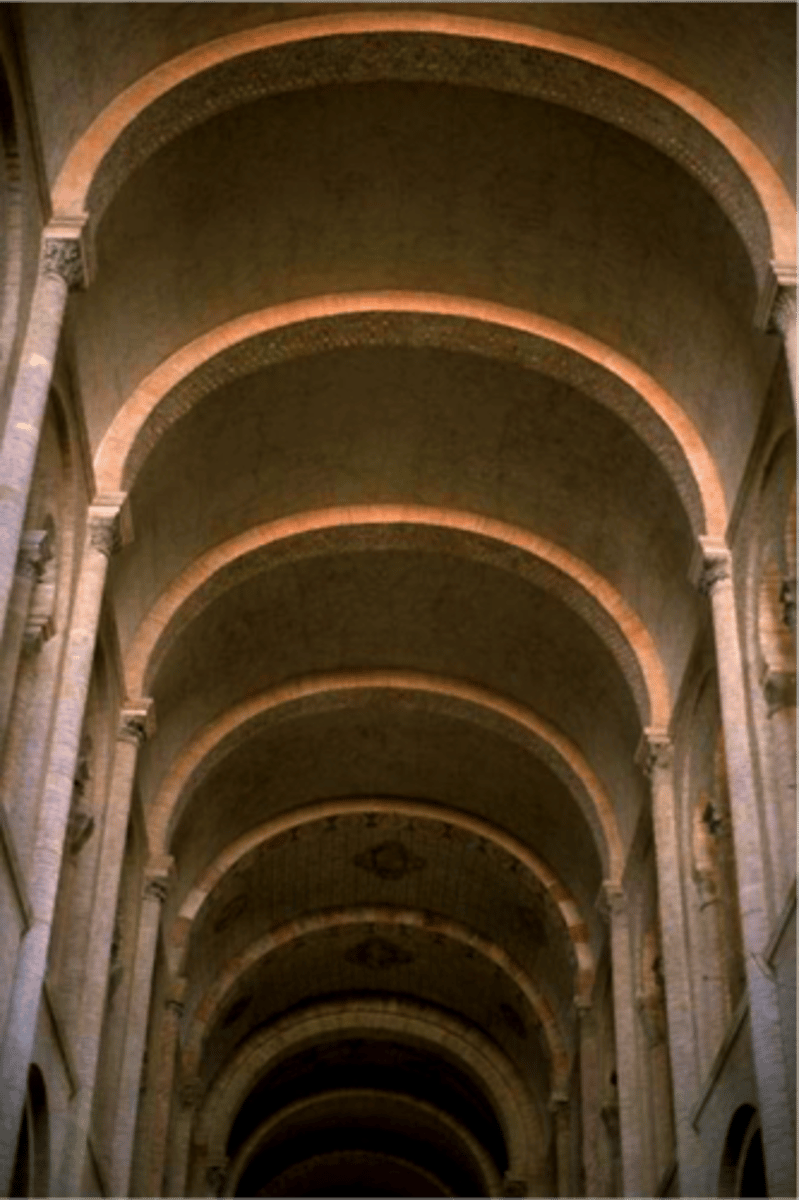
Barrel vault / tunnel vault
A continuous series of arches that creates a semi-cylindrical ceiling or roof structure. It allows for the construction of large, open spaces and distributes weight evenly.

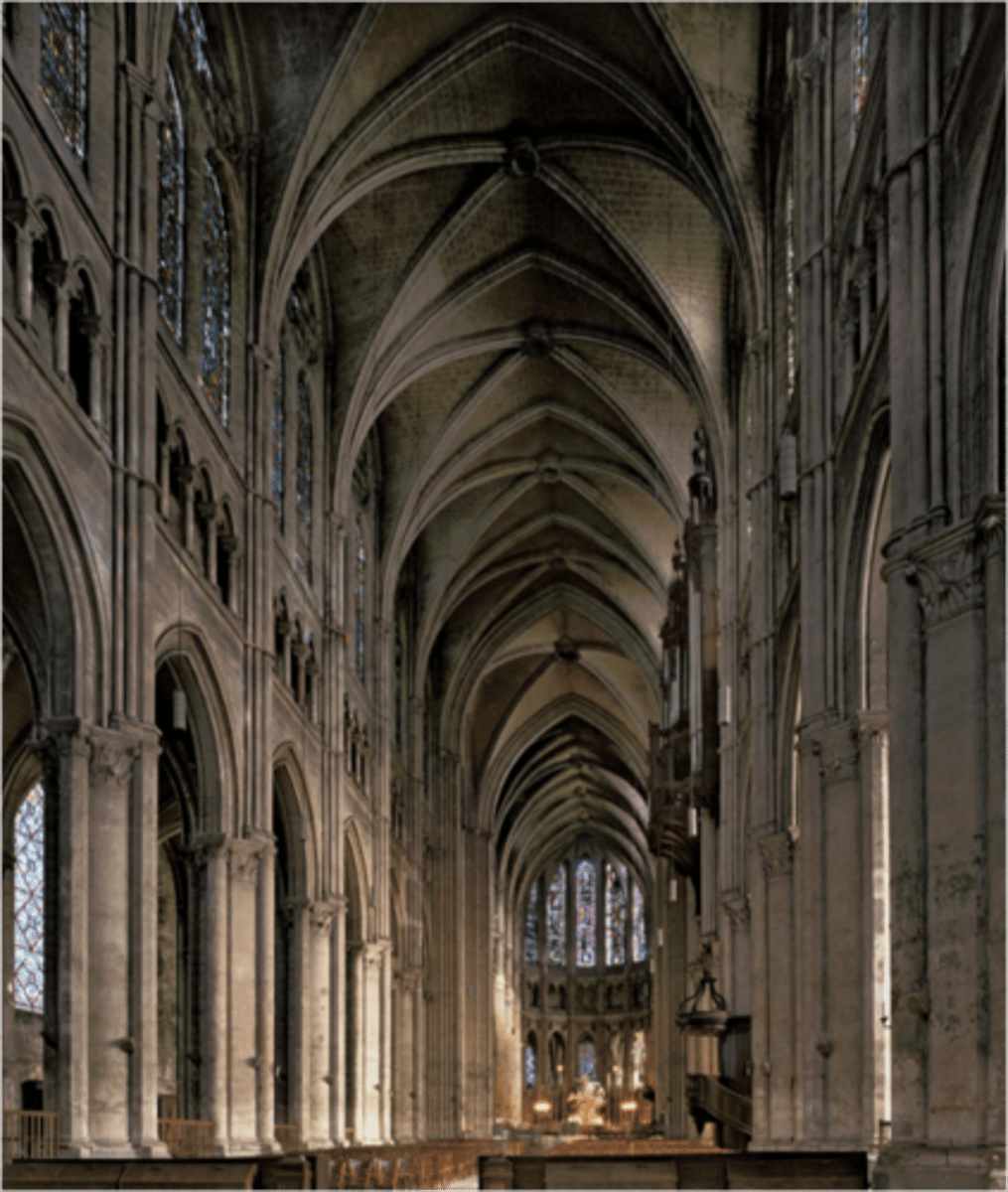
Ribbed vault
An architectural feature for covering a wide space, such as a church nave, composed of a framework of crossed or diagonal arched ribs.
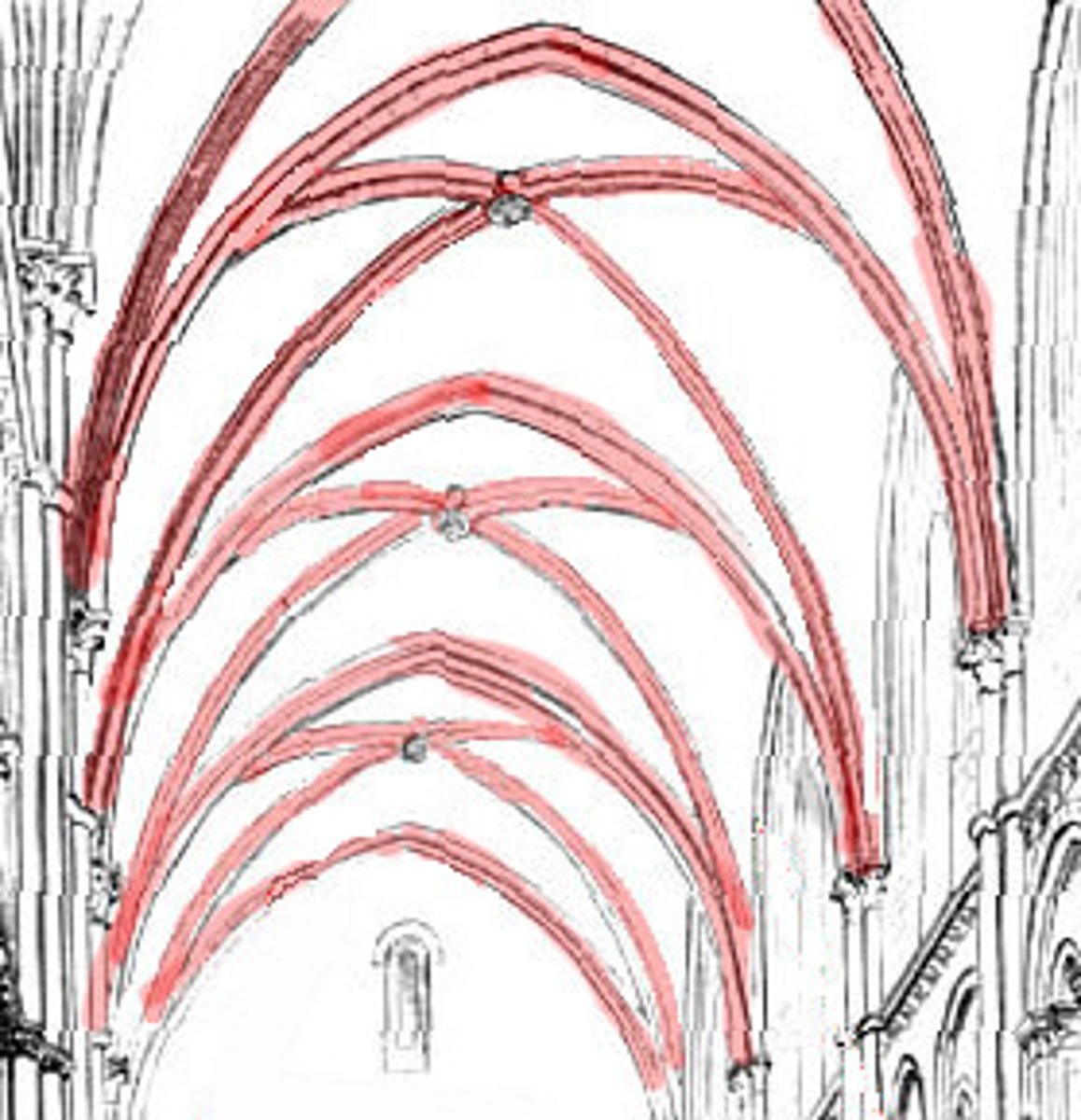

