Biology ✿ required practical
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Some students want to look at onion cells
Suggest a way to prepare the microscope slide [4]
peel off epidermis layer with tweezers
place drop of water onto slide and place sample on top
add drops of iodine
place cover clip using tweezers carefully at an angle to prevent air bubbles
Some students have prepared a slide of onion cells
Suggest a way to observe the cells using a microscope [5]
place the slide on the stage
choose the lowest power objective lens
look through the eyepiece lens and slowly turn the course adjustment knob so the cells are in focus
slowly turn the fine adjustment knob to bring cells into a clearer focus
when cells have been found, switch to a higher power lens
turn the fine adjustment knob to bring cells back into focus
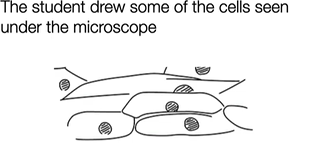
give 3 ways which the student can improve their drawing
write down magnification
do not shade nuclei
label cell parts
why is a thin layer of epidermis used to look through the microscope for the microscopy experiment?
to allow light to pass through
why is a drop of iodine used before looking through the thin layer of epidermis during the microscopy experiment?
allows subcellular structures to be seen
equation for change in mass as a percentage
(change in mass / initial mass) x 100
describe how a student could carry out an investigation on the effect osmosis using potato tissue [6]
cut equal sizes of potato and remove skin, as it is non permeable
weigh using a balance and record the initial mass
place potatoes in test tubes with different concentrations 0 - 0.8 mol/dm³ of sugar solution and leave for a set time
take out potatoes, dab off excess water and weigh
calculate the percentage increase of mass
![<p>Explain why the <strong><em>potato pieces</em></strong> in the <strong><em>0.4 mol/dm³ </em></strong>salt solution decreased in mass [3]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8b5e1e8f-9536-4b5d-a276-5a2254a9aa00.png)
Explain why the potato pieces in the 0.4 mol/dm³ salt solution decreased in mass [3]
water moves outside of cells
by osmosis
because the solution in the cells is less concentrated than outside
describe how a student could carry out an investigation on the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis [5]
fill a tube with sodium hydroxide carbonate solution
cut 10cm of pondweed at an angle while it is submerged in the solution
place a LED lamp 10cm away from the tube and switch it on
wait a few minutes for the rate of photosynthesis to stabilise
count the number of bubbles in one minute
repeat for 5 different distances
counting the number of bubbles per minute isn’t an accurate way of measuring the rate of photosynthesis.
suggest two other ways to accurately measure the rate of photosynthesis
measure the volume of gas using an upside down measuring cylinder or gas syringe
repeat each distance 3 times and calculate a mean
describe how a student could carry out an investigation to determine the optimum pH of an enzyme [5]
prepare a spotting tile and place drops of iodine
measure out 2cm³ of starch solution, pH 1-5 buffer solution and amylase in separate tubes and place in a water bath at 30°C and leave for 5 minutes
mix all reactants, place back into water bath and start stopwatch
at 30 seconds, place a drop of reactant into the spotting tiles using a pipette and continue for every 30 seconds until iodine remains orange (reaction stops)
repeat this with different pH buffers solutions
suggest 2 ways to improve the investigation to determine the optimum pH of an enzyme?
shorter time intervals
use more pH values such as 6 and 7
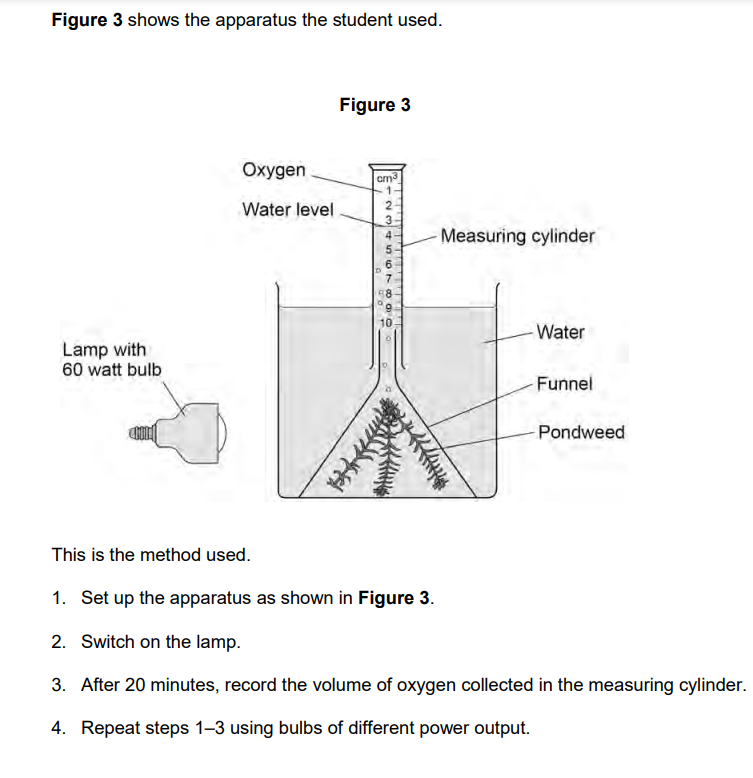
what 2 things can be done to improve this experiment?
repeat and calculate a mean
control the water temperature
how would you test for starch?
add iodine solution
positive result → blue/black
what do you do to the food before using it to do a food test?
grind food using pestle and motor and add distilled water
how would you test for sugars?
add bendicts’s solution
positive result → green, yellow or brick red
how would you test for protien?
add briuet solution
positive result → lilac
independent variable
what is changed
dependant variable
what you measure
control variable
what stays the same in order to keep the test fair
precision
how large the spread of data is
Why did the student leave the starch solution and amylase solution for 5 minutes in the water bath before mixing them?
to allow both solutions to reach 30 °C
The student investigated the effect of temperature on amylase activity.
Describe how the student could extend the investigation to determine the effect of a different factor on amylase activity [2]
keep the temperature the same
but use different pH levels
![<p>Describe <strong>three </strong>aseptic techniques the student should have used. [3]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2b109820-5536-4cb2-b688-d0237cf1451e.png)
Describe three aseptic techniques the student should have used. [3]
sterilise equipment before using
secure lid with tape
only lift lid a little when setting up plate
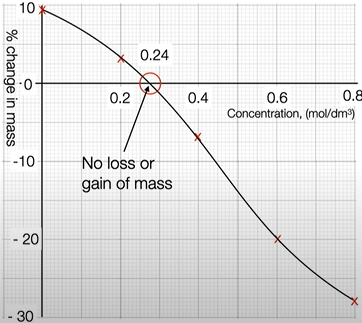
explain why there is no loss or gain of mass of the potato at this point.
there is no net movement of the water as the concentration outside and inside the potato is equal
what causes a gain of mass inside the potato? [2]
solution inside the potato is more concentrated
so water moves inside by osmosis
what causes a loss of mass inside the potato? [2]
solution outside the potato is more concentrated
so water moves outside by osmosis