8th grade Science Midterm Review ~ Created 2024
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
physical change
A change in properties where no new substance is created.

chemical change
Process by which substances are changed into different substances with different properties.

exothermic reaction
A chemical reaction in which heat is RELEASED to the surroundings (so it feels warm to the touch).

endothermic reaction
A reaction that ABSORBS energy in the form of heat (so it feels cold to the touch).

reactant
a substance that is present at the beginning of a chemical reaction, takes part in the chemical reaction, and is changed into a new substance.
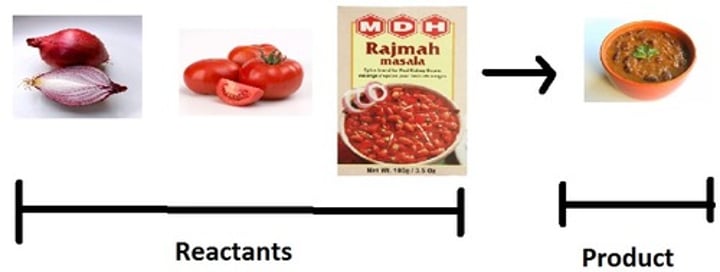
reactive
Property in which a substance is likely to undergo a chemical change
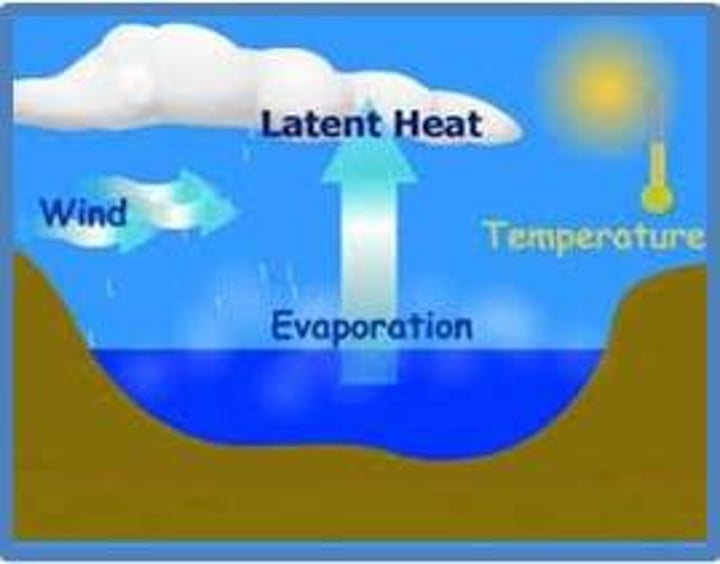
condensation
A change in state from gas to liquid. It releases heat.
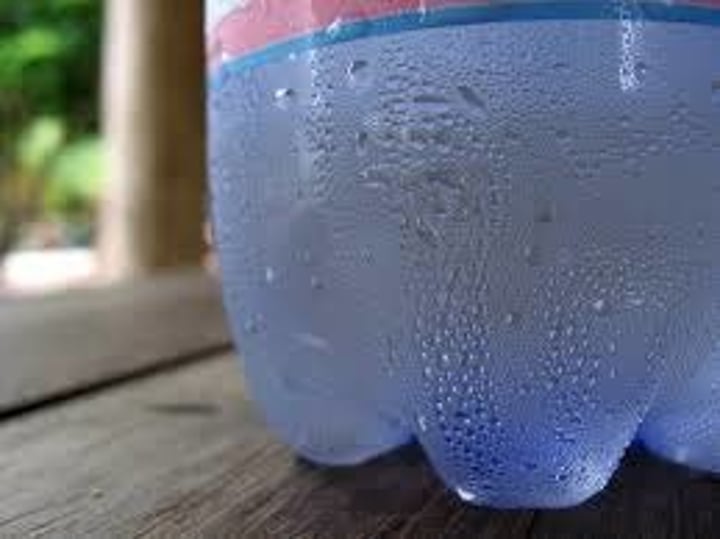

evaporation
A change in state from liquid to gas. It adds heat.
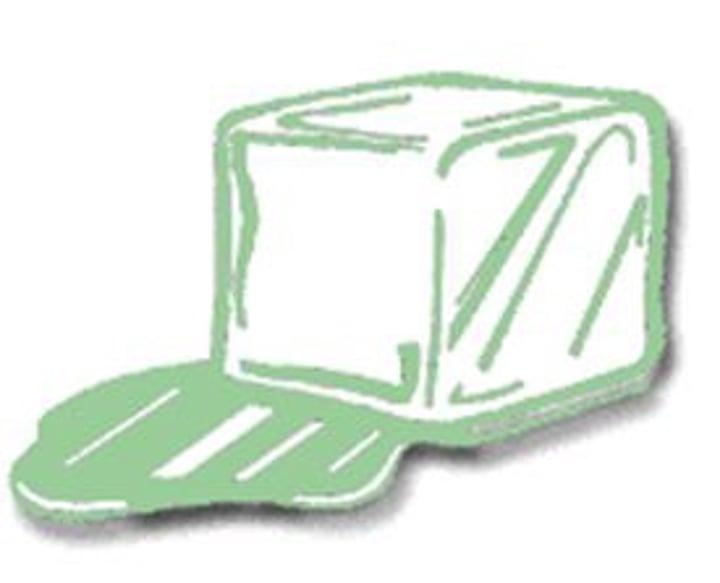
melting
A change in state from solid to liquid. It adds heat.
boiling point
The temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas.
