Chapter 6: Corporate-Level Strategy: Value Creation through Diversification
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Diversification
the process of firms expanding their operations by entering new businesses
Strategy to create value through business expansion.
Diversification initiatives must create value for shareholders through...
- Mergers and acquisitions
- Strategic alliances
- Joint ventures
- Internal development (Creating new ventures within the existing firm)
Diversification should create
synergy (Business 1 + Business 2 = more than two)
A firm may diversify into related businesses
- Benefits derive from horizontal relationships:
- Sharing intangible resources such as core competencies in marketing
- Sharing tangible resources such as production facilities
A firm may diversify into unrelated businesses
Benefits derive from hierarchical relationships:
-Value creation derived from the corporate office
-Leveraging support activities in the value chain
expands into completely different industries or businesses that have nothing to do with each other.
Related Diversification
Expanding into businesses with horizontal relationships
a firm entering a different business in which it can benefit from leveraging core competencies, sharing activities, or building market power
expands into new businesses or industries that are similar to what they already do or are connected in some way.
Economies of Scope (Related Diversification) allow business to:
-Leverage core competencies
-Sharing related activities
-Enjoy greater revenues, enhance differentiation
Cost advantages from sharing resources across businesses.
Core Competencies (Related Diversification)
reflect the collective learning in organizations.
Unique strengths that provide competitive advantages.
Core competencies can lead to the creation of value and synergy if:
-They create superior customer value
-The value-chain elements in separate businesses require similar skills
-They are difficult for competitors to imitate or find substitutes for
Corporations can also achieve synergy by sharing activities across their business units
true (part of Related Diversification)
Market power (Related Diversification)
firms' abilities to profit through restricting or controlling supply to a market or coordinating with other firms to reduce investment
Market power can lead to the creation of value and synergy through
Pooled negotiating power
Vertical integration
Pooled negotiating power
Gaining greater bargaining power with suppliers & customers
When businesses under the same company combine their buying or selling power to get better deals from suppliers or customers
Vertical integration
a firm becomes its own supplier or distributor through:
-Backward integration
-Forward integration
Backward integration
Acquiring control over suppliers
When a company moves backward in the supply chain by owning or controlling suppliers
Example: A car company buying a tire factory
Forward integration
Acquiring control over distributors
When a company moves forward in the supply chain by owning or controlling distribution or retail.
Example: A clothing brand opening its own retail stores instead of selling through other store
Questions to ask regarding issues of vertical integration
-Are current suppliers and distributors good enough? If not, vertical integration might be needed.
-Are there profitable activities being outsourced? If so, the company could take them over for more profit.
-Is demand for the product stable? If demand is unstable, vertical integration could be risky.
-Does the company have the skills to manage it? The company needs the right expertise for vertical integration to work.
-Will it negatively affect stakeholders? It's important to consider if vertical integration might hurt employees, customers, or others involved.
Vertical Integration: Transaction Costs
Every market transaction has costs, including:
-Search costs: Finding what you need
-Negotiating costs: Agreeing on terms
-Contract costs: Creating agreements
-Monitoring costs: Keeping track of progress
-Enforcement costs: Ensuring terms are followed
-Transaction-specific investments: Costs for specialized investments
-Administrative costs: Managing the process
Unrelated Diversification
a firm entering a different business that has little horizontal interaction with other businesses of a firm
enables a firm to benefit from vertical or hierarchical relationships between the corporate office and individual business units through: (1-3)
Corporate Parenting Advantage (1)
Providing competent central functions.
allows the corporate office to create value through management expertise and competent central functions.
Restructuring (2)
to redistribute assets:
Asset, capital, and management restructuring
In restructuring the parent intervenes:
-Asset restructuring: Selling assets that aren't productive
-Capital restructuring: Changing the mix of debt and equity (adding more debt or equity)
-Management restructuring: Changing top management, the organization structure, and how people report to each other
Portfolio Management (3)
BCG growth/share matrix
involves a better understanding of the competitive position of an overall portfolio or family of businesses by
portfolio management continued
...businesses by:
-Suggesting strategic alternatives for each business
-Identifying priorities for the allocation of resources
-Using Boston Consulting Group's (BCG) growth/share matrix
BCG Matrix
Tool for analyzing business unit performance.
