Exercise 20: Electrical Conductivity of the Heart
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
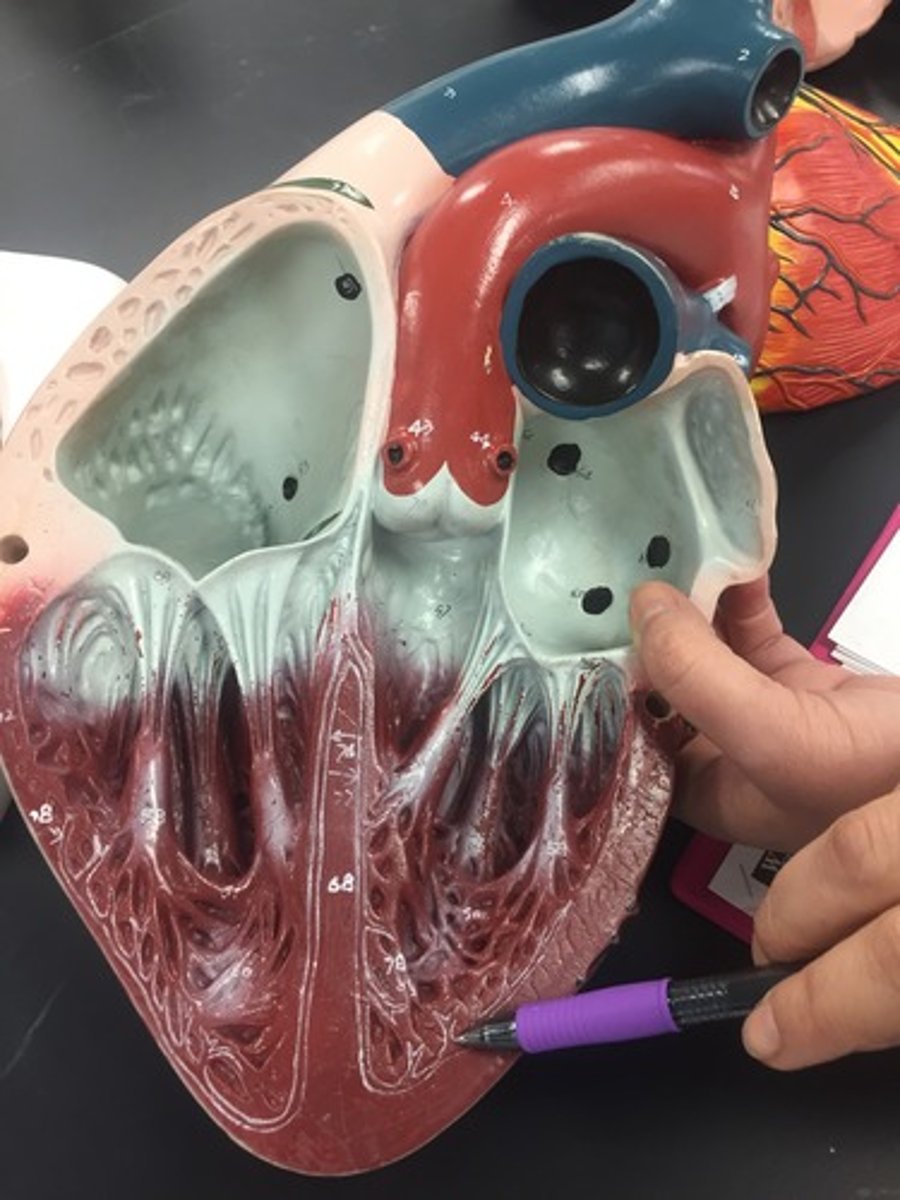
Conduction System
Generates and coordinates the action potentials that control the heartbeat.
Sinoatrial node
superior margin of the right atrium, pacemaker
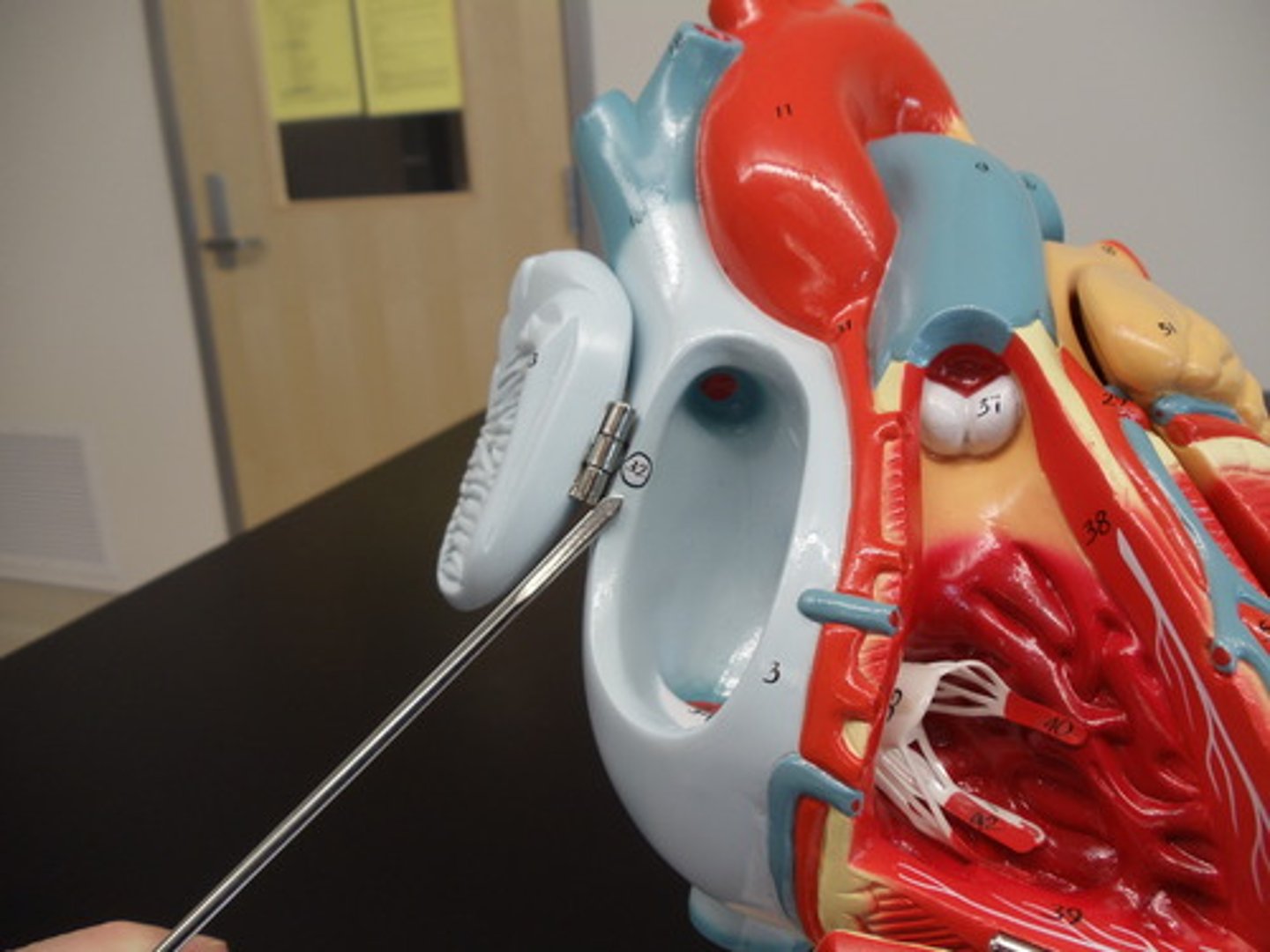
Atrioventricular node
Cluster of specialized cardiomyocytes located in the inferior margin of the right atrium, near the opening of the coronary sinus. Gatekeeper of electrical signal from atria to ventricles.
