The Physical Self: Heredity and Environment
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Physical Self
Individual's perception of their own body.
Heredity
Genetic factors influencing physical characteristics.
Environment
Surroundings affecting personal development and self-view.
Self-Esteem
Confidence in one's worth or abilities.
Cognitive Development
Growth in thinking and understanding processes.
Jean Piaget
Psychologist known for cognitive development stages.
Growth
Physical maturation increasing body size and organs.
Development
Qualitative changes in skills and capacities.
Physical Growth
Changes in height and weight over time.
Mental Development
Intellectual growth and problem-solving abilities.
Emotional Development
Growth in managing feelings and emotions.
Social Development
Changes in interactions and relationships with others.
Maturation
Completion of growth and development processes.
Physical Maturation
Physical changes occurring with aging.
Quantitative Changes
Measurable changes in growth and development.
Qualitative Changes
Non-measurable changes in skills and abilities.
Stages of Growth
Phases marking physical and cognitive development.
Cultural Impact
Influence of culture on body image perceptions.
Self-Discovery
Understanding one's identity and personal needs.
Self-Fulfillment
Achieving personal satisfaction and contentment.
Developmental Stages
Specific phases in human growth and change.
Body Image
Personal perception of physical appearance.
Forces Influencing Development
Factors affecting the growth of the physical self.
Cognitive Maturation
Change in thinking patterns throughout lifespan.
Heredity
Transmission of traits from parents to offspring.
Environment
Forces and experiences influencing personal development.
Infancy
Development stage from birth to 1 year.
Physical Development in Infancy
Rapid changes occur during the first year.
Mental Development in Infancy
Infants understand words by six months old.
Emotional Needs in Infancy
Love and security essential for growth.
Early Childhood
Development stage from 1 to 6 years.
Verbal Growth in Early Childhood
Children recognize letters and ask questions.
Emotional Development in Early Childhood
Frustration arises from inability to perform.
Middle Childhood
Development stage from 6 to 10 years.
Physical Changes in Middle Childhood
Loss of baby teeth and eruption of permanent teeth.
Mental Development in Middle Childhood
Focus on school and learning abstract concepts.
Emotional Development in Middle Childhood
Fear of school environment is managed.
Late Childhood
Development stage from 10 to 16 years.
Physical Changes in Late Childhood
Puberty leads to sexual characteristics development.
Mental Development in Late Childhood
Increase in knowledge and skill sharpening.
Social Relationships
Impact of peer acceptance on emotional needs.
Basic Necessities in Early Childhood
Food, rest, shelter, love, and security required.
Preadolescence
Another term for middle childhood development stage.
Developmental Stages
Phases of growth from infancy to late childhood.
Conflict in Adolescence
Struggle between child and adult expectations.
Emotional Development
Often tumultuous; seeks identity and independence.
Social Development
Increased peer interaction over family time.
Adolescent Needs
Require reassurance, support, and understanding.
Early Adolescence
Ages 10-14; onset of puberty and physical changes.
Physical Changes in Early Adolescence
Includes hair growth, body odor, and menstruation.
Intellectual Development in Early Adolescence
Focus on present; struggles with long-term thinking.
Emotional Challenges in Early Adolescence
Mood swings and low self-esteem are common.
Social Expansion in Early Adolescence
Begins to socialize outside family and close friends.
Middle Adolescence
Ages 15-17; reaching adult height and body awareness.
Physical Development in Middle Adolescence
Focus on grooming and physical fitness increases.
Intellectual Growth in Middle Adolescence
Ability to solve complex problems develops.
Future Orientation in Middle Adolescence
Begins to consider future implications of actions.
Emotional Dynamics in Middle Adolescence
Desire for independence while needing parental security.
Social Relationships in Middle Adolescence
Focus on peer groups and first romantic interests.
Late Adolescence
Ages 18-21; refining physical appearance and fitness.
Intellectual Maturity in Late Adolescence
Understanding long-term consequences of choices improves.
Emotional Confidence in Late Adolescence
Increased self-confidence and expanded social circles.
Career Consideration in Late Adolescence
First serious thoughts about career choices arise.
Social Development in Late Adolescence
Social circles expand beyond earlier cliques.
Middle Adulthood
Age range from 40 to 65 years.
Physical Development
Changes include graying hair, wrinkling skin.
Intellectual Development
Mental abilities can continue to increase.
Emotional Development
Can involve contentment or crisis during mid-life.
Social Development
Restructuring of social life due to family changes.
Late Adulthood
Age 65 years and older.
Cognitive Decline
Mental abilities may decline in elderly individuals.
Alzheimer's Disease
Causes irreversible loss of memory and function.