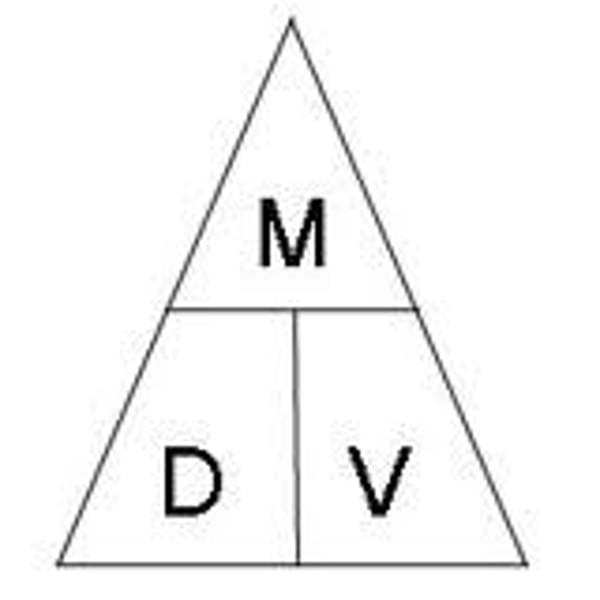
Formula for density
D = M / V
element
A substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance by ordinary chemical changes.
Consists of atoms of only one type.
period
A horizontal row in the Periodic Table.
Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
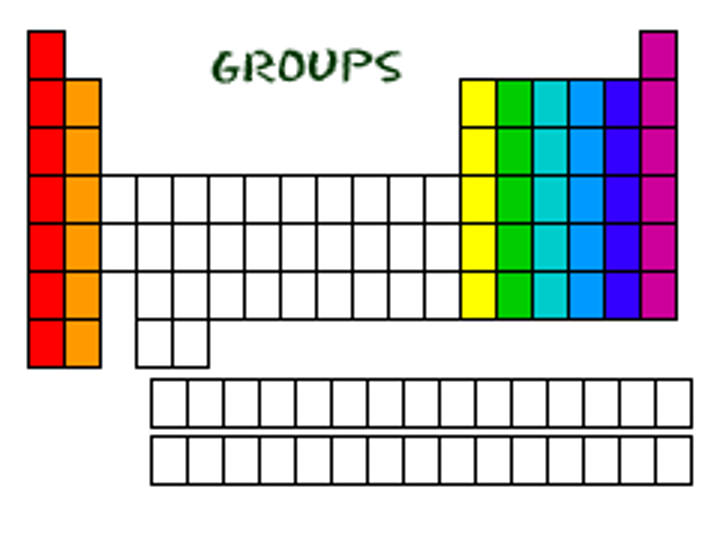
group
A vertical column in the Periodic Table that have similar chemical properties.
Law of Conservation
of Mass
A scientific law stating that during a chemical reaction, matter is not created nor destroyed.
Atomic mass minus atomic number equals the number of _________.
neutrons

The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus is the ___________.
atomic mass #
One physical property of IRON that can be used to separate it from salt or sand is that it is ____________.