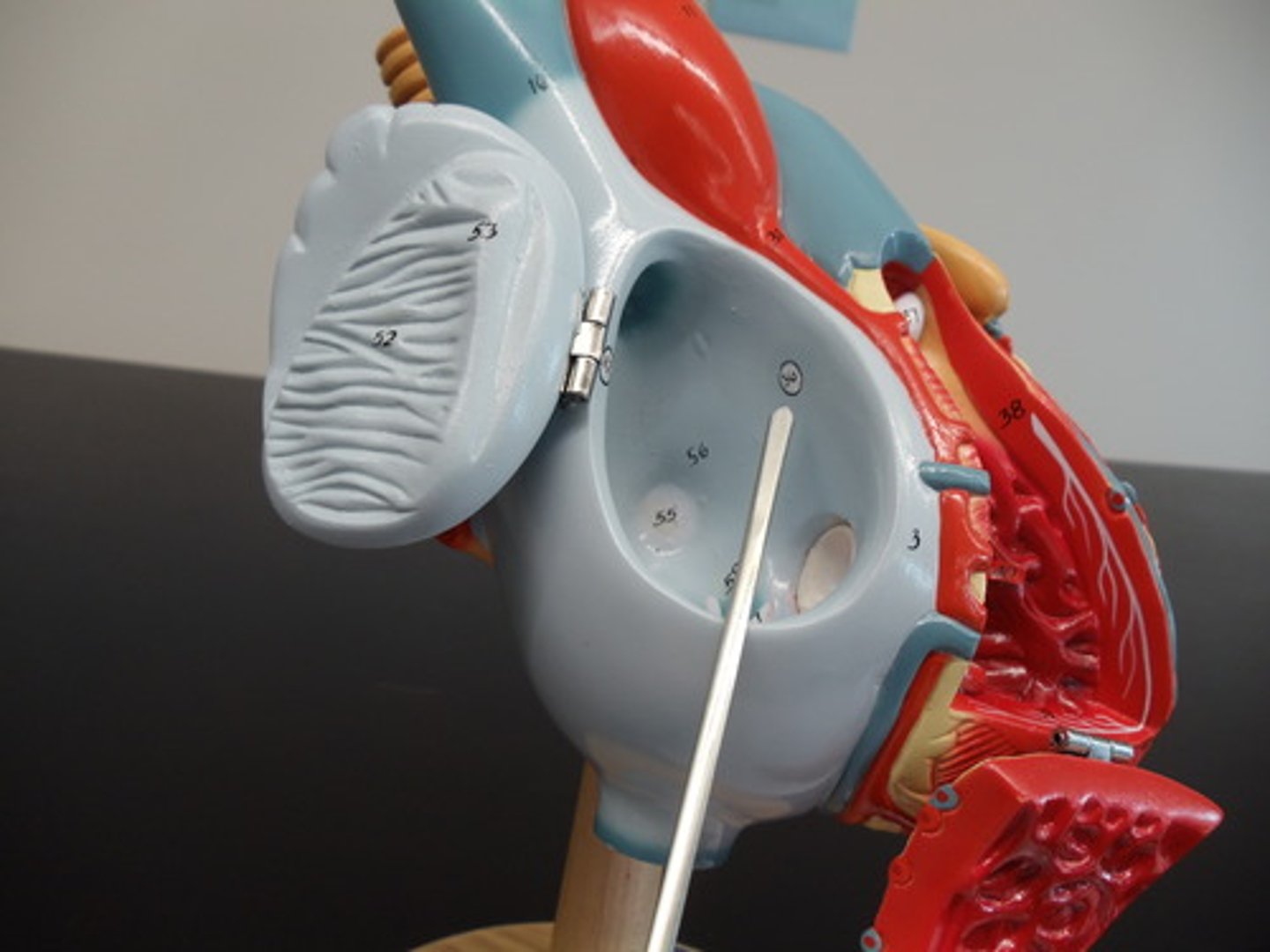
Atrioventricular bundle (Bundle of His)
cardiomyocytes that carries the action potential inferiorly through the interventricular septum to the apex of the heart.
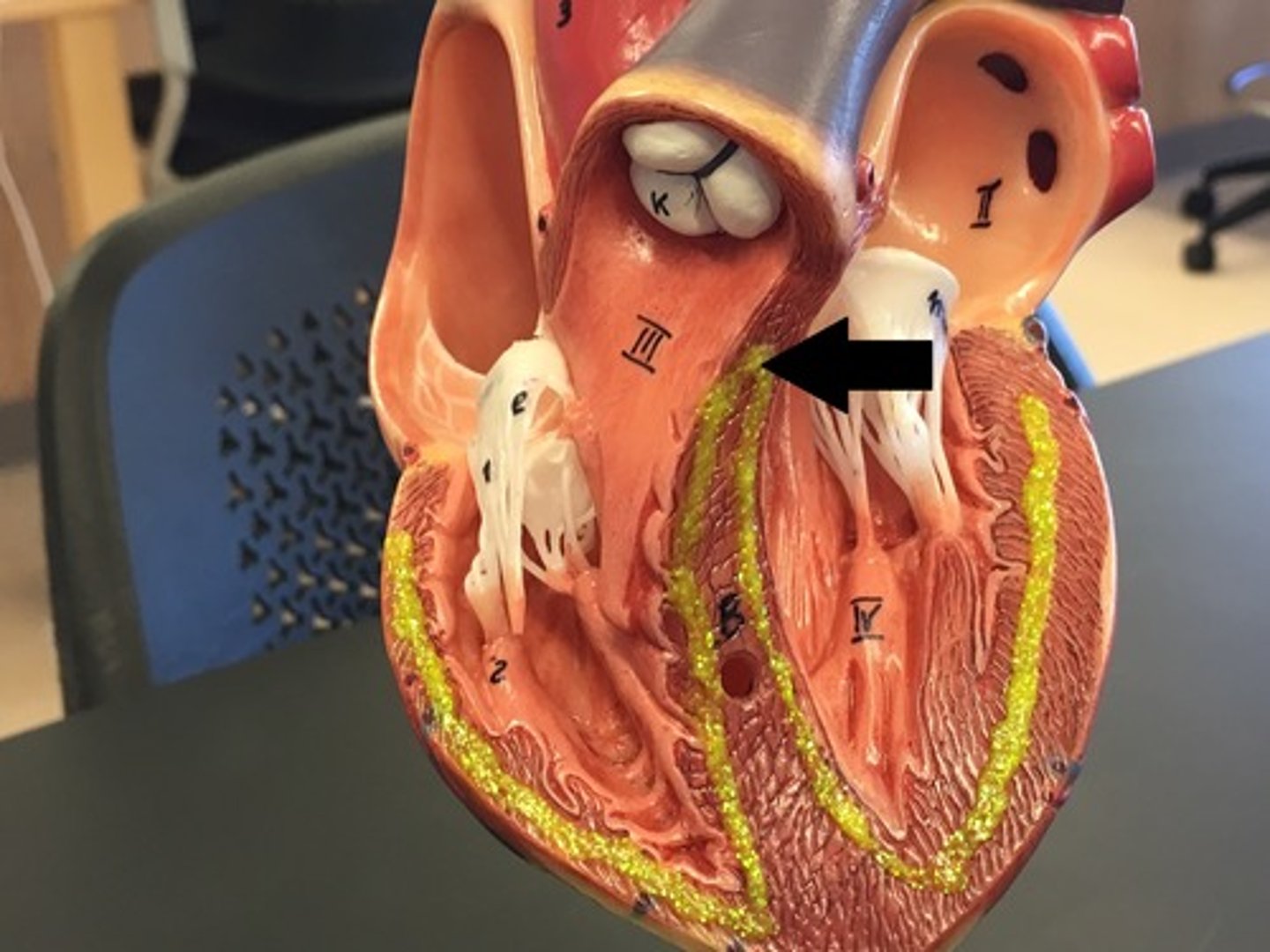
Bundle branch
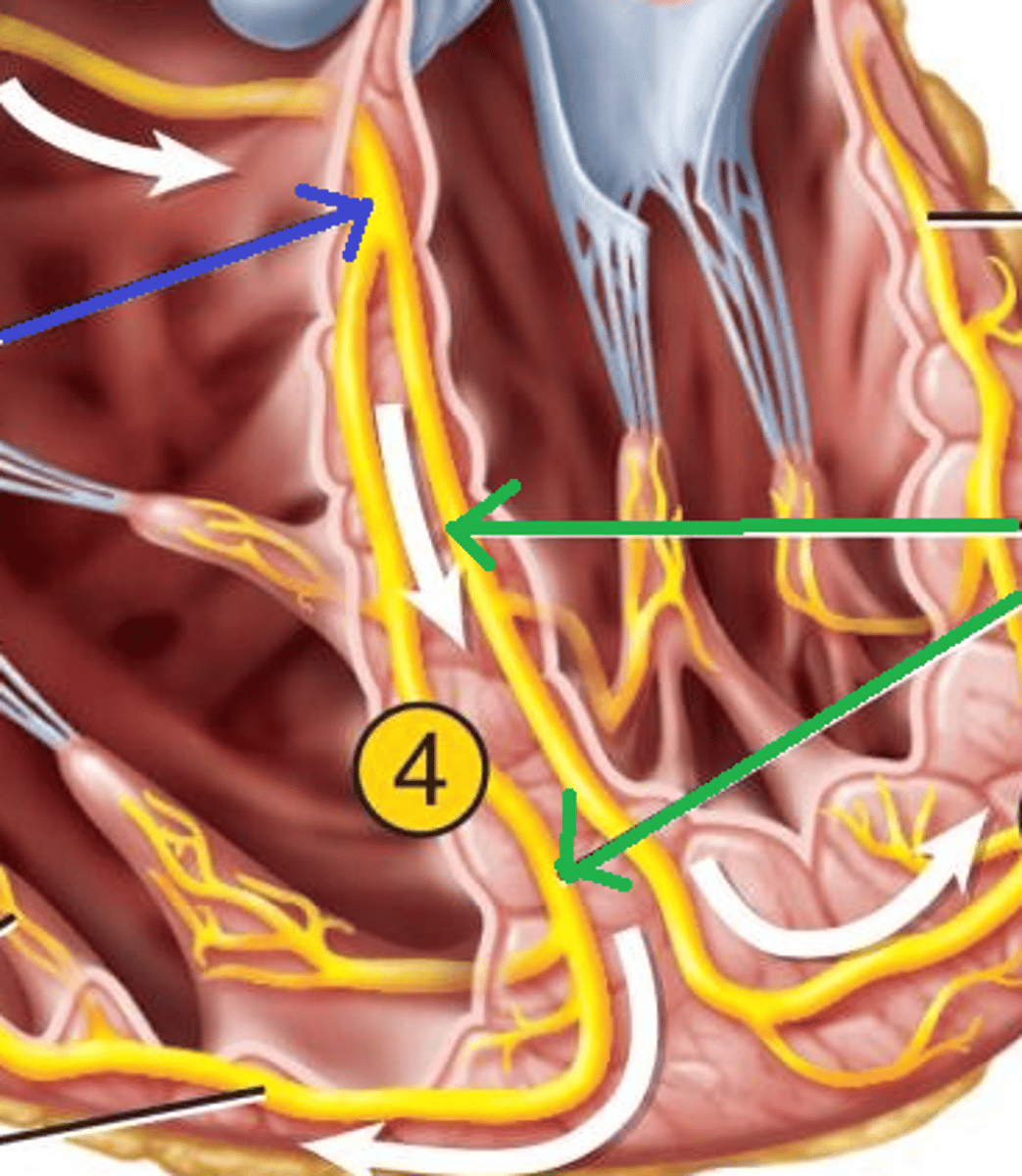
