Urinalysis Sedimentation Test Review
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UGRC Vet Tech (Year 1)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
URINALYSIS SEDIMENTATION TEST REVIEW
you’ve got this pookie ily 😘
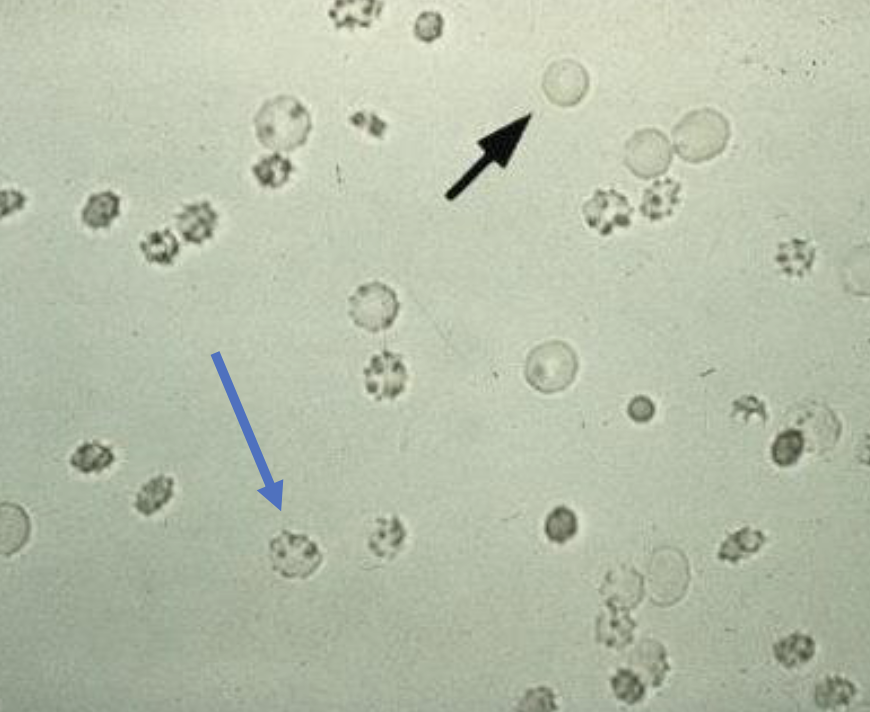
What is the black arrow pointing to?
What is the blue arrow pointing to?
Based on the blue arrow what type of solution is this?
Normal RBCs
Crenated RBC
Hypertonic Solution which causes H2O to leave the cell making them shrink (crenated) and is a result of concentrated urine
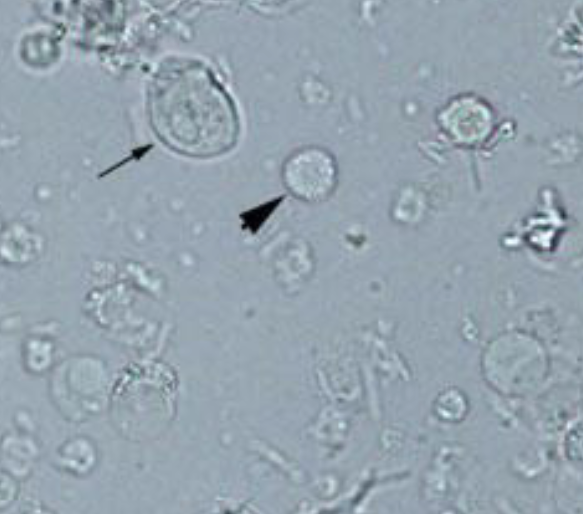
What is the thick black arrow pointing to?
What is the thin black arrow pointing to?
What is the normal range of your answer above?
Normal WBC
Transitional Epithelial Cell
0/HPF
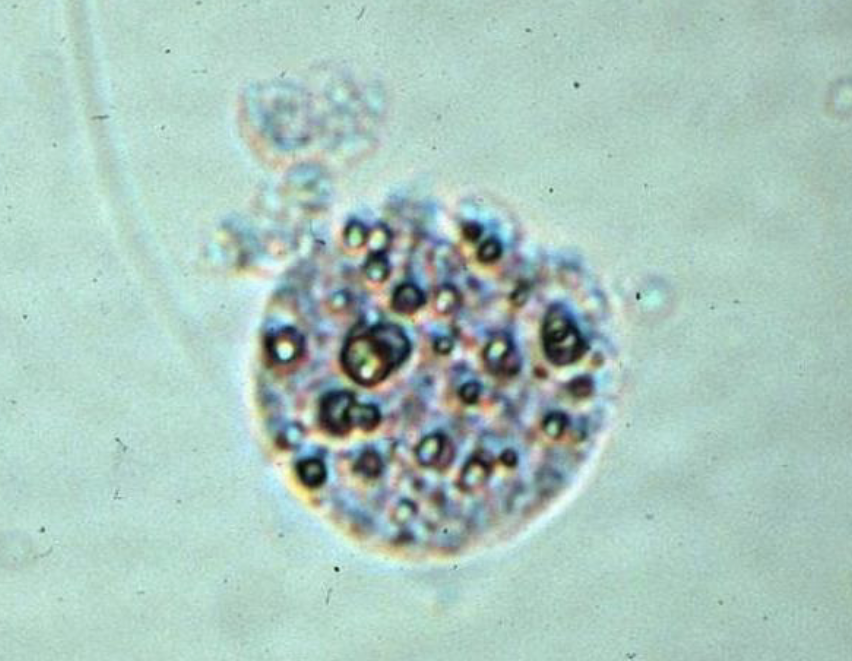
What is this?
What is the correct name for cells with fat in them?
What stain is used for these cells?
Lipid
Oval Fat Bodies
Sudan II (Black-Brown Colour)
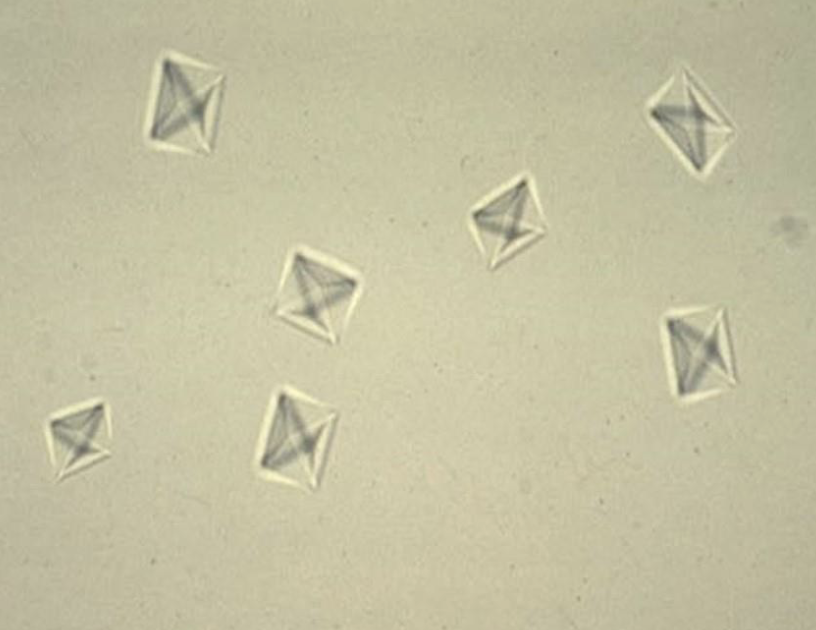
What are these crystals called?
Do these crystals like alkaline or acidic urine?
Are they a common crystal & in what animals?
Calcium Oxalate Dehydrate
Acidic Urine Loving
Yes in Cats & Dogs
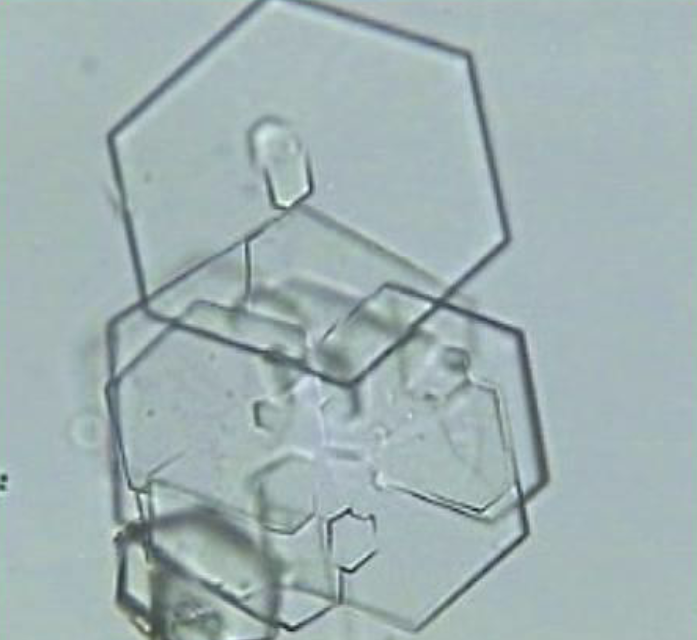

What is this crystal?
