3. Animal Physiology: Body Fluids, Circulatory System
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
1
New cards
Types of circulatory system:
* open
* closed
* closed
2
New cards
Open
* fluid is circulated through an %%**open body chamber**%%
e.g. (__Arthropods and most mollusks__).
* %%**Haemolymph**%% is contained in a __body cavity, the hemocoel.__
* A %%**series of hearts**%% circulates the fluid. __Internal organs are bathed in the fluid__
e.g. (__Arthropods and most mollusks__).
* %%**Haemolymph**%% is contained in a __body cavity, the hemocoel.__
* A %%**series of hearts**%% circulates the fluid. __Internal organs are bathed in the fluid__
3
New cards
Closed
* Fluid is %%**circulated**%% through blood vessels
e.g. (__Vertebrates, annelid worms__, and a few __mollusks__).
* Blood is moved through %%**blood vessels**%% by the heart’s action. It does __not__ come in __direct contact with body organs__
e.g. (__Vertebrates, annelid worms__, and a few __mollusks__).
* Blood is moved through %%**blood vessels**%% by the heart’s action. It does __not__ come in __direct contact with body organs__
4
New cards
Functions of Circulatory Systems
* permits %%**blood to circulate**%% and %%**transport nutrients**%% (such as amino acids and electrolytes), oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones and blood cells to and from the cells in the body
\- to provide nourishment and help in __fighting diseases__, __stabilize temp and pH__ and maintain __homeostasis__
\- to provide nourishment and help in __fighting diseases__, __stabilize temp and pH__ and maintain __homeostasis__
5
New cards
Blood
* body fluid in humans and other animals that %%**delivers necessary substances**%% such as __nutrients and oxygen__ to the cells and
* %%**transports metabolic waste products away**%% from those same cells
* %%**transports metabolic waste products away**%% from those same cells
6
New cards
1. erythrocytes
2. leukocytes
3. thrombocytes
Blood cells:
7
New cards
Plasma
* %%**55%**%% of blood fluid, is %%**mostly water**%%
* contains __proteins, glucose, mineral ions, hormones, carbon dioxide and blood cells__
* contains __proteins, glucose, mineral ions, hormones, carbon dioxide and blood cells__
8
New cards
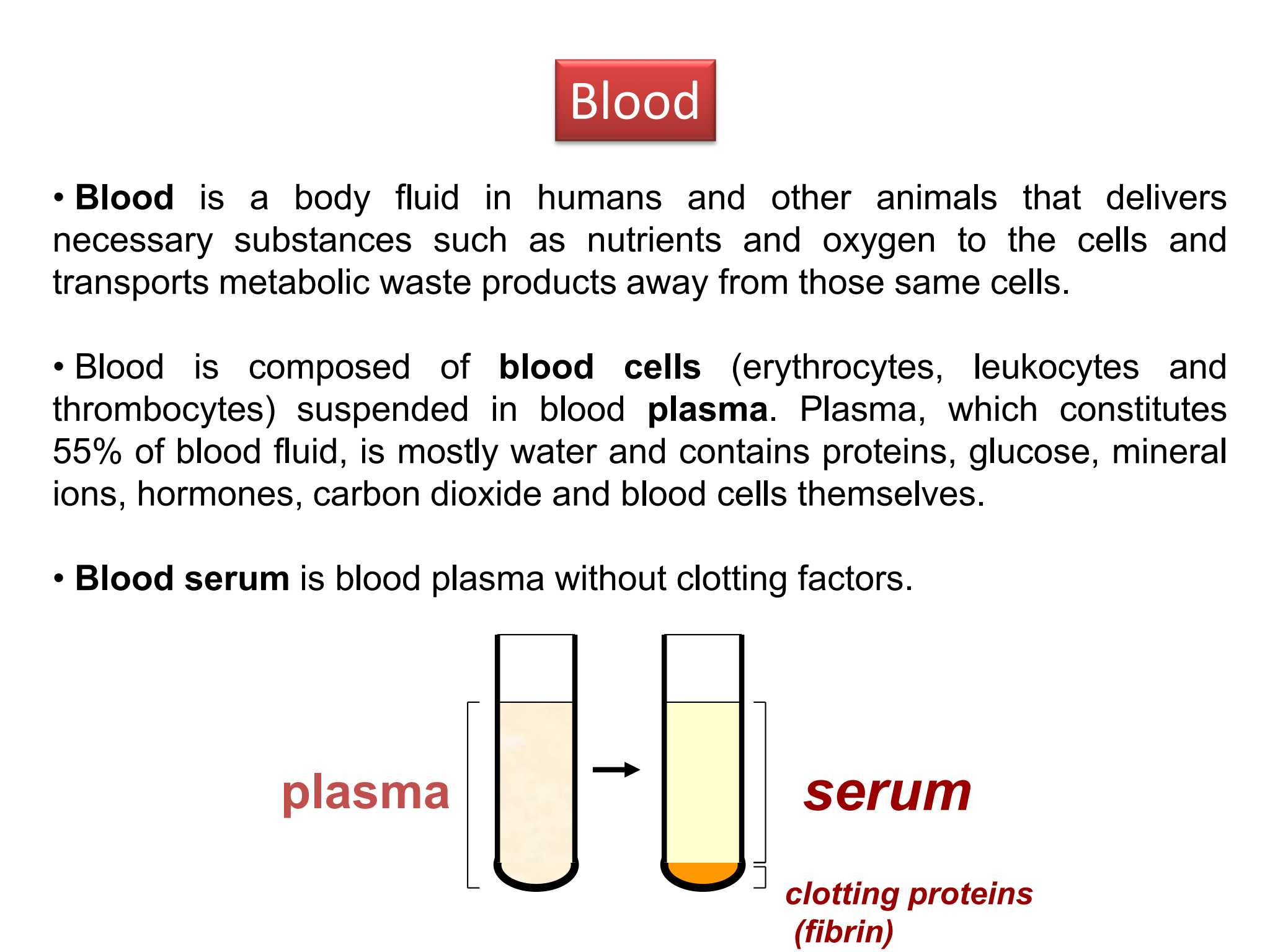
Blood serum
Blood plasma without clotting factors (fibrin)
9
New cards
Osmotic pressure
of blood depends on amount of neorganic and organic substances diluted in plasma
10
New cards
Hemolysis
the rupturing of erythrocytes and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid with low osmolarity
AKA the destruction of red blood cells
This might help to remember: “lysis“= disintegration
AKA the destruction of red blood cells
This might help to remember: “lysis“= disintegration
11
New cards
Coagulation
The process of making blood clot.
Enables the blood to plug and heal a wound. How the body stops any unwanted bleeding
Enables the blood to plug and heal a wound. How the body stops any unwanted bleeding
12
New cards
Red blood cells (RBC) - Erythrocytes
### Structure
Primary cell content is %%***haemoglobin***%%,
the protein that binds oxygen and carbon dioxide.
\-no nucleus nor mitochondria
\
### Appearance
%%***Biconcave*** ***disc***%% shape, which is suited for gas exchange.
The shape is flexible so that RBCs can pass though the smallest blood vessels, i.e. capillaries
\
The average %%**lifespan**%% of erythrocytes is %%**120 days**%%
Primary cell content is %%***haemoglobin***%%,
the protein that binds oxygen and carbon dioxide.
\-no nucleus nor mitochondria
\
### Appearance
%%***Biconcave*** ***disc***%% shape, which is suited for gas exchange.
The shape is flexible so that RBCs can pass though the smallest blood vessels, i.e. capillaries
\
The average %%**lifespan**%% of erythrocytes is %%**120 days**%%
13
New cards
Production of Erythrocytes
* %%***Haematopoiesis***%% - refers to __whole blood cell production__.
HINT: “poiesis“ = process of creation
* %%***Erythropoiesi*****s**%% - refers specifically to __red blood cell production.__
* __All blood cells__, including red and white, are __produced in red bone marrow__.
* On average, one ounce, or __100 billion blood cells__, are __made each day__
HINT: “poiesis“ = process of creation
* %%***Erythropoiesi*****s**%% - refers specifically to __red blood cell production.__
* __All blood cells__, including red and white, are __produced in red bone marrow__.
* On average, one ounce, or __100 billion blood cells__, are __made each day__
14
New cards
Regulation of Erythrocytes Production
\
* regulated by __renal oxygen content__.
* %%***Erythropoietin***%%, a __glycoprotein hormone__, is __produced by renal cells__ in response to a decreased renal blood O2 content.
\-Erythropoietin __stimulates erythrocyte production__ in the red bone marrow
* regulated by __renal oxygen content__.
* %%***Erythropoietin***%%, a __glycoprotein hormone__, is __produced by renal cells__ in response to a decreased renal blood O2 content.
