Biology: Module 2
1/235
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
236 Terms
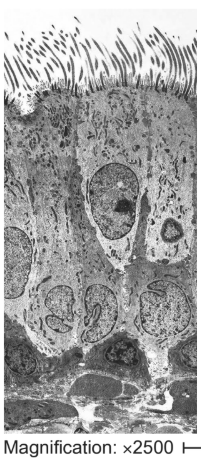
What microscope produced this image and why?
TEM
High magnification, high resolution, 2D image
What are the advantages of light microscopes?
Living organisms, cheap, easy to use
What are the disadvantages of light microscopes?
Low magnification, low resolution, requires thin specimens
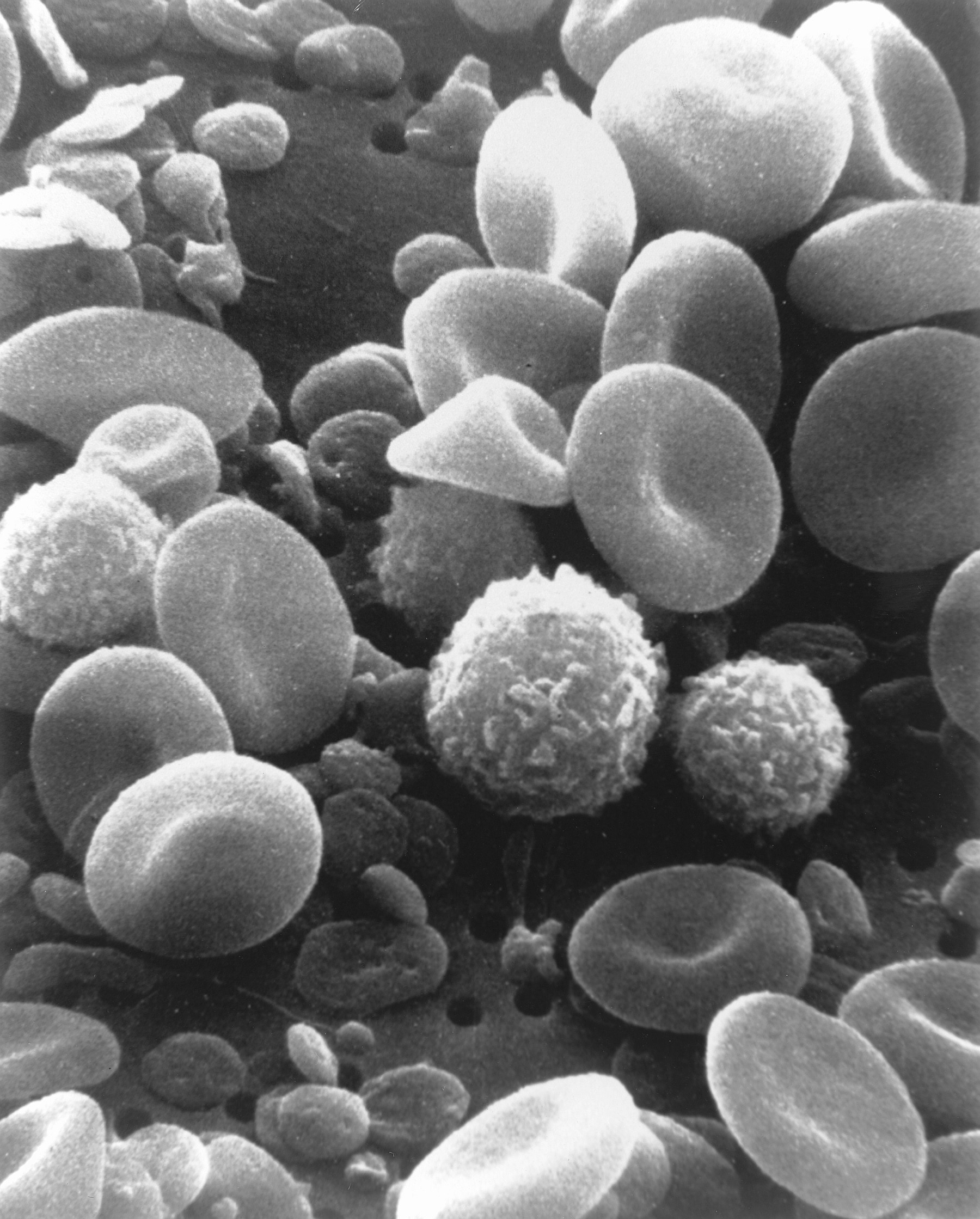
Explain which microscope produced this image?
