Unit 6: Cities and Urban Land-Use Patterns and Processes
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Non-basic industries
enterprises whose customers live in the same community
Basic Industries
Industries that sell their products or services primarily to consumers outside the settlement

Business Services
Services that primarily meet the needs of other businesses, including professional, financial, and transportation services

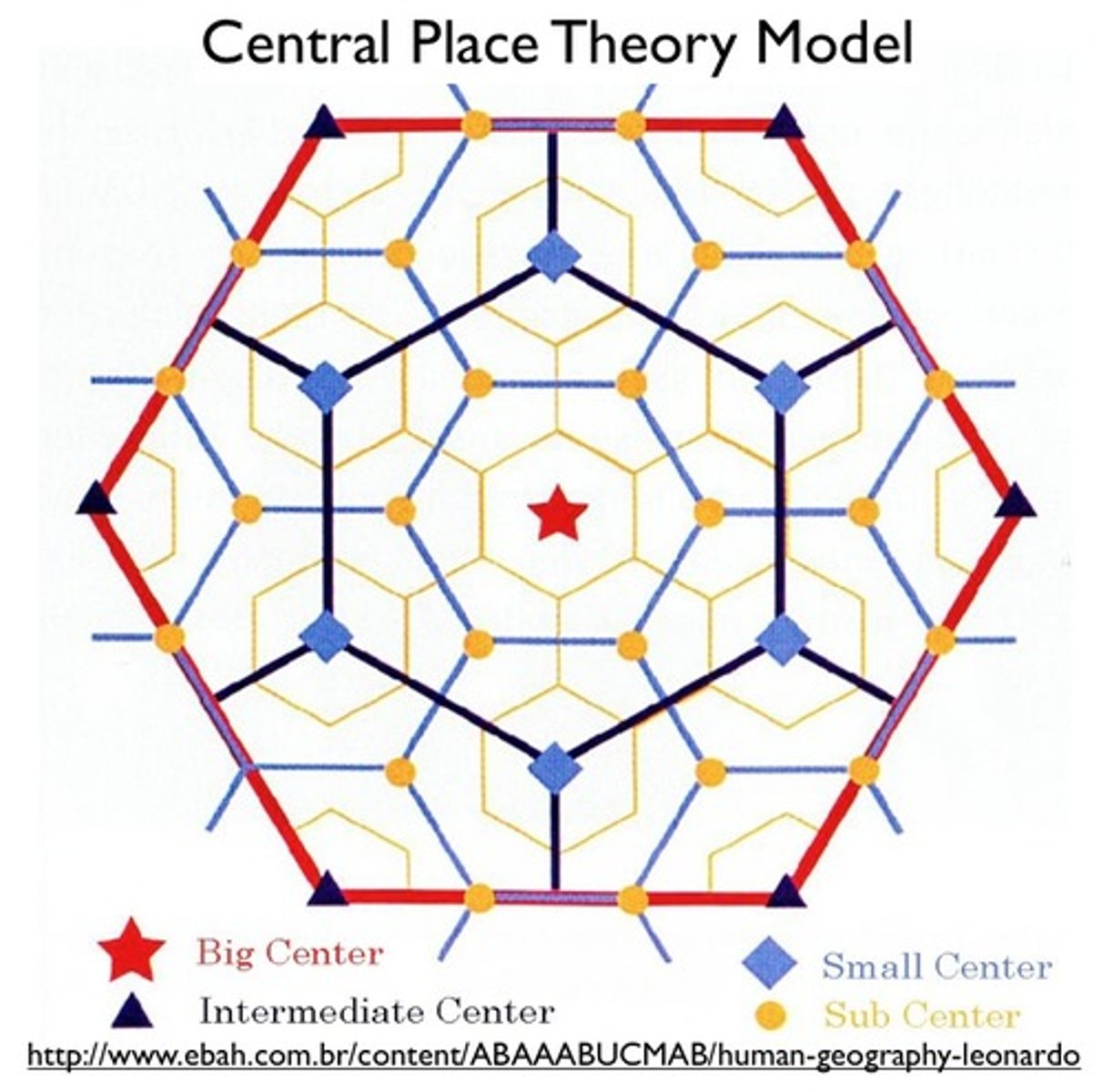
Central Place Theory
A theory that explains the distribution of services, based on the fact that settlements serve as centers of market areas for services; larger settlements are fewer and farther apart than smaller settlements and provide services for a larger number of people who are willing to travel farther.
Consumer Services
Businesses that provide services primarily to individual consumers, including retail services and education, health, and leisure services

Public Services
Services offered by the government to provide security and protection for citizens and businesses.

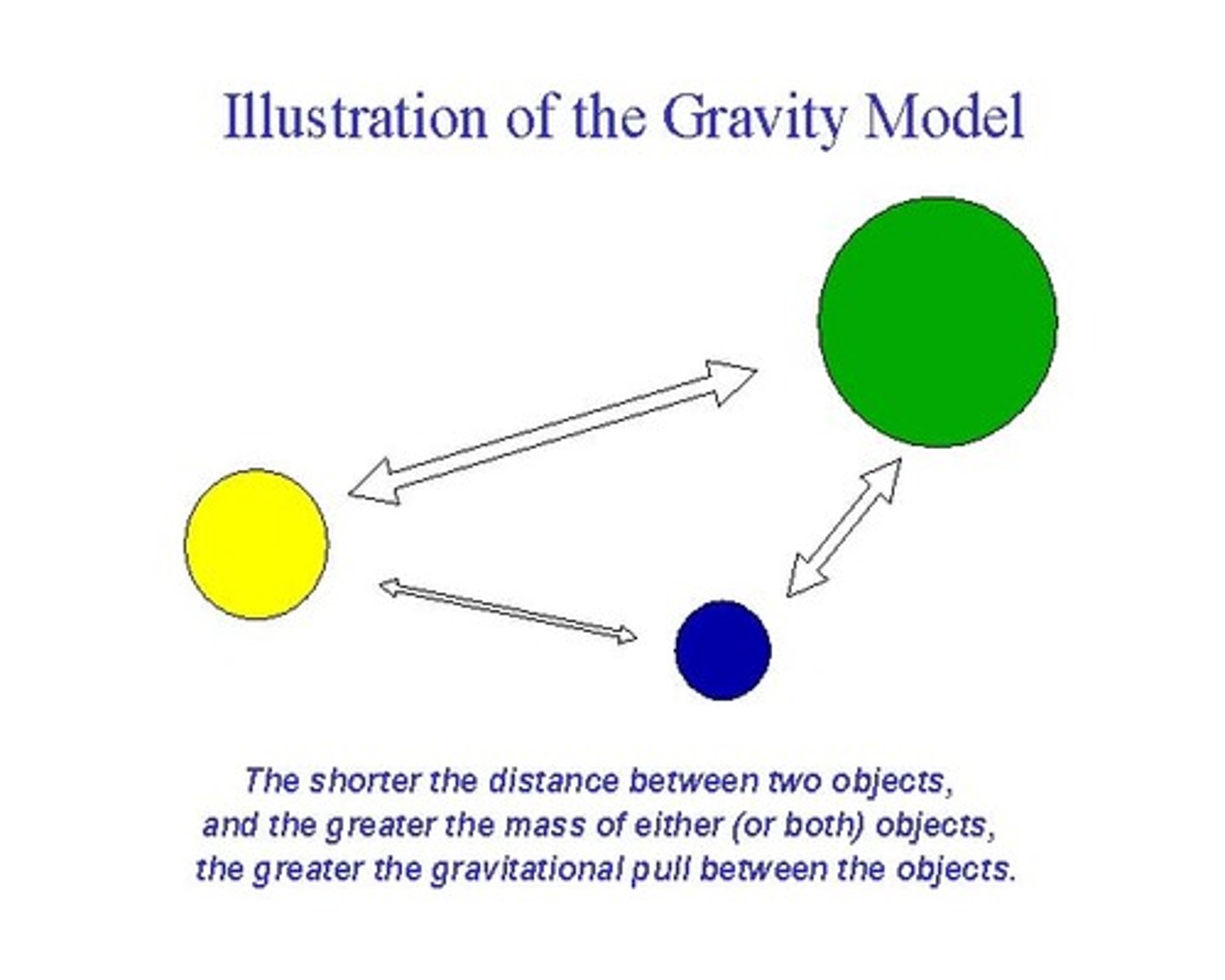
Gravity Model
A model that holds that the potential use of a service at a particular location is directly related to the number of people in a location and inversely related to the distance people must travel to reach the service.
market area (hinterland)
The area surrounding a central place, from which people are attracted to use the place's goods and services.
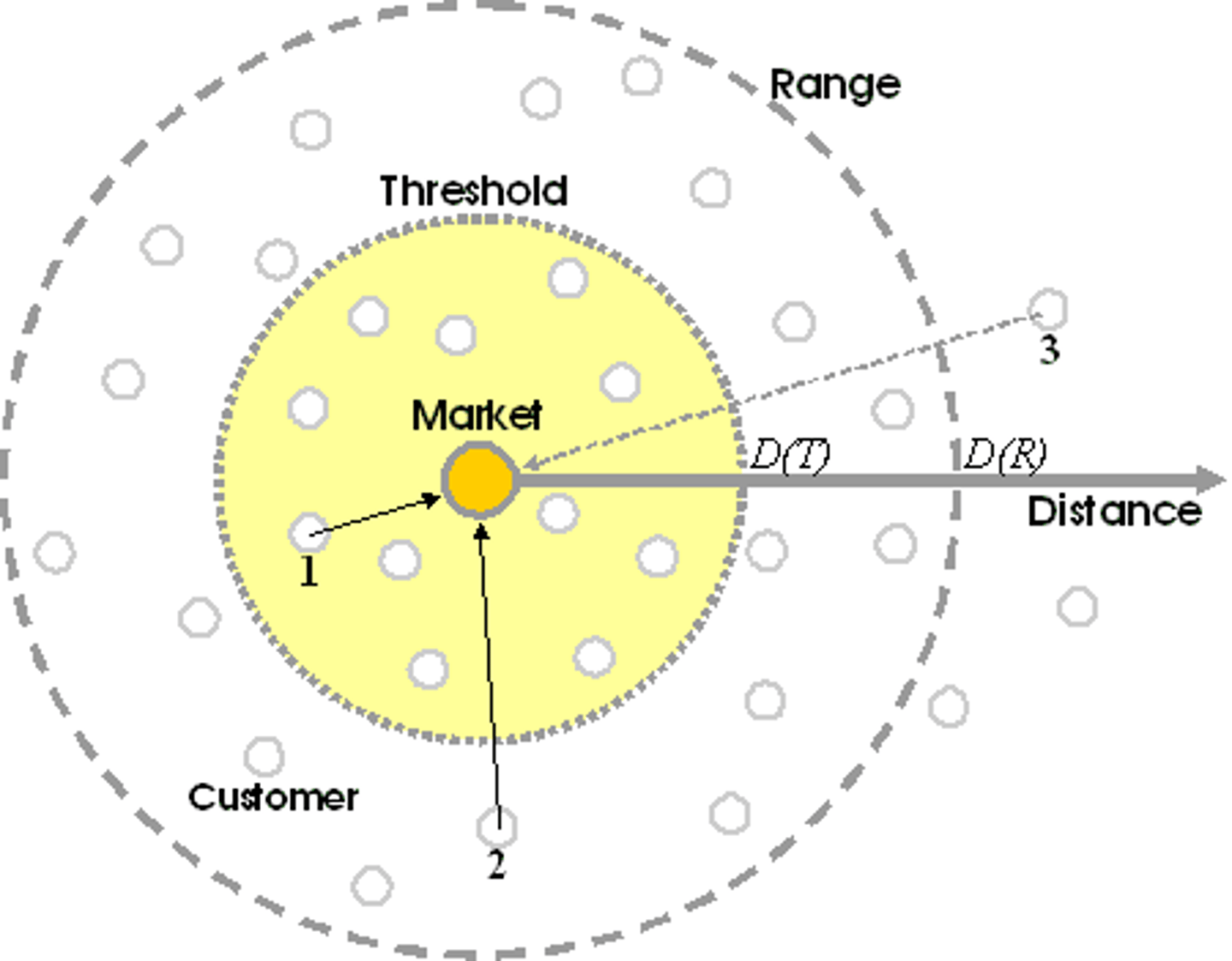
range
The maximum distance people are willing to travel to use a service.
threshold
The minimum number of people needed to support the service
Megacity
City with more than 10 million people

