L35 T cells
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for reviewing key vocabulary and concepts from a lecture on T cells, including T cell development, antigen presentation, and T cell function.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Dendritic Cells (DC)
Stimulate T cells using MHC peptide, occurs in the lymph node or spleen.
MHC-I and MHC-II
Molecules used by dendritic cells to present antigens to CD8 and CD4 T cells, respectively.
T Cell Development
Lymphocytes that arise in the bone marrow and undergo TCR rearrangement in the thymus to become mature, naïve T cells and subsequently differentiate into effector and memory cells.
Thymic gene rearangment
Immature T cells (thymocytes) rearrange the ‘variable’ parts of their TCR genes in thymus. Essentially random process. Ensures individual T cells are unique in terms of TCR.
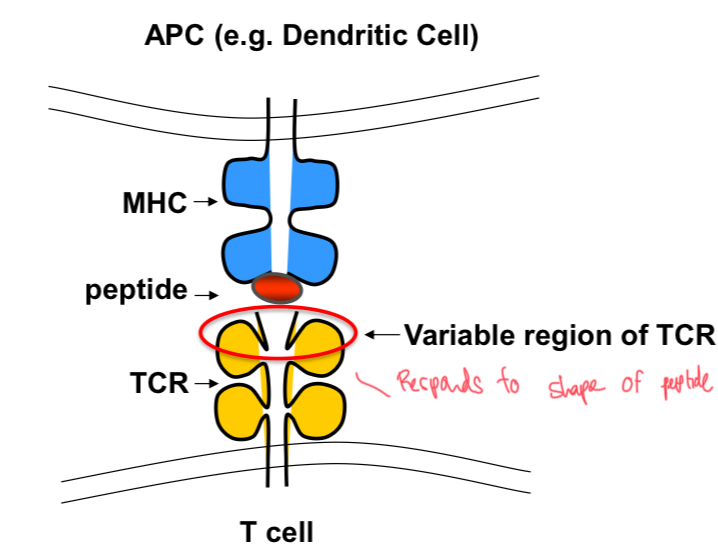
Antigen Presenting Cell (APC)
A cell, such as a dendritic cell, that displays foreign antigen complexed with MHC on its surface to T cells.
MHC Class I Molecules
Molecules that present cytoplasmic antigens (endogenous antigens, e.g., from viruses) to CD8 T cells for immune surveillance and destruction.
Proteasome
A cellular complex that degrades proteins into peptides for presentation on MHC-I molecules.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) in MHC-I processing
Location where peptide loading of MHC-I molecules takes place.
MHC Class II Molecules
Molecules that present exogenous antigens (e.g., from bacteria, virus, fungi) to CD4 T cells for immune surveillance and destruction.
Phagolysosome in MHC-II processing
Acidic compartment where antigenic proteins are degraded and peptide loading of MHC-II molecules takes place.
T Cell Receptor (TCR)
Receptor on T cells that recognises MHC/peptide complexes. TCRs are unique to individual T cell.
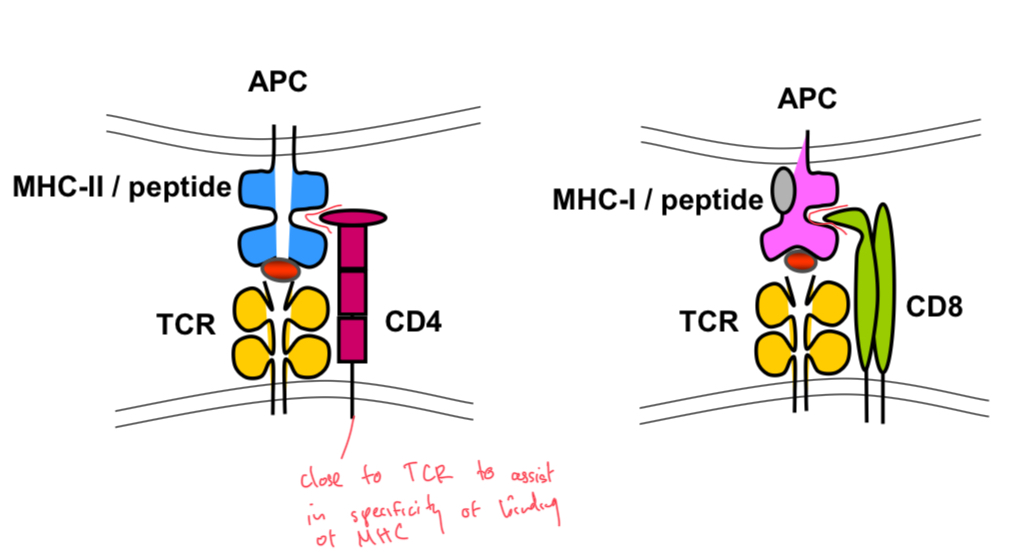
CD4 and CD8 Co-receptors
Molecules on T cells that assist with the docking of the TCR onto MHC-II or MHC-I, respectively.
Naïve T Cells
T cells that have not yet been activated by MHC/peptide complexes.
Effector T Cells
Activated T cells that perform specific immune functions, such as killing infected cells (CTLs) or helping B cells produce antibodies (helper T cells).
CD4 T Helper Cell Function
Recognises MHC-II/peptide complexes, helps activate (CTL) CD8 T cells by secreting cytokines. And helps B cells make antibodies.
CD8 T Cell Function
Recognises MHC-I/peptide complexes and develops into cytotoxic T cell (CTLs) to kill virally infected cells.
Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte (CTL)
Causes virally infected cell to self destruct, depriving virus of host proteins. Causing cell death (apoptosis), where cell shrinks down to cytoskeleton forming convenient blobs for DC to eat.
Memory T Cells
Long lasting T cells that respond more quickly to subsequent encounters with the same antigen.