\-Erythropoietin __stimulates erythrocyte production__ in the red bone marrow
15
New cards
White blood cells (WBC) - Leukocytes
Grouped into two major categories:
### 1. __Granulocytes__
\-contain specialized %%**membrane-bound cytoplasmic granules**%%
\-include %%*neutrophils, eosinophils,*%% and %%*basophils*%%
### 2. __Agranulocytes__
\-%%**lack obvious granules**%%
\-include %%*lymphocytes*%% and %%*monocytes*%%
### 1. __Granulocytes__
\-contain specialized %%**membrane-bound cytoplasmic granules**%%
\-include %%*neutrophils, eosinophils,*%% and %%*basophils*%%
### 2. __Agranulocytes__
\-%%**lack obvious granules**%%
\-include %%*lymphocytes*%% and %%*monocytes*%%
16
New cards
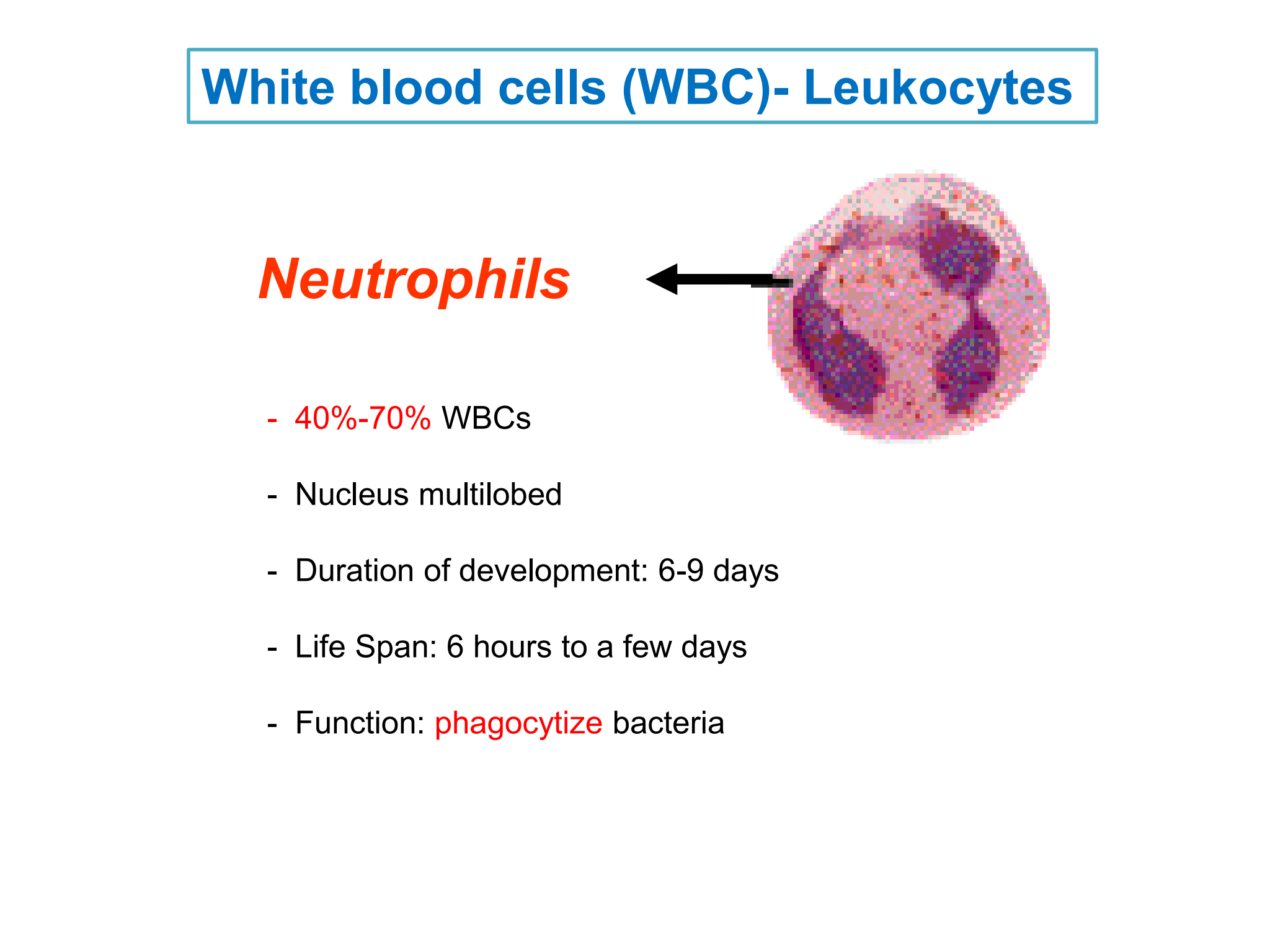
Neutrophils
* %%*40%-70%*%% WBCs
* Nucleus multilobed
* Duration of development: 6-9 days
* Life Span: 6 hours to a few days
* Function: %%***phagocytize***%% bacteria
* Nucleus multilobed
* Duration of development: 6-9 days
* Life Span: 6 hours to a few days
* Function: %%***phagocytize***%% bacteria
17
New cards
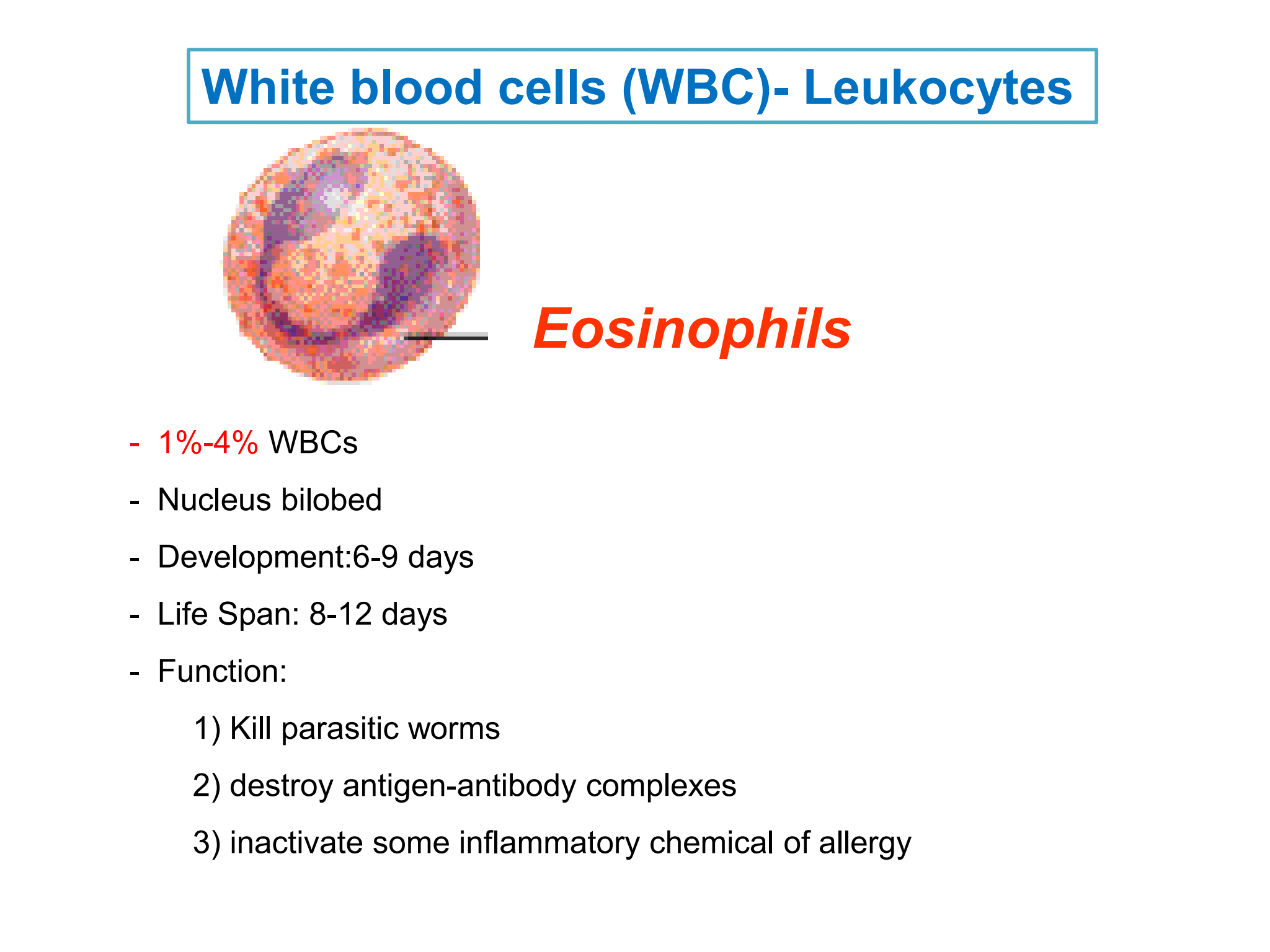
Eosinophils
* %%***1%-4%***%% WBCs
* Nucleus bilobed
* Development: 6-9 days
* Life Span: 8-12 days
* Function:
1. Kill parasitic worms
2. destroy antigen-antibody complexes
3. inactivate some inflammatory chemical of allergy
* Nucleus bilobed
* Development: 6-9 days
* Life Span: 8-12 days
* Function:
1. Kill parasitic worms
2. destroy antigen-antibody complexes
3. inactivate some inflammatory chemical of allergy
18
New cards
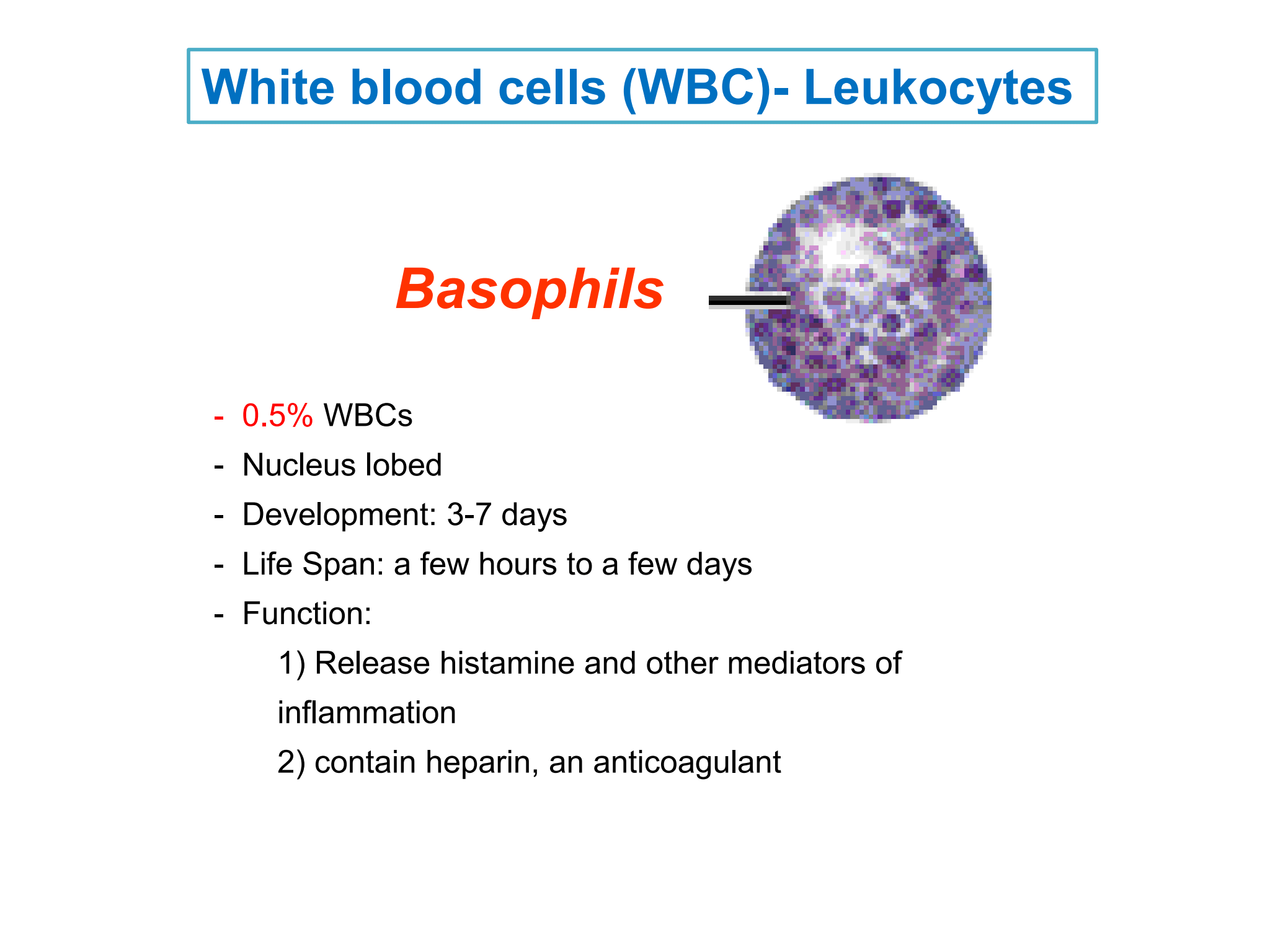
Basophils
%%***0.5%***%% WBCs
* Nucleus lobed
* Development: 3-7 days
* Life Span: a few hours to a few days
* Function:
1. Release histamine and other mediators of inflammation
2. contain heparin, an anticoagulant
* Nucleus lobed
* Development: 3-7 days
* Life Span: a few hours to a few days
* Function:
1. Release histamine and other mediators of inflammation
2. contain heparin, an anticoagulant
19