Metacity
A city with a population over 20 million
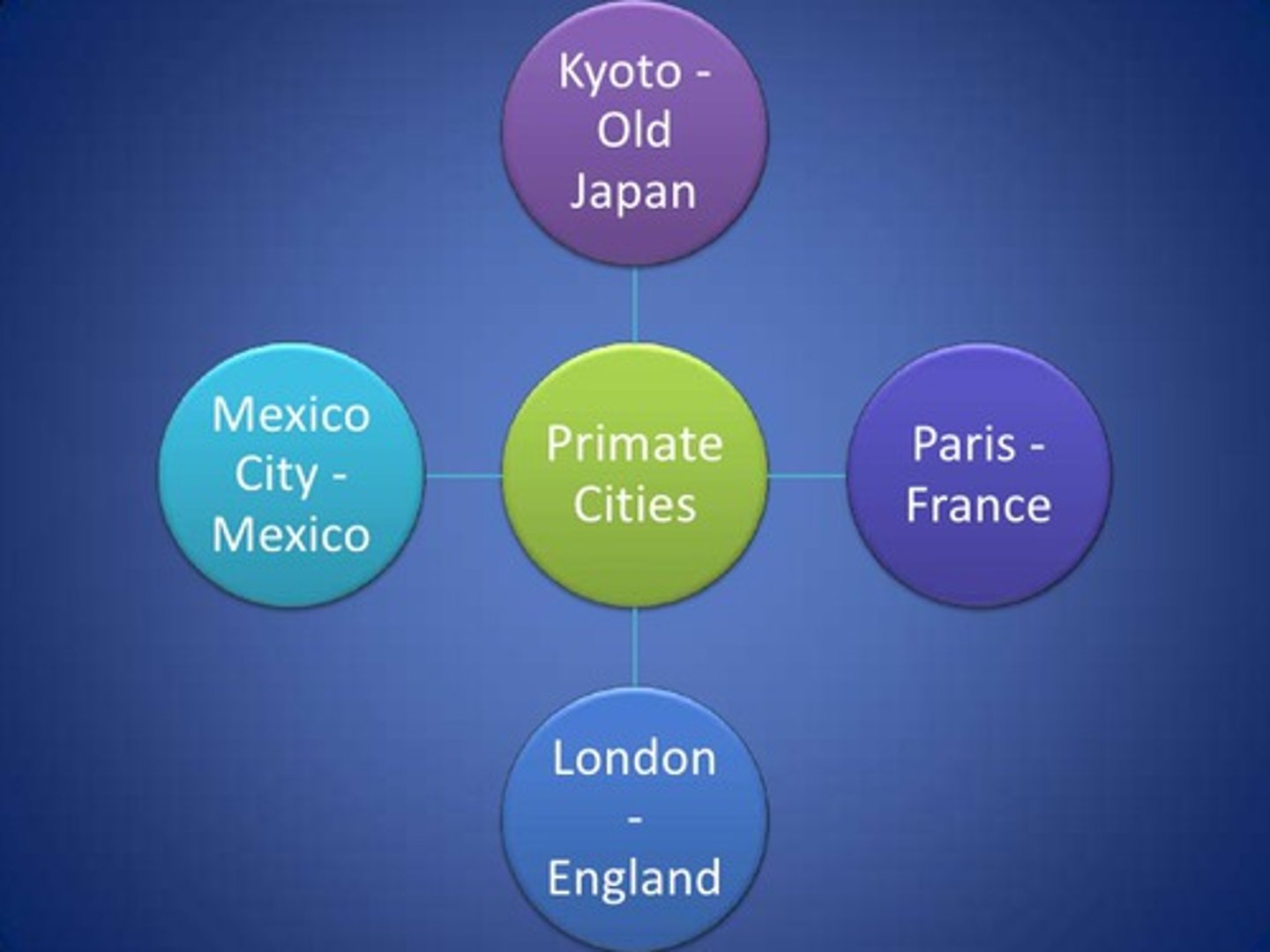
primate city
The largest settlement in a country, if it has more than twice as many people as the second-ranking settlement.
rank-size rule
A pattern of settlements in a country, such that the nth largest settlement is 1/n the population of the largest settlement.
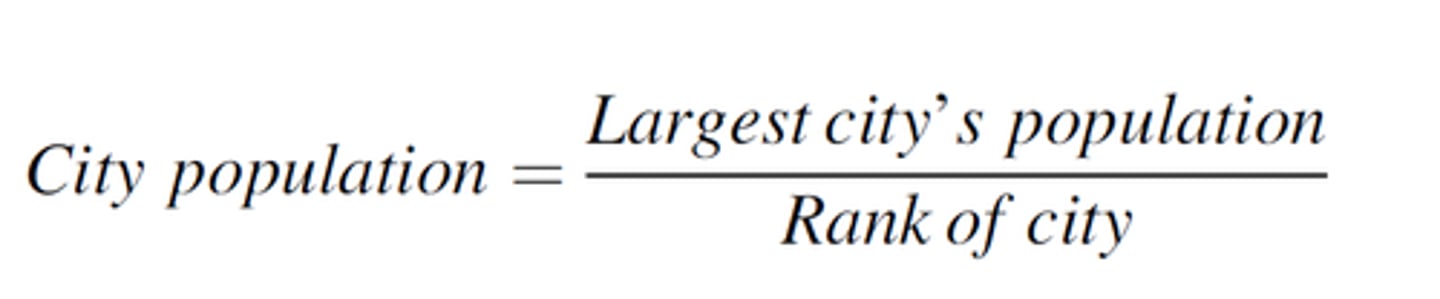
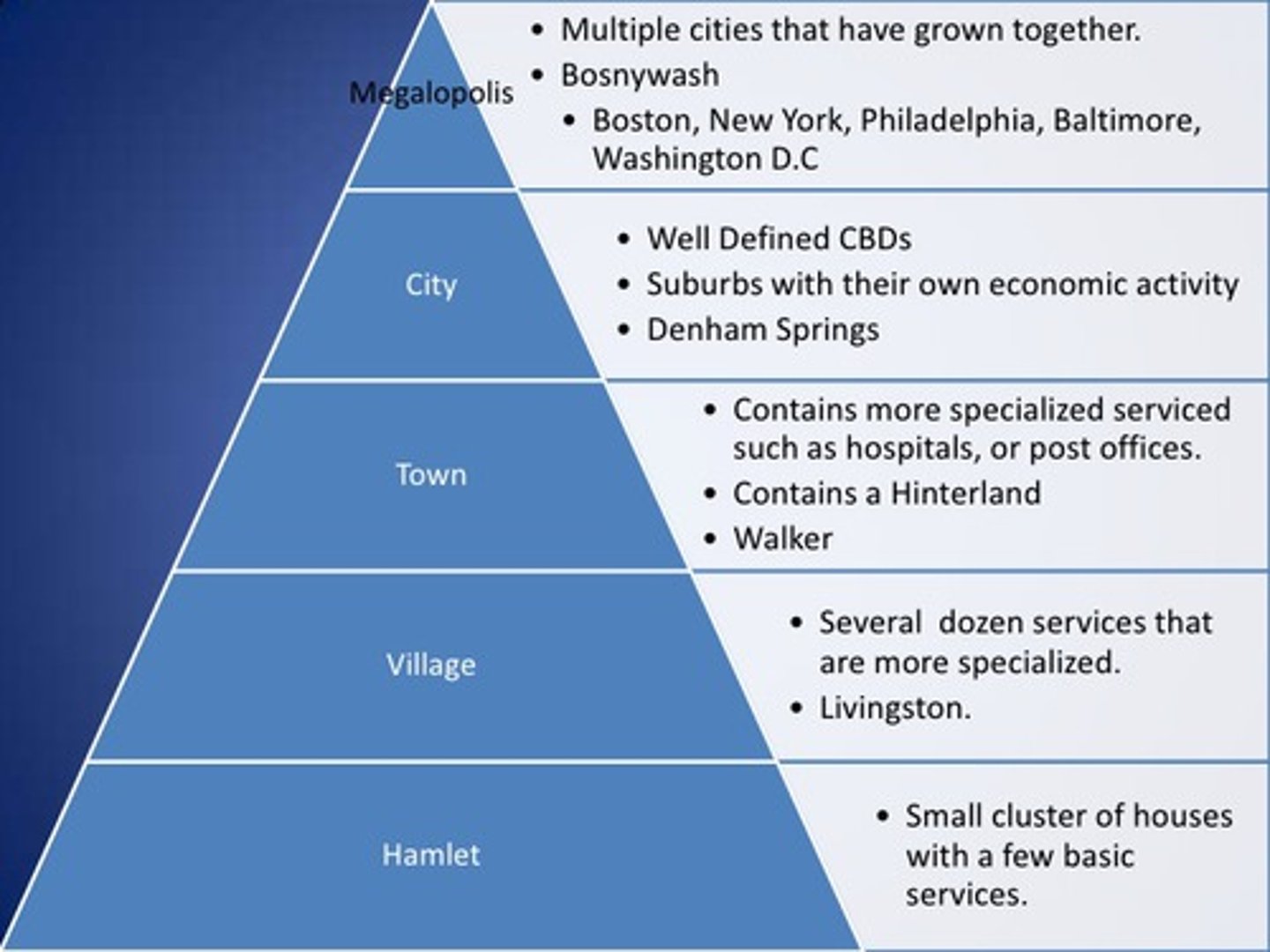
urban hierarchy
A ranking of settlements (hamlet, village, town, city, metropolis) according to their size and economic functions.
world city (global city)
a city that functions as a service center of the world economy
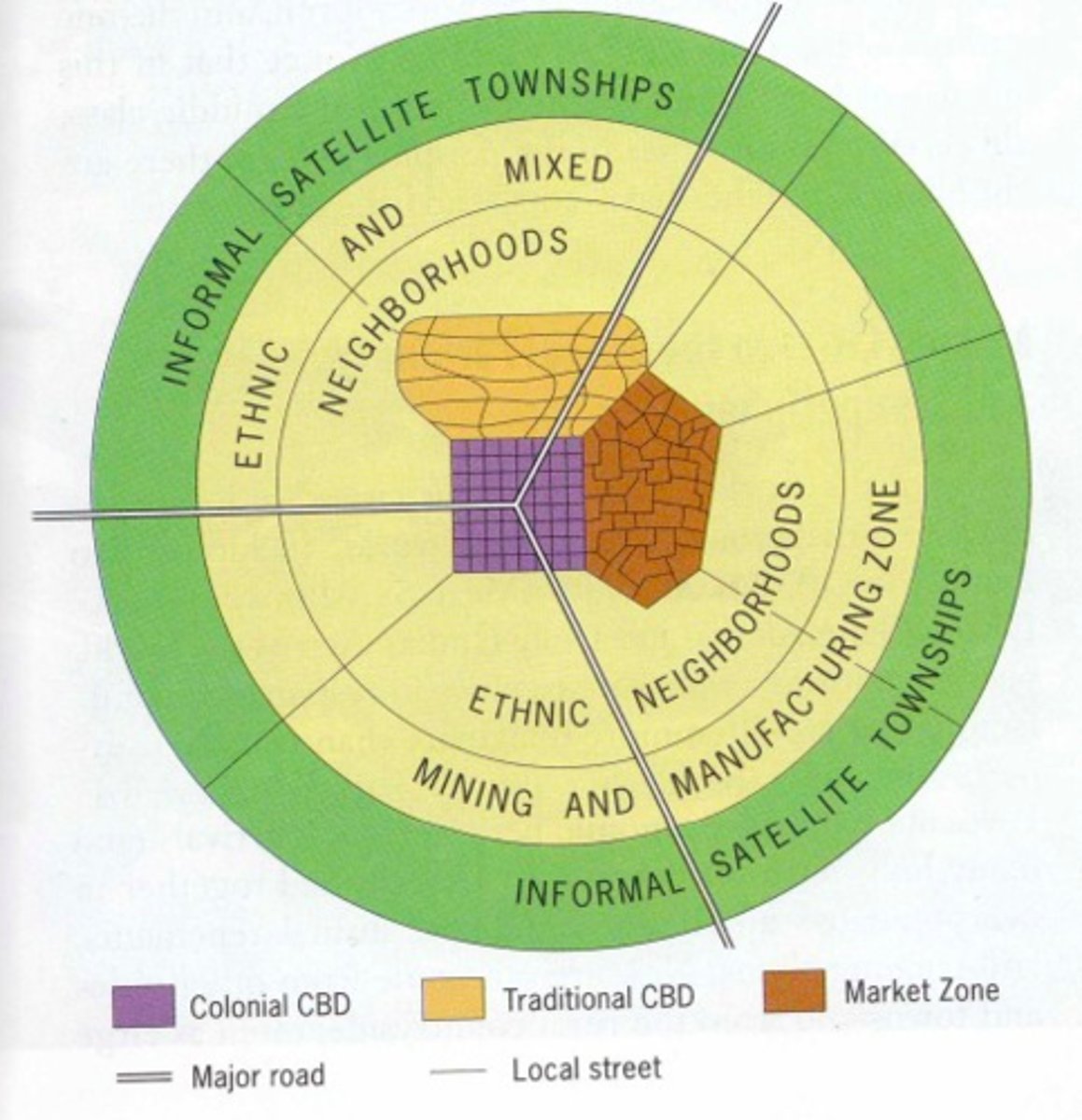
African City Model
model that suggests that African cities have more than one CBD, which is a remanence of colonialism
Annexation
Legally adding land area to a city in the United States
Blockbusting
A process by which real estate agents convince white property owners to sell their houses at low prices because of fear that persons of color will soon move into the neighborhood