magnetic
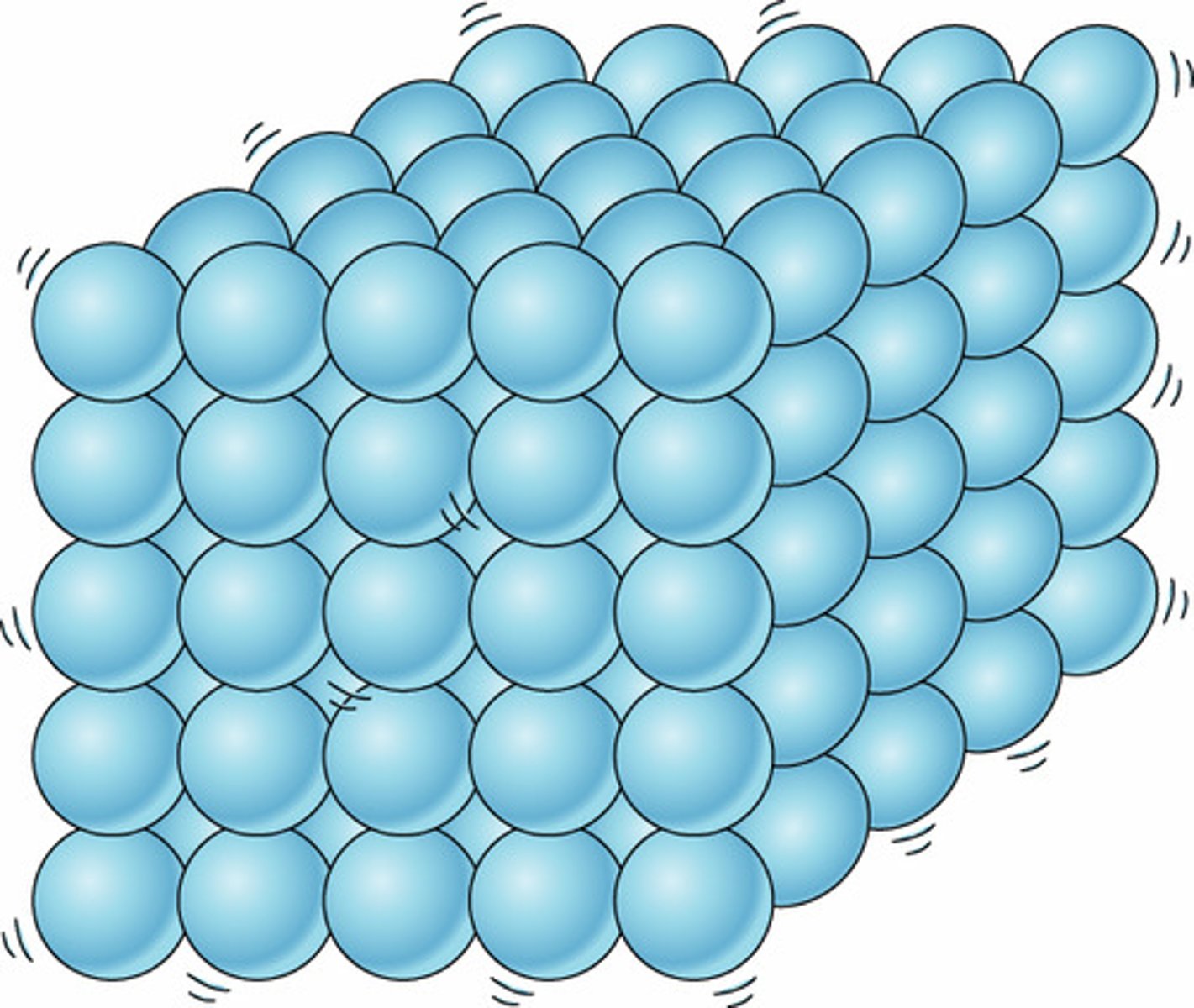
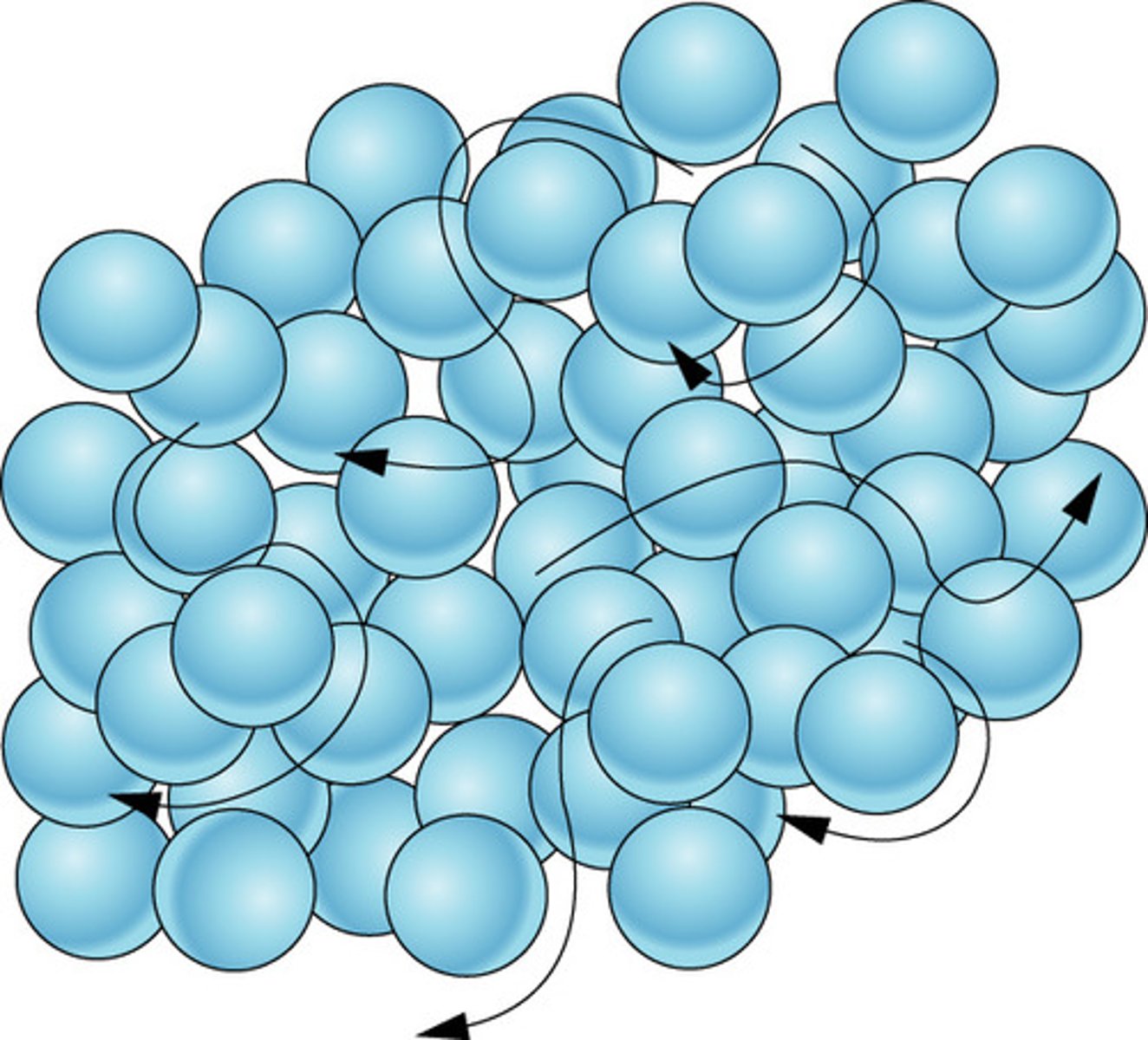
What are the properties of a solid?