New cards
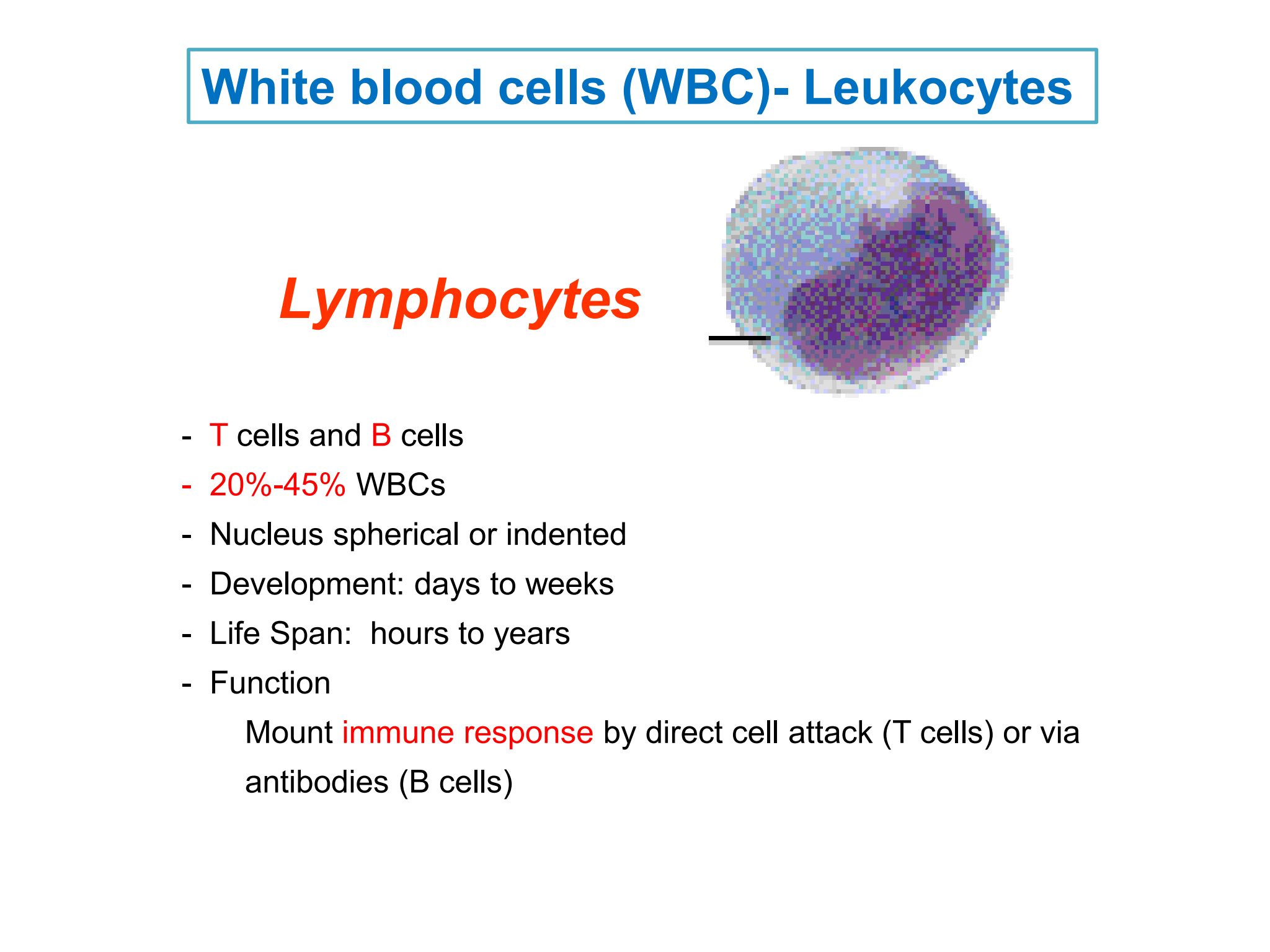
Lymphocytes
* %%***T***%% cells and %%***B***%% cells
* %%***20%-45%***%% WBCs
* Nucleus spherical or indented
* Development: days to weeks
* Life Span: hours to years
* Function:
1. Mount %%***immune response***%% by direct cell attack (T cells) or via antibodies (B cells)
* %%***20%-45%***%% WBCs
* Nucleus spherical or indented
* Development: days to weeks
* Life Span: hours to years
* Function:
1. Mount %%***immune response***%% by direct cell attack (T cells) or via antibodies (B cells)
20
New cards
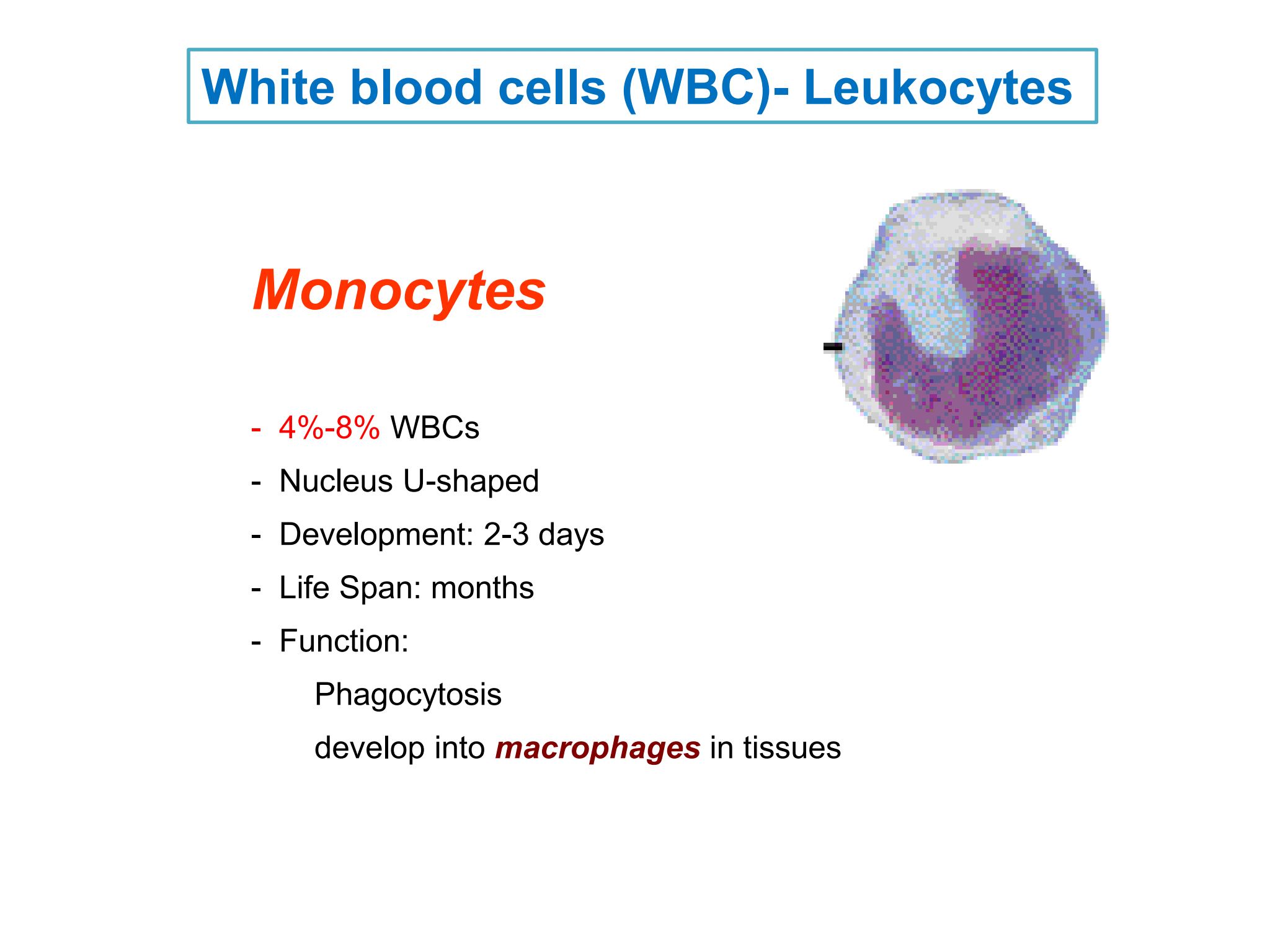
Monocytes
* %%***4%-8%***%% WBCs
* Nucleus U-shaped
* Development: 2-3 days
* Life Span: months
* Function:
Phagocytosis
develop into %%***macrophages***%% in tissues
* Nucleus U-shaped
* Development: 2-3 days
* Life Span: months
* Function:
Phagocytosis
develop into %%***macrophages***%% in tissues
21
New cards
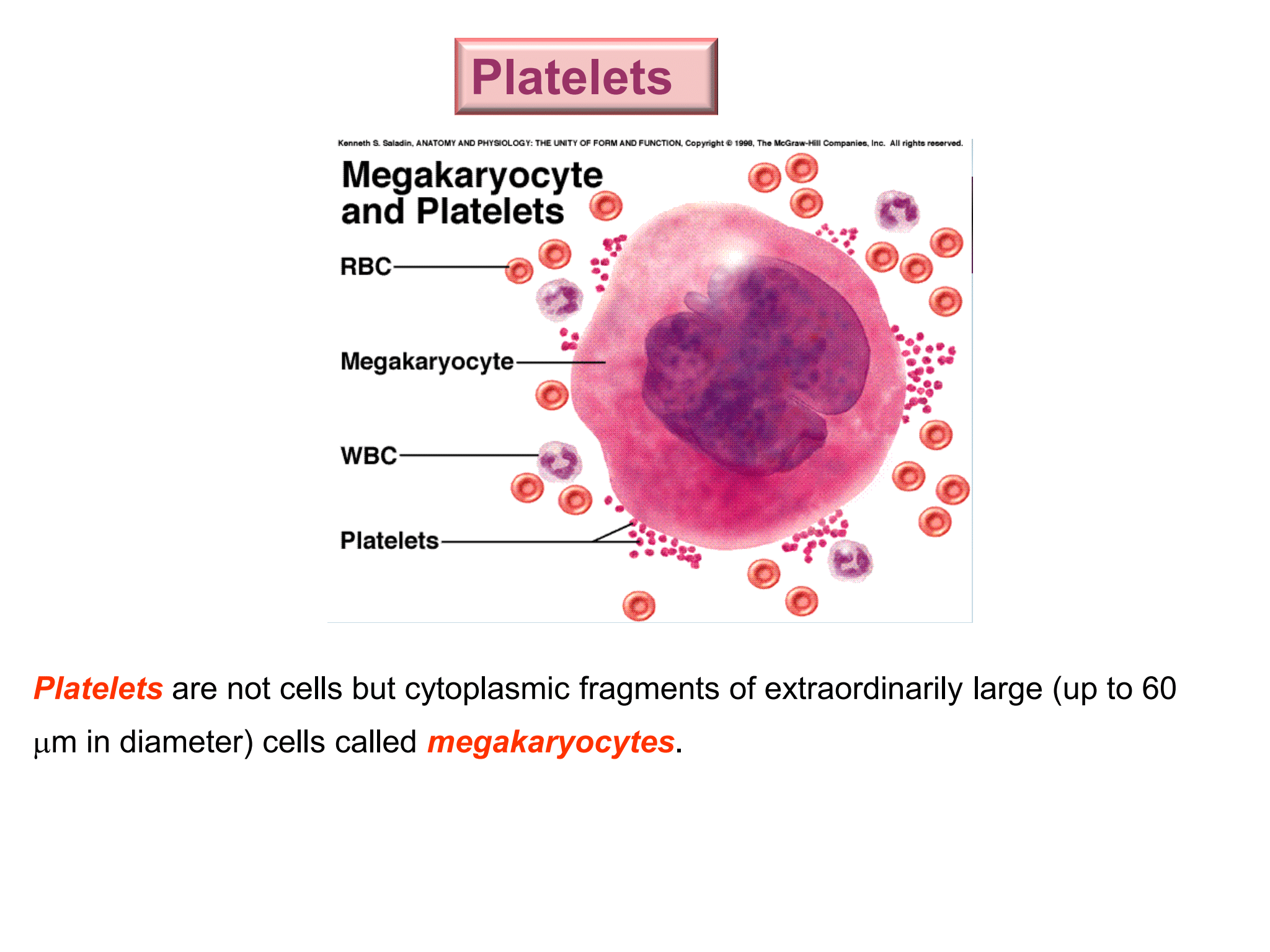
Platelets
are not cells but cytoplasmic fragments of extraordinarily large (up to 60 µm in diameter) cells called %%***megakaryocytes***%%
22
New cards
Function of Platelets
* %%***Secrete vasoconstrictors***%% that cause __vascular spasms__ __in broken vessels__
* Form %%***temporary platelet plugs***%% to __stop bleeding__
* __Secrete chemicals that attract neutrophils and monocytes to sites of inflammation__
* __Secrete growth factors__ that __stimulate mitosis__ in __fibroblasts and smooth muscle__ and __help maintain the linings of blood vessels__
* %%***Dissolve blood clots***%% that have __outlast their usefulness__
* Form %%***temporary platelet plugs***%% to __stop bleeding__
* __Secrete chemicals that attract neutrophils and monocytes to sites of inflammation__
* __Secrete growth factors__ that __stimulate mitosis__ in __fibroblasts and smooth muscle__ and __help maintain the linings of blood vessels__
* %%***Dissolve blood clots***%% that have __outlast their usefulness__
23
New cards