Boomburbs
rapidly growing city that remains essentially suburban in character even as it reaches populations more typical of a large city

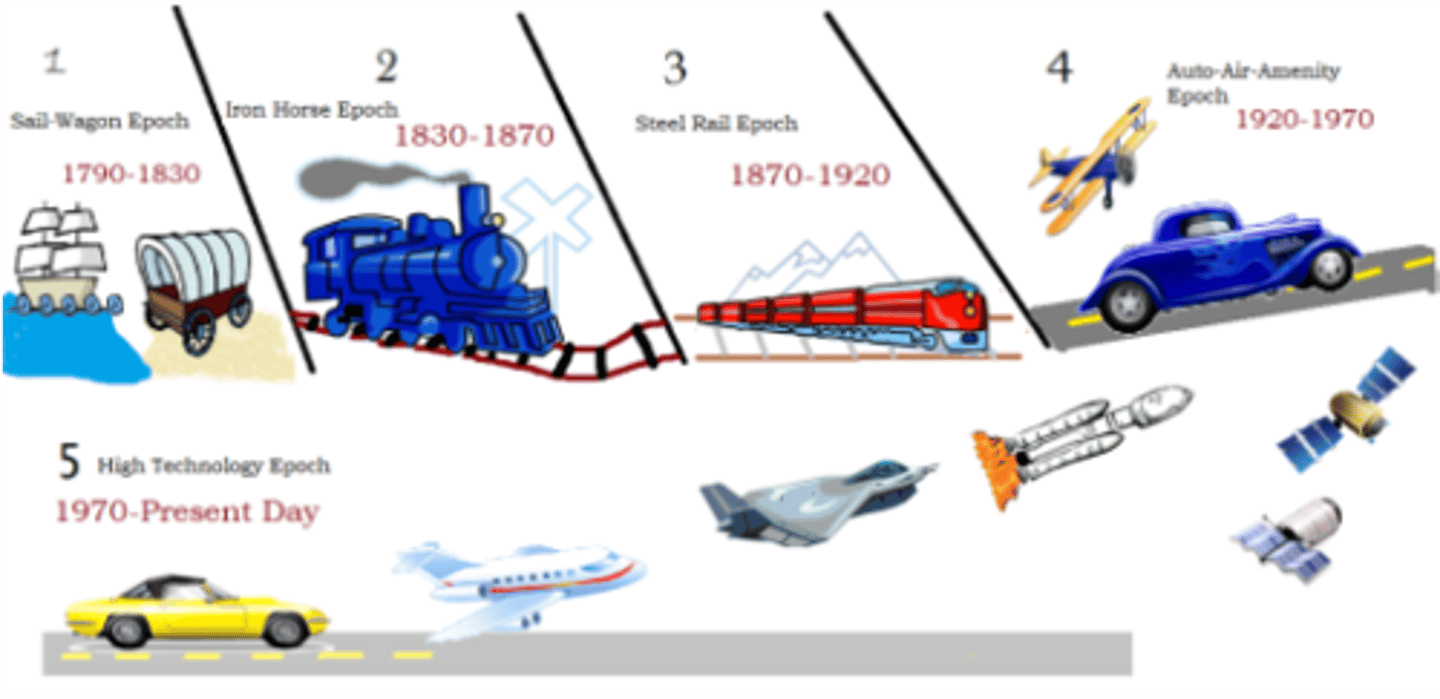
Borchert's epochs
According to the geographer John R. Borchert, American cities have undergone five major epochs, or periods, of development shaped by the dominant forms of transportation and communication at the time. These include sail-wagon epoch (1790-1830), iron horse epoch (1830-1870), steel rail epoch (1870-1920), auto-air-amenity epoch (1920-1970), and satellite-electronic-jet propulsion and high-technology epoch (1970-present).
Brownfields
contaminated industrial or commercial sites that may require environmental cleanup before they can be redeveloped or expanded

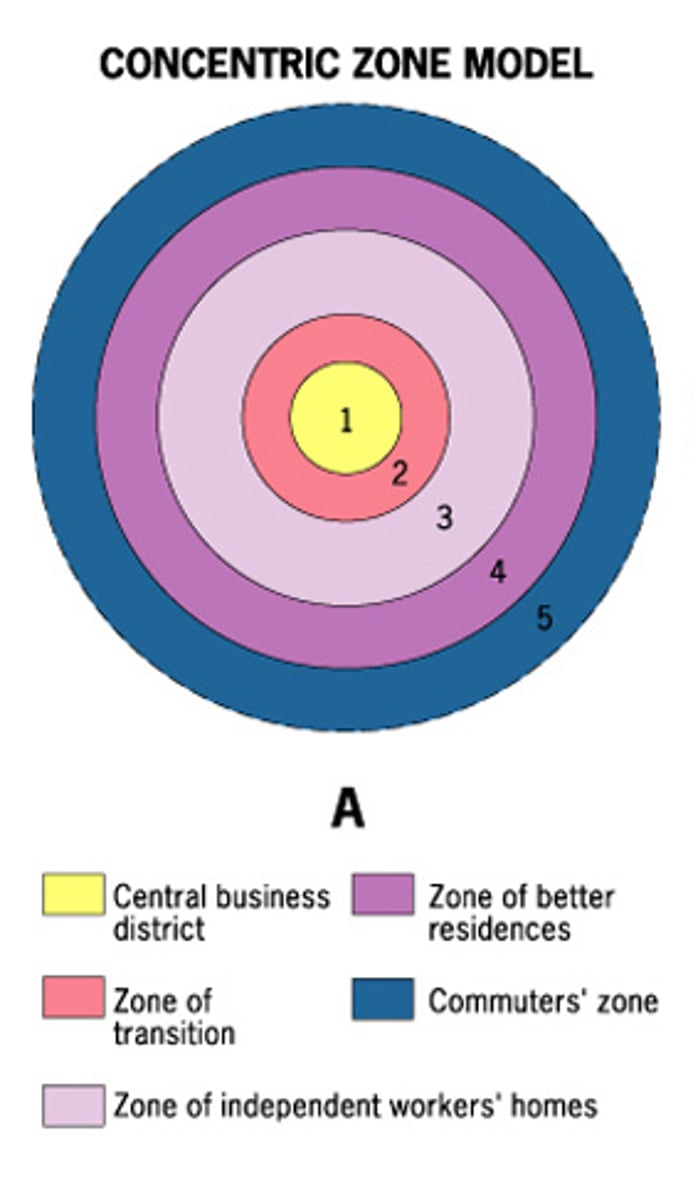
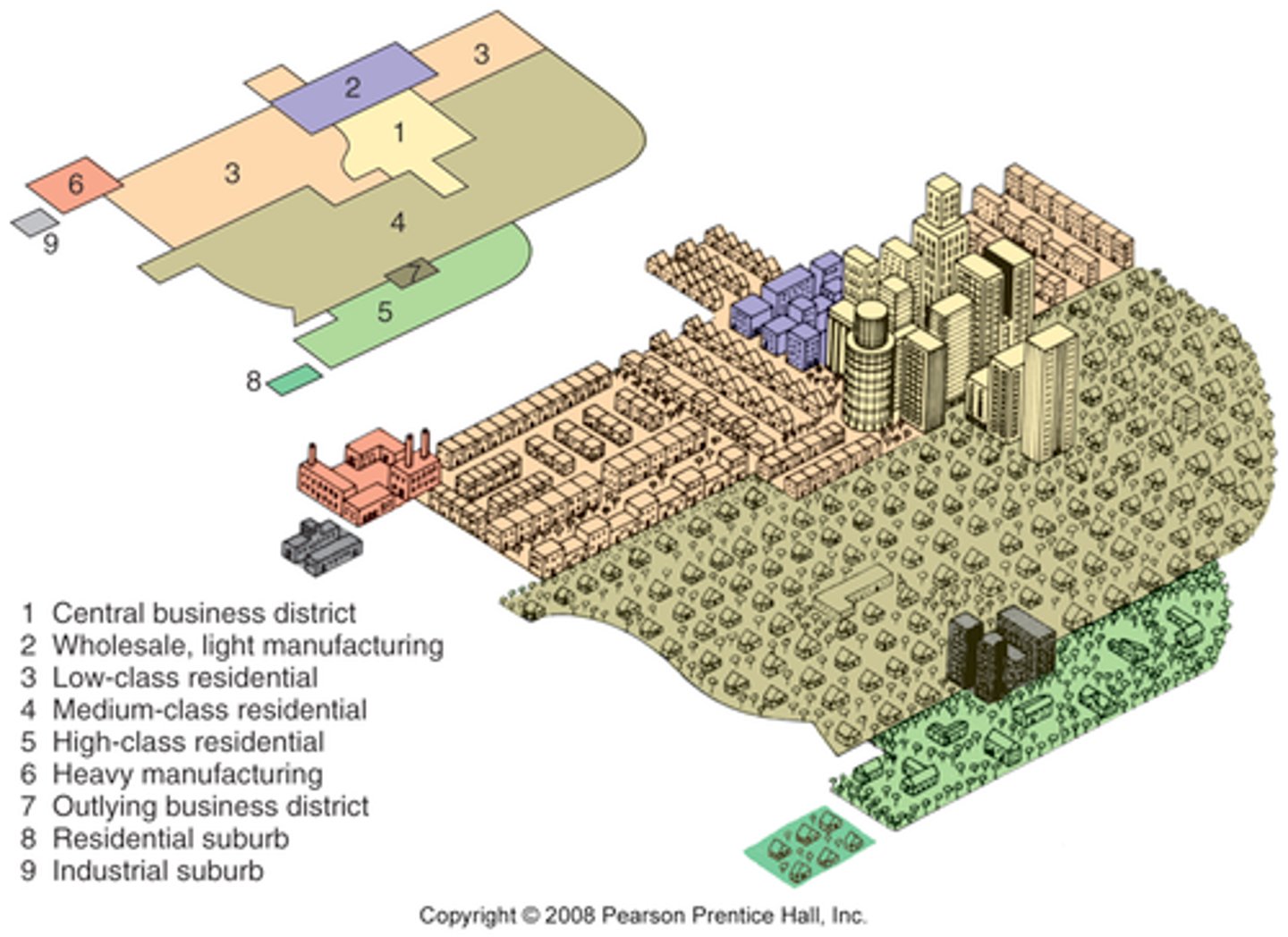
Burgess Concentric Zone Model
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are spatially arranged in a series of rings.
Central Business District (CBD)
The area of a city where retail and office activities are clustered.

