meiosis and genetic diversity
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
ploidy levels
refers to chromosome set number
haploid (1N)
one chromosome set
dipoid
two chromosome sets
triploid
three chromosome sets
homologous chromosomes
paired chromosomes from maternal and paternal sources
similar length and gene content
same genes, different alleles
meiosis
sexual reproduction
produces 4 haploid gamate cells from one diploid parent cell
sexual reproduction
haploid gamete from each parent fuse to generate diploid offspring
importance of meiosis
ensure gamete cells are haploid
meiosis ( process)
process which chromosome number is reduced by half
diploid → haploid
only for gamete cells (specialized haploid cells)
involves 2 nuclear divisions
meiosis i - reduction division
diploid → haploid,
meiosis ii - equational division
separation of chromatids ( like in mitosis)
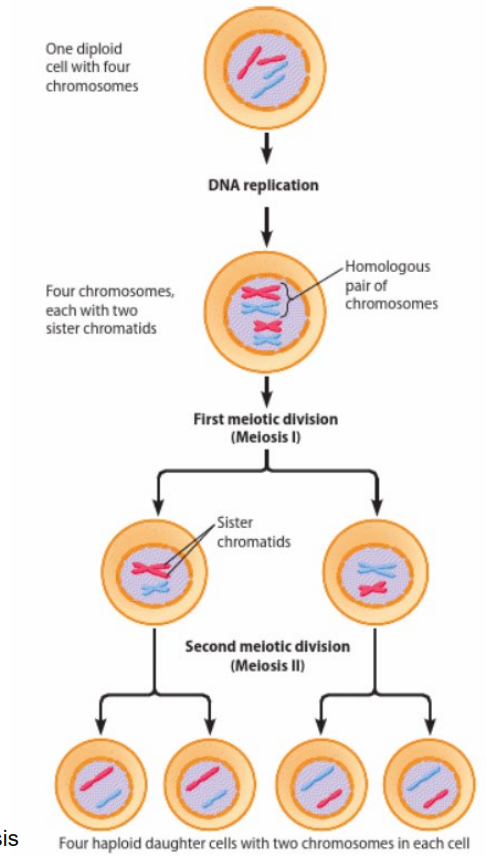