Do these crystals like alkaline or acidic urine?
Why are these crystals present in urine?
Cystine (An Amino Acid)
Acidic Urine Loving
The amino acid cystine is normally reabsorbed in the proximal tubule of the kidney. However, if a defect occurs, it is excreted into the bladder, where it remains unmetabolized in urine
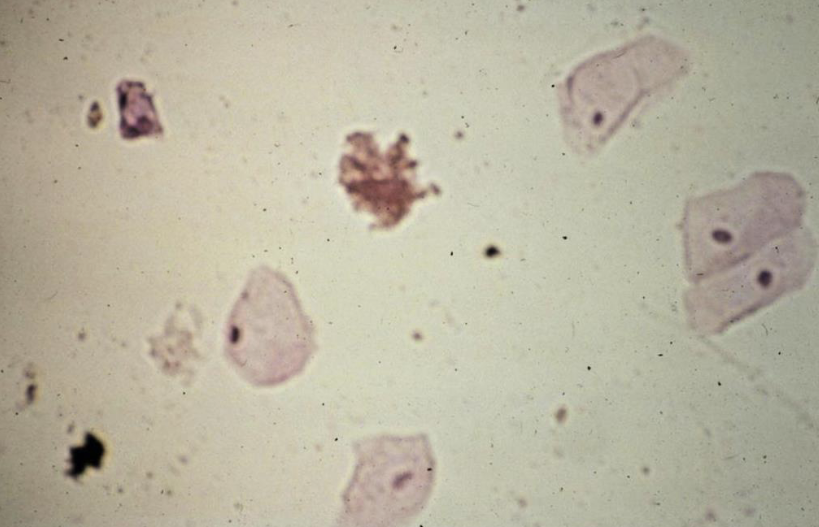
What are these?
Are they common?
Squamous Epithelial Cells
Yes as they line the urethra and are shed into the urine
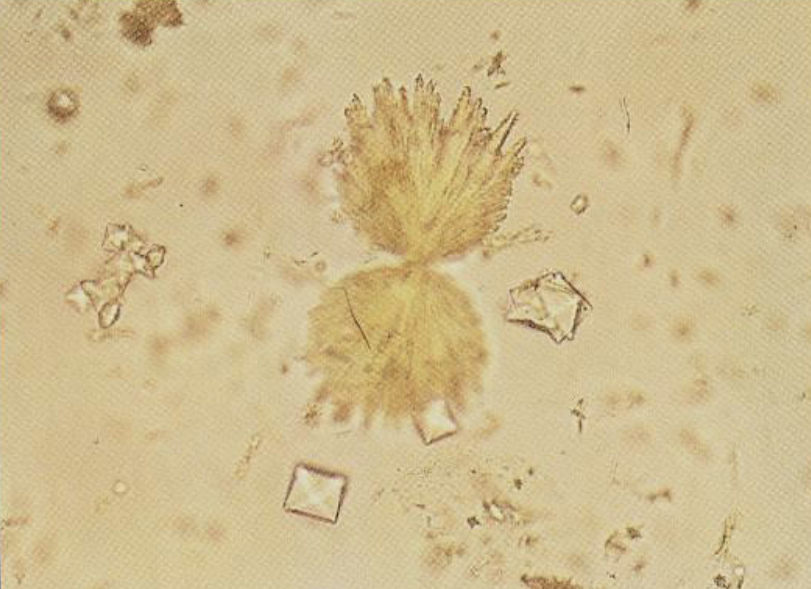
What common antibiotic induced crystal is this?
Is this found in acidic or alkaline urine?
Sulfa
Acidic
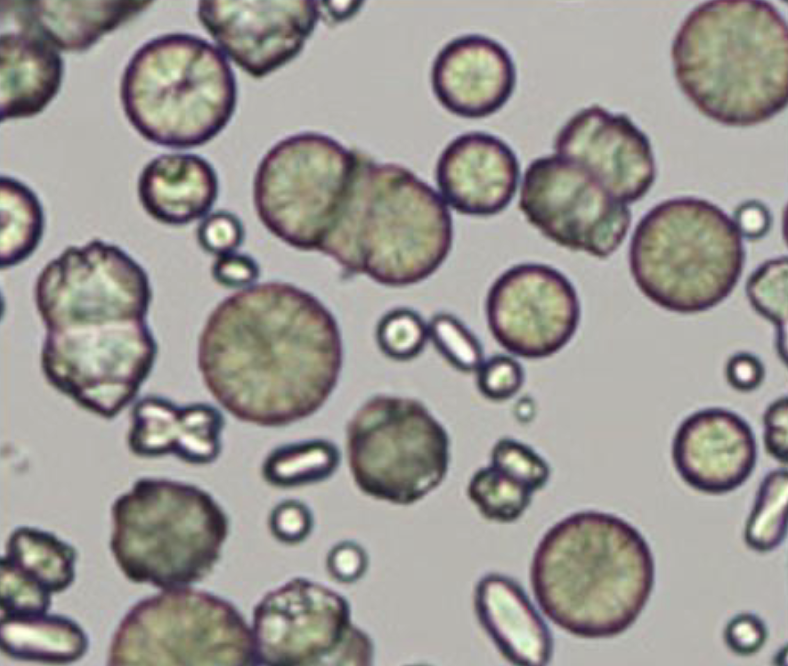
What is this crystal called?
What animals are these crystals normal in?
In what animals are they not seen?
Are they acidic or alkaline?
Calcium Carbonate
Horses, Goats & Guinea Pigs
Cats & dogs
Alkaline giving urine a milky appearance
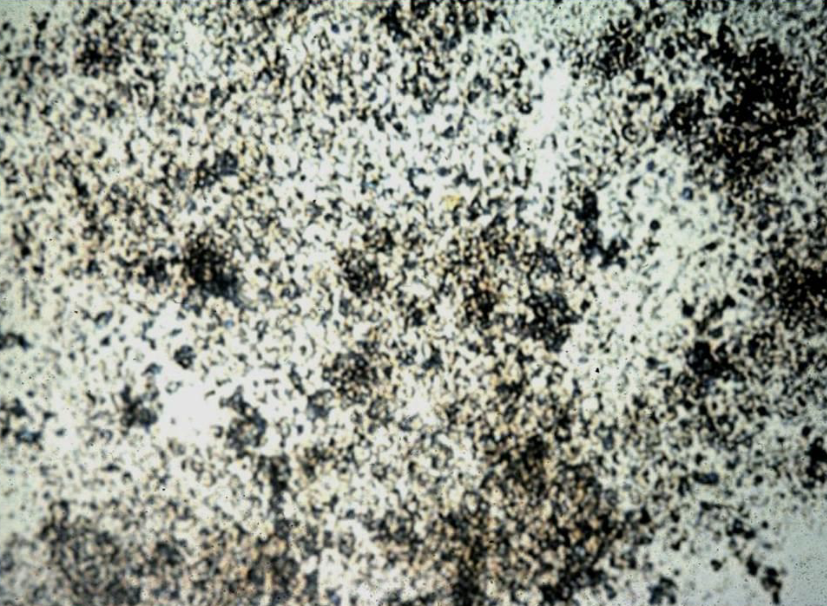
Is this bacteria & how can you confirm or deny this?
What crystals are these called?
What is the named of this crystal when present in alkaline urine?
What is the name of this crystal when present in acidic urine?
No & Line Smears Will Confirm
Amorphous
Amorphous Phosphate (Alkaline)
Amorphous Urate (Acidic)
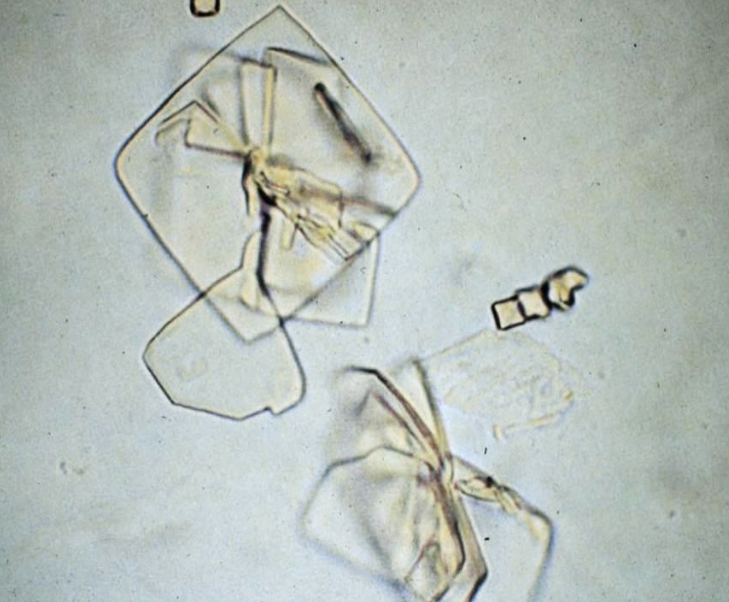

What is the name of this crystal?