Purkinje fiber
branch out from the bundle branches and spread throughout the ventricles.
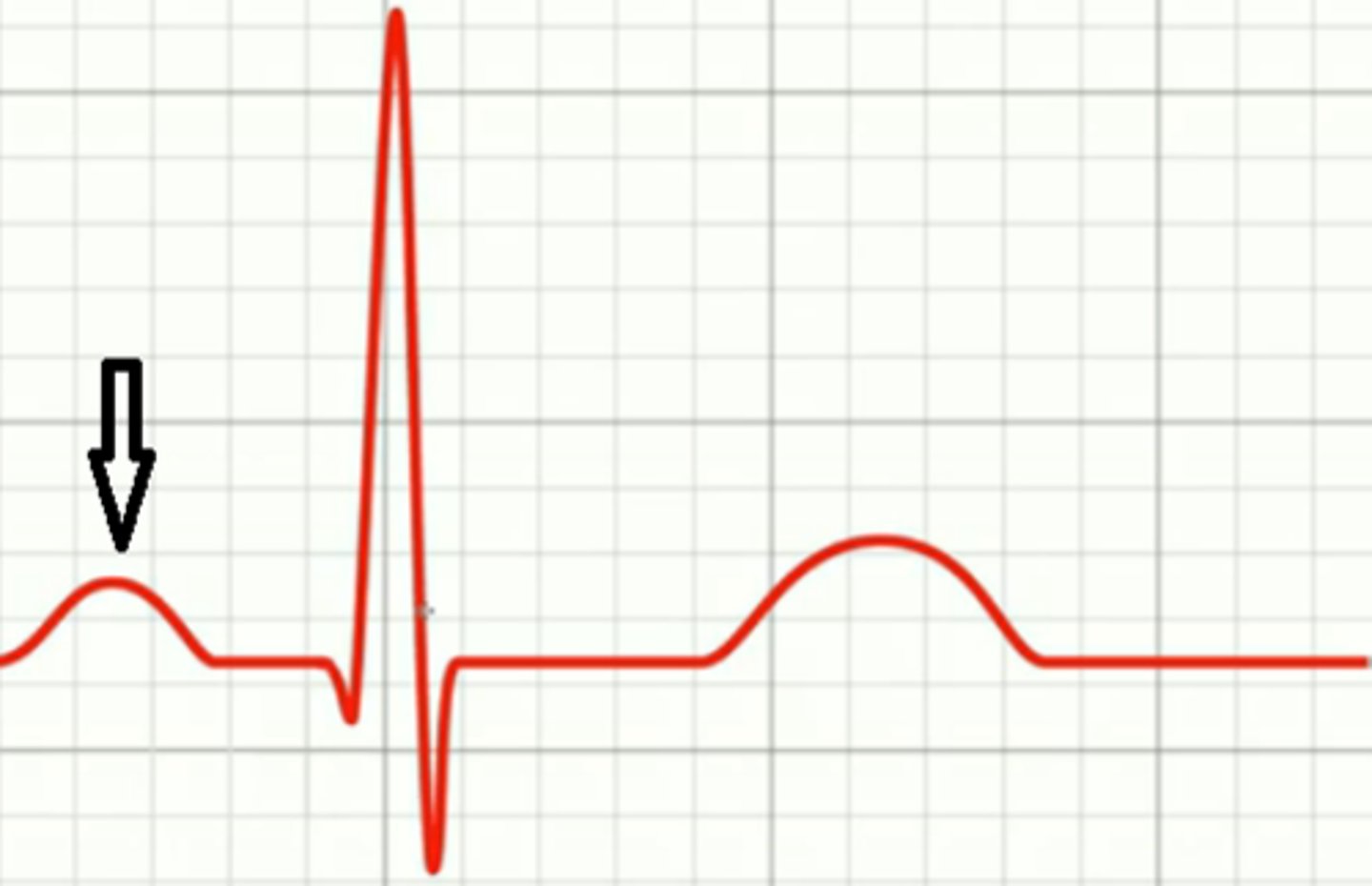
P wave
atria are depolarizing and contracting
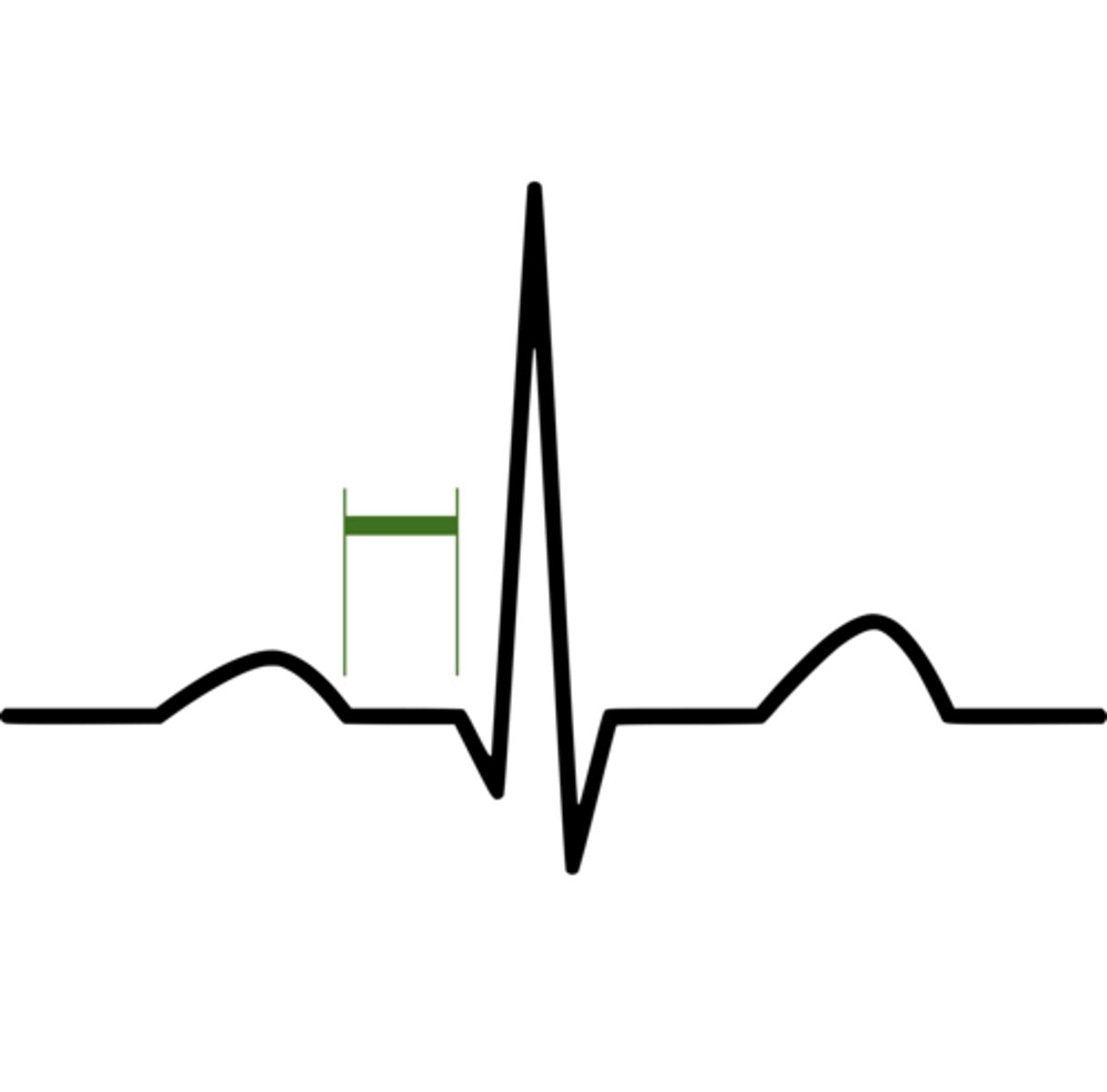
PQ segment (PQ interval)