High magnification, high resolution, 3D image
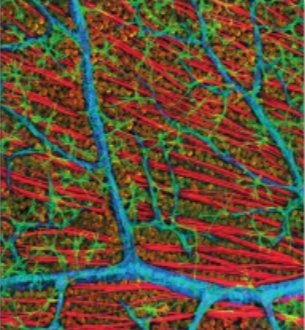
Which microscope produced this image?
Laser scanning microscope
Are laser scanning microscope images B&W or coloured?
Coloured
What are advantages of laser scanning microscopes?
Depth selectivity, high resolution, high contrast
What are the disadvantages of electron microscopes?
Large, expensive, only dead specimens, training required to use
What is the approximate size of a bacterium?
1μm
What is the approximate size of a mitochondria/chloroplast?
1μm
What is the approximate size of a virus?
100 nanometres
What is the approximate size of a ribosome?
10 nanometres
What is the approximate size of a protein?
10 nanometres
What is the approximate size of a human cell?
25μm
Outline how to measure a cell with a light microscope?
Eyepiece graticule
Calibrate eyepiece graticule with stage micrometer
Measure the (something) in epu
Take repeat measurements and calculate mean
Use calibrated epu to calculate actual distance in micrometers
What does differential staining distinguish?
Cell types, cellular components, organisms
What is the purpose of staining a slide?
Image clearer
Higher contrast
More named (e.g. mitochondria) organelles visible as they bind to the stain
See internal structures
State key rules/improvements for scientific drawings?
Add scale/magnification
Do not shade
Sharp pencil
Add a (descriptive) title
Correct proportions of components
State the magnification formula?
I=AM
What is the resolution (of a microscope) defined as?
Smallest distance between two points still distinguishable as two points
What is magnification?
How much bigger the image is than the original orbject
What does acetic orcein stain, and what colour?
Chromosomes dark red
What does iodine stain, and what colour?
Carbohydrates blue/black
What is the approximate magnification of a SEM vs TEM?
SEM is lower - roughly 100,000x
TEM is higher - roughly 50,000,000x
What is the max. magnification of a light microscope?
1500x
Is the nuclear membrane single or double?
Double
What is the function of the nucleus?
Store DNA, control the cell, provide instruction for protein synthesis
What is the function of the nucleolus?
Synthesise ribosomes
What is the function of the RER?
Fold proteins, intracellular transport, large surface area for ribosomes
What is the function of the SER?
Synthesis of cholesterol, lipids, steroid hormones and absorption of lipids from the gut
What is the function of the golgi apparatus?
Modify proteins, package proteins into secretory vesicles
What is the function of mitochondria?
Produce ATP through aerobic respiration
What is the function of chloroplasts?
Site of photosynthesis
What is the function of lysosomes?
Compartmentalising hydrolytic enzymes, engulf old organelles/foreign matter
What is the function of cilia?
Move mucus
What is the function of flagella?
Aid movement of cell
What is the function of the cell wall?
Mechanical strength for the cell
What is the function of centrioles?
Organise spindle fibres to separate chromosomes
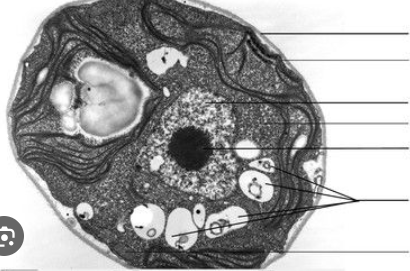
State the organelles from top to bottom of this plant cell?
Cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, nucleolus, vacuoles, mitochondria
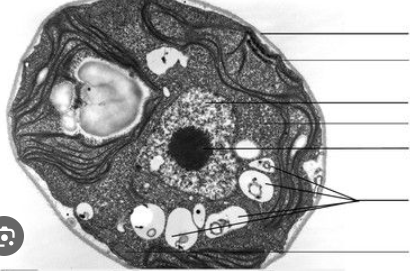
What is the structure near the edge of the cytoplasm with a stringy look?
Chloroplasts
How is a protein synthesised and secreted?
Gene is transcribed to produce mRNA
mRNA is translated by ribosomes
Polypeptide is folded in the RER
Protein travels in vesicles to golgi apparatus
Golgi modifies protein and packages into secretory vesicles
Protein released via exocytosis
What is the function of the cytoskeleton?
Provides mechanical strength to cells
Enabling cell movement
Movement of organelles
Movement of chromosomes/chromatids
What are similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Both have:
plasma membrane
cytoplasm
ribosomes
DNA and RNA
What are differences of prokaryotic compared to eukaryotic cells?
Circular DNA, not chromosomal
Smaller size
No nucleus
No membrane bound organelles
Smaller 70s ribosomes
What evidence supports the endosymbiosis theory?
Mitochondria…
Are similar shape/length to bacterium
Contains 70s ribosomes
Has circular DNA
May have plasmids
Has double membrane
How doba
What are the roles of water?
Solvent, transport medium, coolant, habitat
What are properties of water related to its function?
Polar, hydrogen bonding, high surface tension, adhesion and cohesion, high specific heat capacity, high latent heat of vaporisation
What two groups react in a condensation reaction?
OH
What chemical elements are present in carbohydrates?
C, H and O
What chemical elements are present in lipids?
C, H and O
What chemical elements are present in proteins?
C, H, O, N and S
What chemical elements are present in nucleic acids?
C, H, O, N and P
State the difference between alpha and beta glucose?
Hydroxyl on carbon 1 in alpha glucose is below and beta glucose is above
What are the properties of glucose?
Soluble in water, reducing sugar
What is the structure of ribose?

What is the structure of alpha glucose?

What is the structure of beta glucose?
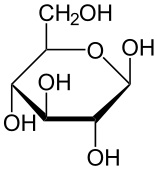
What type of monosaccharide is ribose?
Pentose
What type of monosaccharide is glucose?
Hexose
What is sucrose made from?
Alpha glucose and fructose
What is lactose made from?
Alpha glucose and galactose
What is maltose made from?
2 alpha glucose
State the bond in sucrose, maltose and lactose?
1-4 glycosidic
Describe the structure of starch?
Monomers of alpha glucose
10-30% amylose - coiled
70-90% amylopectin - branched
1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
Describe the properties and related function of starch?
Insoluble - doesn’t affect WP of cell
Coiled/branched - takes up less space in cell
Longer to hydrolyse - plants don’t require energy immediately
Many terminal glucose in amylopectin - hydrolysis/addition
Describe the structure of glycogen?
Monomers of alpha glucose
1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
1-6 produces branching
Describe the properties and related function of glycogen?
Alpha glucose - respired to release energy
Glycosidic bonds - easily hydrolysed to release glucose
Branches - rapid release of glucose monomers
Insoluble - doesn’t affect WP of cell
Describe the structure of cellulose?
Monomers of beta glucose
Alternate monomers flipped 180°
Forms hydrogen bonds between long chains
Describe the properties and related function of cellulose?
Hydrogen bonds - increase mechanical strength to support plant
High tensile strength - withstand turgor pressure
Freely permeable - molecules enter/exit cell
Beta glucose - few organisms have cellulase to hydrolyse cellulose
Draw the structure of a triglyceride?

What is a triglyceride made from?
Glycerol and 3 fatty acids
Draw the structure of a phosphlipid?
