Foot Pt 1 + Osteology (Week 8)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Talocrural
Dorsiflexion/plantarflexion occur at the __ joint (ankle)
Tarsal, subtalar
Inversion/eversion occurs within the foot at the transverse __ and __ joints
2, second
The axis of abduction/adduction passes through digit _ of the foot → Therefore only the __ toe can abduct
Tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges
Divisions of the foot is done by __ (hindfoot), __ (midfoot), and __ (forefoot)
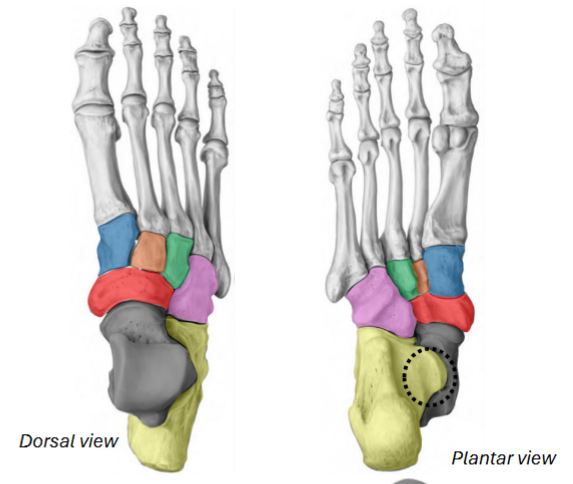
Talus, calcaneus, sustentaculum tali, navicular, cuboid, medial cuneiform, intermediate cuneiform, lateral cuneiform
Grey / yellow / black ring / red / pink / blue / orange / green of the tarsals
Base, shaft, head, 1-5
Orange / shaft / blue / # order from medial (big toe) to lateral of metatarsals
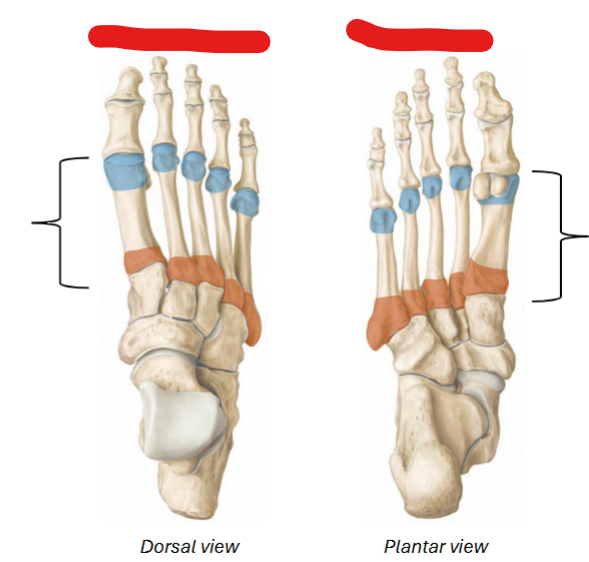
Proximal, intermediate, distal
Blue / red / yellow of phalanges
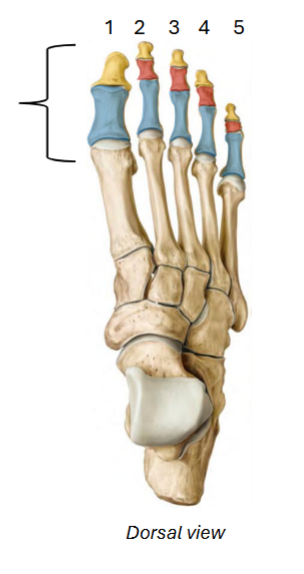
Hallux, 2
The __ (big toe) only has _ phalanges - exception
Ankle joint, talus, medial malleolus, lateral malleolus
Yellow / blue / red / green of talocrural joint
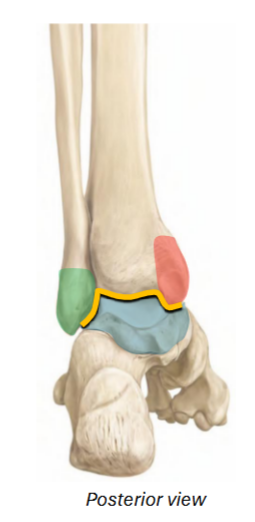
Hinge, dorsi, plantar
The talocrural joint is a __ joint between the talus and leg (crus) cushioned by the malleoli
Permits __flexion and __flexion
Medial deltoid ligament, 4, eversion
The __ __ __ is a series of _ ligaments attaching the medial malleolus to talus / calcaneus / navicular
Strong and limits foot __ (action)
Lateral collateral ligaments, 3, inversion
The __ __ __ is a series of _ ligaments attaching the lateral malleolus to talus / calcaneus
Weak and limits foot __ (action)
Stretching, tearing, inversion, range, lateral
Ankle sprains involve __ or __ of foot ligaments
__ injuries are more common (80%)
As there is a greater __ of motion and relative weakness of __ ligaments
Anterior talofibular, eversion, deltoid
Ankle sprains
The __ __ ligament is most commonly injured, usually from inversion injuries
__ injuries are less common but result in damage to the __ ligaments
Bimalleolar, eversion, rotational, weightbearing, surgery
In a __ fracture, both the medial and lateral malleoli are fractured
60% of these due to __ or __ trauma to ligaments
Sx - Highly unstable, difficulty for __
Require __ to pin/screw pieces together
Subtalar, talus, calcaneus
Intertarsal Joints
The __ joint is main joint for inversion/eversion