end of atria diastolic period and ventricles are beginning of systolic phase
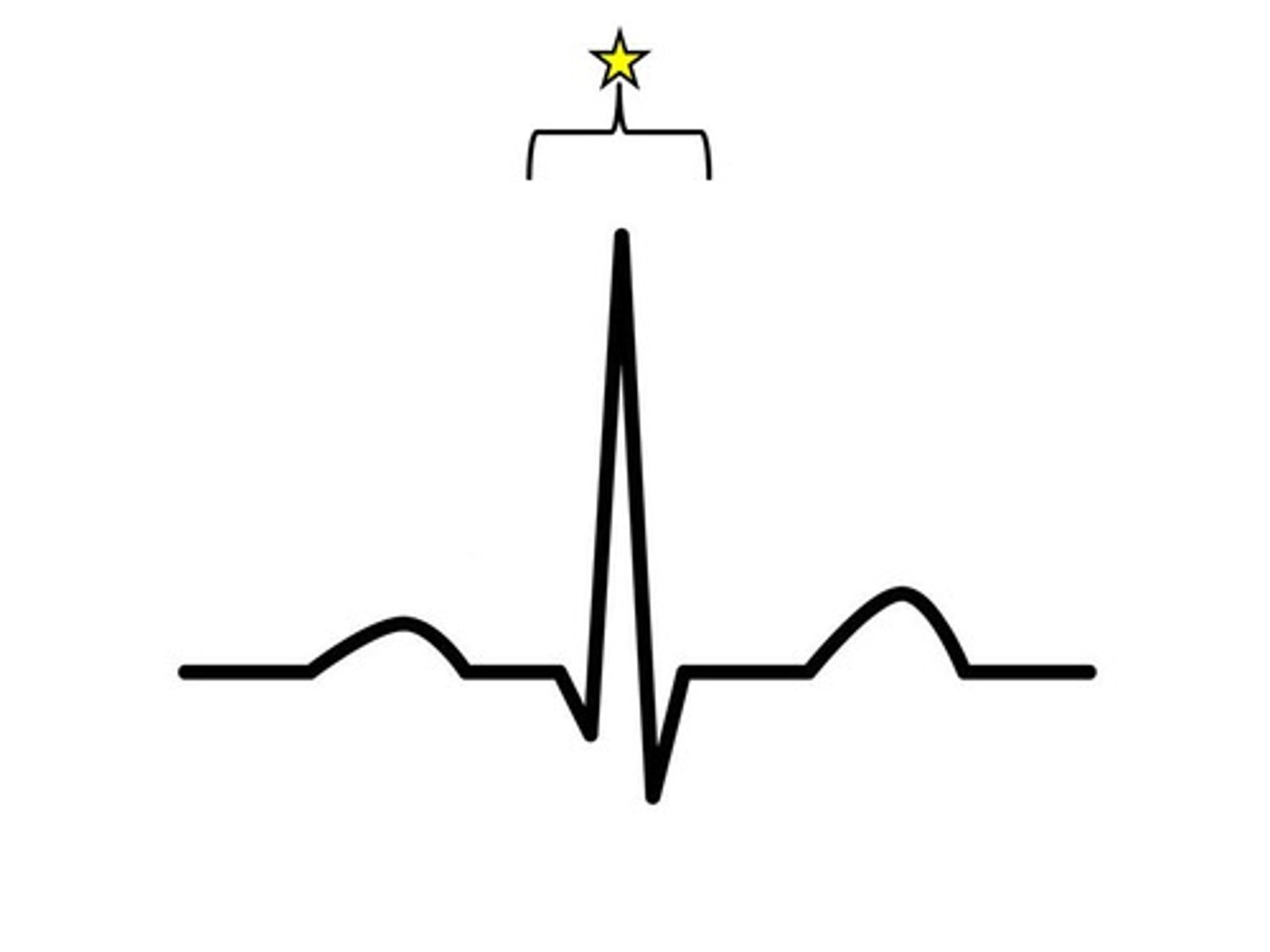
QRS Complex
During the beginning of the QRS complex the atria are repolarizing and relaxing. During the end of the QRS complex, the ventricles are depolarizing and contracting.
