transition metals
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
whats the difference between transition metals and d-block elements?
transition metals form stable ions that have partially filled d-subshell
d-block elements just have outer electron in d orbital
e.g. scandium and zinc are d-block elements but are not transition metals
why is zinc not a transition metal?
zinc is not a transition metal because zinc can only form a +2 ion, Zn2+which has a complete d-orbital
4 chemical properties of transition metals
1. form complex ions
2. form coloured ions
3. variable oxidation states e.g. Fe(II) and Fe(III)
4. acts as catalysts
suggest why ions from s block elements do not usually act as catalysts
bc they only exist in one oxidation state
Why do transition metals have variable oxidation states?
because the electrons sit in the 4s and 3d subshells
- which are very close in energy
types of ligands
monodentate - forms one coordinate bond per ligand
e.g. H2O and NH3 and Cl-
H2O and NH3 ligands are uncharged, therefore the exchange of H2O and NH3 occur without a change in oxidation state
however, the Cl- ligand has a charge and is larger than the H2O and NH3 ligands, so the exchange with a Cl- ligand changes the coordination number
bidentate - coordinate bonds from 2 atoms
e.g. (C2O4)2- and NH3CH2CH2NH3
multidentate - forms 6 coordinate bonds per ligand
e.g. EDTA4-
total oxidation state of metal equation
total oxidation state of metal = the total oxidation state - total oxidation state of ligands
what happens if a compound has a full (3)d subshell?
cannot absorb visible light
therefore compound is white
In terms of bonding, explain the meaning of the term complex.
an atom/ion/transition metal bonded to one or more ligands by coordinate bonds
a central metal atom/ion surrounded by ligands.
coordination number definition
the number of coordinate bonds formed to a central metal ion
coordinate bond definition
Co-ordinate bonding is when the shared pair of electrons in the covalent bond come from only one of the bonding atoms.
where both electrons are donated by one atom
Explain why coordinate bonds can be formed between transition metal ions and water molecules
The oxygen in the water molecule has a lone pair of electrons which it can donate to the transition metal ion
The transition metal ion can accept electron pairs
explain how a coordinate bond is is formed between a transition metal ion and a ligand
An electron pair on the ligand is donated from the ligand to the central metal ion
define ligand
an atom/ion/molecule that has atleast 1 l.p of electrons and donates an electron pair to a central metall ion
forms a co-ordinate bond with a transition metal by donating a pair of electrons.
what allows a molecule to behave as a ligand?
they have a lone pair of electrons
explain why the chloride ions in [Co(NH3)₆]Cl₃ are not considered to be acting as ligands in this complex
because:
the chloride ions are not bonded to the cobalt ion
they dont donate a lone pair of electrons to the cobalt ion
Give an example of a linear complex ion
[Ag(NH3)₂]⁺
Give an example of a tetrahedral complex ion
[CuCl4]2-
Give an example of a square planar complex ion
(NH3)2PtCl2
structure of ethanedioate
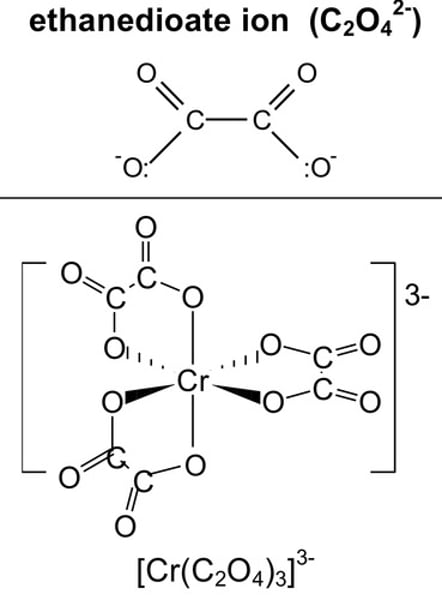
structure of ethane-1,2-diamine

How oxygen is transported in the blood
oxygen forms a coordinate bond to the Fe(II) in the haemoglobin
Why CO is toxic to humans
CO can form a strong coordinate bond with haemoglobin
this bond that CO makes is stronger than the bond that oxygen makes with haemoglobin
so the CO replaces the oxygen
what does the complex shape of ions depend on?
1. size of ligands
2. coordination number
The Chelate effect
The substitution of a monodentate ligands with a bidentate or multidentate ligand, resulting in a more stable complex
positive entropy change, because there are more moles of products than there are moles of reactants
more particles are formed
so therefore disorder increases
the greater the entropy change, the more negative the free energy change (ΔG)
therefore, the reaction is more favourable
the enthalpy change (ΔH) for a ligand substitution reaction is very small
this is because the bonds being formed are very similar to the bonds that are broken
therefore, the enthalpy change is near 0
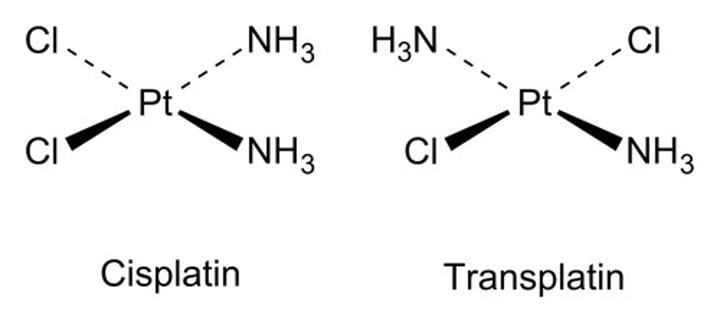
Cisplatin and Transplatin structure
cisplatin: used as an anti-cancer drug
transplatin: no current medical use
explain why complexes formed from transition metal ions are coloured
absorbs wavelengths of light to excite electrons in d-orbital
complementary wavelength of light transmitted to give colour seen
how a calibration graph is produced and used to find the concentration of a complex
add appropriate ligand to intensify colour if necessary
make solutions of known conc.
