Nucleic acids
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
What are nucleotides made of?
Pentose sugar
Nitrogenous base
Phosphate group
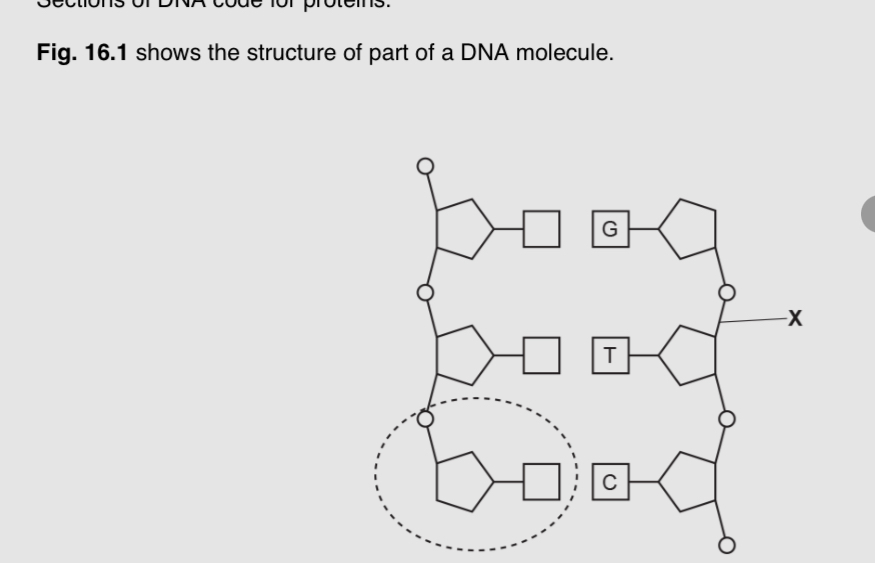
Name the components of this nucleotide
EQ
Guanine
Deoxyribose
Phosphate group
Identify 2 differences between a DNA nucleotide and a molecule of ATP
EQ
Both have adenine
Both have at least 1 phosphate group
How many phosphates does ATP have?
EQ
3
Explain how the pairing of nitrogenous bases allows identical copies of of DNA to be made
EQ
A bind to T
G binds to C
By hydrogen bonding
Purling can only bind with pyrimidine as they are different sizes
Draw a phosphodiester bond between 2 molecules
EQ
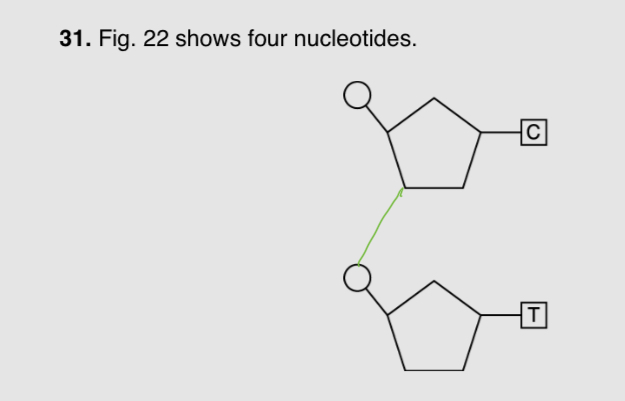
What base is present in ATP
EQ
Adenine
Explain why the mass of ATP in the body decreases near the end of the day
EQ
ATP broken down to provide energy for metabolic reactions
Similarities between DNA replication and Transcription
EQ
DNA unwinds And unzips by helicase
Template DNA in both
H bonds
Free nucleotides
Polymerase enzymes
Differences between DNA replication and transcription
EQ
Small section of DNA unzips in transcription but both strands act as templates during replication
RNA in replication DNA in transcription
RNA polymerase in replication DNA polymerase in transcription
Different helicase enzymes
What does DNA replication form
EQ
2 new daughter strands
That remain bound to the template strand
What does transcription produce
EQ
1 mRNA strand that leaves the nucleus
State 2 enzymes involved in DNA replication
EQ
DNA polymerase
Helicase
Explain the meaning of the phrase semi conservative replication
EQ
DNA contains 1 original strand and one new strand
Function of DNA polymerase
EQ
Forms phosphodiester bonds
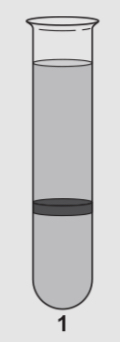
What is shown here
EQ
Shows how DNA contains nitrogen 14 and Nitrogen 15
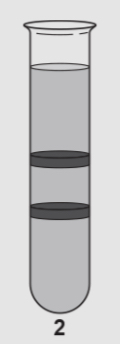
What is shown here
EQ
The highest band gets thicker because More DNA made from nitrogen 14
Outline how the process of DNA replication is completed
EQ
DNA polymerase
Condensation reaction between phosphate and sugar
DNA winds into double helix
Explain why a process know as transcription is necessary for polypeptide synthesis
EQ
DNA is too large to leave teh nucleus
So the gene is copied to mRNA
Explain how the genetic code in the gene for tubulin codes for the protein tubulin
EQ
Every 3 bases code for an amino acid
Non overlapping
Suggest 2 ways tubulin is essential to protein synthesis and protein secretion in eukaryotic cells
EQ
Movement of vesicles from rer to Golgi
Movement of mRNA from nucleus to ribosome
Why can’t pineapple juice be used as a substitute to protease enzyme?
EQ
It contains DNA
Do you always have to use a water bath in a dna extraction process
EQ
No
What does the salt do in dna extraction process?
EQ
Helps DNA precipitate
What type of membrane does detergent break?
