Topic 11: Strategy and Organisation of International Firms
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are the different motivations for internatilisation
traditional and emerging
What are traditional motivations for internalisation
resource seeking motive, market seeking behaviour
What are the emerging motivations for internalisation
more integration, global scanning and learning capabiloity, compettive positioning
What is strategic positioning
selecting a competitive strategy with a value proposition that is either low cost, differentiated or both and configuring internal operations to support that strategy
Waht are the determinants of enterprise vlaue
probability (reduce costs and add vlaue and raise prices) and profit growth (sell more in existing markets and enter new markets)
How to value creation
R and D, production, amrketing sales, after sales service and support
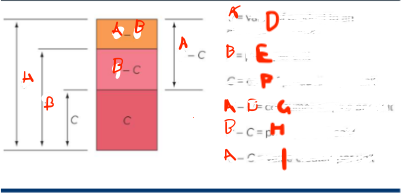
What is A
value of a product to an average consumer
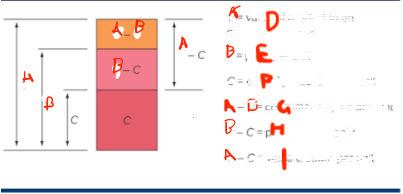
What is B
price per unit
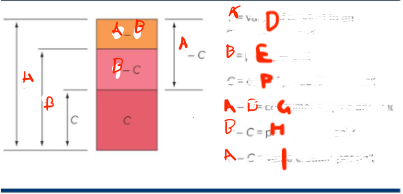
What is C
cost of production per unit
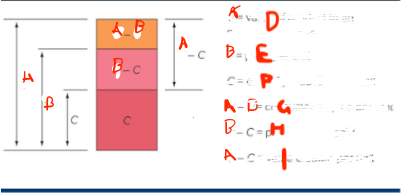
What is G
consumer surplus p
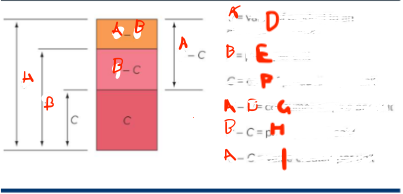
What is H
profit per unit sold
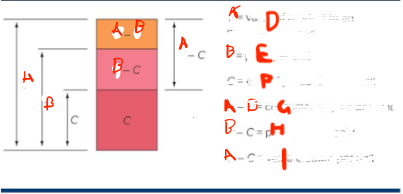
What is I
value created per unit
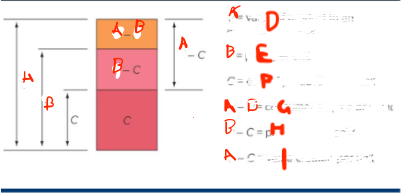
What do you want
for the smallest A - B
What is in the middle of organisational architecture
people
what is the outaide of the orgnaisational architecture
processes, structure, incentives and controls, culture
What are the three dimensions of organisational structure
vertical differentiation, horizontal differentiation and the estbalishment of integrating mechanisms
What is vertical differentiation
the location of decision-making respionsibilties within a structure - either centraliused or decentralised
What is horizontal differentiation
the formal divison of organisation into sub-units
What is the estbalushment of integrating mechanism
the mechanism for coordination of sub-units
What are the differetn types of control systems in an internatinal company
personal, bureacratic, output, cultural
What is prsonal controls example
personal contract between subordinate staff
bureacratic controls example
rules and procedures, budgets, delegations
output controls exmaple
performance metrics such as sales and profit targets
cultural controls example
norms and values that employees enter
Types of controlsystems in an international company - the negative impact on the flow of information between headwuarters and subsidiairies
geographic distance, cultural distance, differing frames of reference between these two organisational units
What is orgnisational culture
the values and norms that employees are encouraged to follow
How can organisational culture be maintained
hiring and promotional practices, reward strategies, socialisation processes, communication strategies
What is the strategic fit
operations strategy and ogranisation architecture should support strategy which fits into the market conditions
How can the international firms incrase profitability and profit growth
exapanding their market, realising location economies, exploiting greater cost economies from exeprience effects, transferring valuable skills within the firm
What are the business level strategy
cost leadership, differentiation, focus
Business level strategy - cost leadership
appeal to the average customer, strong focus on manufacturing and materials management functions e.g. Bunnings
Business level strategy - differentiation
many niches of market segmentation, uniqueness through quality, innovation and customer responsiveness e.g. Ferrari
Business-level strategy - focus
specialisation in a particular niche market (by geographic region, type of customer or segment of product line)
What are the two comptitive pressures that exist in the global marketplace
pressures for cost reduction, pressures to be locally responsiveness
What pressures for cost reductions are the greatest
producing commodity type poroducts that fill universal needs where price is the main competitive weapon, when competitors are low-cost locations, persitstent excess capacity, consumers are powerful and face low switching costs
When are the pressures for local responsivenes the greatest
differences in consumer tastes, traditional practices and infrastructure, distribution channels, host government demands, rise of regionalism
What should be done if pressure for cost reduction and pressure for local responsivessness low
international strategy
What should be done if the pressure for cost reduction is high and the local responsiveness for lows
global standardisation strategy
What if cost reduction is low but local respionsiveness is high
localisation strategy
What is cost reduction is high and local responsiveness is high
transnational strategy