What does it do to the body?
Is this crystal present in alkaline or acidic urine?
Uric Acid
Causes your joints to swell
Acidic hense Uric ACID
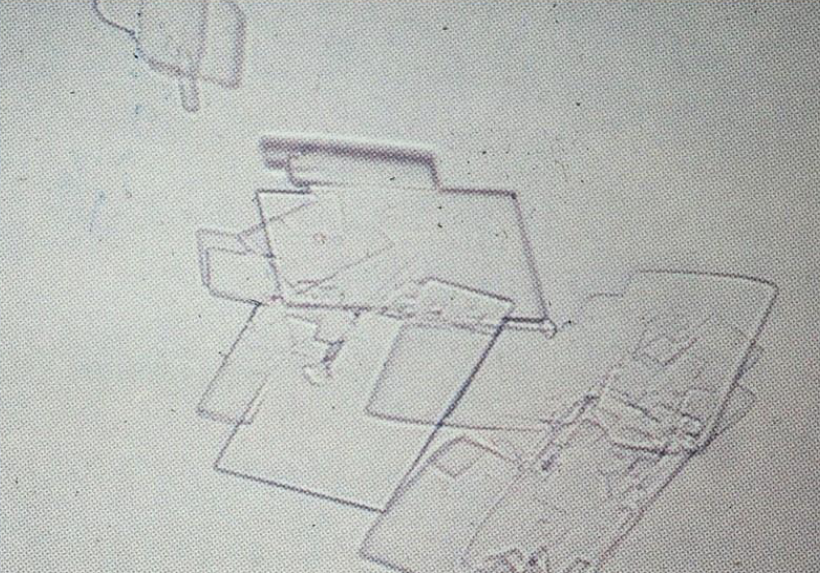
What is this crystal?
Does it like acidic or alkaline urine?
Cholesterol
Acidic Urine
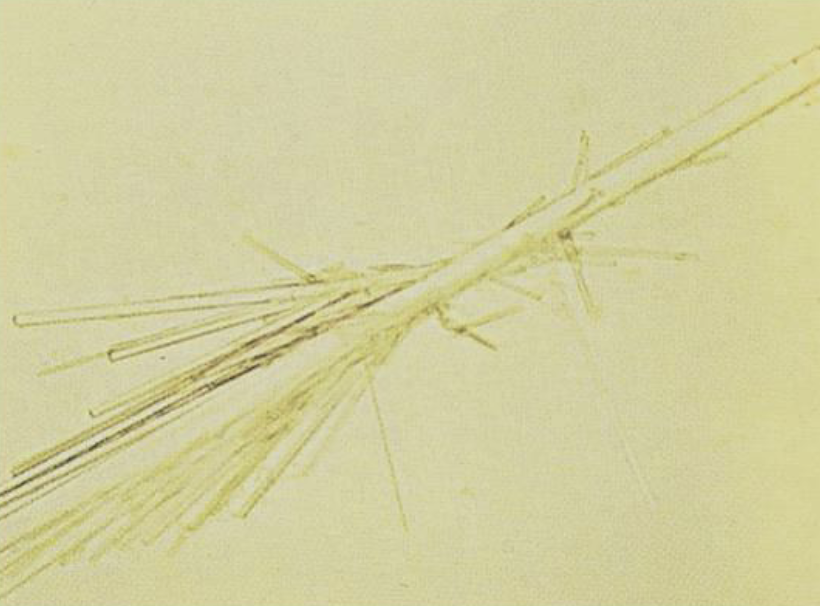

What medication causes this crystal in urine?
Are these crystals found in acidic or alkaline urine?
Renographin or Hypaque
Acidic Urine
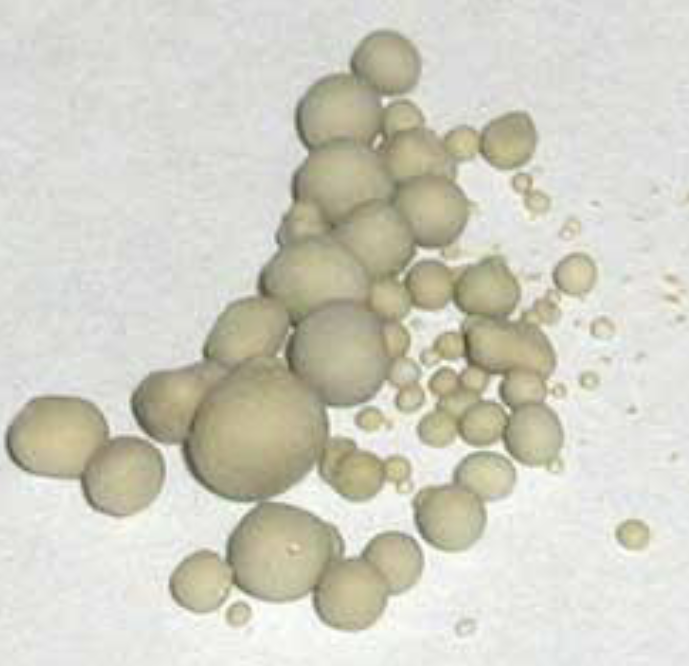
What is the crystal that formed on the exterior of these stones?
What is the nucleus made of?
What is the stones coating made of?
Briefly explain how this may have been formed?
Struvite
Nucleus = Calcium Oxalate Crystals
Stone Coating = Struvite Crystals (Due to Diet Change)
It began in acidic urine, where calcium oxalate crystals developed as the stone's nucleus. A diet change then made the urine more alkaline, leading to the precipitation of struvite crystals, which later coated the stone
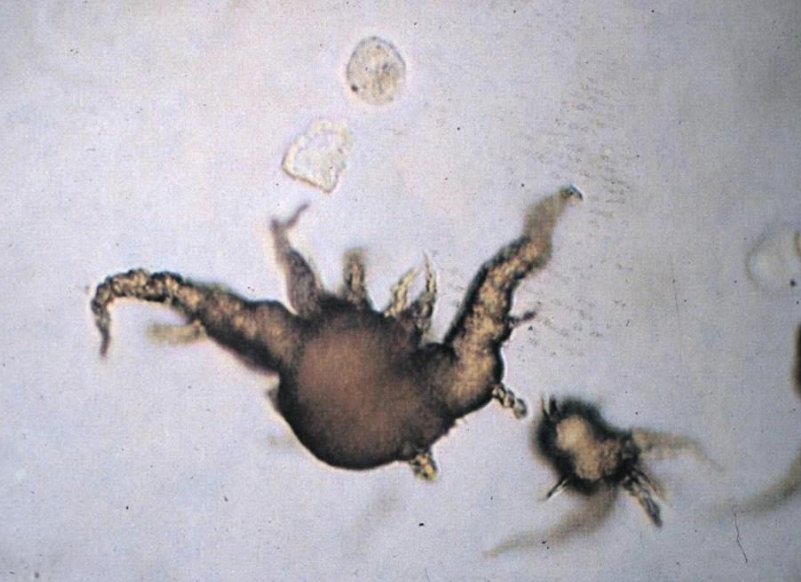
What is the common name for this crystal?
What is the scientific name for this crystal?
What species are they common in? List the breed
What amino acid can they not metabolize?
Are these crystals found in acidic or alkaline urine?
Thorn Apple
Ammonium Biurate Crystal
Dalmatian & English Bulldogs
Purine
Alkaline Urine
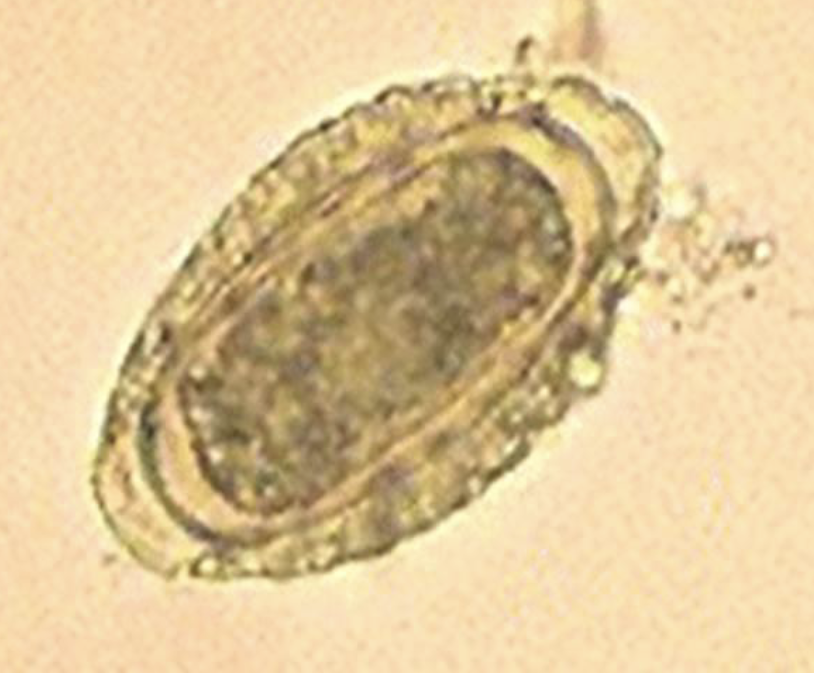
What is the common name of this parasite?
