Zoology lab: practical one
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
pinacocytes
flattned eptiheial cells
choanocytes
cells that create water currents in canals and chambers
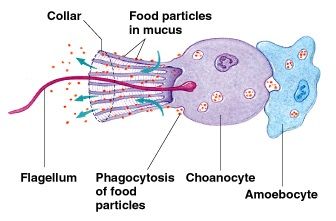
mesohyl
gelatinous matrix with scattered cells
spicules
structral cells made of of eithercalcium carbonte, silica or fibers of spongins
gemmules
internal asexual buds in freshwater
Class Demospongia
siliceous spicules, but never 6 rayed and/or fibers of sponging
all leuconoid
Class Calcarea
spicles are calcerous
asconoid, syconoid, or leucnoid
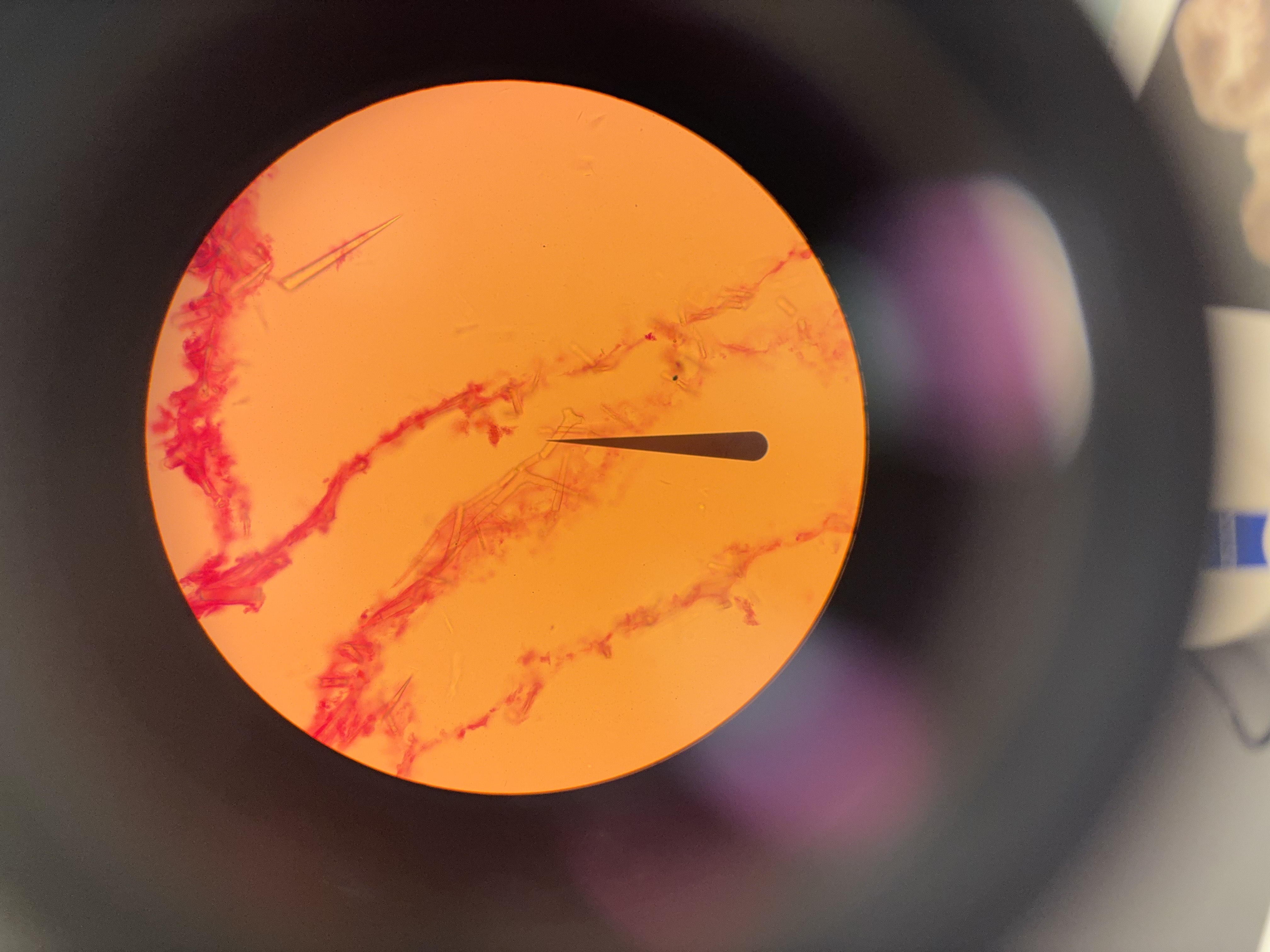
Ascon
incurrent pores, spongocoel lined with choanocytes; osculum