Groin vault
This type of vault is produced by the intersection at right angles of two barrel vaults. Sometimes their arches are pointed instead of round.
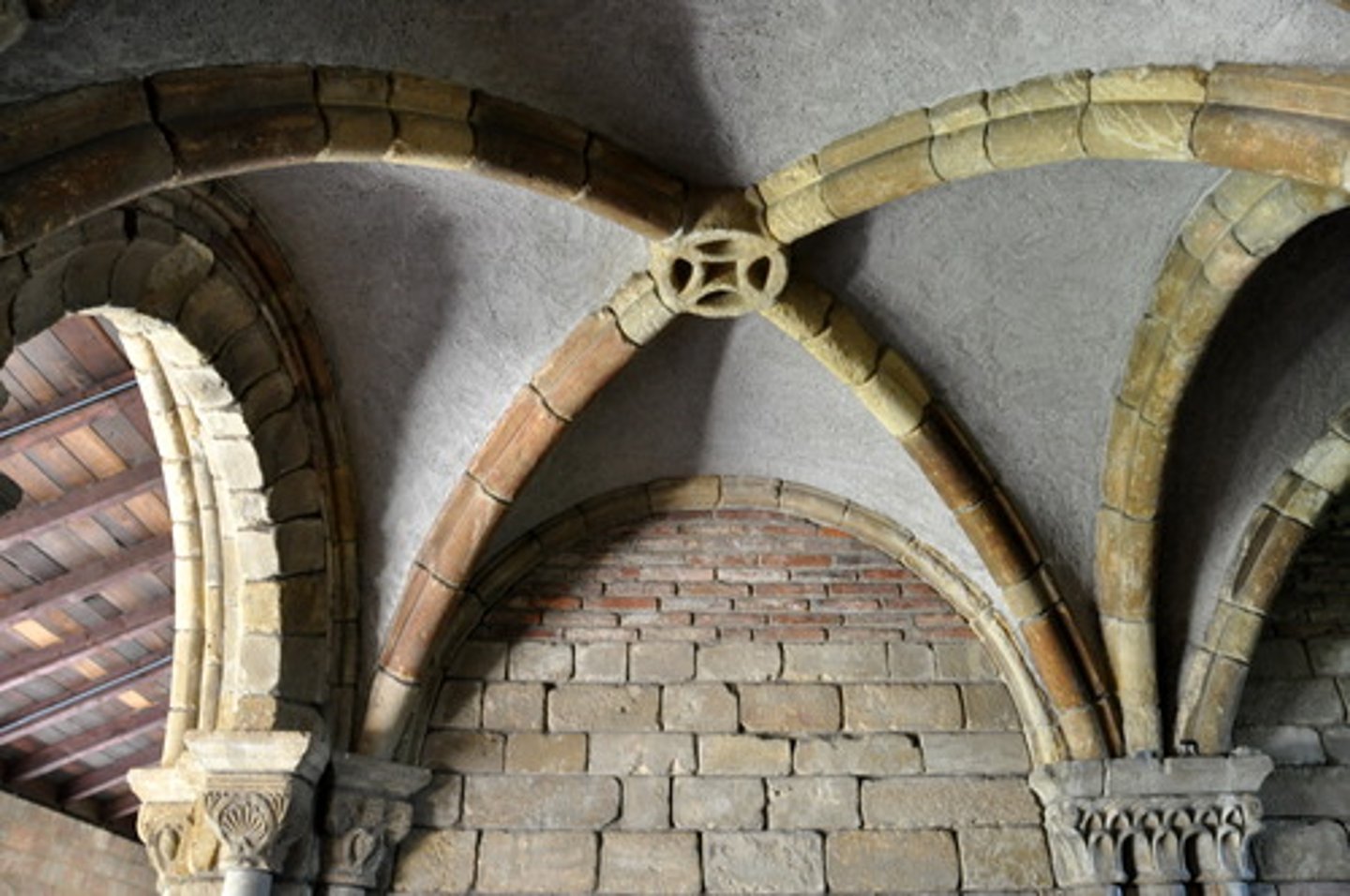

Solid buttress
A buttress in contact with the wall at ground level.
Gothic arch
A pointed arch, especially one with a joint instead of a keystone at its apex.
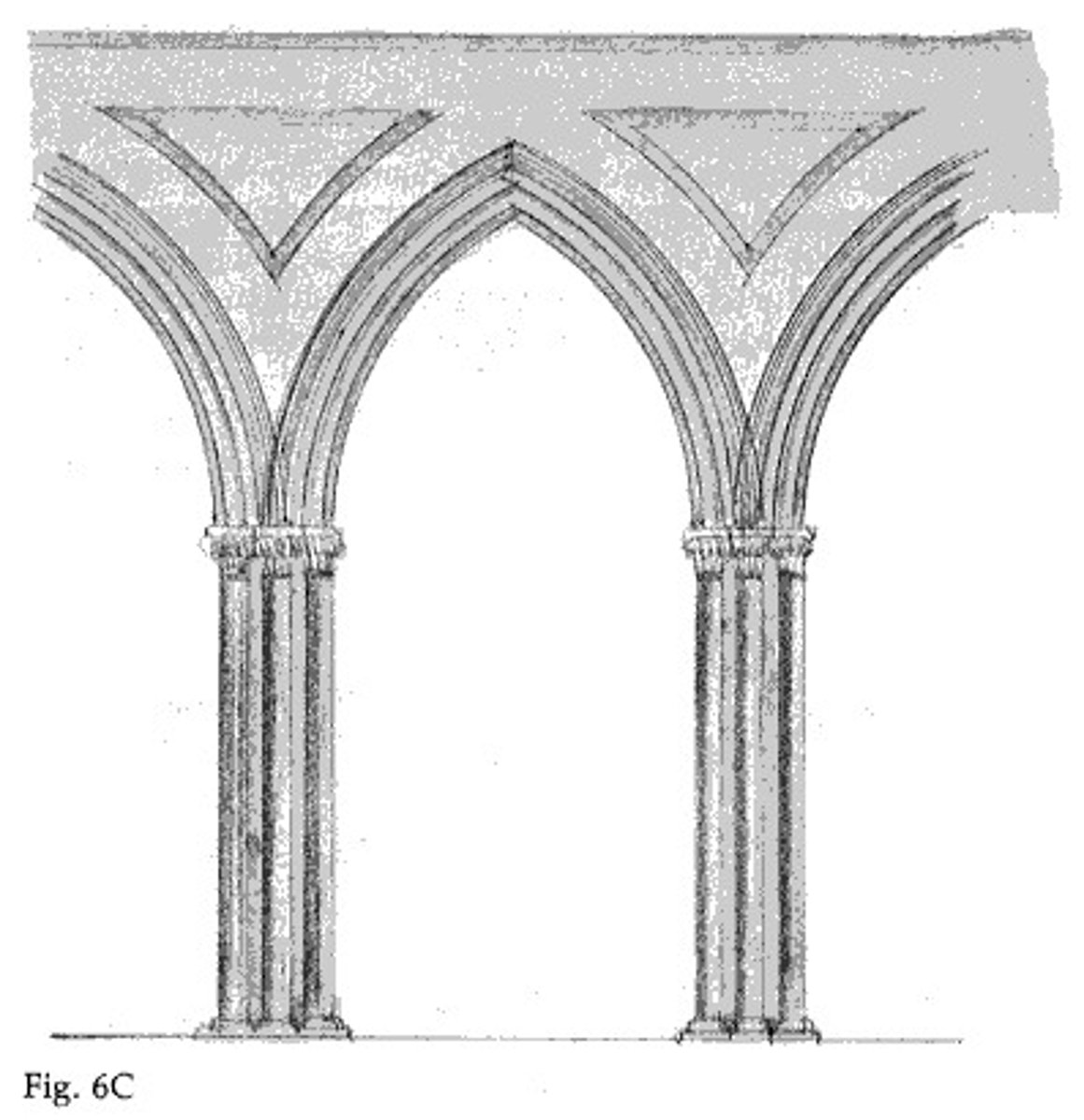
Ribbed groin vault
A type of vaulted ceiling formed by the intersection of two barrel vaults, creating a groined surface, and is distinguished by the addition of structural ribs that run along the intersections of the vaults.

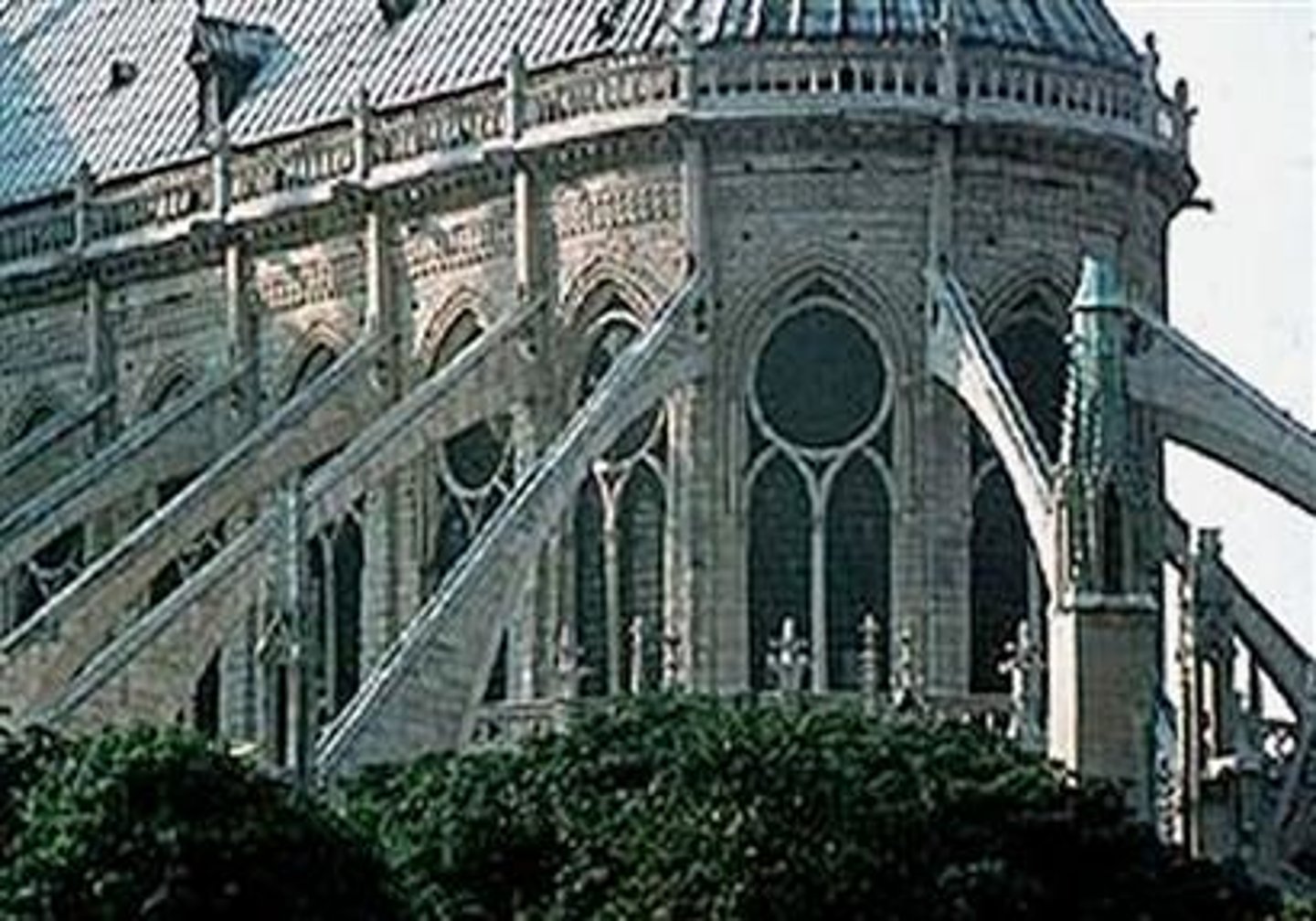
Flying buttress
A specific form of buttress composed of a ramping arch that extends from the upper portion of a wall to a large pier for structural reasons.

