MCAT Psychology & Sociology (2023)
1/629
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
630 Terms
Papillae
taste buds
Kinesthetic sense
sense of the location of body parts in relation to the ground and each other and is sensed joint receptors
retinal height
Monocular depth cue.
Objects that are higher up in the visual field are perceived as being farther away than the objects that are lower in the visual field.
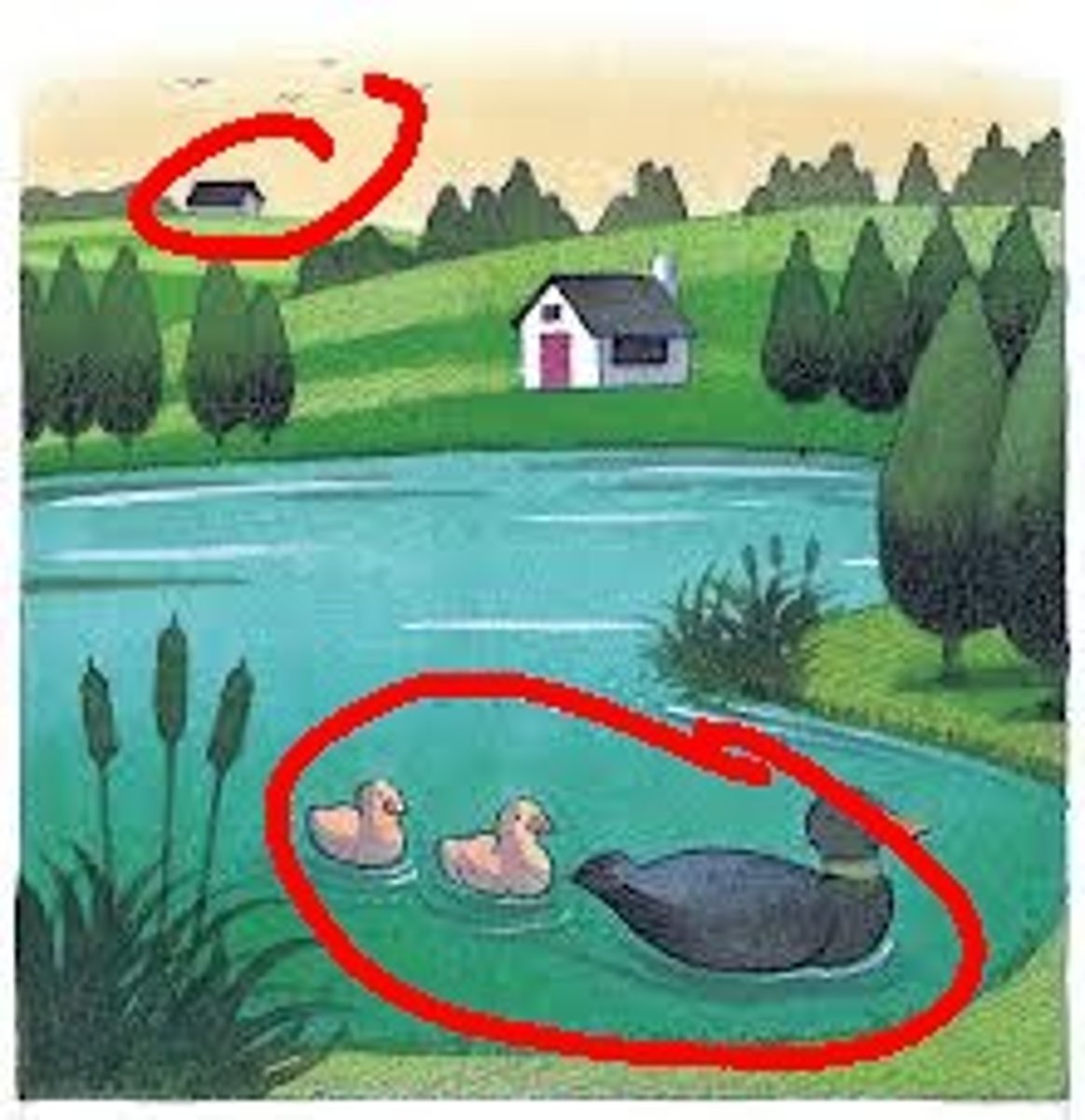

linear perspective
monocular depth cue
the more parallel lines converge, the greater their perceived distance.
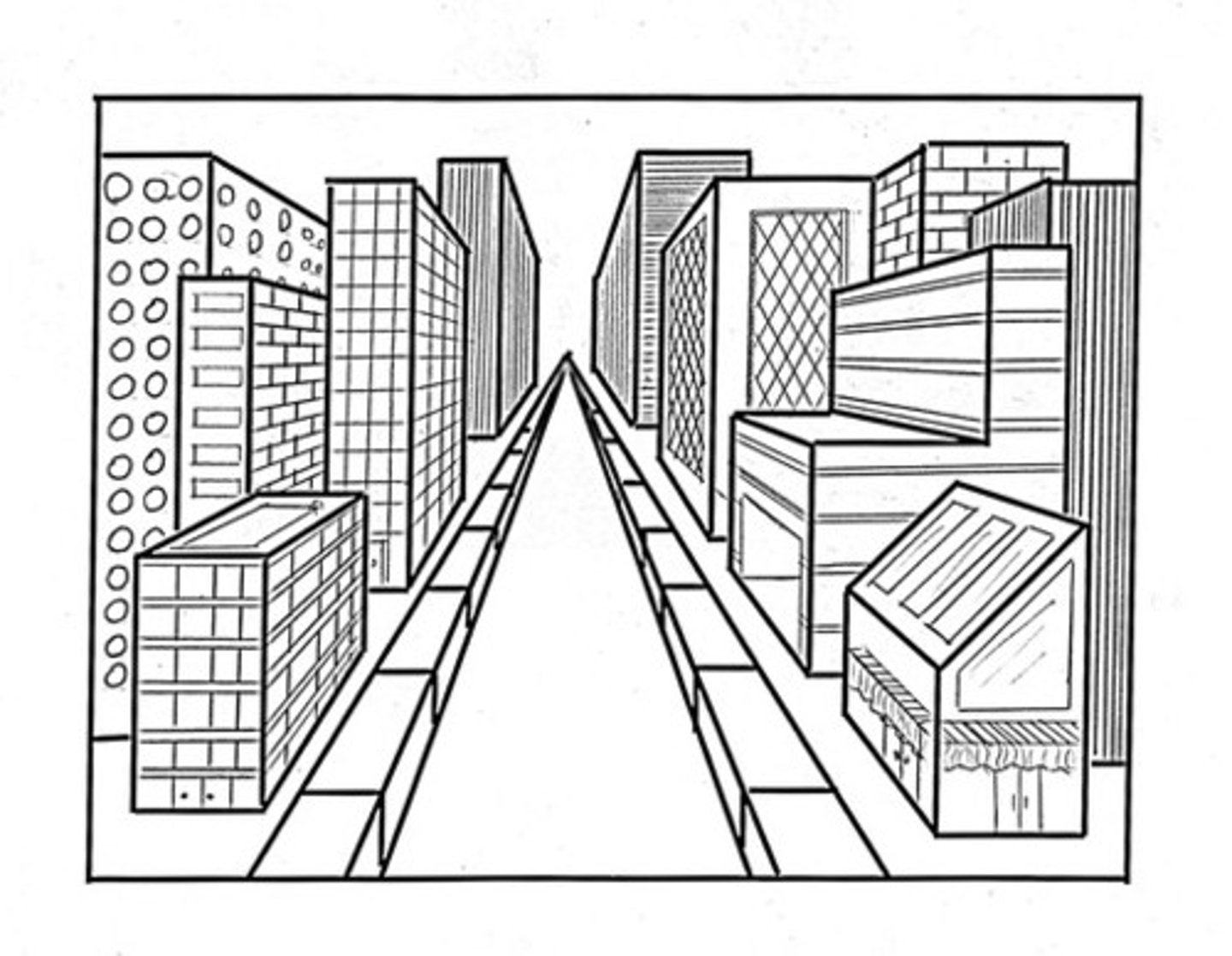
relative size
monocular depth cue
when two objects are presumed to be the same, the one producing the smaller retinal image is judged to be more distant
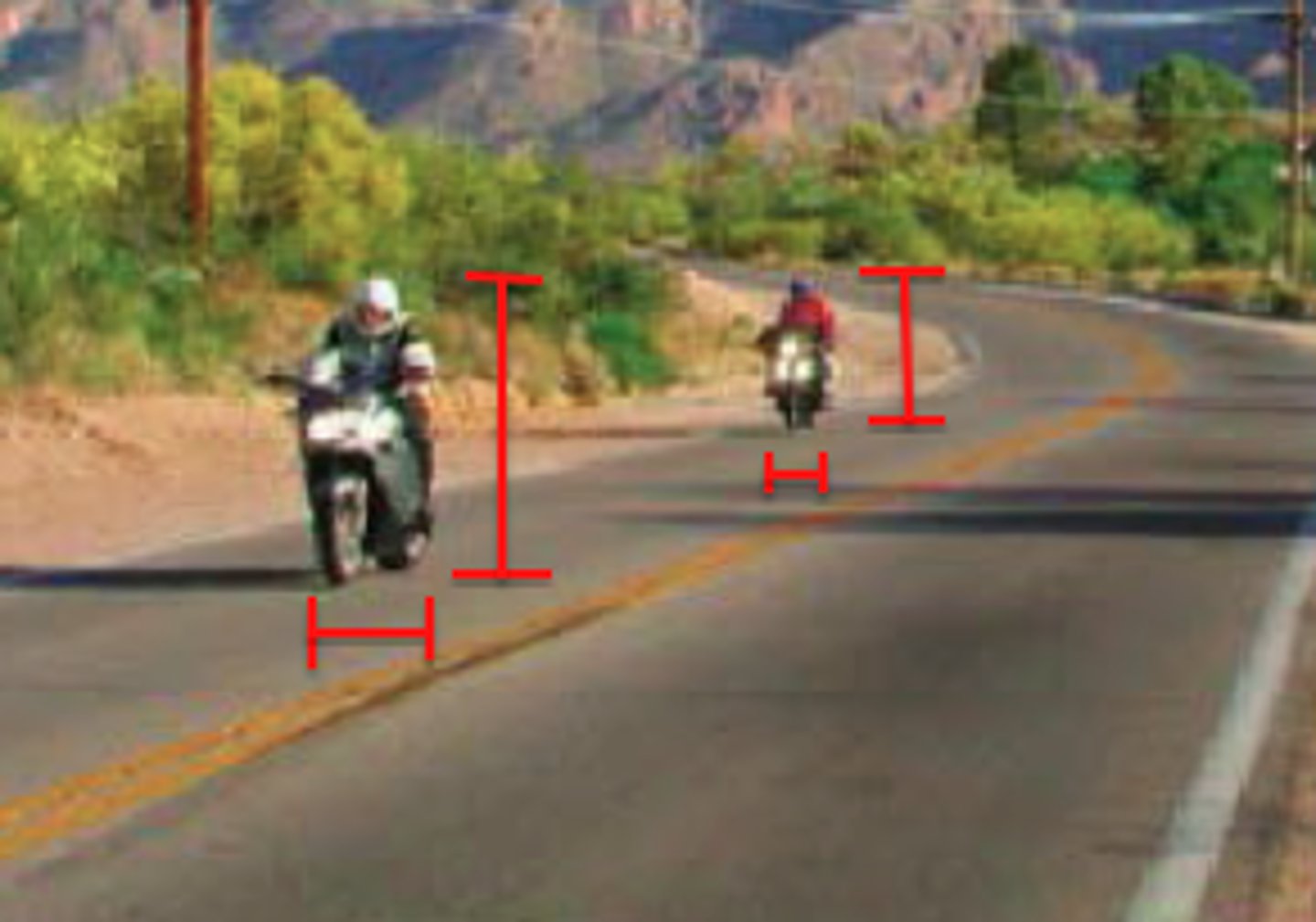

interposition
