stem cells
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
what are the 2 types of stem cells and their simple characteristic
adult stem cells,- cannot differentiate everywhere and are limited(blood cells are for blood only) , age with the body,
embryonic stem cells- can differentiate to all parts of body (can make toes to eyes). they are early cells that can make everything
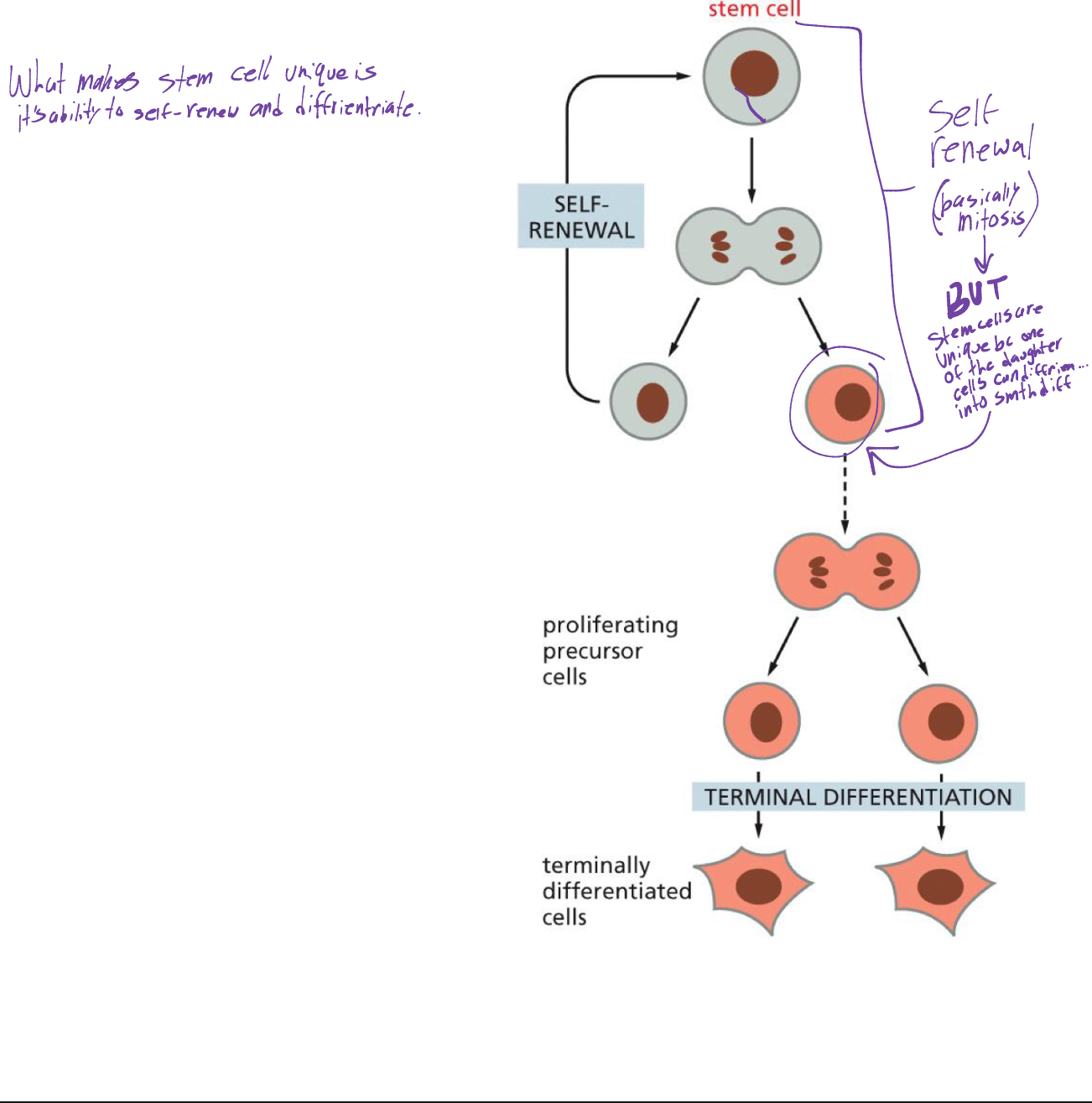
why are stem cells unique
a previous stem cell will undergo self renewal (basically mitosis where cell divides to have