cels199 module 1 lecture 2
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
what are most cells and organelles measure in?
micrometres (μm)
what is the cells range for eukaryote cells?
10-100μm
what are the sizes of prokaryote cells?
less than 5μm
what are the size ranges for organelles (mitochondrion and chloroplast))
mitochondrion: 1-10μm, chloroplast: 2-5μm
What are the components of cells and organelles measured in?
Nanometres (nm)
Size range of ribosomes
25 - 30 nm
Size range for membrane
7- 8 nm
Size range for microtubules
25 nm
Size range for microfilaments
7nm
Size range for DNA helix
2 nm

Name this macromolecule
Carbohydrates
Name this macromolecule
Proteins
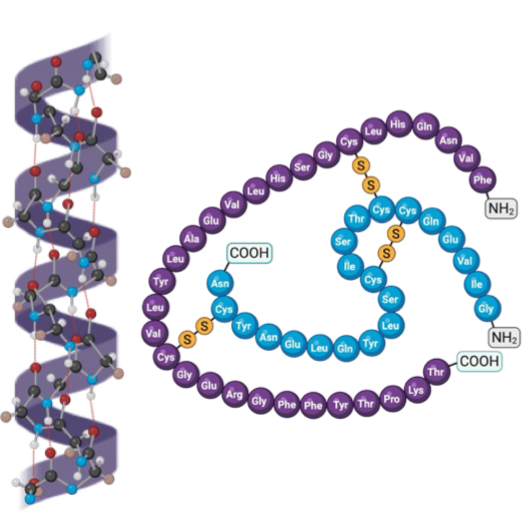
Name this macromolecule
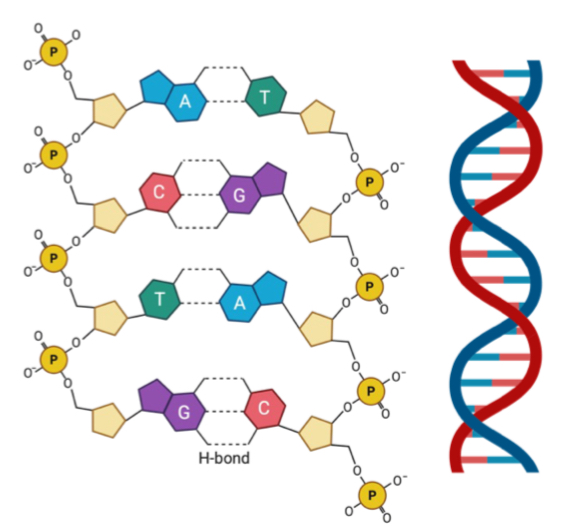
Nucleic acids
What do the structures of carbohydrates, proteins and nuclei acids have in common?
On a molecular scale they are macromolecules (ie very large), they are all polymers made up of monomers, and they are all consistent in structure
How are lipids different from carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and proteins?
They are smaller on a molecular scale, do not form polymers, include a diverse range of structures (heterogeneous)
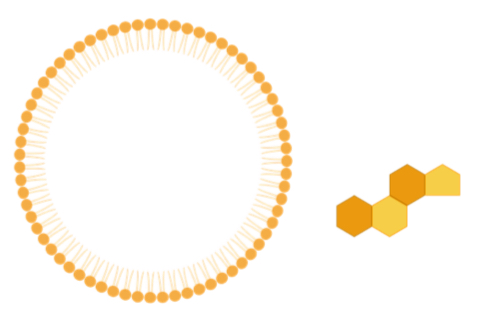
Name this macromolecule
Lipid
What polymer do nucleotides form?