Located between __ and __ bones
(Blue)
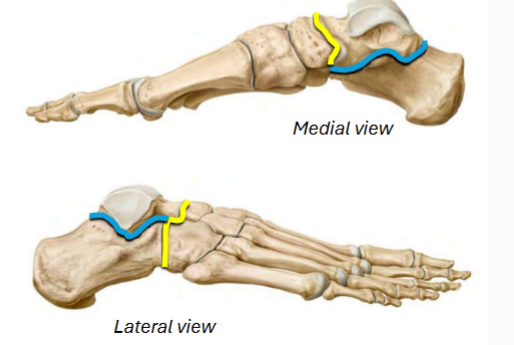
Transverse tarsal, assists
Intertarsal Joints
The __ __ joint __ in inversion/eversion
Located between talus and navicular + calcaneus and cuboid bones
(Yellow)
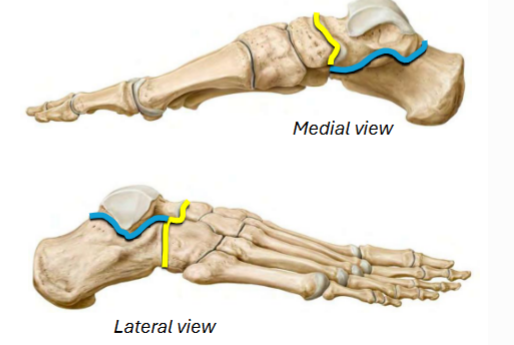
3, springs, impact, ground
There are _ arches within the foot that act as __ during locomotion, dampen __ forces, and adapt foot’s shape to the __
Pes planus, fallen
__ __ is a condition resulting in foot pain, eversion injuries, and pain in structures compensating for altered gait
aka flat feet from a __ arch
Bone, ligaments, muscles
__ shapes form the foot arches, __ add passive support to arches, and __ support the arches dynamically
(Ligaments/bone/muscles)
calcaneonavicular, sustentaculum, longitudinal, talus
The plantar ___ (long name) ligament connects the __ tali of calcaneus to the navicular bone
Strongest supporter of the medial __ arch
Supports the __ bone as the “spring ligament”
Long, calcaneus, cuboid, 4 metatarsal, supports, fibularis
The __ plantar ligament connects the __ to __ bone and lateral _ (#) __ bases
__ longitudinal arches
Creates tunnel for tendon of __ longus
Short, calcaneus, cuboid, maintain
The __ plantar ligament connects the __ to __ bone
Helps __ longitudinal arches
Plantar aponeurosis, calcaneus, metatarsal, supports, dorsiflexion
The __ __ forms from thickening of deep fascia of the foot centrally
Attaches __ to the __ heads
__ longitudinal arches
__ (action) of the toes tenses this tendon, where less foot flexibility leads to more efficient propulsion
Fibularis, tibialis, transverse, posterior
Tendons of the __ longus and __ posterior insert onto the plantar surface of the foot
Muscle tension provides support of the __ arch
Injury of tibialis __ can overload the spring ligament, resulting in collapsed arches
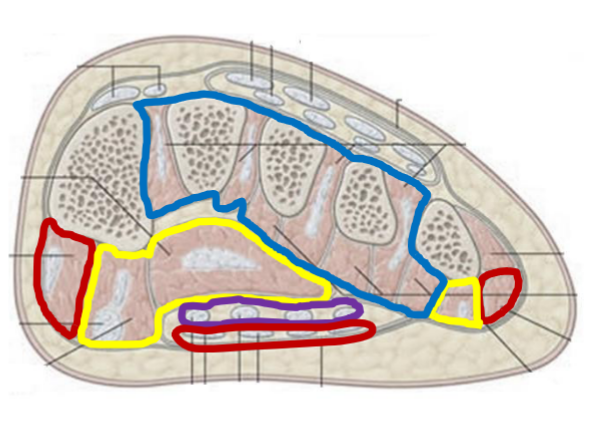
Dorsal Compartment
Digit extensors
Deep fibular nerve
Lateral Compartment
Digit 5 muscle
Lateral plantar artery and nerve
Central Compartment
Digit flexors and adductors
Medial and lateral plantar nerves and arteries
Medial Compartment
Hallux muscle (big toe)
Medial plantar artery and nerve
Red, purple, yellow, blue
4 Layers of the Foot
Layer 1 / Layer 2 / Layer 3 / Layer 4
Answer in colors
Calcaneal tuberosity
Proximal attachment of abductor hallucis (1)
1st proximal phalanx
