NSG 101: LAB Theorys
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
What angle is intradermal injections given?
15 degrees
Where are intradermal injections given?
Given on the forearm or the upper back.
How much medication be given via intradermal injections
0.1 mL
What gauge needled is used for an intradermal injection?
26-28 gauge
What size needle is used for subcutaneous injections?
½ -5/8 inches
Where are subcutaneous injections given?
Given in fatty areas of the body that include, abdomen, thigh, and upper arm.
What angle are subcutaneous injections given
45-90 degrees
True or False: Subcutaneous injections absorb at a slower rate than IM injections?
True, they have a lower bloody supply
Is medication more evenly absorbed through the abdomen, thighs, or the buttocks
The abdomen
True or False: repeated injections should be at least an inch apart
true
What sites are usually used for an IM injection?
Deltoid, ventrogluteal, and vastus lateralis.
What size needle and mL’s can be used for the Ventrogluteal?
1 ½ - 3 inch needle and 3 mL is max for area
What size needle and mL’s can be used for the deltoid?
1- 1 ½ inch needle and 1 mL max
True or False: Can young children get IM injections in their deltoid
False; they need to be more developed
What size needle and mL’s can be used for the Vastus lateralis?
1 ½ -3 and 3-5 mL is max
What is hypoxemia?
Low o2 levels within the blood
What is hypoxia?
Low O2 within the tissues
What is Tidal volume? What is the average?
air inhaled and exhalated during each breath, 400-500mL is normal
What is inspiratory pressue?
Pressure in the lungs during inhalation
What is expiratory pressue?
amount of air left in the lungs after exhalation
What is the % of O2 in room air?
21%
2L of O2 through nasal cannula is?
28% O2
What intervention would help fix CO2 levels?
Bipap
What is a CPAP?
A steady pressure that keeps the air ways open
What is a BIPAP
Different air pressures that reduces effort of exhalation
If a client is receiving biPap therapy, what are some assessment findings the nurse would expect to see?
Capillary refill, mental assessment, blood gas, improved respiratory assessment
What lung sound indicates an emergency?
Stridor
If a pt is having trouble breathing, what is the first move?
Put pt in a semi to high fowlers position
What scale is used to measure pressure injuries
Braden scale
What factors contribute to a pressure injury?
Pressure, moisture, friction, and shear
Describe a stage 1 pressure injury:
Has Non blanchable redness to area, may be painful, or warm. Discoloration was last longer than 30 mins
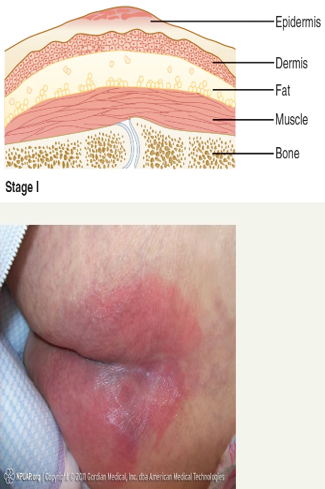
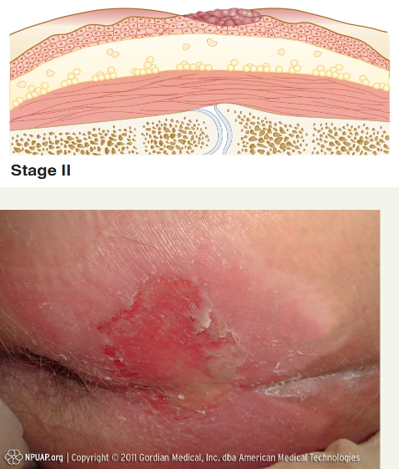
Describe a stage 2 pressure injury
involves partial-thickness loss of the dermis
No slough
Injury is open but shallow
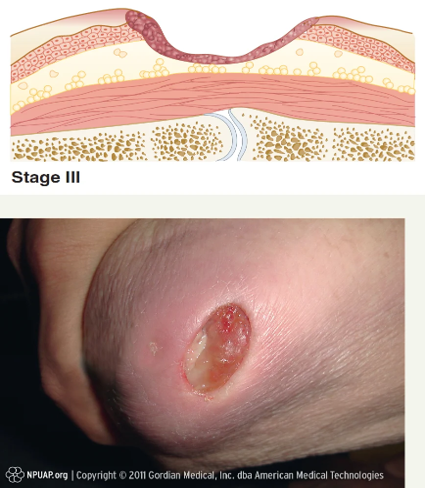
Describe a stage 3 pressure injury
Full- thickness skin loss
Deep crater
Adipose tissue is exposed
No slough or eschar present
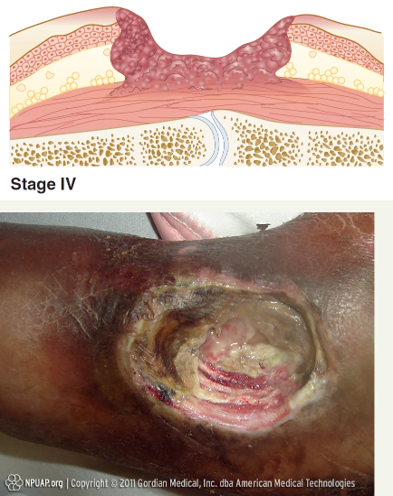
Describe a stage 4 pressure injury
Full- thickness skin loss
Muscle is exposed with damage
Slough and eschar are present
Bone or tendon may also be exposed
What is a Deep tissue injury (DTI)
Skin is intact but there is discoloration
What is an unstageable pressure injury
Full-thickness skin loss
Cant tell what stage it is because there is so much skin loss
True or False: You dont need to calibrate and perform controls on a glucose meter
False
True or False: Tube feed needs to be checked with the glucose meter every 6 hours
True
When is glucose usually measured?