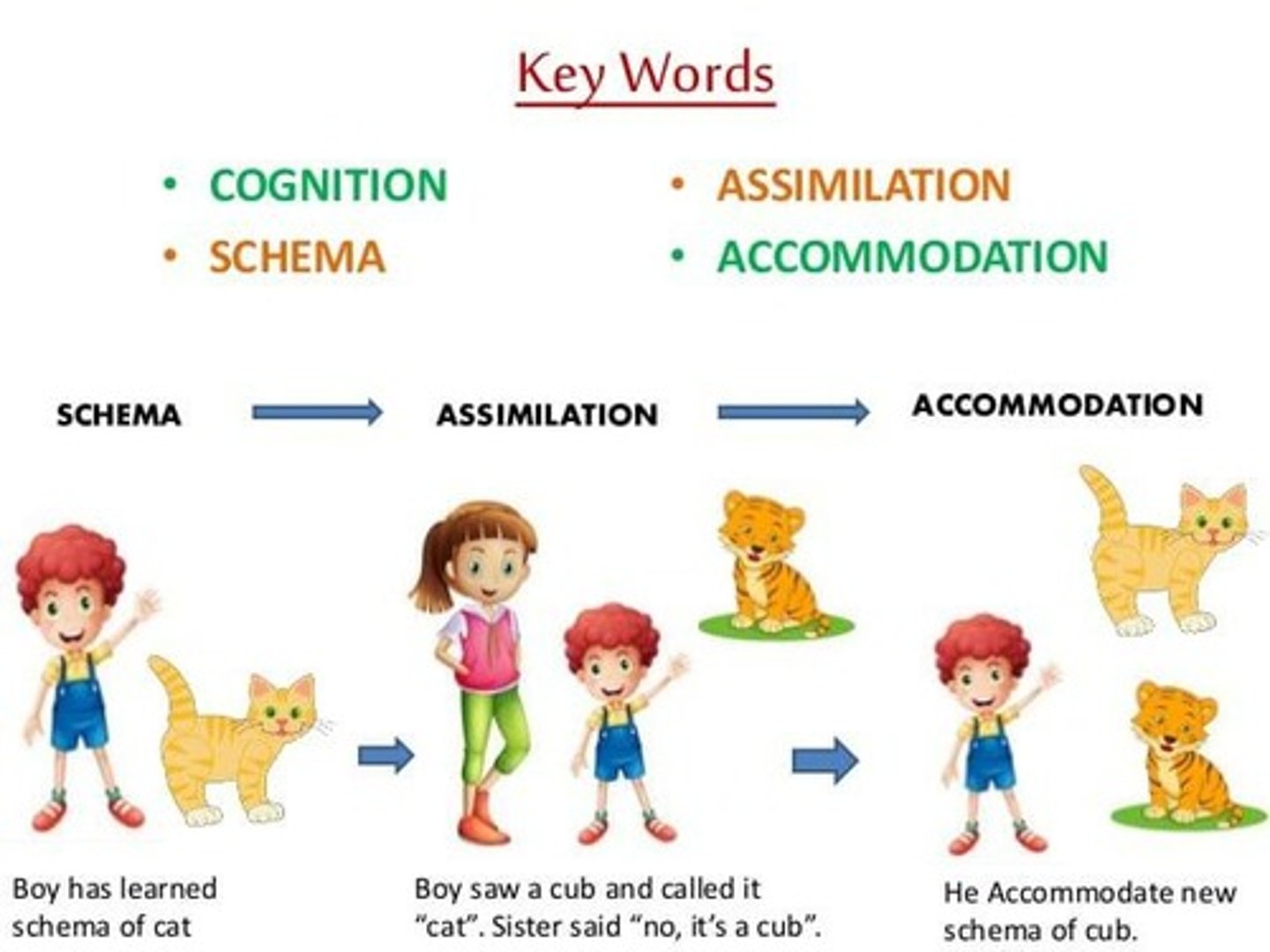
Schema
Pattern of thought organizing knowledge and behavior.
Example of Schema
Restaurant behavior pattern: menu, order, eat, pay.
Assimilation
Incorporating new information into existing beliefs.

Example of Assimilation
Child calls bald man a clown.
Accommodation
Changing schema to fit new experiences.
Example of Accommodation
Father explains man is not a clown.
Vision Decline
Common in late adulthood; affects sight.
Hearing Loss
Begins in middle adulthood; affects communication.
Weight Gain
Common physical change during middle adulthood.
Coping Mechanisms
Developed to handle life stresses in adulthood.
Social Roles
Includes parent, grandparent, and worker responsibilities.
Mental Abilities
Varies widely among elderly individuals.
Contentment in Mid-life
Dependent on job satisfaction and health.
Cognitive Development
Study of how thinking evolves over time.
Accommodation
Adjusting existing schemas to incorporate new information.
Sensori-motor Stage
Development through sensory experiences and movements.
Pre-operational Stage
Stage of fantasy, symbols, and early questioning.
Concrete Operational Stage
Understanding logic and concrete cognitive operations.
Formal Operational Stage
Ability to think abstractly and philosophically.
Schemas
Mental structures organizing knowledge and experiences.
Egocentrism
Inability to see perspectives other than one's own.
Hypothetical Thinking
Ability to consider possibilities beyond current reality.
Cognitive Operations
Mental processes for organizing and manipulating information.
Identity Formation
Development of a sense of self and personal values.
Imaginary Audience
Belief that others are constantly observing one's behavior.
Compassion
Understanding and empathizing with others' feelings.
Developmental Milestones
Key stages marking significant growth in abilities.
Symbolic Representation
Using symbols to represent objects or ideas.