daughter cell). except one of the daughter cells will differentiate into something different. (idk girl)
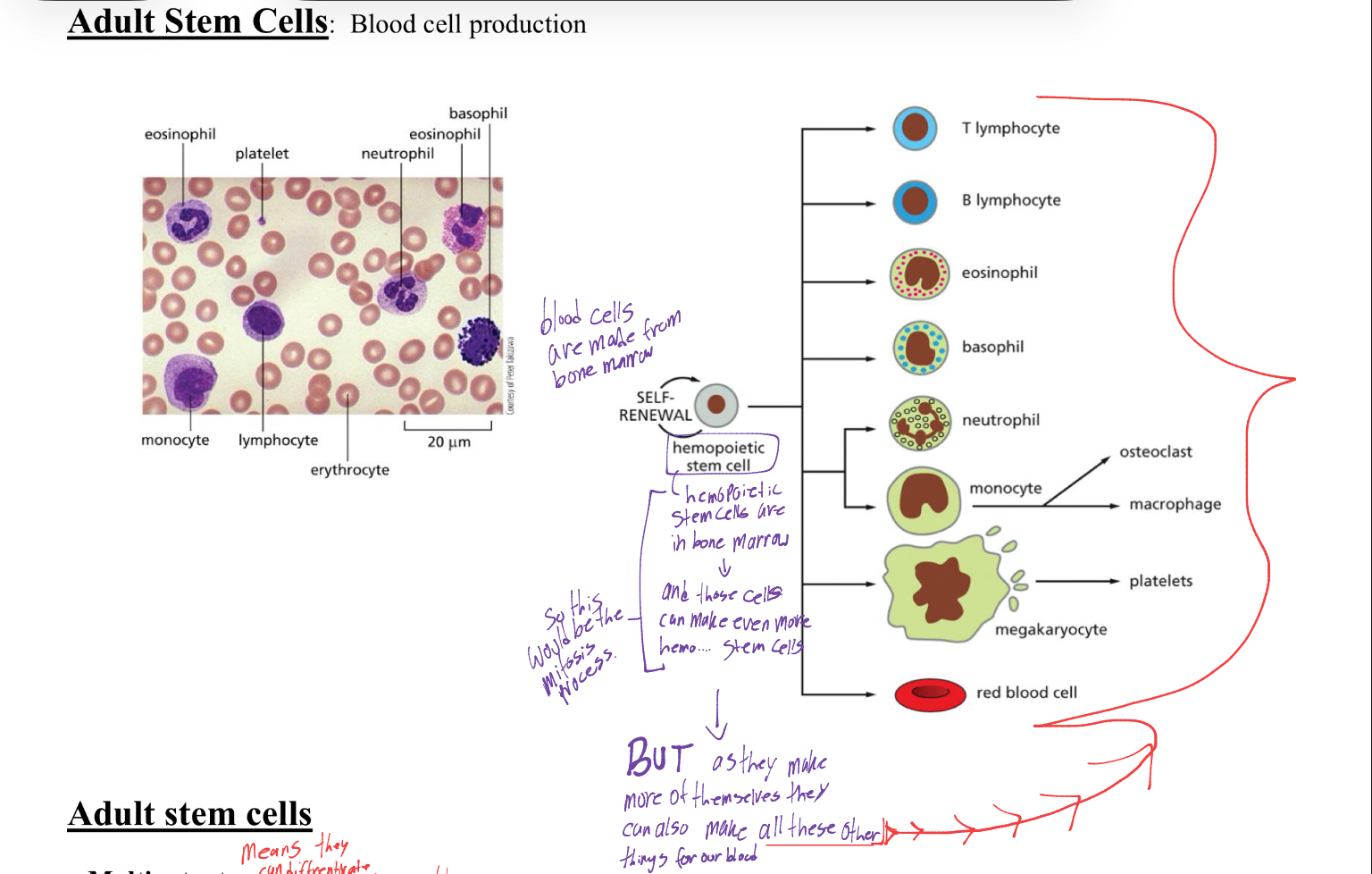
an example for adult stem cells are blood cell production, in the example what occurs with the stem cell, where is it found and what do they do and make
the stem cell is found in bone marrow, the same place blood cells are from. the stem cell undergoes self renewal, splitting itself into daughter cells, while one becomes a blood cell and the other Turns into something else we need in our blood.