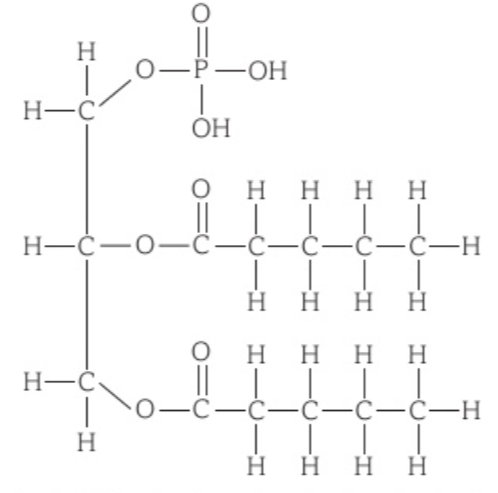
What is a phospholipid made from?
Phosphate, glycerol, 2 fatty acids
What is the structure of unsaturated phosphlipids?
C=C bond, cis acid causes bending of chain - increases membrane fluidity
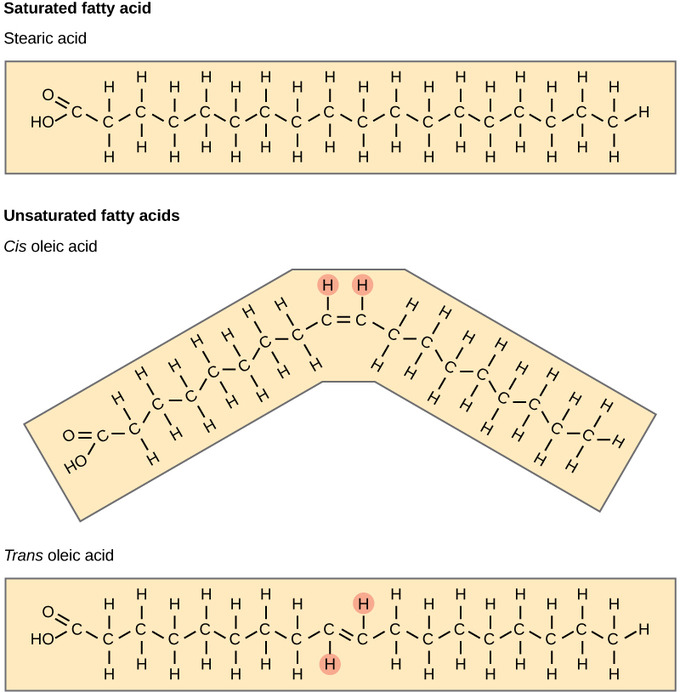
State the bond in a triglyceride?
Ester
Explain how the properties of a triglyceride is related to its function?
Insulation - myelin sheath/adipose tissue
Oxidising C-H - releases metabolic water for desert animals
Energy - lots of C-H bonds so contain lots of energy
Buoyancy - low density
Protection - cushion organs from damage
Explain how the properties of a phospholipid is related to its function?
Higher proportion of unsaturated fatty acids - more fluid of membrane
Polar and non-polar region - form phospholipid bilayer
Lipid core of bilayer - only lipid soluble molecules can diffuse through
Explain how the properties of cholesterol is related to its function?
Hydrophilic and phobic regions - exist in bilayer
Disrupts packing of phospholipids - increase rigidity of membrane
Acts as barrier - prevents water soluble substances passing through bilayer
Draw an amino acid?