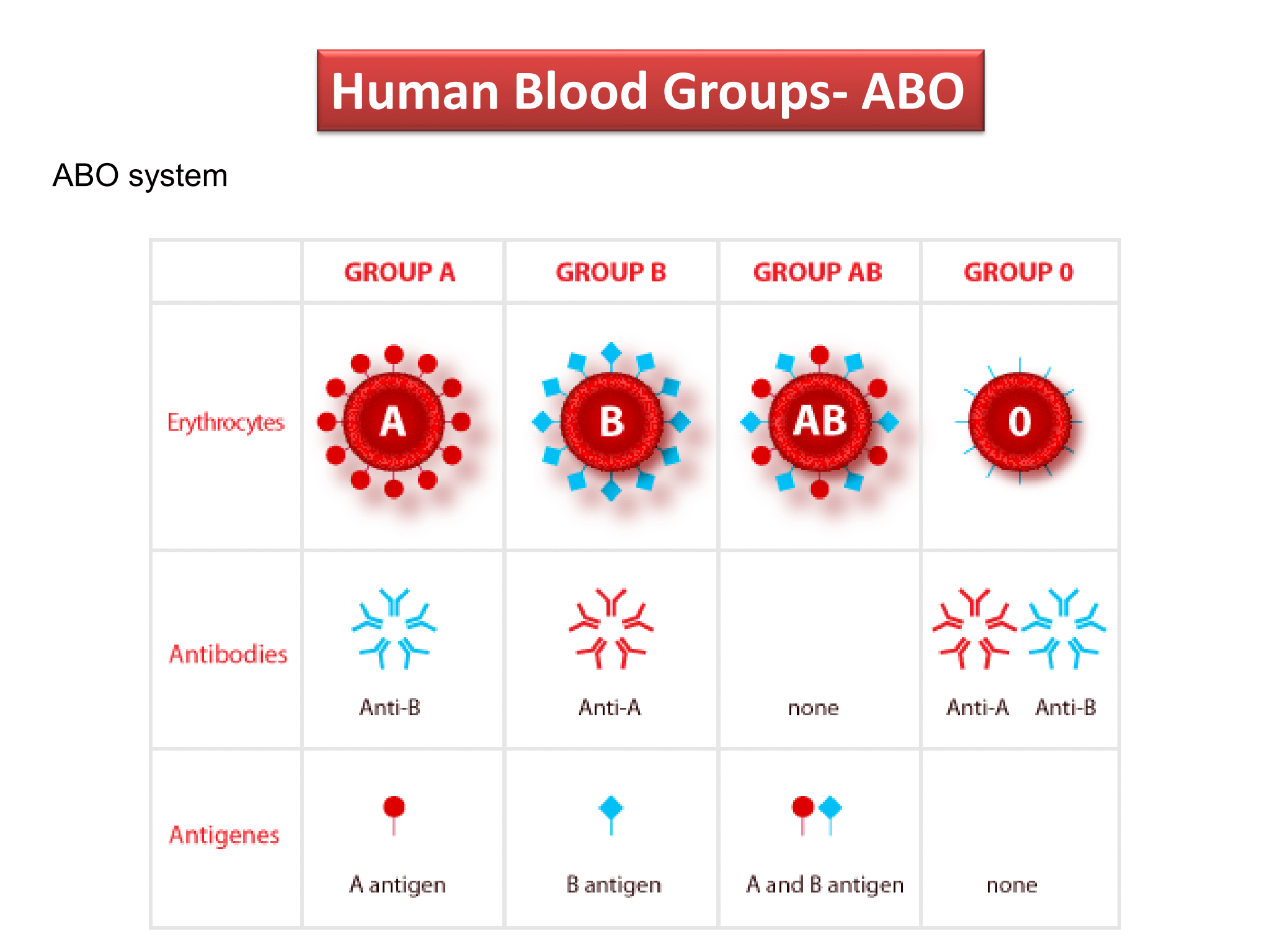
Human Blood Groups - ABO
### ABO system
* __**Type A**__: RBCs carry antigen A, plasma contains anti-B antibodies
* __**Type B**__: RBCs carry antigen B, plasma contains anti-A antibodies
* __**Type O**__: RBCs carry no antigen , plasma contains anti-A and anti-B antibodies
* __**Type AB**__: RBCs carry both antigen A and antigen B, plasma contains no antibodies
* __**Type A**__: RBCs carry antigen A, plasma contains anti-B antibodies
* __**Type B**__: RBCs carry antigen B, plasma contains anti-A antibodies
* __**Type O**__: RBCs carry no antigen , plasma contains anti-A and anti-B antibodies
* __**Type AB**__: RBCs carry both antigen A and antigen B, plasma contains no antibodies
24
New cards
Human Blood Groups - Rh
### Rh positive blood group:
\- RBCs %%***contain Rh antigens***%%.
\- The __majority__ of human beings is Rh positive.
\
### Rh negative blood group:
\-The RBCs contain %%***no Rh antigens***%%.
\-Antibodies against Rh-positive RBCs are produced after Rh-negative blood sees Rh-positive RBCs.
\- RBCs %%***contain Rh antigens***%%.
\- The __majority__ of human beings is Rh positive.
\
### Rh negative blood group:
\-The RBCs contain %%***no Rh antigens***%%.
\-Antibodies against Rh-positive RBCs are produced after Rh-negative blood sees Rh-positive RBCs.
25
New cards
The problem with a Rh-negative mother and her Rh-positive foetus
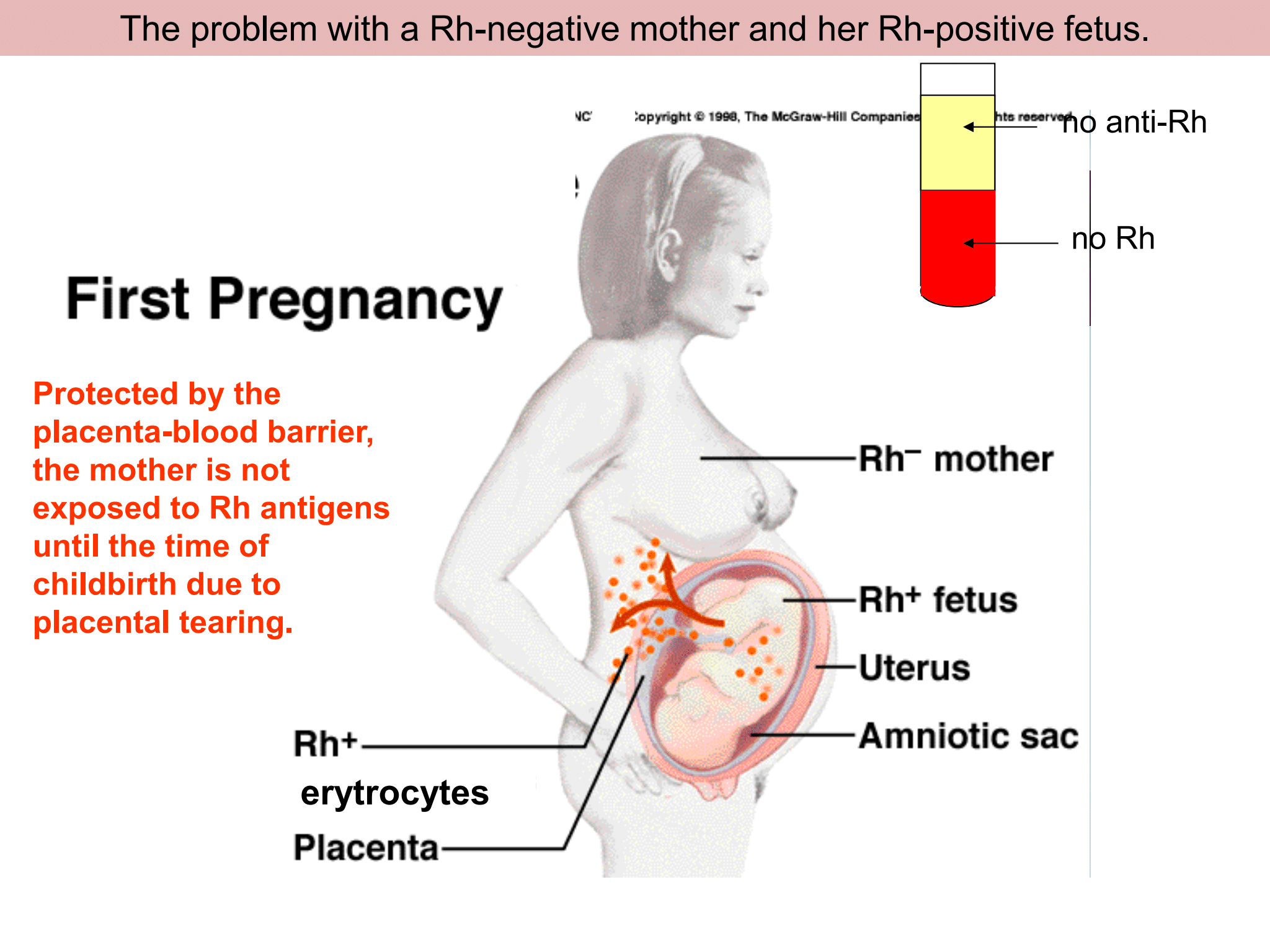
26
New cards
The problem with a Rh-negative mother and her Rh-positive foetus
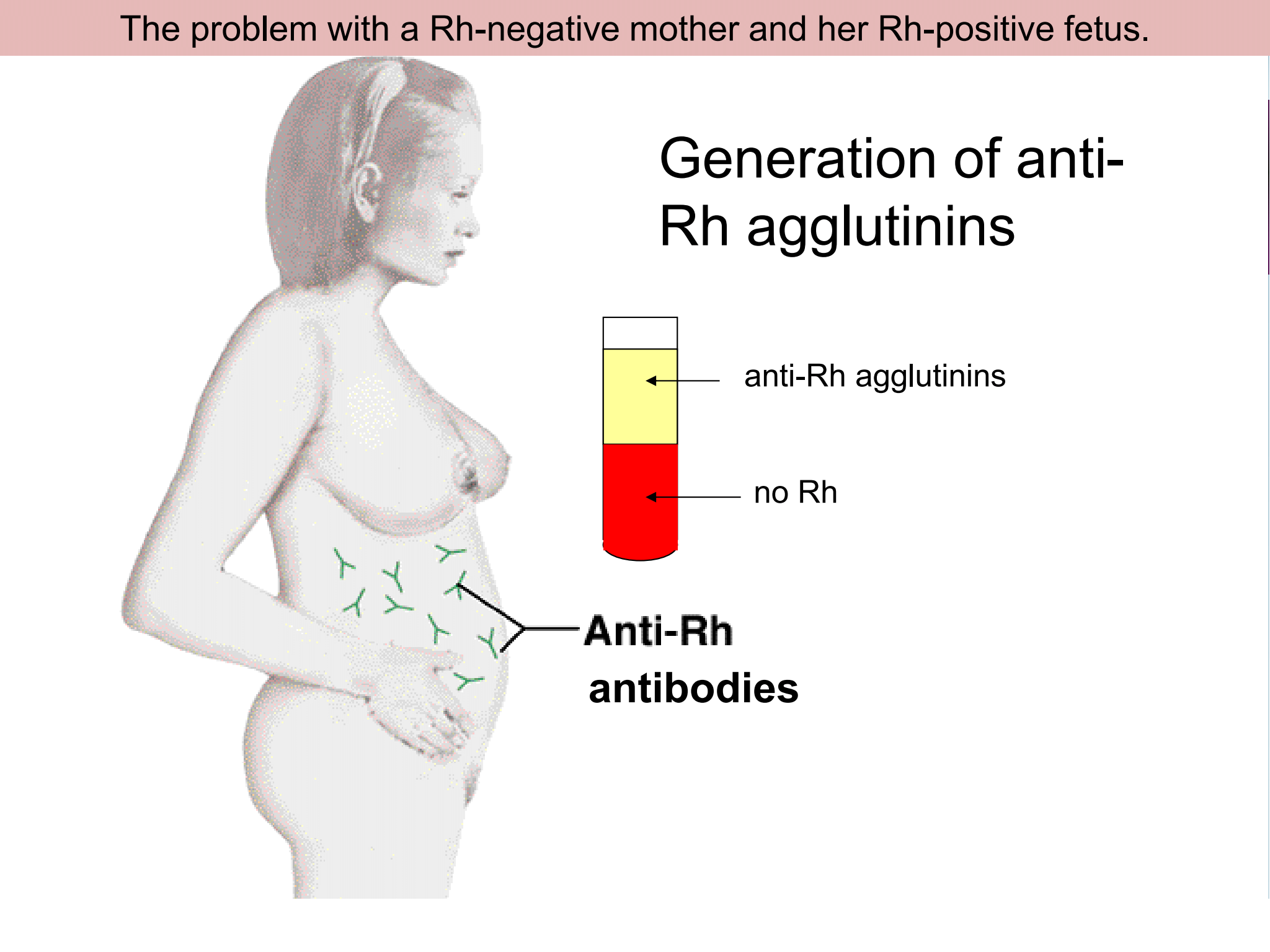
27
New cards
The problem with a Rh-negative mother and her Rh-positive foetus
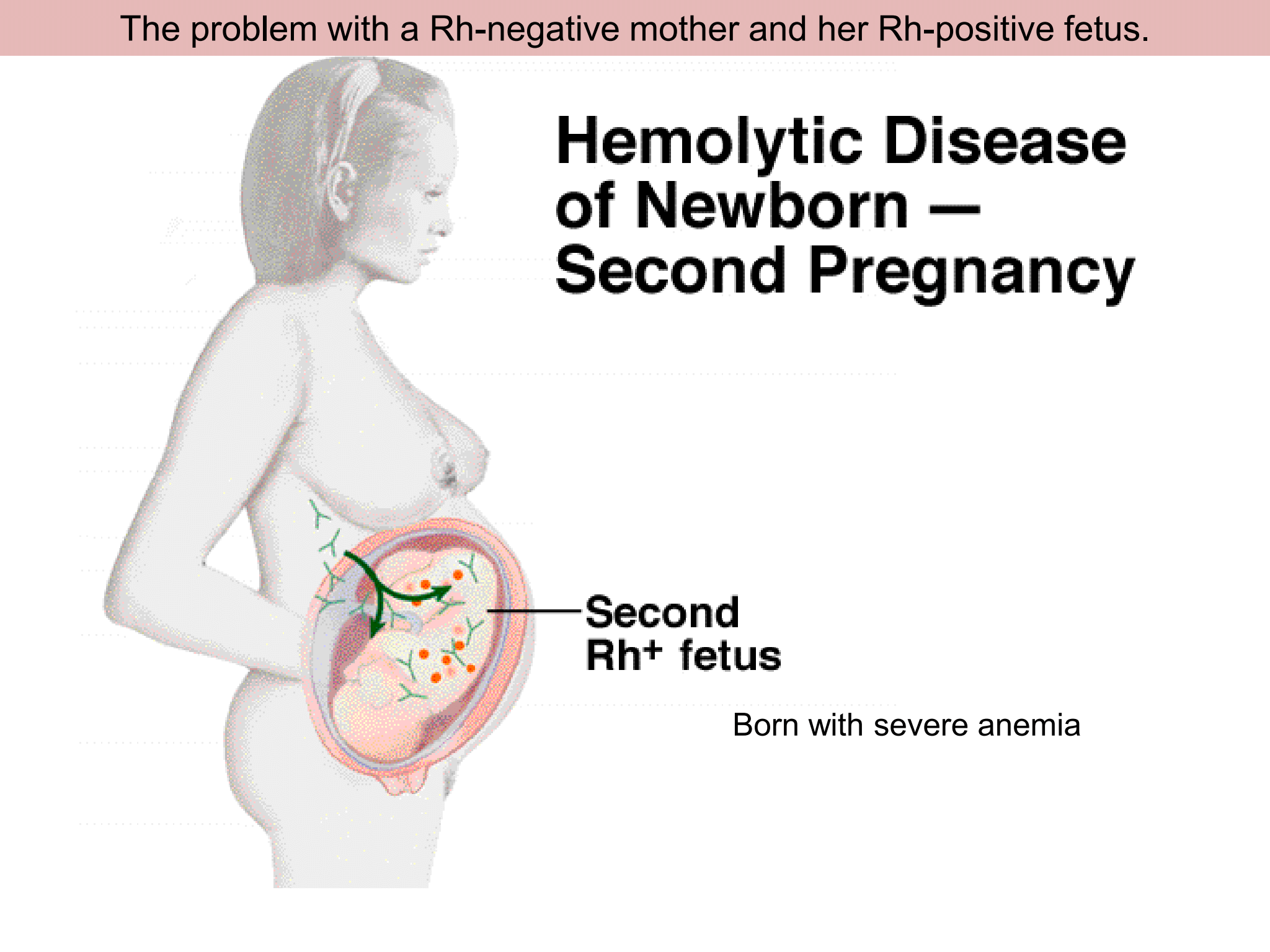
28
New cards
Functional Heart Anatomy
* __Pumps blood filled with oxygen and nutrients through the blood vessels to body tissues__.
* Made up of:
\- **4 chambers (2 atria and 2 ventricles)** that __receive__ blue (__deoxygenated) blood from the body__ and __pump out red (oxygen-rich) blood back to it__:
