Unit 4: Skeletal System
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
bone functions
support against gravity
leverage for muscles
protection of organs
blood cell production
storage of calcium & fat
how many bones are you born with?
350+
how many bones in an adult
206
bone composition
living cells & protein fibers - surrounded by Ca
matrix
2/3 of bone mass containing:
- 85% crystallized calcium
- 10% calcium carbonate
- 5% other minerals
protein fiber
1/3 of bone mass containing:
- collagen (majority)
- glycoproteins, fibrillin
how many types of cells in bones?
4
what kind of tissue is bone?
connective
periosteum
CT covering that joins w tendons & ligaments
are there veins & arteries in bone?
yes
where is bone marrow?
inside bone cavities
red marrow (hemopoietic tissue)
makes blood cells
where do children have red marrow?
nearly in every bone
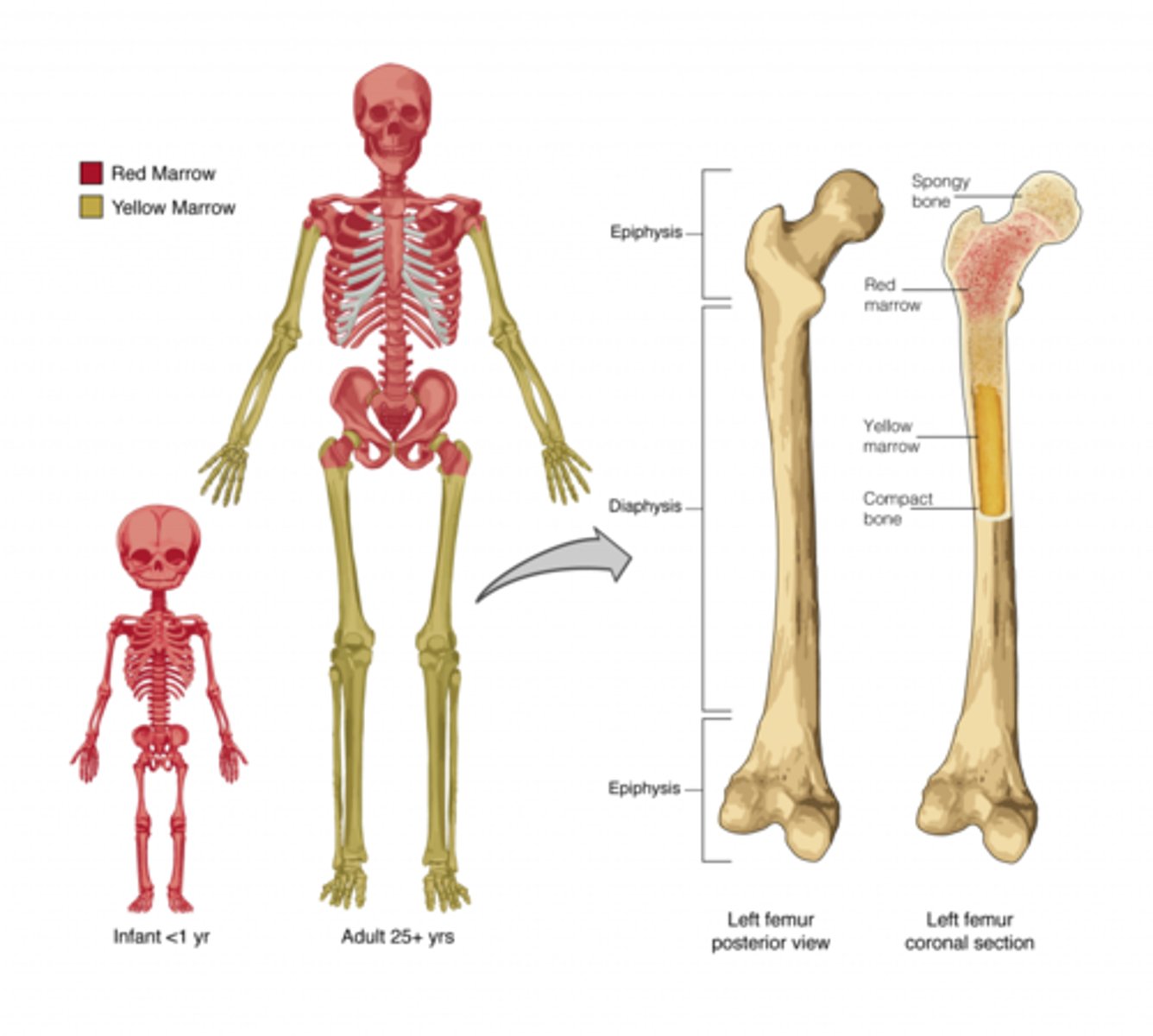
where do adults have red bone marrow?