monocular depth cue
if one object partially blocks our view of another, we perceive it as closer to us.
light and shadow
monocular depth cue
creates the illusion of a 3D object
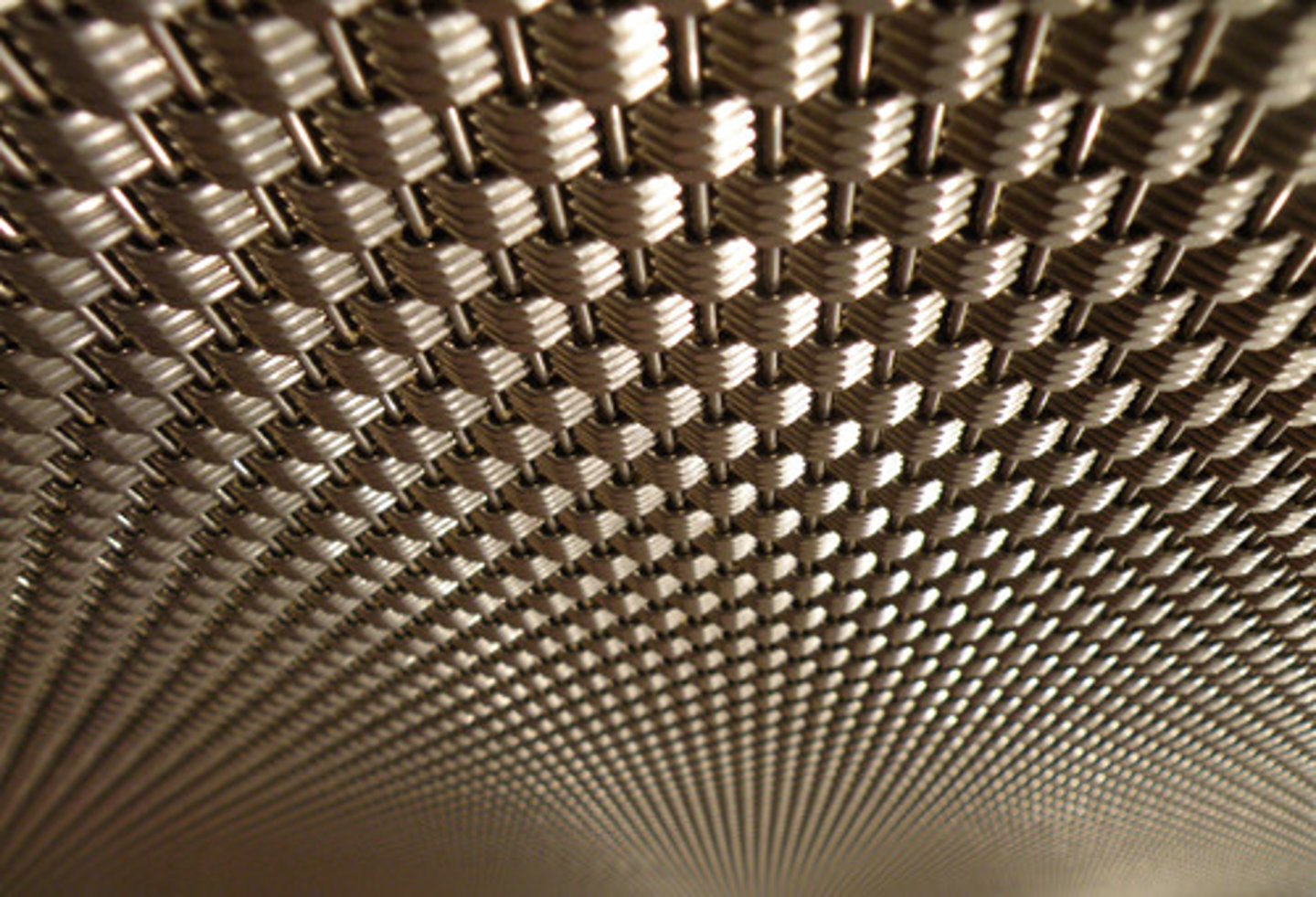
texture gradients
monocular depth cue
closer objects have coarser texture and more detail than distant objects
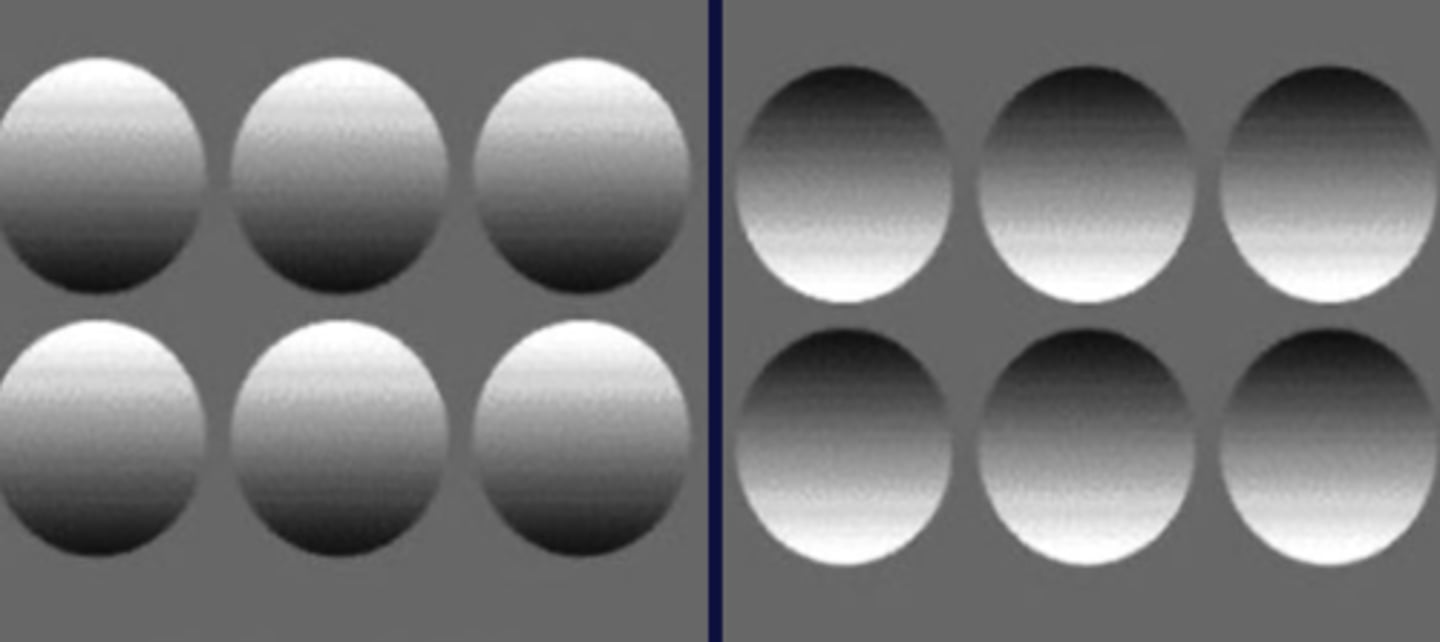
Retinal disparity
binocular depth cue
uses the difference in the images projected on the right and left retinas to inform the brain about the distance of a stimulus, also known as stereopsis
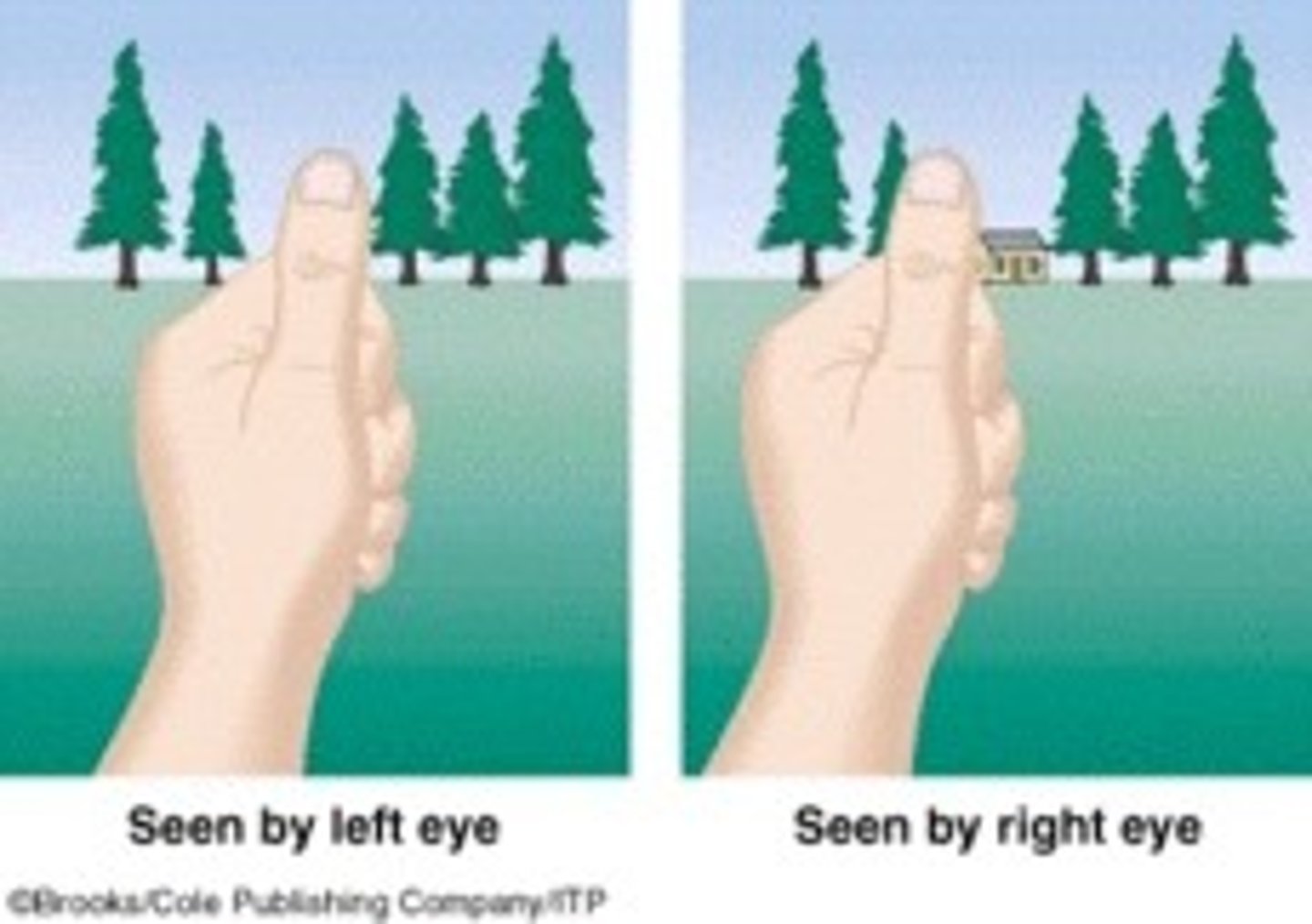
Convergence
A binocular depth cue
The extent to which the eyes turn inward (converge) to focus on an object
speech shadowing
an experimental technique in which subjects repeat speech immediately after hearing it (usually through earphones) while tuning out competing info
Availability bias
People base their decisions on the most salient information (whatever comes to mind first when thinking about a topic)
Hindsight bias
the tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it
Causation bias
tendency to infer a causal relationship among events that are merely correlated
Fixedness
Tendency to view an object as having no purpose other than the one for which it was originally designed
logical-mathematical, linguistic, visual-spatial, musical, kinesthetic, naturalist, interpersonal, intrapersonal
Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences measures:
linguistic and logical-mathematical
Gardner argues that western culture values these types of intelligences over others and are the only two tested on IQ tests.