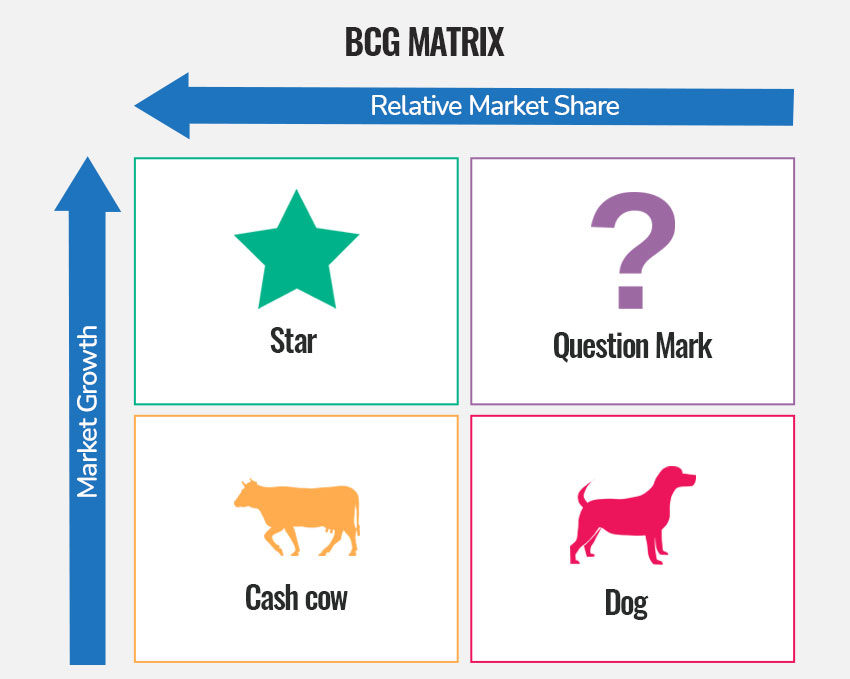
Star (BCG Matrix)
in the portfolio matrix, a business unit that is a fast-growing market leader
Question Marks (BCG Matrix)
high growth, low market share
Cash Cows (BCG Matrix)
low growth, high market share
Dogs (BCG Matrix)
low growth, low market share
Products with low market share in a low growth market. Firms need to use a product extension strategy or dispose of these products altogether.
Portfolio Management: Limitations
-SBUs are compared on just two factors: Each unit is seen as separate, which might not give the full picture.
-Are these the only important factors? Can all units be fairly compared this way? What about synergies between units?
-Oversimplified models: Simple charts can't replace the experience of managers.
-Strict rules for resource allocation: Following rigid rules may harm the company in the long run.
Diversification can be done through:
-Mergers and acquisitions
-Divestments
-Strategic alliances and joint ventures: Pooling resources with other companies
-Internal development: Growing through new ideas or starting new ventures
Acquisitions can destroy value by:
-Paying too much for the target company
-Failing to integrate the acquired business properly
-Diversifying too much in ways competitors can easily copy
Mergers
involve a combination or consolidation of two firms to form a new legal entity
-On a relatively equal basis
-Are relatively rare
Acquisitions
involve one firm buying another either through stock purchase, cash, or the issuance of debt
Mergers and Acquisitions: Motives
-Acquiring is faster than building from scratch.
-Gain valuable resources to expand products, services, or enter new markets.
-Create synergy by leveraging core strengths, sharing activities, and building market power.
-Consolidate industries, forcing others to merge.
Mergers and Acquisitions: Limitations
-High takeover premiums: Acquiring companies often pay a lot
-Competitors can copy advantages.
-Competitors can copy synergies.
-Managers' egos may affect good business decisions.
-Cultural issues can ruin the intended benefits.
Divestment
Selling off business units to focus on core activities.
Mergers and Acquisitions: Divestment
-Objectives
Cut financial losses from a failed acquisition.
-Focus on core businesses.
-Free up resources for better opportunities.
-Raise cash to support existing businesses.
Strategic Alliances and Joint Ventures
-Cooperative relationships between two or more firms with potential benefits
Enter new markets through:
More financial resources, more marketing expertise, lower costs, & new technologies
Strategic Alliances and Joint Ventures: Limitations
Need for the Proper Partner:
Partners should have complementary strengths, unique qualities that create synergies, and trust each other
Internal Development Motives:
-Keep all the profits from new ventures.
-Avoid challenges of combining activities from different companies.
-Avoid merging different corporate cultures.
-Don't need external funding for development.
Internal Development Limitations:
-Takes a lot of time
-Requires continuous development of new capabilities
Managerial Motives
Managers may act in their own self-interest, reducing value creation. This can include:
-Seeking growth just for the sake of growth.
-Gaining more prestige, higher rankings, better pay, and job security.
-Enjoying excitement and drama.
-Acting out of excessive egotism.
-Using antitakeover tactics to protect themselves.