The %%***atria***%% __receive blood coming back to the heart__.
The %%***ventricles***%% pump the __blood out of the heart__.
\- %%***Blood vessels***%%, which include a __network of arteries and veins__ that carry blood throughout the body: %%***Arteries***%% transport blood from the heart to the body tissues.
%%***Veins***%% carry __blood back to the heart__.
\- %%**4 valves**%% to __prevent backward flow__ of blood: Each valve is designed to allow the forward flow of blood and prevent backward flow
* Made up of:
\- **4 chambers (2 atria and 2 ventricles)** that __receive__ blue (__deoxygenated) blood from the body__ and __pump out red (oxygen-rich) blood back to it__:
The %%***atria***%% __receive blood coming back to the heart__.
The %%***ventricles***%% pump the __blood out of the heart__.
\- %%***Blood vessels***%%, which include a __network of arteries and veins__ that carry blood throughout the body: %%***Arteries***%% transport blood from the heart to the body tissues.
%%***Veins***%% carry __blood back to the heart__.
\- %%**4 valves**%% to __prevent backward flow__ of blood: Each valve is designed to allow the forward flow of blood and prevent backward flow
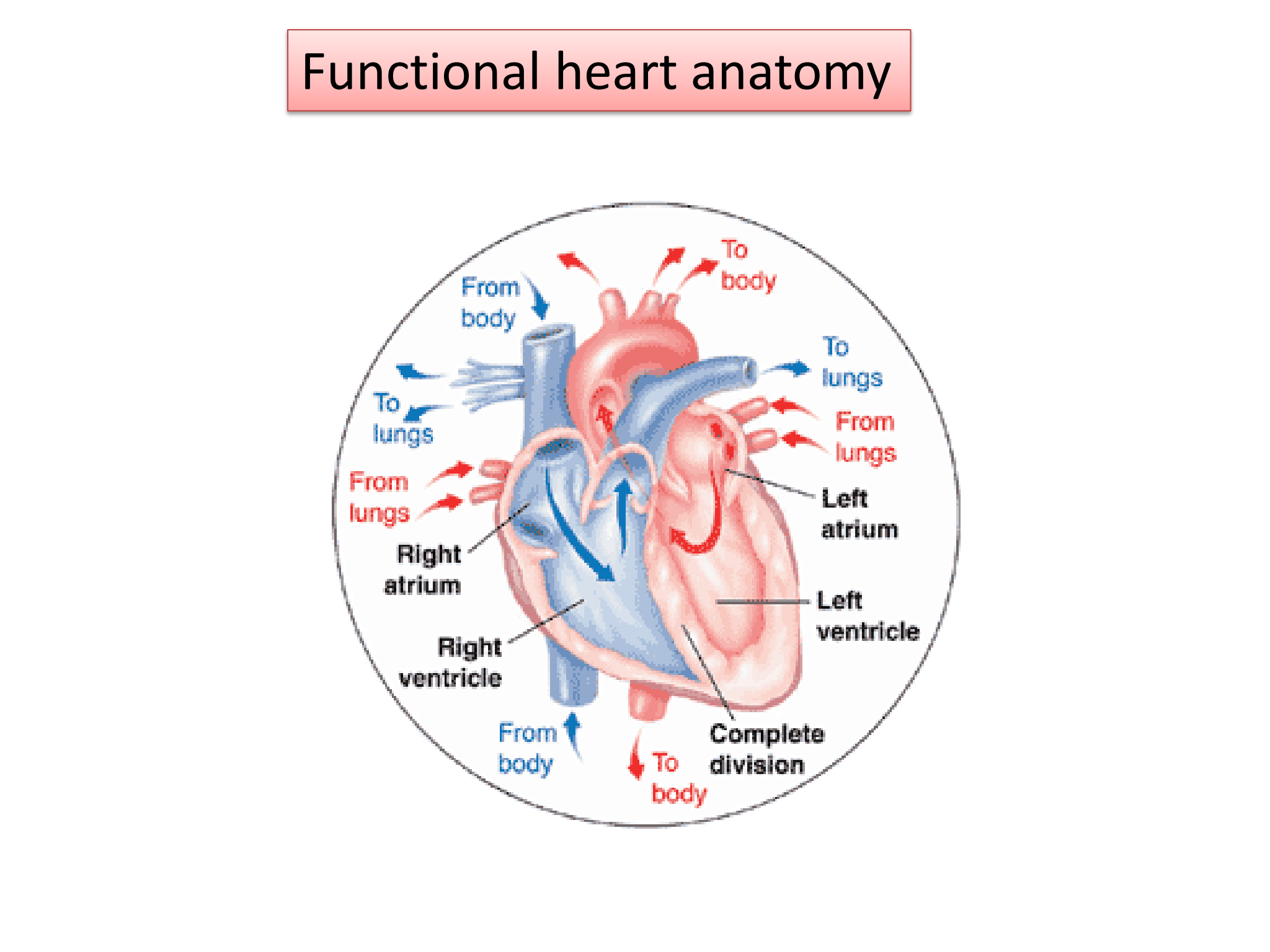
29
New cards
Aortic valve
between the left ventricle and the aorta
30
New cards
Bicuspid (Mitral) valve
between the left atrium and the left ventricle
31
New cards
Pulmonary valve
between the right atrium and the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery
32
New cards
Tricuspid valve
between the right atrium and right ventricle
33
New cards
Heart frequency regulation
* In the upper part of the right atrium of the heart is a specialized bundle of neurons known as the %%***sinoatrial node (SA node)***%%. Acting as the __heart's natural pacemaker__, the SA node "fires" at regular intervals to cause the heart of __beat with a rhythm__ of about __60 to 70 beats per min__ for a healthy, resting heart.