Galton
Intelligence has a biological basis that could be studied by measuring reaction times to certain cognitive tasks
Binet
Measured intelligence based on age group
Spearman
Proposed a form of intelligence called "g" that influences our ability to learn and reason about any topic
Thurstone
Proposed 7 fundamental abilities that contribute to our ability to learn and reason about specific topics
A person could appear smarter with respect to some topics than others
Sternberg
Proposed three types of intelligences (analytical, creative, and practical)
interpersonal attraction
familiarity, physical attractiveness, and similarity in activities can all contribute to one's attraction to another
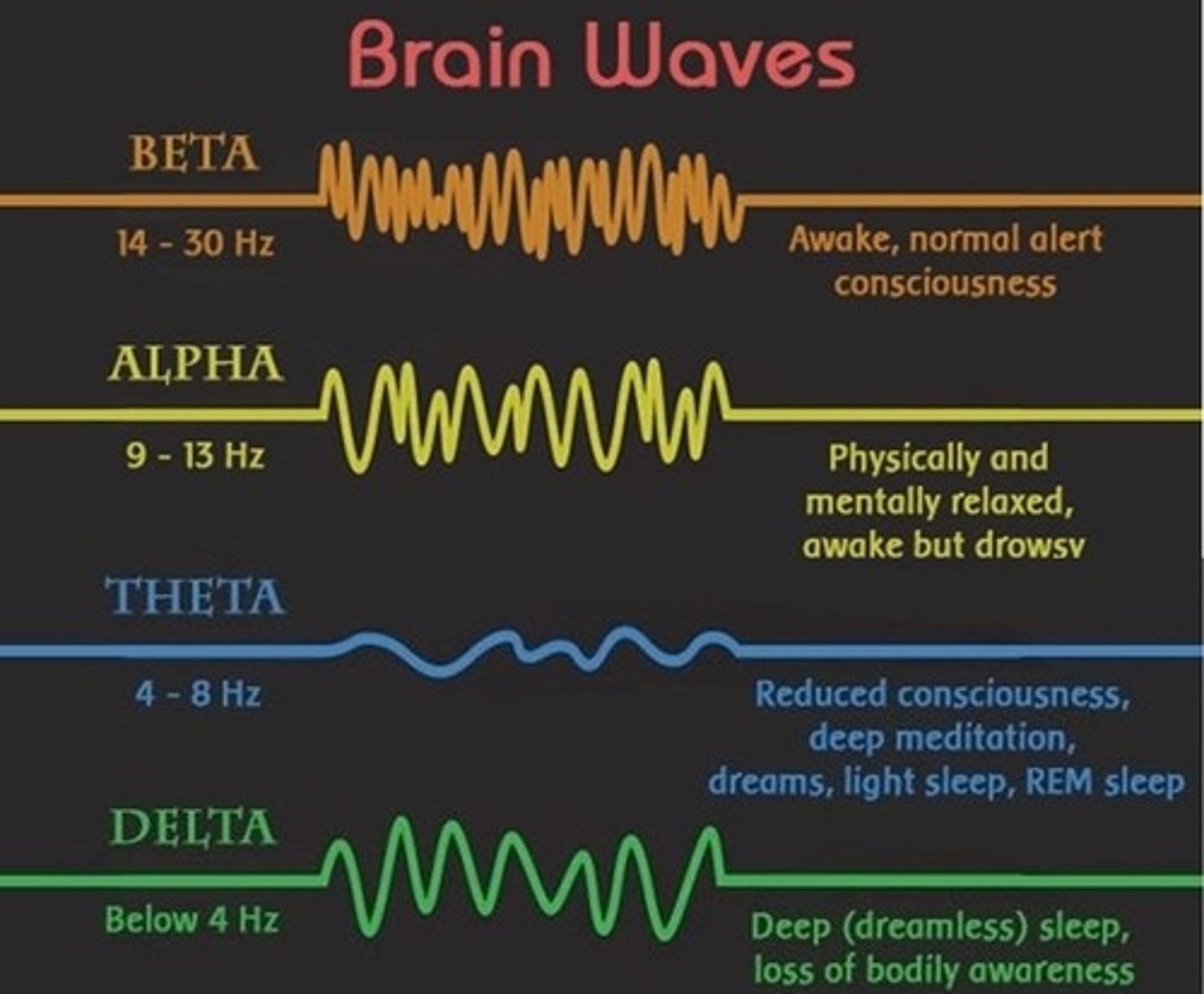
Brain waves
Dyssomnia
a sleep disorder in which one has difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or avoiding sleep
Parasomnia
abnormal behaviors during sleep including somnambulism and night terrors; usually occur during stage 3 or slow wave sleep
Language acquisition device
The innate capacity that would drive language acquisition with minimal environmental input
interactionist perspective
Explores the interplay between genetic and environmental influences and how they shape emerging skills