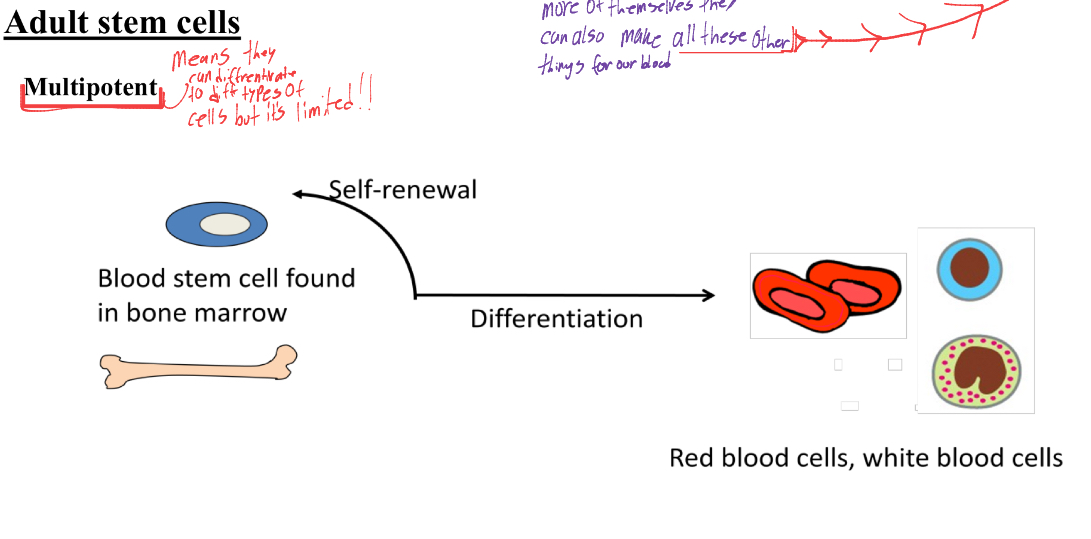
what does the term multipotent mean for adult stem cells.
means that they can differentiate to different types of cells but it is limited.
what are 3 limitations with adult stem cells
skin cells cannot make blood cells, so when studying the cell, one is limited to a certain circle of things
they are also difficult to isolate bc they blend with other cells.
they also age with the body and accumulate mutations as they do.
where are embryonic stem cells and how do you get them
they are In the BLASTOCYST (5 day old embryo)) embryonic stem cells are the inner mass inside the blastocyst. you must destroy the embryo to retrieve the cells.

what is the term that means the embryonic stem cells have the ability to differentiate into anything in human body
pluripotent
why do scientists want embryonic stem cells, more
bc if you add certain things to the cells, you can make anything in the human body.
what issues arise with studying embryonic stem cells
you kill the embryo by removing inner cell mass
what is IPS
(induced pluripotent stem cells)
a different way of getting pluripotent cells without killing an embryo.
what are the first steps of IPS
taking an ill persons cells through blood draw,
then adding 4 certain transcription factors (also called yamanaka factors). that back program cells into embryonic like-state.
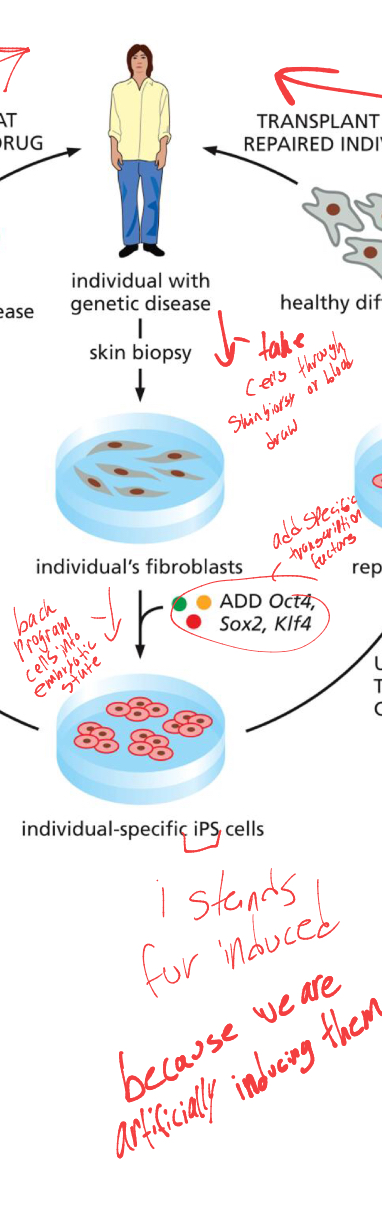
what would scientists then do with artificially created embryonic cells. and why is this difficult
they would attempt to differentiate them by adding specific transcription factors.
this is difficult bc we need to know what transcription factors differentiate to what.