What is this?
Dioctophyma Renale
Giant Parasitic Worm Egg
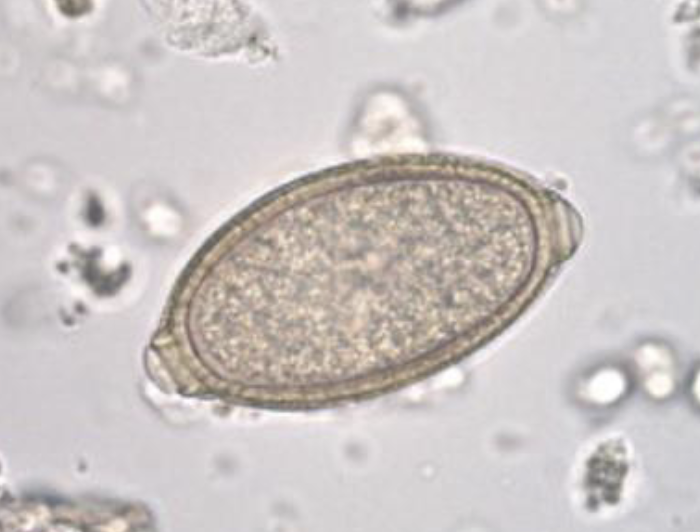
What is the common name of this parasite?
What can this be mistaken for?
Besides a cystocentesis what test can be done?
Capillaria Plica (Roundworm)
Trichuris Vulpis (Whipworm)
Fecal Examination
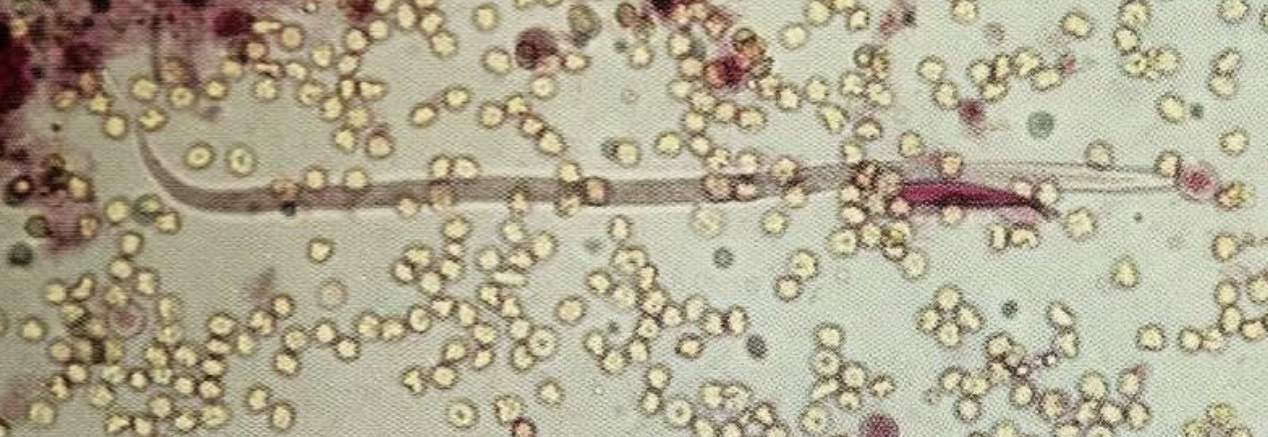
What parasitic worm is this?
What is surrounding it?
When would you see it in urine?
Dirofilaria Immitis (Heartworm)
RBCs
Hemorrhage in urinary tract
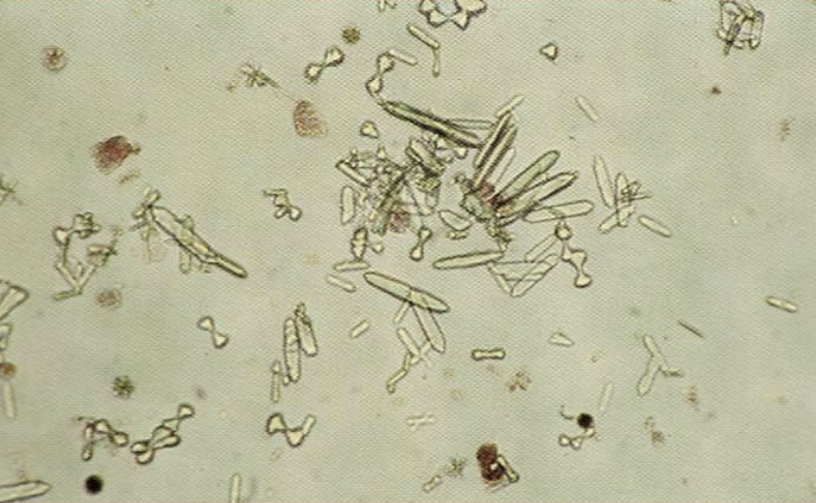
What crystals are these?
What is the name of the chemical/poison associated with this crystal and where is it found?
Are they found in alkaline or acidic urine?
Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate
Ethylene Glycol (Antifreeze)
Acidic Urine
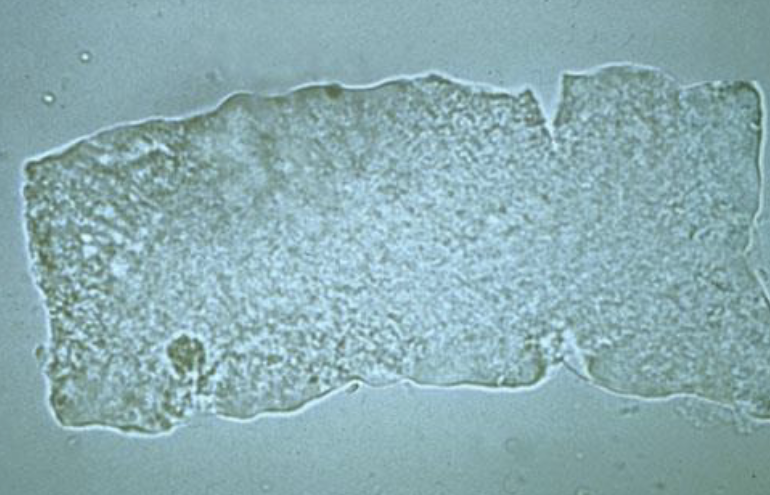
What type of cast is this?
When would you see these?
Broad Waxy Cast
Seen in Renal Failure or Urinary Stasis Patients (unable to fully excrete urine leading to urine retention)
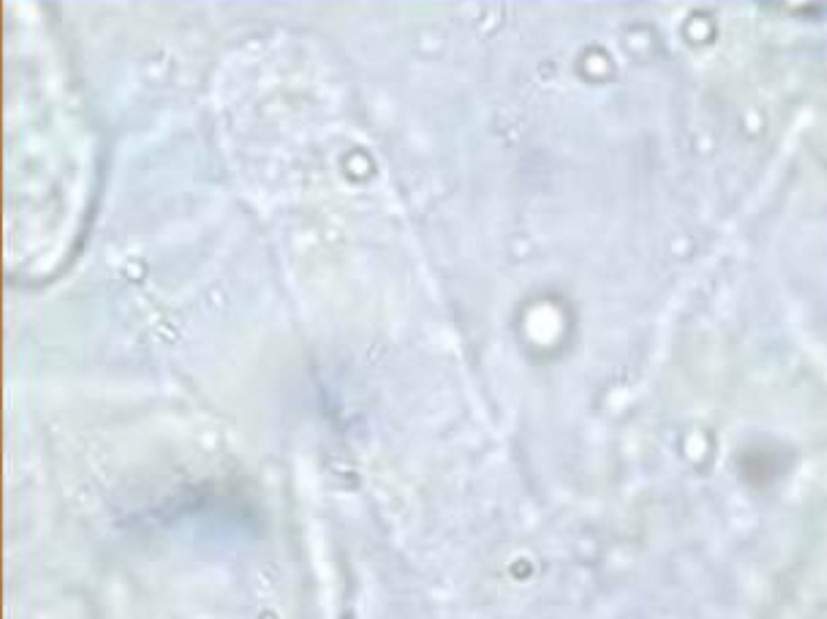
What type of cast is this?
Why is it difficult to see?
What protein is it made of?
When it normal to see small numbers of this?
When is it normal to see high numbers of this?