* __Electrical impulses__ begin in the sinoatrial node and __move down__ until reaching the %%***AV node***%%, a cluster of cells at the __bottom of the heart’s right upper chamber__.
\- The AV node serves as a sort of __electrical relay station__ that __slows the current before the signal passes to the lower chambers__.
* This bundle is a collection of heart muscle cells __specialized for electrical conduction__. It transmits the __electrical impulses from the AV node to the point of the apex of the fascicular branches via the bundle branches__. The %%***fascicular branche*****s**%% then lead to the %%***Purkinje fibres***%%, which provide electrical conduction to the ventricles, causing the __cardiac muscle of the ventricles to contract__
* __Electrical impulses__ begin in the sinoatrial node and __move down__ until reaching the %%***AV node***%%, a cluster of cells at the __bottom of the heart’s right upper chamber__.
\- The AV node serves as a sort of __electrical relay station__ that __slows the current before the signal passes to the lower chambers__.
* This bundle is a collection of heart muscle cells __specialized for electrical conduction__. It transmits the __electrical impulses from the AV node to the point of the apex of the fascicular branches via the bundle branches__. The %%***fascicular branche*****s**%% then lead to the %%***Purkinje fibres***%%, which provide electrical conduction to the ventricles, causing the __cardiac muscle of the ventricles to contract__
34
New cards
Parasympathetic neurons
slow down heart frequency, while sympathetic accelerate
35
New cards
accelerate heart frequency
Adrenalin from adrenal glands and thyroxine from thyroid gland
36
New cards
cardiac cycle
The %%***electrical and mechanical***%% events that occur from the __beginning of one heartbeat at the beginning of the next heartbeat__
37
New cards
%%**Diastole**%%: relaxation
%%**Systole**%%: contraction
%%**Systole**%%: contraction
Two phases of the cardiac cycle:
38
New cards
Blood vessels
1. artery
2. veins
3. capillary
39
New cards
artery
* blood vessel that takes %%***blood away from the heart***%% __to all parts of the body__ (tissues, lungs, etc).
* Most arteries %%***carry oxygenated blood***%%; the two ***exceptions*** are the %%***pulmonary and the umbilical arteries***%%, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it
* Most arteries %%***carry oxygenated blood***%%; the two ***exceptions*** are the %%***pulmonary and the umbilical arteries***%%, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it
40
New cards
Veins
* blood vessel that carry %%***blood toward the heart***%%.
* Most veins %%***carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart***%%;
* ***exceptions*** are the %%***pulmonary and the umbilical veins***%%, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart
* Most veins %%***carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart***%%;
* ***exceptions*** are the %%***pulmonary and the umbilical veins***%%, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart
41
New cards
Capillary
* the %%***smallest blood vessels***%% in the body:
* they convey blood between the arterioles and venules
* they convey blood between the arterioles and venules
42
New cards
Lymph
* is the fluid that __flows through the lymphatic system__, a system composed of lymph vessels and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is %%***to return fluid from the tissues to the central circulation***%%.
* %%***Intestinal fluid***%% is the __fluid__ which is __between the cells in all body tissues__ and __enters the lymph capillaries.__
* This lymphatic fluid is then __transported via__ progressively __larger lymph vessels__ through __lymph nodes__, where %%***substances are removed by tissue lymphocytes and circulating lymphocytes are added to the fluid***%%, __before emptying ultimately into the right or the left__ %%__***subclavian vein***__%%, where it __mixes with central venous blood__
* %%***Intestinal fluid***%% is the __fluid__ which is __between the cells in all body tissues__ and __enters the lymph capillaries.__
* This lymphatic fluid is then __transported via__ progressively __larger lymph vessels__ through __lymph nodes__, where %%***substances are removed by tissue lymphocytes and circulating lymphocytes are added to the fluid***%%, __before emptying ultimately into the right or the left__ %%__***subclavian vein***__%%, where it __mixes with central venous blood__
43
New cards
d) kill parasitic worms
Q1. Eosinophils
a) phagocytize bacteria
b) release histamine and other mediators of inflammation
c) develop into macrophages in tissues
d) kill parasitic worms
a) phagocytize bacteria
b) release histamine and other mediators of inflammation
c) develop into macrophages in tissues
d) kill parasitic worms
44
New cards
a) RBC’S carry antigen A, plasma contains anti-B antibodies
Q2. Mark the CORRECT claim for A-type blood group:
a) RBC’S carry antigen A, plasma contains anti-B antibodies
b) RBC’s carry antigen B, plasma contains anti-A antibodies
c) RBC’s carry no antigen, plasma contains anti-A and anti-B antibodies
d) RBC’s carry both antigen A and antigen B, plasma contains no antibodies
a) RBC’S carry antigen A, plasma contains anti-B antibodies
b) RBC’s carry antigen B, plasma contains anti-A antibodies
c) RBC’s carry no antigen, plasma contains anti-A and anti-B antibodies
d) RBC’s carry both antigen A and antigen B, plasma contains no antibodies
45
New cards
c) between the left ventricle and the aorta
Q3. Aortic valve is located:
a) between the left atrium and left ventricle
b) between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery
c) between the left ventricle and the aorta
d) between the right atrium and right ventricle
a) between the left atrium and left ventricle
b) between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery
c) between the left ventricle and the aorta
d) between the right atrium and right ventricle
46
New cards
b) left ventricle
Q4. The systemic circulation starts from the:
a) right ventricle
b) left ventricle
c) left atrium
d) right atrium
a) right ventricle
b) left ventricle
c) left atrium
d) right atrium
47
New cards
Systemic circulation is the part of the cardiovascular system which carries %%***oxygenated blood away from the heart***%%
to the body, and returns %%***deoxygenated blood back to the heart***%%.
to the body, and returns %%***deoxygenated blood back to the heart***%%.
Q5. Give a short definition for the following term: Systemic circulation
48
New cards
Aorta
*To explain:* The heart pumps oxygenated blood out of the left ventricle and into the aorta to begin systemic circulation. Systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle, through the arteries, to the capillaries in the tissues of the body. From the tissue capillaries, the deoxygenated blood returns through a system of veins to the right atrium of the heart.
*To explain:* The heart pumps oxygenated blood out of the left ventricle and into the aorta to begin systemic circulation. Systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle, through the arteries, to the capillaries in the tissues of the body. From the tissue capillaries, the deoxygenated blood returns through a system of veins to the right atrium of the heart.
Q6. Read the text and answer the question: From which blood vessel does the systemic circulation start?
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood to the heart. They have small diameter and elastic walls. They branch into narrower vessels called venules which branch further to capillaries. The blood is pumped out of the heart under pressure into the aorta and the cardiac artery.
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood to the heart. They have small diameter and elastic walls. They branch into narrower vessels called venules which branch further to capillaries. The blood is pumped out of the heart under pressure into the aorta and the cardiac artery.
49
New cards
* **Blood must always circulate** to sustain life. It carries oxygen from the air we breathe to cells throughout the body. The pumping of the heart drives this blood flow through the arteries, capillaries, and veins. One set of blood vessels circulates blood through the lungs for gas exchange. The other vessels fuel the rest of the body.
\
* **The cardiovascular system is composed of two circulatory paths**: pulmonary circulation, the circuit through the lungs where blood is oxygenated; and systemic circulation, the circuit through the rest of the body to provide oxygenated blood. The two circuits are linked to each other through the heart, creating a continuous cycle of blood through the body.
\
* **Pulmonary circulation** is the movement of blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation, then back to the heart again. Oxygen-depleted blood from the body leaves the systemic circulation when it enters the right atrium through the superior and inferior venae cavae. The blood is then pumped through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. From the right ventricle, blood is pumped through the pulmonary valve and into the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery splits into the right and left pulmonary arteries and travel to each lung. At the lungs, the blood travels through capillary beds on the alveoli where gas exchange occurs, removing carbon dioxide and adding oxygen to the blood. Gas exchange occurs due to gas partial pressure gradients across the the alveoli of the lungs and the capillaries interwoven in the alveoli. The oxygenated blood then leaves the lungs through pulmonary veins, which returns it to the left atrium, completing the pulmonary circuit. As the pulmonary circuit ends, the systemic circuit begins.
\
* **Systemic circulation** is the movement of blood from the heart through the body to provide oxygen and nutrients to the tissues of the body while bringing deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Oxygenated blood enters the left atrium from the pulmonary veins. The blood is then pumped through the mitral valve into the left ventricle. From the left ventricle, blood is pumped through the aortic valve and into the aorta, the body’s largest artery. The aorta arches and branches into major arteries to the upper body before passing through the diaphragm, where it branches further into the illiac, renal, and suprarenal arteries which supply the lower parts of the body. The arteries branch into smaller arteries, arterioles, and finally capillaries. Gas and nutrient exchange with the tissues occurs within the capillaries that run through the tissues. Metabolic waste and carbon dioxide diffuse out of the cell into the blood, while oxygen and glucose in the blood diffuses out of the blood and into the cell. Systemic circulation keeps the metabolism of every organ and every tissue in the body alive, with the exception of the parenchyma of the lungs, which are supplied by pulmonary circulation. The deoxygenated blood continues through the capillaries which merge into venules, then veins, and finally the venae cavae, which drain into the right atrium of the heart. From the right atrium, the blood will travel through the pulmonary circulation to be oxygenated before returning gain to the system circulation, completing the cycle of circulation through the body. The arterial component of systemic circulation the highest blood pressures in the body. The venous component of systemic circulation has considerably lower blood pressure in comparison, due to their distance from the heart, but contain semi-lunar valves to compensate. Systemic circulation as a whole is a higher pressure system than pulmonary circulation simply because systemic circulation must force greater volumes of blood farther through the body compared to pulmonary circulation.
\
* **The cardiovascular system is composed of two circulatory paths**: pulmonary circulation, the circuit through the lungs where blood is oxygenated; and systemic circulation, the circuit through the rest of the body to provide oxygenated blood. The two circuits are linked to each other through the heart, creating a continuous cycle of blood through the body.
\
* **Pulmonary circulation** is the movement of blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation, then back to the heart again. Oxygen-depleted blood from the body leaves the systemic circulation when it enters the right atrium through the superior and inferior venae cavae. The blood is then pumped through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. From the right ventricle, blood is pumped through the pulmonary valve and into the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery splits into the right and left pulmonary arteries and travel to each lung. At the lungs, the blood travels through capillary beds on the alveoli where gas exchange occurs, removing carbon dioxide and adding oxygen to the blood. Gas exchange occurs due to gas partial pressure gradients across the the alveoli of the lungs and the capillaries interwoven in the alveoli. The oxygenated blood then leaves the lungs through pulmonary veins, which returns it to the left atrium, completing the pulmonary circuit. As the pulmonary circuit ends, the systemic circuit begins.