meiosis : reduction division
reduction of chromosome number from diploid to haploid
exchange of genetic information,
results in 2 haploid cells
includes
prophase I - homologous chromosomes pair via synapsis, crossing over occurs
metaphase I - homologous chromosomes align @ equator
anaphase I - homologous chromosome seperation
telophase I & cytokineses - cell divides to form 2 cells
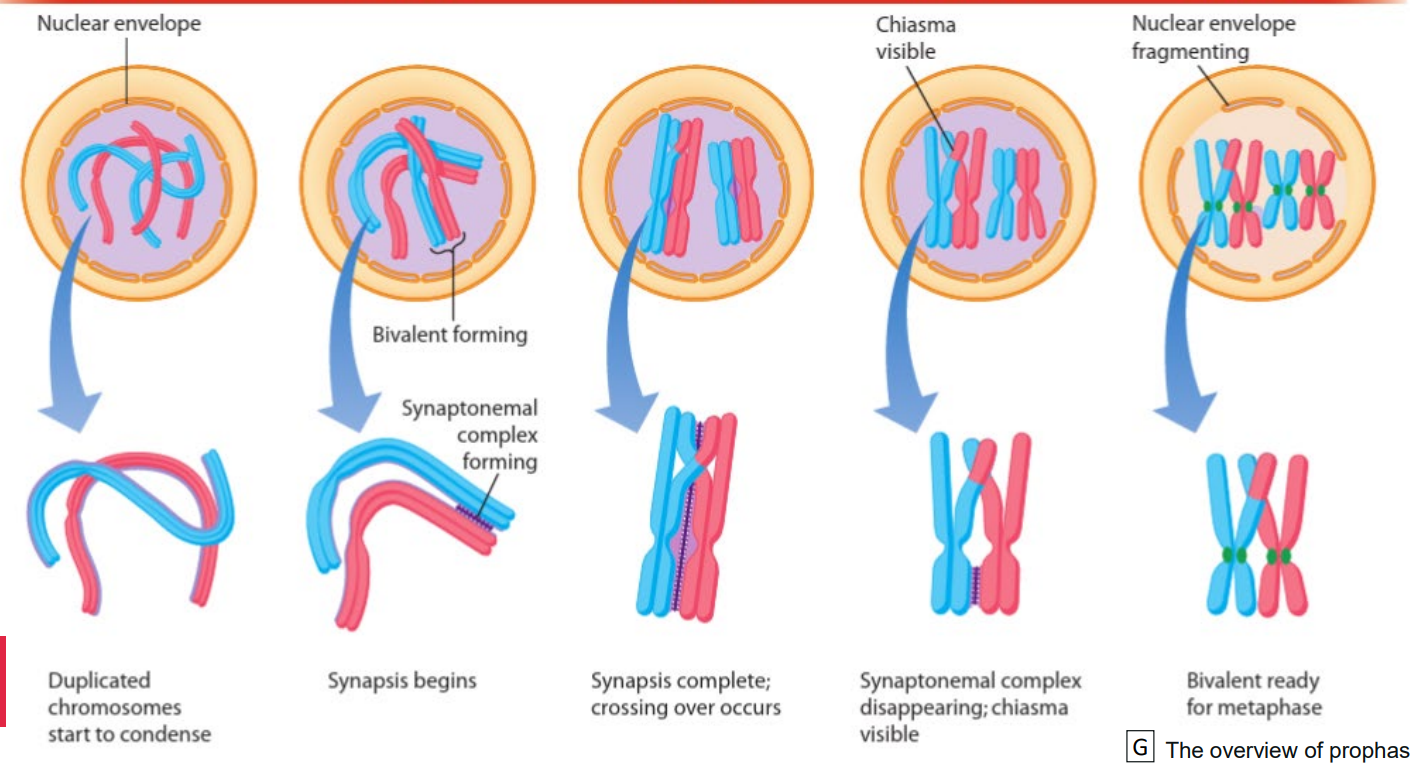
meiosis i : prophase
bivalents form, chromosomes pair up
crossing over occurs between adjacent non sister chromatids
chiasma visible, synaptonemal complex dissapears
nuclear envolope fragments
describe steps leading to synaptonemal complex dissapearing
chromosomes condense
bivalent formation, synaptonemal complex forming
synapsis occurs, crossing over begins
crossing over occurs, chiasmata visible
synaptonemal complex disapears
bivalent ready for metaphase I
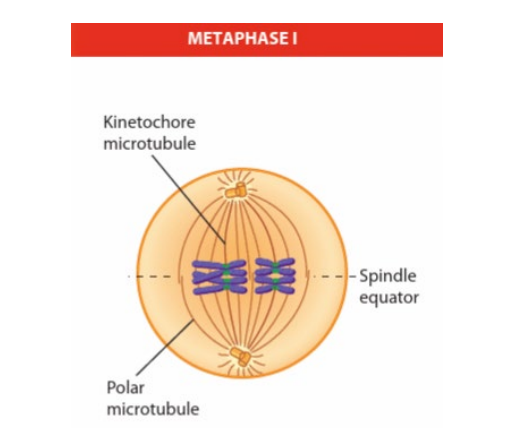