urban decentralization
metropolitan areas sprawl in all directions and suburbs take on many of the characteristics of traditional downtowns

Disamenity Zones
areas not connected to city services and under the control of drug lords and gangs

edge cities
A large node of office and retail activities on the edge of an urban area.
Ethnic Neighborhood
a neighborhood, typically situated in a larger metropolitan city and constructed by or comprised of a local culture, in which a local culture can practice its customs

Exurbs
communities that arise farther out than the suburbs and are typically populated by residents of high socioeconomic status

Farmland protection policies
Policies enacted by governments that protect farmland and prevent it from being sold into other use. Uses zoning to identify areas of agricultural land use

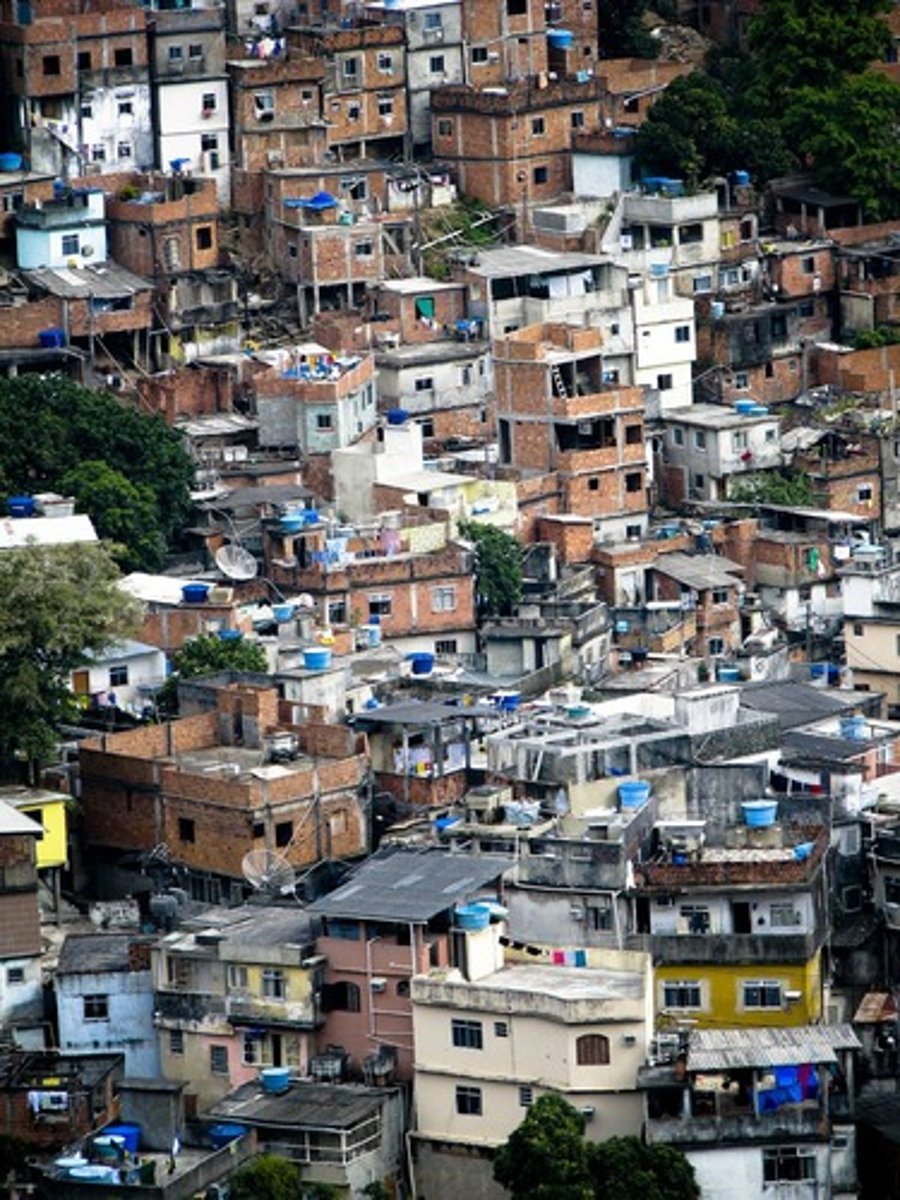
Favela
a slum community in a Brazilian city

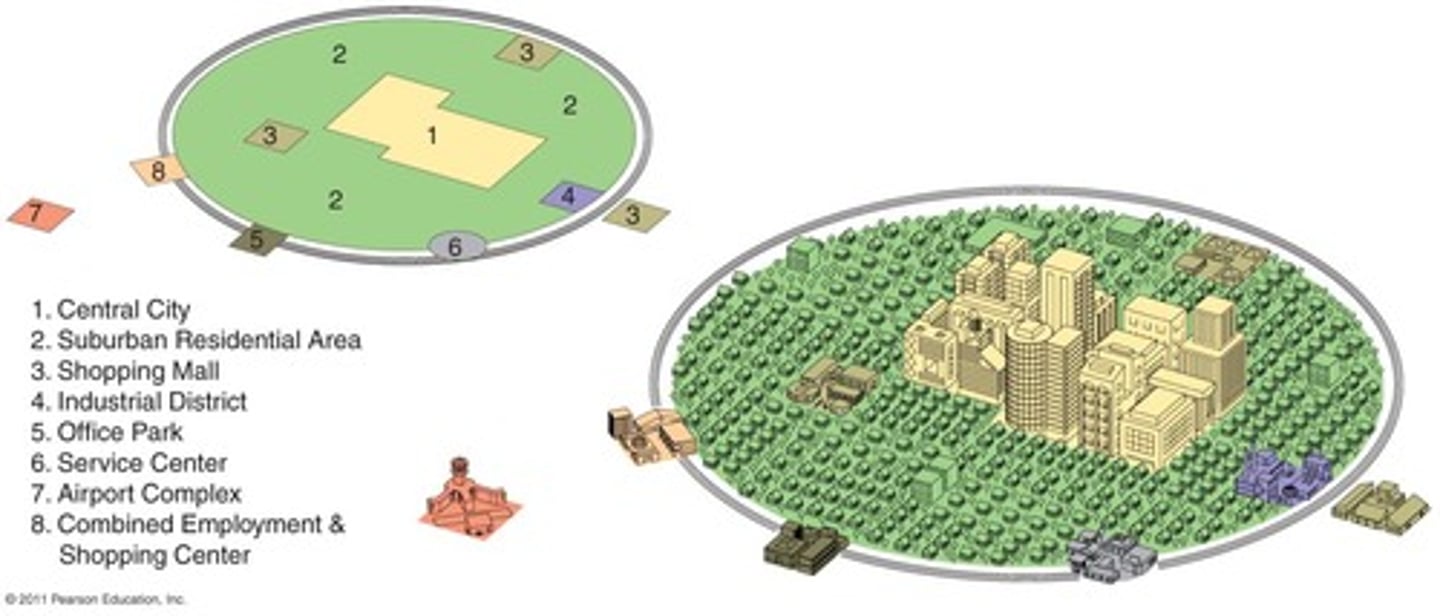
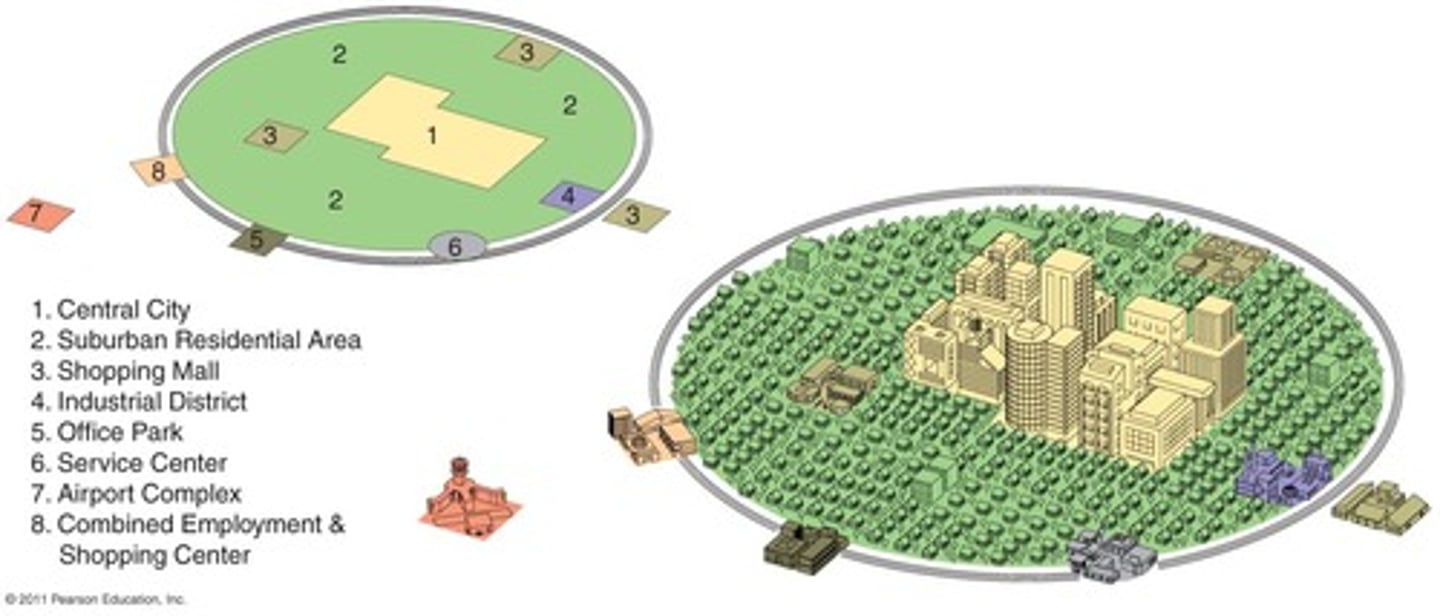
Galactic City Model
represents the post-industrial city with its several, dispersed business districts. This model represents a distinct decentralization of the commercial urban landscape as the economy has transitioned to services as the leading form of production. Manufacturing has declined significantly and become specialized.
Gentrification
A process of converting an urban neighborhood from a predominantly low-income renter-occupied area to a predominantly middle-class owner-occupied area.