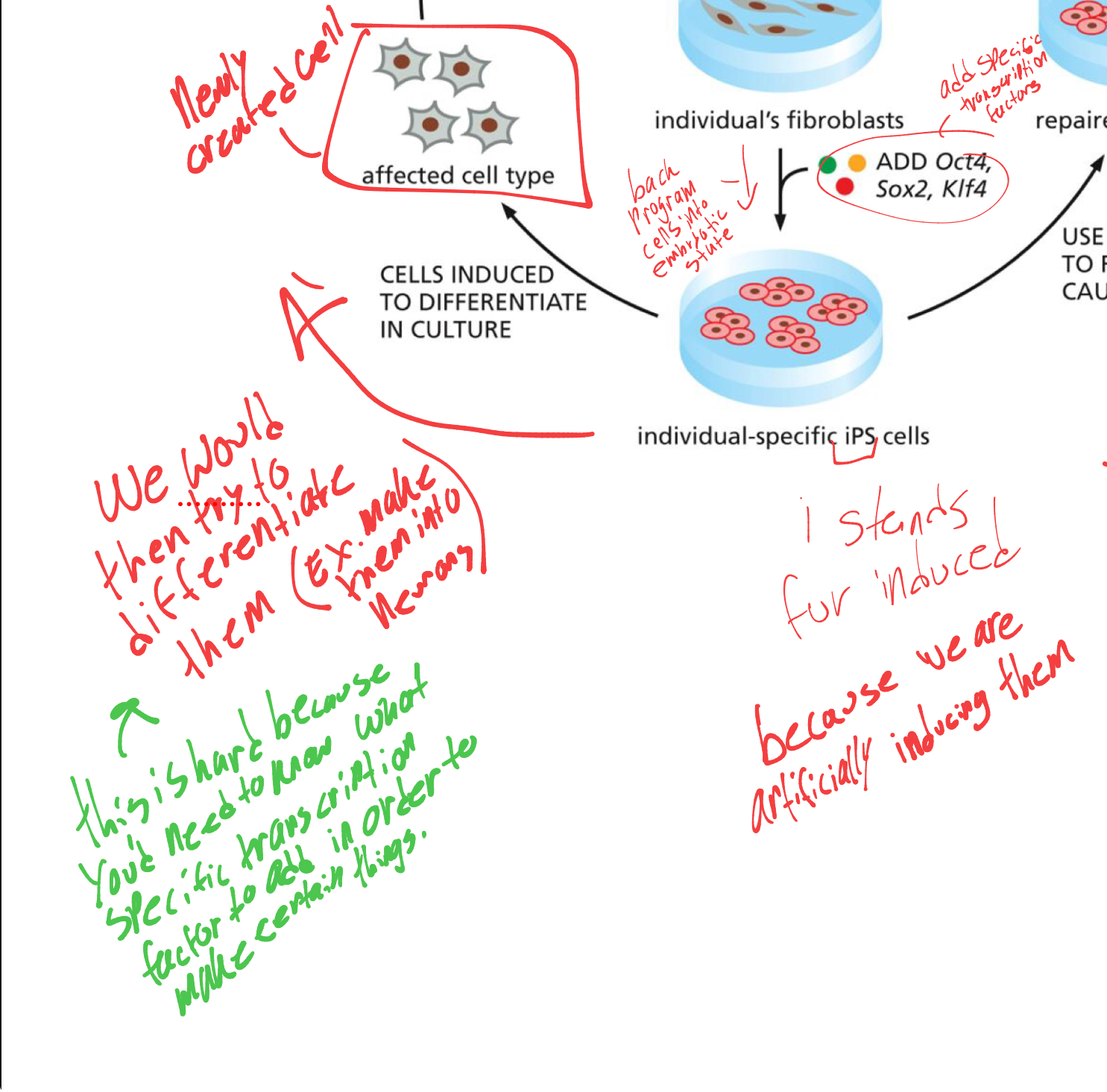
what would be the next step after successfully differentiating into new cells.
they would screen the new specific cells with a drug library specific to the disease being studied in the patient.
to see if any of the drugs would improve what is wrong.