Hyaline Cast
Lower Refractive Index
Tamm-Horsfall Protein
Stress, Post Anesthesia & High Exercise
Congestive Heart Failure, Pyelonephritis
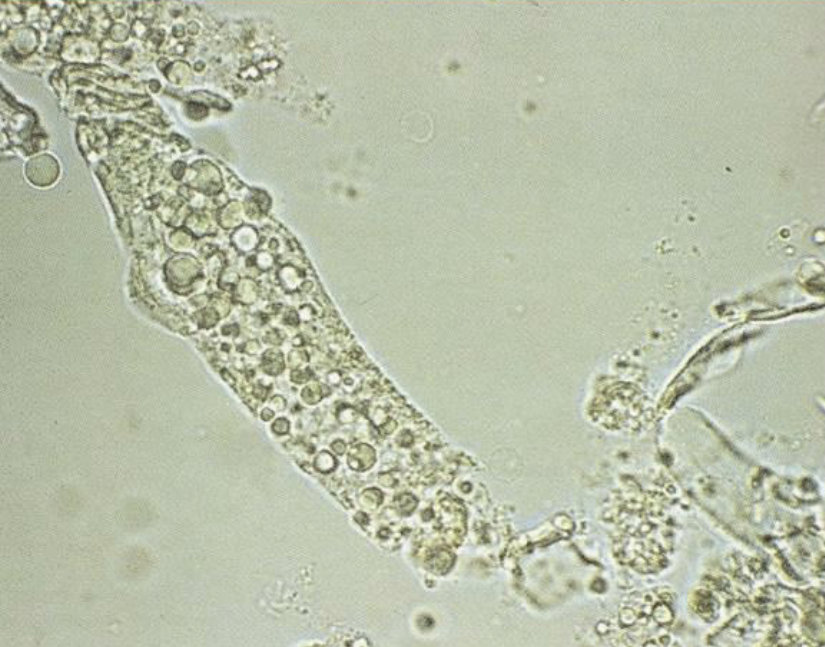
What type of cast is this?
What species will you see this as normal in?
When will you see large numbers?
Fatty Cast
Cats
Fatty Degeneration of Renal Epithelium (build-up of lipid in cells) in Severe Nephritis Patients
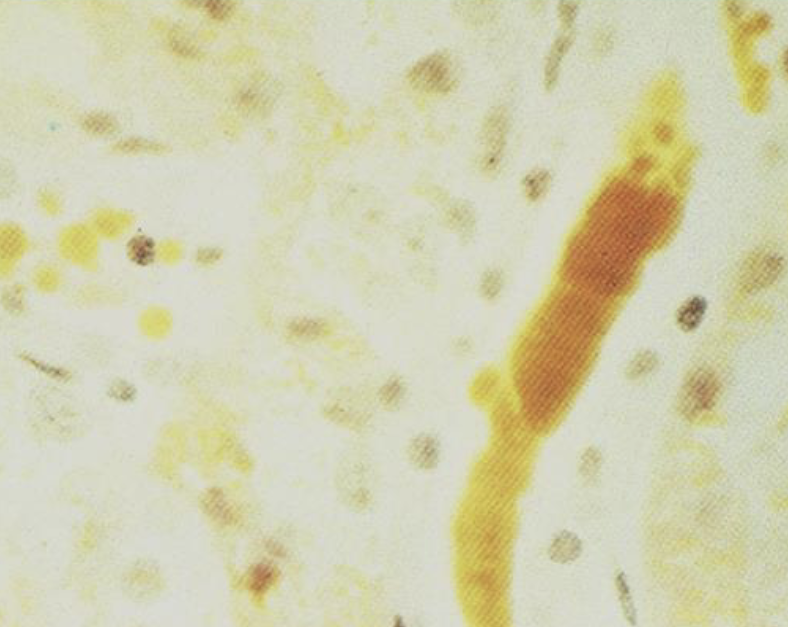
What type of non-stained cast is this?
If this is seen what would you expect to see?
Bio-Stained Cast or Bilirubin Stained Cast
Bilirubin Crystals
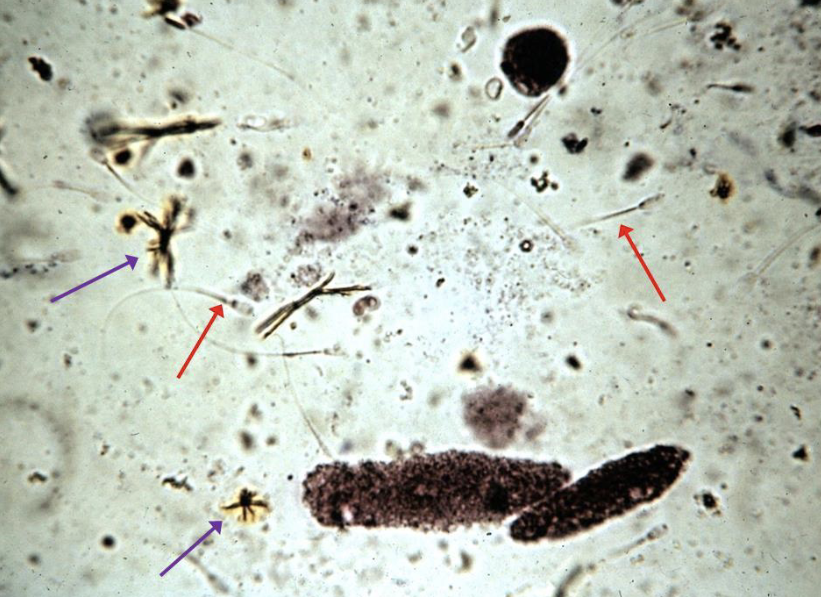
What type of cast is seen in this slide?
What are the red arrows pointing to?
What are the purple arrows pointing to?
Granular Cast
Sperm
Bilirubin Crystal
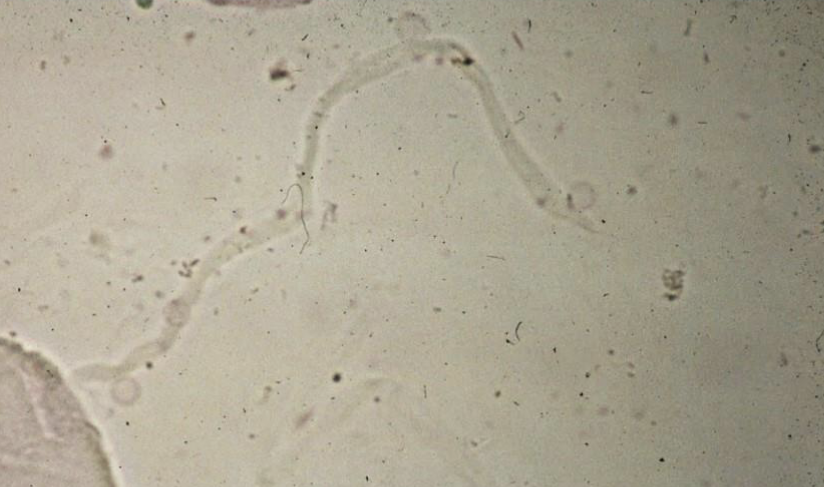
What is this?
Fibre
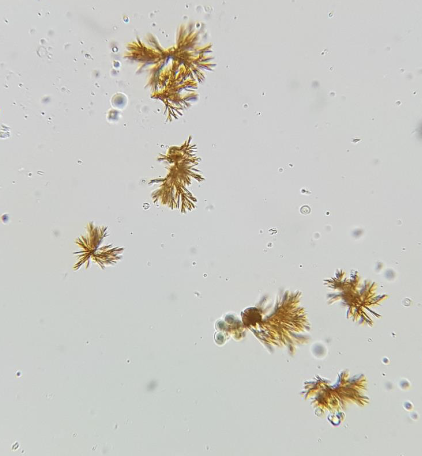
What are these?
When are they normal & are they in alkaline or acidic urine?
How might these negatively affect results of chemstrips?
Bilirubin Crystals
Normal when dog urine is very concentrated & are found in acidic urine
Bilirubin is yellow so it may dye the chemstrip giving wrong results
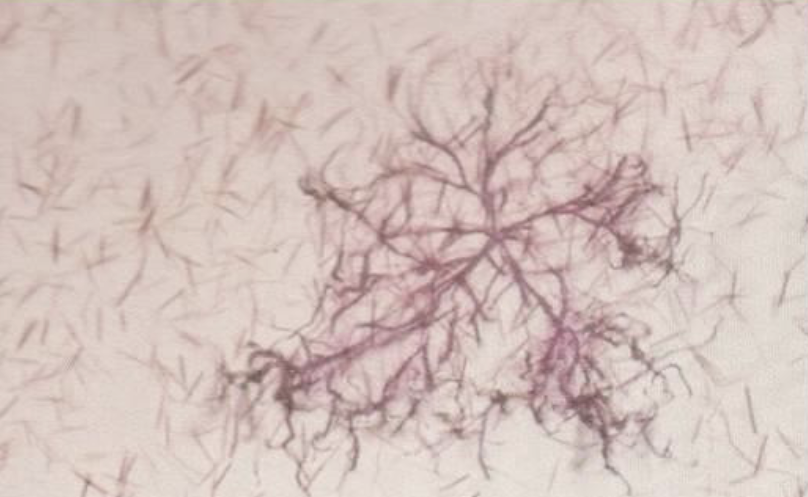
What is this?