usually Class Calcarea
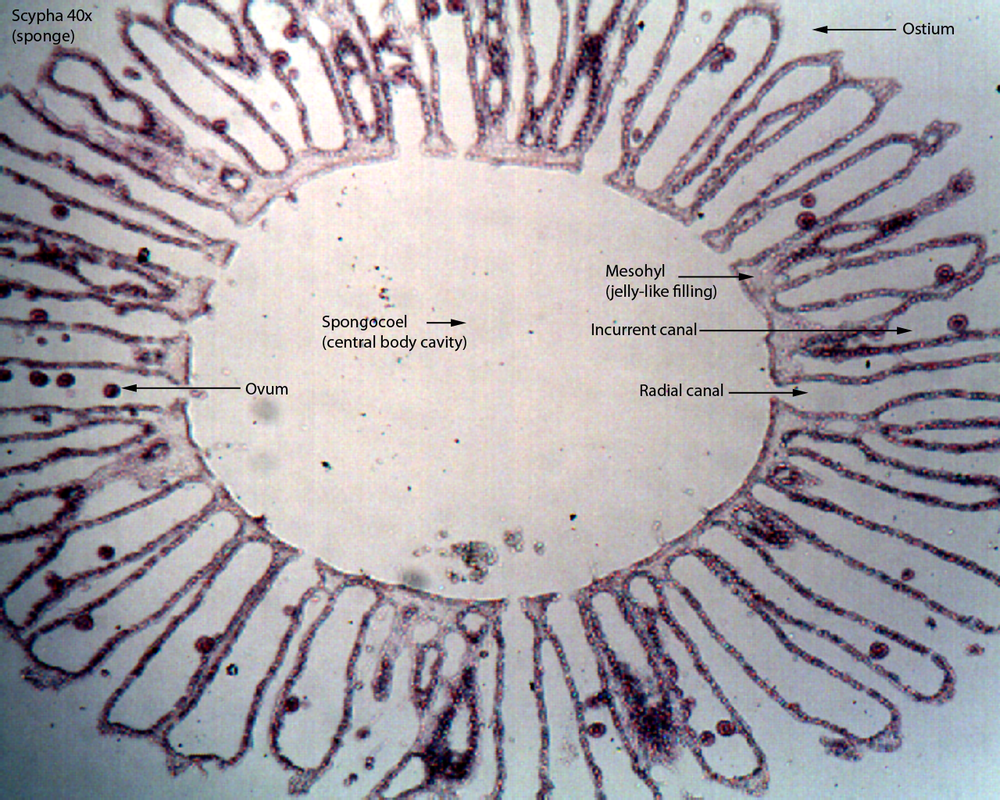
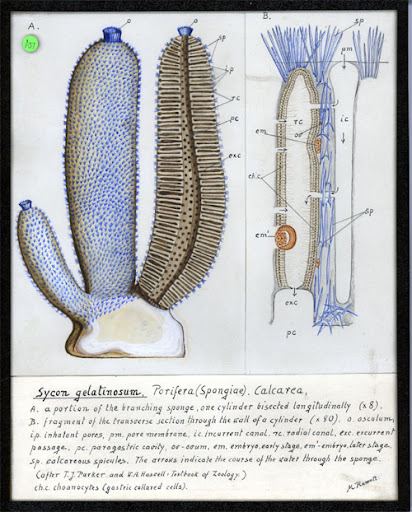
Sycon
ostium, incurrent canals, radial CANALS lined with choanocytes, spongocoel; osclum
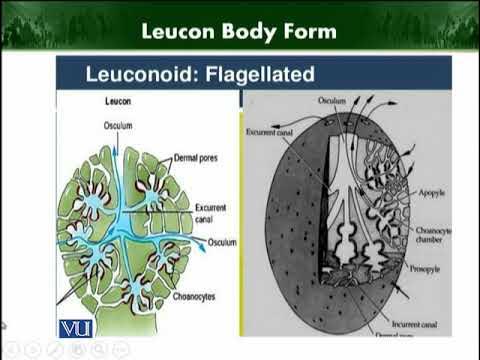
Leucon
body plan with pores; incurrent canals; radial canals; flagellated chambers with choancytes; osculum
Class Hexactinellida
Spiclues are siliecous, 6 rayed and fused
Euplectella

radial canal
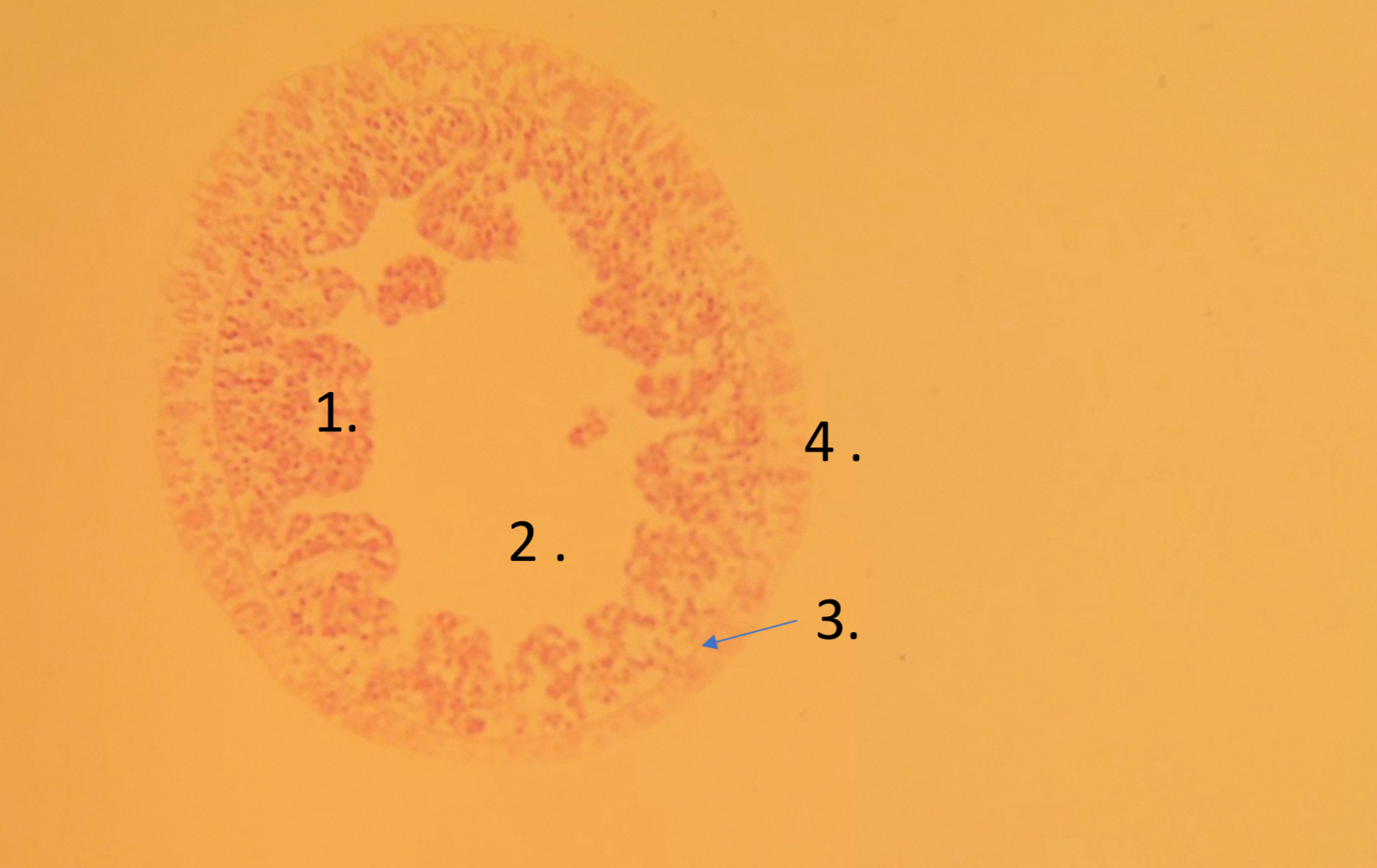
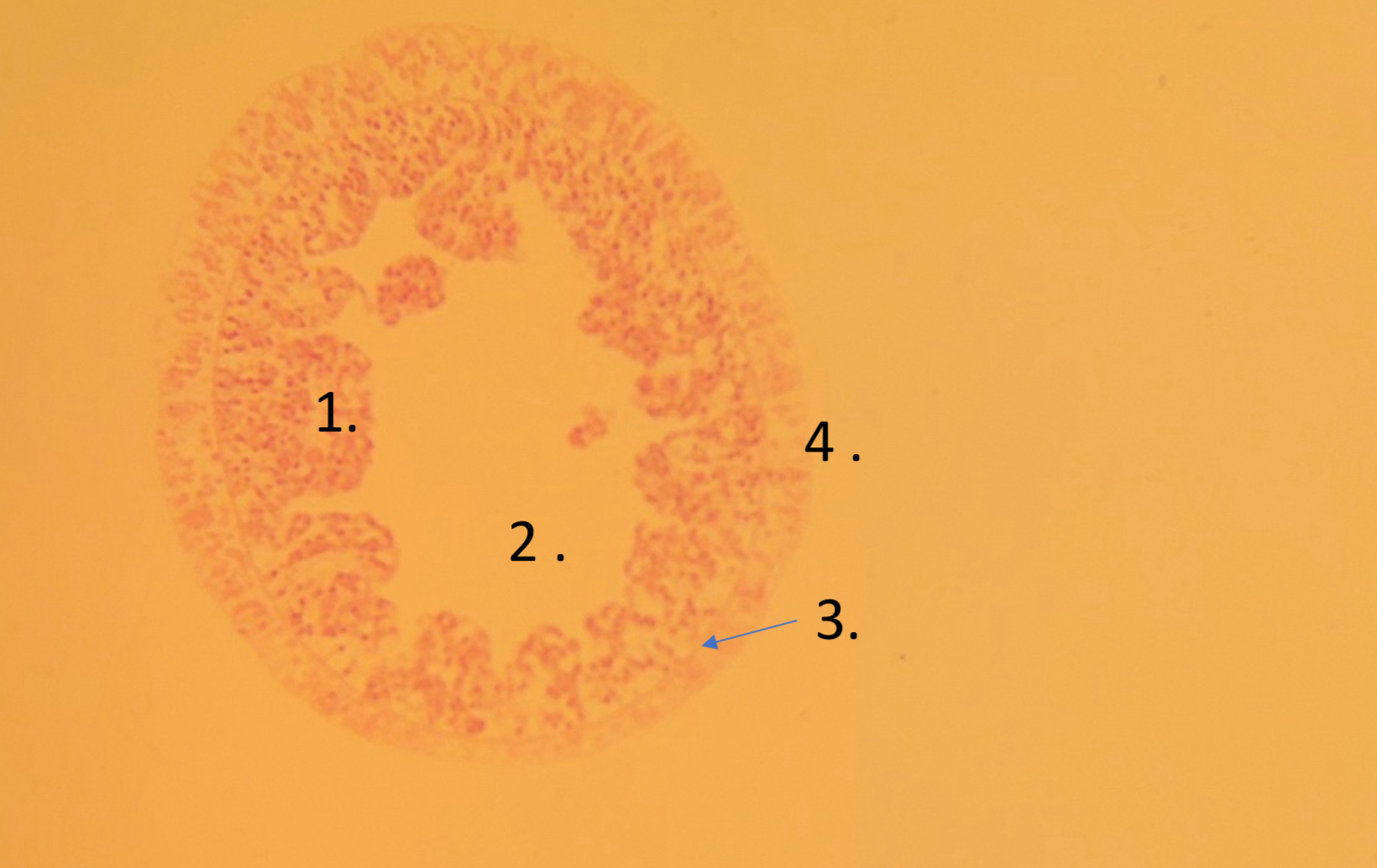
what is number 1
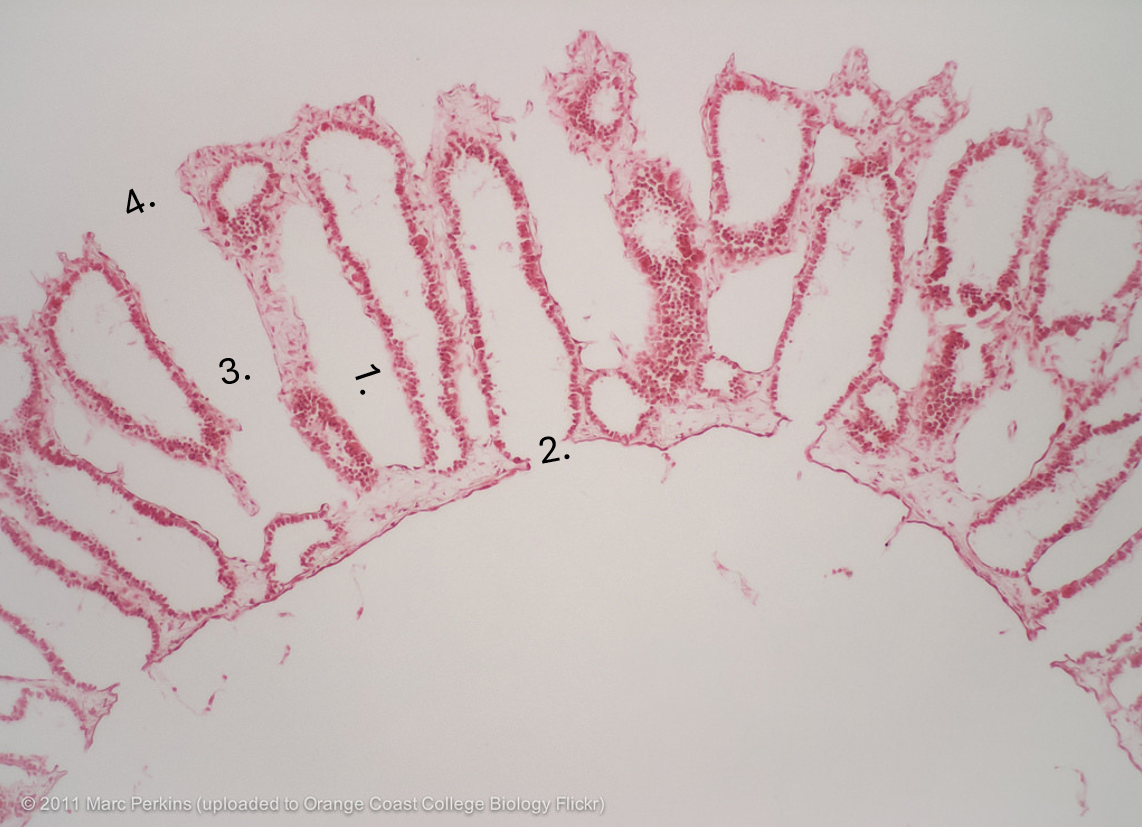
apopyle
what is 2
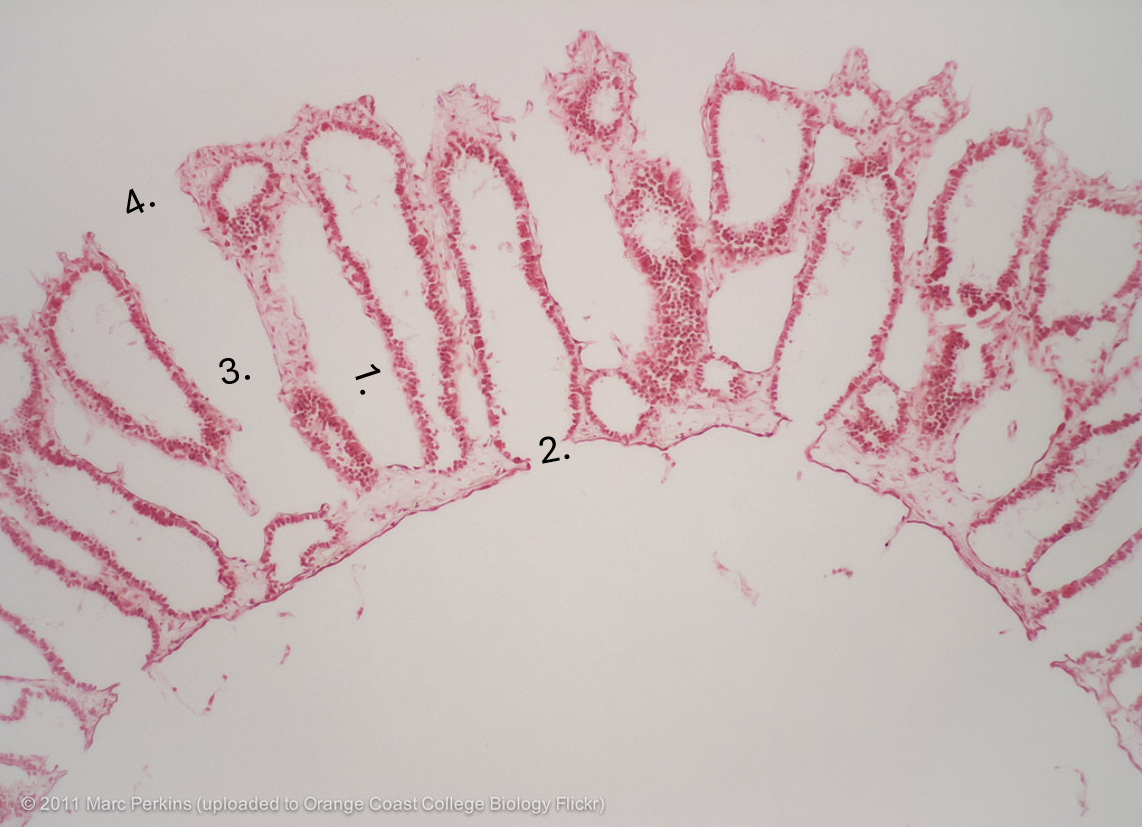
incurrent canal
what is 3.