meisois i - metaphase i
bivalents ( paired chromosome pairs) move and line up at equator
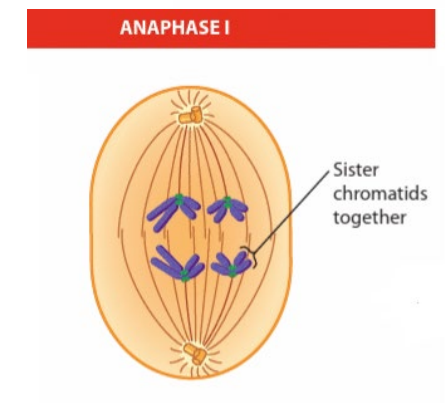
meiosis i - anaphase i
sister chromatids ( chromatids) move towards the spindle poles
each spindle pole carries one set of chomosomes ( haploid)
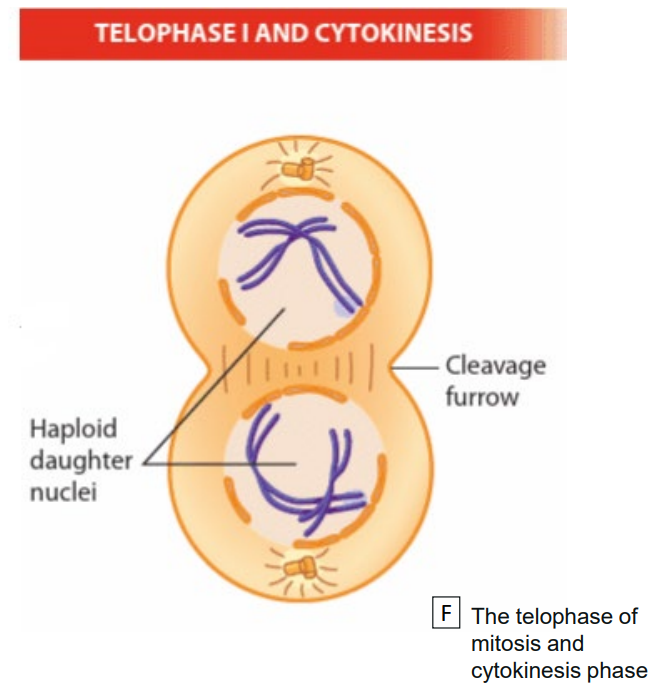
meiosis i : telophase i and cytokinesis
telophase i - when chromosomes reach spindle poles
formation of nuclear envolopes at spindle poles
formation of cleave furrow
cytokinesis,
generates 2 haploid cells, each cell contains chromosomes that has two sister chromatids
exchange of genetic information
2 ways
independent assortment
crossing over
independent assortment
chromosomes distribute randomly
in humans 223 chromsome combinations possible
crossing over
requires homologous chromosomes to be close togethr
physical exchange of genetic information
creates new genetic combinations
