Atomic Structure, Bonding and Periodicity
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CSEC Chemistry - Grade 10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Which two subatomic particles can be found in the nucleus of an atom?
Protons and neutrons.
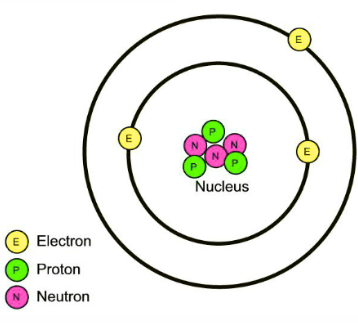
Where can electrons be found?
Electrons are outside surrounding the nucleus on electron shells/ orbitals/ clouds
What is a major characteristic of neutral atoms?
The number of electrons is always equal to the number of protons. They are uncharged.
Define 'atomic number'.
This is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Atomic number also known as proton number.
How is the periodic table arranged?
All known elements are arranged based on their atomic (proton) number in sequence.
Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons.
Elements in the same period have the same number of orbitals occupied with electrons.
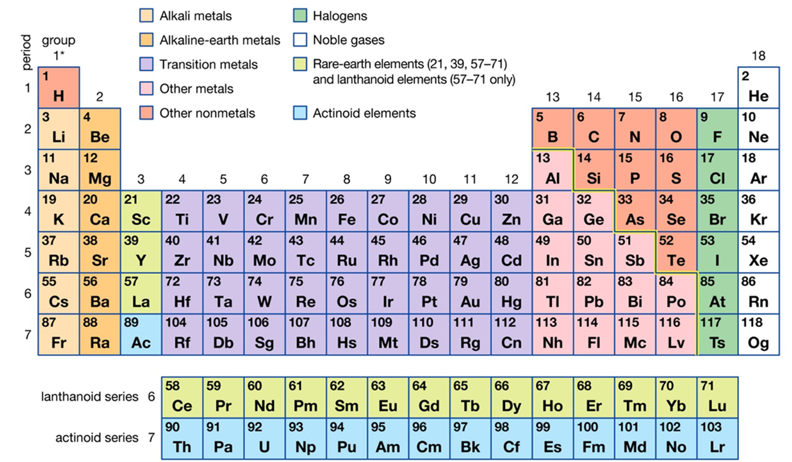
What is the maximum number of electrons which can be held on the first, second and third electron shell respectively?
2, 8, 8 (the third shell can actually hold up to 18) - that's covered in advanced A level Chemistry.
What is the relative mass of a proton?
1
What is the relative mass of a neutron?
1
What is the relative mass of an electron?
0.0005
What is the relative charge on a proton?
+1
What is the relative charge on a neutron?
0 : No charge
What is the relative charge on an electron?
-1
Define 'mass number'
This is the number of protons + number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
What is the name for positively charged ions? E.g. Mg2+
Cations
What is the name for negatively charged ions? E.g. O2-
Anions
What are ions?
Atoms which have lost or gained electrons
What is the electronic configuration of H ?
1
When non-metals gain electrons they become
negatively charged ions (anions)
What is an atom?
An atom is the smallest component of an element that can exist and still have the same chemical properties as the element.
State the names of the three main subatomic particles.
Protons, neutrons and electrons
Where is most of the mass of an atom found?
In the nucleus
Which part of the atom participates in chemical reactions such as bonding?
The electrons
Which subatomic particle acts as the unique identifier for each element ?
Protons (number of protons) No two elements have the same number of protons.
How can the number of neutrons in an atom be calculated?
Number of neutrons = mass number - atomic number
Which subatomic particle is responsible for volume of an atom?
Electrons ( occupying space on orbitals outside nucleus)
Which subatomic particles are responsible for mass of an atom?
Protons and neutrons (found in the nucleus of an atom)
What do electrons on the same energy orbital/shell have in common?
They have the same amount of energy. |
What are valence electrons?
The outermost electrons.
Why do atoms undergo bonding?
To achieve a stable electronic configuration (also called noble gas configuration since all noble gases are stable).
Describe 3 ways in which an atom can achieve stability through chemical change.
They can:
1) Donate valence electron(s) to another atom
2) Gain valence electrons(s) from another atom
3) Share valence electron(s) with another atom