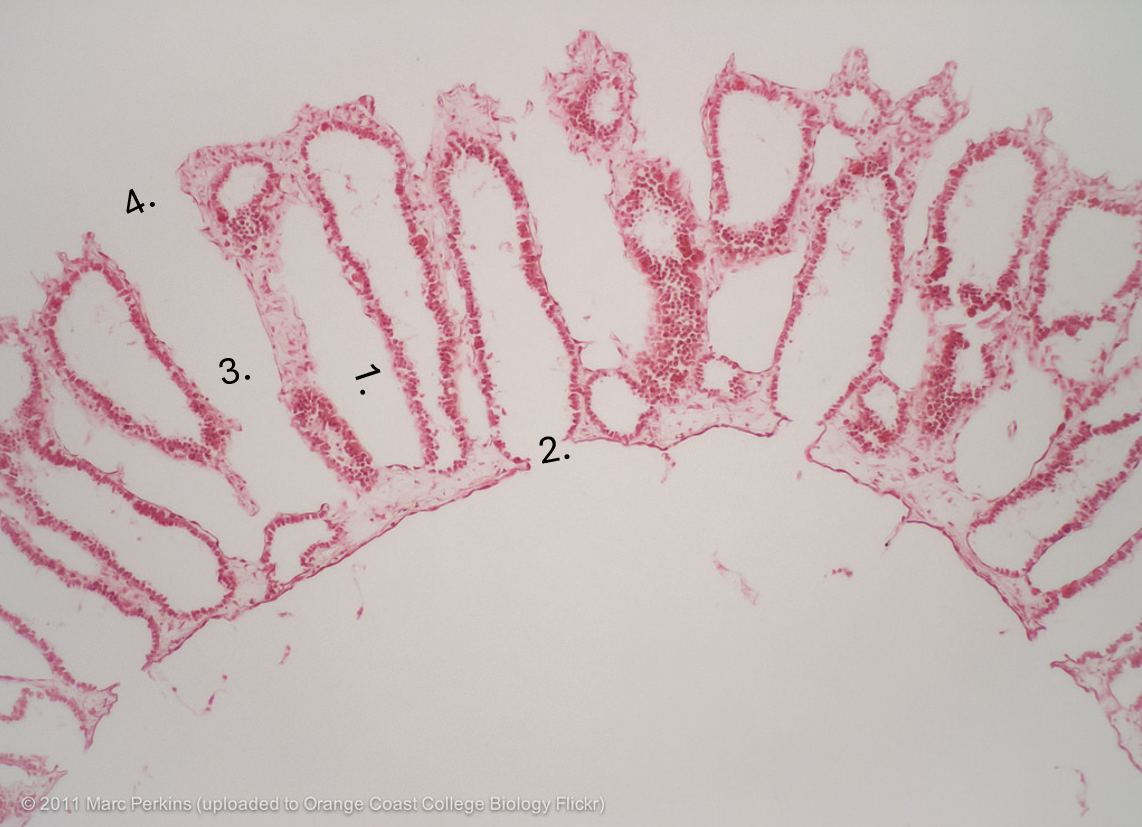
dermal ostimum
what is 4
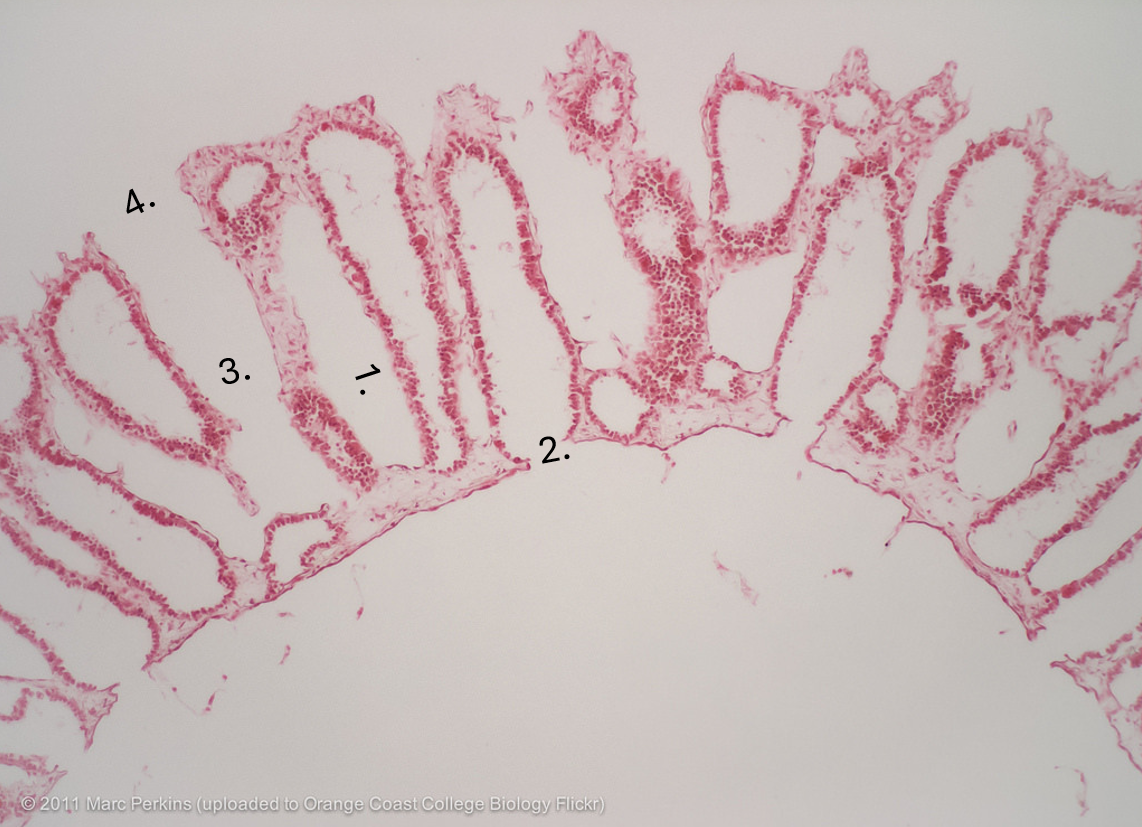
Amphiblastula
what is 1. pointing to
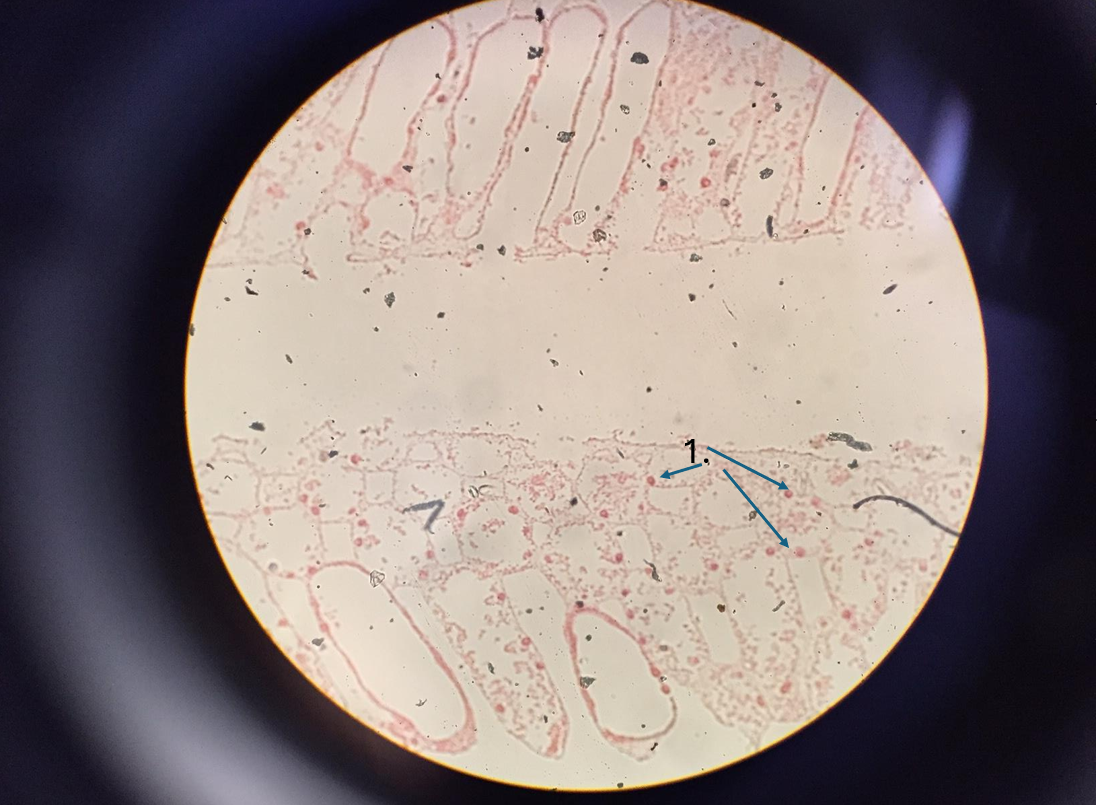
Planula
Larval form of cnidarian species
Formed from either a Medusa or a polyp

Phylum Cnidaria, Class Hydrozoa
hydra sp.
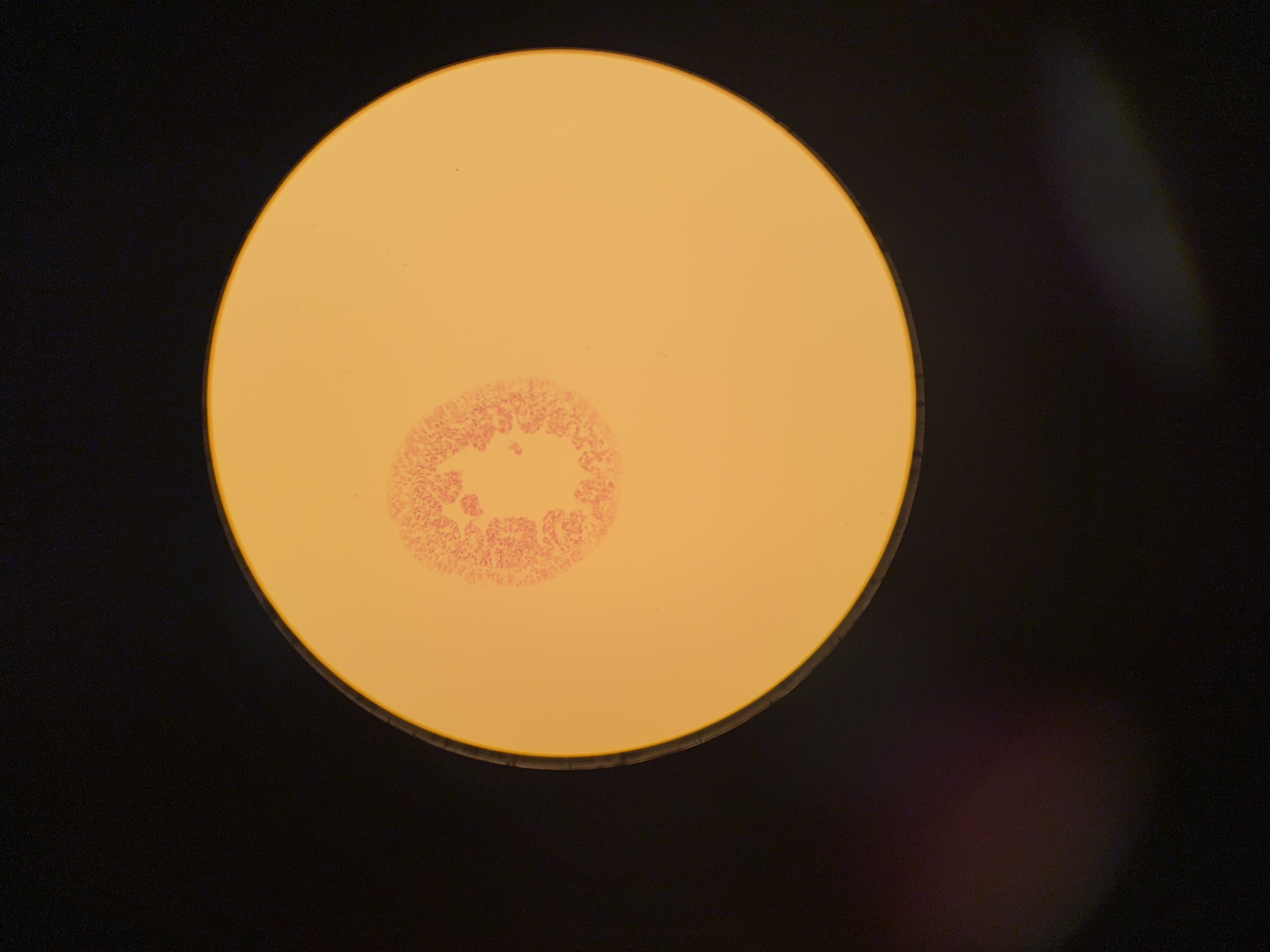
Scyphistoma
2nd stage of the scyphozoa development
Gastrodermis
What is 1
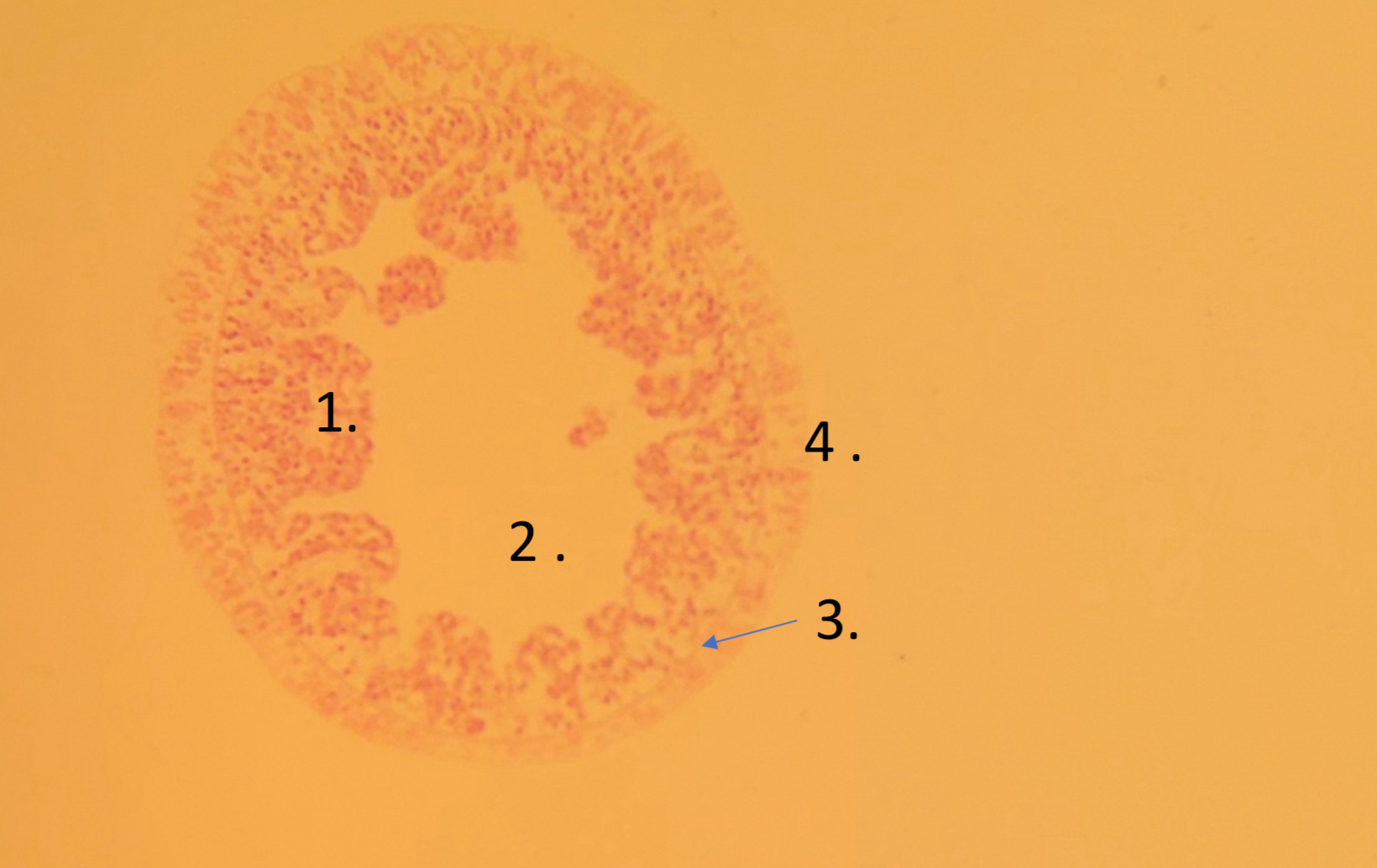
Gastovascular cavity
What is 2
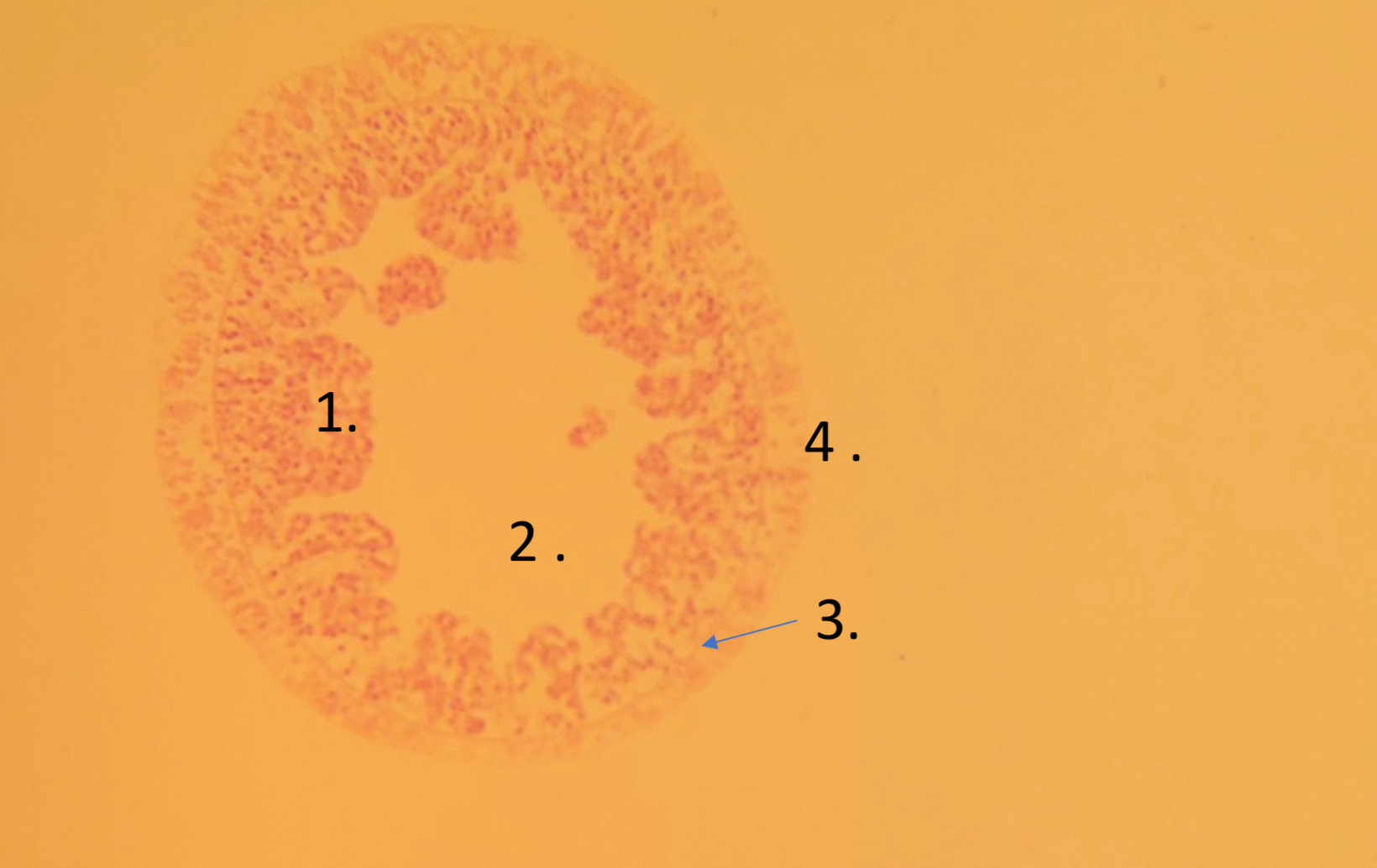
mesoglea
What is 3
Epidermis
What is 4
Ephyra