Lancet window
A tall, narrow window with a sharp pointed arch at its top.
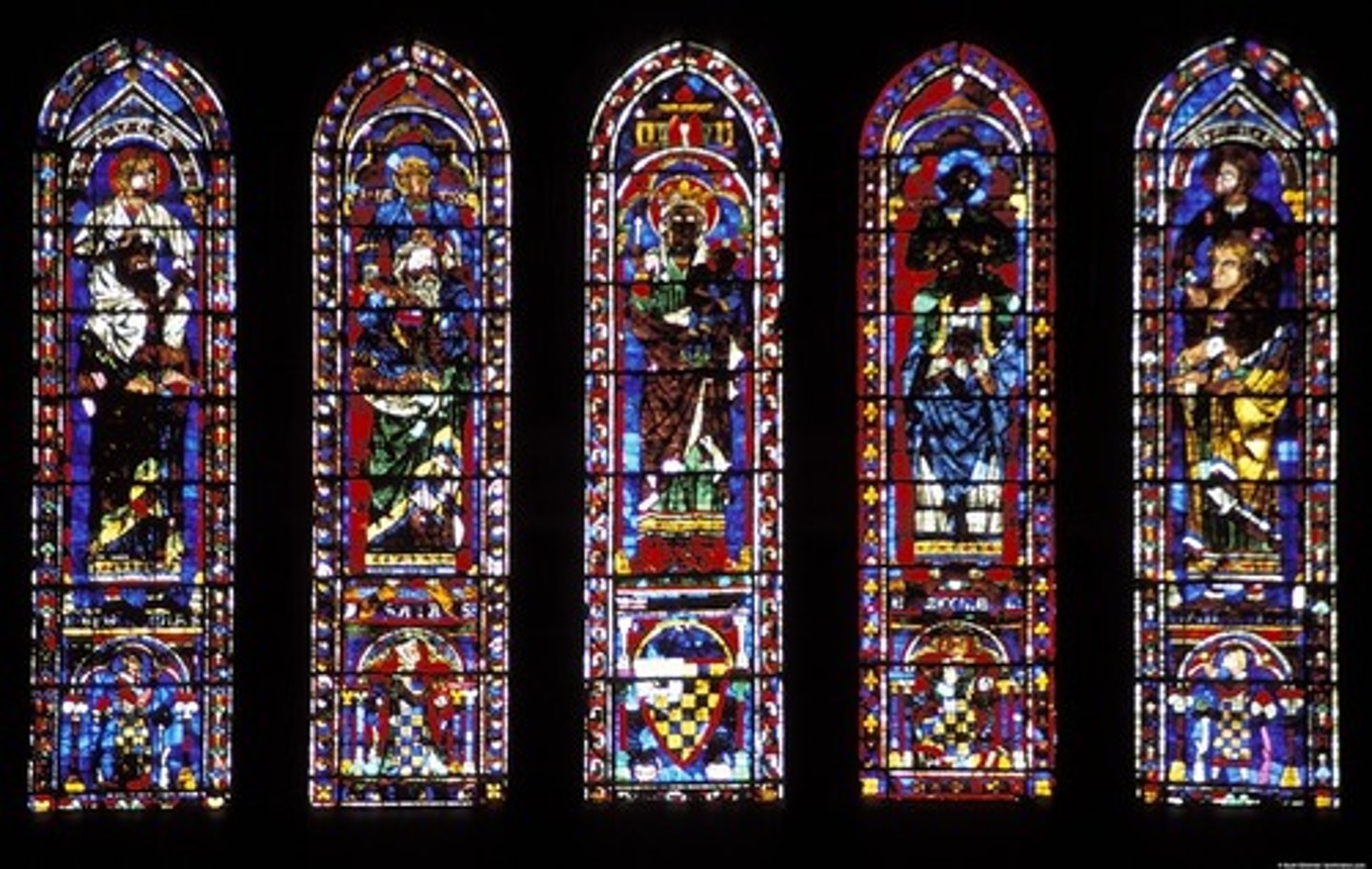

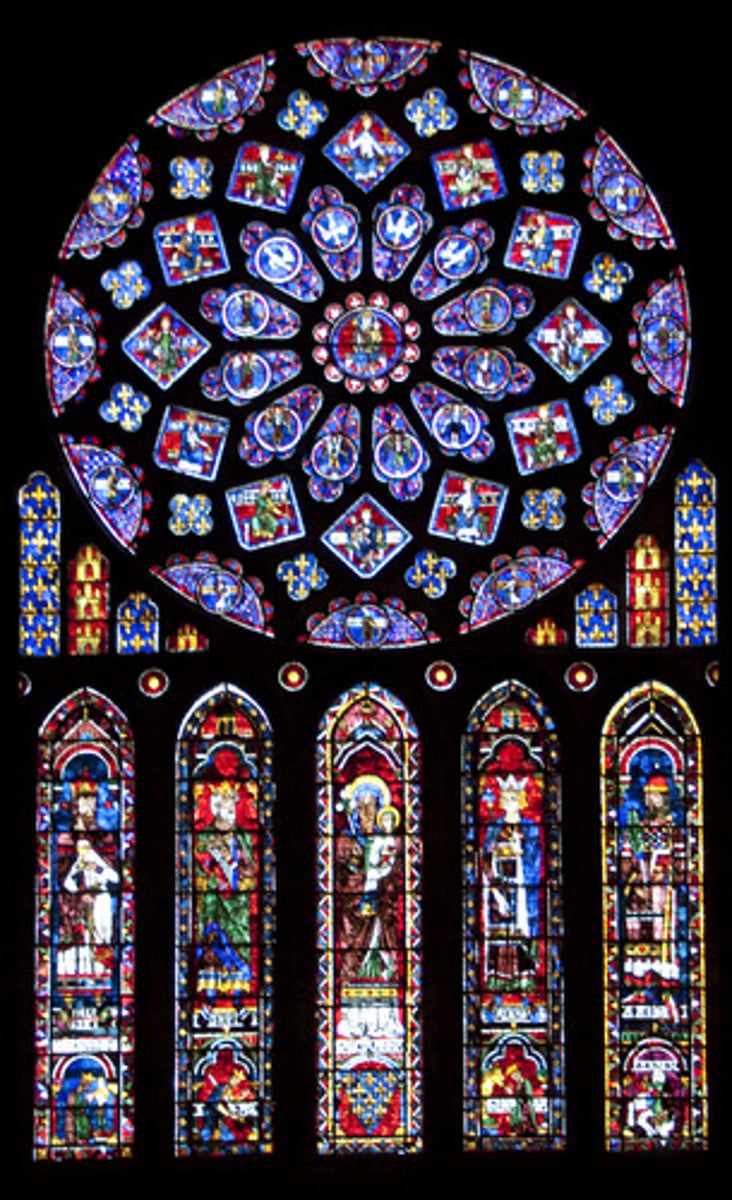
Rose window
A decorated circular window in Gothic architecture, often glazed with stained glass.

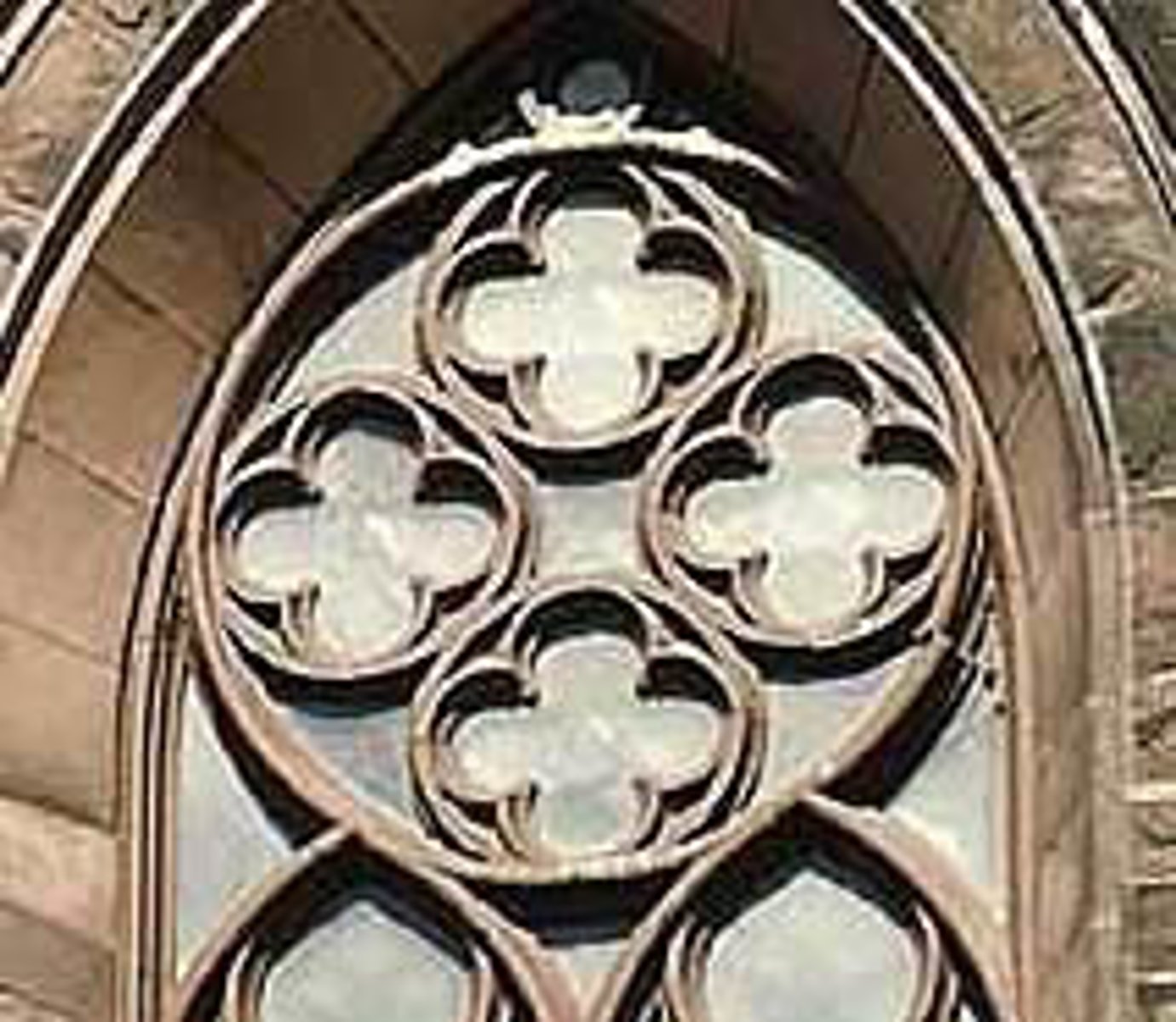
Quatrefoil
A design element made of four symmetrical lobes or foils that resemble the petals of a flower. The symbol represented the four Gospels.