Greenbelt
A ring of land maintained as parks, agriculture, or other types of open space to limit the sprawl of an urban area.
Harris-Ullman Multiple Nuclei Model
Developed in the 1950s by Chauncy Harris and Edward Ullman, this model explains the changing growth pattern of urban spaces based on the assumption that growth occurred independently around several major foci (or focal nodes), many of which are far away from the central business district and only marginally connected to it.
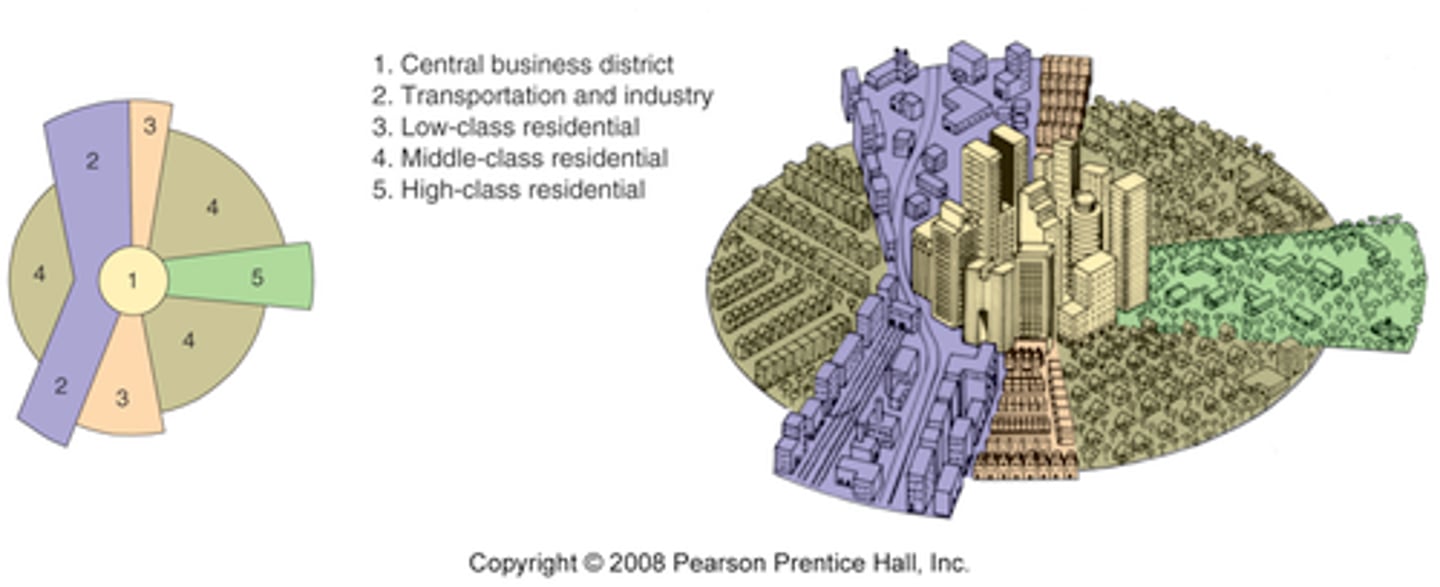
Hoyt Sector Model
the theory of urban structure that a city develops in a series of certain sectors, instead of rings.
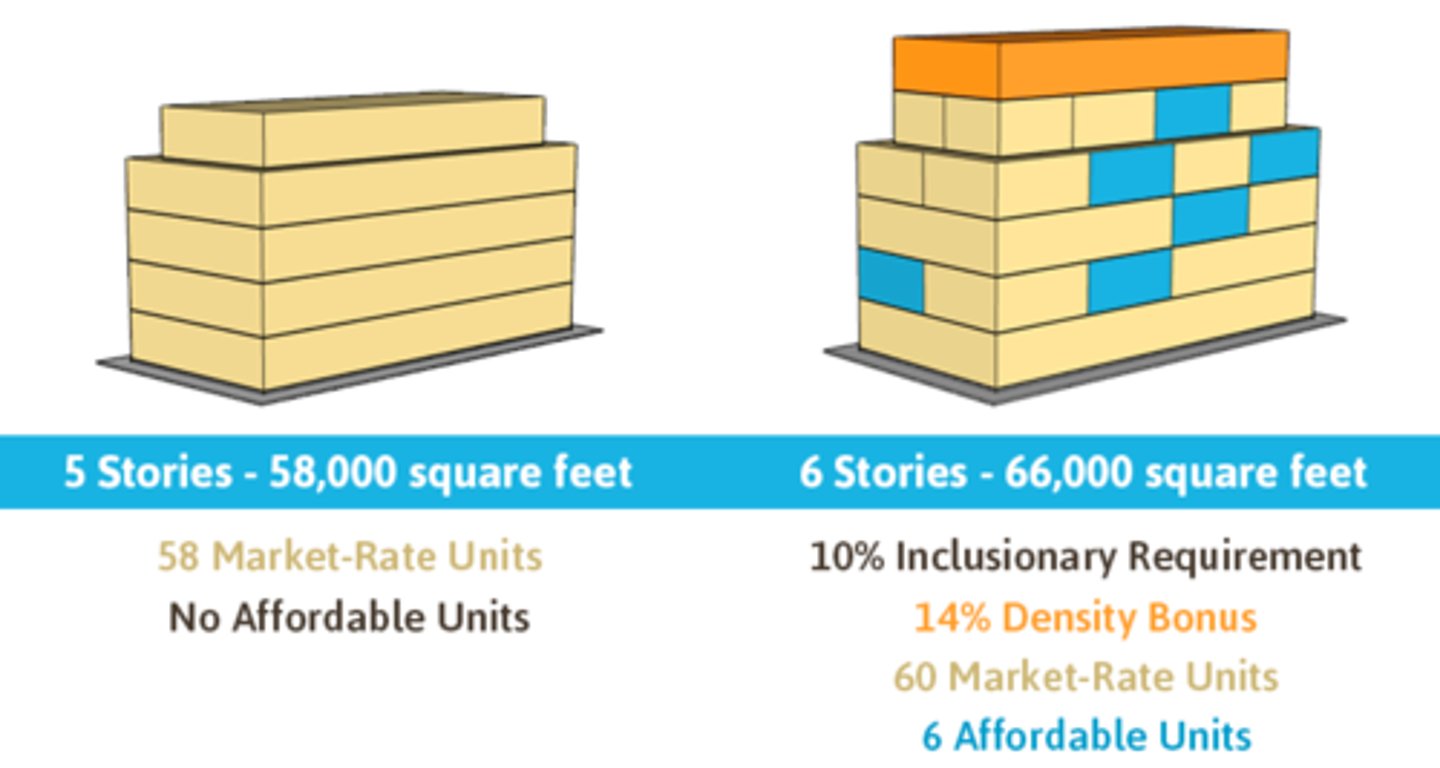
Inclusionary Zoning
Specifies inclusions within a development, such as a playground or that a percentage of homes must be affordable for low-income families.
infrastructure
the basic physical and organizational structures and facilities (e.g., buildings, roads, and power supplies) needed for the operation of a society or enterprise.