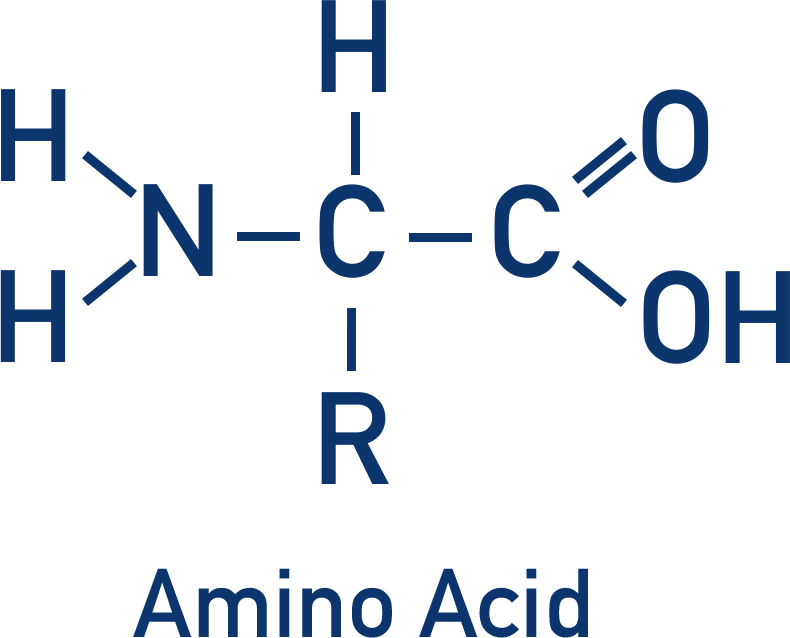
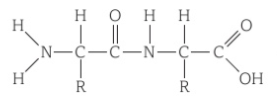
What type of reaction is forming a di/polypeptide?
Condensation
What bonds are formed in primary protein structure?
Peptide bonds
What bonds are formed in secondary protein structure?
Hydrogen
What structures can be formed in secondary protein structure?
B-plated sheet or A-helix
What bonds are formed in tertiary protein structure?
Disulfide bridges, ionic bonds, hydrophilic/phobic interactions
What is only present in quaternary protein structure?
Multiple subunits (polypeptides), prosthetic groups
Describe the structure of haemoglobin?
2 alpha and 2 beta subunits
4 prosthetic haem groups - bind to oxygen
Hydrophobic R groups inward and hydrophilic outwards
Globular protein
Variable amino acid sequence
Describe the structure of insulin?
2 polypeptide chains
A has 21 amino acid
B has 30 amino acids
3 disulfide bridges
Hydrophilic R groups face outwards - soluble
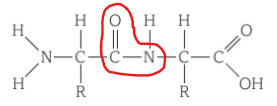
Circle the peptide bond?
Describe the properties and functions of collagen?
Mechanical strength
prevent arterial wall bursting under high pressure
harden bones reinforced with collagen
Tensile strength - tendons connect muscles to bone so muscles can pull
Describe the properties and functions of keratin?
Mechanical protection - nails, hair, claws, hooves, scalels
Impermeable to pathogen - prevents infection
Waterproof - prevents entry of waterborne pathogen
Describe the properties and functions of elastin?
Elastic:
Skin stretches around bones and muscles
Lungs to inflate and deflate
Bladder expands and contain urine
Arteries can stretch and recoil
What is the structure and function of pepsin?
Globular protein - complementary active site to substrate
Mostly acidic R groups - stable in acidic environment of stomach
Hydrogen bonds and disulfide bridges - maintain 3D shape
Describe the test for protein?
Add biuret reagent slowly and shake
Positive - violet colour
Describe the test for reducing sugar?
Add benedict’s reagent and heat
++ brick red, + yellow, - green
Describe the test for non-reducing sugar?
Add dilute HCl and boil
Cool and neutralise
Add benedict’s reagent
++ brick red, + yellow, - green
Describe the test for starch?
Add iodine
+ turns blue/black
Describe the test for lipids?
Add water and ethanol and shake
+ cloudy emulsion forms
What are key points for colorimetry?
Measures % absorbance
Provides quantitative data, not subjective
Calibrate colorimeter
Use a calibration curve to estimate concentration
Outline chromatography for a protein?
Hydrolyse protein with protease enzyme
Place sample on pencil line on chromatography paper
Dry and repeat
Place in solvent
Ensure solvent lower than pencil line
Leave for a few hours
Stain with ninhydrin to visualise amino acids
Calculate Rf and compare with known Rf values