The particles are tightly packed.
The particles vibrate but do not move around.
What are the properties of a liquid?
The particles are close together.
The particles move and slide past each other.
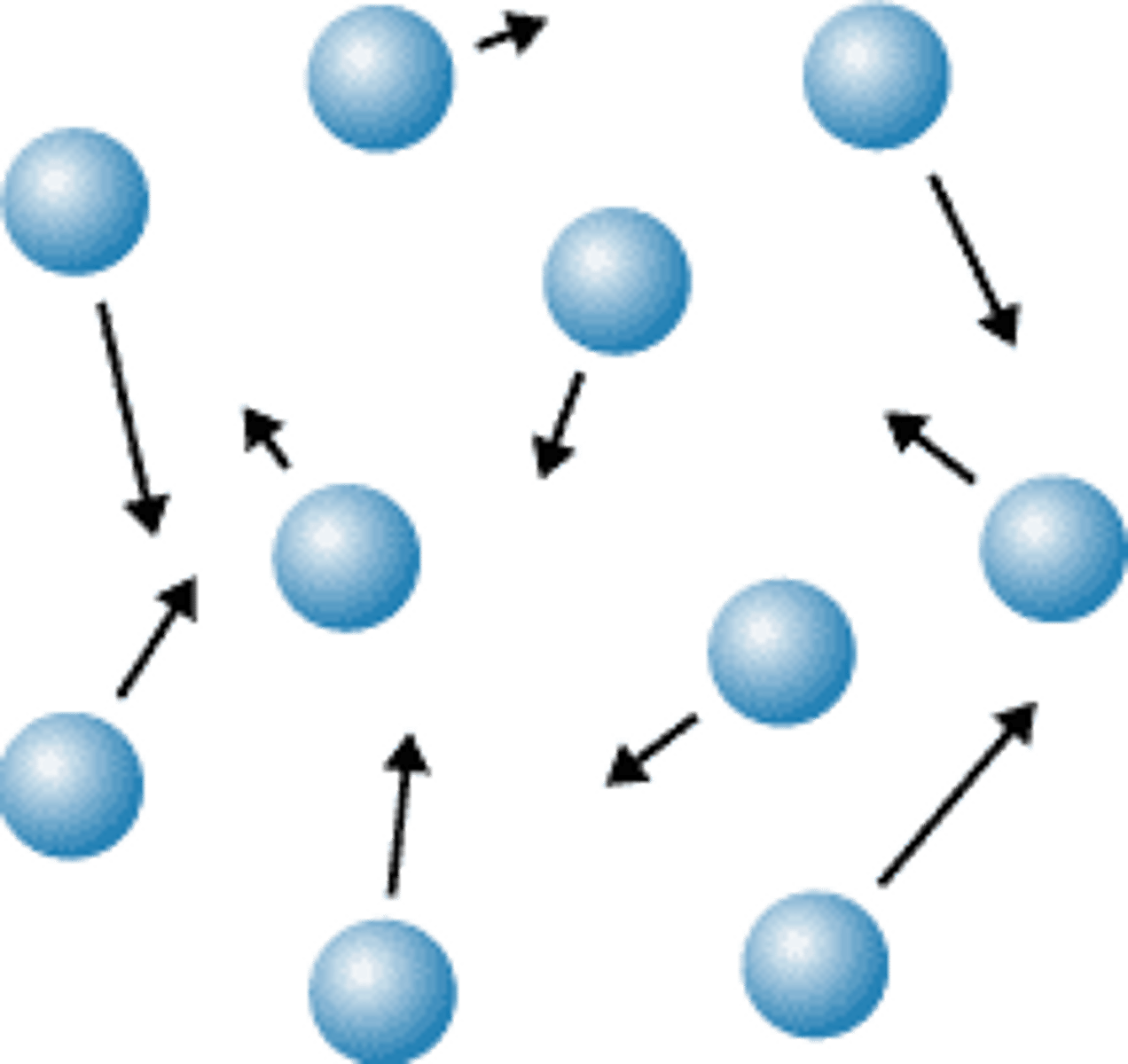
What are the properties of a gas?