skull
vertebrae
ribs
sternum
pelvic girdle
proximal heads of humerus and femur
yellow marrow
fatty CT
what happens to red marrow as you age?
most turns into yellow marrow & no longer produces blood
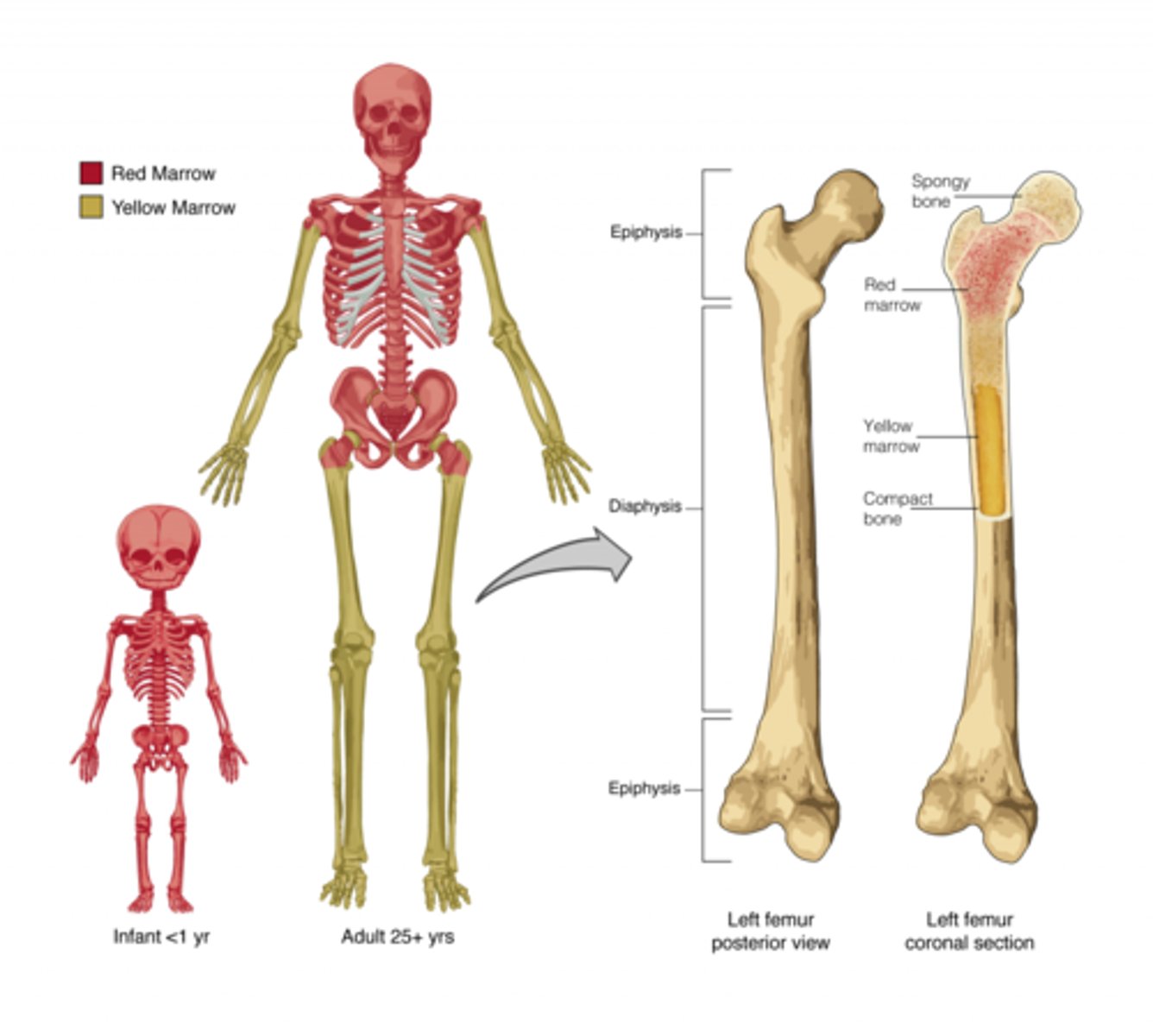
bone shapes
long
short
flat
irregular
sesamoid
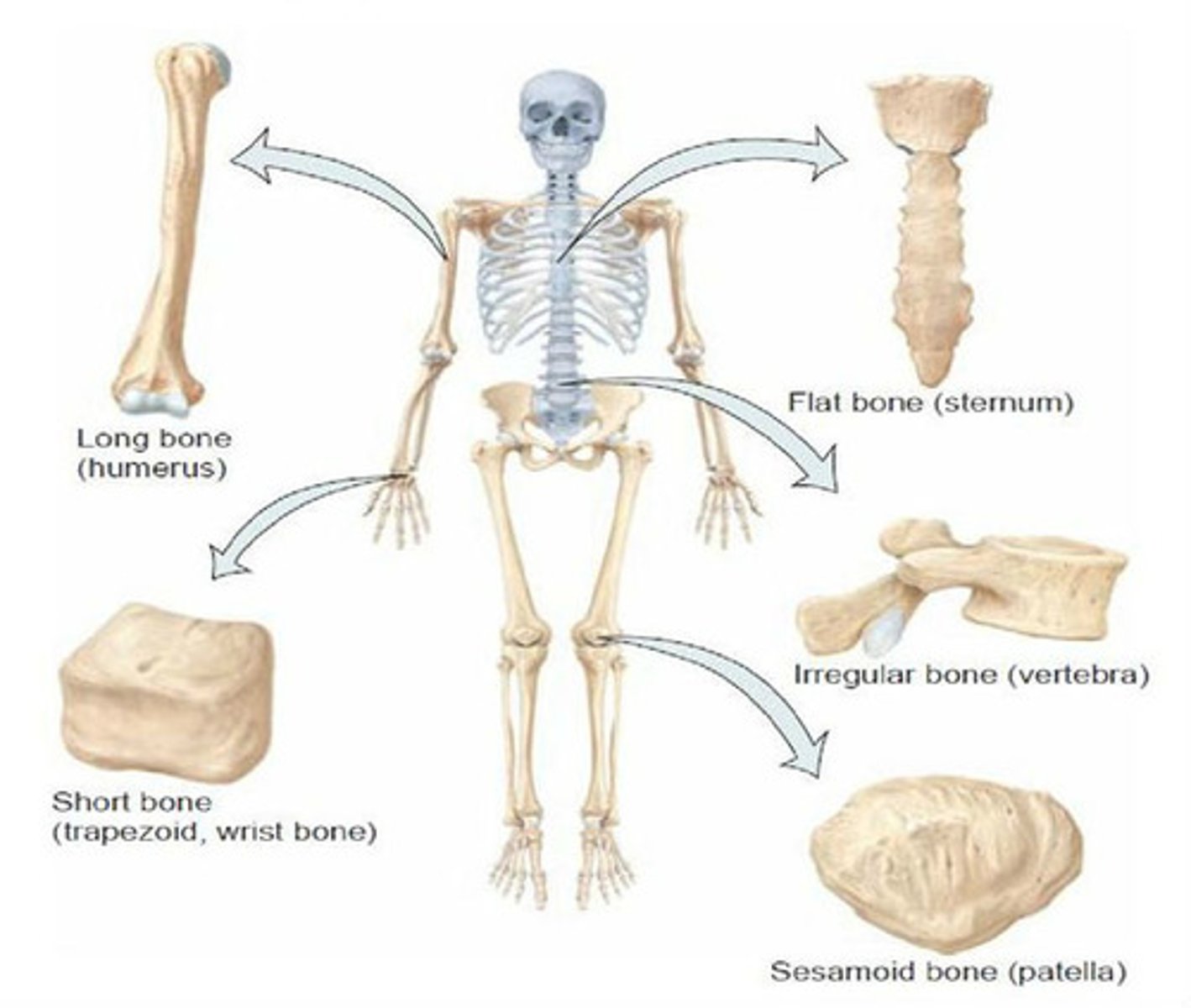
what are the types of cells in bones?