Budded off Medusa’s from the schiystoma via strobilation. Will mature into a Medusae

Class Anthozoa, order Octocorallia
Give class and order for this species

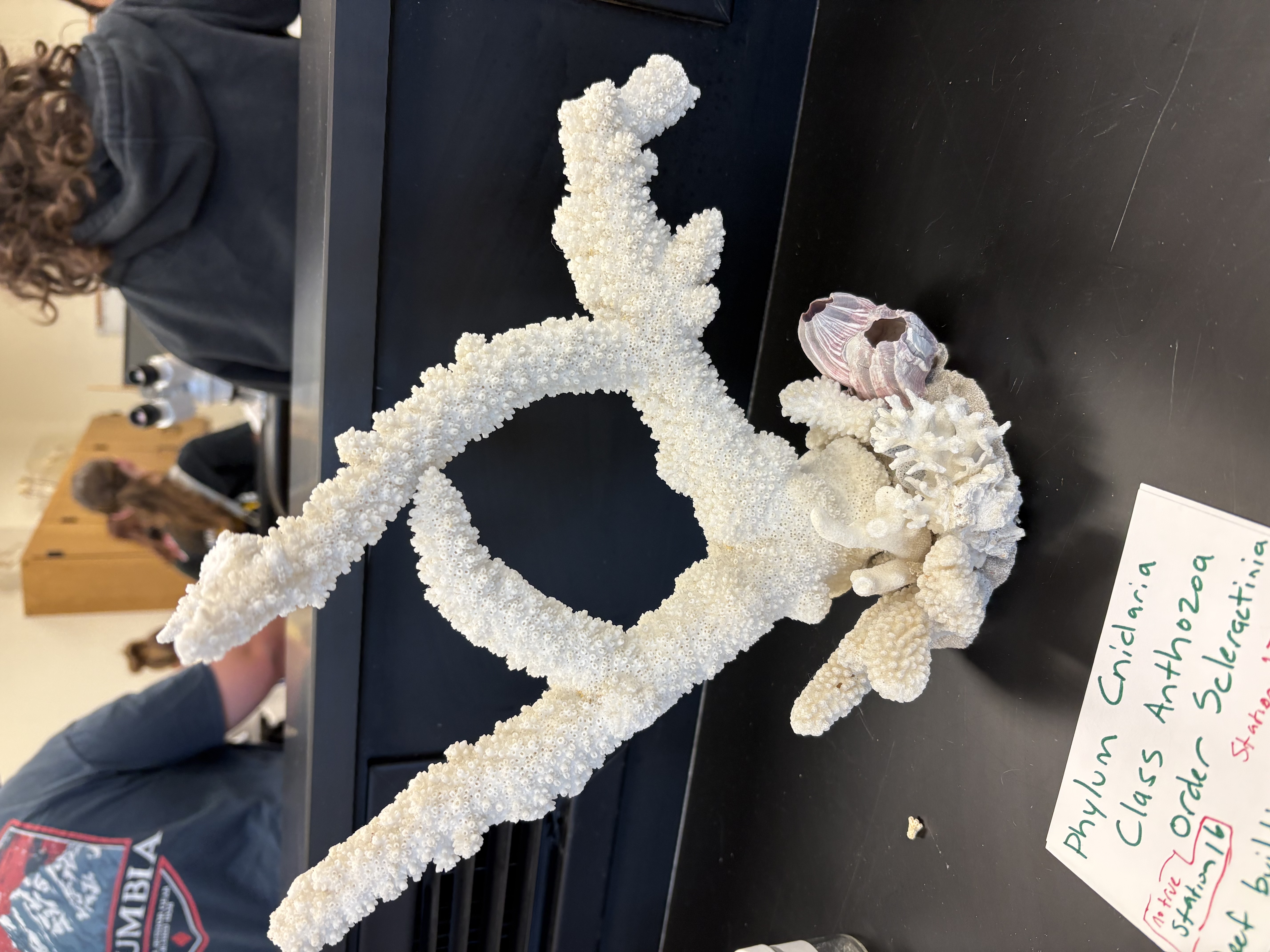
Class Anthozoa order Scleractinia
Name class and order

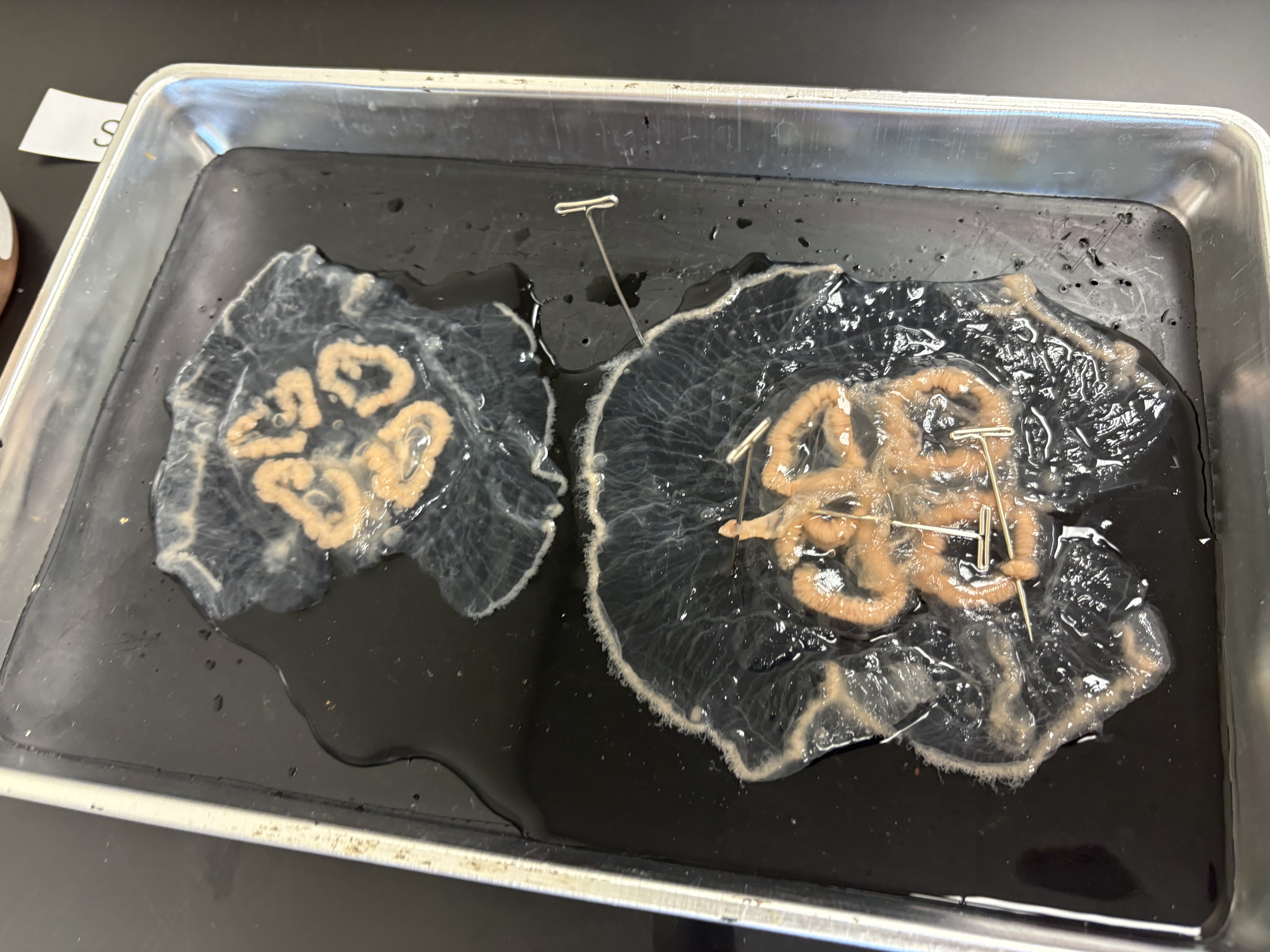
Gastric/gonad pouches
What are the areas pinned in this specimen (Class Scyphozoa)

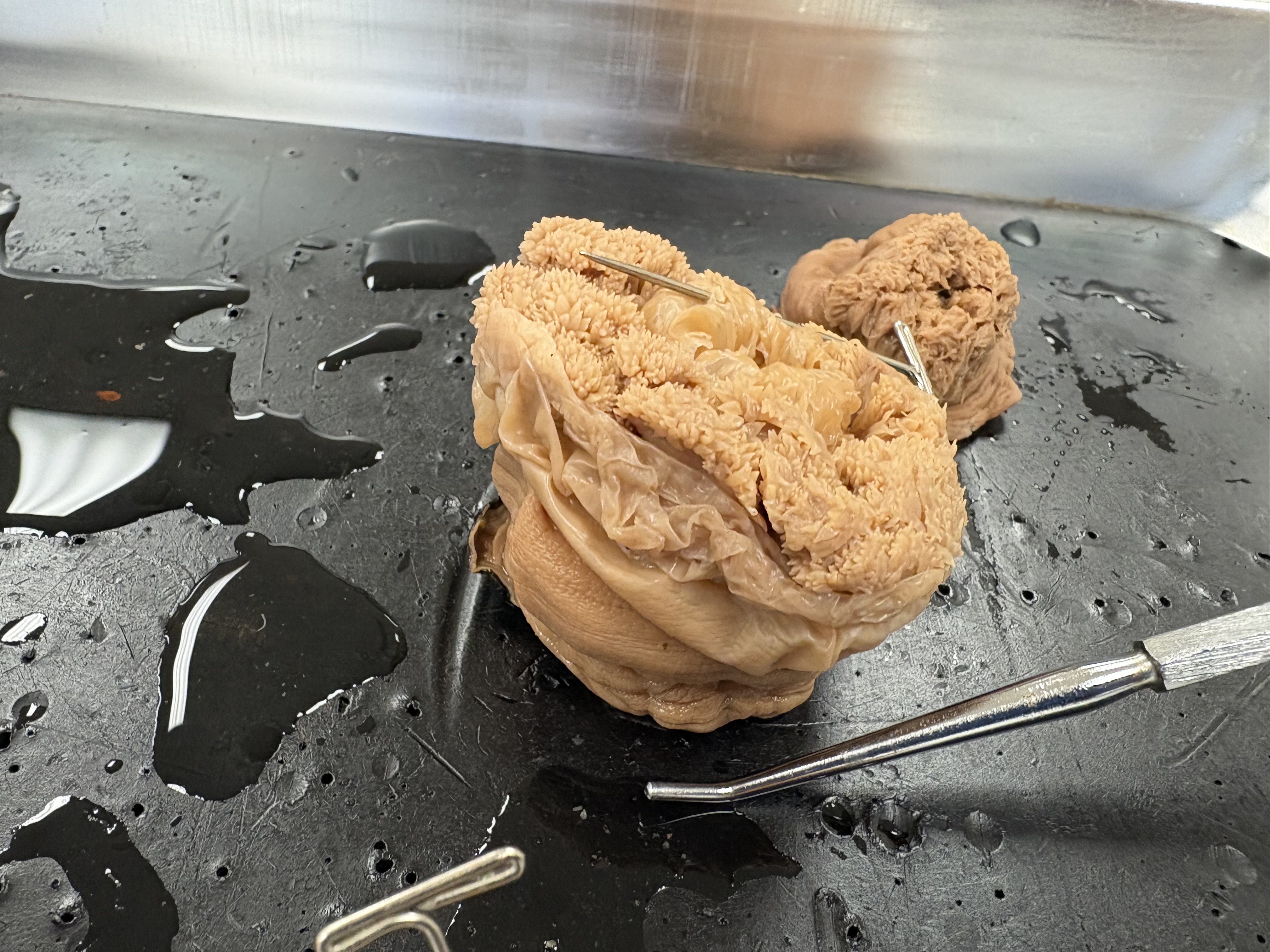
Cnidarian, Anthozoa
Name phylum and class

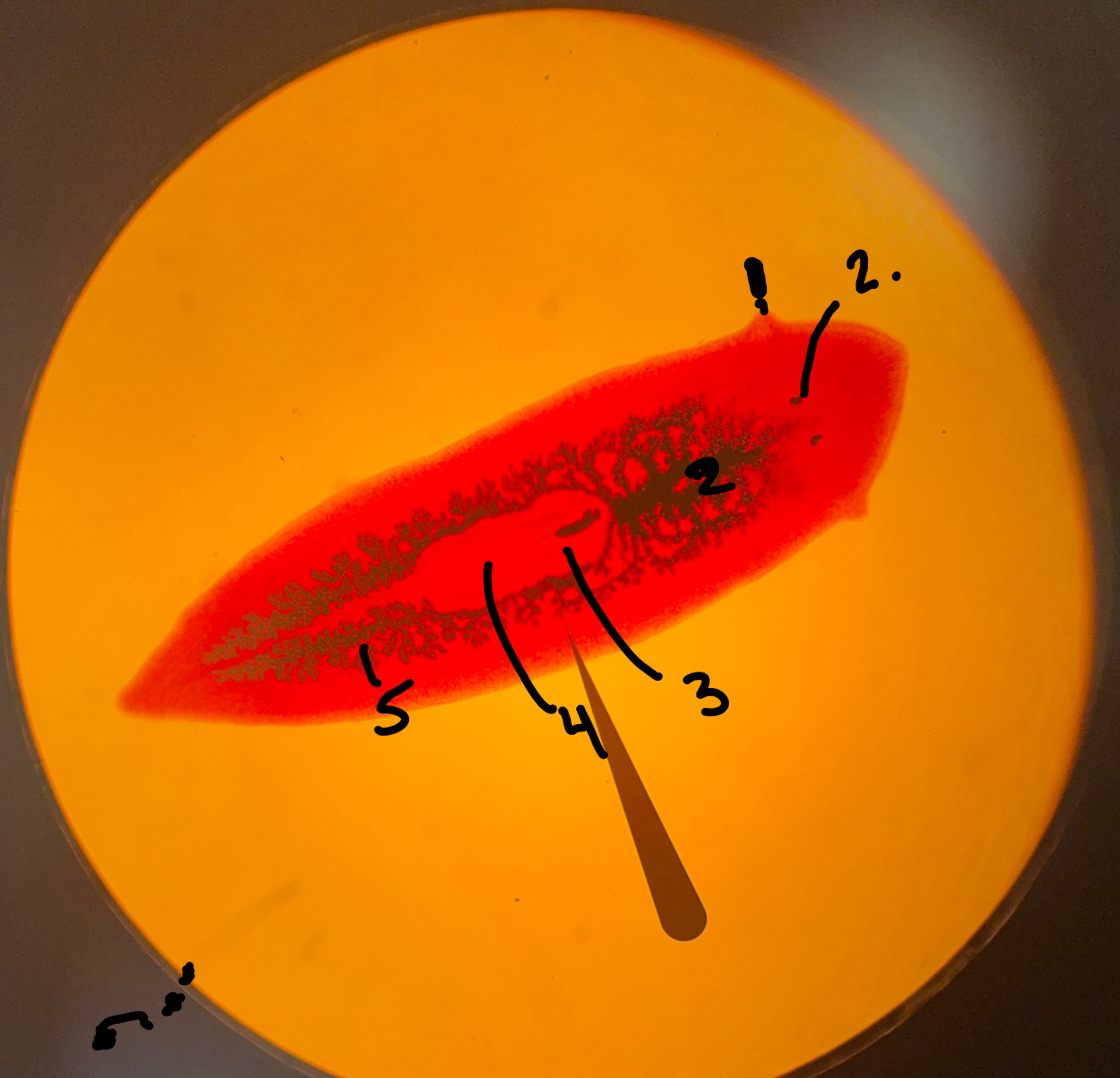
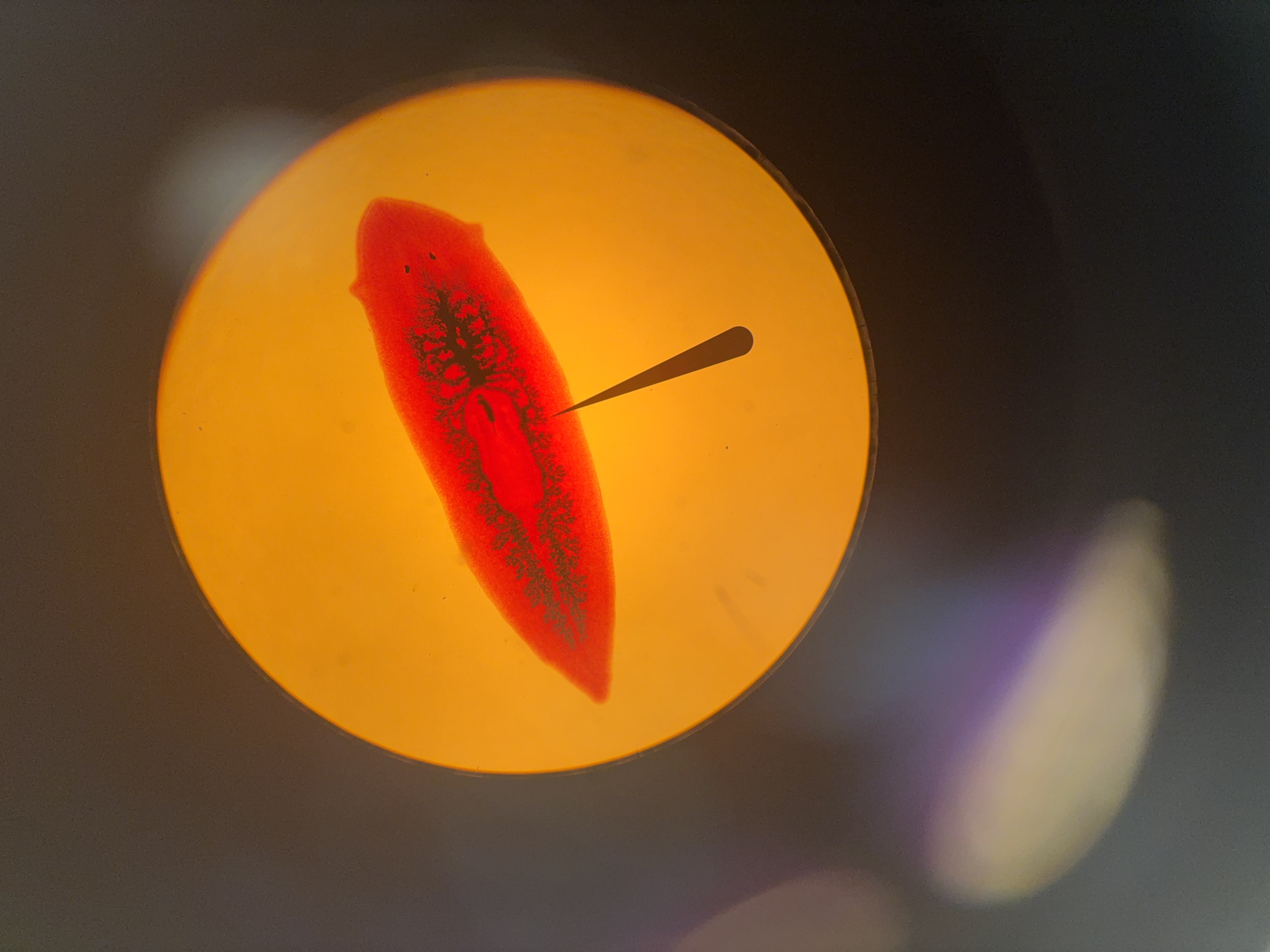
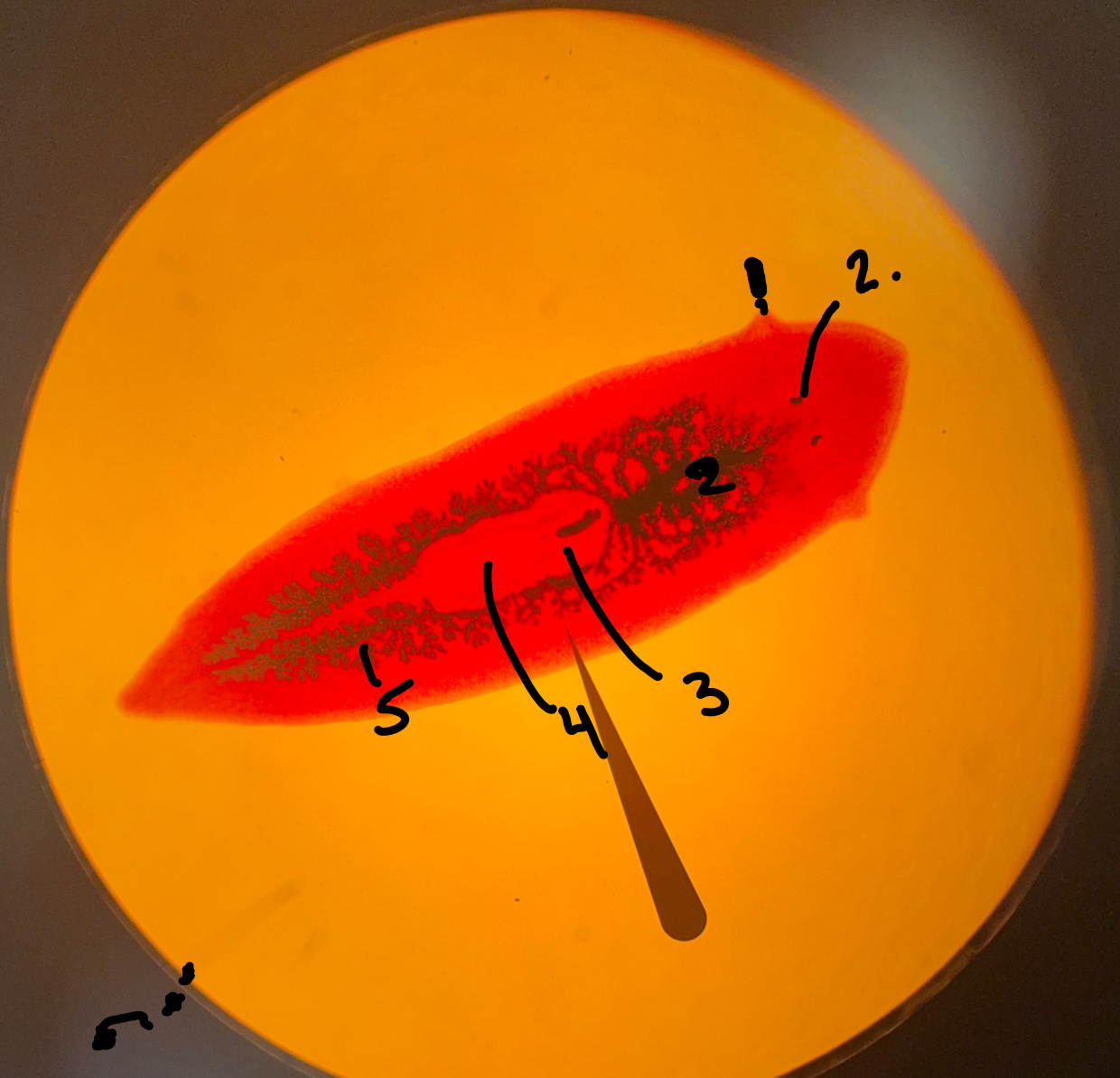
Auricle
What is 1
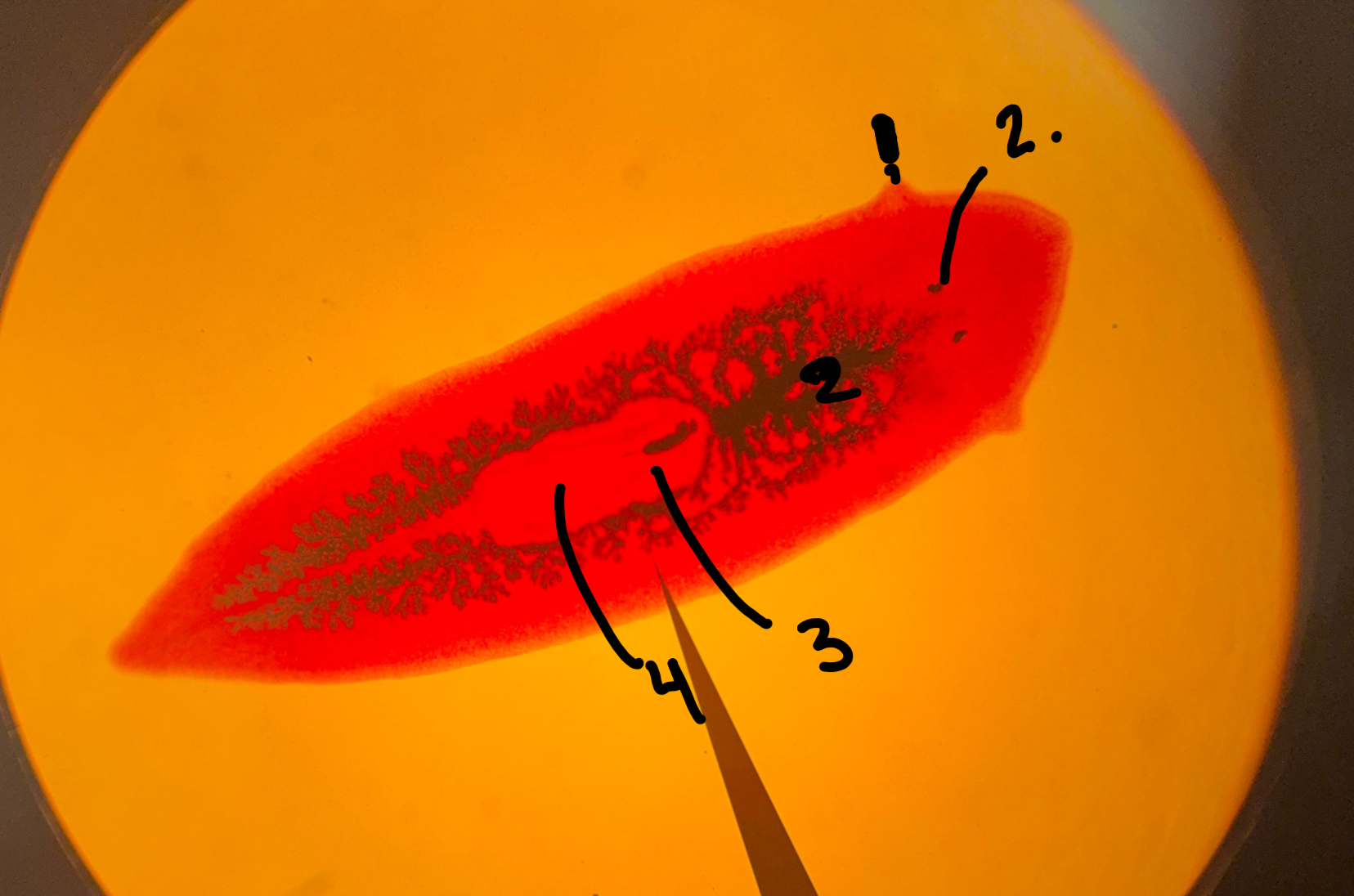

Eye spots