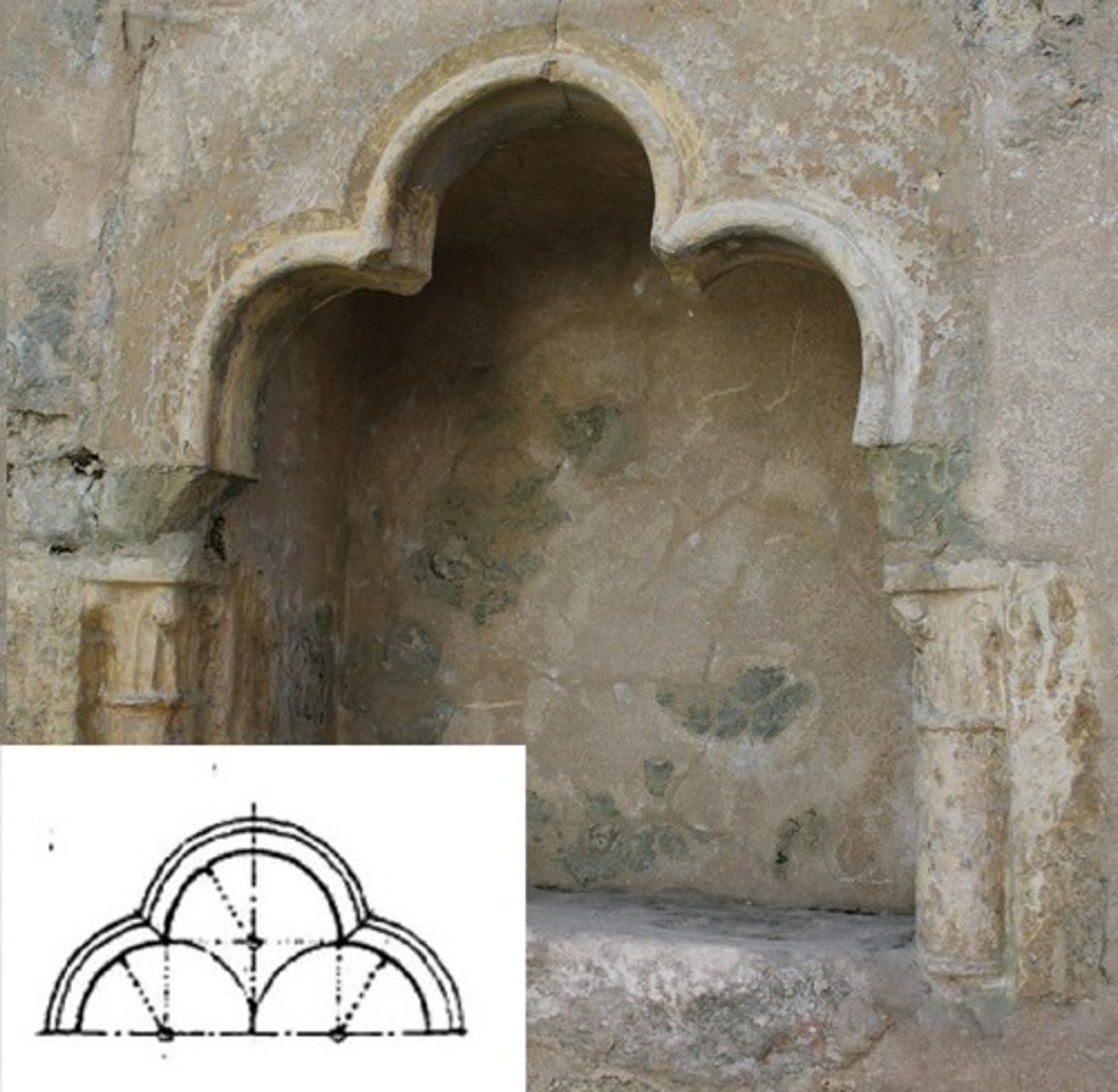
Trefoil arch
An arch incorporating the shape or outline of three overlapping circles.

Tripartite facade
When a building's facade or elevation is divided into 3 distinct sections.
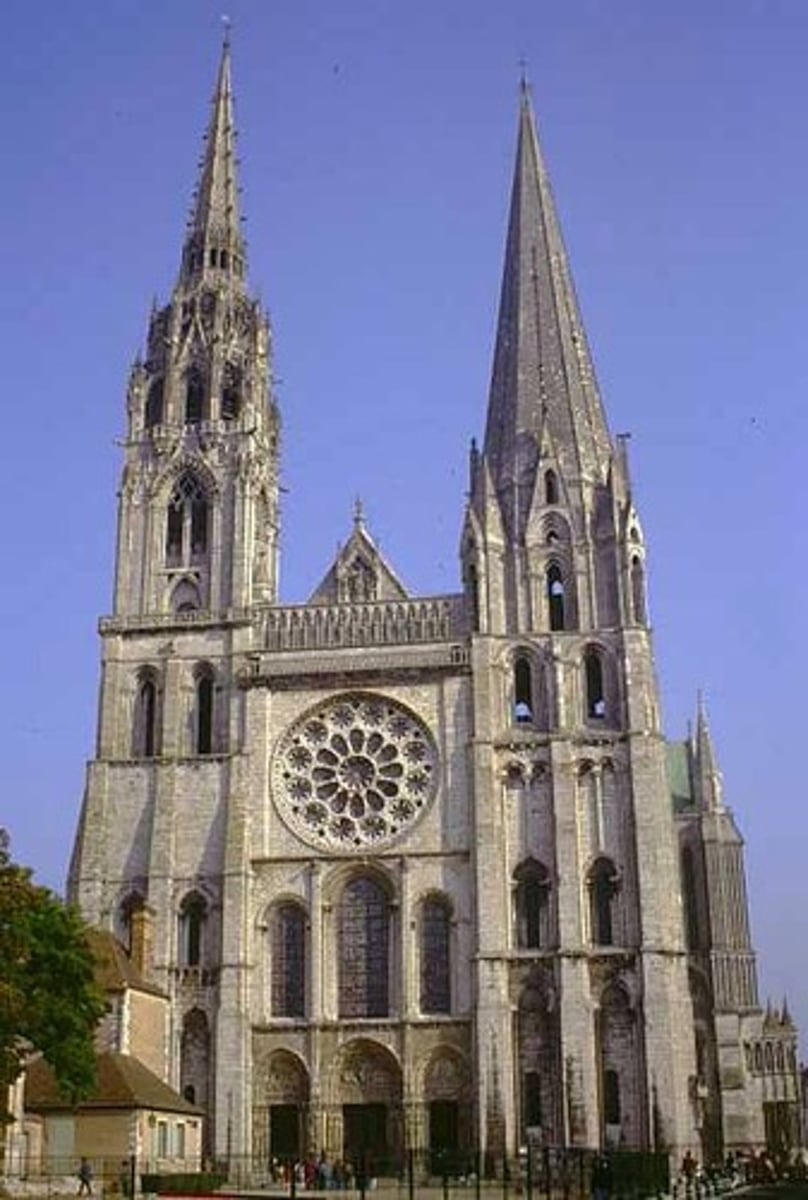

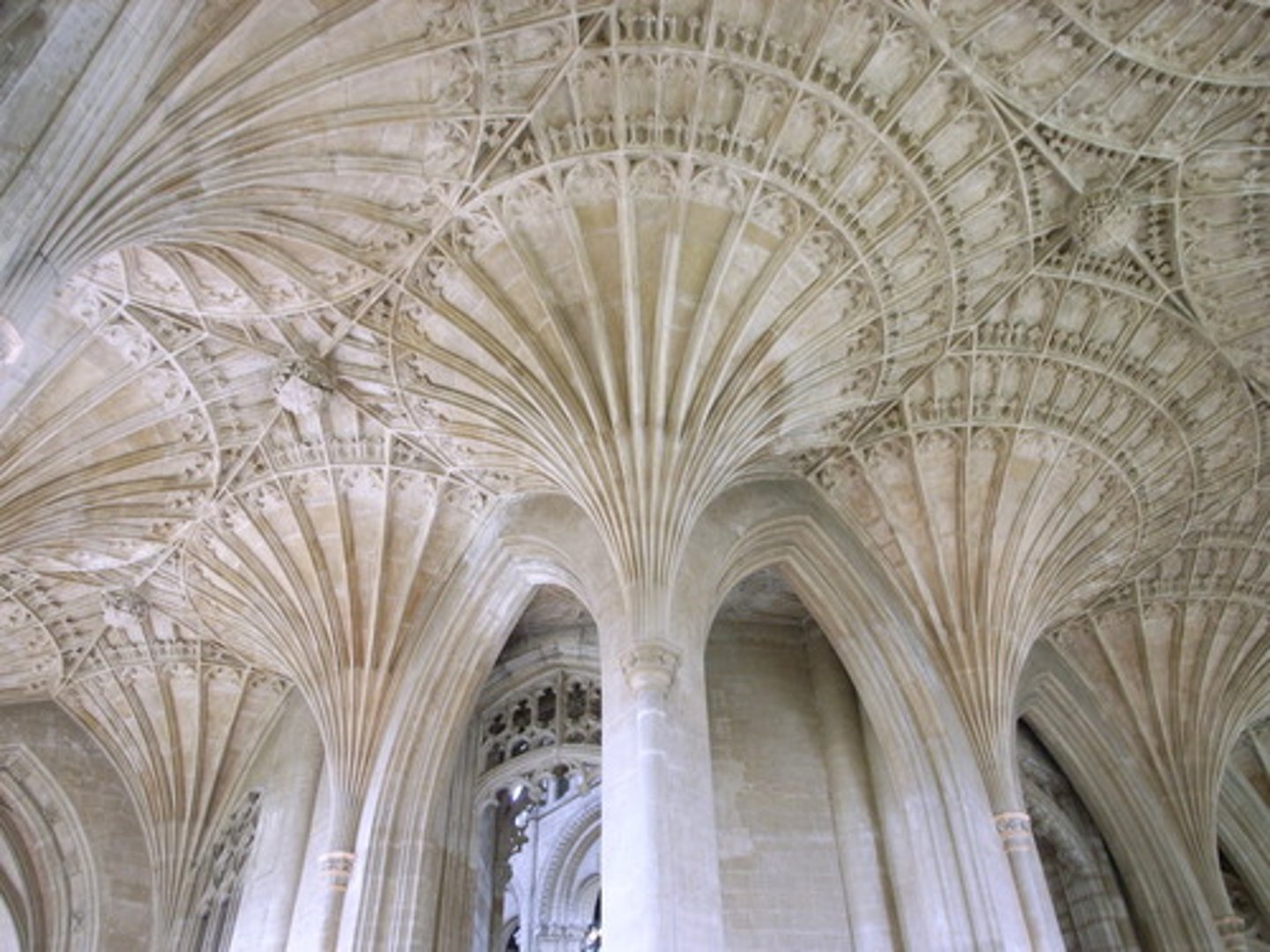
Fan vault
A form of vault used in the Gothic style, in which the ribs are all of the same curve and spaced equally, in a manner resembling a fan.

