Case 10- Lipid Metabolism
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What are lipids?
They are molecules that are rich in carbon and hydrogen, but contain little oxygen
List types of lipids
Fatty acids, triacylglycerols, membrane lipids
What are fatty acids?
They are the simplest lipids consisting of long chains of hydrocarbons and a carboxylate group at one end
What yields more ATP per carbon between fatty acids and glucose?
Fatty acids
Describe the differences in fatty acids, triacylglycerols, and membrane lipids.
Fatty acids are the simplest form of lipids, consisting of long chains of hydrocarbons and a carboxylate group at one end and most commonly used as a fuel. Triacylglycerols are the storage form of fatty acids, they are made up of one glycerol and three fatty acids. Membrane lipids are phospholipids consisting of a 3-carbon glycerol linked to a negatively charged phosphate group and 2 fatty acids that are a large component of cell membrane since they are amphipathic
Enzymes called lipases hydrolyze triacylglycerols to yield fatty acids and glycerol. What molecule is glycerol converted into so that it can enter glucose metabolism?
Glycerol is oxidized into dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) with the help of Glycerol kinase which is isomerized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate with the help of glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase which is then able to enter glycolysis or gluconeogenesis
Write the chemical reaction for activation of stearate (C18).
StearateCOO- + CoA + ATP + H2O -> C18CO-CoA + AMP + 2Pi
How many equivalents of ATP are consumed during fatty acid activation? Use the reaction above to explain how you arrived at this number.
2 ATP equivalents are consumed during fatty acid activation since the ATP in the reaction above becomes AMP + 2Pi rather than ADP + Pi meaning that 2 ATP was consumed rather than 1.
Write the chemical reaction for complete beta-oxidation of stearyl-CoA.
Stearate + 8 FAD + 8 NAD+ + 8 CoA + 8 H2O --> 9 acetyl CoA + 8 FADH2 + 8 NADH + 8 H+
Calculate how much net ATP is generated by the catabolism of stearate (C18). Show your work.
120 ATP is generated from the catabolism of stearate

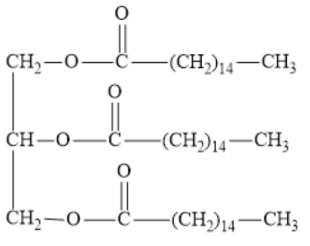
When a mole of glycerol tri-Palmitate (Triacylglycerol) is completely oxidized, how many moles of ATP are formed?
When one mole of glycerol tri-Palmitate is completely oxidized, 336.5 moles of ATP are formed.
Palmitate being C16 forms 106 moles ATP which can be multiplied by 3 since this is a triacylglycerol to get 318. 18.5 ATP can then be added from the complete oxidation of the glycerol attached to it to get 336.5
A gram of fats produces about 9 calories when the fats are converted to carbon dioxide and water, while a gram of carbohydrate or protein produces about 4 calories.
Why is more energy released from 1 g of fats than 1 g of glucose?
Fatty acids release more energy than carbohydrates since carbohydrates are partially oxidized due to their attached OH group. Fats lack such a phenomenon, allowing them to release more energy when oxidized.
Name three molecules that are ketone bodies
Acetoacetate, D-3-Hydroxybutyrate (B-hydroxybutyrate), and Acetone
In what cell type and subcellular location does ketogenesis occur?
Ketogenesis occurs in the mitochondria of the liver
How are ketone bodies used as fuel? At what point do the metabolites enter cellular respiration?
Ketone bodies are water soluble which makes them an easily transportable form of acetyl units. When D-3-Hydroxybutyrate is converted to acetyl CoA, 2 acetyl CoA is produced and 1 NADH is produced. Dehydrogenase helps D-3-Hydroxybutyrate become acetoacetate and reduces NAD+ to NADH, CoA transferase helps Acetoacetate become Acetoacetyl CoA while releasing succinate that can feed into the citric acid cycle, and Thiolase turns Acetoacetyl CoA into 2 Acetyl CoA’s.
Suppose that, for some bizarre reason, you decided to exist on a diet of whale and seal blubber, exclusively.
a) How would a lack of carbohydrates affect your ability to use fats?