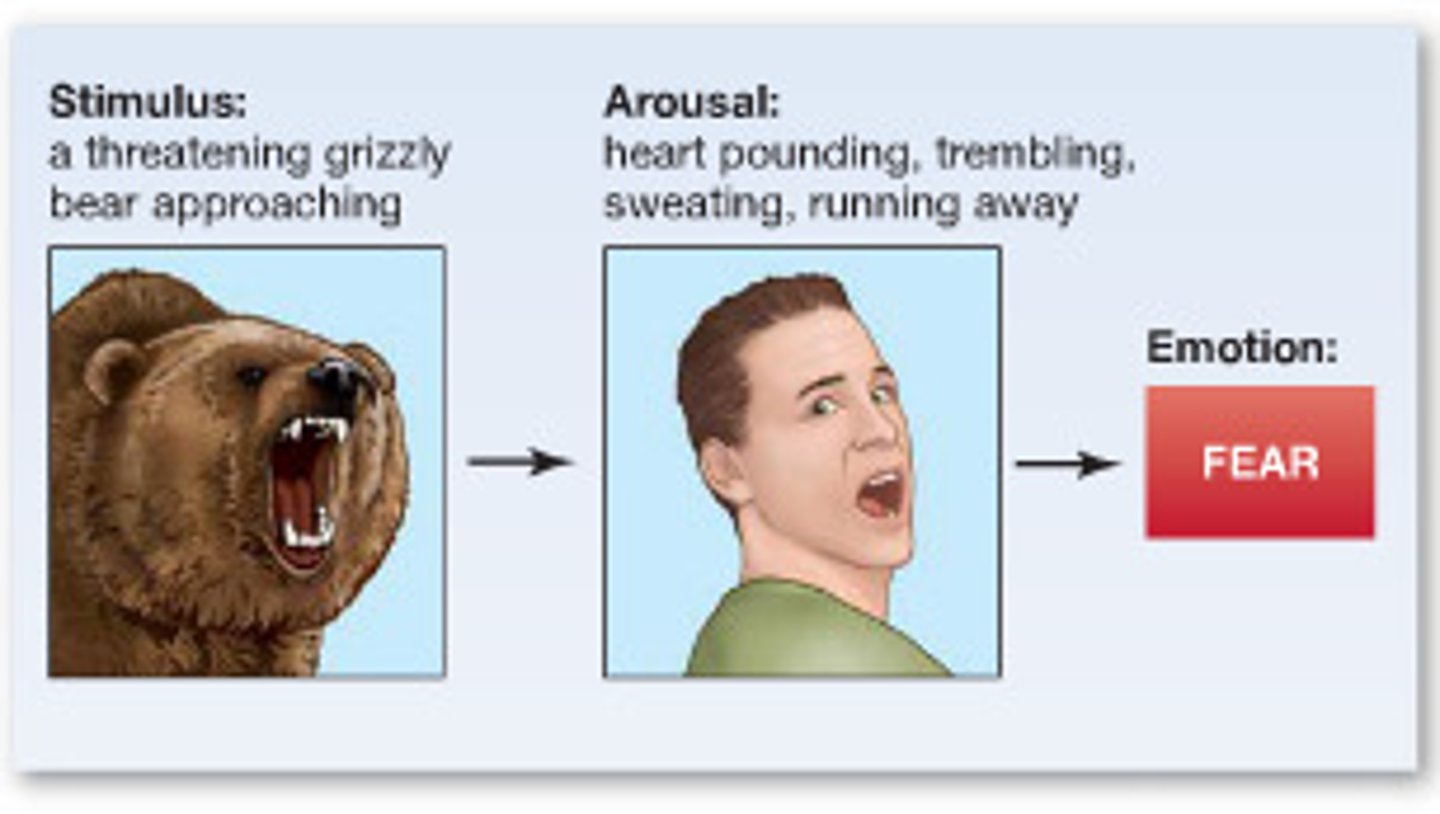
James-Lange Theory
Cannon-Bard Theory
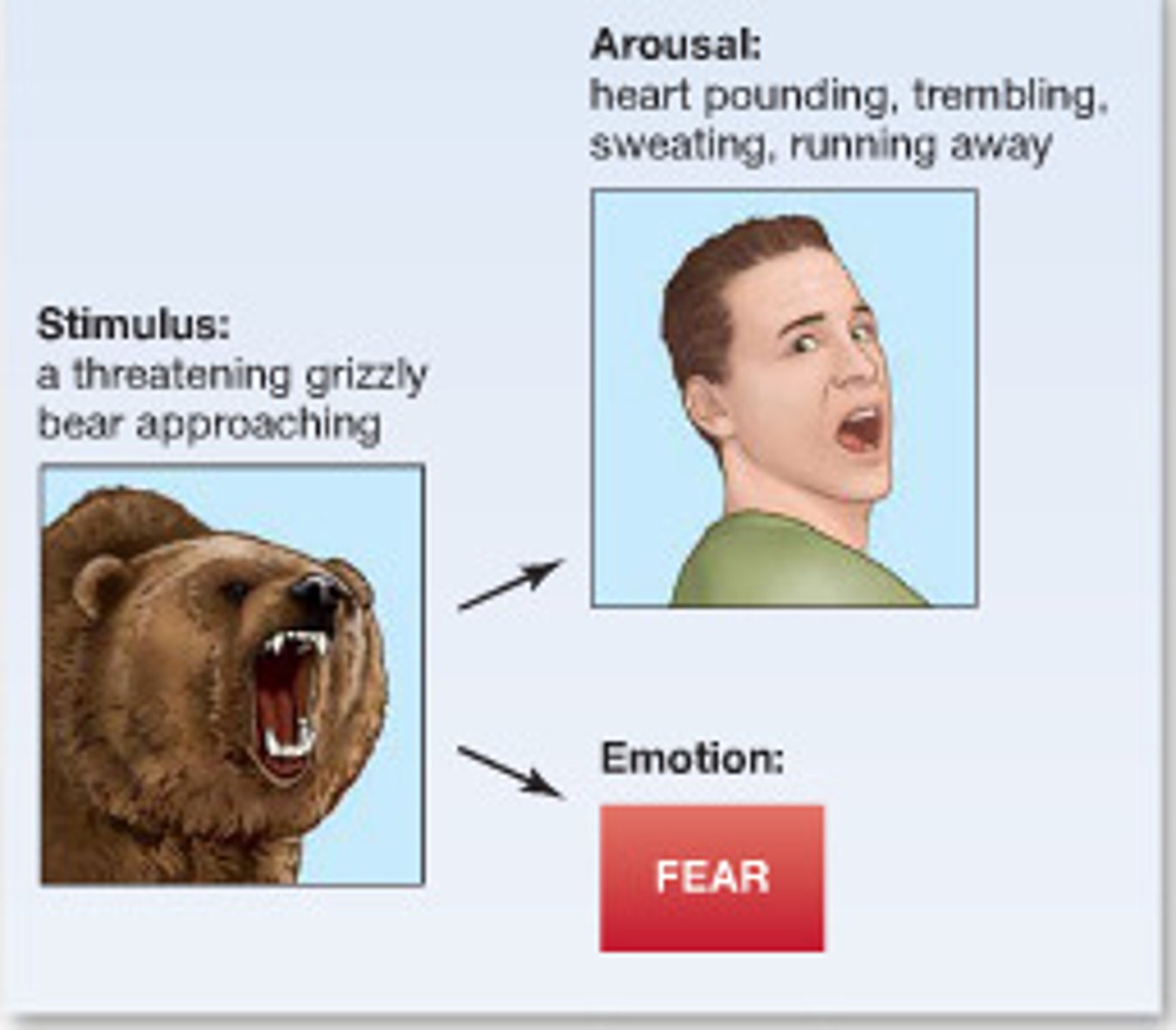
Schachter-Singer Theory
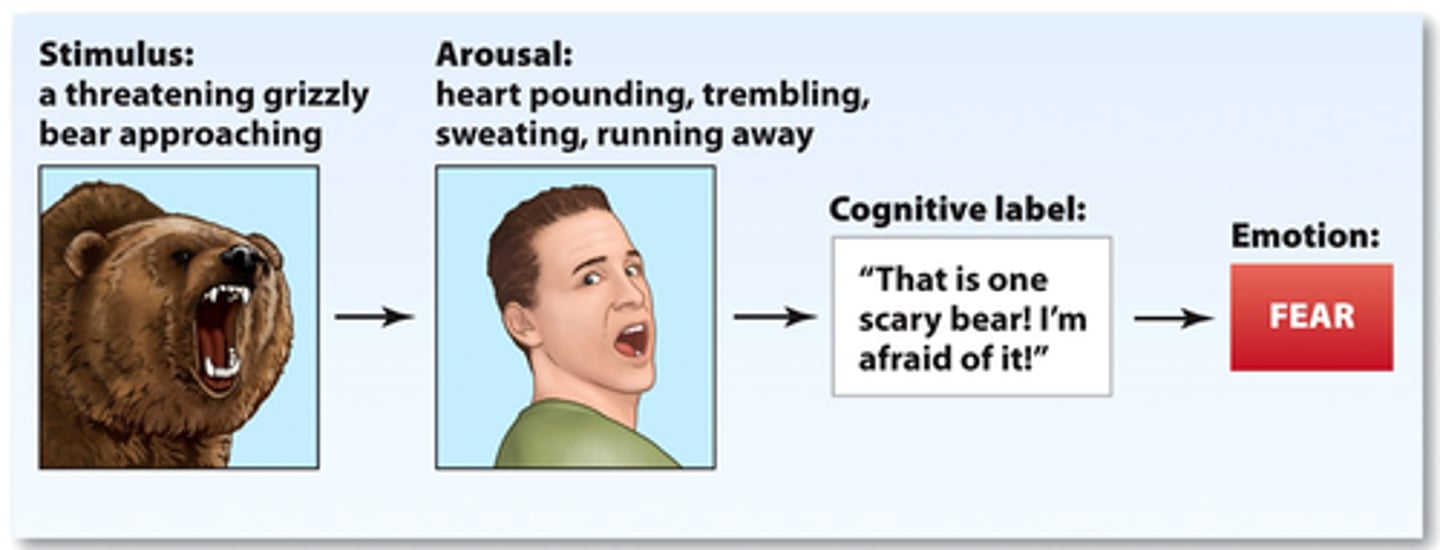
Primary appraisal
Process of evaluating a situation to determine whether a threat is present
Secondary appraisal
If primary appraisal reveals a threat, this appraisal is directed at how the organism will respond to the threat / cope with the stress
maladaptive coping
Unsuccessful attempts to decrease the anxiety without even attempting to solve the problem
maladaptiveness
behavior interferes with the person's life
fMRI
a form of magnetic resonance imaging of the brain that registers blood flow to functioning areas of the brain
helpful for monitoring neural activity and deep brain structures
Id
Unconscious source of biological urges
Freud
Ego
Mediates between instinctual demands of id and moral constraints of superego
Freud
Superego
Self-critical, morality drive component of personality
Freud
pleasure principal
in psychodynamic theory, the id's boundless drive for immediate gratification
Factitious disorder
Condition in which a person acts as if he or she has a physical or mental illness when he or she is not really sick.