The particles are very separated.
The particles move quickly in all directions.
The rate of a chemical reaction increases as the temperature ___________.
increases
One method to separate sand and water is by ___________.
filtering
Another method to separate salt and water is by ___________.
evaporation
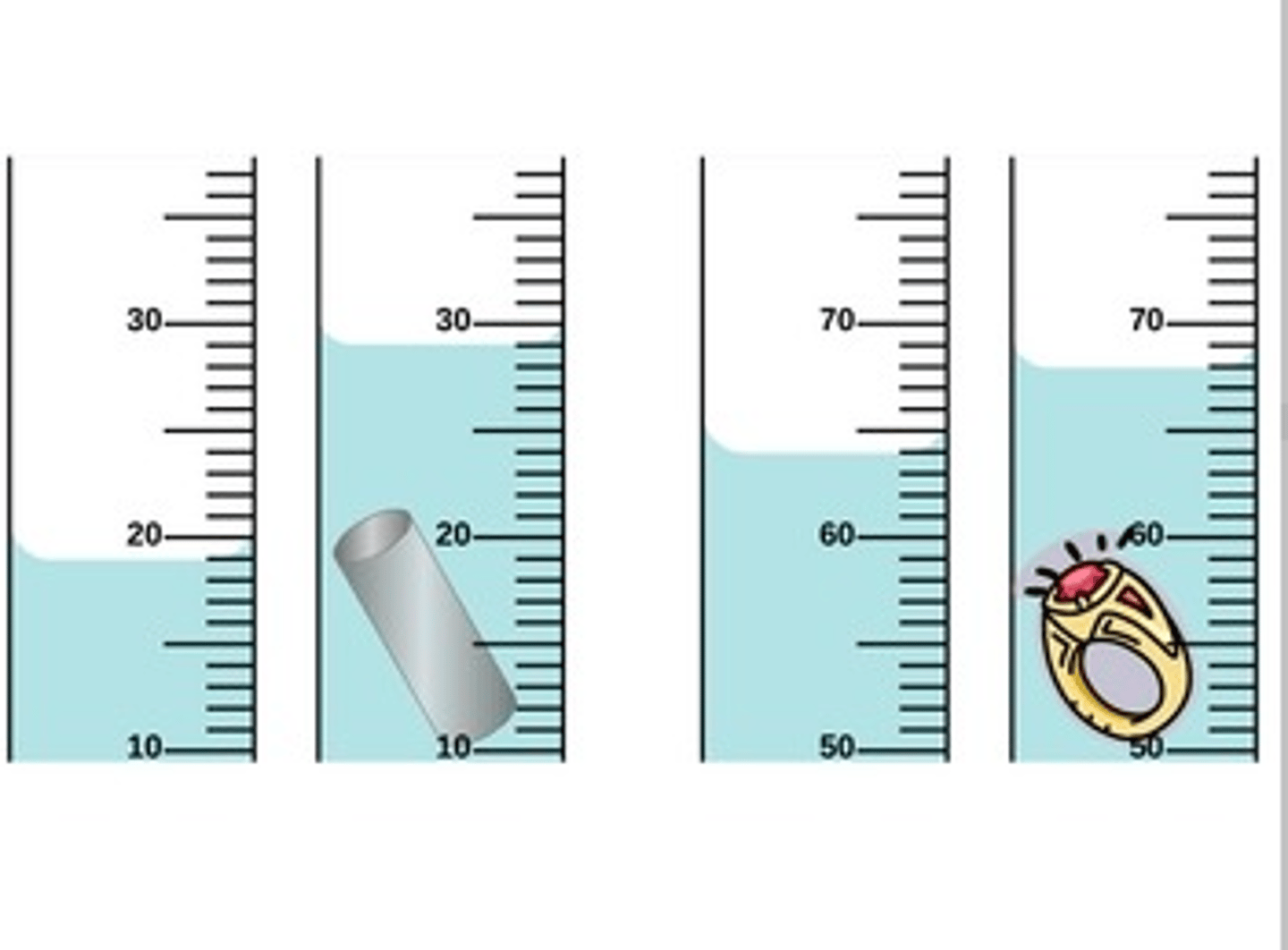
Looking at the 2 cylinders on the right what is the volume of the ring?
4 ml
manipulated (independent) variable
The variable in the experiment that is purposely changed. The factor that is being tested.
responding (dependent) variable
The factor is the experiment that changes in response to the independent variable. The data or results.