osteogenic
osteoblasts
osteocytes
osteoclasts
osteogenic cells
create osteoblasts
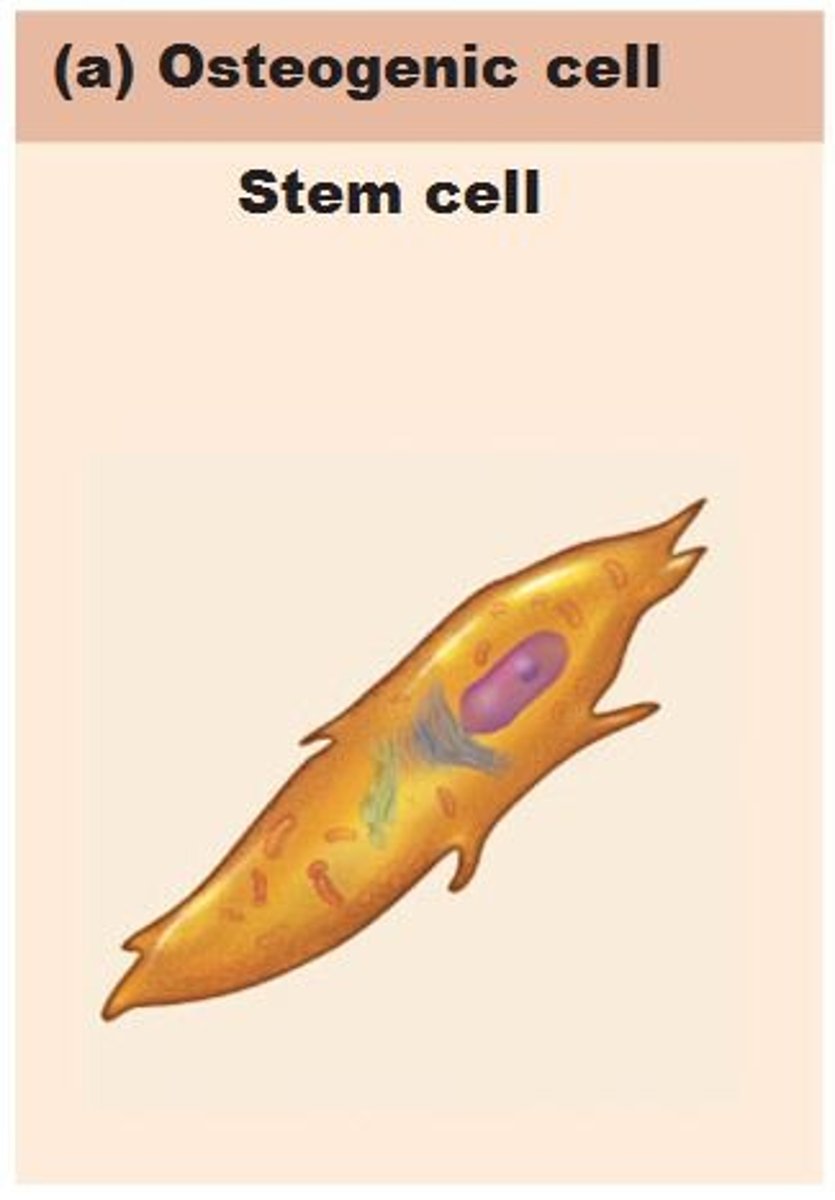
where are osteogenic cells found?