What is 2

Diverticulum
What is 5
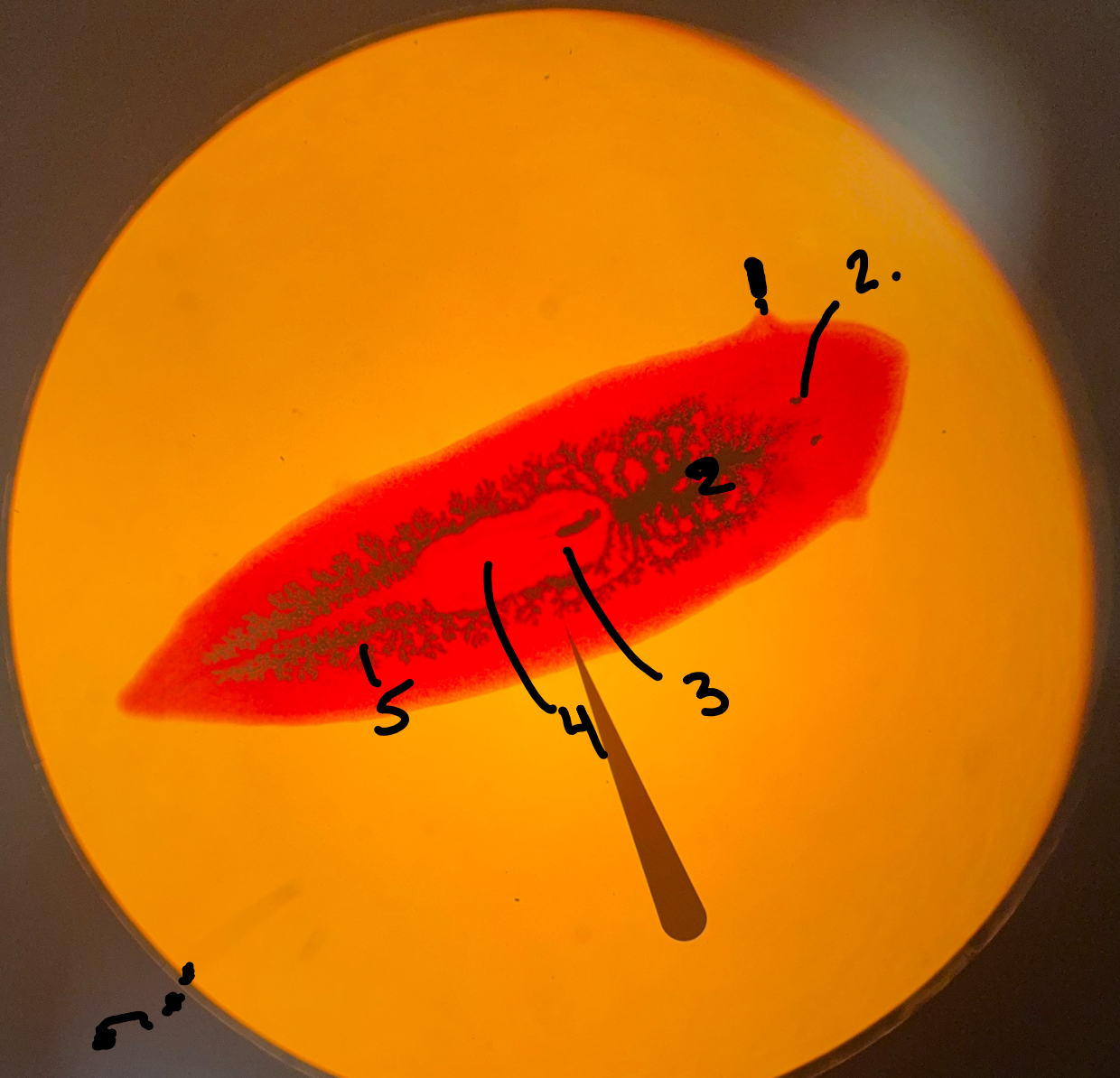
Gastrovascular cavity
What is 2
pharynx
What is 3
Phylum Platyhelminths, class turbellaria, order Tricladida
Names phylum class and order
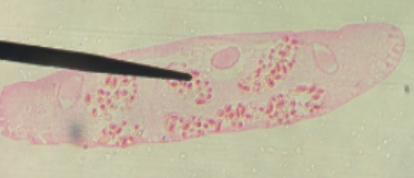
Mouth
What is 4=
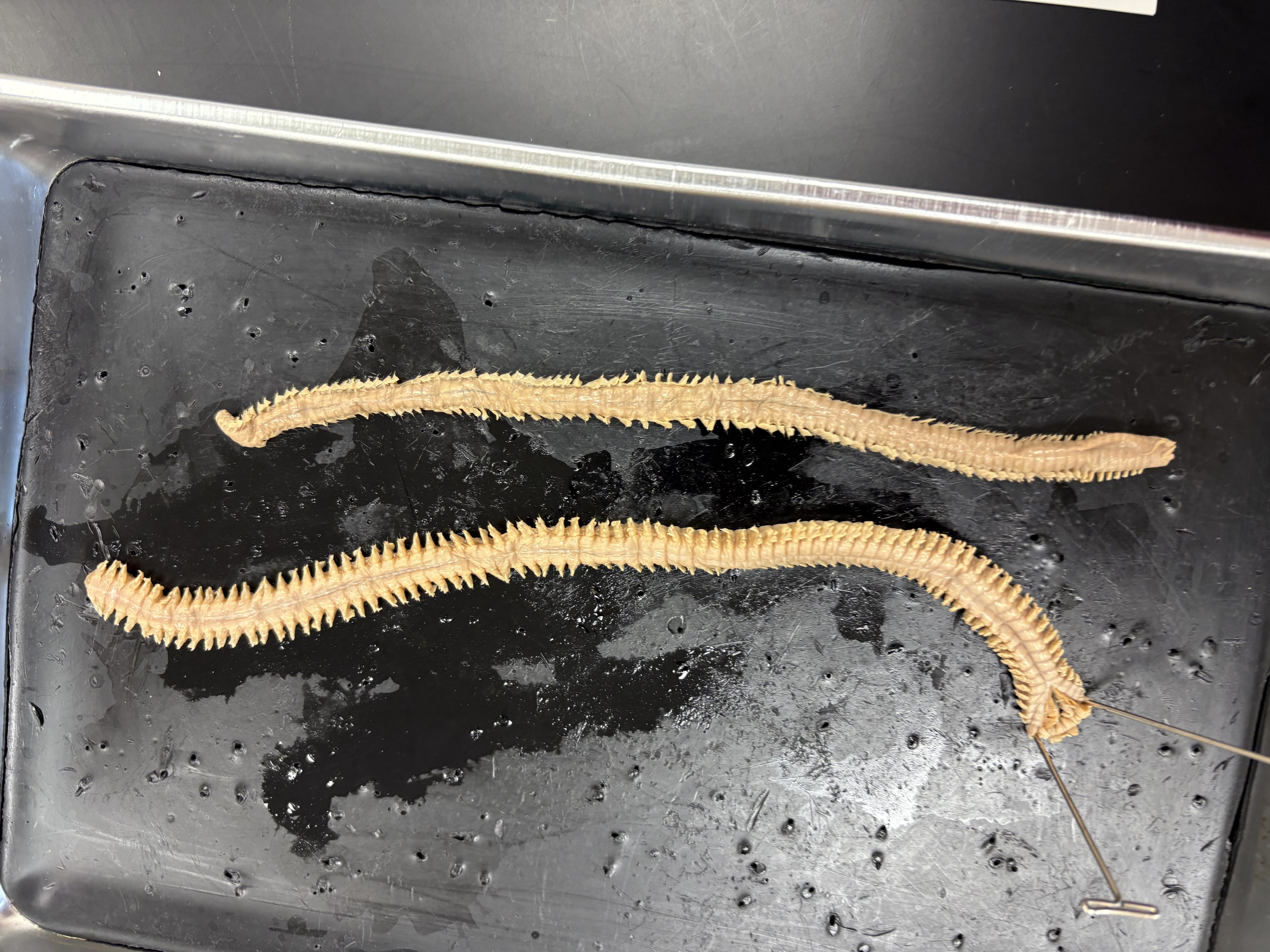
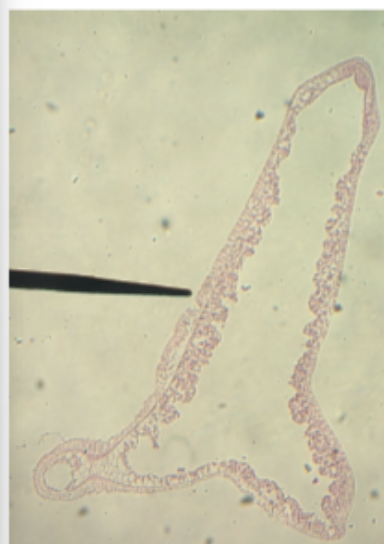
Phylum annelida, class polychaetae, Clade erradica
What is class and phylum

Phylum porifera class demospongiae
Bath sponge phylum and class
phlyum platyhelimnths, class tremadtoda (flukes)
name phlyum and class
Acolemoates
plathyhelmnths, class trematoda body plan