The total number of protons in an atom is equal to the __________.
atomic number
qualitative observation
An observation that deals with descriptions that cannot be expressed in numbers.
quantitative observation
An observation that deals with a number or amount.
prediction
A statement about what will happen or might happen in the future.
controlled experiment
An experiment in which only one variable is manipulated at a time.
problem
A question to be investigated.
hypothesis
A testable prediction.
conclusion
A summary/results of the experiment.
inference
A logical conclusion based on observations (past or present tense).
The formula used to find volume of a regular shaped solid:
V = L x W x H
water displacement method
A method that involves putting an object into water and carefully recording how much the water level rises.
mass
A measure of the amount of matter in an object.
volume
The amount of space an object takes up.
length
The distance between two points.
ruler
A tool used to measure length.
graduated cylinder
An instrument used to measure volume of a liquid or irregular solid.
triple beam balance
An instrument used to measure mass.
proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom.
electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge. Found outside the nucleus.
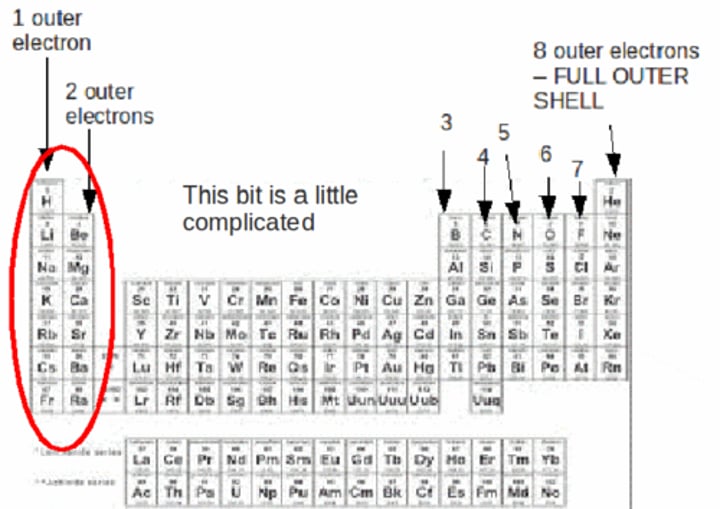
valence electrons
The electrons in the outermost shell.
valence shell
The outermost shell of an atom.
compound
A substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements and their properties change.

mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined. Properties stay the same.
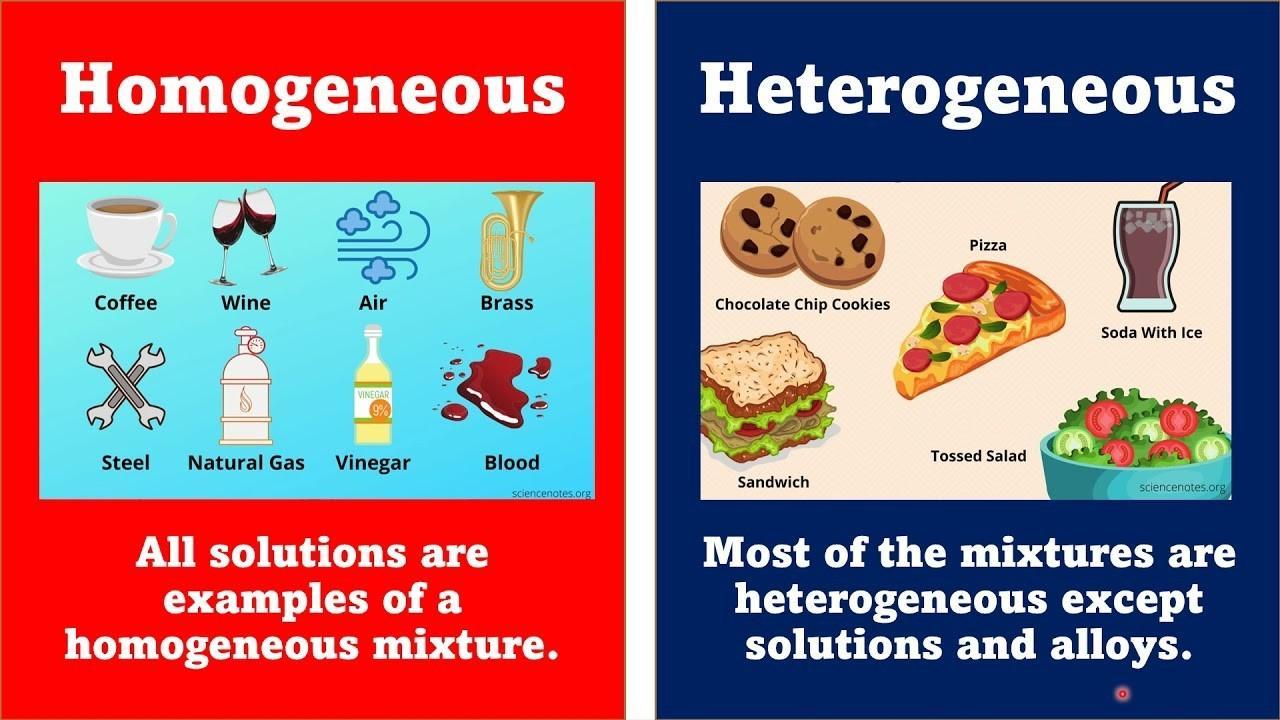
homogeneous mixture
A mixture in which substances are evenly distributed throughout the mixture.