endosteum, periosteum, central canals
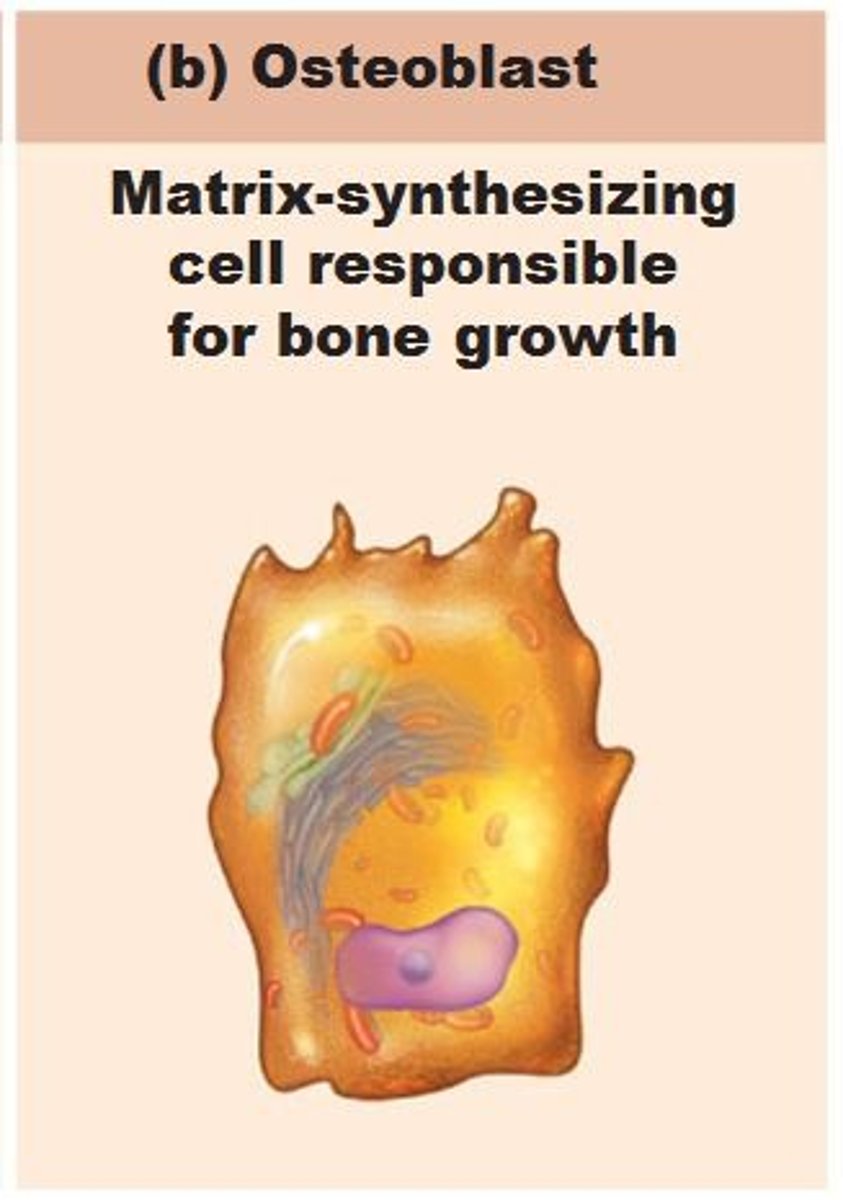
osteoblasts
create new bone
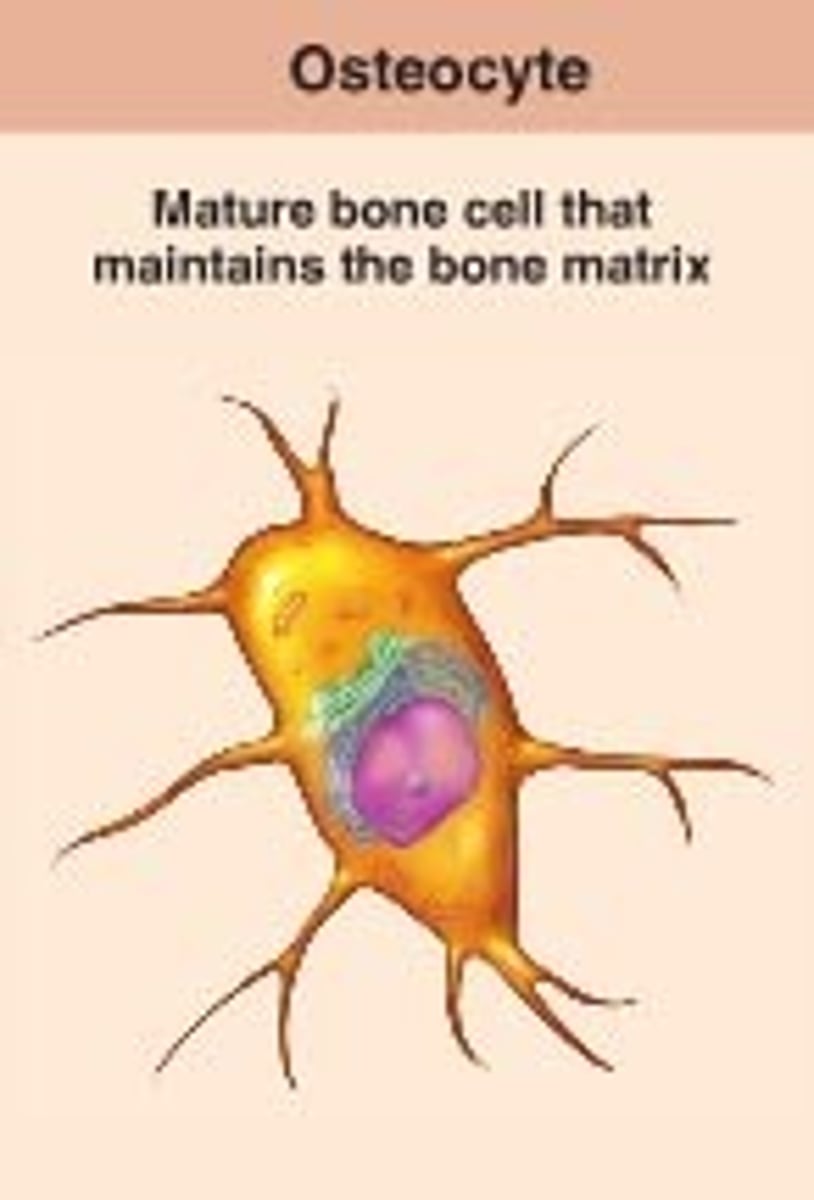
osteocytes
mature bone cells that maintain bone structure
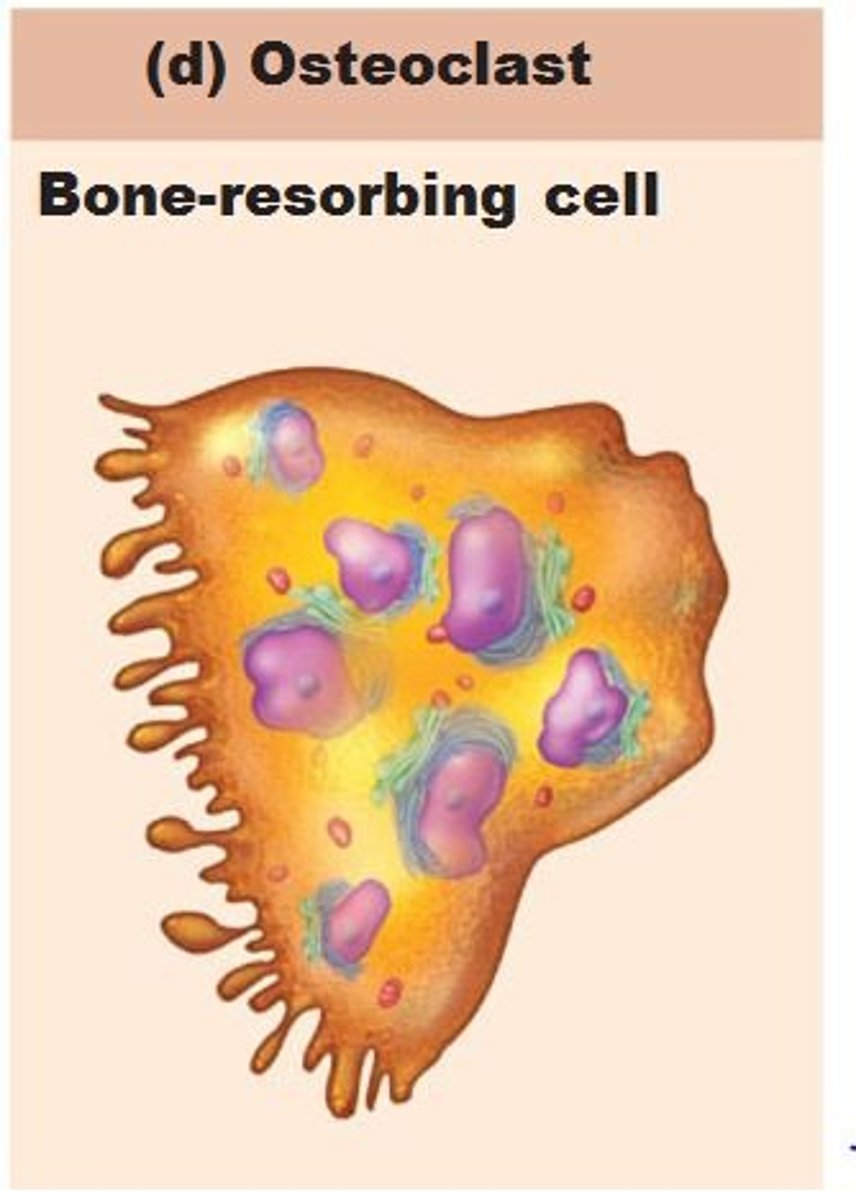
osteoclasts
break down bony matrix and release minerals
where are osteoclasts found?
on the surface
compact bone
dense
osteon (haversian system?
basic functional unit w osteocytes around canals
spongy bone
lattice adds strength w/o mass
do spongy bones have a lot of osteons?
no only a few bcs no central canals
trabeculae
calcified matrix developing along bone's lines of stress
what are the spaces in spongy tissue filled w?
red marrow
flat bone
sandwich-like construction
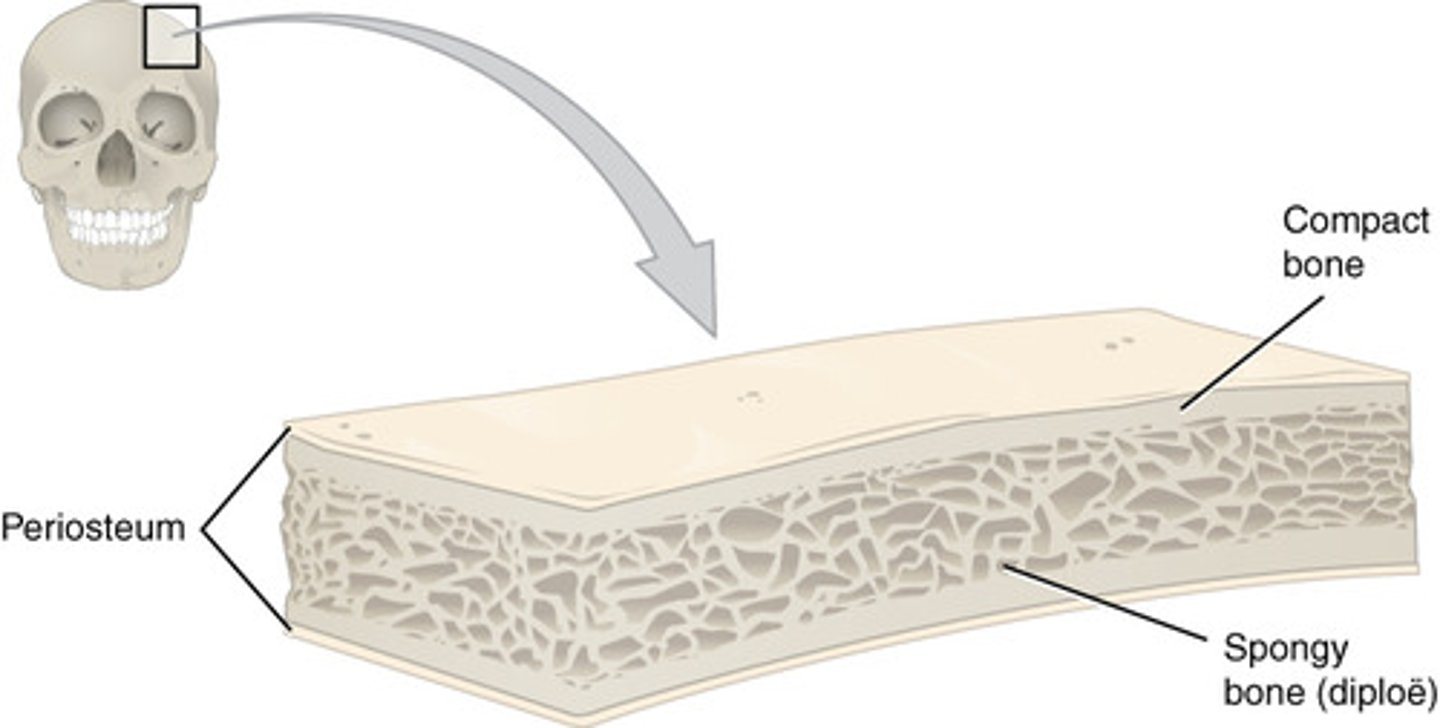
what are both surfaces of flat bone covered w?
periosteum
ossification (osteogenesis)