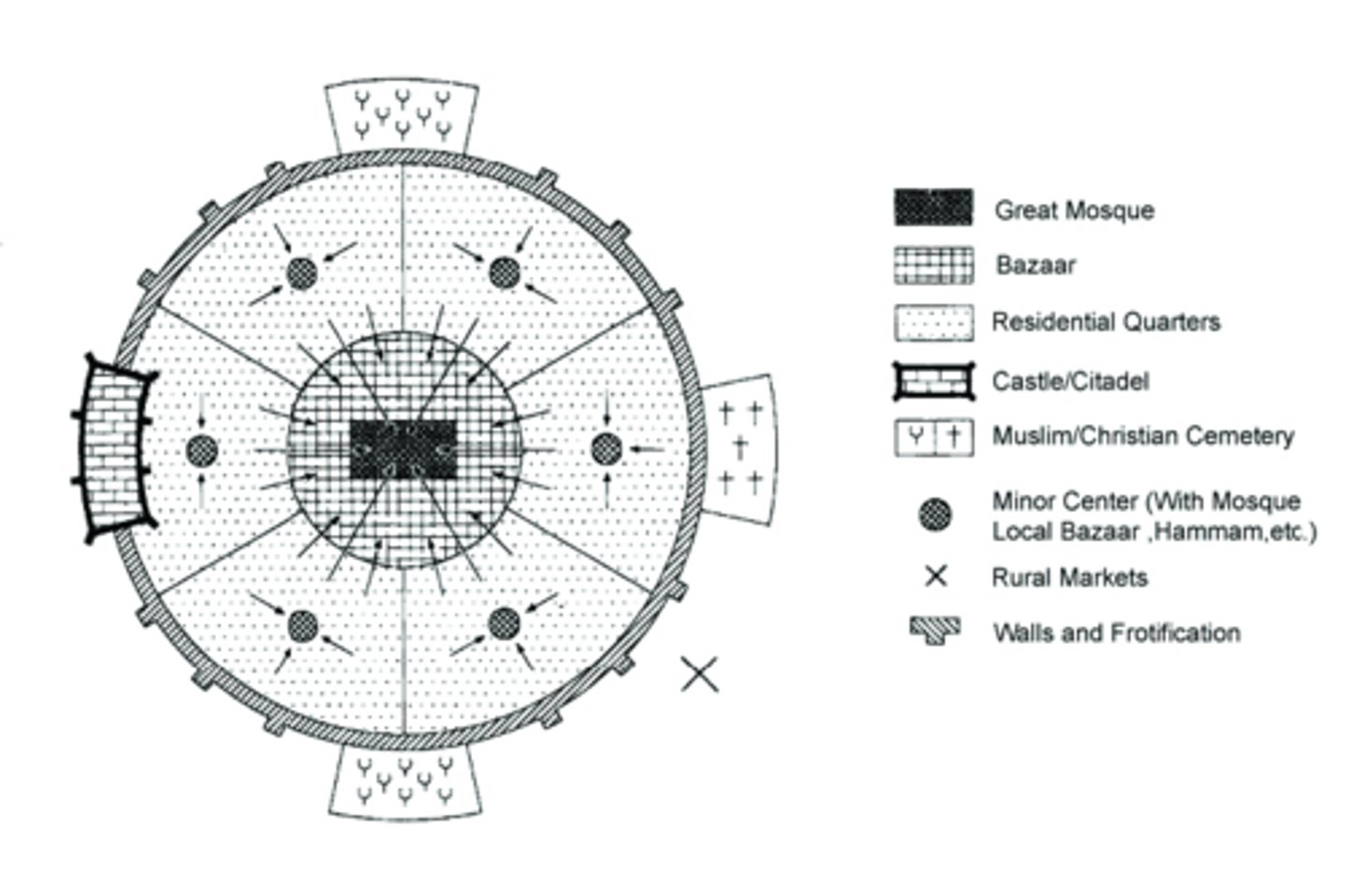
Islamic City Model
Cities in Muslim countries that owe their structure to their religious beliefs. Islamic cities contain mosques at their center and walls guarding their perimeter. Open-air markets, courtyards surrounded by high walls, and dead-end streets, which limit foot traffic in residential neighborhoods, also characterize Islamic cities.
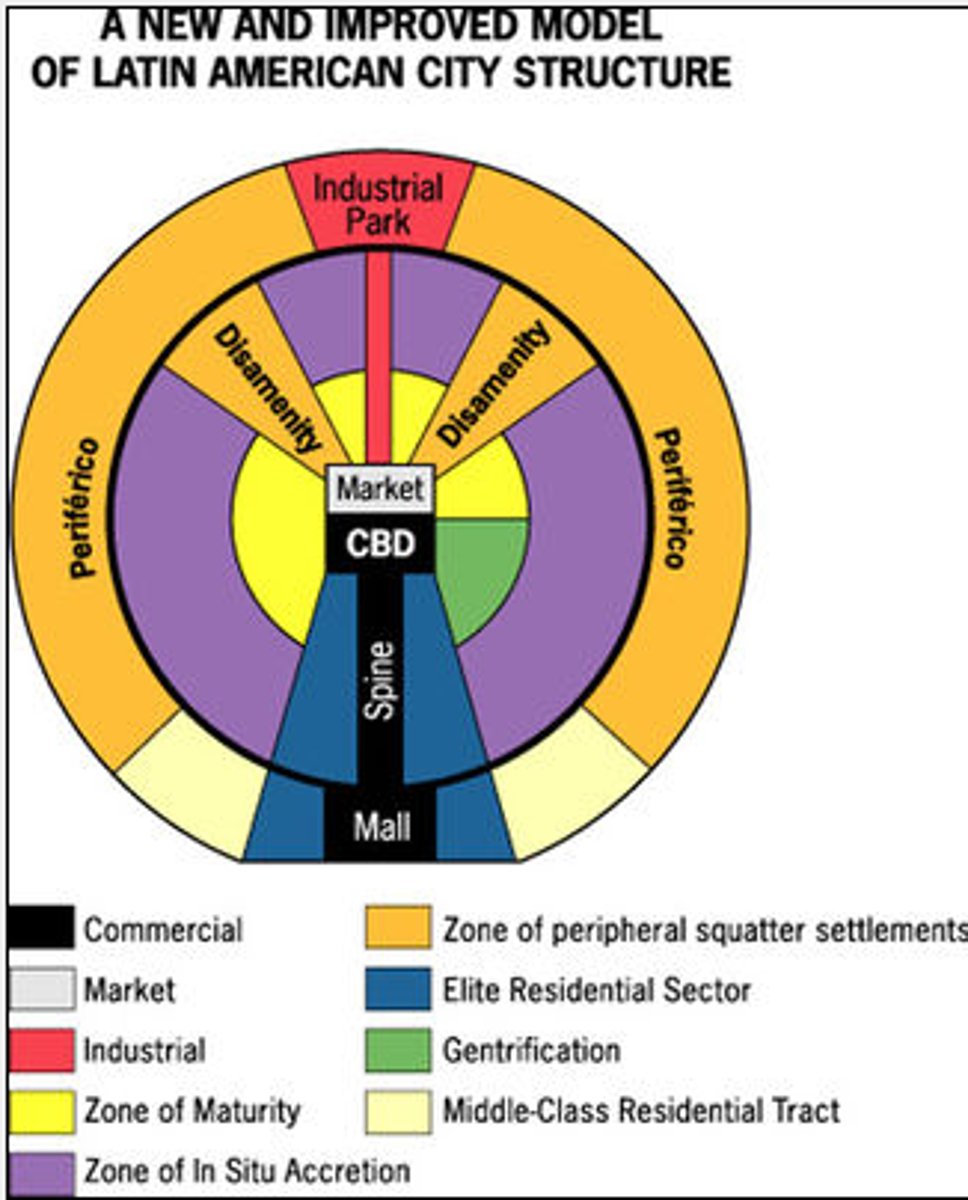
Latin American City Model
Griffin-Ford model. Developed by Ernst Griffin and Larry Ford. Blends traditional Latin American culture with the forces of globalization. The CBD is dominant; it is divided into a market sector and a modern high-rise sector. The elite residential sector is on the extension of the CBD in the "spine". The end of the spine of elite residency is the "mall" with high-priced residencies. The further out, less wealthy it gets. The poorest are on the outer edge.
low/medium/high density housing
the number of dwellings per unit of land that would constitute a low/medium/high density housing depends on the place defining it
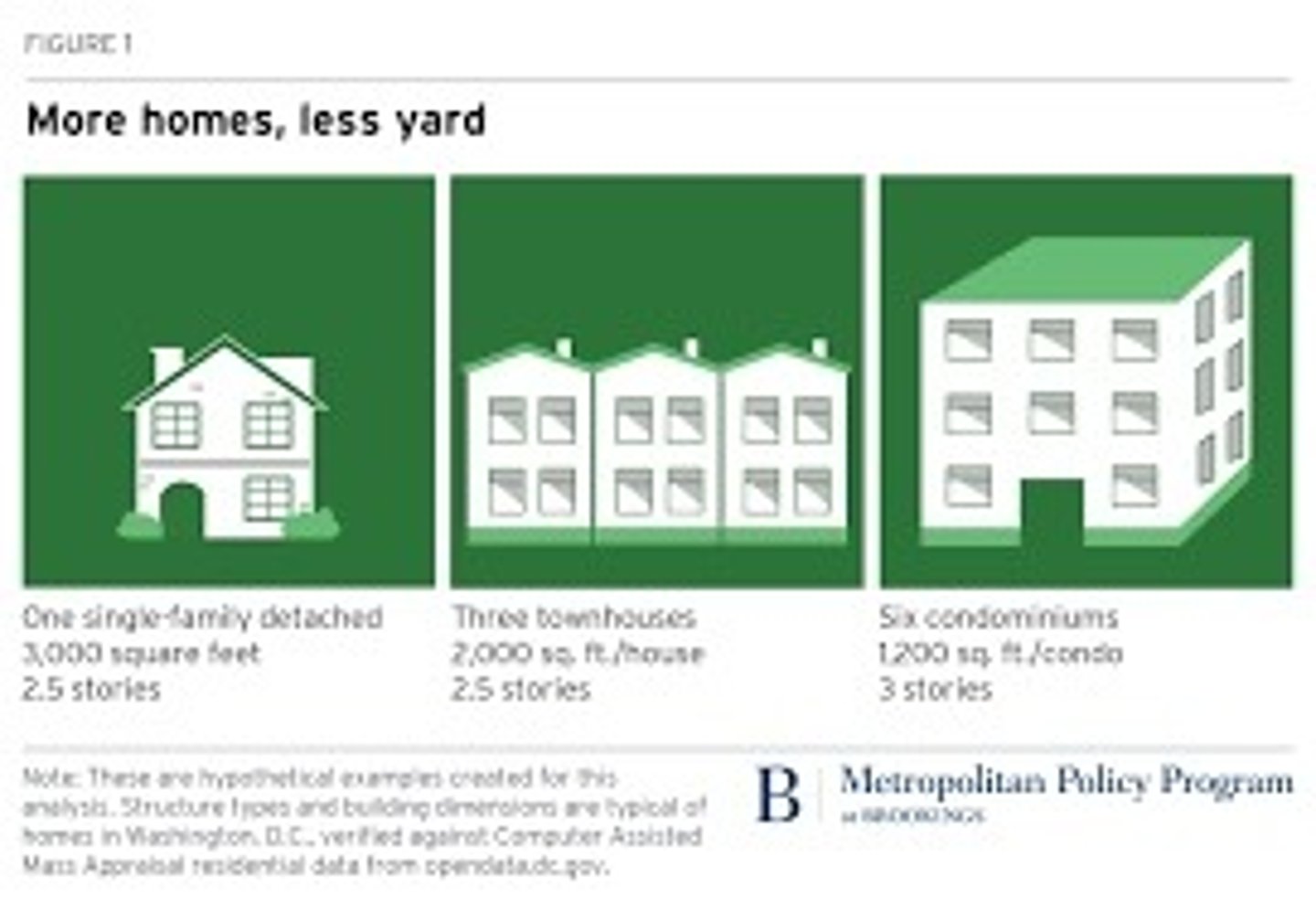
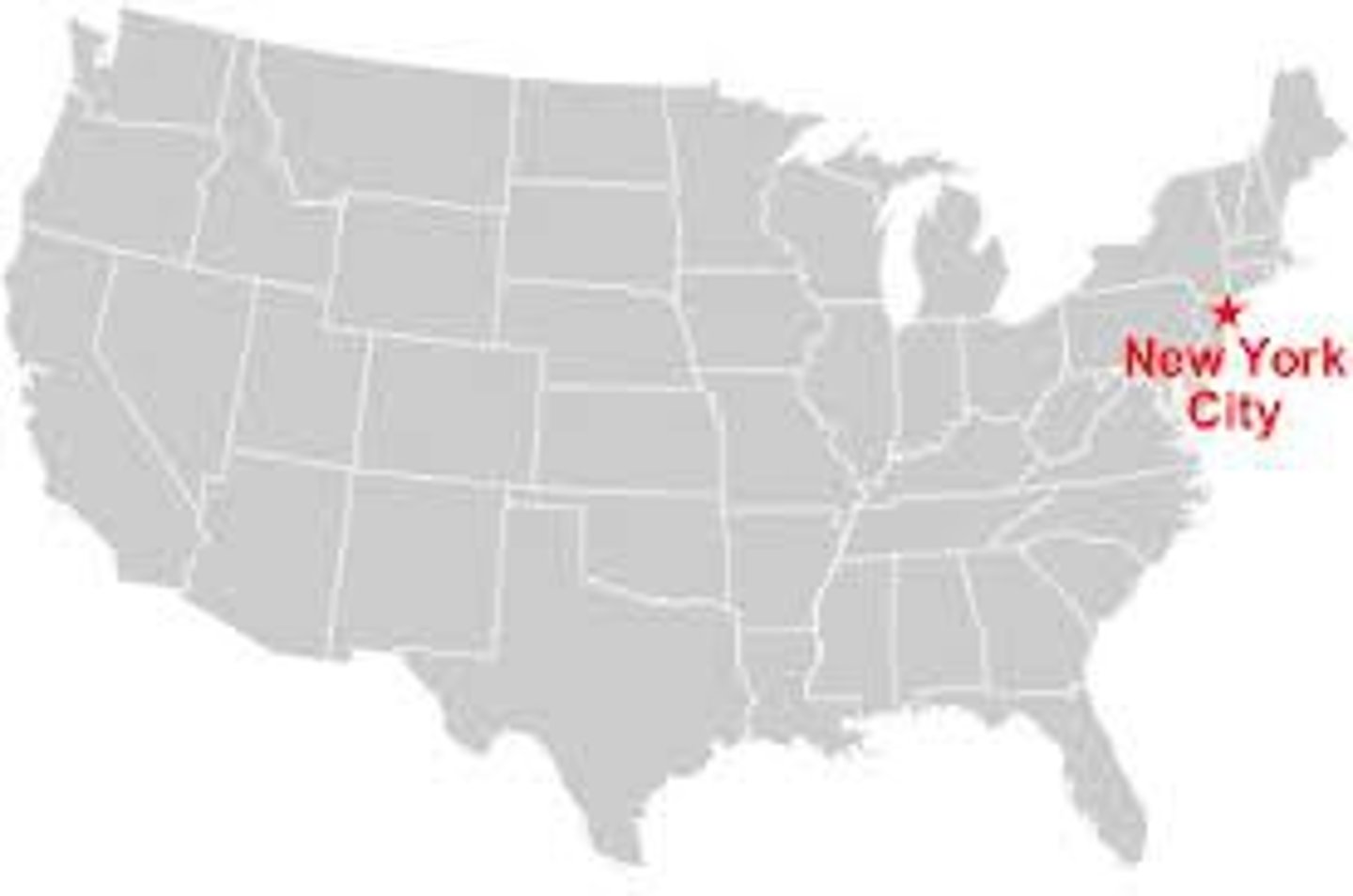
Megalopolis
a region in which several large cities and surrounding areas grow together
mixed land use
land development that blends a combination of residential, commercial, cultural, institutional and/or industrial uses
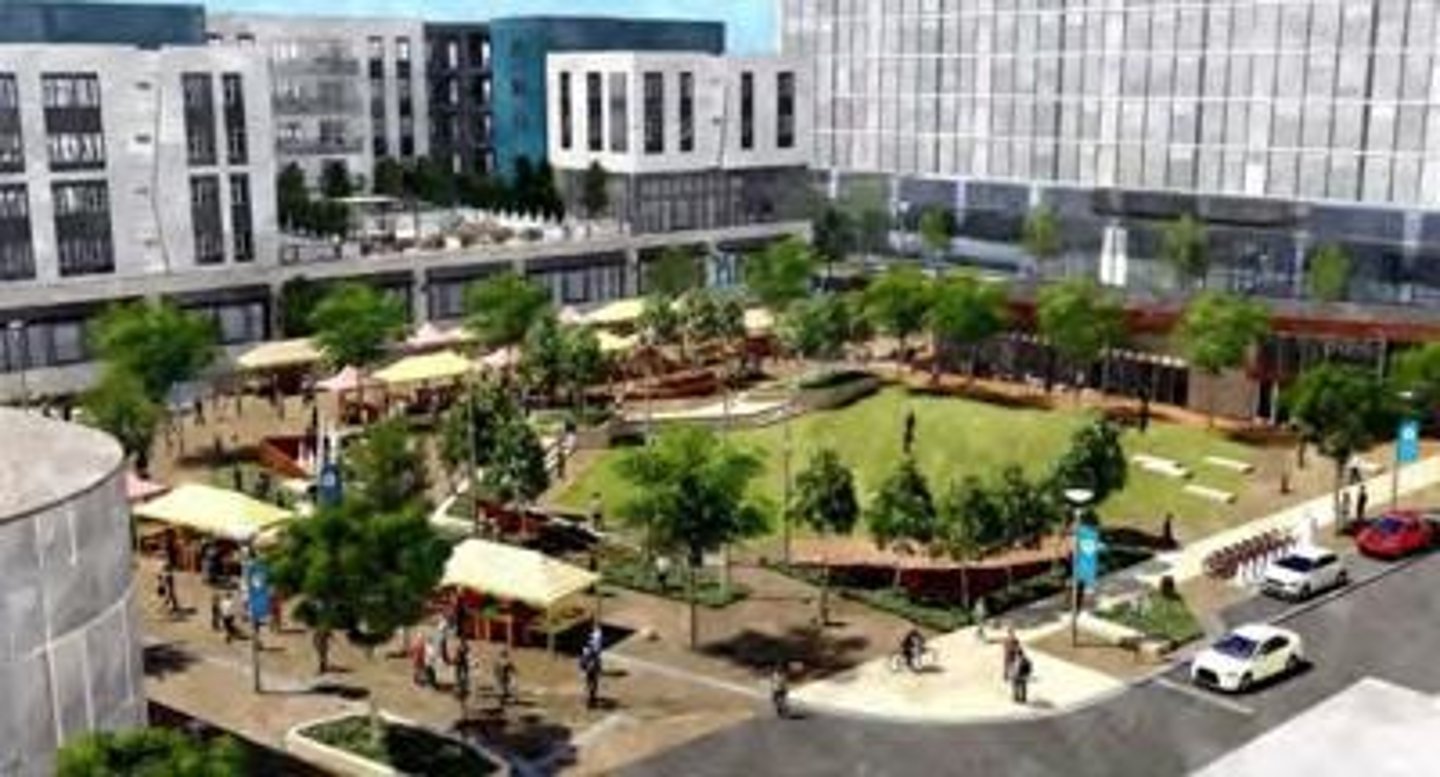

New Urbanism
A movement in urban planning to promote mixed use commercial and residential development and pedestrian friendly, community orientated cities. New urbanism is a reaction to the sprawling, automobile centered cities of the mid twentieth century.