\
* **Systemic circulation** is the movement of blood from the heart through the body to provide oxygen and nutrients to the tissues of the body while bringing deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Oxygenated blood enters the left atrium from the pulmonary veins. The blood is then pumped through the mitral valve into the left ventricle. From the left ventricle, blood is pumped through the aortic valve and into the aorta, the body’s largest artery. The aorta arches and branches into major arteries to the upper body before passing through the diaphragm, where it branches further into the illiac, renal, and suprarenal arteries which supply the lower parts of the body. The arteries branch into smaller arteries, arterioles, and finally capillaries. Gas and nutrient exchange with the tissues occurs within the capillaries that run through the tissues. Metabolic waste and carbon dioxide diffuse out of the cell into the blood, while oxygen and glucose in the blood diffuses out of the blood and into the cell. Systemic circulation keeps the metabolism of every organ and every tissue in the body alive, with the exception of the parenchyma of the lungs, which are supplied by pulmonary circulation. The deoxygenated blood continues through the capillaries which merge into venules, then veins, and finally the venae cavae, which drain into the right atrium of the heart. From the right atrium, the blood will travel through the pulmonary circulation to be oxygenated before returning gain to the system circulation, completing the cycle of circulation through the body. The arterial component of systemic circulation the highest blood pressures in the body. The venous component of systemic circulation has considerably lower blood pressure in comparison, due to their distance from the heart, but contain semi-lunar valves to compensate. Systemic circulation as a whole is a higher pressure system than pulmonary circulation simply because systemic circulation must force greater volumes of blood farther through the body compared to pulmonary circulation.
Q7. Describe and explain: Systemic and pulmonary circulation
50
New cards
FALSE
Q8. TRUE or FALSE. Blood transfusion could be performed with any blood type available
51
New cards
Haemoglobin is a %%***red protein***%% responsible for __transporting oxygen in the blood of vertebrates__.
Its molecule comprises __four subunits__, each containing an %%***iron atom bound to a haem group***%%.
Its molecule comprises __four subunits__, each containing an %%***iron atom bound to a haem group***%%.
Q9. Give a short definition for the following term: Haemoglobin
52
New cards
FALSE
Q10. TRUE or FALSE. The second heart sound is systolic
53
New cards
FALSE
Q11. TRUE or FALSE. Red blood cells perform phagocytosis
54
New cards
FALSE
Q12. TRUE or FALSE. The systemic circulation starts with the capillaries
55
New cards
TRUE
\
*To explain*:
* Fibrinogen is %%**made in**%% your %%**liver**%% and %%**helps**%% your %%**blood clot**%%.
* __Low__ fibrinogen may make it __difficult__ for your __blood to clot__.
* If you have symptoms of __excessive bleeding__, your healthcare provider may order this test to __check__ your __fibrinogen levels__.
* Another name for a fibrinogen test is a %%**factor I activity test**%%
\
*To explain*:
* Fibrinogen is %%**made in**%% your %%**liver**%% and %%**helps**%% your %%**blood clot**%%.
* __Low__ fibrinogen may make it __difficult__ for your __blood to clot__.
* If you have symptoms of __excessive bleeding__, your healthcare provider may order this test to __check__ your __fibrinogen levels__.
* Another name for a fibrinogen test is a %%**factor I activity test**%%
Q13. TRUE or FALSE. Fibrinogen plays a major role in blood clotting
56
New cards
\
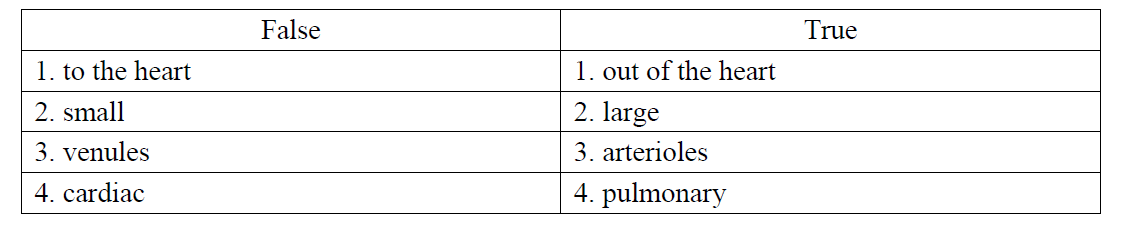
Q14. Read the text. There are 4 false words in the text. Write them in the table and provide their true counterparts.
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood to the heart. They have small diameter and elastic walls. They branch into narrower vessels called venules which branch further to capillaries. The blood is pumped out of the heart under pressure into the aorta and the cardiac artery.
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood to the heart. They have small diameter and elastic walls. They branch into narrower vessels called venules which branch further to capillaries. The blood is pumped out of the heart under pressure into the aorta and the cardiac artery.
57
New cards
TRUE
Q15 TRUE or FALSE. There are no antibodies against the Rh factor in human blood plasma
58
New cards
False 1: lymphatic
True 1: blood
False 2: tendon
True 2: ventricle
False 3: two
True 3: three
False 4: myocardium
True 4: endocardium
True 1: blood
False 2: tendon
True 2: ventricle
False 3: two
True 3: three
False 4: myocardium
True 4: endocardium
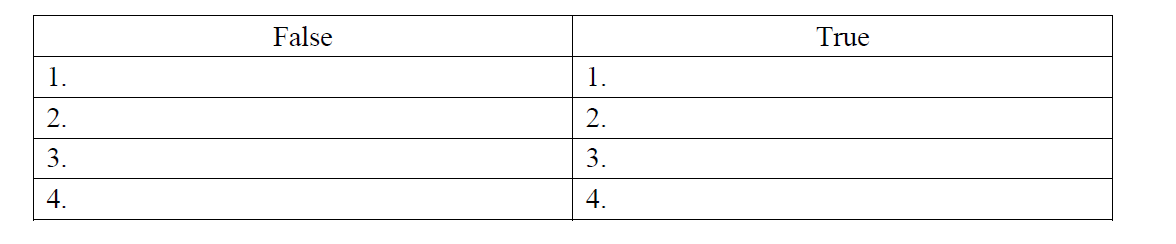
Q16. Read the text. There are 4 false words in the text. Write them in the table and provide their true counterparts.
The heart is a muscular organ which pumps blood into the lymphatic vessels. Longitudinally, a wall divides the heart into right and left parts. In each part there is an atrium and a tendon. The heart walls are built up of two layers. The inner layer of the heart wall is made up of a simple squamous epithelium and is called myocardium.
The heart is a muscular organ which pumps blood into the lymphatic vessels. Longitudinally, a wall divides the heart into right and left parts. In each part there is an atrium and a tendon. The heart walls are built up of two layers. The inner layer of the heart wall is made up of a simple squamous epithelium and is called myocardium.
59
New cards
FALSE
Q17. TRUE or FALSE. Systematic circulation starts with the pulmonary artery
60
New cards
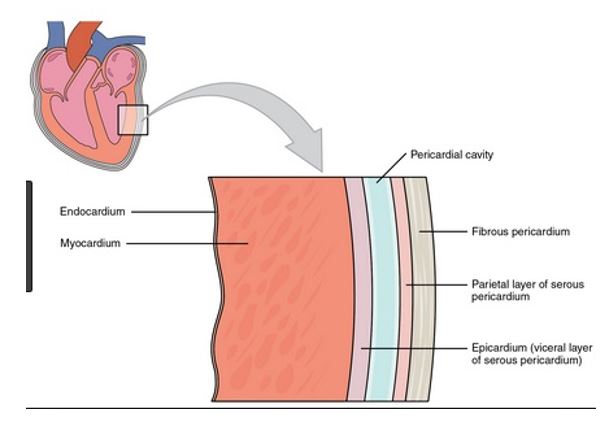
c) epicardium
*To explain*:
The wall of the heart consists of __three layers__:
the %%***epicardium (external layer),***%%
%%***the myocardium (middle layer),***%%
%%***the endocardium (inner layer)***%%.
The epicardium is the __thin__, __transparent__ outer layer of the wall and is composed of __delicate connective tissue__.
*To explain*:
The wall of the heart consists of __three layers__:
the %%***epicardium (external layer),***%%
%%***the myocardium (middle layer),***%%
%%***the endocardium (inner layer)***%%.
The epicardium is the __thin__, __transparent__ outer layer of the wall and is composed of __delicate connective tissue__.
Q18. Which is the outermost layer of the heart?
a) myocardium
b) pericardium
c) epicardium
d) endocardium
a) myocardium
b) pericardium
c) epicardium
d) endocardium
61
New cards
* The heart is a %%***muscular organ***%% in most %%***animals***%%, which %%***pumps blood through the blood vessels***%% of the %%***circulatory system***%%.
* %%***Blood***%% provides the body with %%***oxygen and nutrients***%%, as well as __assisting__ in the %%***removal of metabolic wastes***%%.
* In __humans__, the heart is %%***located between the lungs***%%, in the %%***middle compartment of the chest***%%.
* %%***Blood***%% provides the body with %%***oxygen and nutrients***%%, as well as __assisting__ in the %%***removal of metabolic wastes***%%.
* In __humans__, the heart is %%***located between the lungs***%%, in the %%***middle compartment of the chest***%%.
Q19. Give a short definition for the following term: Heart
62
New cards
1. **The human heart is located within the thoracic cavity, medially between the lungs in the space known as the mediastinum**. Within the mediastinum, the heart is separated from the other mediastinal structures by a tough membrane known as the pericardium, or pericardial sac, and sits in its own space called the pericardial cavity. The dorsal surface of the heart lies near the bodies of the vertebrae, and its anterior surface sits deep to the sternum and costal cartilages. The great veins, the superior and inferior venae cavae, and the great arteries, the aorta and pulmonary trunk, are attached to the superior surface of the heart, called the base. The base of the heart is located at the level of the third costal cartilage. The inferior tip of the heart, the apex, lies just to the left of the sternum between the junction of the fourth and fifth ribs near their articulation with the costal cartilages. The right side of the heart is deflected anteriorly, and the left side is deflected posteriorly.
2. **The wall of the heart consists of three layers**: the epicardium (external layer), the myocardium (middle layer) and the endocardium (inner layer). The epicardium is the thin, transparent outer layer of the wall and is composed of delicate connective tissue. The myocardium, comprised of cardiac muscle tissue, makes up the majority of the cardiac wall and is responsible for its pumping action. The thickness of the myocardium mirrors the load to which each specific region of the heart is subjected. The endocardium is a thin layer of endothelium overlying a thin layer of connective tissue. It provides a smooth lining for the chambers of the heart and covers the valves. The endocardium is continuous with the endothelial lining of the large blood vessels attached to the heart.
3. **The heart has four chambers**:
\- The right atrium receives blood from the veins and pumps it to the right ventricle.
\- The right ventricle receives blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the lungs, where it is loaded with oxygen.
\- The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle.
\- The left ventricle (the strongest chamber) pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body. The left ventricle’s vigorous contractions create our blood pressure.
4. The heart is the main organ in the circulatory system, the structure **primarily responsible** for delivering the circulation of blood and transportation of nutrients in all parts of the body. This continuous task uplifts the role of the heart as a vital organ whose normal operation is constantly required. The heart’s blood-pumping cycle, called cardiac cycle, ensures that blood is distributed throughout the body. The oxygen distribution process begins when oxygen-free blood enters into the heart through the right atrium, goes into the right ventricle, enters the lungs for oxygen refill and release of carbon dioxide, and transfers into the left chambers, ready for redistribution
Q20. Describe and explain: Heart – localization, wall structure, main parts, function
63
New cards
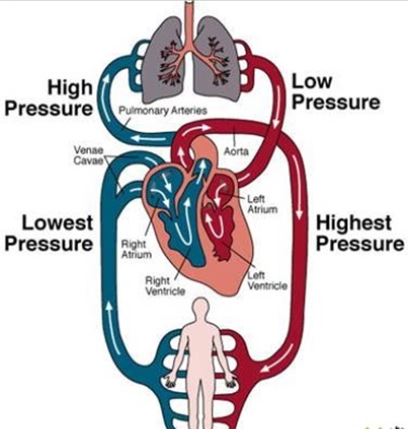
b) the aorta
*To explain*:
The highest arterial blood pressure is at the aorta. The __systemic circulation__ has a lot __more blood vessels__ therefore provides __much greater resistance to blood flow and increases the pressure__. %%***Blood pressure is highest as it leaves through the aorta***%%.