Cnidaria, hydrozoa
name phylum and class
Diploblastic, has mesoglea + fluid filled gastrovascaulr cavity
skeleton/body plan of hydrozoa
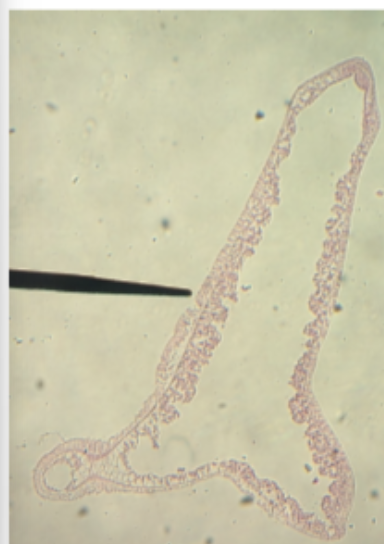
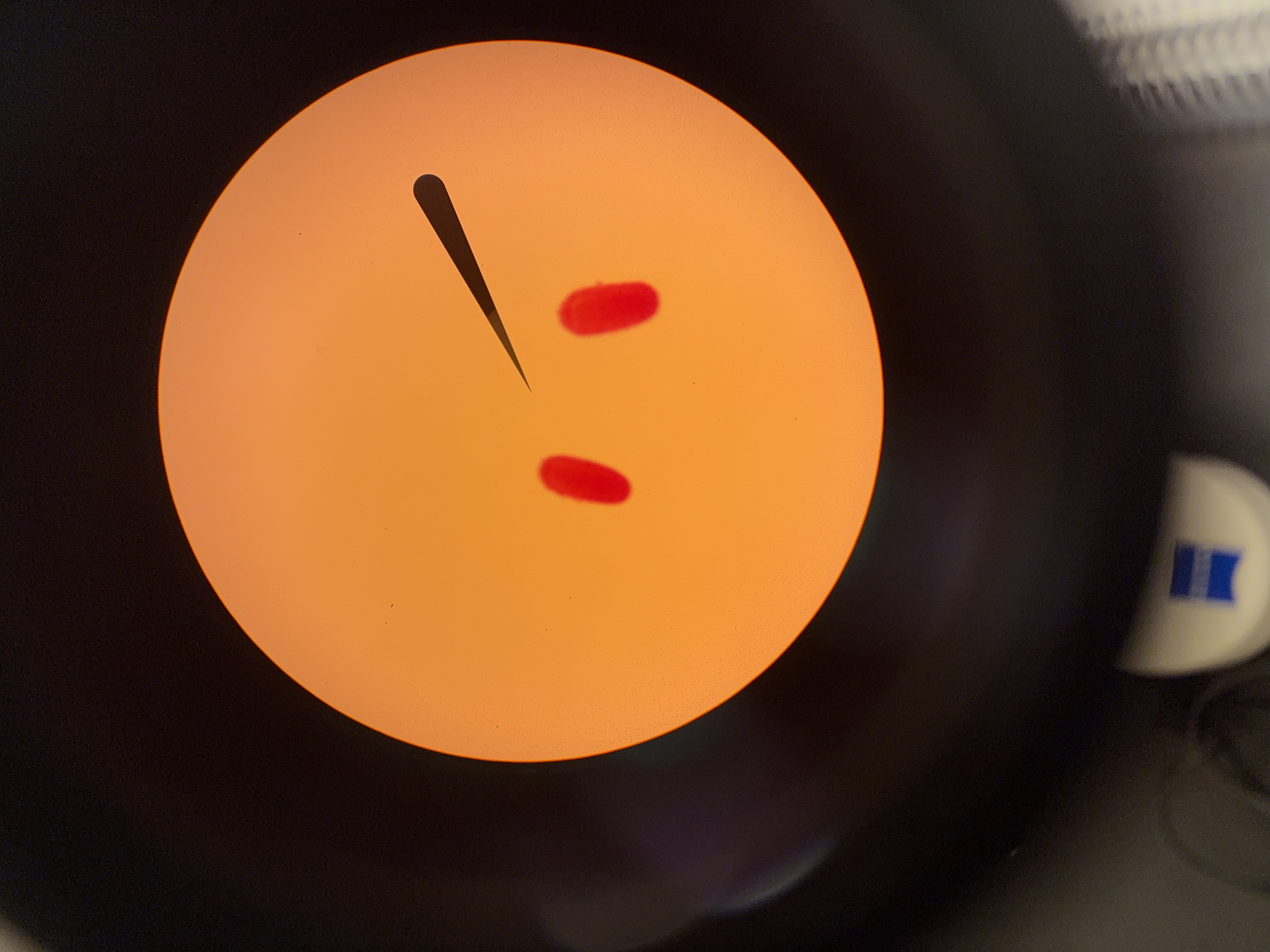
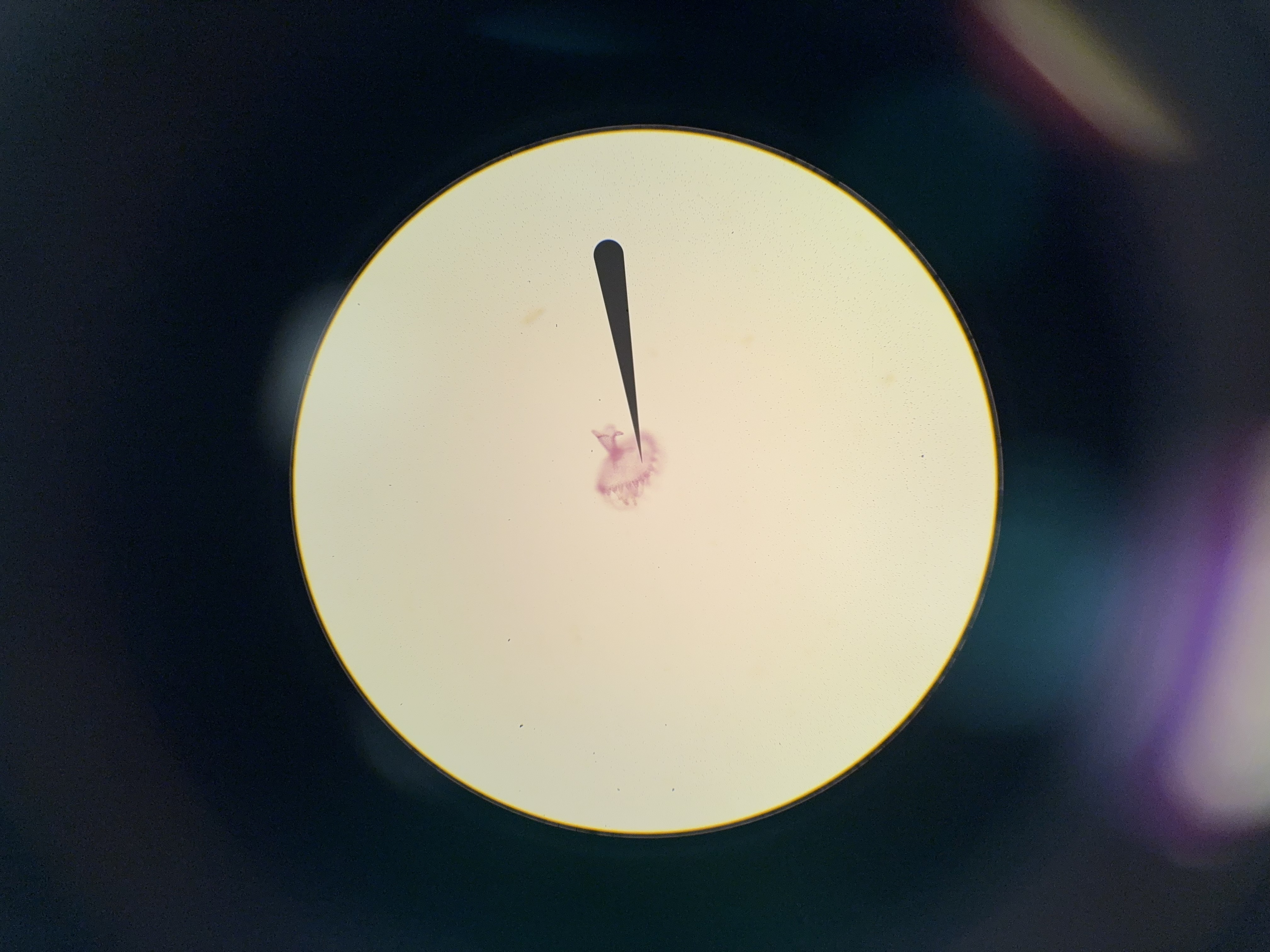
budding hydra
what is the needle pointing to
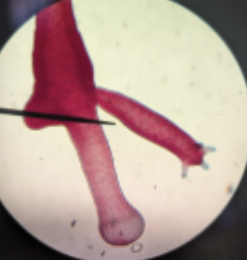
center of tentacles
where is the mouth/oral opening at the buds of this hydra
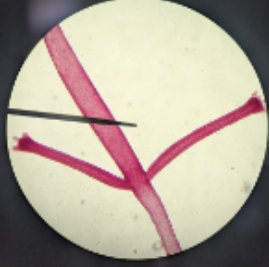
class cestoda mature proglotitds
this slide represents phylum platyhelimthes
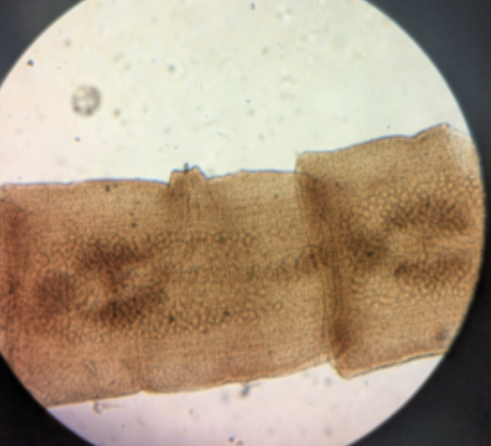
septa
the thick radial partionins divding the gastrovascular cavity into chambers