Informational influence
conformity occurring when people accept evidence about reality provided by other people in a group because they probably have a good reason
High response rate, no pause
Variable ratio is reinforcing behavior after an unknown /variable number of responses
What is the activity?
Ex: slot machine pays off on average once every 50 pulls
Slow after reinforcement, then increases
Fixed ratio is einforcing behavior after a fixed number of responses
What is the activity?
Ex: trick or treating and getting one piece of candy for saying trick or treat per house.
steady activity
Variable interval is reinforcing behavior after an unknown/variable amount of time
What is the activity like?
Ex: fishing and getting the fish on first bite on average once every 20 minutes
Increases as deadline nears
Fixed interval is reinforcing behavior after a fixed or set amount of time
What is the activity like?
Ex: working and getting paid 20$ per hour
Social more
a social norm with a morally-based expectation
Anomie
lack of the usual social or ethical standards in an individual or group
Generalizability
the extent to which we can claim our findings inform us about a group larger than the one we studied
Reliability
consistency of measurement
Symbolic interactionism
micro theory
emphasizes how people interact through a share set of symbols, including shared words and gestures. All of these symbols have assigned meanings that are dynamic
Ex: the word "dog" is a series of letters, but you associety a fluffy canine with it
ethnocentrism
judging people who are not part of one's own group according to standards, values and beliefs of one's own group
functionalism
Focuses on the actions of individuals and contributions to society (no objects) to promote stability
social products embedded with norms and values
Functions: actions that contribute positively to society
Dysfunctions: actions with negative consequences
Ex: family, school, religion (parts of society as a cohesive whole)
Conflict theory
Macro theory that societies change and adapt in response to conflict between social classes
Focuses on the unequal distribution of resources and power, status quo
Creates interclass competition
social constructionism
macro theory
societies are formed by people agreeing on social constructs, like honor and justice, work ethic, gender roles, or even value of physical money
arise from humans communicating and working together to agree on significance of concept or principle. Intersections ideas.
Ex: the idea that pink is for girls and blue for boysre
Latent function
the unrecognized and unintended consequences of any social pattern
ex: college libraries being open all night during finals week, and students sleep in them (which was not intended by the school)
manifest function
intended and recognized consequence of some element of society
Cultural diffusion
The spread of ideas, customs, and technologies from one culture to another
cultural transmission
The passing down cultural values from one generation to the next
cultural relativism
Refers to an awareness of differences across cultures in norms, values, and other elements of culture.
cultural lag