NIMBY (not in my backyard)
Term used to describe local (residential) opposition to development projects.

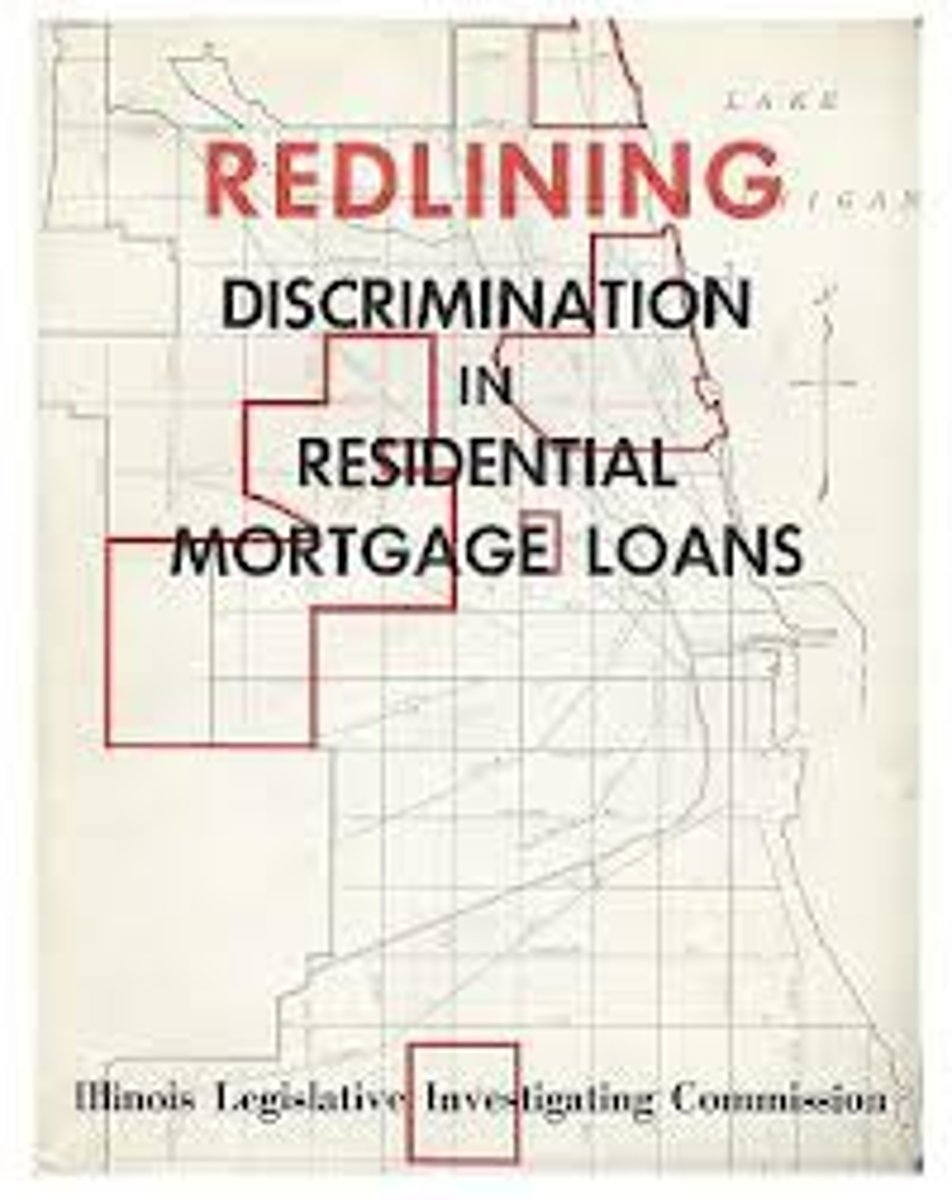
Redlining
A discriminatory real estate practice in North America in which members of minority groups are prevented from obtaining money to purchase homes or property in predominantly white neighborhoods. The practice derived its name from the red lines depicted on cadastral maps used by real estate agents and developers. Today, redlining is officially illegal.
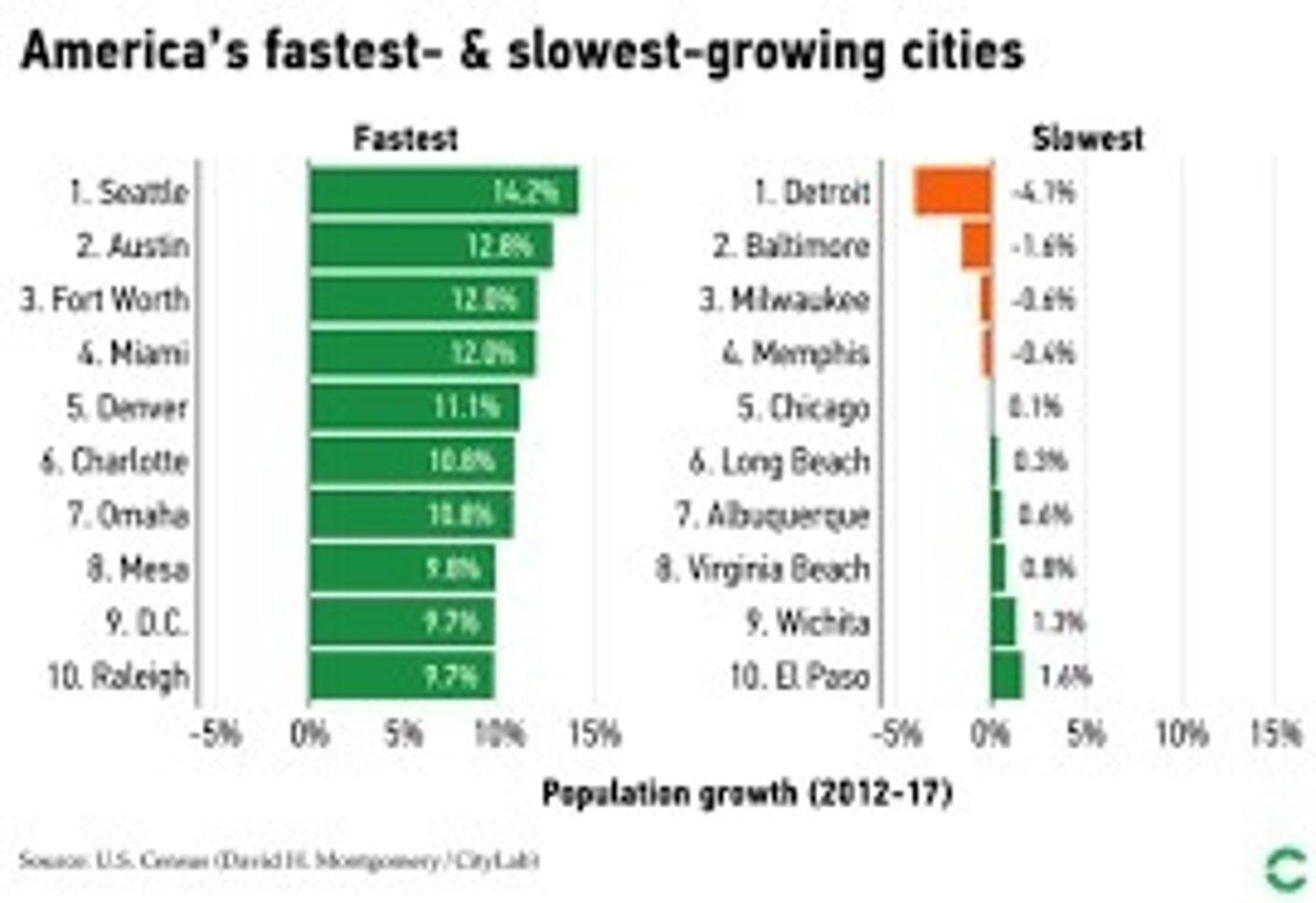
Slow-growth cities
urban communities where the planners have put into place smart growth initiatives to decrease the rate at which the city grows horizontally to avoid the adverse affects of sprawl
smart growth policies
an urban planning theory that concentrates walkable city areas to prevent urban sprawl

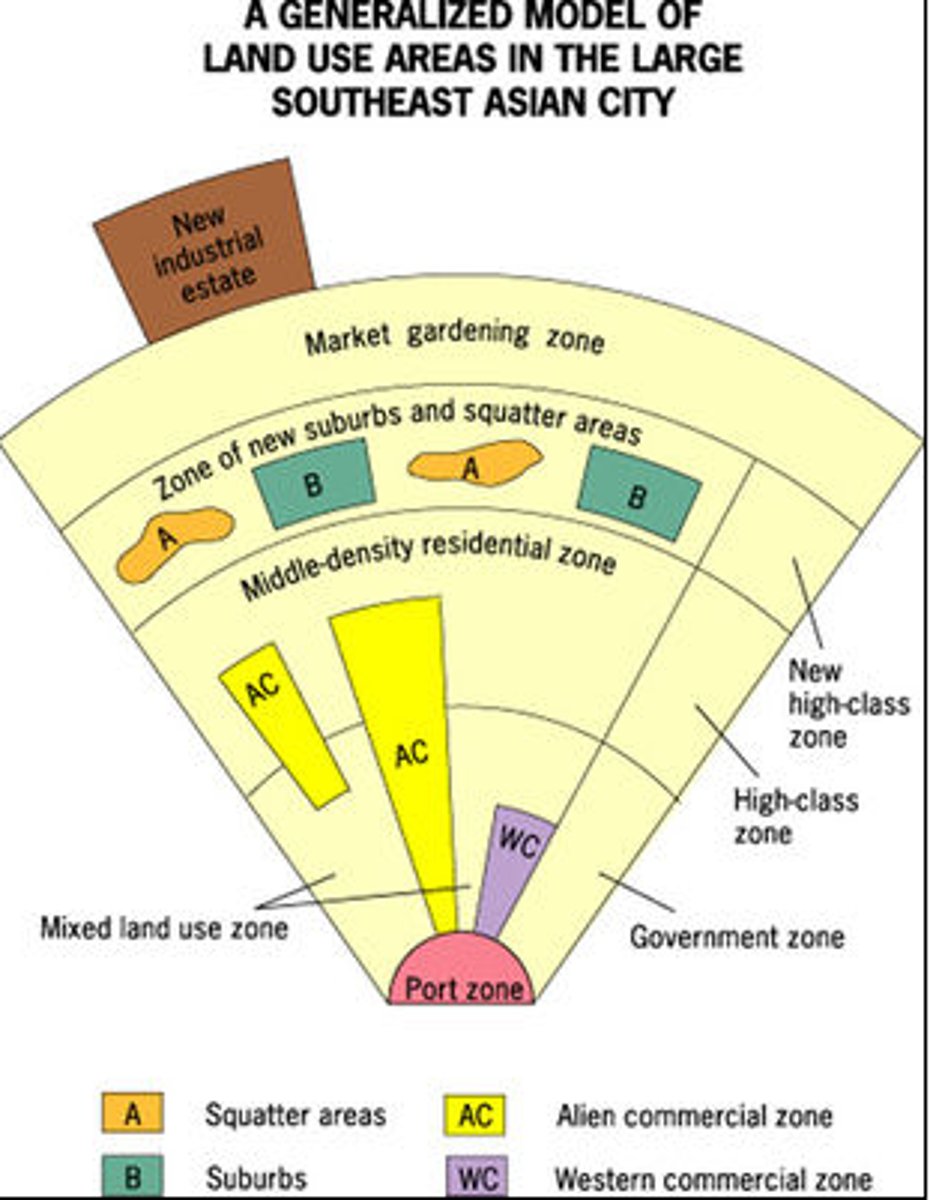
southeast asia city model
port is key aspect, suburbs present in two patches, alien commercial zone and western commercial zone, zone and function based
sprawl
Development of new housing sites at relatively low density and at locations that are not contiguous to the existing built-up area.