Ex: salt water
heterogeneous mixture
A mixture that is not evenly distributed, in which different samples may have different compositions. Ex: salad
Which is the the compound and which is the element?
CO and Co
Element: Co (Cobalt)
Compound: CO (Carbon Monoxide)
electron shells (energy levels)
Electrons occupy orbits or generally fixed regions of space around the nucleus.
In a neutral atom, the number of protons also equals the number of _________.
Electrons
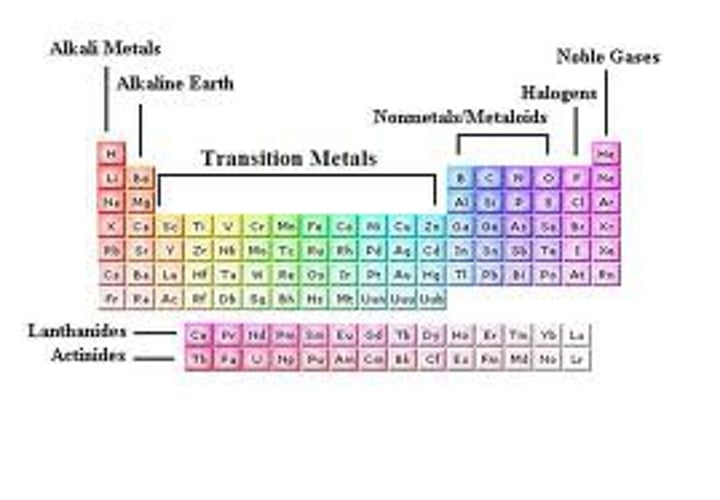
The Periodic Table of Elements
A table that is arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
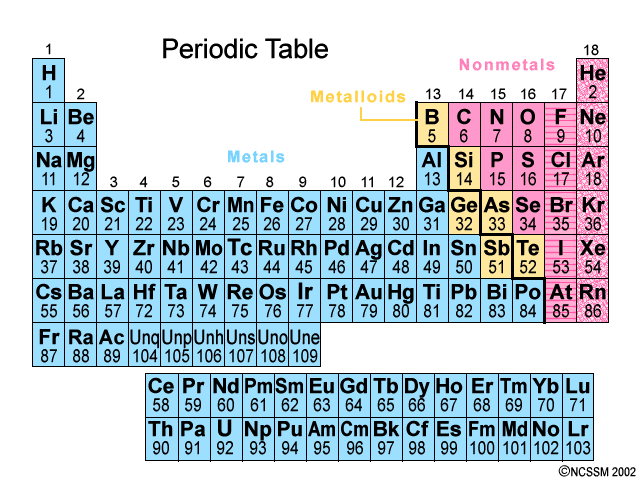
Which element can be found in Period 2, Group 17?
Fluorine
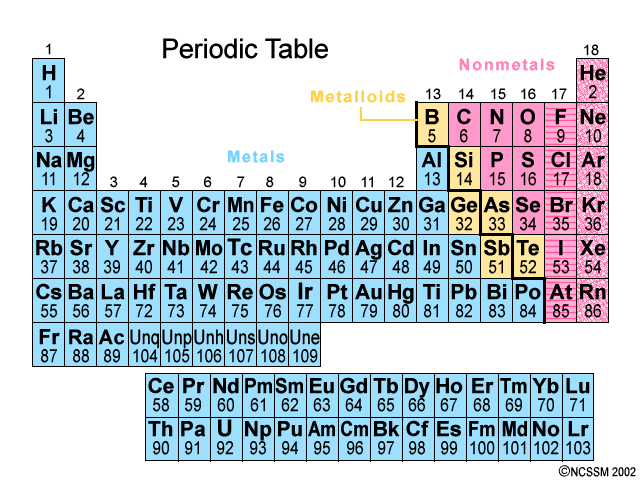
How many valence electrons does chlorine have?
7 valence electrons
chemical bond
The force that holds two atoms together.