ST segment (ST interval)
Isovolumetric contraction, ventricles are between depolarization and repolarization
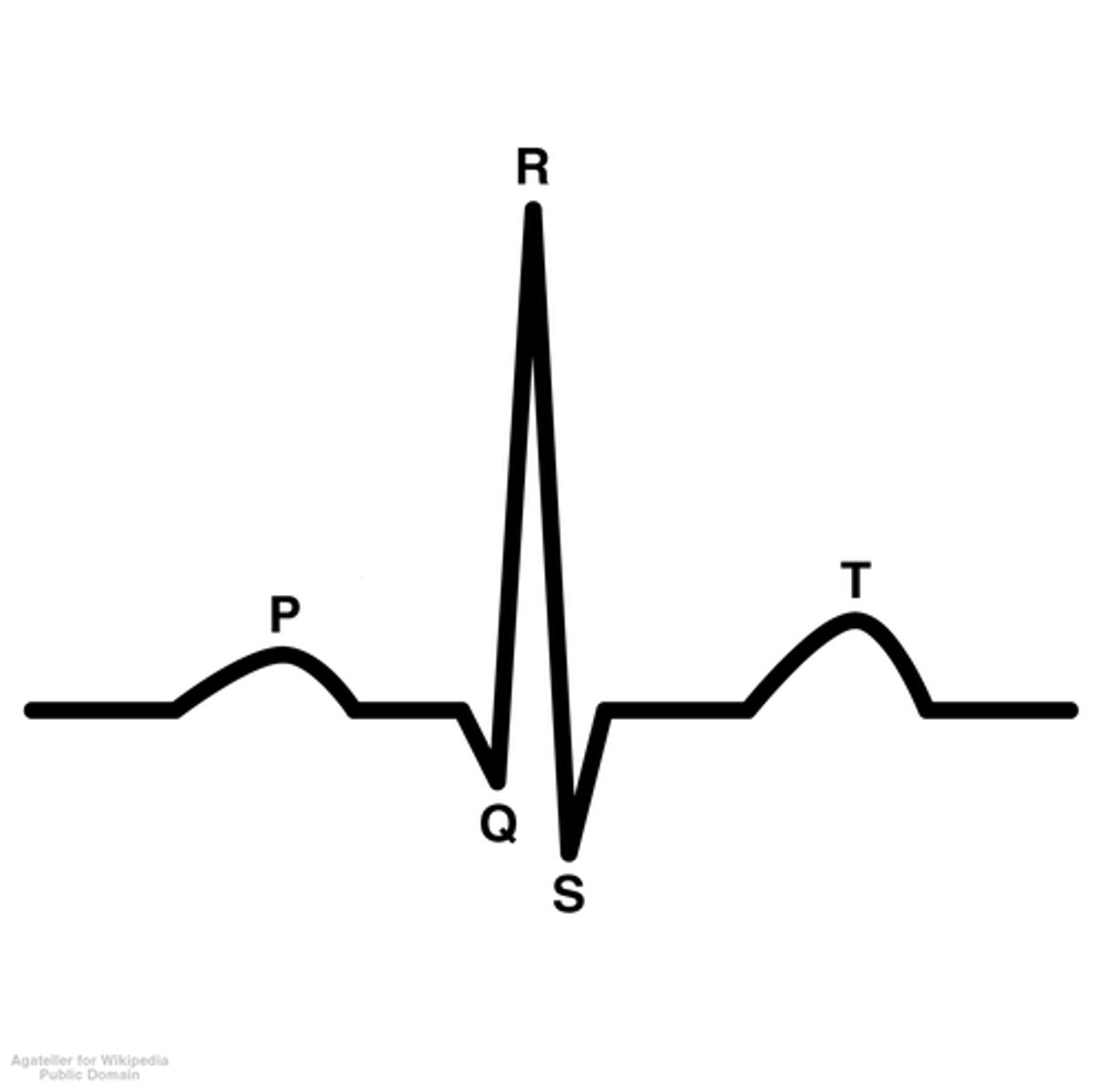
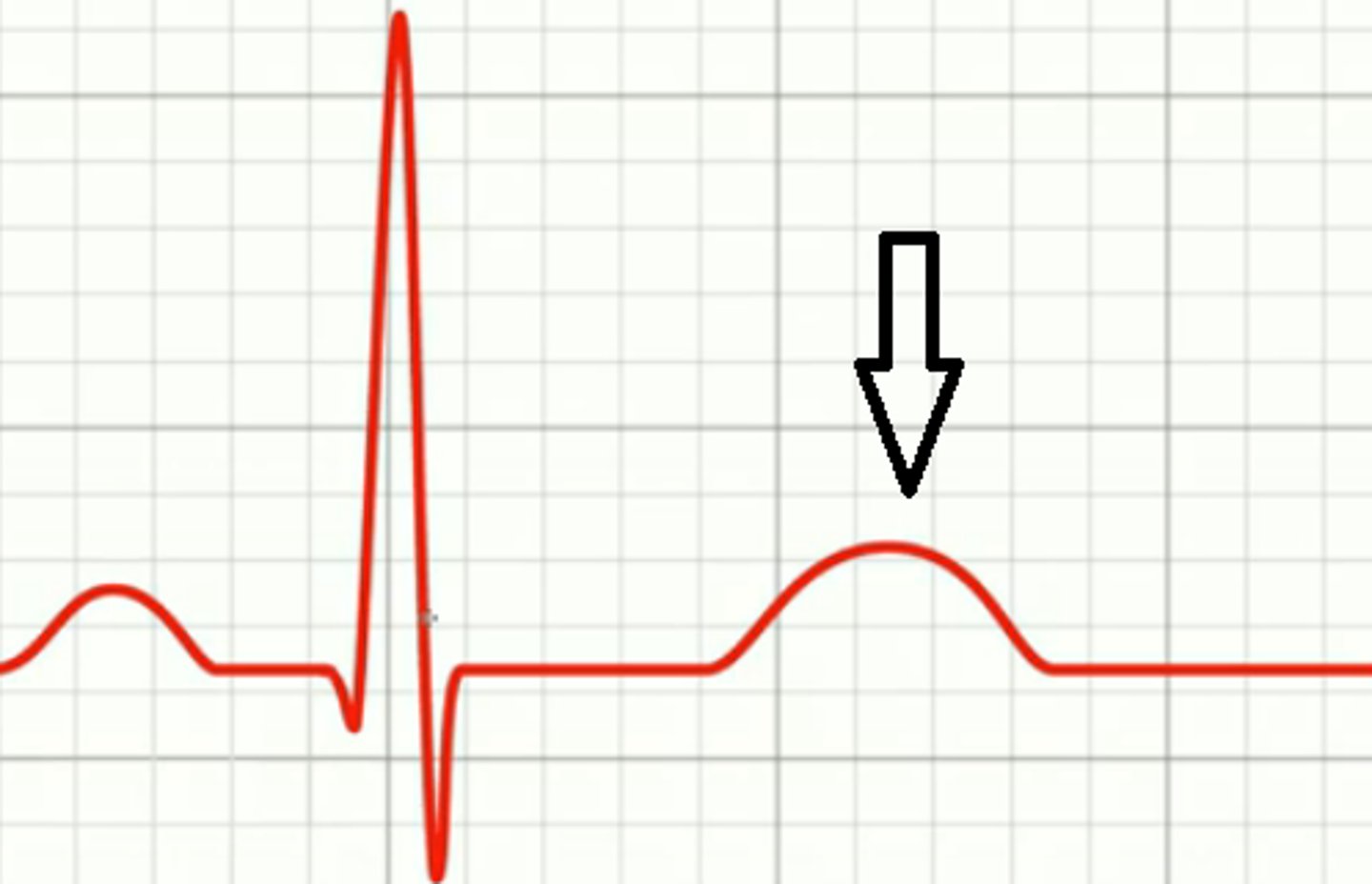
T wave
ventricles are repolarizing and relaxing
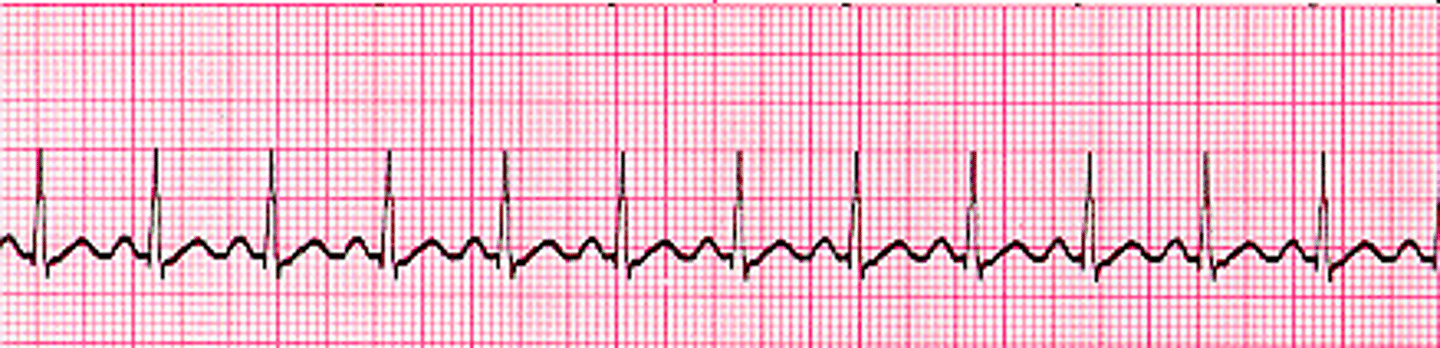
Tachycardia