culture takes time to catch up with technological innovations, resulting in social problems
intergenerational mobility
difference in position between a child and their parents in society
intragenerational mobility
difference in position an individual mobilizes in their own lifetime
patient centered psychotherapy
Developed by Carl Rogers who believed people have the freedom to control their own behavior.
No solutions or diagnoses are provided, but people are helped with reflection, making choices, and determining their own destiny and self-actualization
No environment, only individual
humanistic
Roger's concept of incongruence
The belief that people strive to become self actualized or the "the best version" of themselves or the "ideal self"
The gap between the "ideal" self and the real self can cause discomfort, unpleasant feelings, and lead to defensive behaviors
Behaviorist approach
Sees outcomes, not cognition, as the drive behind an individual's choices and behaviors.
Concerned with how environmental factors affect observable behavior
social cognitive theory
Emphasize the role of cognitive processes, such as thinking, beliefs and judging, in the development of personality
Behaviors are learned through observing others and modeling their actions
biological perspective
personality can be explained as a result of genetic expression in the brain
ex: diathesis stress model
rational choice perspective
assumes that individual behavior will be based on an implicit analysis of the costs and benefits of actions
Ex: Reduce the cost of fruits and vegetables while increasing the cost of processed foods
personality disorder
1. include a pattern of behavior that is inflexible (unwilling to change) and maladaptive (no adjust to environment)
2. cause distress/impaired functioning in two of the following (cognition, emotion, interpersonal functioning, impulse control)
3. Ego-syntonic: perceives their behavior as correct, normal, or in harmony with their goals
ego-dystonic
the individual sees the illness as something thrust upon her that is intrusive and bothersome
confounding variable
A variable that offers an alternative explanation for the observed effect
Produces the same results, but offers a different reason.
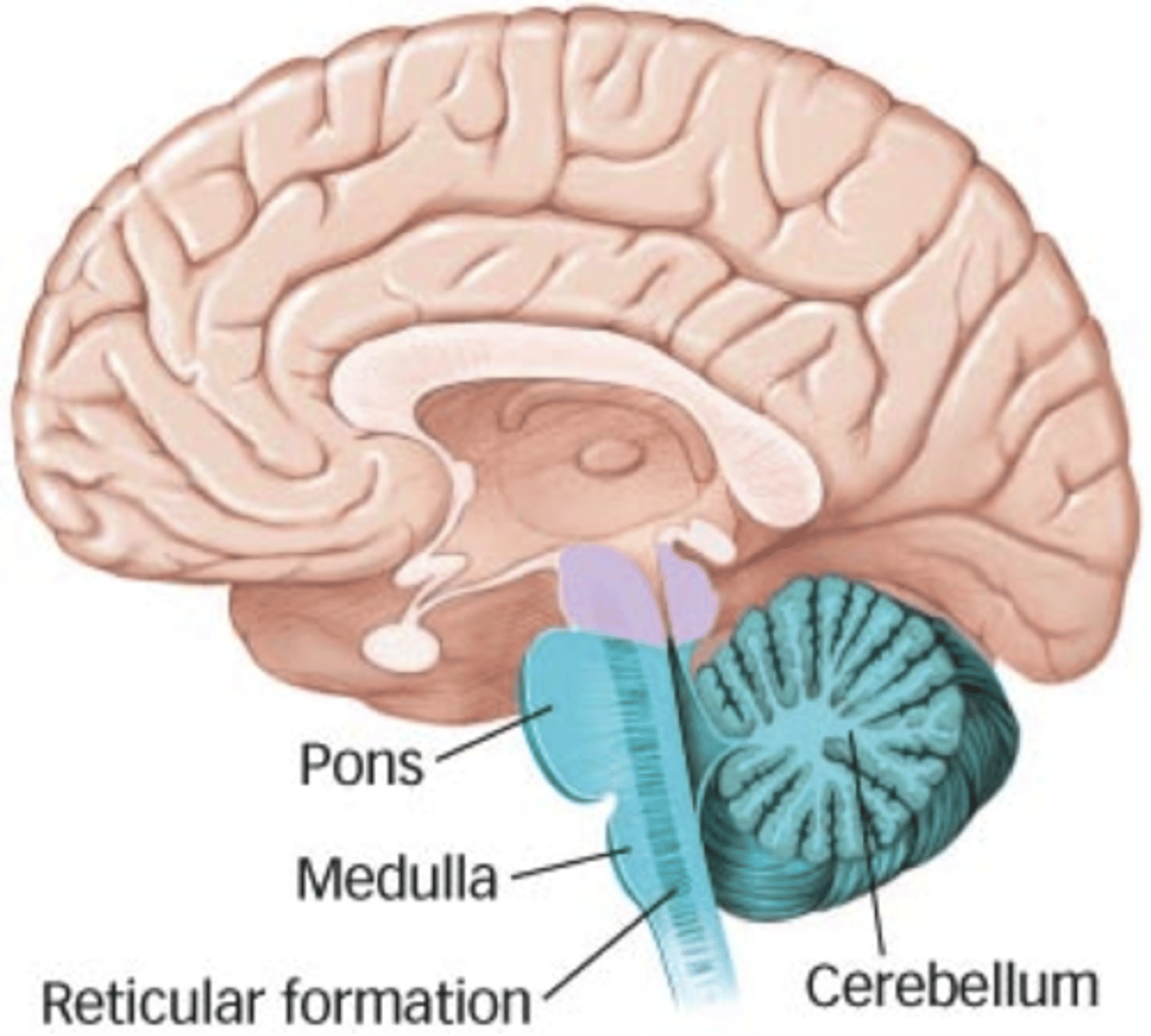
hindbrain
evolved first
Portion of the brain that controls balance, motor coordination, breathing, digestion, and general arousal processes
Cerebellum, medulla oblongata, and reticular formation
metencephalon, rhombencephalon, myelencephalon
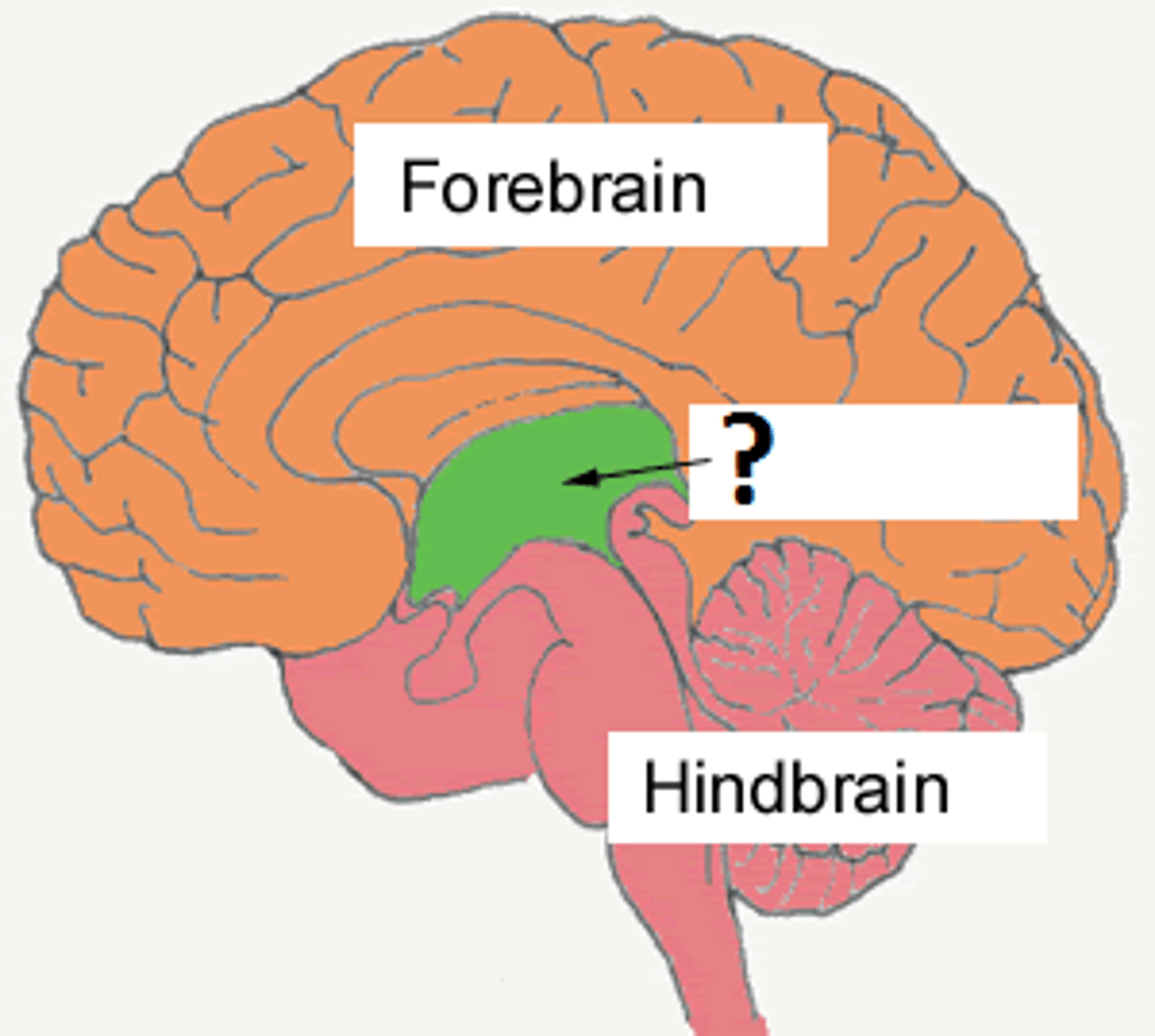
midbrain
inferior and superior colliculi
with hindbrain they are the most primitive region
Portion of the brainstem that manages sensorimotor reflexes to visual and auditory stimuli and gives rise to some cranial nerve
mesencephalon
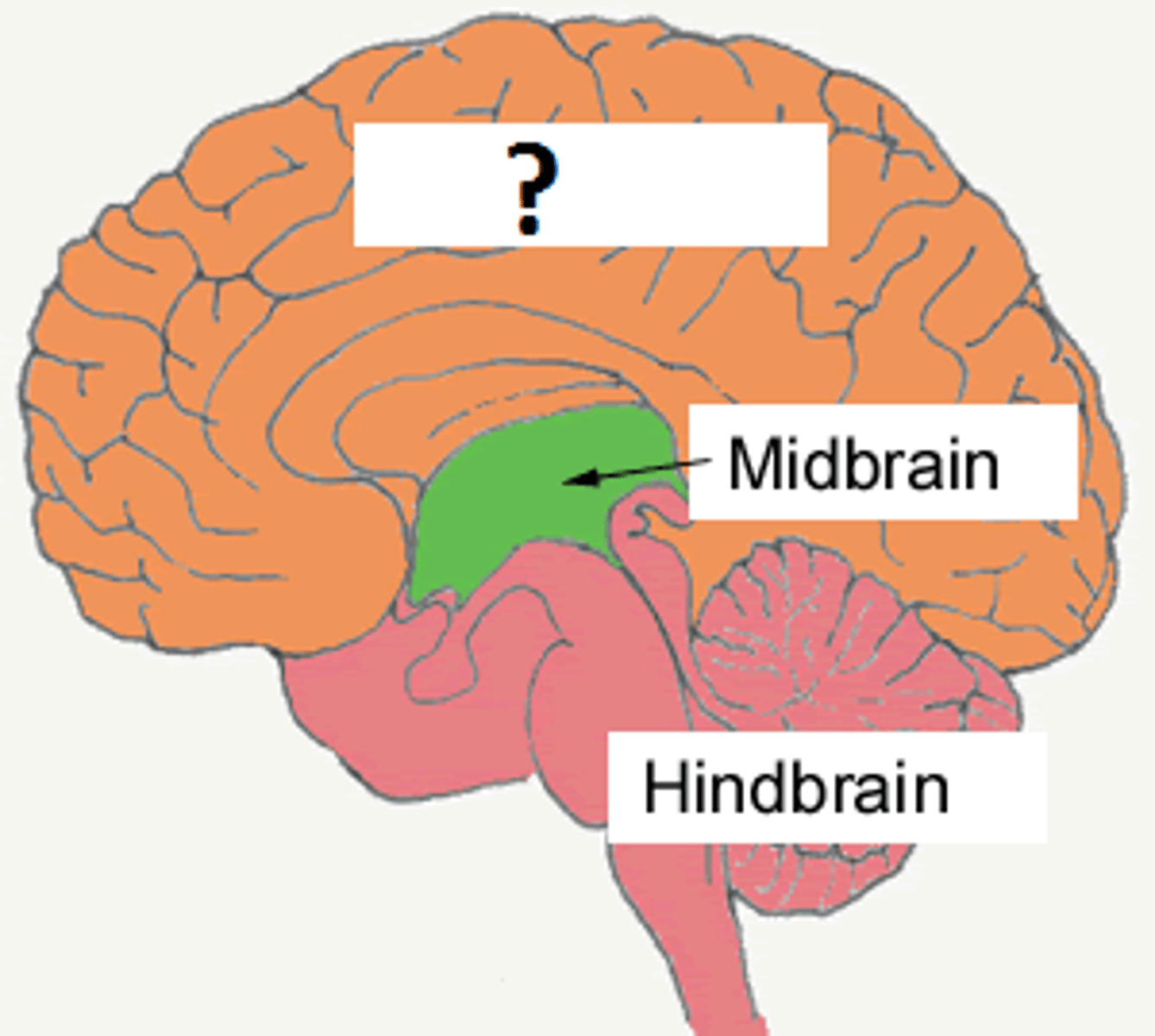
forebrain
The largest and most complicated region of the brain, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia limbic system, and cerebral cortex
telencephalon, diencephalon, prosencephalon
EEG
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity (culmination of action potentials) that sweep across the brain's surface under varying conditions.