What is a chemical bond?
A chemical bond is a force of attraction between atoms that results from the redistribution of their electrons.
Describe the 3 main types of chemical bonding.
1) Ionic bonding - occurs when a metal bonds with a non-metal
2) Covalent bonding - occurs when two or more non-metals bond
3) Metallic bonding - occurs within a bulk of metal itself
Which two types of bonding result in formation of chemical compounds?
Ionic bonding and covalent bonding.
What is a compound?
Structures formed when atoms combine chemically with each other.
What happens in ionic bonding?
Valence electrons from metal atoms are transferred to non-metal atoms.
How many valence electrons do metals usually have?
1 to 3
Exceptions Hydrogen and Boron (non-metals)
How many valence electrons do non-metals usually have?
4 to 7
What do metals do to obtain noble gas (stable) configuration?
They lose their valence electrons.
What do non-metals do to obtain noble gas (stable) configuration?
They gain electrons into their valence shell.
What happens when an atom becomes an ion?
It has either lost or gained electrons and is now charged. The number of electrons is no longer the same as the number of protons. It is no longer neutral.
Cations are positively charged ions. How are they formed?
They are formed when a metal atom loses electrons. The ion formed has more protons than electrons and so it is positively charged.
Anions are negatively charged ions. How are they formed?
They are formed when a non-metal atom gains electrons. The ion formed has more electrons that protons and so it is negatively charged.
How are anions named?
First part of the element name is kept, the end always ends with 'ide'. Eg. chloride, oxide, nitride etc... more on this in later topics.
What are ionic bonds?
These are chemical bonds created by the electrostatic forces of attraction between positively charged cations and negatively charged anions in ionic compounds.
What is a lattice structure?
It is a regular, three-dimensional arrangement of particles.
What is a covalent bond?
It is a chemical bond formed by sharing electrons between non-metal atoms.
What is a molecule?
A group of two or more atoms which are covalently bonded together strongly enough to behave as a single unit in a chemical reaction.
What happens in covalent bonding?
Non-metal atoms overlap to share their unpaired valence electrons in order to achieve stability. This can occur between atoms of the same element or different elements.
What is electronegativity?
This is a measure of how strongly an atom attracts electrons.
What is periodicity?
It is the recurrence of elements with similar physical and chemical properties at regular intervals in the periodic table.
How are elements arranged in the periodic table?
In increasing order of atomic number. Into rows and columns based on their structure and properties. All elements in a period have the same number of atomic orbitals occupied. All elements in a group have the same number of valence electrons.
What is the periodic table?
It is a classification of all known elements arranged according to their physical and chemical properties.
Name the scientist (in 1789) who compiled the first list of 33 known elements and grouped them into gases, metals, nonmetals, and earths.
Antoine Lavoisier