high HR, 100-150 BPM. Caused by physical exertion, sympathetic stimulation, and fever.
Bradycardia
Low HR, less than 60 BPM. Vagus nerve stimulation, old age, opiates, and overconsumption of alcohol.
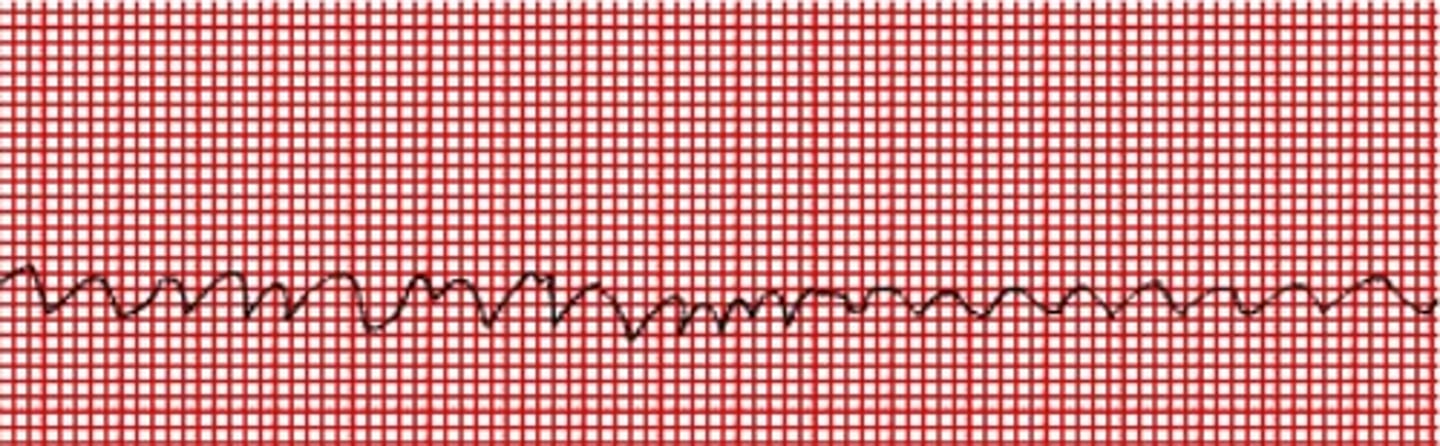
Fibrillation
rapid, irregular, and unsynchronized contraction of muscle fibers
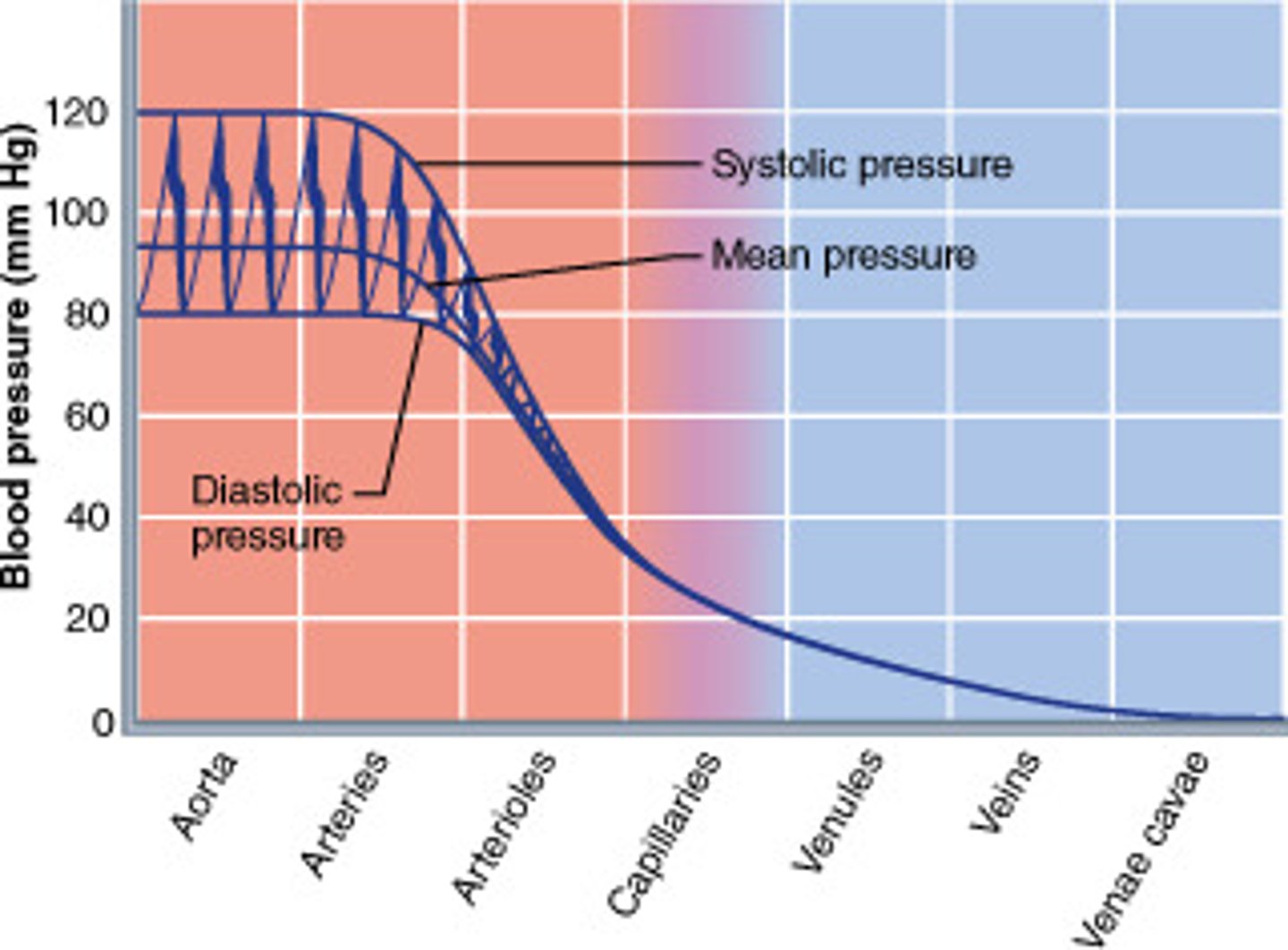
Blood pressure