EQ
ALWAYS say plasma membrane
A dna molecule contains 2 polynucleotide chains
Describe how theses 2 chains are held together
EQ
Phosphodiester bonds in backbone
Hydrogen bonding
Purine bonds to pyrimidine
Explain how the nucleotides in a dna molecule are arranged as 2 polynucleotide strands
EQ
Nucleotide adjoined by phosphodiester bonds
Hydrogen bonds between complementary bases
Antiparallel

D
Are ribosomes membrane bound?
EQ
No
Are mitochondria membrane bound?
EQ
Yes
Are lysosomes membrane bound?
EQ
Yes
Do purine bases always pair with pyrimidine bases?
EQ
Yes

A
What bond is present between 2 nitrogenous bases holding 2 polynucleotide chains together
EQ
Hydrogen
Do phosphodiester bonds break and reform during DNA replication?
EQ
No
Do hydrogen bonds break and reform during DNA replication?
Yes
Function of DNA polymerase
EQ
Make phosphodiester bonds between adjacent nucleotides
Evidence that DNA replication is semiconsservative
EQ
After one replication number of Adenine nucleotides is equal to the number of guanine nucleotides
After 2 replications two DNA molecules have one original and one new strand and 2 DNA molecules have 2 new strands
In what direction can DNA polymerase work?
EQ
From the 3’ end to the 5’ end
Means that the lagging strand has small gaps left in the backbone
DNA polymerase can only work From the 3’ end to the 5’ end
What does this mean for the lagging strand?
EQ
Small gaps left in the backbone
What seals the gaps in the lagging strand?
EQ
DNA ligase
Non-overlapping definition
EQ
Each nucleotide is only part of one triplet of bases
Degenerate definition
EQ
More than 1 triplet codes for a specific amino acid
How many nitrogen carbon rings does purine have?
EQ
2
Are lipids polymers?
EQ
No
What are lipids?
EQ
PolysaccharidEs
Are nucleic acids polymers?
EQ
Yes
Are proteins polymers?
EQ
Yes
What parts of a molecule bond to phosphate when phosphodiester bonds are formed?
EQ
OH
OH
Describe how a polynucleotide is formed from its monomers
EQ
Nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds in a condensation reaction
Describe the action of helicase
EQ
Unzips double helix
Breaks hydrogen bonds between 2 strands
Explain how errors may occur during DNA replication
EQ
Mutation
Change in DNA base sequence
What does salt do in DNA extraction process
EQ
Breaks hydrogen bonds between dna and water
What does ethanol do in DNA extraction process?
EQ
Precipitate out dna
What does the detergent do in DNA extraction investigation?
EQ
Breaks down the plasma membrane
Why is ice cold ethanol used during the DNA extraction process
EQ
Reduces enzyme activity
What forms phosphodiester bonds?
EQ
Deoxyribose
Phosphate
Is ADP a nucleotide?
EQ
Yes
State the role of DNA polymerase
EQ
Catalyses the formation of phosphodiester bonds
Suggest how a mutation in the cytoskeleton genes could cause a disease of the nervous system
EQ
Change in structure of protein
Affects speed of nerve impulses
What enzyme hydrolyses DNA
EQ
Protease
Outline the role of RNA polymerase in the production fo mRNA sequence
EQ
Joins nucleotides
Forms phosphodiester bonds
Suggest why modified proteins last longer
EQ
Change in primary structure means change in tertiary structure
No longer complementary to enzymes
Transcription + translation
EQ
From gene to when polypeptide is made
Transcription produces mRNA
mRNA leaves nucleus
Translation at ribosomes
tRNA with specific amino acids binds to its anticodon
What enzyme joins nucleotides together
EQ
RNA polymerase
What is a ribosome made of
EQ
RRNA
Protein
What brings the specific amino acids to be joined at the polypeptide?
EQ
TRNA
What elements do nucleotides contain elements?
H
O
N
P
C
What type of acid are DNA and RNA?
Nucleic acids
What is DNA used for?
Store genetic information
Function of RNA
Make proteins from instructions in DNA
What type of sugar does DNA contain?
Deoxyribose a type of pentose sugar
What are ADP and ATP used for?
To store and transport energy in cells
Does each DNA nucleotide have the same phosphate group
Yes
Name the 4 bases
Cytosine.
Guanine
Thymine
Adenine
How many polynucleotide chains does DNA contain?
2
What sugar is in nucleotides in RNA
Ribose sugar
In RNA …… replaces thymine
Uracil
How many polynucleotide chains does RNA contain
One
What type of bases are adenine and guanine
Purines
What type of bases are cytosine uracil thymine?
Pyrimidine
What does a purine base contain?
2 carbon nitrogen rings
What does a pyrimidine base contain?
One carbon nitrogen ring
Which is smaller
A pyrimidine base or purine base
Pyrimidine base
What type of nucleotides are ADP or ATP
Phosphorylated Nucleotides
How do you phosphorylate a nucleotide
Add one or more phosphate groups
What bases does ADP contain?
Adenine
Ribose sugar
2 phosphate group
What does ATP contain?
Adenine
Ribose sugar
3 phosphate groups
Why is ATP used instead of the pure energy?
Cells can’t get its energy directly from glucose
What is ATP used for
Provide energy for chemical reactions
What is ATP synthesised from
ADP and inorganic phosphate
How is ATP made from ADP
ADP is phosphorylated to form ATP
So phosphate bond is formed
How is energy used from a cell
ATP broken down to ADP and inorganic phosphate
Energy released from phosphate bond
What do nucleotides join together to form
Polynucleotides
How do nucleotides join together
Join by phosphate group of one nucleotide and sugar of another via condensation reaction
Form phosphodiester bond
How can phosphodiester bonds be broken
Hydrolysis
What shape do polynucleotide strands join to form
Anti-parallel strands
Double helix
How do the strands join together
Hydrogen