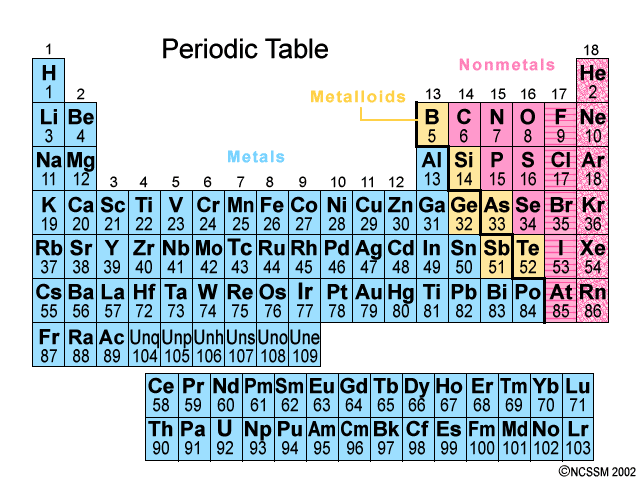
Found on the left hand side of the periodic table of elements. All of the elements in Groups 1-12 except for Hydrogen
Metals
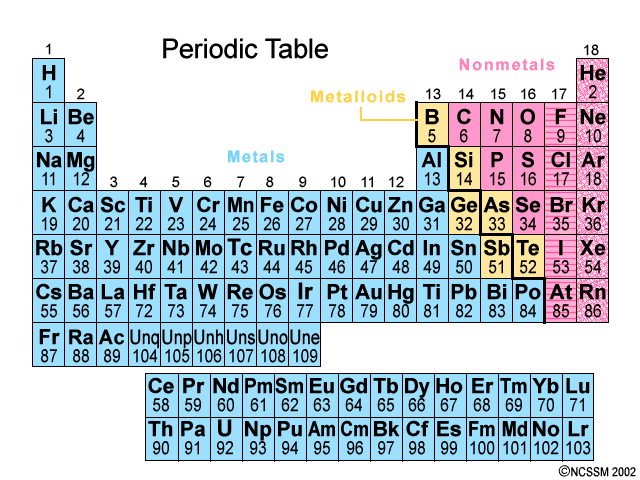
Found on the right hand side of the Periodic Table ~ there are only 17 of them. It is all of the elements in Groups 13-18, except the ones that touch the bolded staircase, those are metalloids.
Non-metals
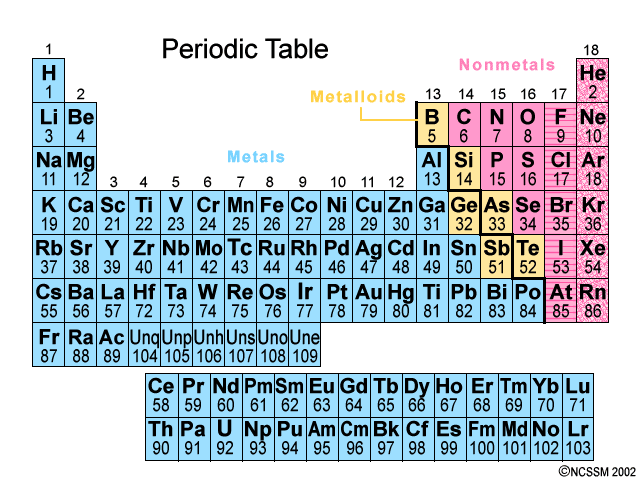
Elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals. They are found along the bolded staircase on the Periodic Table.
Ex: Silicon
Metalloids
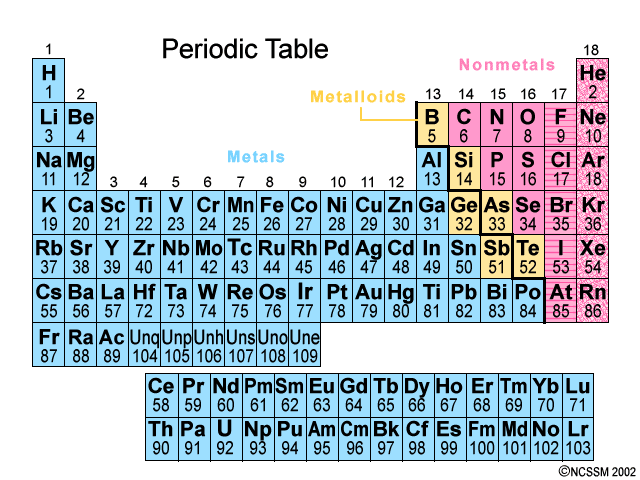
Group 18 elements-they do not interact with other elements because they have a full valence shell.
noble gases
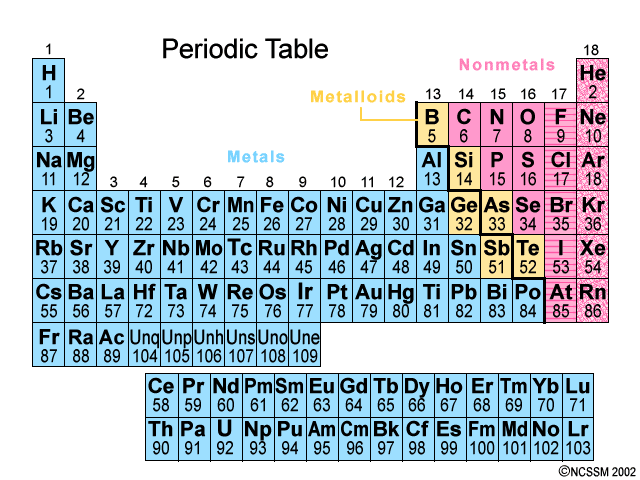
The most reactive metals in the periodic table because they want to lose that one valence electron
Group 1: Alkali Metals