Name the scientist (in 1829) who proposed the Law of Triads, grouping elements with similar properties in threes (e.g., Li, Na, K).
Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner

Name the scientist (in 1864) who proposed the Law of Octaves, stating that when elements are arranged by increasing atomic mass, every 8th element had similar properties.
John Newlands

Name the scientist (in 1869) who created the first widely recognized Periodic Table arranged by atomic mass. He left gaps for undiscovered elements (like gallium, scandium, germanium) and accurately predicted their properties.
Dmitri Mendeleev

Name the scientist (in 1913) who used X-ray experiments to discover that atomic number (number of protons) – not atomic mass – determines an element’s identity. This led to the modern Periodic Law.
Henry Moseley

What are metalloids?
Intermediates between metals and non-metals. These include boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po).
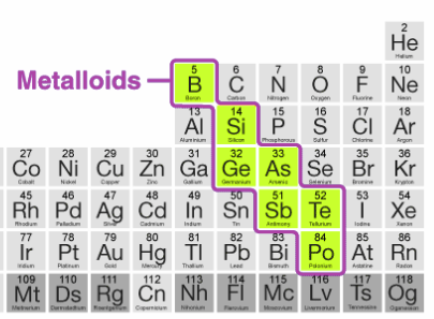
What is a group?
It is a vertical column of elements.
What is a period?
It is a horizontal row of elements.
Group I metals are called
alkali metals
Group II metals are called
alkaline earth metals
Group VII metals are called
halogens
Group 0 ( or VIII) elements are called
noble/ inert gases
Between groups II and III, ten groups of elements are located. These are called
transition metals
What does IUPAC stand for?
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
All elements in group VIII (or 0) have
full outermost (valence) electron shell / stable electronic configuration.
What determines the chemical properties of an element?
The number of valence electrons they have.
Define 'ion'.
An electrically charged particle formed when an atom loses or gains electrons. The atom becomes ionised.
What is the 'ease of ionization'?
The ease with which atoms lose or gain valence electrons.
What is electronegativity?
It is a measure of how strongly an atom attracts electrons.
What is the MOST electronegative element in the periodic table?
Fluorine (F)
What is the LEAST electronegative element (most electropositive) in the periodic table?
Francium (Fr)
What is the link between reactivity and ease of ionization?
The easier it it for an atom to become ionized, the more reactive it will be.
What are the 3 main factors which affect the ease of ionization/reactivity of an atom?
1) Atomic radius - distance between nucleus and valence electrons.
2) Nuclear charge - the number of protons in the nucleus.
3) Shielding/screening - the number of electron shells between the nucleus and the valence shell.
What happens DOWN a group of metals with respect to atomic radius, electrostatic force of attraction and reactivity?
Atomic radius INCREASES due to greater shielding effect
Tendency of the atom to LOSE its valence electrons increases (i.e. ELECTROPOSITIVITY increases).
Electrostatic force of attraction between nucleus and valence electrons DECREASES
What happens UP a group of non-metals with respect to atomic radius, electrostatic force of attraction and reactivity?
Atomic radius DECREASES due to less shielding effect
Tendency of the atom to GAIN electrons from another atom increases (i.e. ELECTRONEGATIVITY increases)
Electrostatic force of attraction between nucleus and valence electrons INCREASES
What happens ACROSS a period from left to right with respect to atomic radius , electrostatic force of attraction and reactivity?
Atomic radius DECREASES but shielding effect remains the same.
Size of NUCLEUS increases due to increasing number of protons in the nucleus (nuclear force increases).
Electrostatic force of attraction therefore increases. Electronegativity increases.
What is the shielding effect?
This refers to the effect of atomic shells/orbitals between the nucleus and the electrons on the valence shell. The more shells there are, the weaker the electrostatic force of attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons.
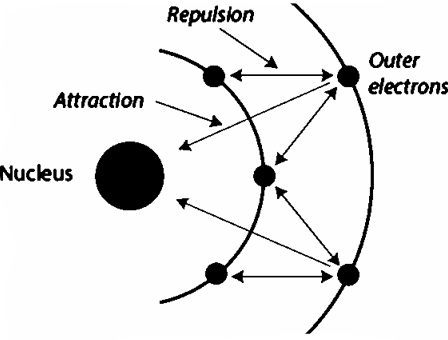
What is electropositivity?
The tendency of metals to lose their valence electrons
What is ionization energy?
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom. The greater the amount of energy, the more difficult it is for that atom to lose electrons.
What is electron affinity?
The degree to which an atom attracts electrons (super simplified definition - more advanced later).
List the 7 elements which exist naturally as diatomic molecules (two atoms bonded together)
Hydrogen - H2
Nitrogen - N2
Oxygen - O2
Fluorine - F2
Chlorine - Cl2
Bromine - Br2
Iodine - I2
List characteristics of Group 1 - Alkali metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr)
Very reactive metals (stored in oil to prevent reaction with air/water).
Soft, low melting points compared to other metals.
React vigorously with water to form alkali (e.g., NaOH) and hydrogen gas.
Reactivity increases down the group.
List characteristics of Group 2 - Alkaline Earth Metals (Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra)
Reactive metals (but less reactive than Group 1).
Form alkaline oxides and hydroxides.
Reactivity increases down the group.
Important for biological systems (e.g., Mg in chlorophyll, Ca in bones).
List characteristics of transition metals
Hard, strong, high melting and boiling points.
Good conductors of heat and electricity.
Often form colored compounds.
Can have multiple oxidation states.
Many used as catalysts (e.g., Fe in Haber process, Pt in catalytic converters).
List characteristics of Group 7 - Halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At, Ts)
Very reactive nonmetals.
Exist as diatomic molecules (F₂, Cl₂, Br₂, I₂).
Reactivity decreases down the group.
Strong oxidizing agents.
Combine with metals to form salts (halides).
List characteristics of Group 8 (Noble Gases) - (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn, Og)
Colorless, odorless, inert gases.
Very stable due to full outer shells (octet rule).
Low boiling and melting points.
Used in lighting, welding, and as inert atmospheres.