Oligopoly
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is an oligopoly?
A market dominated by a few large firms.
What are the characteristics of an oligopoly?
Each firm has a large market share
high level of market concentration
product differentiation
non-price competition
significant barriers to entry
Interdependency
LR and SR SN profits
What is the formula for market share?
Firm’s sales/Total market sales x100
What is market concentration?
The degree to which market share is distributed in a market.
What is ‘x’ firm concentration ratio?
The proportion of market share that the ‘x’ largest firms in the market have collectively.
What is product differentiation?
Methods that firms use to make their products stand out from the competition.
What is an example of product differentiation?
Branding, advertising, customer service etc.
What is an example of non-price competition?
Branding and other forms of product differentiation.
What is meant by interdependency?
Firms make their decisions based upon how they believe their competitors will react to these decisions.
What are the three oligopoly behaviours?
Price leadership
Price stability
Collusion
What is price leadership?
This occurs when there is one dominant firm in the market, usually with a larger market share and very strong brand loyalty. If it changes its prices other firms will follow.
What is price stability?
This occurs when prices tend to be stable for long periods of time, in these situations there may also be a tendency to price wars.
What is a price war?
Successive competitive cuts in prices to steal market share from the competition?
What else is price war known as?
Destroyer pricing
Why will firms cutting their prices be damaging to all firms in the LR?
There will be huge drops in revenue and profits, only the richest firm will survive.
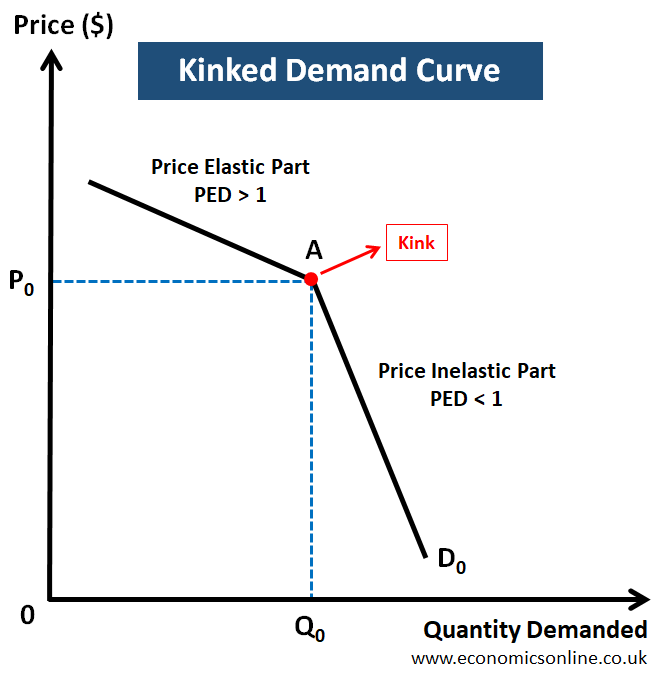
The kinked demand curve
If price is raised above P0, it will lead to a reduction in total revenue.
If price is reduced below P0, it will lead to a reductio in total revenue, because firms’ competitors will also reduce so the firm will receive few extra customers.
The MR curve in the kinked demand curve
The vertical discontinuity in the MR curve means that the cost structure can change radically but the maximsation output and price won’t, suggesting that firms will absorb any cost change in their profit rather than their prices.
What is collusion?
Occurs when firms make joint agreements to exploit consumers to increase their own profits.
What is collusion dependent on?
That a majority of the firms in the market must be in agreement.
What are the two types of agreement in collusion?
Explicit collusion
Implicit collusion
What is explicit collusion?
There is a formal agreement to restrict output and raise prices by a group of producers.
What is implicit collusion?
An informal agreement and no communication between firms, but prices remain higher than they would with competition.
What are the two types of collusion?
Raising prices
Market sharing
What is involved in raising prices?
Restricting supply means firms will push up prices and their revenue and profit will rise.
What is market sharing?
Firms agree not to compete in certain market segments thus leaving their rivals free to be effective monopolists over the market segment in which they operate.
What is collusion an example of?
Join profit maximisation
Why does collusion not usually last in the LR?
Firms begin to make a supernormal profit in the SR which attracts new firms.
There is always the temptation to cheat on the agreement as they will steal significant market share.
What is the prisoners’ dilemma scenario?
A classic game theory scenario that demonstrates how cooperation can be difficult to achieve even when it is in everyone's best interest.
How can the prisoners’ dilemma scenario be applied to economics?
Oligopoly competition, each firm has an incentive to maximise its profits, but if all firms do so, it can lead to a suboptimal outcome