What do we add to urine to make it this colour?
Stained Precipitate Artifact
Sedistain
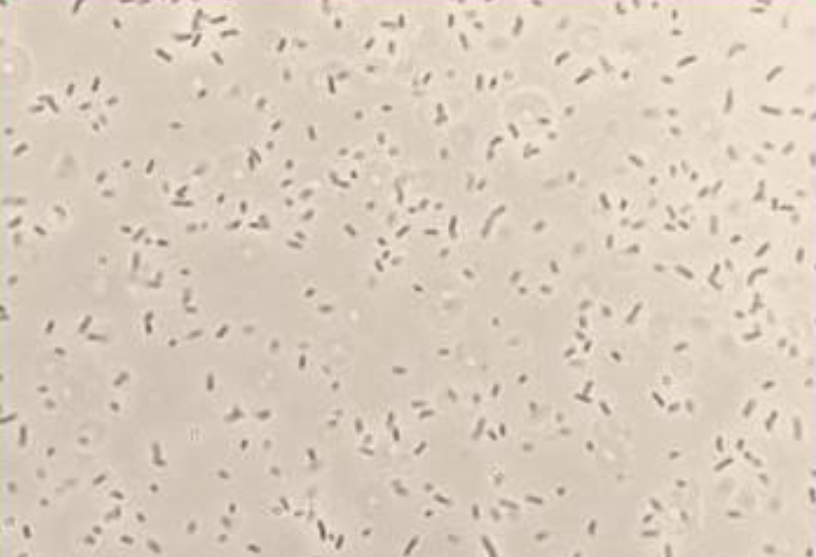

What would you rate this bacteria?
3+
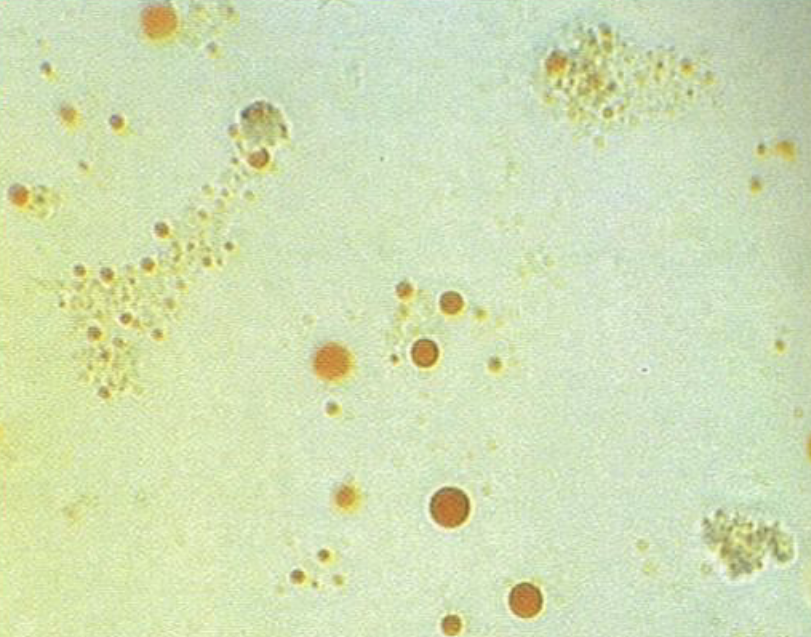
What is this?
What is the stain used to identify them?
Fat Globules
Sudan III Stain
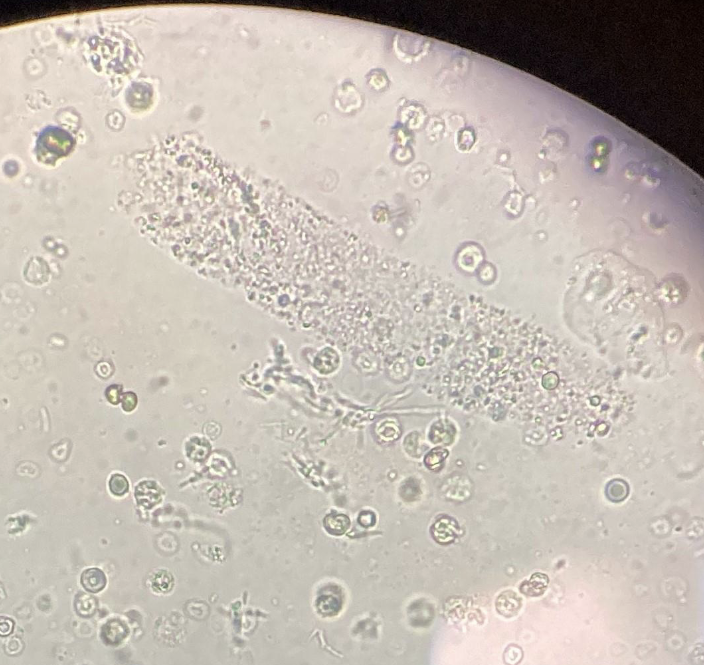
What type of cast is this?
What is the cell seen on the top right corner?
Be able to identify RBCs & Yeast on this slide
Granular Cast
Squamous Epithelial Cell
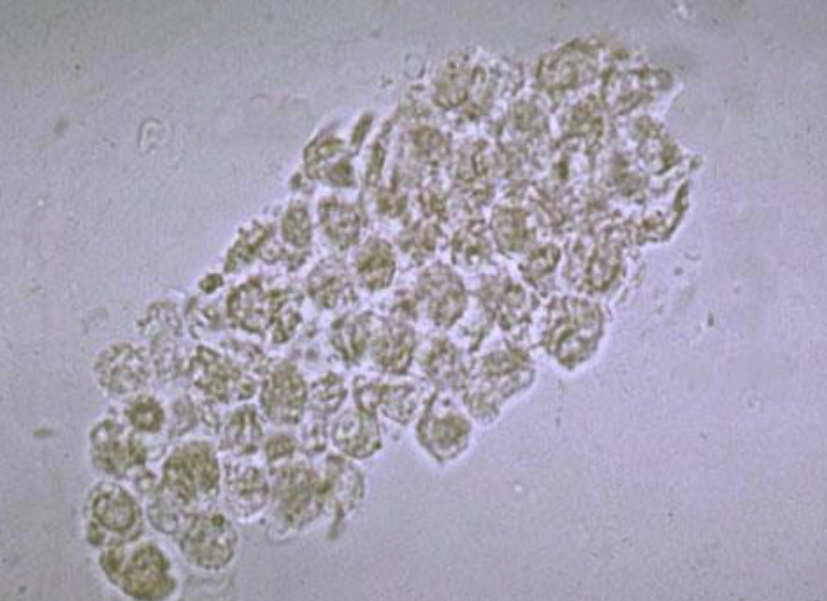
What is this cast?
When is it seen?
WBC Cast
In Kidney Infection/Inflammation
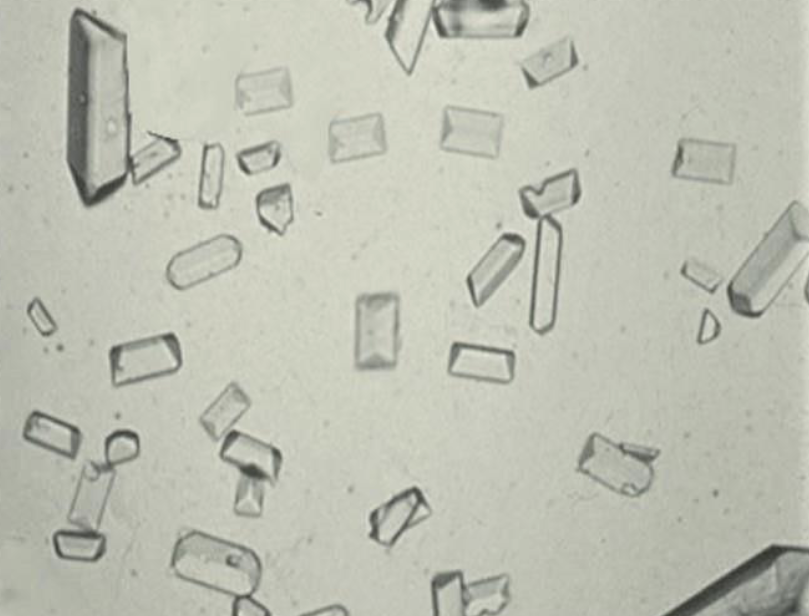
What are these crystals?
What is their habitat?
What is the full name of the disease that these crystals are associated with?
What pH do these crystals like?
What are the three different names for this crystal?