Distal attachment of abductor hallucis is the medial base of the __ __ __
Medial plantar nerve
Innervation of abductor hallucis (1)
Abducts digit 1, flexes digit 1
Actions of abductor hallucis (2)
1st proximal phalanx
Distal attachment of flexor hallucis brevis is the base of the __ __ __
Medial plantar nerve
Innervation of flexor hallucis brevis (1)
Flexes digit 1
Actions of flexor hallucis brevis (1)
Posterior, distal, 1, flexion
Tendon of flexor hallucis longus goes from __ leg to tarsal tunnel to __ aspect of phalanx of digit _
Actions is __ of this digit
Calcaneal tuberosity
Proximal attachment of abductor digiti minimi (1)
5th proximal phalanx, 5th metatarsal
Distal attachment of abductor digiti minimi (2) are the
lateral base of the __ __ __ and the base of the __ __
Lateral plantar nerve
Innervation of abductor digiti minimi (1)
Abducts digit 5, flexes digit 5
Actions of abductor digiti minimi (2)
5th proximal phalanx
Distal attachment of flexor digiti minimi brevis (1) is the base of the __ __ __
Lateral plantar nerve
Innervation of flexor digiti minimi brevis (1)
Flexes digit 5
Actions of flexor digiti minimi brevis (1)
Calcaneal tuberosity
Proximal attachment of flexor digitorum brevis (1)
Intermediate phalanges
Distal attachment of flexor digitorum brevis (1) are __ __ of digits 2-5
Medial plantar nerve
Innervation of flexor digitorum brevis (1)
Flexion of lateral 4 digits
Actions of flexor digitorum brevis (1)
Posterior, distal, 2-5, flexion
Tendon of flexor digitorum longus goes from __ leg to tarsal tunnel to __ aspect of phalanges of digit _
Actions is __ of these lateral digits
Tendons pass thru the split in flexor digitorum brevis tendons
Calcaneal tuberosity
Proximal attachment of quadratus plantae (1)
Flexor digitorum longus
Distal attachment of quadratus plantae (1) is the tendon of __ __ __
Lateral plantar nerve
Innervation of quadratus plantae (1)
pull of flexor, posterior
Actions of quadratus plantae is redirecting and increasing __ of __ digitorum longus
Also allows for __ digit flexion
Digitorum longus
Proximal attachment of lumbricals is the tendons of __ __
Extensor expansions
Distal attachment of lumbricals is medial aspect of respective __ __
Medial plantar, lateral plantar
Innervations of lumbricals (2)
1st lumbrical - __ __ nerve
Lumbricals 2-4 - __ __ nerve
Flexion, 2-5, extension, 2-5
Actions of lumbricals (2)
__ of MTP joints of digits _-_
__ of PIP/DIP joints of digits _-_