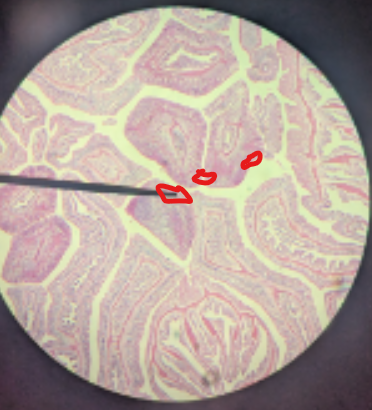
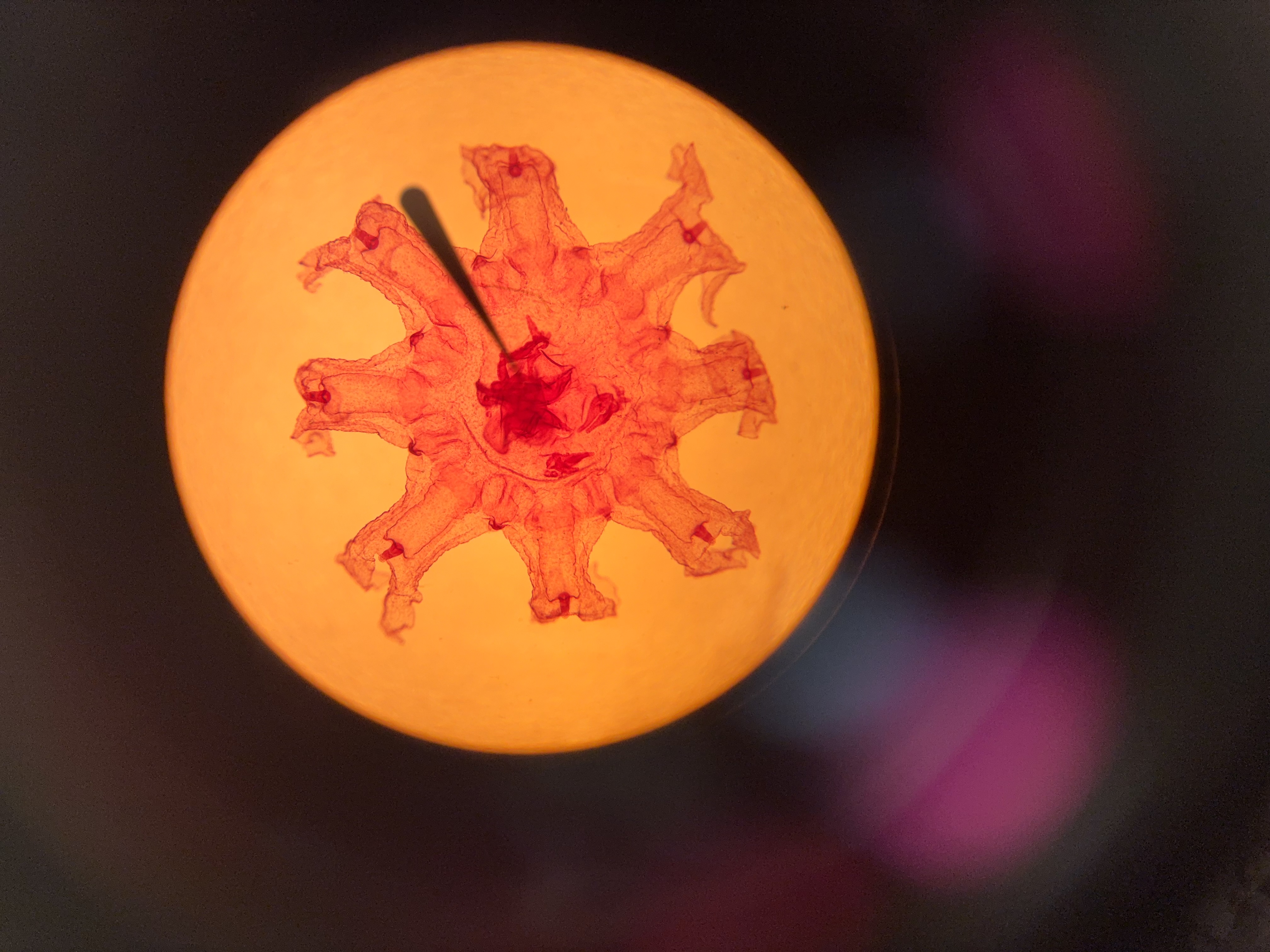
zooids on the tentacles porotions, medusoids produce gametes
how does Physalia reproduce
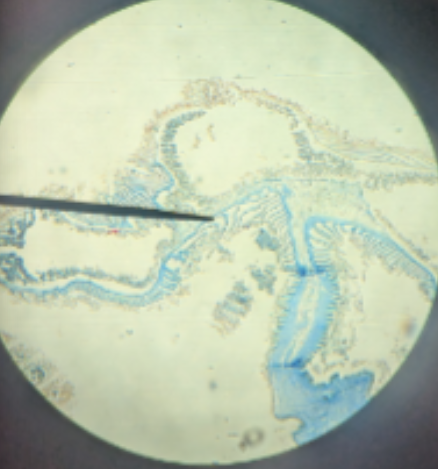
phlyum Cnidaria, class hydrozoa
name phylum and class
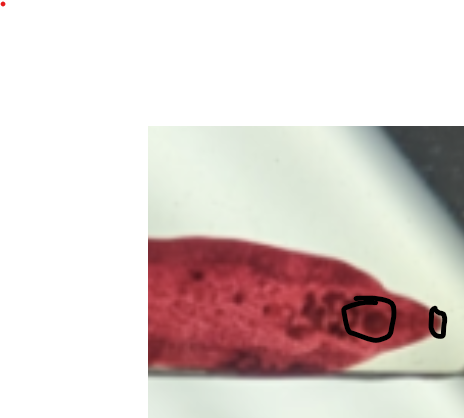
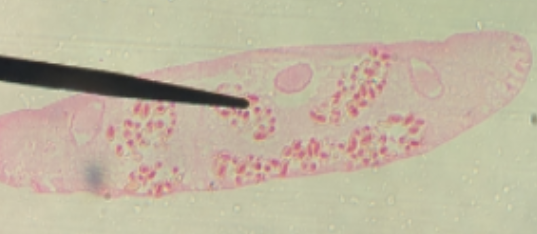
oral sucker, acetabulum
two structures in trematoda that aid in the capture of food and attachment onto hosts

phlyum platyhelimnths, class trematoda
name phlyum and class
immature
uniform tissues, with no obovious reproductive organs