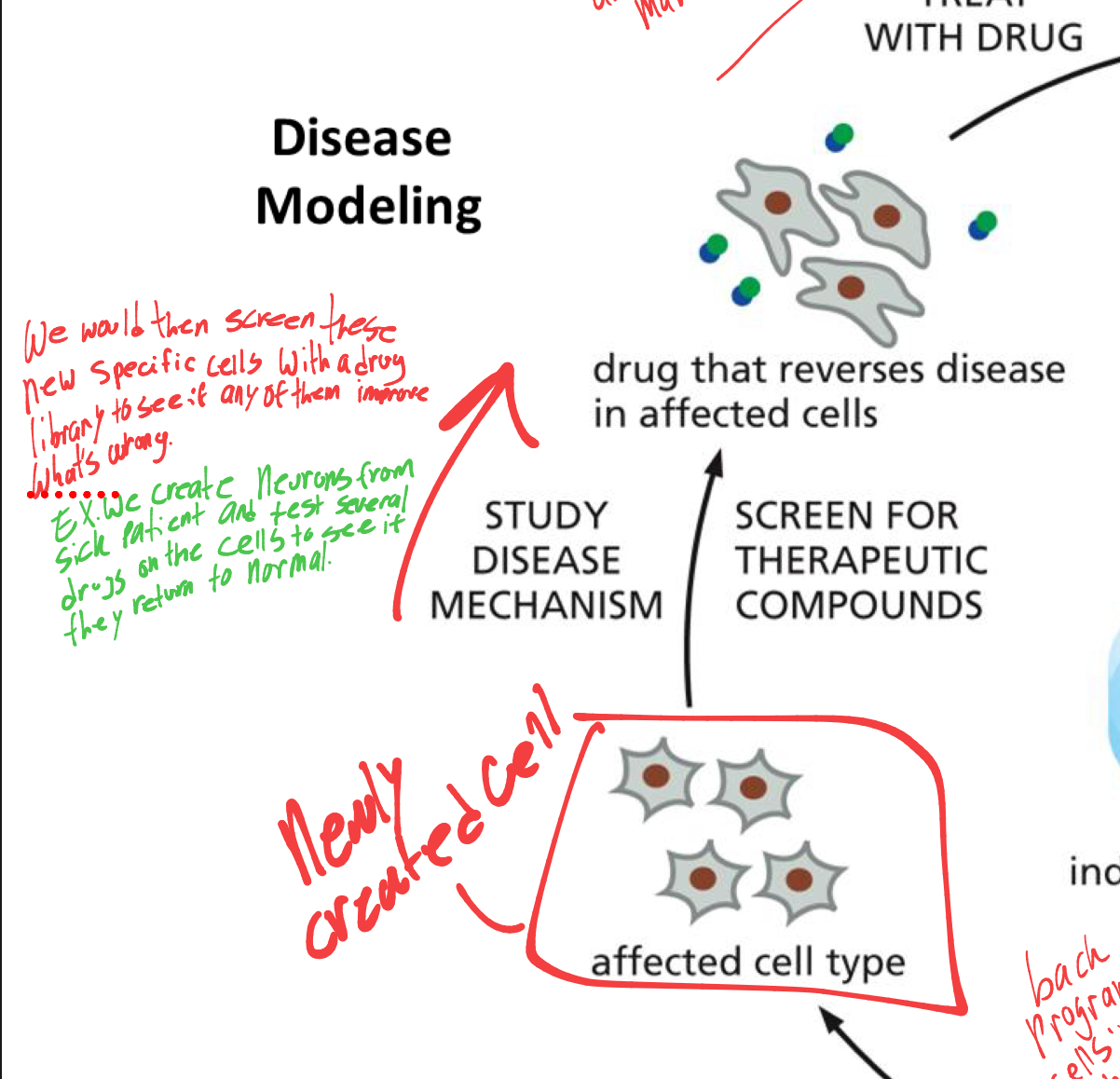
what would the last step be
we would use the drug that made a positive affect in the cells and treat the patient with the drug.