Decalcomania
A technique used by some surrealist artists which involves pressing paint between sheets of paper.
Rembrandt, Deposition from the Cross, Dutch Baroque
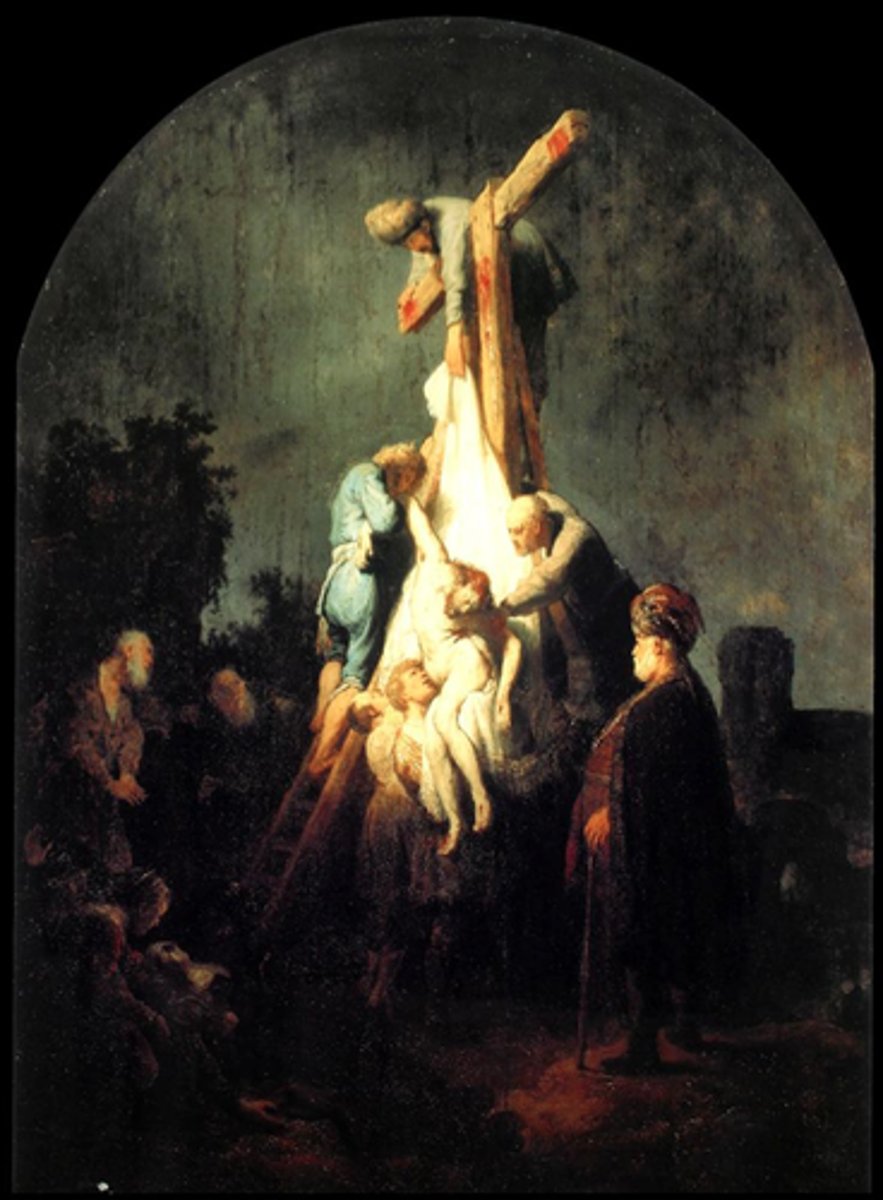
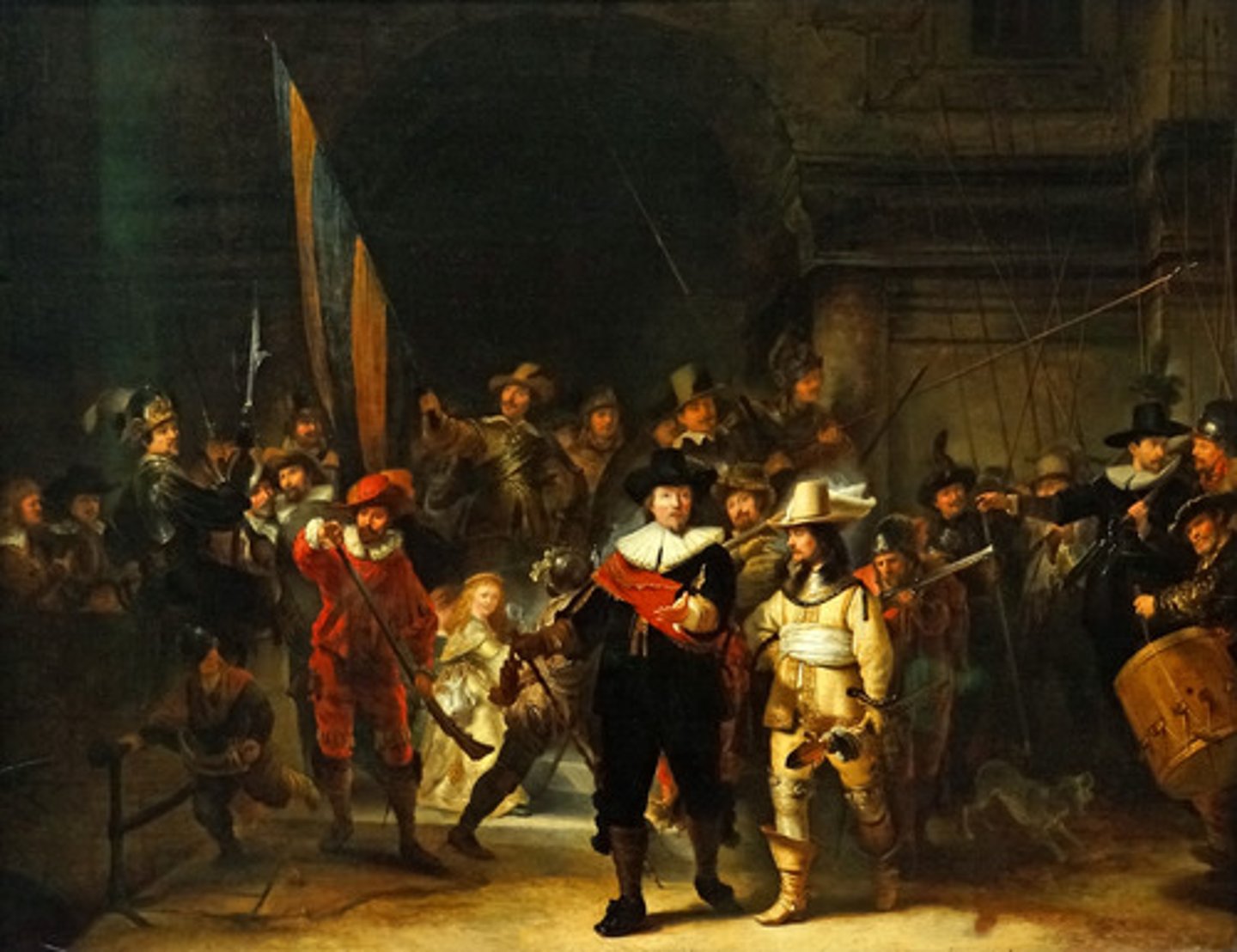
Rembrandt, The Night Watch, Dutch Baroque

Gustav Klimt, The Kiss, Symbolism

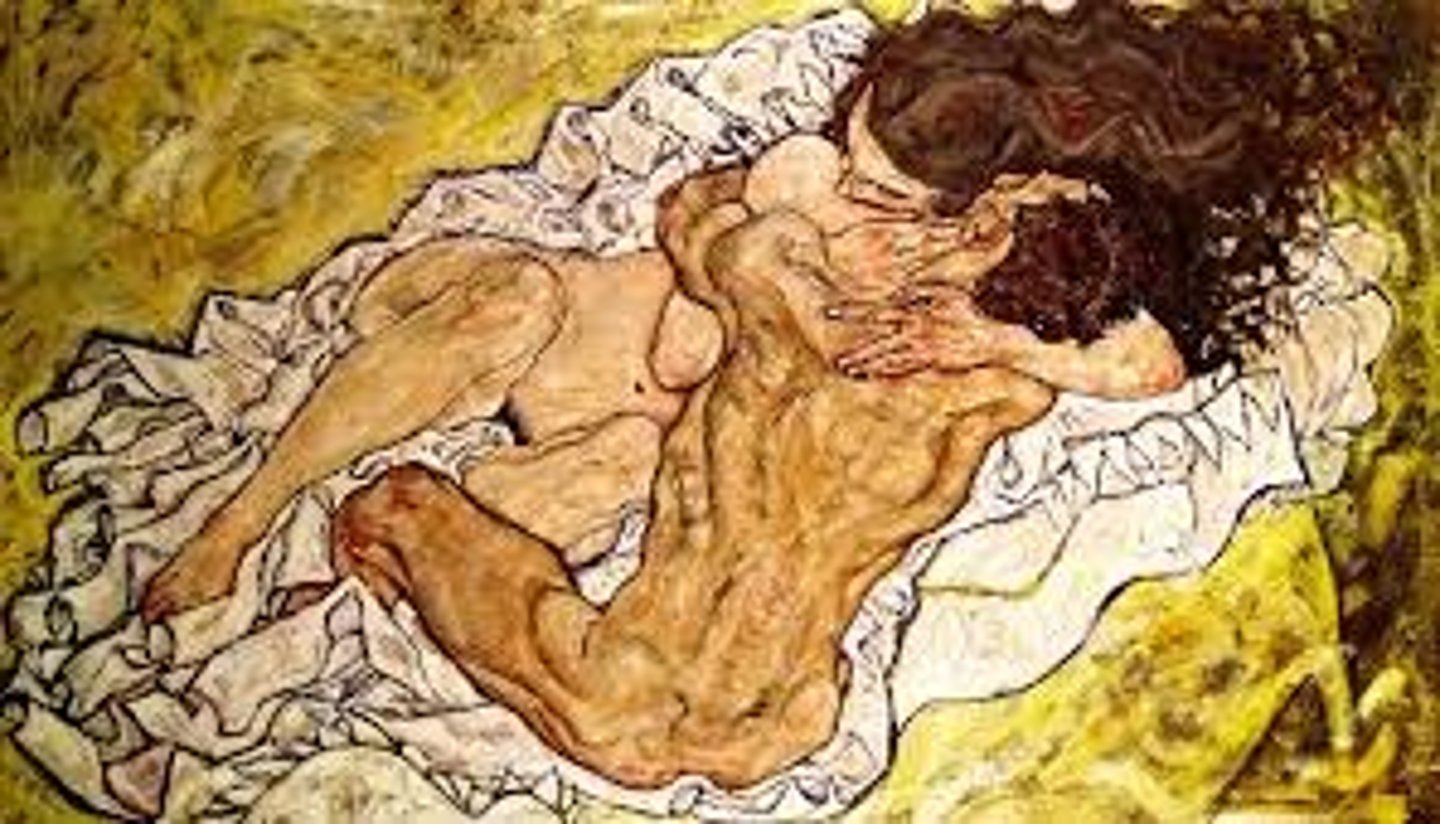
Egon Schiele, The Embrace, Symbolism
Nicola Pisano
An Italian sculptor whose work is noted for its classical Roman sculptural style during the Early Italian Renaissance. Sometimes considered to be the founder of modern sculpture.
Giotto
An Italian painter and architect from Florence in the Early Italian Renaissance. He was a student of Cimabue.
Masaccio
One of the first artists to use vanishing point in his work, employing the use of scientific perspective in his paintings. Typically painted frescoes.
Lorenzo Ghiberti
This artist began his career as a goldsmith, but later moved to bronze sculpture. He won a competition to find the best sculptor in Florence.
Jan van Eyck
A Northern Renaissance painter known for being the first to create a mix of oil pigments with varnish that didn't crack after drying. Known for his detailed realism and innovative techniques.
Albrecht Durer
A Northern Renaissance artist who created many small prints, engravings, and woodcuts. He frequently signed and dated his work.
Parmigianino
An Italian painter who was one of the first artists to develop the elegant, sophisticated, and elongated version of Mannerist style. Influenced by Leonardo da Vinci.
Bernini
A Baroque sculptor who sculpted people in complex poses that resulted in a sense of movement.
Peter Paul Rubens
A prolific Flemish Baroque artist who studied Michelangelo in Italy and took that Renaissance style to the next level of drama, motion, and color. He was known for his dynamic compositions and vibrant use of color.
Jacques Louis David
A Neoclassical painter and ideologist of the French Revolution, favored using art of the ancients and of the great Renaissance artists as models.
Gustave Courbet
A French painter who led the Realism movement in 19th-century French painting. His work was poorly received by critics and the academy, who believed that his life-size works were too radical.
Edouard Manet
A pivotal figure in the transition to Impressionism, influencing contemporaries like Monet and Degas. He sought to liberate artists from the constraints of academicism, which he found outdated and stifling.
Claude Monet
A French painter who founded Impressionism. He believed in expressing his perception of something rather than painting it perfectly accurately.
Edgar Degas
This artist is best known for his paintings, drawings, and sculptures of race horses and ballerinas. He attempted to show realism and immediacy.
Marcel Duchamp
This artist aimed to break artistic tradition by discarding fundamental values of beauty and artisanship. His work is associated with Cubism, conceptual art, and Dadaism.
Benvenuto Cellini
An Italian goldsmith, sculptor, draftsman, musician, and artist who also wrote a famous autobiography and poetry. He was one of the most important artists of Mannerism sculpture.
Rembrandt
A famous Dutch Baroque painter whose qualities included glowing light against dark backgrounds and truthful renderings of his subjects.
Jan Steen
A Dutch Baroque painter who specialized in domestic interior scenes of middle class life. Typically did genre paintings.
Francois Boucher
A French painter, draughtsman, and etcher who worked in the Rococo style. Depicted courtly love and mythological scenes.
Jan van Eyck, Madonna in the Church, Northern Renaissance

A diptych
What was Jan van Eyck's Madonna in the Church originally (probably)?
Mary's virginity
In the context of the Virgin Mary and Christ within a painting, what does light represent?
Hans Holbein the Younger, The Merchant Georg Gisze, Northern Renaissance