Struvite
Coffin-Lid
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease
Alkaline
Triple Phosphate, Magnesium Ammonium Phosphate & Struvite
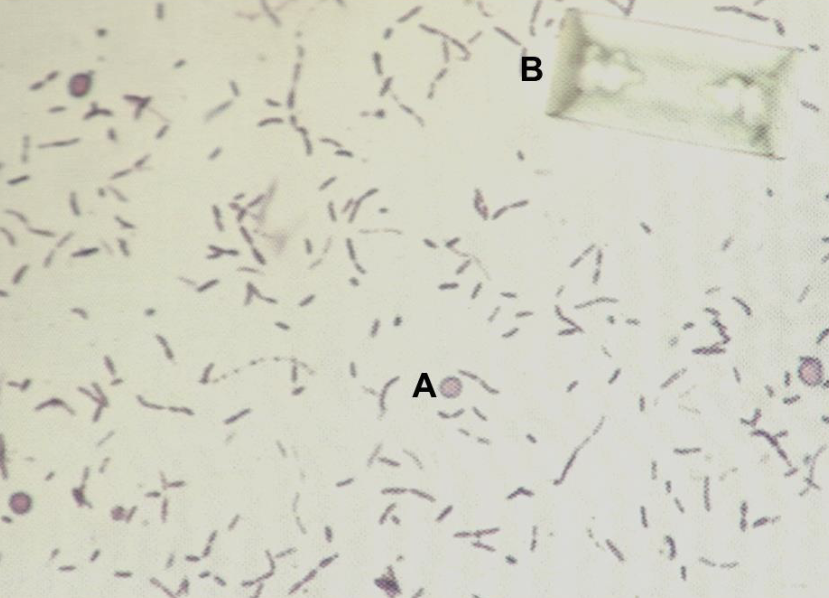
What is A?
What is B?
What would you grade this bacteria?
What is the majority of the sediment present?
If this was a feline urine sample, would it be primary or secondary disease?
If this was a canine urine sample, would it be primary or secondary disease?
RBC
Struvite Crystal
2+
Bacteria (Bacilli) Rods
Secondary
NOTE: Struvtes form → irritate bladder → inflammation = higher chance of bacterial infection
Primary
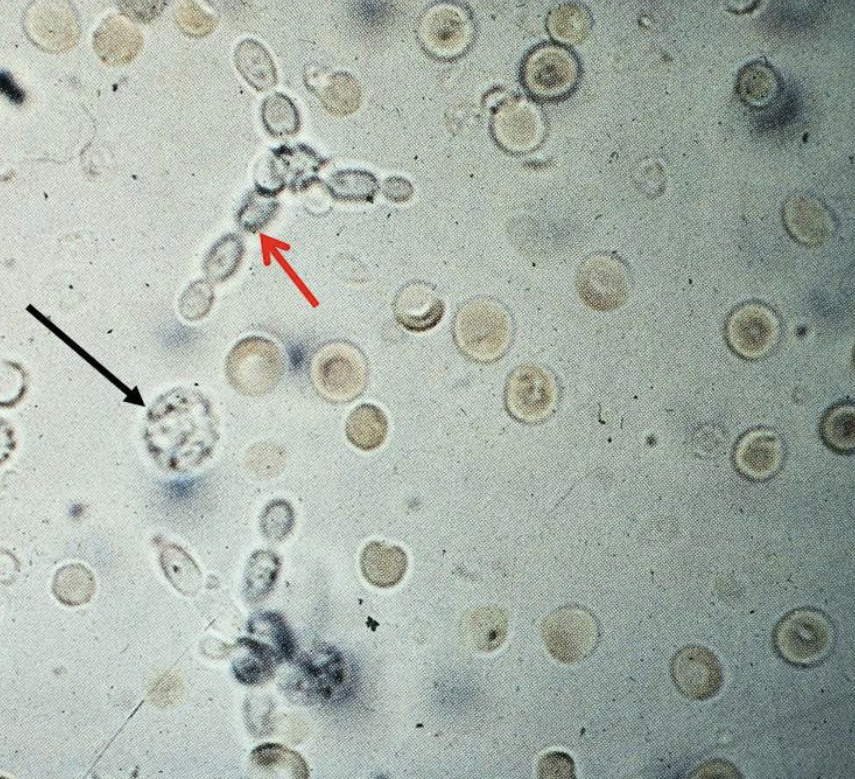
What is the red arrow pointing to & what is it doing?
What is the back arrow pointing to?
Yeast (Budding)
WBC
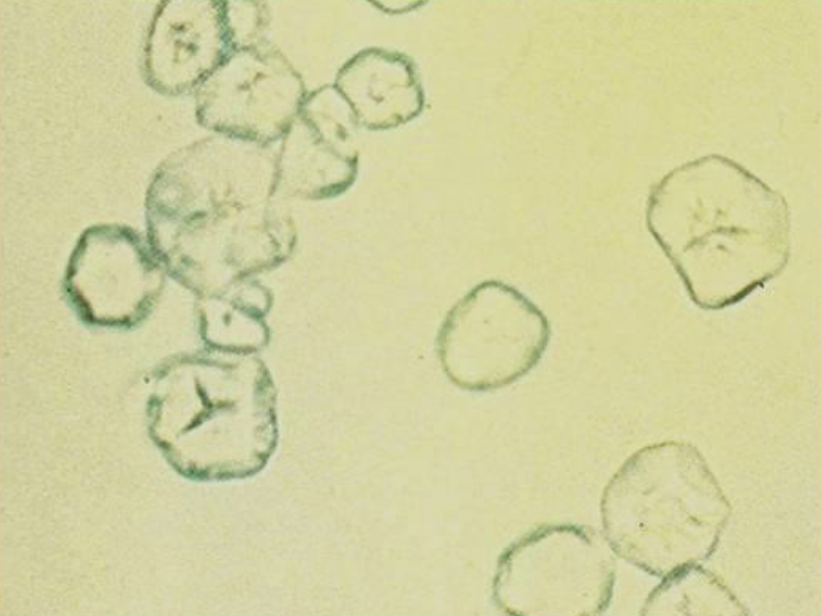
What is this?
Blood Starch
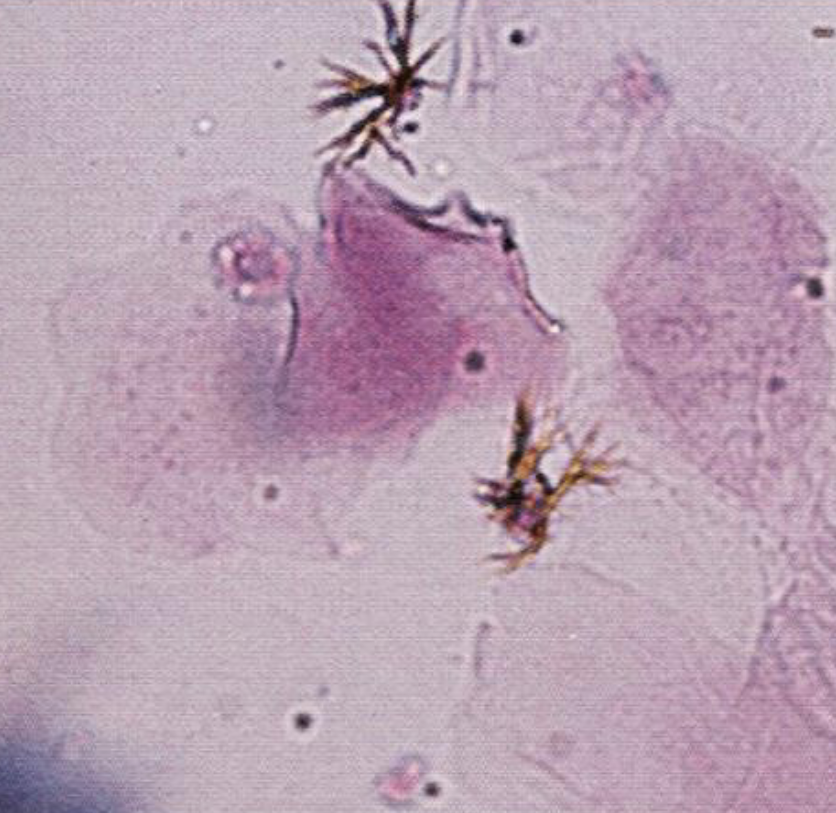
What is the crystal present?
Name the cells present?
What else might be present that is out of focus?