gametogenisis
generation of either male of female gamete cells
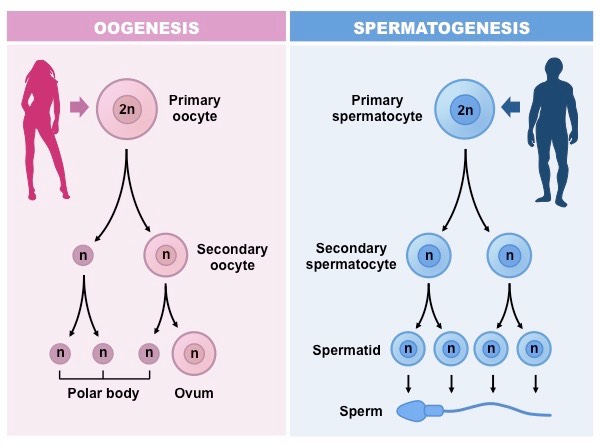
gametogenisis of sperm cells
a diploid spermatocyte → 4 haploid spermatids → 4x sperm cells
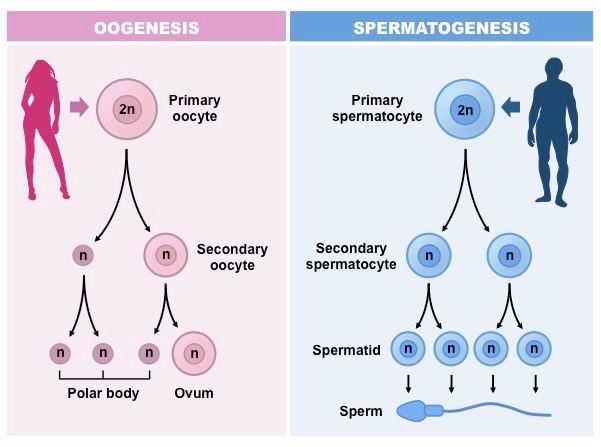
gametogenisis of eggcells
a diploid oocyte → 3 polar bodies + 1 ovum
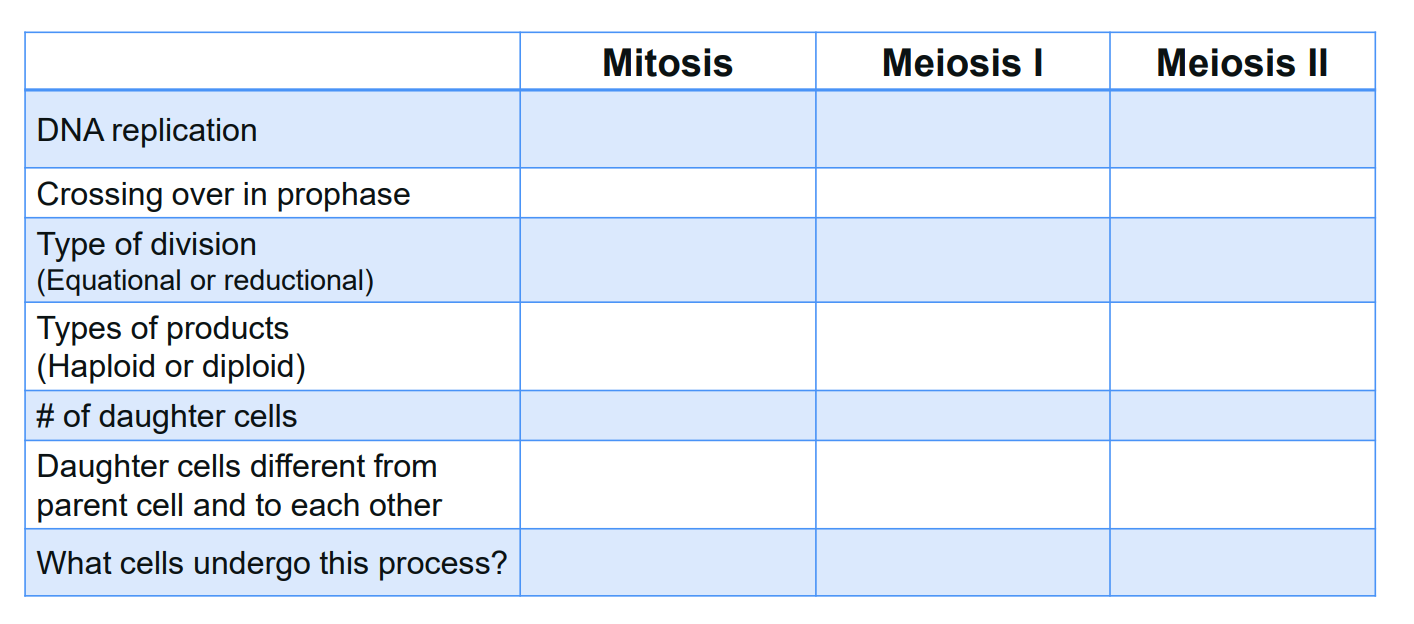
differences with mitosis and meiosis stages
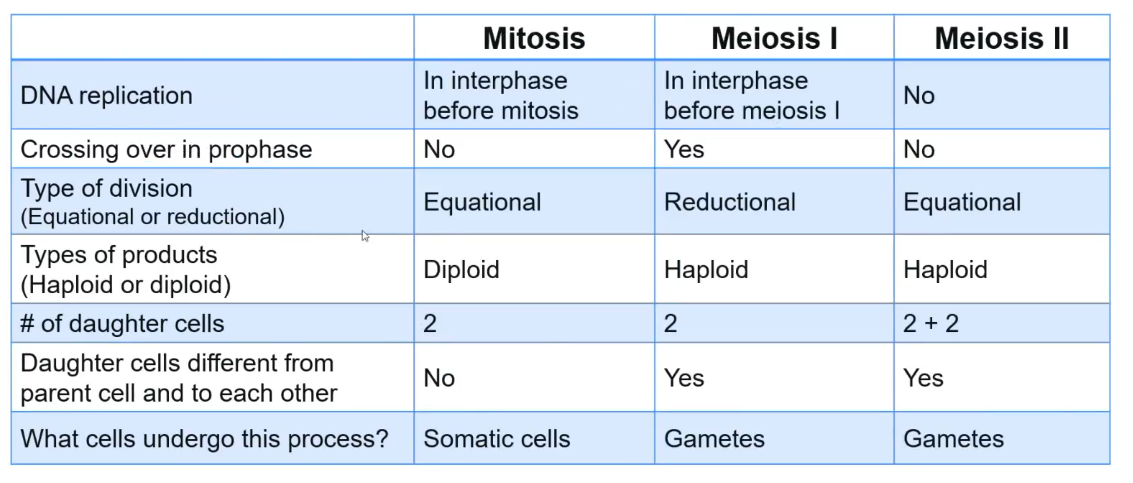
meiosis ii - equation division
occurs in all 4 stages
sister chromatid seperation
produces 4 genetically different haploid cells
outcome of meioisis
production of 4 genetically differing haploid cells
defects in meiosis
nondisjunction ( chromosome number )
chromosome structure
nondisjunction
chromosome partitioning error
causes aneuploidy - abnormal chromosome number
eg down syndrome
defects mitosis : structural
deletions
duplications
translocations
diversions
potential cancer associations