The carnations
How can you tell that the man in The Merchant Georg Gisze has recently been engaged?
Memento mori / vanitas
Still life paintings that are reminders of death, typical of the Northern Renaissance.
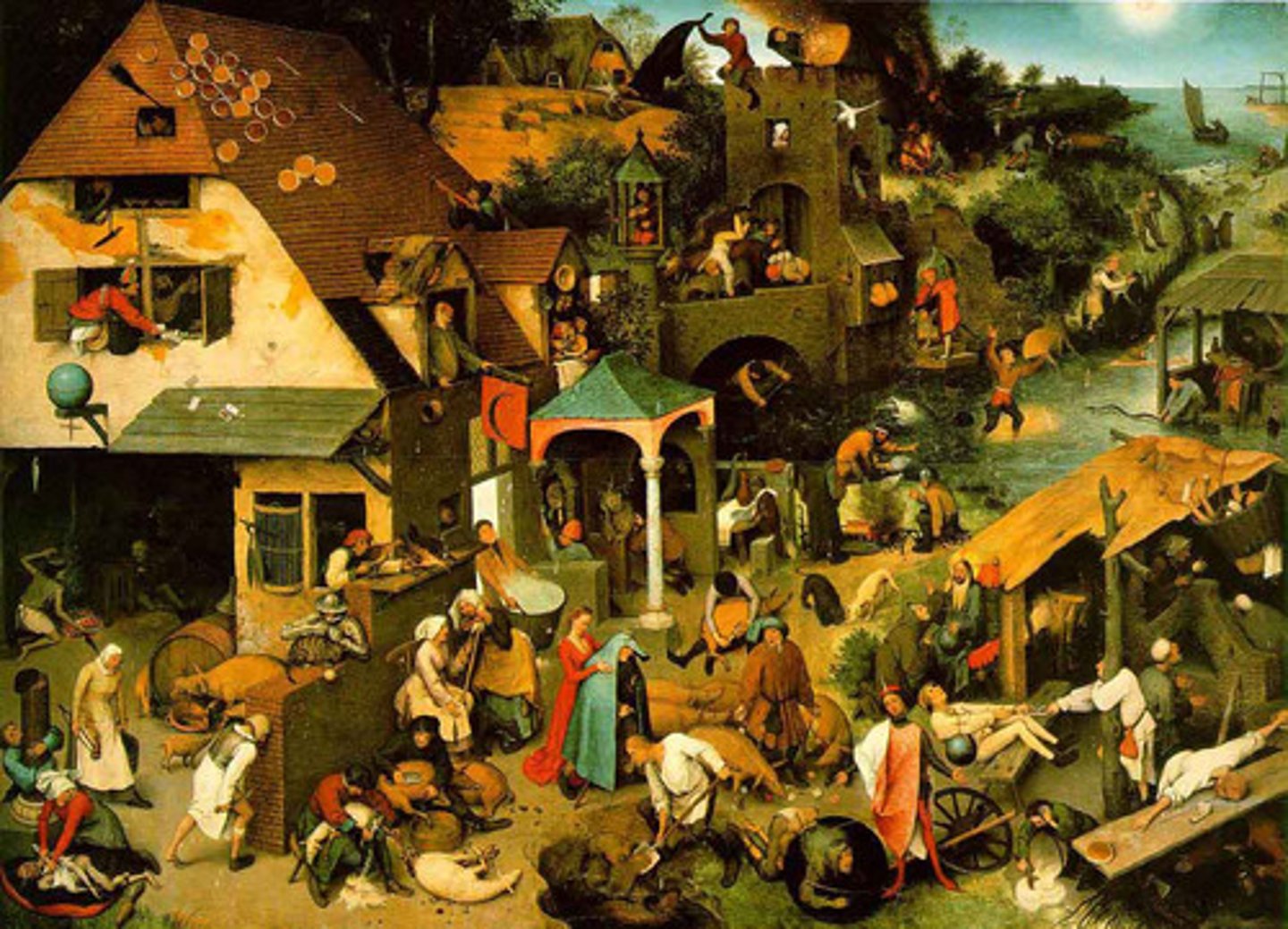
Pieter Bruegel, Netherlandish Proverbs, Northern Renaissance

love conquers all
The Latin phrase "amor vincit omnia" means:
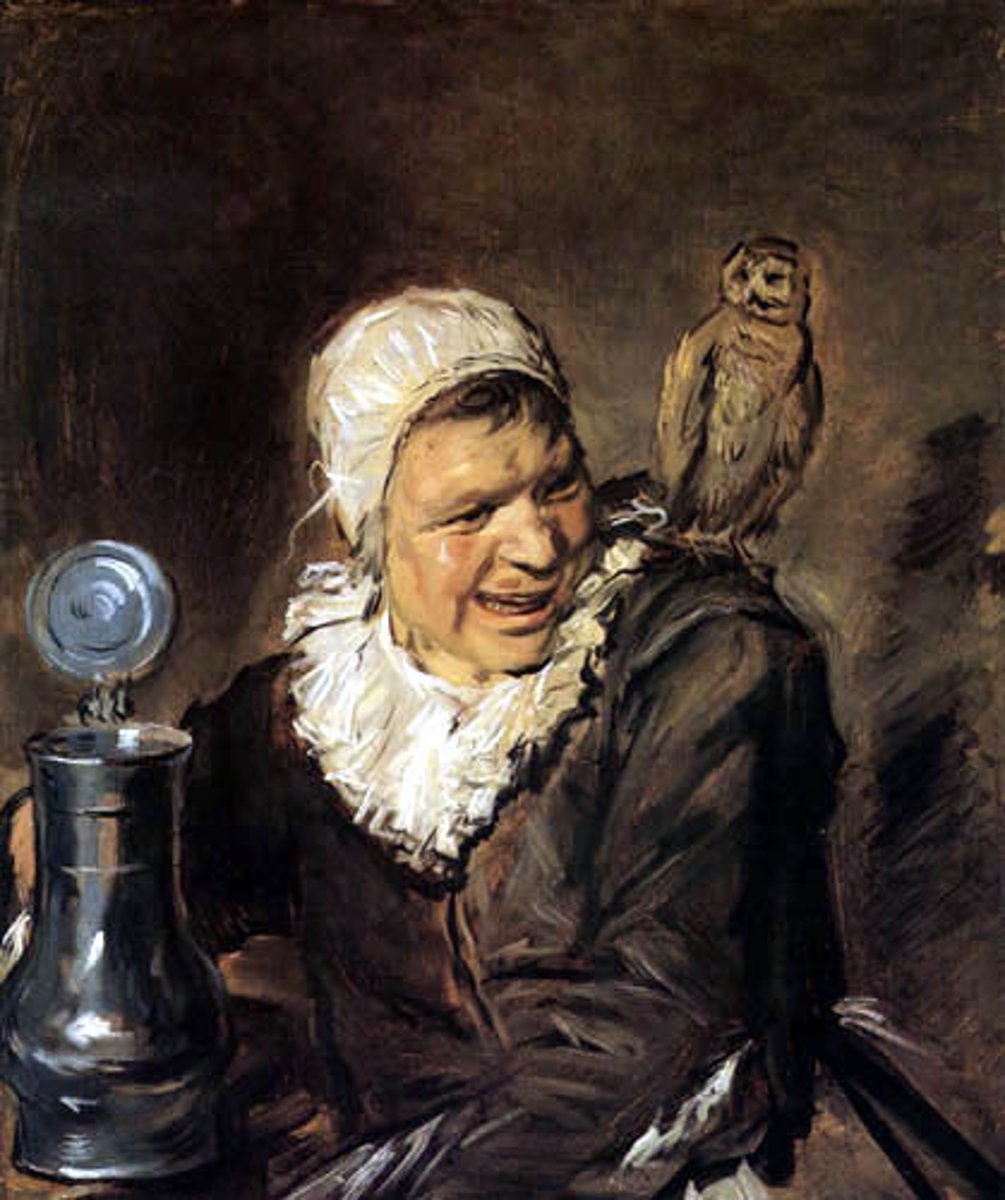
Frans Hals, Malle Babbe, Dutch Baroque

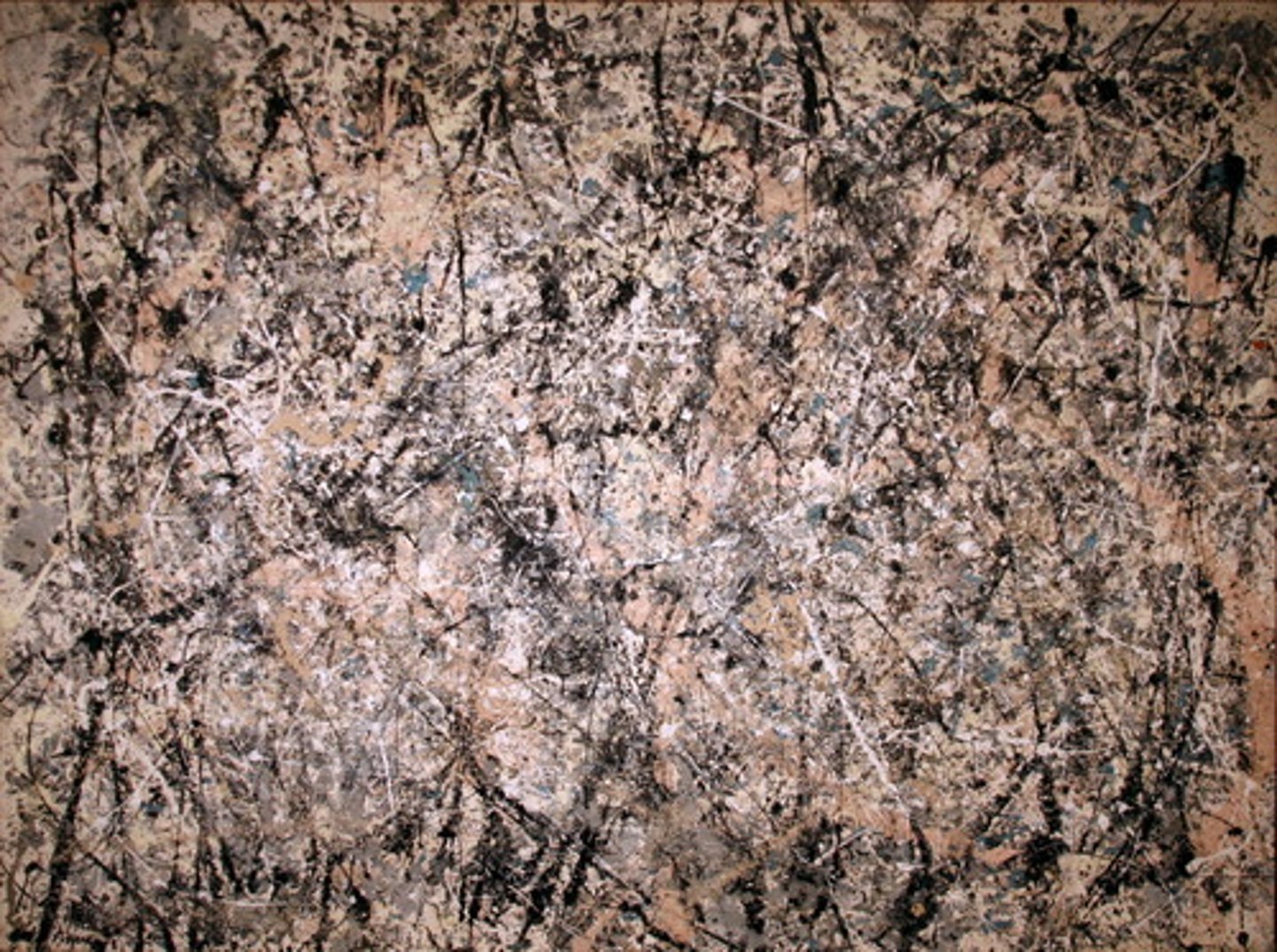
Jackson Pollock, Lavender Mist, Modernism / Ab Ex