Bilirubin
Squamous Epithelial Cells
Lipid
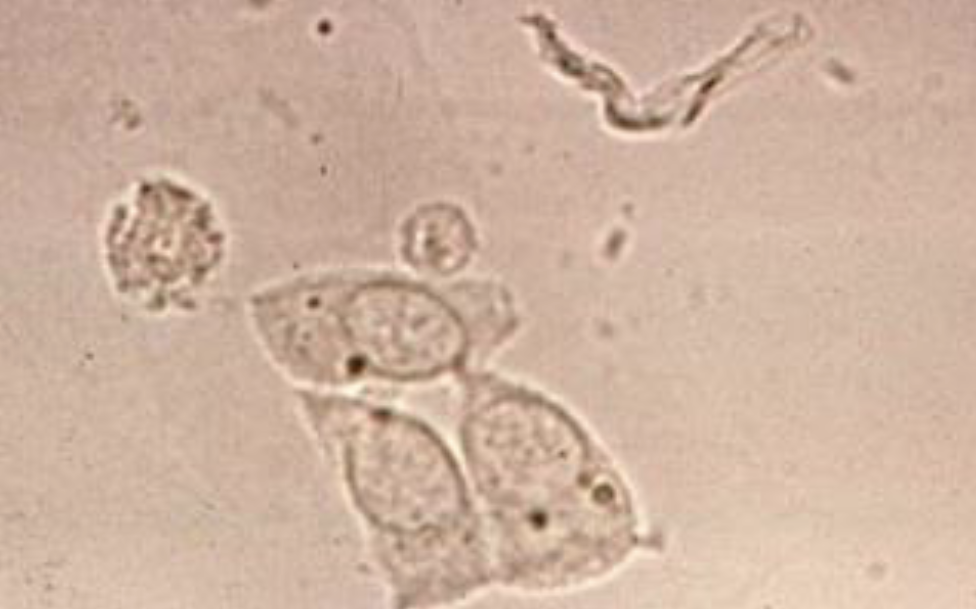
What is located beside the WBC?
Where are these produced?
What does it normally indicate when you see these?
Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells
Renal Tubules
Damage or stress to the renal tubules
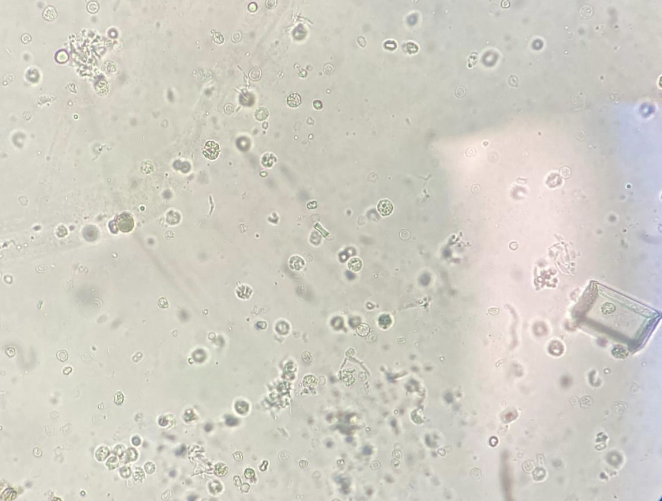
What is the crystal?
What else do you see on this slide?
Struvite
WBCs, RBCs & Mucous
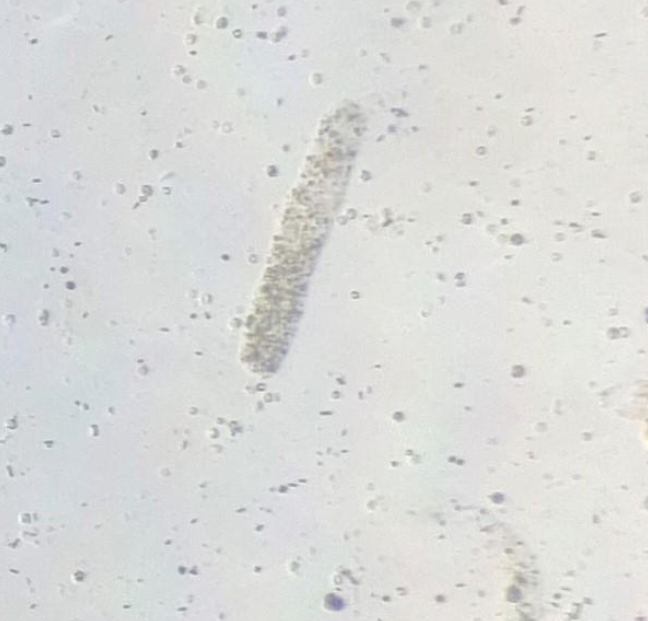
What type of cast is this?
What are the cells behind it?
Renal Cast
RBCs
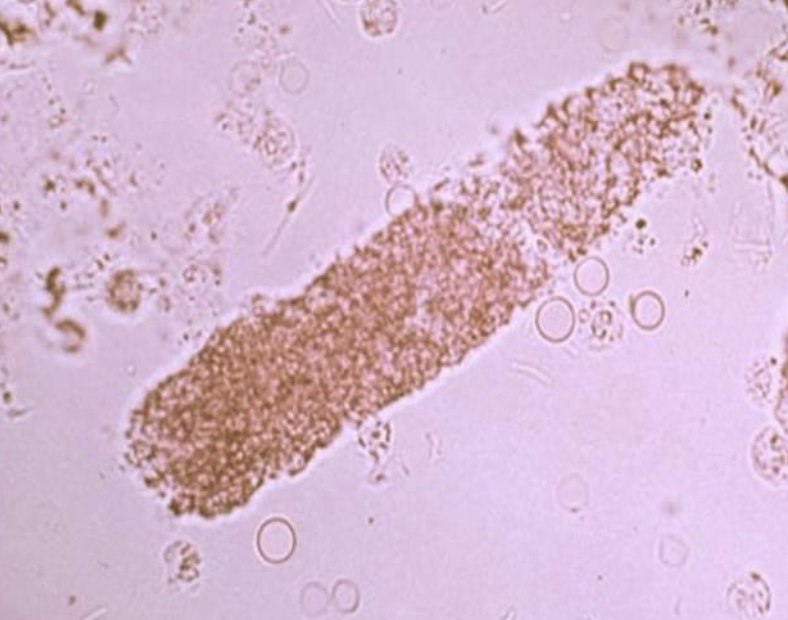
What type of cast is this?
What is a granular cast made up of?
Granular Cast
Degenerated Cells which stick to it
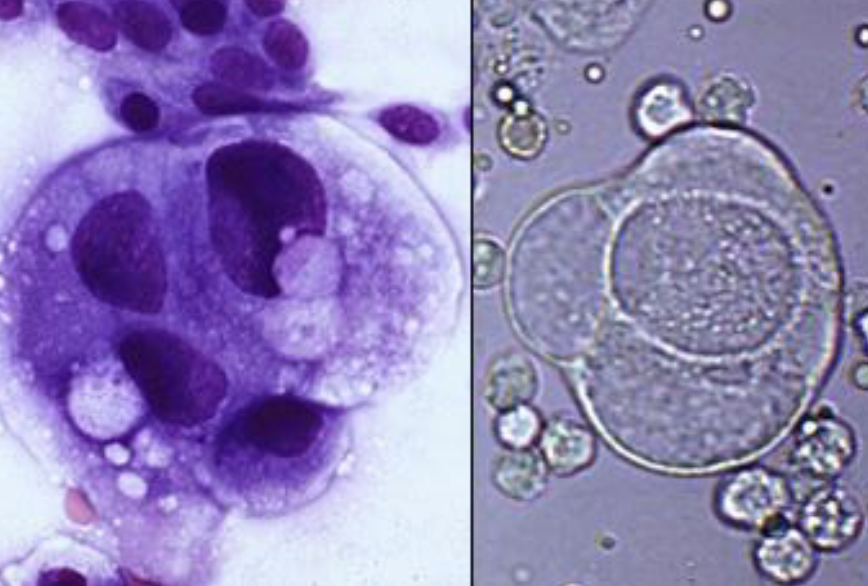
If you made a line smear and saw this, what would be your first thought?
What are the dark purple dots in the cell?
Neoplasia (Uncontrolled Growth of Cells Leading to Tumours)
Chromatin
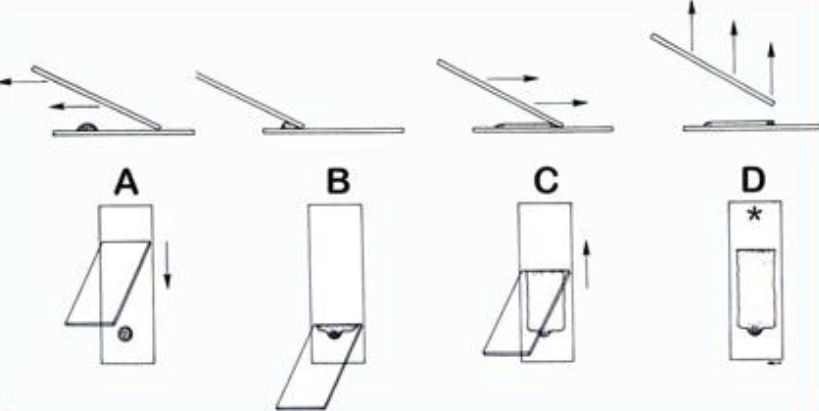
What is this technique called?
Why is this performed, list 3 reasons?
Line Smear
To confirm between amorphous crystals & bacteria
Decrease cellular confusion with hypotonic (swell) & hypertonic (shrink) effects.
Rule out neoplasia seen with abnormal cellular clusters.
Name two things that must be adjusted when changing from a vet prep to a line slide and briefly explain why this must happen
Drop the stage as low as it can go & subdue light
Iris Diaphragm (leaver under condenser) should be partially or fully closed
These two things allows you to see sediments with low refractive index