Before meals and at bedtime
What does calibrating mean
Sets the meter to 0 or gives it a reset
What does a control do?
Makes sure the meter is reading correctly
What is the average glucose goal for adults? What about for someone with no diabetes
80- 130 fasting
Less than 100 for no diabetes
What are critical glucose values?
Less than 40 or higher than 400
True or False: If you get a critical reading for glucose, you need to redraw
True
What is the rule of 15?
If a pt has a reading lower than 70 then, drink 15g of carbohydrates and then wait 15 minutes
If pt still remains less than 70 then do it again
What are examples of 15 grams of carbohydrates
4 oz of juice
3-4 glucose tablets
1 tbs of honey
100-125 fasting is what?
Pre-diabetes
125+ fasting is what
Diabetes
What is medical asepsis?
Clean technique
Controls microorganisms
Basic hand hygiene
What is surgical asepsis?
Sterile technique
Absence of microorganisms
Surgical scrub is used
Steps to don PPE
Hand hygiene
Gown
Mask
Eye protection
Gloves
Steps to doff PPE:
Remove gloves
Remove gown
Hand hygiene
Remove eye protection
Remove mask
Hand hygiene
What does serous drainage color look like
Clear and normal
What does sanguineous drainage color look like?
Red, bloody and fresh
What does serosanguinous drainage look like?
Pink
What does purulent drainage look like
Yellow and pus. Infection
Why are enemas used?
To clear the colon, treat constipation, treat fecal impaction, and give medications
What is a cleansing enema?
Used to treat severe constipation, clear colon for procedure or clear colon for bowel training
Return flow enema?
Used to expel and flatus (fart)
What is a retention enema? and give 2 examples
Given to be retained for a longer period of time
Ex. Medicated and Nutritive
True or False: Pt should be on the left side when giving an enema
True
True or false: Enema solution needs to be room temperature
True; if solution is cold then it can cause cramping
What is a stimulant laxative? Examples?
Stimulates the intestines to contract and push out stool
Ex. castor oil and aloe vera
What is an osmotic laxative? Examples?
Draws in water to soften stool to make it easier to push out
ex. Lactulose and polyethylene glucose
What is a bulk forming laxative? Examples?
Makes stool bulkier to make the large intestines to contract
Ex. dietary fiber and methylcellulose
What are stool softeners and examples?
They make stool softer by adding some water
ex. Docusate sodium or calcium
What are lubricants and example?
Coats the surface of the stool
ex. Mineral
What are prokinetic agents?
stimulate contractions
What 2 things cause cramping during an enema?
Cold and height
True or False: You need to use sterile technique to insert a catheter
True
How far do you insert a catheter for a male?
To the Y
True or False: Keep the cath bag below the bladder
True
Should you stop if you receive resistance ?
Yes
How far do you insert a cath on a female?
Til you get urine return
How often do you empty the collection bag of a cath?
Every 8 hours
What is an IV push (bolus)
When medications are injected into the vein
True or False: IV tubing does not need to be initialed and dated
False
Infection comes with what?
Fever
Phlebitis comes with?
Red line
Infiltration comes with?
Swollen
Extravasation comes with?
Buring pain
Hematoma comes with?
Dark spots/ brusing
Air embolism is?
Fatal
When removing an IV you pull it out which way?
Same direction it was inserted