A lack of carbohydrates would create a lack of glucose in the body. This lack of glucose would create a lack of pyruvate which would create a lack of oxaloacetate for the citric acid cycle. The slowing of the citric acid cycle would result in fatty acids releasing acetyl CoA and producing ketone bodies.
Suppose that, for some bizarre reason, you decided to exist on a diet of whale and seal blubber, exclusively.
What would your breath smell like?
Fruity due to the acetone being created
Suppose that, for some bizarre reason, you decided to exist on a diet of whale and seal blubber, exclusively.
One of your best friends, after trying unsuccessfully to convince you to abandon this diet, makes you promise to consume a healthy dose of odd-chain fatty acids. Does your friend have your best at heart? Explain.
This friend does have your best interest at heart because unlike even-chain fatty acids, odd-chain fatty acids have the ability to activate the citric acid cycle. Odd-chain fatty acids release acetyl CoA propionyl CoA which can be converted into succinyl CoA which feeds into the citric acid cycle. This replenishes the citric acid cycle, which replenishes Oxaloacetate, which allows gluconeogenesis to occur and create glucose.
What metabolic compounds can be converted into acetyl CoA and what are their subcellular locations?
Fatty acids
Mitochondrial matrix
Pyruvate
Mitochondrial matrix
Ketone bodies
Mitochondrial matrix
What metabolic compounds can be created by acetyl CoA and what are their subcellular locations?
Ketone bodies
Mitochondrial matrix
Citrate
Mitochondrial matrix
Fatty acid synthesis
Cytoplasm
Fatty acid synthesis occurs as three stages of processing:
In a preparatory step, acetyl CoA is transferred from mitochondria to the cytoplasm. Explain why this process is necessary.
Acetyl CoA must be transferred from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm in order to produce fatty acids. Acetyl CoA is produced in the mitochondrial matrix from PDH, ketone bodies, and the beta oxidation of fatty acids. Fatty acid synthesis however, happens in the cytoplasm meaning the acetyl CoA must be transferred.
How are acetyl CoA molecules transferred from mitochondria to the cytoplasm?
Citrate carries acetyl groups from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm.
Fatty acid metabolism is stringently controlled so that synthesis and degradation are highly responsive to physiological needs. Fatty acid synthesis is maximal when carbohydrates and energy are plentiful and when fatty acids are scarce. Acetyl CoA carboxylase play essential roles in regulating fatty acid synthesis and degradation.
Write the reaction catalyzed by Acetyl CoA carboxylase
Acetyl CoA + ATP + HCO3- ---> Malonyl CoA + ADP + Pi + H+
Explain how phosphorylation affects the activity of the Acetyl CoA carboxylase.
Adding a phosphoryl group to acetyl CoA carboxylase inactivates it. This activation would stop acetyl CoA’s conversion into malonyl CoA.
Insulin stimulates fatty acid synthesis by activating the Acetyl CoA carboxylase, Why does it make good biochemical sense for fatty acid synthesis to be activated by insulin?
Acetyl CoA carboxylase being activated means that there is a need for more acetyl CoA. In order to get more acetyl CoA, the body would need more pyruvate which requires more glucose which would cause an increase in the amount of insulin present.
Predict how high levels of NADH would impact glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, citric acid cycle, fatty acid oxidation, and fatty acid synthesis
-Glycolysis: Inhibit
-Gluconeogenesis: Stimulate
-Citric acid cycle: Inhibit
-Fatty acid oxidation: Inhibit
-Fatty acid synthesis: Stimulate
What is the relationship between your predictions and cellular energy charge concerning the 5 pathways and NADH?
ATP generating pathways should be inhibited by high levels of NADH and ATP utilizing pathways should be stimulated by the high levels of NADH
As described on Ch 28.4 in the textbook, which pathway is not impacted as expected? State how flux is actually impacted and why.
Gluconeogenesis is inhibited rather than stimulated because lactate dehydrogenase is inhibited due to the lack of NAD+. Ethanol metabolism creates a lot of NADH which requires a lot of NAD+. NAD+ being used in this way prevents there being enough NAD+ to convert lactate into pyruvate in the Cori cycle, hence the inhibition of gluconeogenesis.