Polynucleotides
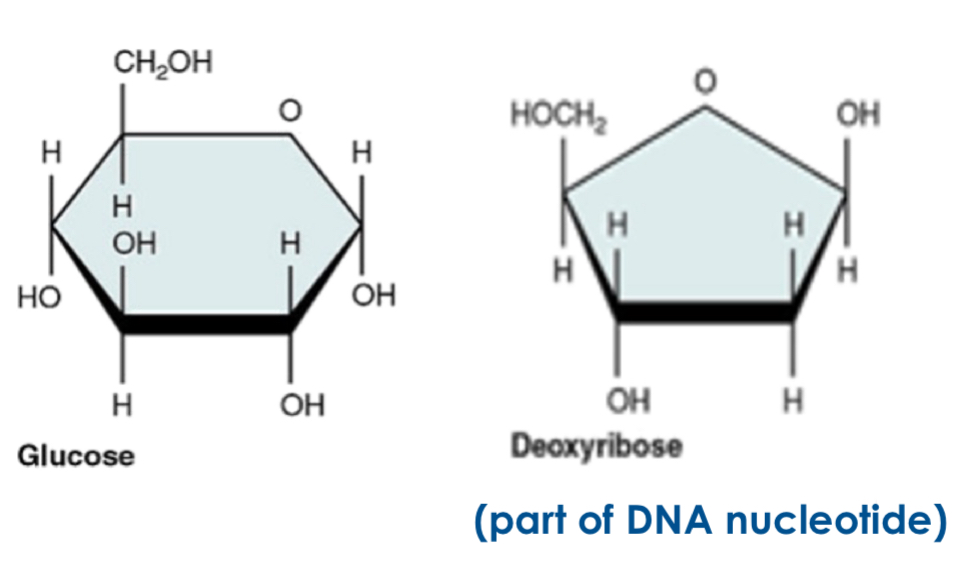
What are the monomer subunits for carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides (simple sugars: mono = one, saccharide = sugar)
What are some examples of monosaccharides?
Glucose (hexose sugar) and deoxyribose (pentose sugar)
What are polymers of monosaccharides called?
Polysaccharides
What is an example of polysaccharides?
Cellulose (cell wall of plants)
What are the three functions of carbohydrates?
Recognition, energy, structure
What are known to be the information molecules of a cell?
Nuclei's acids
What are the two types of polynucleotides of nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA
What are nucleic acid monomers called?
Nucleotides
What is the basic structure of nucleotides
A 5 carbon sugar (deoxyribose or ribose), a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group
Are there H or OH in a DNA helix?
H
Are there H or OH in a RNA strand?
OH
What are the functions of nucleic acids?
Unit of inheritance (makes up chromosomes), informational molecule - DNA is involved in gene expression, RNA controls protein synthesis (mRNA , tRNA, rRNA)
which of the four basic macromolecules are the most diverse and abundant?
proteins
what are the monomers for proteins?
amino acids
what polymers do amino acids form?
proteins
how many different amino acids are there?
20
describe the structure of amino acids
they have the same basic structure, the only difference between them being the R group
functions of proteins (8)
structural, regulatory, contractile, transport, storage, protective, catalytic, toxic
give an example of a structural protein
collagen - a protein in skin and bones
give an example of a regulatory protein
insulin - a peptide hormone
give two examples of a contractile protein
actin, myosin - muscle proteins
give two examples of transport proteins
haemoglobin (carries oxygen) and cytochrome (eg. carries electrons)
give two examples of storage proteins
egg white (albumin) and seed proteins
give an example of protective proteins
antibodies - immune proteins
give two example of catalytic proteins
hydrolytic in lysosomes, and RNA polymerase - enzymes
give two examples of toxic proteins
botulinum toxin, and diphtheria toxin
can lipids form polymers?
no
which macromolecule is the smallest?
lipids
are lipids heterogeneous or do they have similar structures?
they are heterogeneous
What are the 4 types of lipids?
Triacylglycerols , steroids, phospholipids, fat soluble vitamins
What do the 4 types of lipids have in common?
They are all hydrophobic
What are the 3 functions of lipids?
Structural, regulatory, and energy