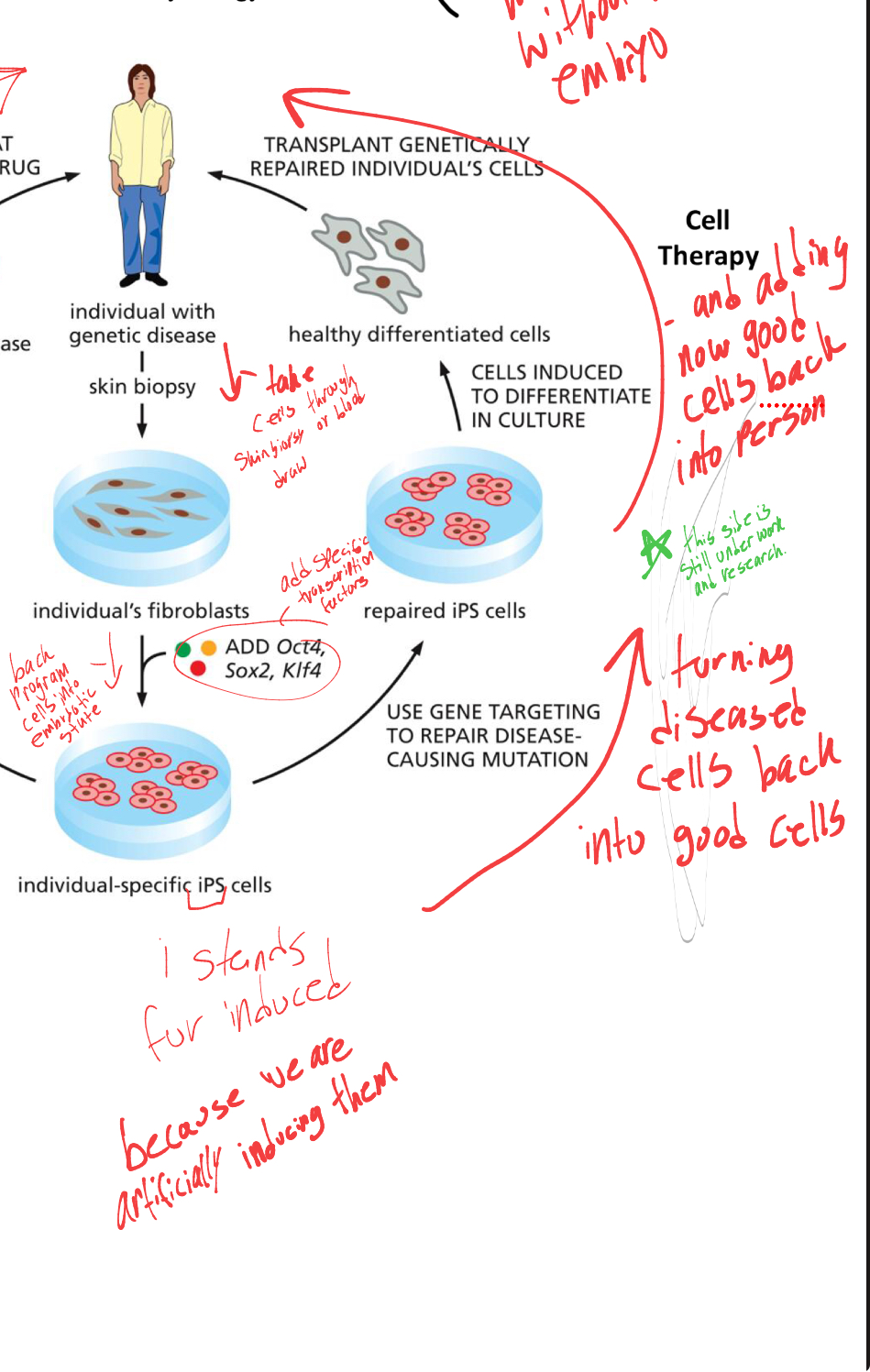
what is the other sides process that’s under research
they would take the lab created embryonic cells and turn the cells back into healthy cells and add the new cells into the diseased person.
when saying the difference between adult stem cells and embryonic stem cells what do you include
adult: multipotent
emb: pluripotent
where is the shank 2 protein located and what does it do
its located in post synaptic neuron, and it is a molecular scaffolding protein (big protein that binds to. other proteins)
what type of mutation is the SHANK 2
Autosomal dominant, meaning it only needs 1 dominant allele in gene to be infected. (Aa AA)
whats a bio repository and why is It created
a collection of biological samples such as blood, urine. and can be used by researches that want to study a certain condition
whats a VUS
a Variable of Unknown Significance. the mutations that affect the cells are unknown, and its not ideal to use these patients for research bc we want a good candidate to be a representation of all patients with disease. (WE WANT PATHOGENIC PATEINTS SAMPLES)
what can be bd about using a patient sample that has multiple mutations
we do not know which symptom is due to the mutation we are studying or another mutation.
what group oversees special regulations and makes sure federal guidelines are followed
institutional review board. (IRB)