Arterial pressure results from the pressure exerted by the blood in the large arteries. __Blood pressure depends on cardiac output and total peripheral resistance__. Arterial pressure fluctuates with each heart beat, according to the pumping of the heart.
*To explain*:
The highest arterial blood pressure is at the aorta. The __systemic circulation__ has a lot __more blood vessels__ therefore provides __much greater resistance to blood flow and increases the pressure__. %%***Blood pressure is highest as it leaves through the aorta***%%.
Arterial pressure results from the pressure exerted by the blood in the large arteries. __Blood pressure depends on cardiac output and total peripheral resistance__. Arterial pressure fluctuates with each heart beat, according to the pumping of the heart.
Q21. The highest arterial blood pressure is registered in:
a) pulmonary arteries
b) the aorta
c) the upper vena cava
d) the lower vena cava
a) pulmonary arteries
b) the aorta
c) the upper vena cava
d) the lower vena cava
64
New cards
b) erythrocytes
Q22. The red blood cells are called:
a) thrombocytes
b) erythrocytes
c) phagocytes
d) leukocytes
a) thrombocytes
b) erythrocytes
c) phagocytes
d) leukocytes
65
New cards
b) A and B antigens
*To explain*:
Blood group AB individuals have both A and B antigens on the surface of their RBCs, and their blood plasma does not contain any antibodies against either A or B antigen.
*To explain*:
Blood group AB individuals have both A and B antigens on the surface of their RBCs, and their blood plasma does not contain any antibodies against either A or B antigen.
Q23. A person from blood group AB has:
a) A antigens
b) A and B antigens
c) B antigens
d) no antigens
a) A antigens
b) A and B antigens
c) B antigens
d) no antigens
66
New cards
d) antigen A
*To explain*:
There are four main blood groups defined by the ABO system:
\- **blood group A** – has A antigens on the red blood cells with anti-B antibodies in the plasma
\- **blood group B** – has B antigens with anti-A antibodies in the plasma
\- **blood group O** – has no antigens, but both anti-A and anti-B antibodies in the plasma
\- **blood group AB** – has both A and B antigens, but no antibodies
*To explain*:
There are four main blood groups defined by the ABO system:
\- **blood group A** – has A antigens on the red blood cells with anti-B antibodies in the plasma
\- **blood group B** – has B antigens with anti-A antibodies in the plasma
\- **blood group O** – has no antigens, but both anti-A and anti-B antibodies in the plasma
\- **blood group AB** – has both A and B antigens, but no antibodies
Q24. A person with blood group A has on his erythrocytes:
a) antigens A and B
b) antigen B
c) no antigens
d) antigen A
a) antigens A and B
b) antigen B
c) no antigens
d) antigen A
67
New cards
d) no antibodies
Q25. A person with blood group type B has:
a) anti-B antibodies
b) B antigens
c) A and B antigens
d) no antibodies
a) anti-B antibodies
b) B antigens
c) A and B antigens
d) no antibodies
68
New cards
c) connective tissue
Q26. Blood is a type of:
a) epithelial tissue
b) muscle tissue
c) connective tissue
d) nervous tissue
a) epithelial tissue
b) muscle tissue
c) connective tissue
d) nervous tissue
69
New cards
b) antigens B
Q27. Blood group B erythrocytes contain:
a) antibodies β
b) antigens B
c) antibodies a, β
d) antigens A
a) antibodies β
b) antigens B
c) antibodies a, β
d) antigens A
70
New cards
d) no antigens
Q28. A person from blood group O has:
a) A antigens
b) B antigens
c) A and B antigens
d) no antigens
a) A antigens
b) B antigens
c) A and B antigens
d) no antigens
71
New cards
c) cardiac valves
Q29. Blood moves in one direction due to the:
a) trachea
b) nerve impulses
c) cardiac valves
d) arteries
a) trachea
b) nerve impulses
c) cardiac valves
d) arteries
72
New cards
d) antigens A
Q30. Blood group A erythrocytes possess:
a) antibodies a
b) antigens B
c) antibodies a, β
d) antigens A
a) antibodies a
b) antigens B
c) antibodies a, β
d) antigens A
73
New cards
d) are without nuclei
*To explain*:
The blood cells without nuclei are Erythrocytes/Red blood cells. Because of the __lack of nuclei and organelles__, __mature red blood__ cells __do not contain DNA__ and __cannot synthesize any RNA,__ and consequently __cannot divide__ and have __limited repair capabilities__.
*To explain*:
The blood cells without nuclei are Erythrocytes/Red blood cells. Because of the __lack of nuclei and organelles__, __mature red blood__ cells __do not contain DNA__ and __cannot synthesize any RNA,__ and consequently __cannot divide__ and have __limited repair capabilities__.
Q31. Erythrocytes:
a) have a protective function
b) are several types
c) participate in blood clotting
d) are without nuclei
a) have a protective function
b) are several types
c) participate in blood clotting
d) are without nuclei
74
New cards
HIV
*To explain*: The CD4+ T lymphocyte is one of the central cells involved in immune responses in vivo. HIV mainly infects CD4+ T lymphocytes.
*To explain*: The CD4+ T lymphocyte is one of the central cells involved in immune responses in vivo. HIV mainly infects CD4+ T lymphocytes.
Q32. Read the text and answer the question: Which virus affects human T helper lymphocytes?
75
New cards
Diastole
*To explain:* Diastole is a phase in the cardiac cycle, during which the heart relaxes and allows blood to refill each atrium and each ventricle.
*To explain:* Diastole is a phase in the cardiac cycle, during which the heart relaxes and allows blood to refill each atrium and each ventricle.
Q33. Read the text and answer the question: What is the term for the cardiac relaxation?
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood to the heart. They have small diameter and elastic walls. They branch into narrower vessels called venules which branch further to capillaries. The blood is pumped out of the heart under pressure into the aorta and the cardiac artery.
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood to the heart. They have small diameter and elastic walls. They branch into narrower vessels called venules which branch further to capillaries. The blood is pumped out of the heart under pressure into the aorta and the cardiac artery.
76
New cards
b) thyroid gland
Q34. Thyroxin is secreted by the:
a) pituitary gland
b) thyroid gland
c) testes
d) ovary
a) pituitary gland
b) thyroid gland
c) testes
d) ovary
77
New cards
a) systole
b) diastole
c) pause
d) pulse
b) diastole
c) pause
d) pulse
Q35. The myocardial contraction is known as:
a) systole
b) diastole
c) pause
d) pulse
a) systole
b) diastole
c) pause
d) pulse
78
New cards
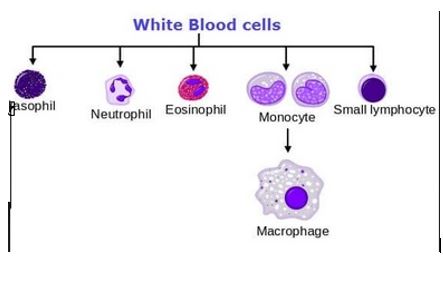
c) monocytes
\
*To explain:*
Monocytes are the %%__largest type of white blood cells__%%, and can be up to %%20µm%% in diameter. They have a large eccentrically placed nucleus, which is %%**kidney bean shaped**%%. They have abundant cytoplasm, and some fine pink/purple granules in cytoplasm.
\
*To explain:*
Monocytes are the %%__largest type of white blood cells__%%, and can be up to %%20µm%% in diameter. They have a large eccentrically placed nucleus, which is %%**kidney bean shaped**%%. They have abundant cytoplasm, and some fine pink/purple granules in cytoplasm.
Q36. Which cells have the largest nucleus?
a) phagocytes
b) leukocytes
c) monocytes
d) erythrocytes
a) phagocytes
b) leukocytes
c) monocytes
d) erythrocytes
79
New cards
Thrombocytes which are also known as blood platelets, are one of the many components - including the different types of cells that, together, form blood. **The structure of thrombocytes** (or 'blood platelets') can be summarized as follows: Thrombocytes are cell fragments, disk-shaped, diameter 2-4 um, have many granules but no nucleus, have a longevity of approx. 5-9 days, there are approx. 150,000 - 400,000 platelets per micro-litre of blood. Their structure is comprised of four different zones, we will study them from the peripheral to the innermost:
* Peripheral Zone (The outer part of the zone is made up of glycoprotein for the adhesion of platelets, their aggregation and activation too),
* Sol-gel Zone (The second outermost layer is said to be rich in microfilaments and microtubules, and they help in maintaining the discoid shape of platelets in the blood);
* Organelle Zone (The third most peripheral zone of the thrombocyte is rich in alpha granules, protein granules and also contains clotting mediators like factor VIII, factor V, fibrinogen, platelet derived growth factors, chemotactic agents and fibronectin. Dense bodies or delta granules also contain Serotonin, Calcium and ADP, which are considered as platelet activating mediators);
* Membranous Zone (The Membranous zone is the innermost zone, which contains various other membranes derived from megakaryocytic smooth endoplasmic reticulum and is said to be organized into a deep tense kind of tubular system. This tubular system is also used in the synthesis of thromboxane A2 and also connects to the various surface platelet membranes to aid the release of thromboxane A2)
The **functions of thrombocytes** (or 'blood platelets') include facilitating blood clotting - the purpose of which is to prevent loss of body fluids. Thrombocytes play a number of roles in haemostasis. Thrombocytes contain most of the blood serotonin and great amounts of histamine, adrenaline and lysosomic enzymes. Secreting vasoactive substances both actively and passively under the influence of various irritants, thrombocytes are important for tonicity and permeability of the vessel wall.
* Peripheral Zone (The outer part of the zone is made up of glycoprotein for the adhesion of platelets, their aggregation and activation too),
* Sol-gel Zone (The second outermost layer is said to be rich in microfilaments and microtubules, and they help in maintaining the discoid shape of platelets in the blood);
* Organelle Zone (The third most peripheral zone of the thrombocyte is rich in alpha granules, protein granules and also contains clotting mediators like factor VIII, factor V, fibrinogen, platelet derived growth factors, chemotactic agents and fibronectin. Dense bodies or delta granules also contain Serotonin, Calcium and ADP, which are considered as platelet activating mediators);
* Membranous Zone (The Membranous zone is the innermost zone, which contains various other membranes derived from megakaryocytic smooth endoplasmic reticulum and is said to be organized into a deep tense kind of tubular system. This tubular system is also used in the synthesis of thromboxane A2 and also connects to the various surface platelet membranes to aid the release of thromboxane A2)
The **functions of thrombocytes** (or 'blood platelets') include facilitating blood clotting - the purpose of which is to prevent loss of body fluids. Thrombocytes play a number of roles in haemostasis. Thrombocytes contain most of the blood serotonin and great amounts of histamine, adrenaline and lysosomic enzymes. Secreting vasoactive substances both actively and passively under the influence of various irritants, thrombocytes are important for tonicity and permeability of the vessel wall.
Q37. Describe and explain:
Thrombocytes – structure and function
Thrombocytes – structure and function