Which altered pathway flux from question 14a links heavy drinking with fatty liver disease? What type of molecule accumulates?
The synthesis of fatty acids links heavy drinking with fatty liver disease and acetaldehyde builds up.
When ethanol is consumed at high levels, the acetaldehyde produced through ethanol metabolism is the cause of hangover symptoms. When ethanol is continually consumed at high levels, acetaldehyde can significantly damage the liver. Explain how acetaldehyde damages the liver.
Acetaldehyde is a toxic product produced by ethanol in the liver that covalently binds to a variety of proteins. This binding alters the liver function and structure. It decreases the polymerization of microtubules which impairs protein secretion, impairs enzyme activity, and alters mitochondrial functions.
What is glycerol?
A three-carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon
What is the difference between a saturated fat and an unsaturated fat?
Unsaturated fats include at least one double bond
What happens when an unsaturated fat is trans instead of cis?
The fat is more stable and thus harder to break down as well as solid at room temperature. These kinds of fats are worse for you since enzymes are not designed to recognize them , allowing them to stay in the body
What effect do trans fats have on LDLs and HDLs?
The raise levels of LDL and lower levels of HDLs
How does the digestive system overcome the complications created by the hydrophobicity of lipids?
The stomach converts lipids into emulsions, a mixture of lipid droplets and water, which makes them easier to break down.
What are the 3 stages of fatty acid processing?
Lipolysis
Activation
B-oxidation
What happens in lipolysis?
Triacylglycerols are degraded to fatty acids and glycerol
What happens in activation?
Fatty acids must be activated and transported into mitochondria for degradation?
What happens in B-oxidation?
Fatty acids are broken down in a step-by-step fashion into acetyl CoA, which is then processed in the citric acid cycle
Describe fatty acid degradation
Triacylglycerols must be liberated from adipose. Lipids are hydrolyzed by lipases to yield fatty acids and glycerol and these fatty acids are taken up by cells and used as a fuel. Glycerol also enters the liver, where it can be metabolized by the glycolytic or gluceoneogenic pathways
How are fatty acids used for fuel by many tissues?
Through B-oxidation
What does transport across the inner membrane require fatty acids to be linked to?
Carnitine
How many rounds of B-oxidation would a C10 fatty acid go through?
4
Which requires more oxidation to become CO2 and H2O between fats and carbohydrates?
fats
Out of the series of oxidation, hydration, oxidation, and thiolysis needed for the degradation of saturated fatty acids, which step is not required for unsaturated fatty acids?
The first oxidation is not needed, an Acyl CoA is non needed to perform the oxidation since it doesn’t occur and FADH2 is not created
What kind of fat releases more energy between saturated and unsaturated?
Saturated
What molecules are generated by beta oxidation?
Acetyl CoA, FADH2, and NADH
Rank the following in terms of ATP generated from most to least:
-Saturated fat with 0 double bonds
-Unsaturated fat with 1 double bond
-Unsaturated fat with 3 double bonds
-Saturated fat with 0 double bonds
-Unsaturated fat with 1 double bond
-Unsaturated fat with 3 double bonds
What does most acetyl CoA produced by fatty acid degradation do?
It enters the citric acid cycle
What does fatty acid synthesis require as a reducing power?
NADPH
Is carboxylation favorable or unfavorable?
Unfavorable
Fatty acid synthesis consist of a series of what?
Condensation, reduction, dehydration, and reduction reactions
Does regulation by glucagon stimulate or inhibit fatty acid synthesis?
Regulation by glucagon inhibits fatty acid synthesis. When glucagon is the regulator, AMP is high and AMP-dependent protein kinase works to shut down acetyl CoA carboxylase
Does regulation by insulin stimulate or inhibit fatty acid synthesis?
Regulation by insulin stimulates fatty acid synthesis. When insulin is the regulator, insulin activated protein phosphatase 2A ia active and dephosphorylates Acetyl CoA carboxylase
What can partly activate the phosphorylated carboxylase?
Citrate
What is the density of a lipoprotein if they have a protein > lipid ratio?
High density
What is the density of a lipoprotein if they have a lipid > protein ratio?
Low density