Squatter settlements/shantytowns
Areas of poverty in which the people do not own the land, little planning, no public services or infrastructure

suburbs
Residential areas surrounding a city. Shops and businesses moved to suburbia as well as people.

Sustainable Design Initiatives
Communities that use smart growth and green building techniques to create neighborhoods that are economically thriving and environmentally responsible

traditional zoning
zoning that creates separate zones based on land-use type or economic function such as various categories of residential (low-, medium-, or high-density), commercial, or industrial
Urban growth boundary
Geographical boundaries placed around a city to limit suburban growth within that city.
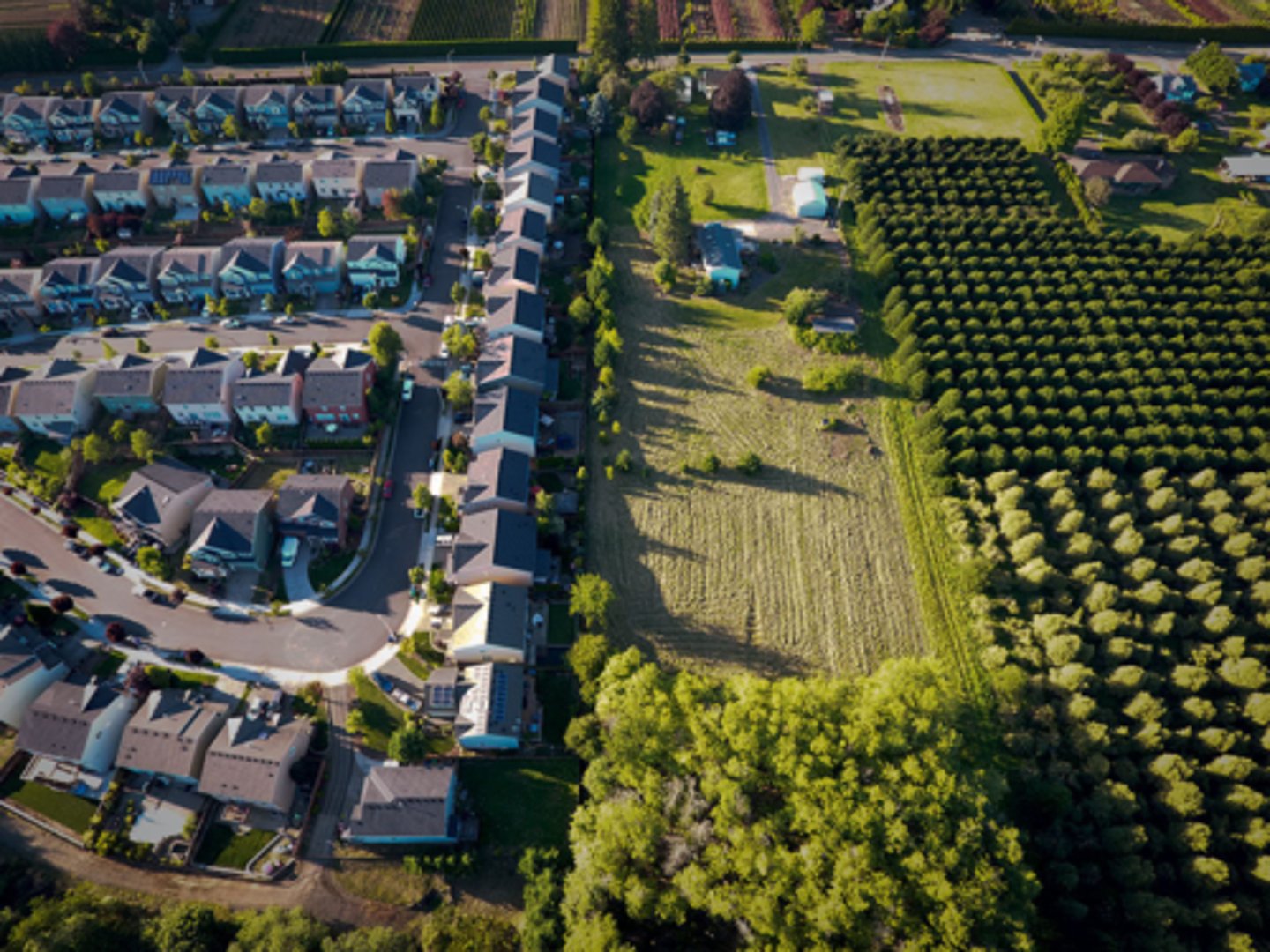

Urbanization
An increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban settlements.
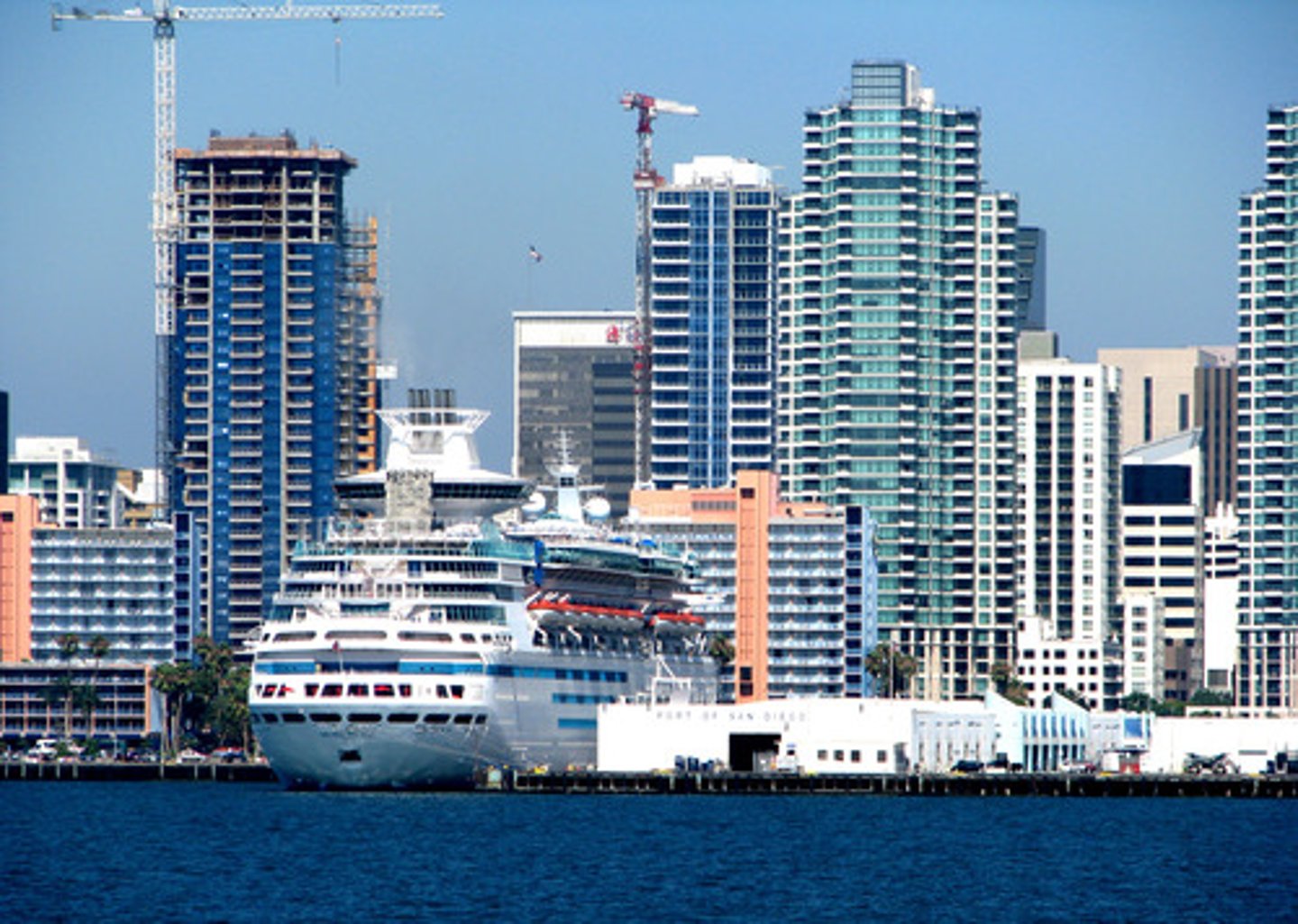

urban renewal
Program in which cities identify blighted inner-city neighborhoods, acquire the properties from private members, relocate the residents and businesses, clear the site, build new roads and utilities, and turn the land over to private developers.
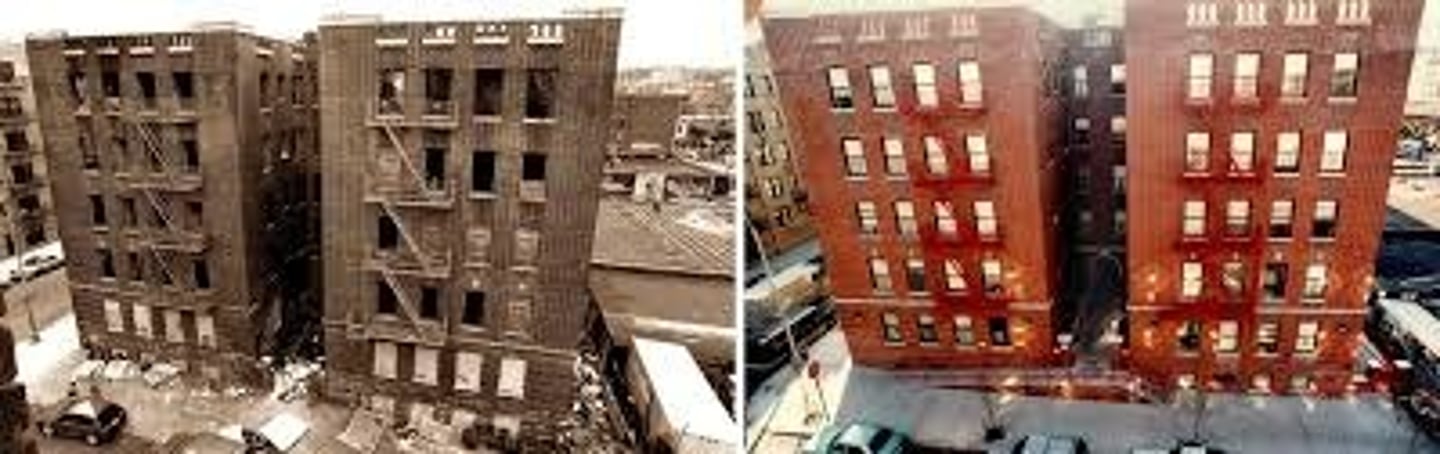

Vertical Geography
Building up a city instead of out, like tall buildings.

Zones of Abandonment
areas that have been deserted in a city for economic or environmental reasons