the pressure that is exerted by the blood against the walls of blood vessels
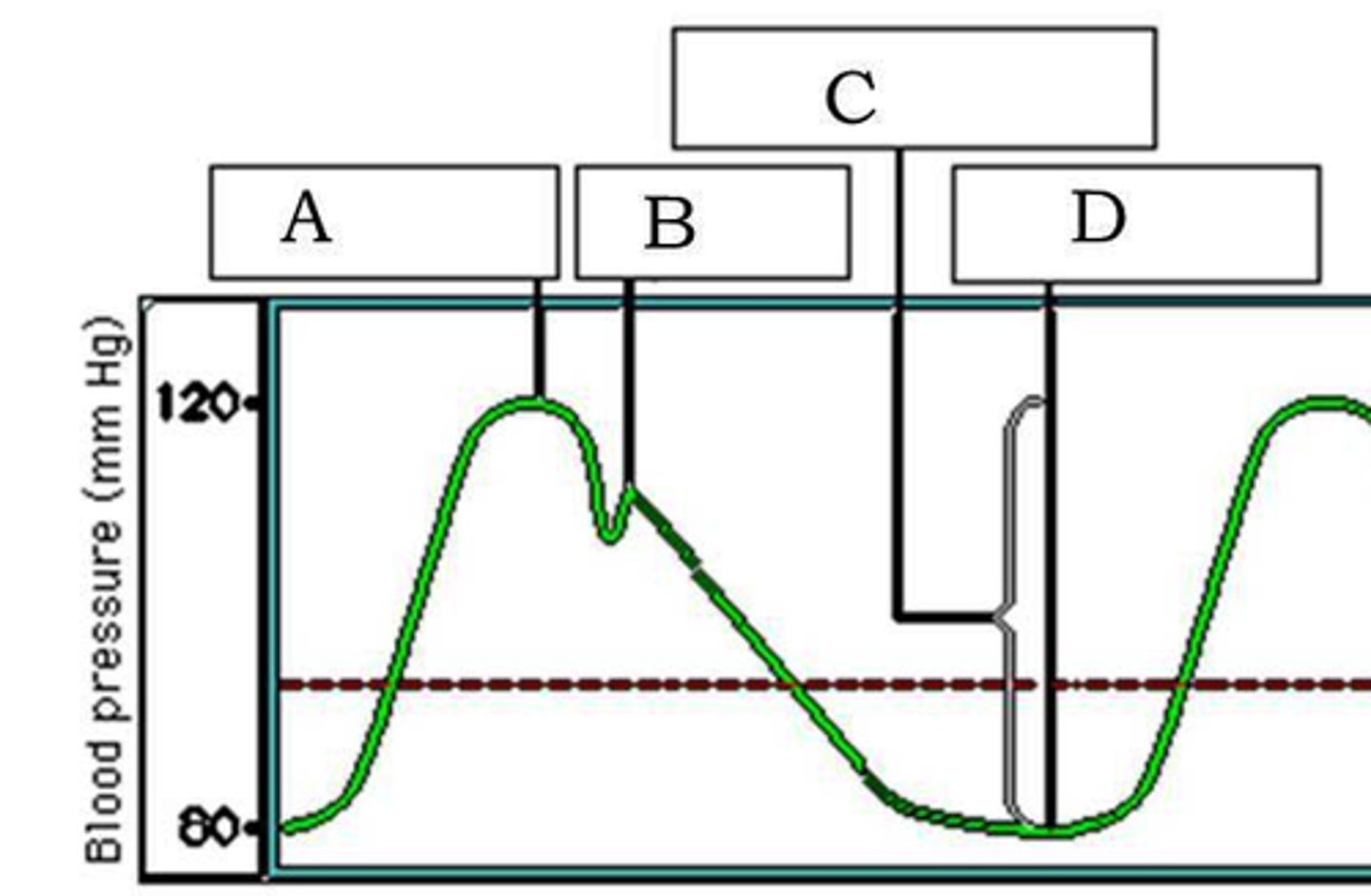
Systolic pressure
ventricle contraction (1)
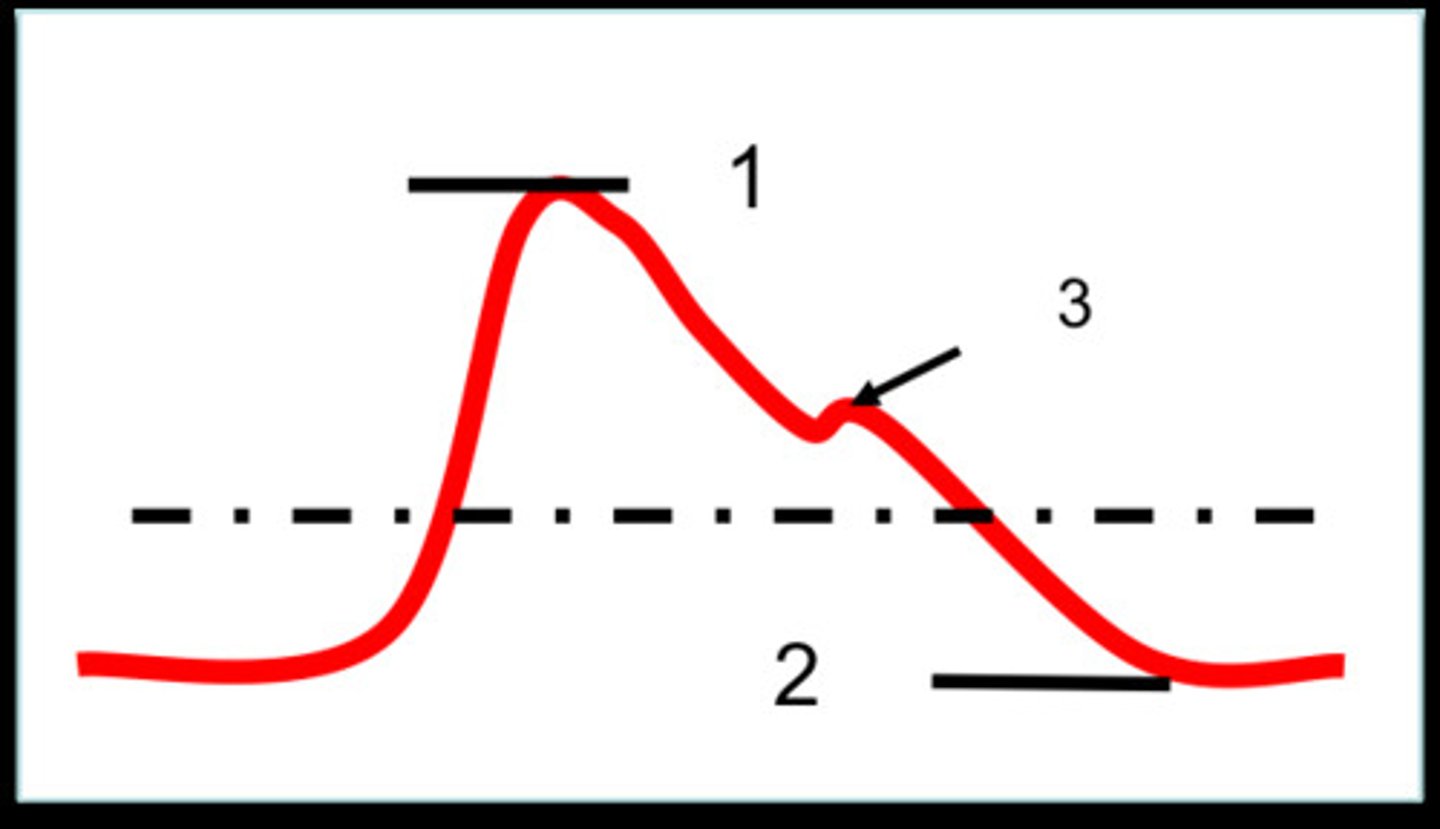
Diastolic pressure
ventricle relaxation (D)
Pulse Pressure
pulse pressure = systolic pressure - diastolic pressure
