CEEN 5550 - Water Resources - 2nd Exam
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Types of Systems
Natural, Social, and Abstract
How is what’s included in a system determined
Depends on how we define the system.
What is Systems Thinking
Solving complex, dynamic, ill-defined problems
Designing systems as well as components
Communicating with the wider community
Working with people from various disciplines and cultures
Meeting social, ethical, and environmental responsibilities while addressing challenges from engineering and science.
Managing projects and operating within business and political environments.
Three Tools for System Thinking
Rich Picture Diagrams
Casual Loop Diagrams
Behavior-over-time Graphs
Rich Picture Diagram
Uses diagrams to explore a situation or system, creating a mental model.
Pictures, Connections, Facts, Subjective Info, Conflict, Structure, and Process
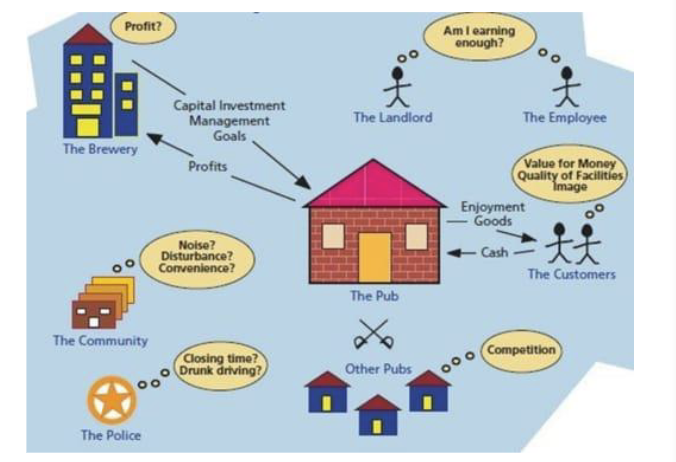
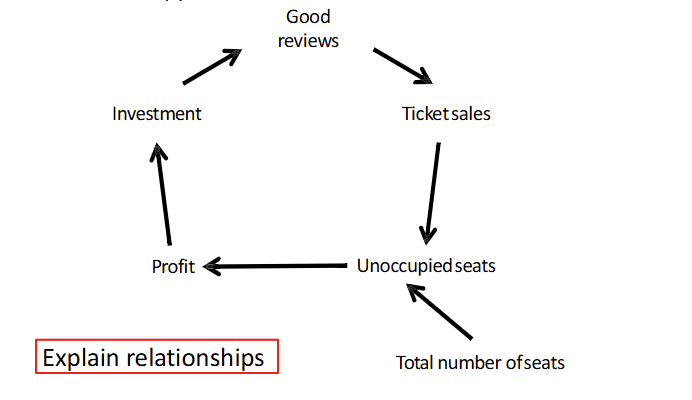
Casual Loop Diagram
Explains the relationships between different variables in a system and how one variable can influence another which can drive feedback loops.
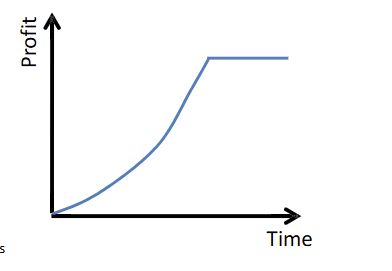
Behavior-over-time Graphs
A line graph showing how a variable changes across a period of time. Can sketch trends in data.
Why use modeling?
Predict System Behavior
Test Scenarios Safely
Support planning and decision making
Types of Water Resource Models
Hydrologic
Hydraulic
Urban Stormwater
Watershed & Water Quality
Planning & Allocation
Hydrologic Modeling Application
Rainfall - runoff
Hydraulic Modeling Application
River flow, floodplain
Urban Stormwater Modeling Application
Sewer systems
Watershed & Water Quality Modeling Application
Land use impacts
Planning & Allocation Modeling Application
Supply-demand
Modeling Process (6 Steps)
Define Problem
Set system boundaries
Collect Data
Build & Calibrate the model
Run Scenarios
Interpret results
HEC-HMS Applications
Watershed-scale hydrologic modeling for both rural and urban areas.
Flood forecasting and analysis, including design storms and historical events.