is this proglottid mature of immature
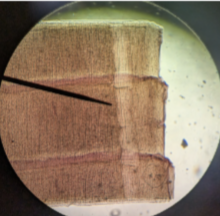
Scolex
rounded head of at the bottom og slide
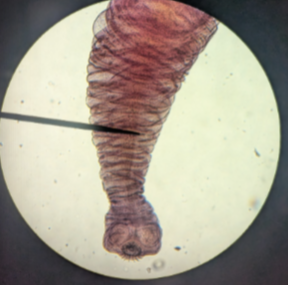
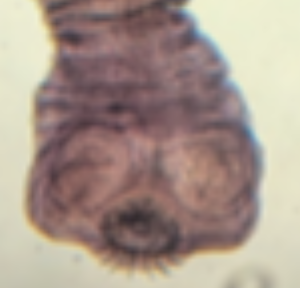
suckers that attach host intestinal tract
the circular structures on this Taenia scolex is
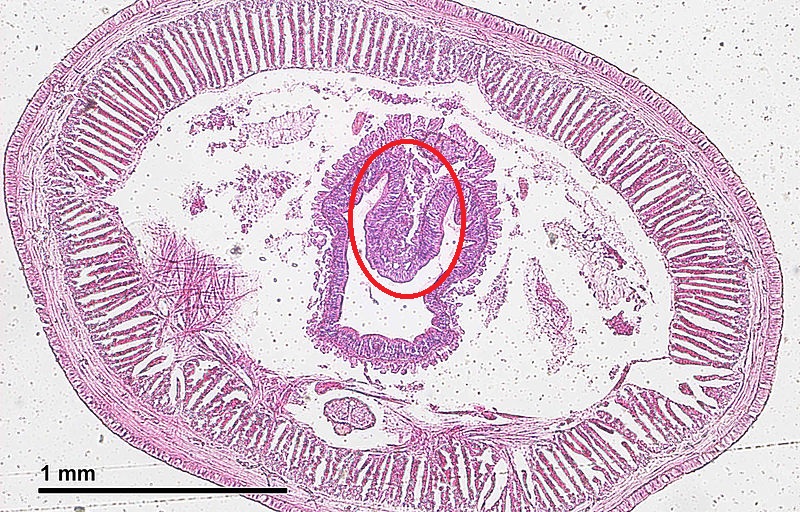
gential pore
opening on side of proglottids
ovaries and vitelline glands
what is circled on this mature proglottid
ecdysozoa
superphlyum of Nemerta, which differs from other worms
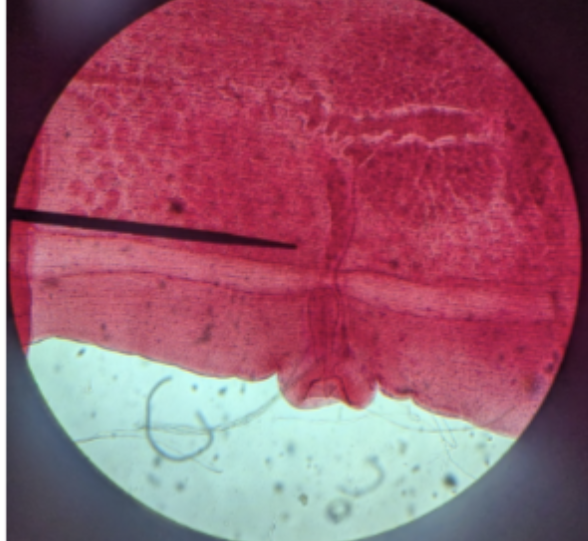
typhysole
what is circled here in this Olgiochaete cross section