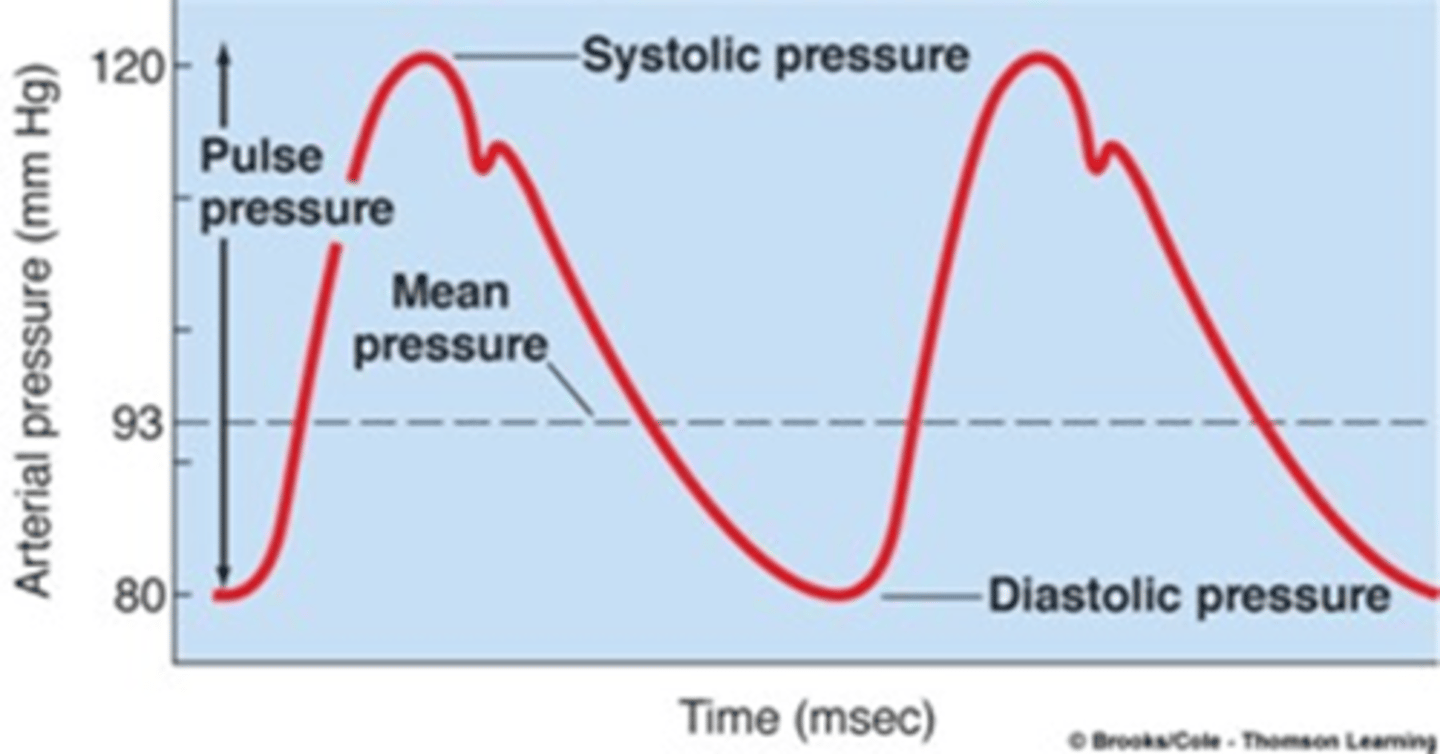
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
MAP= diastolic pressure + 1/3 (systolic pressure − diastolic pressure)
Sphygmomanometer
Korotkoff sounds
Sounds you listen for when taking BP, 1st is the systolic and last is the diastolic.
Procedure for measuring blood pressure
Baseline blood pressure
120/80