Storm water management and infrastructure design.
Climate change and land use impact studies on hydrology
HEC-HMS Outputs
Hydrographs
Peak discharge and volume
Rainfall-runoff relationships
Water balance components: Precipitation, Infiltration, Evapotranspiration
Scenario comparisons
HEC-HMS Data Required
Watershed Geometry
Meteorological Data
Land Surface Characteristics
Hydrologic Parameters
Calibration / Validation Data
HEC-HMS Loss Method: SCS Curve Number
Empirical method used to estimate direct runoff from rainfall events.
HEC-HMS Transform Method: SCS Unit Hydrograph
Empirical method used to transform excess precipitation into direct runoff hydrographs.
HEC-HMS Basin Model Creation Steps
Create a new project
Create a new basin model
Add hydrologic elements to the basin model
Select modeling methods
Parametrize modeling methods
HEC-HMS Components
Basin Model Structure
Meteorological Model Inputs
Control Specifications
Simulation Execution
Hydraulic Model
A mathematical representation of a water/sewer/storm system and is used to analyze the system’s hydraulic behavior.
Hydraulic Model Types
1D - Flow is one dimensional in both channel and floodplain
2D - Flow is two dimensional in both channel and floodplain
1D/2D - Combined 1D/2D, 1D in channel and 2D in floodplain
3D - Flow is considered 3D in both channel and floodplain
HEC-RAS Purpose
HEC-RAS models hydraulics of water flow through rivers and channels.
HEC-RAS Applications
Floodplain Management
River Engineering and Design
Dam Break Analysis
Environmental Modeling
HEC-RAS Components
Geometry Data
Flow Data
Boundary Conditions
Plan Files
Manning’s Roughness Coefficient (N)
A coefficient representing surface roughness and resistance to flow.
Steady Flow
Flow parameters do not change with time.
Unsteady Flow
Flow parameters change with time.
HEC-RAS Boundary Conditions
Inputs that define how water enters and exits the modeled system.
HEC-RAS Data Requirements
Topographic Data
Hydrologic Data
Land Use and Infrastructure
HEC-RAS Modeling Steps
Import terrain and geometry
Define river reaches and cross-sections
Add hydraulic structures (if needed)
Input flow data and boundary conditions
Run simulations and analyze results
Stormwater Modeling Purpose
Simulates stormwater movement and quality in urban areas to manage flooding and pollution.
SWMM Purpose
Models stormwater runoff quality and quantity for urban areas using dynamic simulations.
SWMM Applications
Design and sizing of drainage system components including detention facilities
Flood plain mapping of natural channel systems
Control of combined and sanitary sewer overflows
Generating non-point source pollution loading for wasteload allocation studies
Evaluating BMPs and LIDs for sustainability goals
SWMM Limitations
Not applicable to large-scale, non-urban watersheds
Not applicable to forested areas or irrigated cropland
Cannot be used with highly aggregated rainfall data
It’s an analysis tool, not an automated design tool
SWMM Components
Rainfall and Evaporation Inputs
Subcatchments
Drainage Network
Flow Routing and Water Quality
SWMM Required Data
Rainfall and Land Use Data
Soil Characteristics
Drainage Network Layout
Water Quality Parameters
SWMM Modeling Steps
Project Area and Base Maps
Subcatchments and Drainage Network
Climatic Data and Simulation Parameters
Simulation and Validation
Watershed & Water Quality Modeling Purpose
Simulates precipitation, infiltration, runoff, and streamflow in watersheds
SWAT Purpose
Predicts environmental impacts of land management on water and sediment in watersheds.
SWAT Applications
Water Quality
Agricultural Impacts
Watershed Management
Climate Studies
SWAT Limitations
Need extensive data and calibration; less precise for small-scale hydrological processes.
SWAT Components
Weather Generator
Hydrology
Soil erosion
Sediment Transport
Nutrient cycling modules
SWAT Required Data
DEM,
Land Use
Soil Properties
Detailed Climate Data
SWAT Modeling Steps
Defining Watershed Boundaries
Inputting Spatial and Temporal Data
Calibrating and Validating Model
Applying SWAT for Predictions