measure absorbance from known conc.
plot the graph of calibration curve: plot graph of conc. vs absorbance
read value of conc. for the measured absorbance from this graph
How to calculate ΔE (change in energy)
ΔE = hv = hc / wavelength
ΔE : energy absorbed by the electron, from ground to excited state
h: planks constant
v: frequency of light (Hz)
c: speed of light (m/s)
how does ΔE determine colour
ΔE affects frequency of absorbed photons
determines colour
what affects the colour of transition metal compounds
oxidation state of metal
no. of ligands
type of ligands
shape
coordination no.
Complete ligand substitution of hexaaquacobalt with ammonia
[Co(H2O)6] 2+ + 6NH3 -----> [Co(NH3)6]2+ + 6H2O
when do incomplete ligand substitution of hexaaquacopper reactions occur?
when you use excess ammonia with copper
incomplete ligand substitution of hexaaquacopper and colour change
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 2NH3 —> Cu(H2O)4(OH)2 + 2NH4+
Cu(H2O)4(OH)2 + 4NH3 —> [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+ + 2OH- + 2H2O
blue ppt. dissolves to form deep blue solution
colour change from blue solution to dark blue solution
ligand substitution reaction of hexaaquacopper and Cl- ligand, including colour change
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl- ----> [CuCl4]2- + 6H2O
colour change from blue solution to yellow solution
ligand substitution reaction of hexaaquacobalt and Cl- ligand, including colour change
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl- ----> [CoCl4]2- + 6H2O
colour change from pink solution to blue solution
ligand substitution reaction of hexaaquairon (II) and Cl- ligand, including colour change
[Fe(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl- ----> [FeCl4]2- + 6H2O
colour change from purple solution to yellow solution
Ligand subsitution reaction of ethane-1,2-diamine w/ hexaaquacopper
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 3NH2CH2CH2NH2 -----> [Cu(NH2CH2CH2NH2)3]2+ + 6H2O
Ligand substitution reaction of ethanediaote w/ hexaaquacopper
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 3C2O42- -----> [Cu(C2O4)3]4- + 6H2O
when does the partial substition of ethanedioate ions occur?
may occur when a dilute aqueous solution containing ethanedioate ions is added to a solution containing aqeous copper (II) ions
partial substitution of ethanedioate ions reaction equation
[Cu(H₂O)6]²⁺ + 2C₂O₄²⁻ ——> [Cu(C₂O₄)₂(H₂O)₂]²⁻ + 4H₂O
vanadium chemistry
oxidation state | colour | |
VO2⁺ | +5 | yellow |
VO²⁺ | +4 | blue |
V³⁺ | +3 | green |
V²⁺ | +2 | violet |
ratio between between MnO₄⁻ and Fe²⁺
1:5
ratio between between MnO₄⁻ and C₂O₄²⁻
2:5
ratio between between C₂O₄²⁻ and Fe²⁺
1:2
role of catalysts
catalysts speed up reaction and lowers Ea for reaction and is left unchanged
heterogenous catalyst
catalyst in different phase from reactants
homogenous catalyst
catalyst in same phase as reactant
how platinum acts as a catalyst by providing an alternative route
platinum provides an active site
reaction on the surface: bonds weakening/breaking
desorption of the product
catalyst poisoning
sulfur poisons/binds to catalyst
active sites blocked
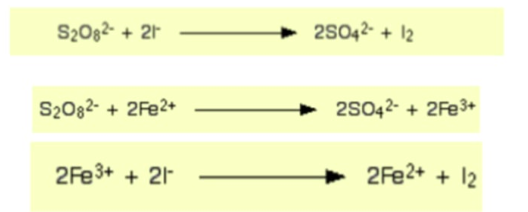
why reaction b/w peroxodisulfate (VI) ions and iodide ions is slow before catalyst is added
2 negative ions repel
therefore Ea is high
Write the equation for reaction between iodide ions and peroxodisulfate ions
Explain why the activation energy for each of these reactions is low
Explain why Fe3+ ions are as effective as Fe2+ ions in catalysing this reaction
Ea is low bc each reaction has oppositely charged ions which attract
Fe3+ ions as effective as Fe2+ ions since equations 1&2 can occur in any order
autocatalysis reaction
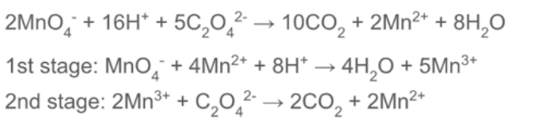
catalytic converter
uses solid Rh catalyst
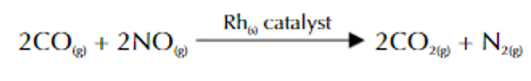
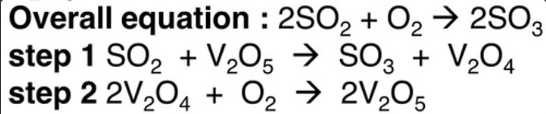
contact process
uses solid V2O5 as a catalyst
haber process
uses solid iron catalyst