Native American sand painting
A ceremony where Native Americans made temporary art around a sick person in hopes of healing them.
Joseph Beuys, How to Explain Pictures to a Dead Hare, Performance Art
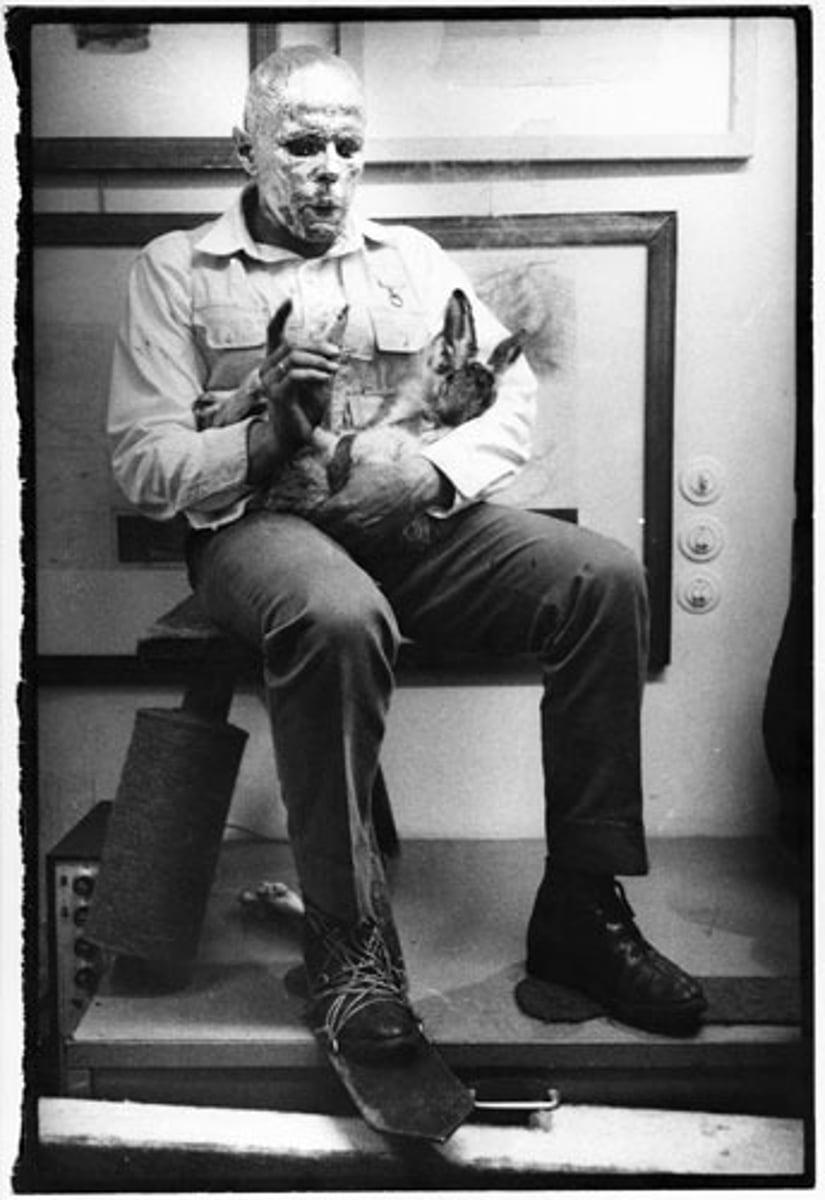

Joseph Beuys, I Like America and America Likes Me, Performance Art
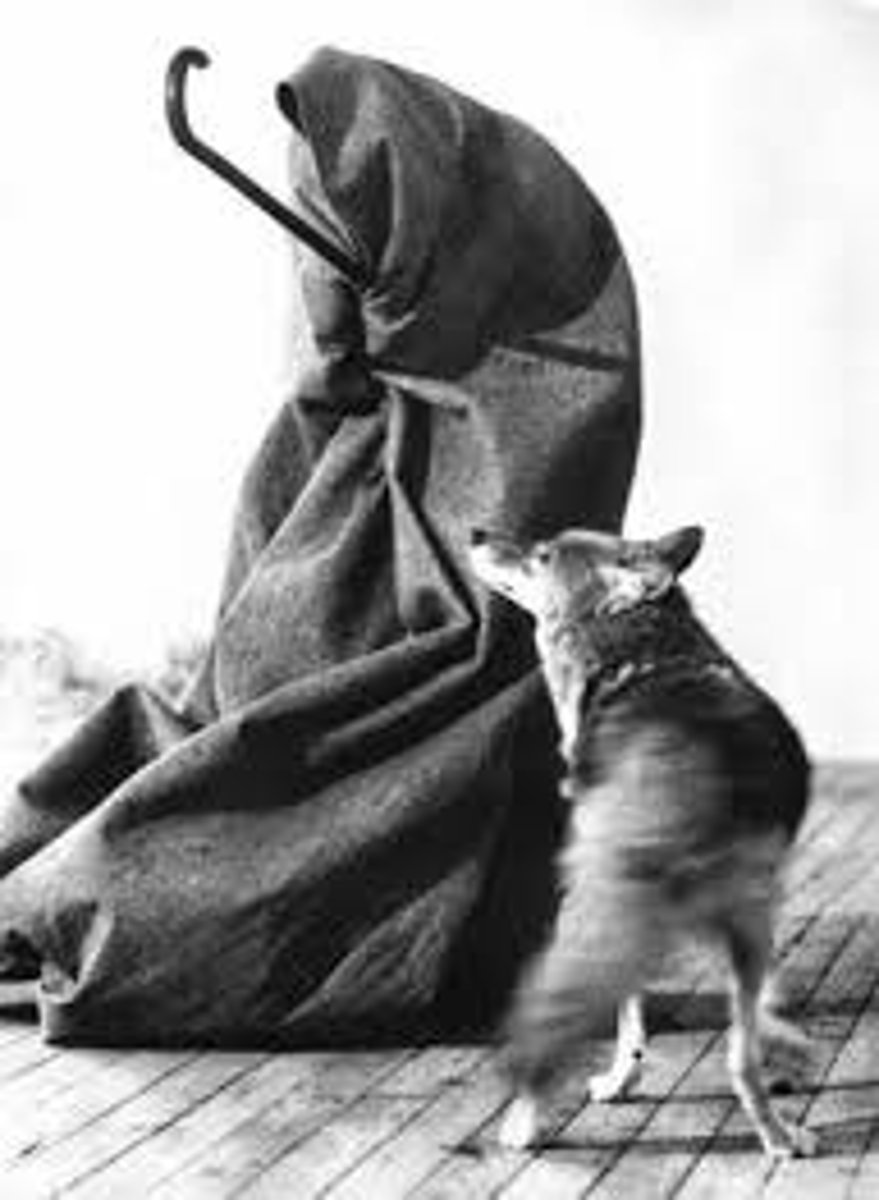

Joseph Beuys, The End of the Twentieth Century, Installation Art

Lucas Cranach, Portrait of Martin Luther, Northern Renaissance

Andrea Bregno, St. Jerome, Italian Renaissance
___ carved a relief of ___ in the ___. The figure in the marble relief has a halo, a book, and a lion next to it.
three tassels
You can tell that a hat is a cardinal's if it has:
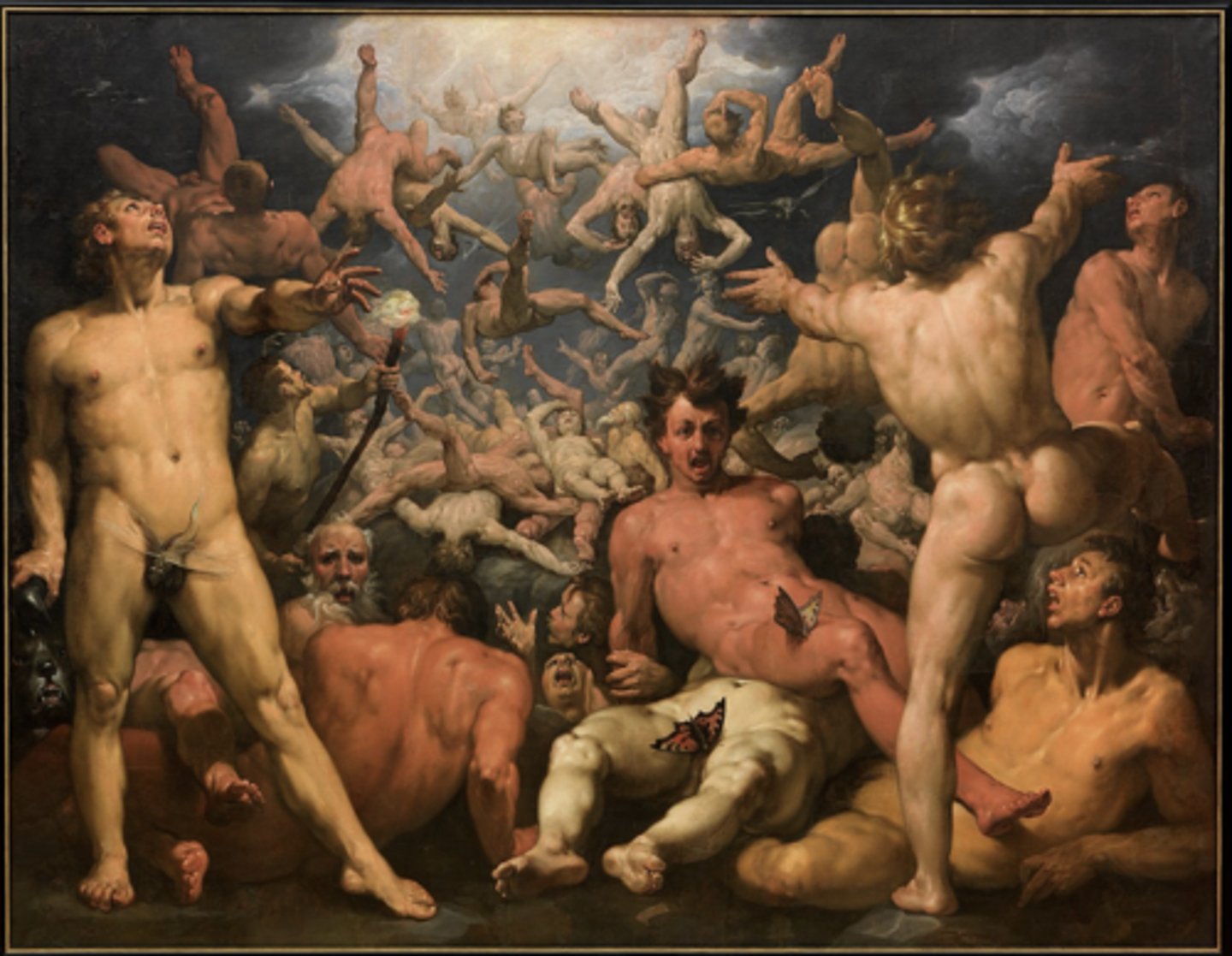
Cornelis van Haarlem, Fall of the Titans, Mannerism

Pronk stilleven
An ostentatious/fancy still life, typically showing banquet or decorative foods, typical of the Dutch Baroque.
Trompe l'oeil
A French saying meaning "to deceive the eye," an art historical tradition in which the artist fools us into thinking we're looking at the real thing.
Auguste Rodin, Burghers of Calais, Impressionism