These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
Chunking
A memory technique also known as clustering that takes individual items on a large list and groups them together into groups with related meanings
Ex: breaking down the 100 digits of pi into parts that are the length of phone numbers
Acrostics
Use the first letters of each word in a list to create a sentence or phrase that also starts with those letters but is more easily memorized (acronyms)
Method of loci
A memory technique that associates each item on a list with a location along a route through a building that has already been memorized
mental walk through locations with items
peg-word system
A memory trick that associates numbers with items that rhyme with or resemble numbers
ex: personal peg list like "one with a sun" translated to "eggs being fried by the sun" on a grocery list
ex: assigning items to a list of colors mentally
semantic encoding
the process of relating new information in a meaningful way to knowledge that is already stored in memory
ex: remembering a birthday based on a person's name
The best way to remember something
Retrieval
Process of demonstrating that something that has been learned and retained can be pulled back from long term memory
sensory memory
short-term memory with which the brain perceives and stores auditory and visual information
<1 sec
synaptic pruning
The process over time (months or years) that the brain goes through to remove connections that are weak or unhelpful and strengthens connections that are helpful
self-reference effect
the tendency to recall information best when we can put it into the context of our own lives
7 +/- 2 rule
Notion that short-term memory (immediate) is limited in capacity to approximately 7 +/- 2 items
cohort study
Also known as longitudinal studies, involve a case-defined population who have a certain exposure or receive a particular treatment that are followed over time and compared with another group
case-control study
Patients who already have a certain condition/sickness are compared with people who do not
Draw conclusions from comparing each history
Experimental study
the random selection of participants and the random assignment of the participants to groups in the study
observational research
involves studying subjects in non-experimental settings and without changing of variables
correlational research
involves measuring variables and their relationships
implies that each variable may cause each other (very different from causation)
admiration stereotype
High warmth (no competition with ingroup) and high competence (high status)
Viewed with pride and other positive feelings
"she really applied herself and worked hard" or "she is just such a nice person, her promotion is well deserved"
contemptuous stereotypes
Low warmth and competence
Viewed with resentment, annoyance or anger
Poor people and welfare recipients perceived as "work shy" or "not willing to improve their own situation"
envious stereotypes
low warmth, high competence
viewed with jealousy, bitterness, or distrust
"she was born with a silver spoon"
paternalistic stereotypes
high warmth, low competence
looked down upon as inferior, dismissed, or even ignored
elderly or disabled people, 50s housewife
"he is just an old geezer" or "she drives like a grandma"
Parasympathetic nervous system
rest & digest
constrict pupils
slow heartbeat
vasodilation
constrict airways
stimulate stomach activity
inhibit glucose release
stimulates bladder contraction
stimulate sexual arousal
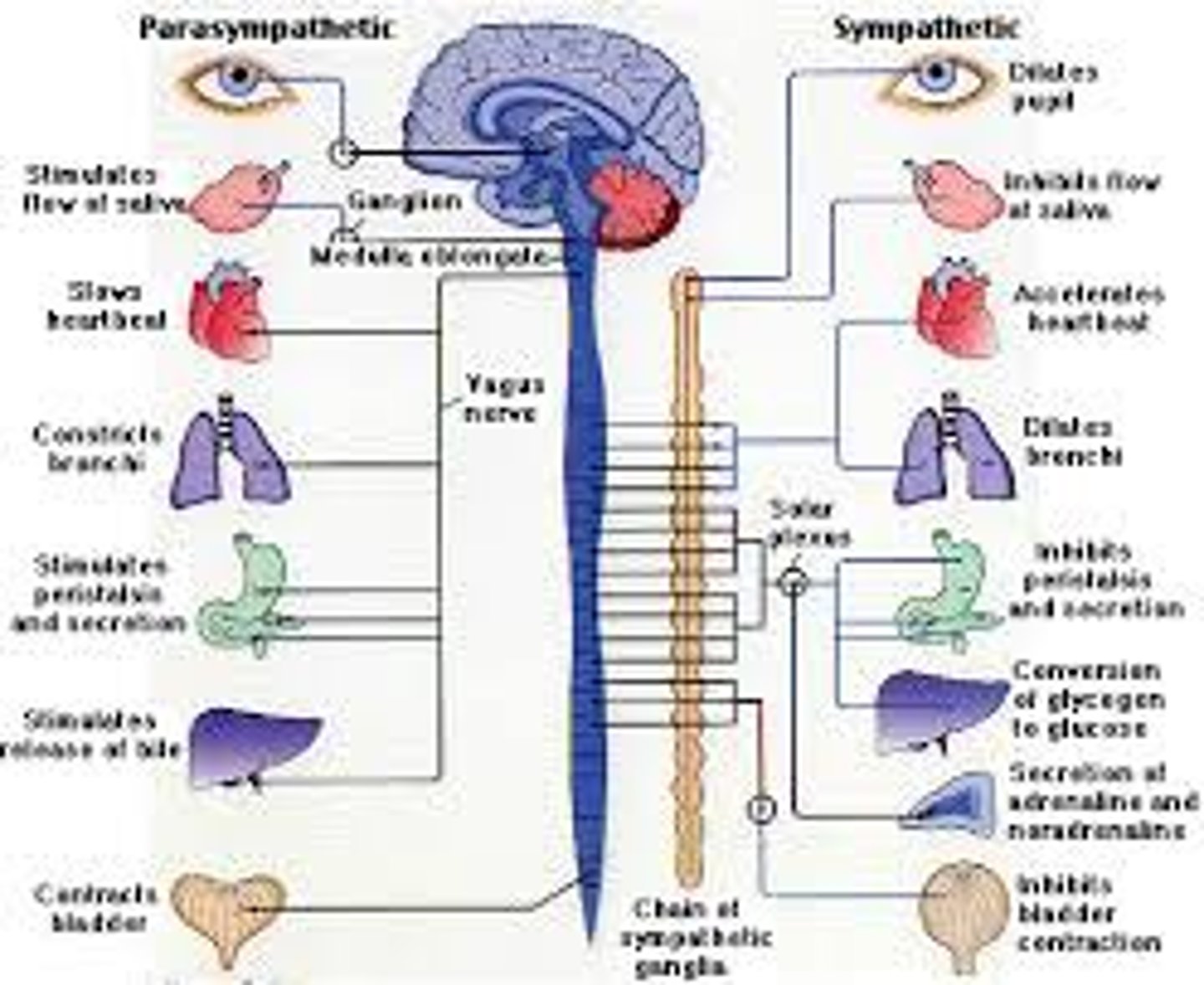
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
dilate pupils but decreased field of vision
increase heartbeat
vasoconstriction
relax airways
inhibit stomach activity
stimulate glucose release
secrete adrenaline
inhibits bladder contraction
promote orgasm
family study
Compare rates of a given trait among family members to those among unrelated individuals/the population
Limited as families share both genetic and environmental components
stimulus discrimination
Process by which two similar but distinct conditioned stimuli produce different responses
Ex: when participants answer 5 numbers, they get a reward. When participants answer more than 5 numbers, they get an electric shock.
sustained attention
the ability to maintain attention to a selected stimulus for a prolonged period of time