replacing tissues with bone
intramembraneous
bone grows in membranes - baby's soft spots turn to bone
endochrondal
bone replaces cartilage - growth zone for elongation w age
turnover rate in children
100%
turnover rate in adults
10%
osteoporosis
loss of bone density
axial skeleton supports _________________ & encases ___________________.
central axis, viscera
sutures
immovable joints of the skull
foramina
allow blood vessels and nerves to enter/leave cranium
foramen magnum
(largest opening) where medulla oblongata projects out from skull
fontanels
newborn soft spots
hyoid fuses from ________________
3 bones in early adulthood
hyoid function
provides anchor point for muscles of tongue and neck
intervertebral discs
fibrocartilaginous rings that contain a jelly-like fluid
intervertebral discs function
bearing weight
thoracic cage function
protects the visceral organs
sternum made up of ________________
manubrium, body, xiphoid process
appendicular skeleton suspended from _________________
axial system
appendicular includes bones of
1. ________________
2. ________________
3. ________________
limbs, pelvis, shoulders
pectoral girdle components
1. ________________
2. ________________
clavicles, scapula
shoulder function
arm mvmt & articulation
humerus head articulates w _____________
scapula
distal condyle articulates w _____________
forearm
radius
lateral bone of the forearm (thick)
ulna
medial bone of the forearm (thin)
carpal bones
wrist bones
phalanges
fingers
pelvic girdle components
two coxae
femur articulates w _______________
patella
ankle has _______________ bones
7 taraal
foot components
1. _______________
2. _______________
3. _______________
calcaneous, metatarsal, phalanges
articulates are/are not between every 2 bones
are even if not mvpable
synarthrosis
held tightly together with tough fibers
amphiarthrosis
permits some mvmt thru cartilage
diarthrosis
freely movable w fluid filled cavities
synarthrosis types
1. ______________
2. _______________
3. _______________
suture, gomphoses, syndesmosis
gomphosis
attachment of tooth to socket
syndesmosis
bones connected by ligaments (fibrous joint)
amphiarthrosis types
1. _______________
2. _______________
synchondroses, sympheses
synchondroses
bones bound by hyaline cartilage
simphyses
bones joined by fibrocartilage
types of diarthrosis
1. _______________
2. _______________
3. _______________
4. _______________
5. _______________
6. _______________
gliding, hinge, pivot, ellipsoidal, saddle, ball&socket
bursae
shock absorbers
synovial fluid
lubricating fluid