Auguste Rodin, Danaid, Impressionism

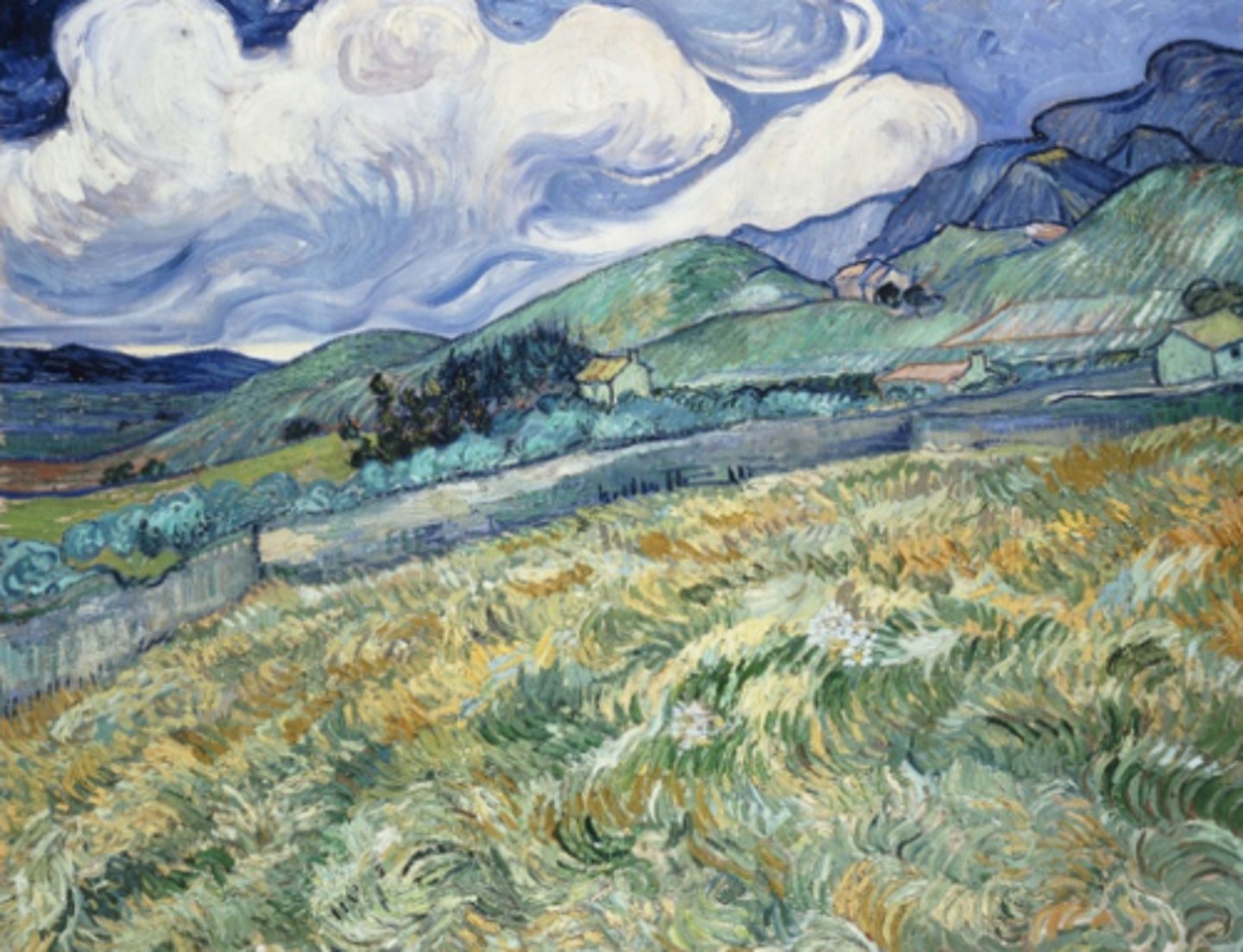
Van Gogh, Mountainous Landscape behind Saint-Paul Hospital, Post-Impressionism

Matisse, The Green Stripe (Madame Matisse), Fauvism

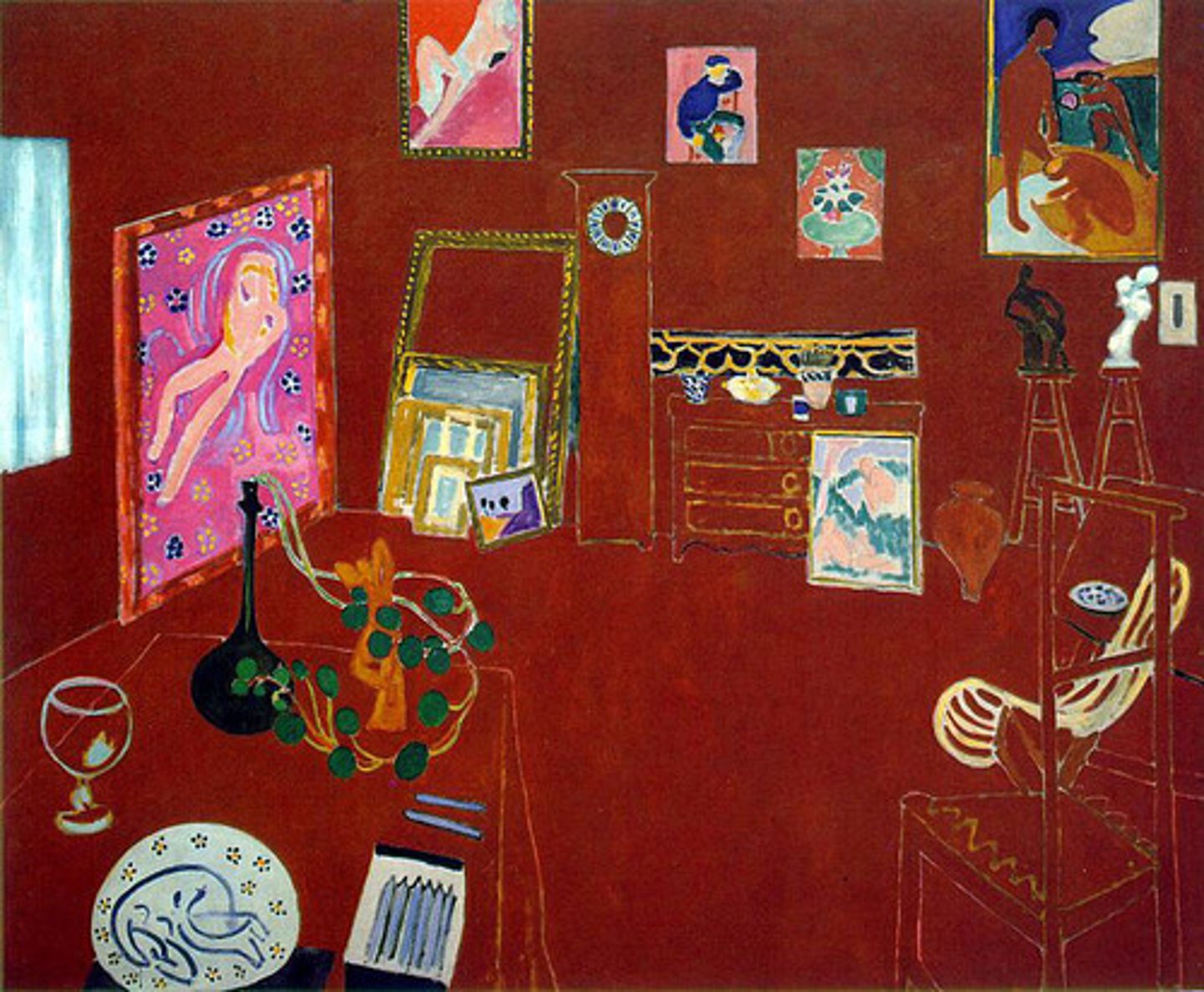
Matisse, The Red Studio, Fauvism

Hugo van der Goes, Adoration of the Magi, Northern Renaissance
___ painted ___ in the ___. It depicts the three magi visiting Christ after his birth, showing them as coming from all ages and all corners of the world.
Titian, Venus with an Organ Player, Venetian Renaissance

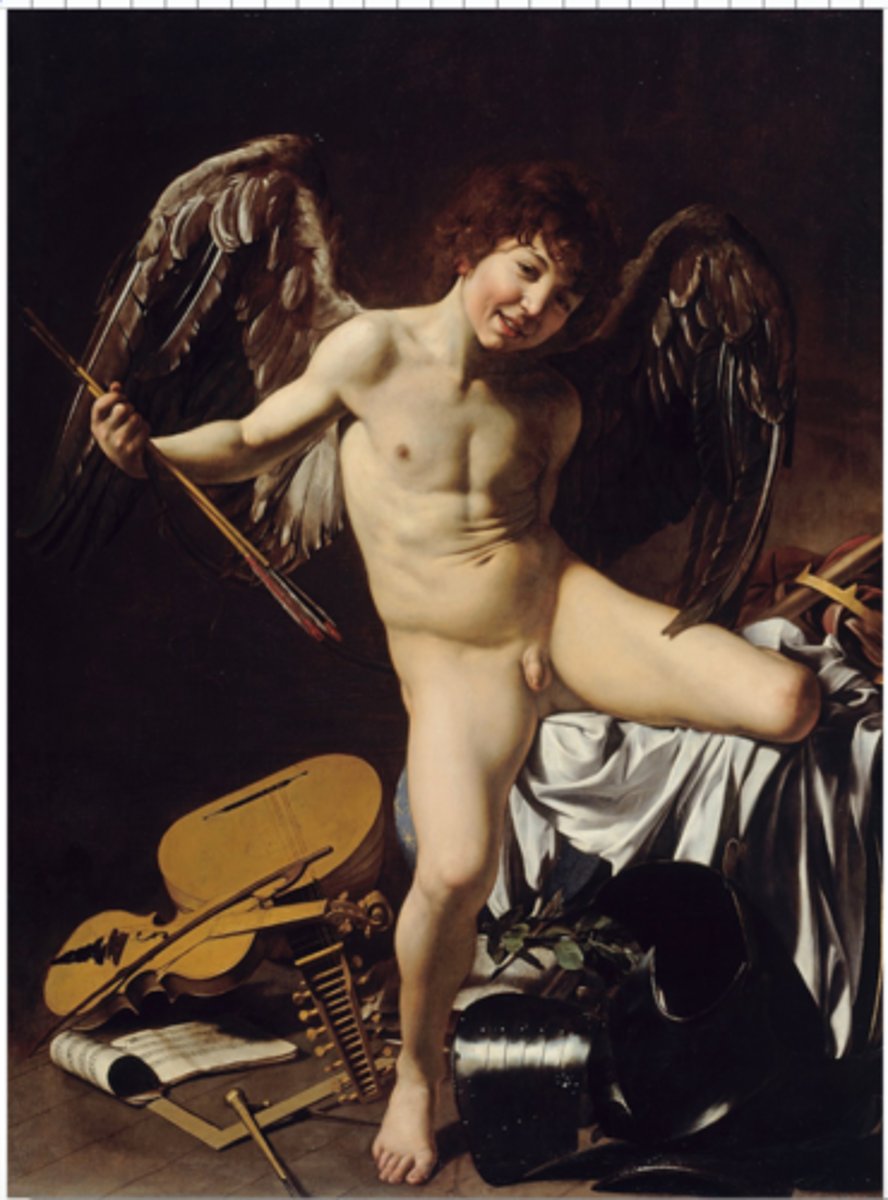
Caravaggio, Amor Vincit Omnia / Cupid as Victor, Italian Baroque

Cornelius Gijsbrechts, Easel with a Piece of Fruit, Flemish Baroque

Rembrandt, Simeon and Anna in the Temple, Dutch Baroque
___ painted ___ in the ___. It depicts a couple who recognized Jesus as the Messiah when he was presented at the Temple.
Jan van Goyen, View of the City of Arnheim, Dutch Baroque
___ painted ___ in the ___. It's a landscape painting that depicts a city, and is very monochrome because of the reflection of the sky in the water.
Jan Davidsz de Heem, Still Life with Romer, Dutch Baroque
___ painted ___ in the ___. It's a typical Dutch still life painting, with a crab on the right and a halfway-peeled lemon on the left.